CC CARBOHYDRATES
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
130
grams or 520 kcal per day
The minimum recommended intake of
carbohydrates necessary for survival is_______________
the central nervous system, red blood
cell production, and tissues dependent on
glucose
130
grams or 520 kcal per day level is recommended only to
support_________________; it does not support any physical
activity.
Carbohydrates
______________are the immediate sources of
energy for the body.
monosaccharide glucose
The____________ serves as the
major entry point for all foodstuffs to the
metabolic pathways of the body
Exogenous carbohydrates
______________ are usually
obtained from plant products. They are
commonly in the form of starch.
Glycogen or "animal starch"
_______________easily
disintegrates upon death of the animal. Thus,
meats are not good sources of carbohydrates.
the liver and in the muscles
When there is excess of carbohydrates, the
body stores them in the form of glycogen in
___________________.
Muscle
glycogen
These carbohydrate stores constitute the
body's endogenous carbohydrates. ___________, however, is available only for the
muscles and not for other tissues.
monosaccharides, disaccharides, and
polysaccharides
Carbohydrates are classified into
________________ depending on the chemical
complexity of the molecule
Monosaccharides
building blocks of carbohydrates. They include
glucose, fructose, and galactose
Disaccharides
made up of two monosaccharide units. Examples
of these are sucrose (glucose + fructose), maltose
(glcose + glucose) and lactose (glucose +
galactose)
Polysaccharides
polymers of monosaccharides
Starch, cellulose and glycogen
_______________are all
polymers of glucose. They just differ in how the
glucose units are joined together.
starch, sucrose,
lactose and cellulose
The usual carbohydrates taken in by the
body are in the form of _________________.
the
body does not have the necessary enzymes
to degrade this polysaccharide.
Of these, cellulose is not changed as it passes
through the gastrointestinal tract because_______________
Cellulose fibers
However, it contributes to the bulk of the stool
as it is formed in the colon._____________ are
therefore important in the normal passage of
wastes through the gastrointestinal tract.
salivary amylasw
Carbohydrate digestion starts in the mouth
where the enzyme ________________ is
secreted by the salivary glands.
starch dextrins,
maltose and glucose
The enzyme
amylase converts starch into ________________.
the
breakdown of starch into smaller fragments
In Digestion
The end result of this enzymatic digestion is_____________
which are still large enough to be absorbed in
the intestines.
in
the brush border of the cells lining the lumen
of the small intestine.
In Digestion
These products plus the other disaccharides
(lactose and sucrose) ingested are then
acted upon by disaccharidases located _________________.
brush border enzymes
The __________ act on maltose,
isomaltose, a-limit dextrins, sucrose, and
lactose to form the monosaccharides glucose,
fructose, & galactose.
Stool
In Digestion
Cellulose remains unchanged and is
eventually excreted via ______.
the
intestines.
In Digestion
In certain instances, the body may not
tolerate the presence of disaccharides in _________
intestinal ulcers
In Digestion
Body may not tolerate disaccharides in intestines. This happens when certain brush border
enzymes are genetically absent or are
destroyed when there are ___________
lactase deficiency,
(with lactose-fermenting bacteria)
In Digestion
For example, when there is___________, this results
in the formation of gases leading to
abdominal cramps and flatulence "Lactose
Intolerance".
monosaccharides
Can be absorbed by the intestines
Glucose and Galactose
______________are absorbed from
the lumen of the intestine principally by an
active process involving cotransport with
sodium.
Cotransport
What pic is this?
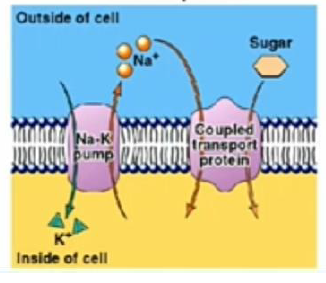
facilitated
diffusion
Glucose and galactose then leave the mucosal cells by____________ as they enter the portal circulation.
passive diffusion
In Digestion
In
contrast, fructose is absorbed from the lumen of
the intestine by______________.
portal circulation
Once the monosaccharides reach the liver
via the__________, interconversion of
hexoses occurs.
Glucose
Interconversion of hexoses occurs, converting fructose and galactose to__________
galactokinase and
galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase
Specifically, galactose is converted to
glucose by the action of two important
enzymes, namely, _____________________
Galactosemia
Absence of any of these enzymes results in the
leakage of galactose in the circulation, a
condition called ___________.
galactilol &
cataract formation
An important
consequence of galactosemia is the accumulation of a
by-product called__________ which contributes
to ____________.
the
different extrahepatic tissues in need of
an energy source.
After the interconversion process, the liver
dispatches the glucose molecules to _________________
glycolytic pathway
Embden-Meyerhof pathway
Glucose enters the ___________ or the
_____________ which extracts
energy from glucose and convert it in the
form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Glycogen
When not needed, the glucose is stored in the
liver in the form of ____________
Glycogenesis
The process of
building glycogen from glucose is called
______________.
Glycogenolysis
During starvation, however, when the
tissues run out of glucose fuel, the
glycogen stores from the liver are
mobilized. The glycogen is converted to
glucose via a process called______________
100 g
The glycogen reserve, however is only about
________
10-18 hours
After about ____________ fasting, it
becomes depleted.
Muscle Protein
Therefore, to further maintain the blood
glucose level within normal, the__________must be mobilized
amino acids
Muscle Proteins are degraded to form _________
many of which are glucogenic, i.e., they can
be converted into glucose.
gluconeogenesis
The amino acids produced, particularly
alanine, are brought to the liver where they
are converted into glucose, a process called___________
.
stored
triglycerides
Concurrently, there is degradation of _________________ in the adipose (fat) tissue to
provide an alternative energy source for the
tissues.
acetyl CoA
Fatty acids are also brought to the liver where
they are converted to_____________, the
precursor of ketone bodies
Ketone bodies
___________________serve as an important source
of energy for many vital organs including the
brain and the heart especially in cases of
starvation.
proteolysis
Moreover, the utilization of fatty acids and
ketone bodies, spares the proteins from further__________
which could result in reduction of
muscle mass.
all possible pathways
It is apparent that ______________ are
utilized by the body just to ensure that the
level of glucose in the circulation is within
normal range.
50-110 mg/dL
(2.8- 6.2 mmol/L).
The level of glucose in a fasting individual is
maintained within the range of__________________
Insulin
Only__________ is active as a hormone. This hormone pushes & store glucose into the tissues.
ẞ cells of the Islet of Langerhans
Insulin is Produced
by the______________________ of the
pancreas as a pro-hormone called pro-insulin.
Pro-insulin
________________ is processed by cleavage to form
C-peptide and insulin.
One is to one
____________ ratio between insulin and C-peptide.
the rapid
elimination of insulin.
As calculated, however, the ratio of Cpeptide
to insulin is 5:1. This is due to_________________
C-Peptide
________________has become
a marker for endogenous production of insulin
to differentiate it from administration of
exogenous insulin.
Hyperinsulinism
A high level of C-peptide (>1.9 ng/mL)
suggests__________________ which is
characterized by severe hypoglycemia.
glucose
is the most important
stimulus of insulin secretion.
amino acids particularly arginine
_______________________________
stimulate the ẞ cells to secrete insulin. This
happens after a protein-rich meal.
the intestinal
peptide secretin and other GI hormones
______________________________
stimulate secretion of insulin. These hormones
are released usually after ingestion or food.
inhibiting gluconeogenesis and
glycogenolysis.
Effects on Carbohydrate Metabolism
In the liver, insulin decrease production of
glucose by__________________
increases
glycogenesis
In the muscle and the liver, insulin_______________
increases glucose uptake.
In the muscle and the adipose tissue, insulin___________
bind with
its receptor on these cells
The increase in the glucose uptake has been
attributed to the ability of insulin to___________________
glucose transporters (especially GLUT-4
which is very rich in the muscles and adipose
tissues
Insulin also triggers the increase in the number
of ___________________ in the cell membrane.
decrease in fatty acid levels
Effects on Lipid Metabolism: the immediate
effect of insulin on lipid metabolism is the
triglyceride degradation (lipolysis)
Effects on Lipid Metabolism: Insulin decrease
____________________ in the
adipose tissue.
hormone-sensitive
lipase
Insulin decrease
triglyceride degradation (lipolysis) by inhibiting the ____________________present in the adipose.
increasing transport of glucose into the
adipocytes providing the glycerol-3-
phosphate needed in triglyceride synthesis.
Moreover, Insulin decreasing triglyceride degradation promotes triglyceride synthesis by_____________________
needed fatty
acids in the synthesis of triglycerides.
Insulin also increases the activity of the
lipoprotein lipase or lipemia clearing factor in
the plasma. This provides the____________________
insulin stimulates
the entry of amino acids into the cells. It also
promotes the synthesis of proteins in most
tissues.
Insulin Effects on Protein Synthesis
Glucagon
is a polypeptide hormone secreted
by the a-cells of the pancreatic Islets.
counter-regulatory hormones
Glucagon, together with other hormones e.g.,
epinephrine, cortisol, and growth hormone
are ______________________ i.e., they
oppose many actions of insulin.
"hyperglycemic
glycogenolytic factor."
Glucagon is also called the
the liver
Unlike insulin, glucagon has only one target
tissue______________
1. Glycogenolysis
2. Gluconeogenesis
Glucagon increases glucose by activating the following processes
hepatic lipolysis
Moreover, Glucagon increases____________. Thus,
there is an attendant increase in glucose and
fatty acids.
elevated levels of blood sugar
and insulin which increases after a meal.
The release of glucagon is markedly
depressed by________________
Blood Glucose
Glucagon secretion is stimulated by the following
factors:
A decrease in_____________ is the primary stimulus for
glucagon secretion. During an overnight fast,
elevated glucagon levels prevent
hypoglycemia.
AMINO ACID
Glucagon secretion is stimulated by the following
factors:
______________ from food stimulate
the release of both glucagon and insulin.
Glucagon prevents hypoglycemia that would
otherwise occur as a result of increase insulin
secretion after a protein meal
Epinephrine
Nonrepinephrine
_____________from adrenal medulla and
_____________ from sympathetic innervations
of the pancreas both stimulate the release of
glucagon.
stress, trauma, and excessive
exercise
During periods of __________________, the elevated epinephrine levels
override the effects on the a-cell of circulating
substrates.
Elevated
Depressed
In these situations, regardless of the
concentration of blood glucose, glucagon
levels are ___________ in anticipation of
increased glucose use. In contrast, insulin
levels are ______________.
cyclic adenosine
monophosphate (cAMP)
Epinephrine produced by the adrenal
medulla activates the adenylate cyclase
which produces__________________
phosphorylase
High levels of cAMP activate the enzyme
______________ causing increase
glycogenolysis.
hormone-sensitive lipase of
adipocytes.
cAMP also stimulates the breakdown of triglyceride
by activating the_______________
Cortisol
_____________is a glucocorticoid produced by the
adrenal cortex.
They play a role in the long-term regulation of
glucose metabolism.
the
adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Cortisol is produced by________________
produced by the anterior pituitary gland
promoting
protein catabolism and deamination.
Cortisol’s main activity is to stimulate
gluconeogenesis. It does this by_______________
glucose metabolism in the peripheral
tissue
Cortisol inhibits____________
Cortisol and growth hormone
are less
important in the short-term maintenance of
blood glucose concentration.
Growth Hormone
This is produced by the anterior pituitary.
It has an antagonistic action on insulin.
It inhibits the uptake of glucose by cells and
lipogenesis from carbohydrates
It promotes release of fatty acids from
adipocytes.
T3 and T4
The thyroid hormones ______________, promote the
absorption of glucose in the intestinal tract.
They also stimulate glycogenolysis and
accelerates the degradation of insulin.
In effect, they increase glucose levels in the
blood.
Somastostatin
produced by D cells of the pancreas.
inhibits pituitary, gastrointestinal, & pancreatic
hormones
Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
a major health problem in the Philippines.
a heterogeneous group of syndromes
characterized by an elevation of fasting
blood glucose caused by a relative or
absolute deficiency of insulin
glucagon ratio is very low.
The metabolic alterations are caused by
inadequate release of insulin aggravated by
an excess in glucagon. With diabetes mellitus,
the insulin
Polyuria
classic manifestations of DM
as the filtered blood passes through
the renal tubules, more water is absorbed by
the hyperosmotic ultrafiltrate thus increasing
the urinary output.
Polydipsia
classic manifestations of DM
this is excessive thirst
Polyphagia
classic manifestations of DM
this is excessive hunger