Cellular Respiration
1/9
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
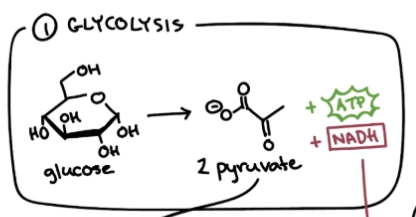
Glycolysis
Breakdown of glucose (sugar) into pyruvate using small amounts of ATP.
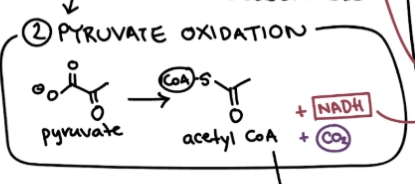
Pyruvate Oxidation
Prepares pyruvate for citric acid cycle by converting it into Acetyl CoA. This process links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle.
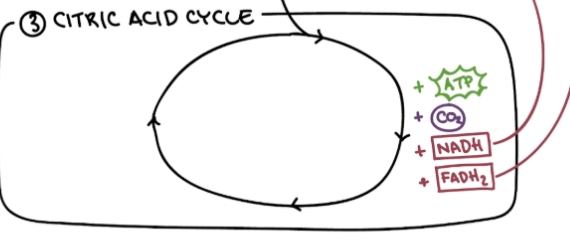
Citric Acid Cycle
Oxidize remaining carbon atoms from the original glucose molecule, generating electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) that will fuel the electron transport chain, and some ATP.
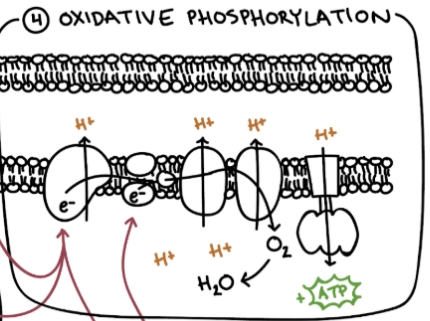
Oxidative Phosphorylation and the Electron Transport Chain
To use the electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) generated in the previous steps to produce the majority of ATP through the process of chemiosmosis, while using oxygen.
Where is most of the ATP produced in cellular respiration?
Oxidative Phosphorylation or Electron Transport Chain.
What is the main function of ATP synthesis?
Synthesize ATP by using energy from a proton gradientcreated during electron transport.
What role do NADH and FADH2 play in cellular respiration?
They act as electron carriers that transport high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain, facilitating ATP production. “Electron carriers” in other words
When does fermentation take place?
In anaerobic conditions or respiration. This is an alternative pathway cell used to generate ATP.
Where does fermentation take place?
Cytoplasm of the cell, where glucose is metabolized in the absence of oxygen.