DSA05 - Abnormal TFTs and Thyroid Nodules
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
B/c 99% of TH is bound to protein in the blood (but still metabolically inactive)
Why does any condition that alters blood protein concentration affect TH concentration?
Only FREE TH is metabolically active
Why should FREE T4 (vs Total T4) be measured to diagnose Thyroid Disease?
TOTAL T3 (Free T3 concentration is VERY LOW)
If you need to measure SERUM T3 concentration, what do you need order and why?
Thyroid Dysgenesis
Define Cause of Hypothyroidism:
D/t embryologic MALdevelopment of thyroid gland (agensis = complete failure/no gland, hypoplasia = partial failure/small gland)
-Hx: Causes 85% of congenital hypothyroidism
-Path: Maldeveloped glands may be ectopically located
Most have no Abns at birth (T3 crosses placenta, so there's enough circulating TH through fetal development) --> Only if UnTx will they have Sx
-Sx:
> Fatigue
> Weakness
> Cold Intolerance
> Constipation
> Wt Gain
> Depression
> Female = Irregular Menses
>> Amenorrhea
>> Oligomenorrhea
>> Frequent periods
>> Menorrhagia
> Child =
>> Vertical growth failure
>> Intellectual disability
-PE:
> Bradycardia
> HTN (Inc PVR)
> Wt Gain
> Non-pitting edema (infiltration of skin w/ glycosaminoglycans)
> Diminished DTRs
-Dx:
Labs
> TSH = ELEVATED
> Free T4 = Low
> Hyponatremia
> Elevated LDL
> Elevated CK
> Anemia (usually normochromic, normocytic)
Imaging = Thyroid US & Radionuclide Scans
-Tx: Levothyroxine (Synthetic TH) --> Normal Health, Growth, and Neurodevelopment
Thyroid Dyshormonogenesis
Define Cause of Hypothyroidism:
D/t inborn error of metabolism ANYWHERE in TH synthesis
-Hx: 15% of cases of Congenital Hypothyroidism
Most have no Abns at birth (T3 crosses placenta, so there's enough circulating TH through fetal development) --> Only if UnTx will they have Sx
-Sx:
> Fatigue
> Weakness
> Cold Intolerance
> Constipation
> Wt Gain
> Depression
> Female = Irregular Menses
>> Amenorrhea
>> Oligomenorrhea
>> Frequent periods
>> Menorrhagia
> Child =
>> Vertical growth failure
>> Intellectual disability
-PE:
> Bradycardia
> HTN (Inc PVR)
> Wt Gain
> Non-pitting edema (infiltration of skin w/ glycosaminoglycans)
> Diminished DTRs
> ENLARGED THYROID GLAND (High TSH stimulates growth)
-Dx:
Labs
> TSH = ELEVATED
> Free T4 = Low
> Hyponatremia
> Elevated LDL
> Elevated CK
> Anemia (usually normochromic, normocytic)
Imaging = Thyroid US & Radionuclide Scans
-Tx: Levothyroxine (Synthetic TH) --> Normal Health, Growth, and Neurodevelopment
Autoimmune Thyroiditis (Hypothyroid phase) - aka "Hashimoto/Chronic Autoimmiune/Chronic Lymphocytic Thyroiditis"
Define Cause of Hypothyroidism:
Autoimmune injury to Thyroid Gland --> Impairs ability to make TH
-Hx:
> MCC of Hypothyroidism in Iodine SUFFICIENT parts of world (in 1% of population)
> MC in WOMEN
> Can occur at any time from childhood to adulthood
-Path: At beginning, TRANSIENT hypothyroidism (4-8 wks) when initial autoimmune destruction of thyroid gland --> "Leaks" preformed TH
-Sx:
> Fatigue
> Weakness
> Cold Intolerance
> Constipation
> Wt Gain
> Depression
> Female = Irregular Menses
>> Amenorrhea
>> Oligomenorrhea
>> Frequent periods
>> Menorrhagia
> Child =
>> Vertical growth failure
>> Intellectual disability
-PE:
> Bradycardia
> HTN (Inc PVR)
> Wt Gain
> Non-pitting edema (infiltration of skin w/ glycosaminoglycans)
> Diminished DTRs
> Thyroid gland slightly enlarged/firm (NONTENDER)
-Dx: Labs
> Key Findings
>> TPO (Thyroid Peroxidase) Ab - aka antimicrosomal Ab
>> TG (Thyroglobulin) Ab
> TSH = Elevated
> Free T4 = Low to Normal
> Hyponatremia
> Elevated LDL
> Elevated CK
> Anemia (usually normochromic, normocytic)
-Tx: Levothyroxine (Synthetic TH)
Thyroid insult/injury
Define Cause of Hypothyroidism:
Impairs ability of gland to synthesize and secrete TH
-Hx:
> RADIATION (cancer tx)
> SURGERY (removal of thyroid nodule - esp for Graves)
-Sx:
> Fatigue
> Weakness
> Cold Intolerance
> Constipation
> Wt Gain
> Depression
> Female = Irregular Menses
>> Amenorrhea
>> Oligomenorrhea
>> Frequent periods
>> Menorrhagia
> Child =
>> Vertical growth failure
>> Intellectual disability
-PE:
> Bradycardia
> HTN (Inc PVR)
> Wt Gain
> Non-pitting edema (infiltration of skin w/ glycosaminoglycans)
> Diminished DTRs
-Dx: Labs
> TSH = Elevated
> Free T4 = Low to Normal
> Hyponatremia
> Elevated LDL
> Elevated CK
> Anemia (usually normochromic, normocytic)
-Tx: Levothyroxine (Synthetic TH)
Riedel thyroiditis
Define Cause of Hypothyroidism:
Thyroid gland undergoes fibrotic changes (unknown cause) --> gland's synthetic function decreases
-Hx:
> RARE
> MC in WOMEN from 30-50 y/o
-Path:
> 1/3 pts = Hypothyroidism
> 2/3 pts = Euthyroid
-Sx: (Hypothyroid)
> Fatigue
> Weakness
> Cold Intolerance
> Constipation
> Wt Gain
> Depression
> Female = Irregular Menses
>> Amenorrhea
>> Oligomenorrhea
>> Frequent periods
>> Menorrhagia
-PE: (Hypothyroid)
> Bradycardia
> HTN (Inc PVR)
> Wt Gain
> Non-pitting edema (infiltration of skin w/ glycosaminoglycans)
> Diminished DTRs
> Thyroid Gland = Asymm, Enlarged, NONTENDER but "Hard as Wood" Texture
-Dx:
Biopsy = Not Necessary
Labs (HYPOTHYROID)
> TSH = Elevated
> Free T4 = Low to Normal
> Hyponatremia
> Elevated LDL
> Elevated CK
> Anemia (usually normochromic, normocytic)
-Tx: If HYPOTHYROID --> Levothyroxine
-Prog: Fibrosis may extend to NEARBY STRUCTURES
> Esophagus
> Trachea
> RLN (Dysphagia/Hoarseness)
> IgG4-related disease (Multiorgan fibro-inflammatory disorder)
Iodine deficiency
Define Cause of Hypothyroidism:
Hypothyroidism d/t low nutritional iodine
-Hx:
> Uncommon in U.S., but large global problem
> Affects 40% of global population, but uncommon in coastal/industrialized regions (seen in seafood and table salt) --> Occurs in REMOTE/INLAND parts of world
-Path: Iodine needed for T4 and T4 synthesis
Issues present AT BIRTH (UNIQUE TO CHILDREN)
-Sx:
> Fatigue
> Weakness
> Cold Intolerance
> Constipation
> Wt Gain
> Depression
> Female = Irregular Menses
>> Amenorrhea
>> Oligomenorrhea
>> Frequent periods
>> Menorrhagia
> Child =
>> Vertical growth failure
>> Intellectual disability
-PE:
> Bradycardia
> HTN (Inc PVR)
> Wt Gain
> Non-pitting edema (infiltration of skin w/ glycosaminoglycans)
> Diminished DTRs
> Enlarged Thyroid Gland (more TSH)
-Dx: Labs
> TSH = High
> Free T4 = Low to Normal
> LOW Urine Iodine!
> Hyponatremia
> Elevated LDL
> Elevated CK
> Anemia (usually normochromic, normocytic)
-Tx: Iodine Replacement (Tablets or Solution) --> If unsuccessful = Levothyroxine
Subacute thyroiditis (hypothyroid phase) - aka de Quervain/Subacute Granulomatous/Painful Thyroiditis
Define Cause of Hypothyroidism:
Transient, PAINFUL inflammatory process affecting thyroid gland (often after Viral URI)
-Hx:
> Hx of Viral URI (2-8 wks before inflammation)
> RARE
> MC in Young Adulthood to Middle Age
-Path: Maladaptive immune response to initial viral infex
> Phase 1 = HYPERTHYROIDISM for 2-8 wks (d/t initial thyroid gland inflammation --> LEAKS preformed TH)
> Phase 2 = NORMAL TH levels for 2-8 wks (transition)
> Phase 3 = HYPOTHYROIDISM for 2-8 wks (inflammation stops synthesis)
> Phase 4 = EUTHYROID (inflammation stops)
-Sx: Depends on Phase
-PE: Depends on Phase
> TENDER (severely) Thyroid gland - may be mildly enlarged
> Neck pain radiating to jaw
-Dx: Labs
> ESR (elevated) > 50 mm/hr
> Hyperthyroid = Low TSH, normal to high T4
> Normal = TSH & T4 normal
> Hypothyroid = High TSH, low to normal T4
-Tx:
> NSAIDs (manage pain)
> Beta-blockers (if Hyperthyroid significant)
> Levothyroxine (if Hypothyroid significant)
Medication-induced Hypothyroidism
Define Cause of Hypothyroidism:
-Hx: Use of...
> Lithium (5-50%)
> Amiodarone (15%)
-Path:
> Lithium
>> Stops coupling of iodotyrosine residues to form T3/T4
>> Inhibits release of T3/T4 from Thyroid gland
> Amiodarone
>> Decreases conversion of T4 to T3 via deiodinases
>> Blocks binding of T3 to TH receptors
>> May directly destroy thyroid tissue
-Sx:
> Fatigue
> Weakness
> Cold Intolerance
> Constipation
> Wt Gain
> Depression
> Female = Irregular Menses
>> Amenorrhea
>> Oligomenorrhea
>> Frequent periods
>> Menorrhagia
> Child =
>> Vertical growth failure
>> Intellectual disability
-PE:
> Bradycardia
> HTN (Inc PVR)
> Wt Gain
> Non-pitting edema (infiltration of skin w/ glycosaminoglycans)
> Diminished DTRs
> ENLARGED THYROID GLAND
-Dx: Labs
> TSH = HIGH
> Free T4 = Low to Normal
>> Amiodarone = Low to Normal T4, Low T3
> Hyponatremia
> Elevated LDL
> Elevated CK
> Anemia (usually normochromic, normocytic)
-Tx: Stop med --> Start Levothyroxine
-Prog:
Central Hypothyroidism
Define Cause of Hypothyroidism:
When normal thyroid gland receives INADEQUATE STIMULATION d/t disorder of pituitary ot hypothalamus
> Pituitary = Secondary
> Hypothalamus = Tertiary
-Hx:
> Less common than Primary
> In 1 per 50,000 people
> Causes =
>> Trauma
>> Radiation
>> Neurosurgical injury
>> CNS Infex
>> Adjacent tumor growth
-Path: Insult or injury to central brain structures
-Sx:
> Fatigue
> Weakness
> Cold Intolerance
> Constipation
> Wt Gain
> Depression
> Female = Irregular Menses
>> Amenorrhea
>> Oligomenorrhea
>> Frequent periods
>> Menorrhagia
> Child =
>> Vertical growth failure
>> Intellectual disability
-PE:
> Bradycardia
> HTN (Inc PVR)
> Wt Gain
> Non-pitting edema (infiltration of skin w/ glycosaminoglycans)
> Diminished DTRs
-Dx: Labs
> TSH = Low or Inappropriately Normal
> Free T4 = Low
> Hyponatremia
> Elevated LDL
> Elevated CK
> Anemia (usually normochromic, normocytic)
-Tx: Levothyroxine (Synthetic TH)
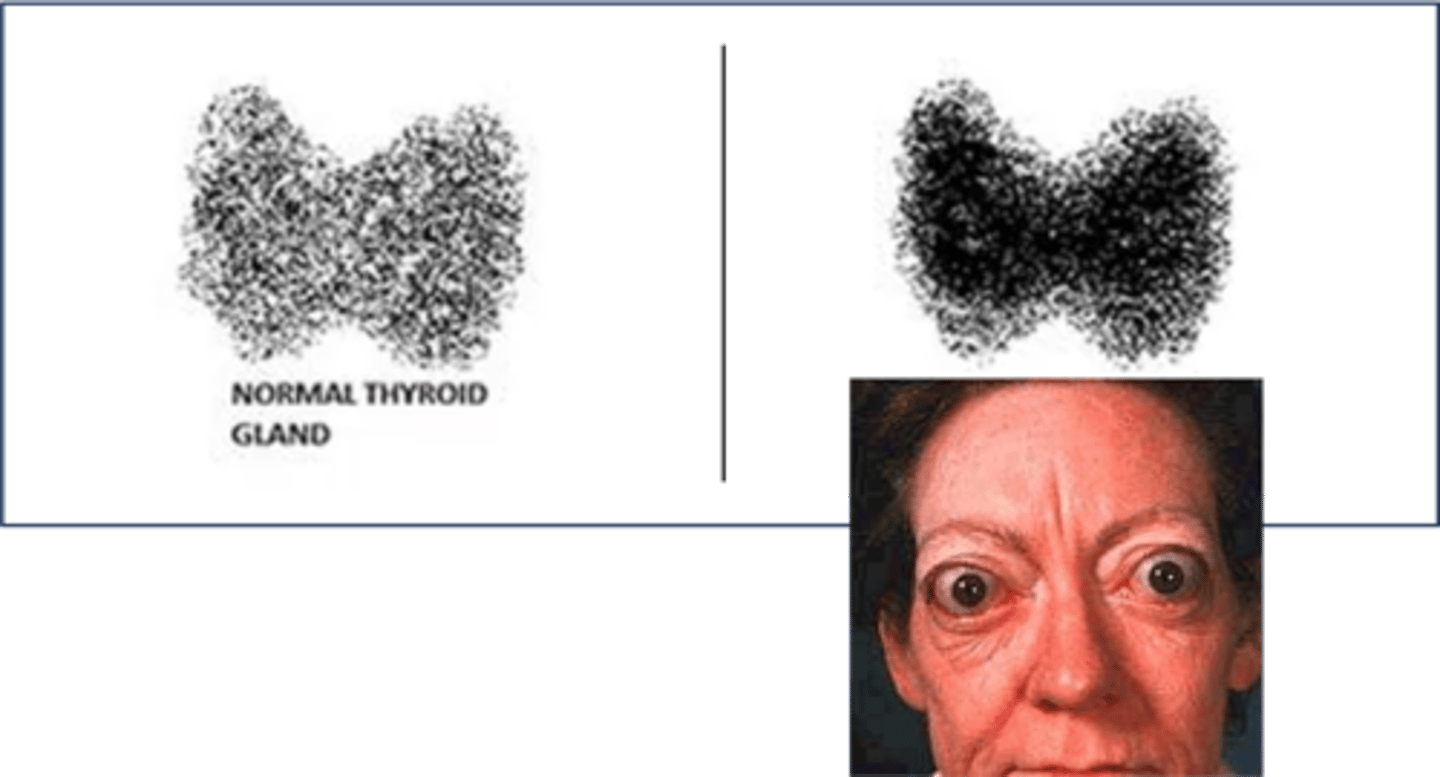
Graves Disease
Define Cause of Hyperthyroidism:
Autoimmune condition where AutoAbs bind to and stimulate TSH receptor
-Hx:
> MCC of Hyperthyroidism
> MC in WOMEN (usually from 20-50 y/o, but can occur in childhood to adolescence)
-Path:
-Sx:
> Tremors
> Palpitations
> Anxiety
> Diarrhea
> Heat Intolerance
> Wt Loss
> Fatigue
-PE:
> Tachycardia
> Systolic HTN w/ widened pulse pressure
>> High SBP d/t increased cardiac output
>> Low DBP d/t less PVR
> Wt Loss
> Eyelid Lag (abnormally raised upper eyelid d/t SNS hyperactivity --> still see sclera when they look down)
> ENLARGED THYROID GLAND (Stimulation of TSH receptor)
> Exophthalmos (Proptosis)
-Dx:
Labs
> TSH receptor Ab (TRAb) = POSITIVE
> TSH = Low
> Free T4 = High (Total T3 = HIGH - rises before Free T4)
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Scan
> High = LOTS of new TH
-Tx: ALL 1st Line
> Thionamides = Methimazole, PTU (Antithyroid)
> Thyroidectomy --> Life time Levothyroxine
> Radioactive Iodine Ablation --> Life time Levothyroxine
> Beta Blocker (Sx relief when TH High)
Toxic nodule/multinodular goiter
Define Cause of Hyperthyroidism:
Autonomous nodules w/n thyroid gland --> secrete excess TH (INDEPENDENT OF TSH REGULATION)
-Hx:
> 2nd MCC of Hyperthyroidism (20%)
> MC in WOMEN around 50 y/o
-Path: BENIGN!
> D/t somatic mutation (occurring after fertilization) in thyroid cell --> focal excess growth of functioning Thyroid tissue (activating mutation to gene for TSH receptor)
> Longstanding, untreated hypothyroidism ==> chronic elevation in TSH
-Sx:
> Tremors
> Palpitations
> Anxiety
> Diarrhea
> Heat Intolerance
> Wt Loss
> Fatigue
-PE:
> Tachycardia
> Systolic HTN w/ widened pulse pressure
>> High SBP d/t increased cardiac output
>> Low DBP d/t less PVR
> Wt Loss
> Eyelid Lag (abnormally raised upper eyelid d/t SNS hyperactivity --> still see sclera when they look down)
> PALPABLE NODULE of Thyroid Gland
-Dx:
Labs
> TSH = Low
> Free T4 and/or Total T3 = High
Thyroid US = Nodules
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Scan (CONFIRM)
> High = LOTS of new TH (focal hyper-functionality)
-Tx:
> Thionamides = Methimazole, PTU (Antithyroid)
> Thyroidectomy --> Life time Levothyroxine
> Radioactive Iodine Ablation --> Life time Levothyroxine
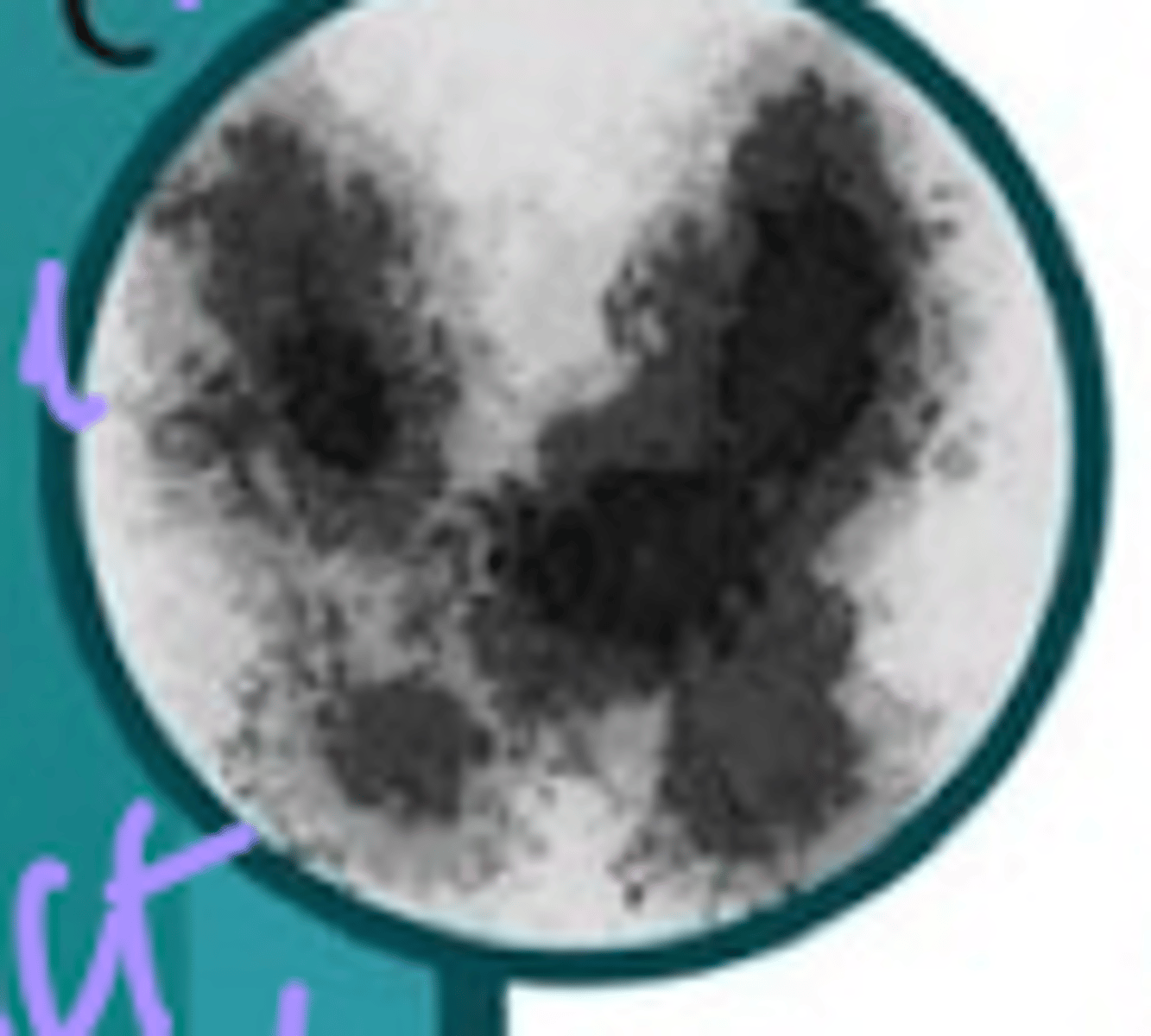
Autoimmune thyroiditis (toxic phase)
Define Cause of Hyperthyroidism:
Autoimmune injury to gland impairs ability to produce TH --> TRANSIENT Phase (destruction of gland --> "Leak" preformed TH) for 4-8 wks
-Sx:
> Tremors
> Palpitations
> Anxiety
> Diarrhea
> Heat Intolerance
> Wt Loss
> Fatigue
-PE:
> Tachycardia
> Systolic HTN w/ widened pulse pressure
>> High SBP d/t increased cardiac output
>> Low DBP d/t less PVR
> Wt Loss
> Eyelid Lag (abnormally raised upper eyelid d/t SNS hyperactivity --> still see sclera when they look down)
> Thyroid gland slightly enlarged/firm (NONTENDER)
-Dx:
Labs
> Key Findings
>> TPO (Thyroid Peroxidase) Ab - aka antimicrosomal Ab
>> TG (Thyroglobulin) Ab
> TSH = Low
> Free T4 = High
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Scan
> Low = NOT making new TH
-Tx:
> Beta Blocker = Sx Relief during Phase
Subacute thyroiditis (toxic phase)
Define Cause of Hyperthyroidism:
Transient, PAINFUL inflammatory process affecting thyroid gland (often after Viral URI)
-Hx:
> Hx of Viral URI (2-8 wks before inflammation)
> RARE
> MC in Young Adulthood to Middle Age
-Path: Maladaptive immune response to initial viral infex
> Phase 1 = HYPERTHYROIDISM for 2-8 wks (d/t initial thyroid gland inflammation --> LEAKS preformed TH)
> Phase 2 = NORMAL TH levels for 2-8 wks (transition)
> Phase 3 = HYPOTHYROIDISM for 2-8 wks (inflammation stops synthesis)
> Phase 4 = EUTHYROID (inflammation stops)
-Sx: HYPERTHYROID
> Tremors
> Palpitations
> Anxiety
> Diarrhea
> Heat Intolerance
> Wt Loss
> Fatigue
-PE: HYPERTHYROID
> TENDER (severely) Thyroid gland - may be mildly enlarged
> Neck pain radiating to jaw
> Tachycardia
> Systolic HTN w/ widened pulse pressure
>> High SBP d/t increased cardiac output
>> Low DBP d/t less PVR
> Wt Loss
> Eyelid Lag (abnormally raised upper eyelid d/t SNS hyperactivity --> still see sclera when they look down)
-Dx:
Labs
> ESR (elevated) > 50 mm/hr
> Hyperthyroid = Low TSH, normal to high T4
> Normal = TSH & T4 normal
> Hypothyroid = High TSH, low to normal T4
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Scan
> Low = NOT making new TH
-Tx:
> NSAIDs (manage pain)
> Beta-blockers (if Hyperthyroid significant)
> Levothyroxine (if Hypothyroid significant)
TSH-producing adenoma
Define Cause of Hyperthyroidism:
BENIGN Pituitary tumor autonomously secreting excess TSH
-Hx:
> VERY RARE
> Mean Age = 40 y/o
-Sx:
> Tremors
> Palpitations
> Anxiety
> Diarrhea
> Heat Intolerance
> Wt Loss
> Fatigue
-PE:
> Tachycardia
> Systolic HTN w/ widened pulse pressure
>> High SBP d/t increased cardiac output
>> Low DBP d/t less PVR
> Wt Loss
> Eyelid Lag (abnormally raised upper eyelid d/t SNS hyperactivity --> still see sclera when they look down)
> DIFFUSE GLAND ENLARGEMENT
> VFDs (Bitemporal Hemianopsia) & HAs (if large)
-Dx:
Labs
> TSH = Low
> Free T4 = High or Inappropriately Normal
> Alpha Subunit of TSH = High
MRI of Pituitary = Reveal Tumor
-Tx:
> Somatostatin Analog (Octreotide, etc)
> Removal of Pituitary Adenoma
Exogenous Hyperthyroidism
Define Cause of Hyperthyroidism:
High circulating concentration of TH d/t taking too much TH medication (ex: Levothyroxine)
-Hx:
> Accidental excess ingestion (trying to find right dose)
> Intentional excess ingestion (to induce weight loss)
-Sx:
> Tremors
> Palpitations
> Anxiety
> Diarrhea
> Heat Intolerance
> Wt Loss
> Fatigue
-PE:
> Tachycardia
> Systolic HTN w/ widened pulse pressure
>> High SBP d/t increased cardiac output
>> Low DBP d/t less PVR
> Wt Loss
> Eyelid Lag (abnormally raised upper eyelid d/t SNS hyperactivity --> still see sclera when they look down)
> GLAND is NOT ENLARGED
-Dx:
Labs
> TSH = Low
> Free T4 = High
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Scan
> Low = NOT making new TH
-Tx: Have the stop taking meds, or reduce dose --> For Sx = Beta Blockers
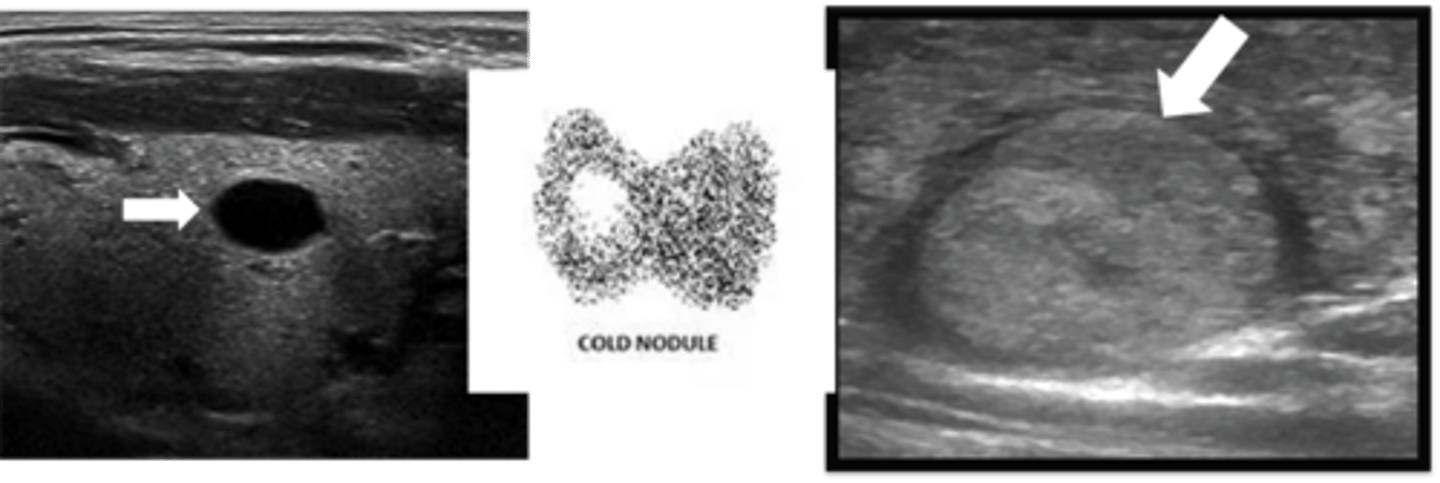
Benign & Non-Functional Thyroid Nodule
Define Condition:
Abnormal growth of thyroid cells --> lump in thyroid gland
-Hx: Extremely common
-PE: Asymm enlargement of Thyroid Gland
-Dx:
Labs
> TSH = Normal to High
Imaging
> Incidental Finding
> Radioiodine = COLD (low)
> Thyroid US = Nothing or Worrisome --> Fine Needle Aspiration = Reassuring (CYSTIC, SMOOTH MARGINS)
-Tx: OBSERVE
Benign but FUNCTIONAL (Toxic) Thyroid Nodule
Define Condition:
Abnormal growth of thyroid cells --> lump in thyroid gland
-Hx: Extremely common
-PE: Asymm enlargement of Thyroid Gland
-Dx:
Labs
> TSH = Normal to High
Imaging
> Incidental Finding
> Radioiodine = HOT (high)
-Tx: Tx for Sx
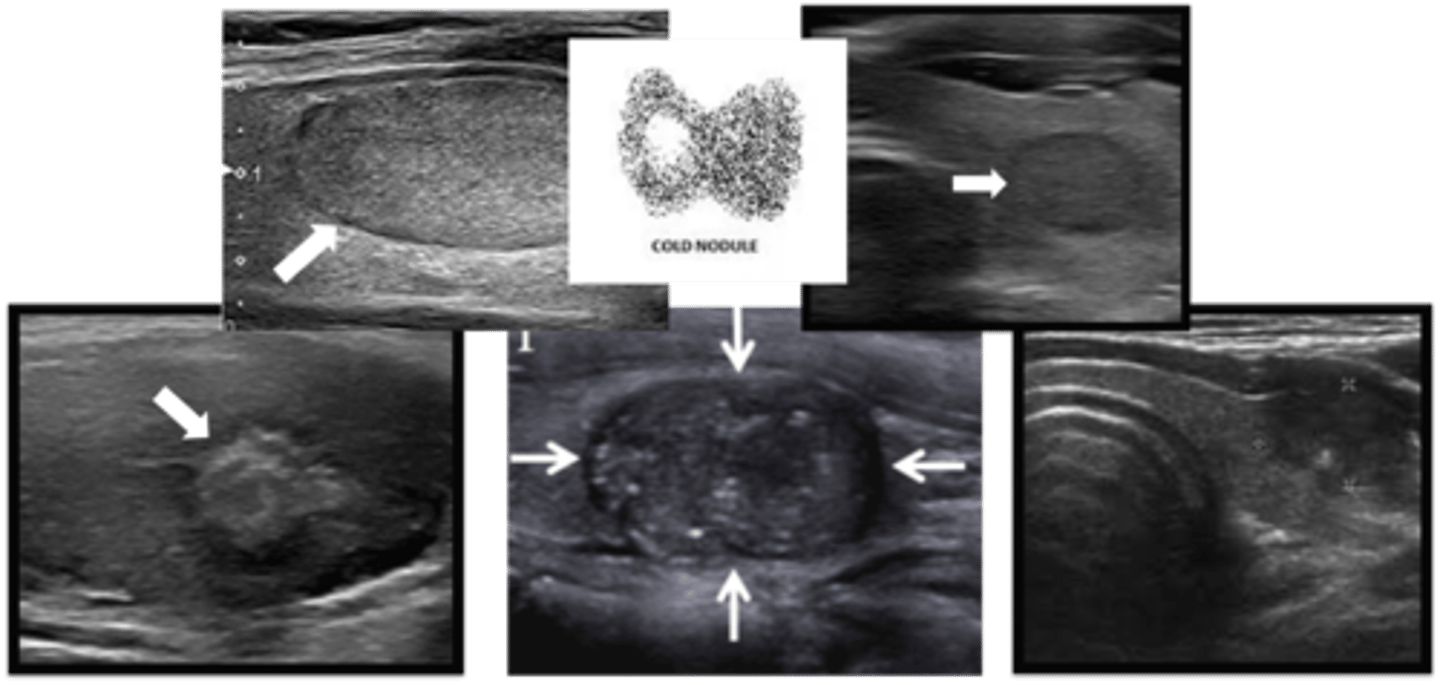
Malignant Thyroid Nodule
Define Condition:
Abnormal growth of thyroid cells --> lump in thyroid gland
-Hx: Only 5%
> Age < 30 yrs
> Hx of Radiation to head/neck
> FHx of Thyroid Cancer
-Types:
> Papillary Carcinoma
> Follicular Carcinoma
> Medullary Carcinoma
> Anaplastic Carcinoma
-PE:
> Asymm enlargement of Thyroid Gland
> Fixed and/or Firm
-Dx:
Labs
> TSH = LOW
Imaging
> Incidental Finding
> Radioiodine = COLD (low)
> Thyroid US = Nothing or Worrisome --> Fine Needle Aspiration = WORRISOME (SOLID, HYPOECHOIC, IRREGULAR MARGINS, EXTRATHYROIDAL EXTENSION, CALCLIFICATIONS)
-Tx: REMOVAL
MEN2A and MEN2B
Define Condition:
Hereditary Cancer Syndromes a/w multiple endocrine tumors
-Hx: AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT
> Most who have MEN2 = MEN2A (only 5% have MEN2B)
> Appears around 30 y/o
-Path:
> D/t gain-of-function mutation to RET proto-oncogene on chromosome 10 (encodes TK receptor playing role in cell growth)
> MEN2A
>> 1st = Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
>> Parathyroid hyperplasia
>> Pheochromocytoma
> MEN2B
>> 1st = Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
>> Pheochromocytoma
>> Non-endocrine = mucosal neuroma, intestinal ganglioneuromas, marfanoid habitus
Pheochromocytoma
Define Condition:
Catecholamine producing tumor from chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla
-Hx:
> VERY RARE
> Around 40s-50s
-Path:
> MOST = SPORADIC
> 25%-40% = MEN2A, MEN2B, VHL, NF1
**Rule of 10s**
> 10% = Malignant
> 10% = Bilateral
> 10% = OUTSIDE Adrenal Glands (paragangliomas = thorax, abdomen, pelvis)
> 10% = Children
-Sx/PE: EPISODIC
> HTN
> HA
> Palpitations/Tachycardia
> Sweating
> Pallor
-Dx:
Labs
> 24-hour urine fractionated catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine)
> 24-hour urine fractionated metanephrines (metanephrine and normetanephrine)
> Plasma fractionated metanephrines (metanephrine and normetanephrine)
Imaging (MRI or CT) = Locate Tumor
-Tx:
> 1st = (Phenoxybenzamine) Alpha-Adrenergic Receptor Blockade, 7 days before operation
> 2nd = (Propanolol, Metoprolol) Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Blockage, 2-3 days before operation
> 3rd = Remove Adrenal Gland w/ Tumor