COMM1101 Test 1 Study Guide: Key Concepts and Definitions in Attribution, Labeling, and Self-Esteem
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Why do we study communication?
1. Necessary for relationships
2. Necessary for goal achievements
3. Necessary for identity development and identity management.
Define Critical thinking
Critical Thinking: Reflecting on your own and others' communication, behavior, and ideas before responding.
What are messages and what is shared meaning?
Messages: Building blocks of communication - Messages are symbols - both words and nonverbal communication
Shared Meaning: The goal of communication - Sender and Receiver interpret the message the same
What is the difference between content level and relational level meaning?
Content level: based on the words and nonverbal cues the messenger is receiving, you understand what they say
Relationship level: you run their message through another filter based on the relationship with that person
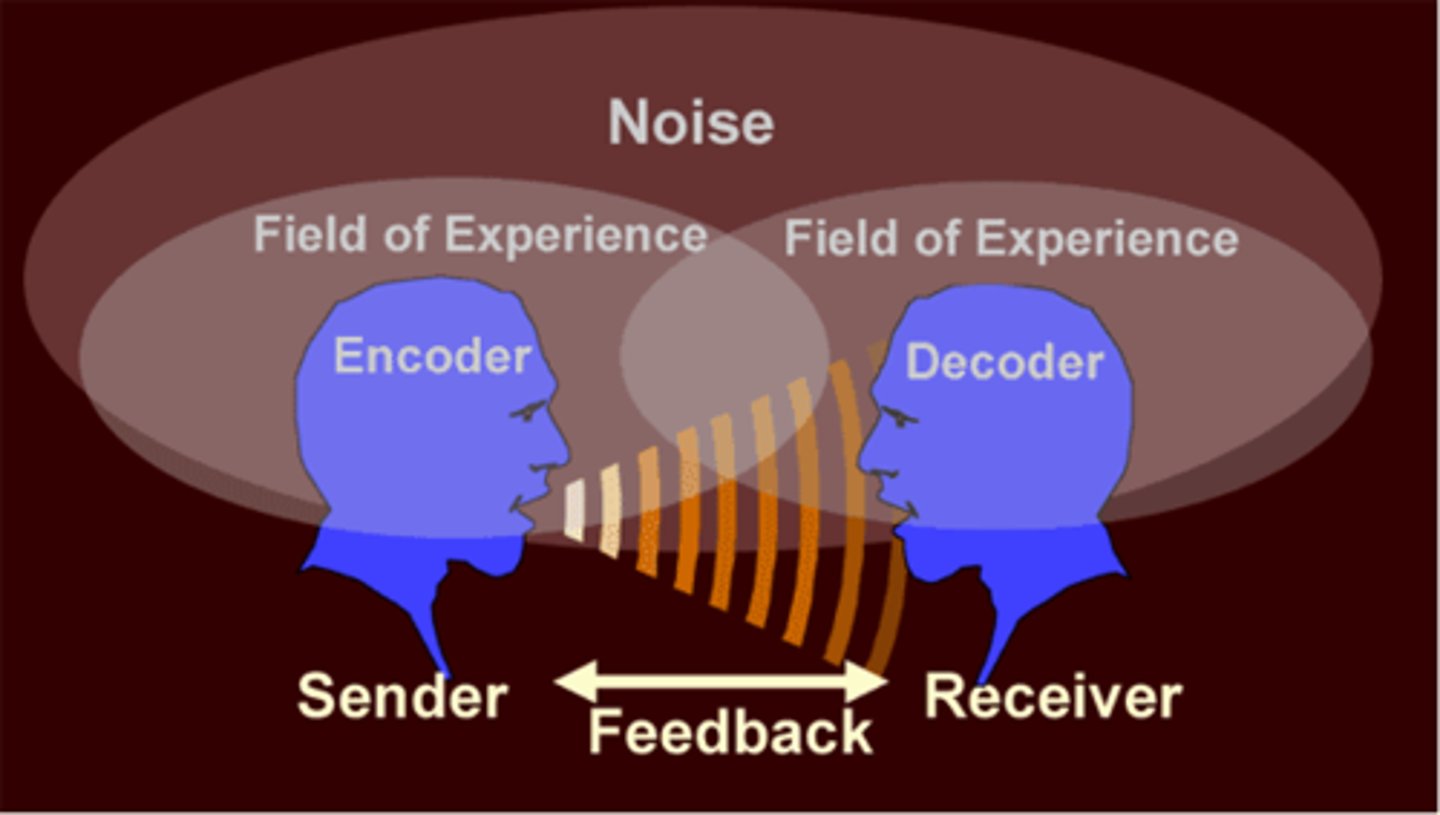
Seven components of communication process
setting, participants, message creation, meaning creation, channel, noise, feedback
Can you name/define/explain participants
Who are the people interacting during the communication
Can you name/define/explain Setting
Setting: Physical surroundings
(location, daytime, proximity)
Can you name/define/explain message creation
Encoding/decoding - saying and interpreting the communication
Encoding: converting ideas into messages
Decoding: receiving a message and interpreting its meaning
Can you name/define/explain meaning creation
content/relationship
Can you name/define/explain channel
Through which the message is being transmitted
(face-to-face, zoom, etc.)
Can you name/define/explain noise
Interferes with/degrades the quality of a message
(audible distractions, psychological noise, computer distractions)
Can you name/define/explain feedback
Response to a message
linear model of communication
one person transmits, the other listens

transactional model of communication
both people share meaning simultaneously
Synergetic Model of Communication
Transactional model + individual, cultural, and societal forces
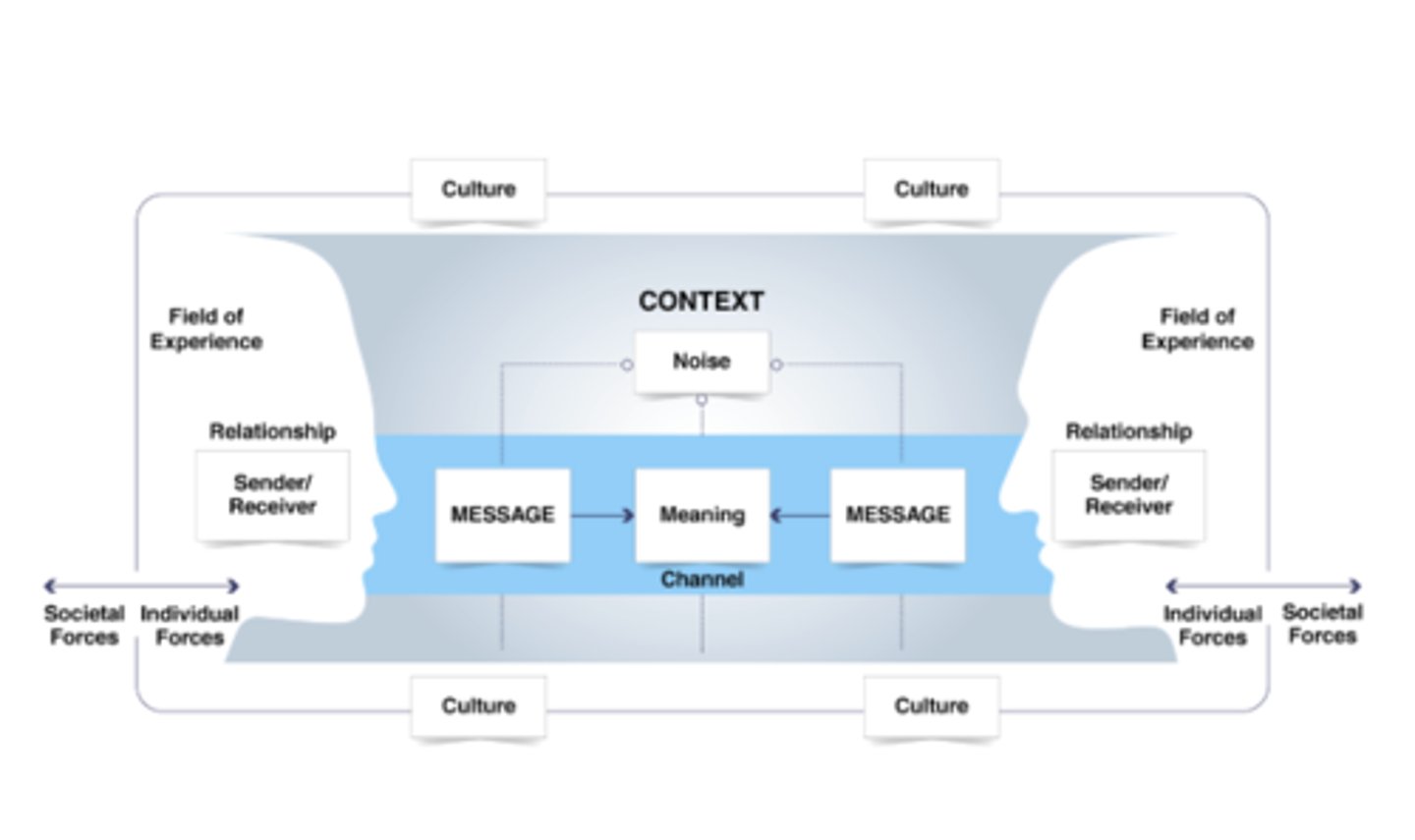
What individual forces influence communication?
Demographics, personality, cognitive ability, physical ability, field of experience
Can you define communication competence?
The ability to react appropriately and reach the goal intended with your message.
What are the goals that are studied in interactions? What do they mean?
Content Goals: What you want to achieve or learn in a specific context
Relationship Goals: How you want to be perceived by others and how you want to interact with them
Identity Goals: How you want to perceive yourself and how you want to express your identity to others
What is the definition of communication according to Alberts, Nakayama, and Martin?
"A transactional process in which people generate meaning through the exchange of verbal and nonverbal messages in specific contexts, influenced by individual and social forces, and embedded in culture."
How are communication and identity connected?
1. Your identity comes with you with every communication encounter.
2. Communication helps shape and create identity.
3. Identity is important when it comes to intercultural communication
Can you define and provide characteristics of identity?
Identity: the combination of self-concept and social categories
Identities exist on an individual(personal) and societal level
Identities can change and stay the same, also created through communication
Can you define and explain Reflected appraisals
Your opinion of yourself is determined by how others see you
Can you define and explain Social comparisons:
All things become meaningful through comparisons
Can you define and explain Self-fulfilling prophecies:
When you expect something to happen, it more likely will.
Self-fulfilling prophecies affect performance.
Can you define and explain self concept:
how you see yourself - affects the image you project externally
Learned through reflected appraisal and social comparisons
Can you define and explain self-esteem
Your evaluation of your worth - affects how you communicate
Can be inconsistent with how others see you
Performance of Identity:
the process or means by which we show the world who we think we are.
EX: clothing, jewelry, names
Self-Presentation:
influencing others' impressions by creating an image that is consistent with one's personal identity
Enacting Identities:
using scripts for the roles we're playing at that moment
Role Expectations:
the expectation that one will perform in a particular way because of the social role occupied
Can you identify the difference between primary and secondary identities?
Primary Identity: identities that have the most consistent and enduring impact on our lives
- EX: Race, gender, nationality
Secondary Identity: more fluid and often dependent on the situation
- EX: College major, relationship status, occupation, sports team
Can you identify the difference between racial, national, and ethnic identity?
Racial identity: the identification with a particular racial group, develops as a result of societal forces - because society defines what a race is and what it is called
National identity: a person's citizenship
Ethnicity identity: identification with a particular group with which they share some or all of these characteristics: national or tribal affiliation, religious beliefs, language, and/or cultural and traditional origins and background - Most complex
Racial Identity:
Identification with a particular racial group, developed from societal forces
National Identity:
Refers to citizenship
Ethnic Identity:
Identification with a particular group with which they share some or all of these characteristics: national or tribal affination, religious beliefs, language, and/or cultural and traditional origins and background
Gender Identity:
To what extent one identifies with the social construction of masculinity and femininity
Sexual Identity:
Refers to the various categories of sexuality one identifies with
Age Identity:
Self-perception of age along with what others understand age to mean
Social Class Identity:
based on income, occupation, and education.
- Ex. Middle class, upper class
Disability Identity:
Having an impairment of some kind
Religious Identity:
One's spiritual beliefs in terms of a particular belief system and depth of belief
How does someone formulate their own communication ethic?
From all identity characteristics. What we decide ourselves based on our ethics
What is the definition of communication ethics?
the standards of right and wrong that one applies to messages that are sent and received.
What are some of the ways we judge ethical decisions in communication?
Truthfulness
Sharing/withholding information
Benefit and harm of messages
Can you define and identify the difference between absolutism and relativism?
Absolutism: the belief that there is a single correct moral standard that holds for everyone, everywhere, every time
Relativism: the belief that moral behavior varies among individuals, groups, cultures, and across situations
Can you define and identify the difference between utilitarianism and pragmatism?
Utilitarianism: Weighing the harm/benefits of communicative decisions (ex. lying).
- The goal is to bring the most happiness to the most people, if an action/message results in the most happiness for the most people, it is right.
Pragmatism: emphasizes the practical effects of speech.
- Use what works, discard what doesn't
What is the framework for ethical decision-making?
Recognize ethical issues
Get all the facts
Evaluate alternative actions
Make a decision and test it
Act and reflect on the outcome
Can you define perception and the perception process
Perception: the process of selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory information into a coherent or lucid depiction of the world around us
Perception Process: We collect and understand information through our senses
Selection: attending to stimuli
Organization: arranging stimuli
Interpretation: understanding stimuli
Can you define selection, organization, and interpretation?
Selection: the process of choosing which sensory information to focus on
Organization: the process by which one recognizes what sensory input represents
Interpretation: involves assigning meaning to stimuli that we have selected to attend to
What types of stimuli are we more likely to attend to?
We tend to select stimuli with certain characteristics
Stimuli with intensity
Stimuli that are large in size
Stimuli that contrast with surroundings
Stimuli that are repeated
Stimuli with sudden movement
We also notice stimuli that are negative, violate expectations, or occur in important situations
Primacy effect, recency effect
Primacy effect: the tendency to form a judgment or opinion based on the first information received
Recency Effect: the tendency to form a judgment or opinion on the most recent information received
What is the difference between cognitive representation and categorization?
Cognitive Representation: A mental model or map humans can create to represent their surroundings and can later refer to when circumstances call for them
- 3 types of maps: schemas, prototypes, scripts
Categorization: a process of grouping objects or categories of information together with linguistic symbols
Can you define Schemas(CR):
cognitive structures that help us organize information
Can you define Prototypes(CR):
a representative or idealized version of a concept
Can you define Scripts(CR):
a relatively fixed sequence of events that function as a guide or template for communication or behavior
Can you define Labeling(C):
name assigned to a category based on one's perception of that category (usually with other people)
Can you define Stereotyping(C):
creating schemas that overgeneralize attributes of a specific group
Can you define Frames(I):
function as lenses that shape how we create meaning and understanding
Can you explain and give an example of attribution theory?
Attribution Theory: We attribute behavior as being either internally caused (based on someone's personality or choices) or externally caused (based on the environment of the situation)
Classmate doesn't smile at me → She's rude (internal)
Classmate doesn't smile at me → She's having a rough day (external)
Can you explain attributional bias
my negative behaviors are because of external causes and my positive behaviors are because of my internal state (my being, focused on myself)
Can you explain self-serving bias
the tendency to give yourself more credit than is due when good things happen and accept very little responsibility when things go wrong (focused on yourself)
Can you explain fundamental attribution error
tendency to attribute others' negative behavior to internal causes and their positive behaviors to external causes (focused on others)
Can you explain overattribution?
selecting an individual's most obvious characteristic and using it to explain almost anything that person does
What are synesthesia, misophonia, and color blindness, and what are they examples of?
Physical Differences that influence the way ppl perceive their environment and the way they communicate about stimuli
Synesthesia: stimulation in one sense simultaneously produces sensation in a different sense
Misophonia: affected emotionally by common sounds
Color Blindness: seeing colors differently (usually harder to tell diff between colors)
What is cognitive complexity?
Cognitive complexity: refers to how detailed, involved, or numerous a person's constructs are
- The higher your cognitive complexity, the more ways you have of explaining, understanding, and perceiving interpersonal interactions
How can someone's personality characteristics influence perceptions?
Each person is a mix of personality, temperament, and experience
Individual characteristics influence perception
Factors to consider:
- Emotional state (our attitude influences perception)
-----Feeling happy vs. depressed → interpret and respond to sensory input differently
-----EX: feeling angry → hearing other people's music → irritated
-----EX: feeling happy → more likely to help others
Outlook (tend to interpret the world in consistent ways)
- Optimistic vs. Pessimistic
Knowledge (awareness and understanding)
- Ppl interpret what they perceive based on what they know
The Role of Power:
Your relative position of power or lack of power influences how others perceive you, how you perceive, others, and how you interpret events in the world
The Role of Culture:
Each person perceives or values the other based on expectations that were shaped by own cultural perceptions, values, and meanings typical for his or her own culture
- Helps shape individuals' thoughts, feelings, perceptions, and behaviors
----EX: East Asian cultures are highly interdependent and community-based over individual → anti bragging, self-critical
----Can view independent, self-confident Americans as arrogant and selfish
The Role of Social Comparison:
social categorization leads us to specific expectations about how others should or should not behave
- Shaped by our culture
----EX: US valuing youth over age vs. Korea celebrating aging and elders
----Koreans could see Americans as misguided and wrong in treatment of the elderly
The Role of Historical Time Period:
The historical period in which one grows up and lives influences perception and communication
- 9/11 → Those older than 5-6y/o during likely to have perceptions changed by the event
----Perceptions of air travel, safety, patriotism, Muslims
Cohort Effect:
the process by which historical events influence the perceptions of people who grew up in a given generation and time period
Social Roles:
the specific position or positions one holds in a society
- The role one plays socially can influence one's perception and communication
- Ex. job positions, familial roles, positions in society
Can you define and differentiate paradigm?
Paradigm: a belief system that represents a particular worldview
- Set of assumptions about knowledge, nature of reality, and human nature
Can you define and differentiate Theory:
a set of statements that explains a particular phenomenon
- Theories are developed over time, tested, and retested
Can you define and differentiate Hypothesis:
a supposition or proposed explanation
- Assumptions made before any research or experiments
Can you define and differentiate Methods:
the specific ways that scholars collect and analyze data which they then use to test hypotheses and prove or disprove their theories
Where and why was rhetoric first studied?
- It was first studied in Ancient Greece
- Greek citizenry, democracy, public sphere, language & persuasive skills were highly valued
Can you explain the difference between humanism and behaviorism? Can you identify the main divide?
Behaviorism: the focus on the study of behavior as a science
- Focuses on observable/external behavior
- Social Science Approach
- Quantitative Methods
- Goal = predicting human behavior
Humanism (I): celebrates human nature and potential
- Focuses on individual as a whole
- Interpretive & Critical Approach
- Qualitative Methods
- Goal= change society
What is the difference between the social science approach and the interpretive approach, and which is humanist and which is behaviorist?
Social science approach: Behaviorist
- Predictions are possible if you observe behavior in a controlled environment (lab) or a naturalistic setting
- Often use surveys, focused interviews, and observation to collect data
Interpretive approach: Humanist
- Researchers study naturally occurring communication rather than assembling data
- Focuses on how reality is constructed through communication
Can you identify the difference between quantitative research and qualitative research, and which approach is associated with each?
Quantitative Methods: methods that convert data to numerical indicators, which are then analyzed using statistics to establish relationships among the concepts
- EX: observing subjects in a lab or naturalistic setting, surveys, conducting interviews
Qualitative Methods: methods in which researchers study naturally occurring communication rather than assembling data and converting it to numbers
- EX: Ethnography: active engagement with participants
- EX: participant observation, ethnographic interviewing, Steve's dissertation
- Content analysis: focusing on the specific aspects of content of a text or group of texts
- EX: conversation analysis, media analysis, narrative
What is the critical approach?
Aims to change society through an understanding of power and other forces affecting communication and human behavior
- Typically use textual analysis and observations
What are the goals of each approach (social science, interpretive, critical)?
Social Science Approach Goal: predicting future behavior
Interpretive Approach Goal: explore and explain the world around us
Critical Approach Goal: to change society