Unit-1 (cell structure and variety of organisms) [igcse biology edexcel]
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
function of:
nucleus
cytoplasm
cell membrane
mitochondria
ribosome
cell wall
permanent vacuole
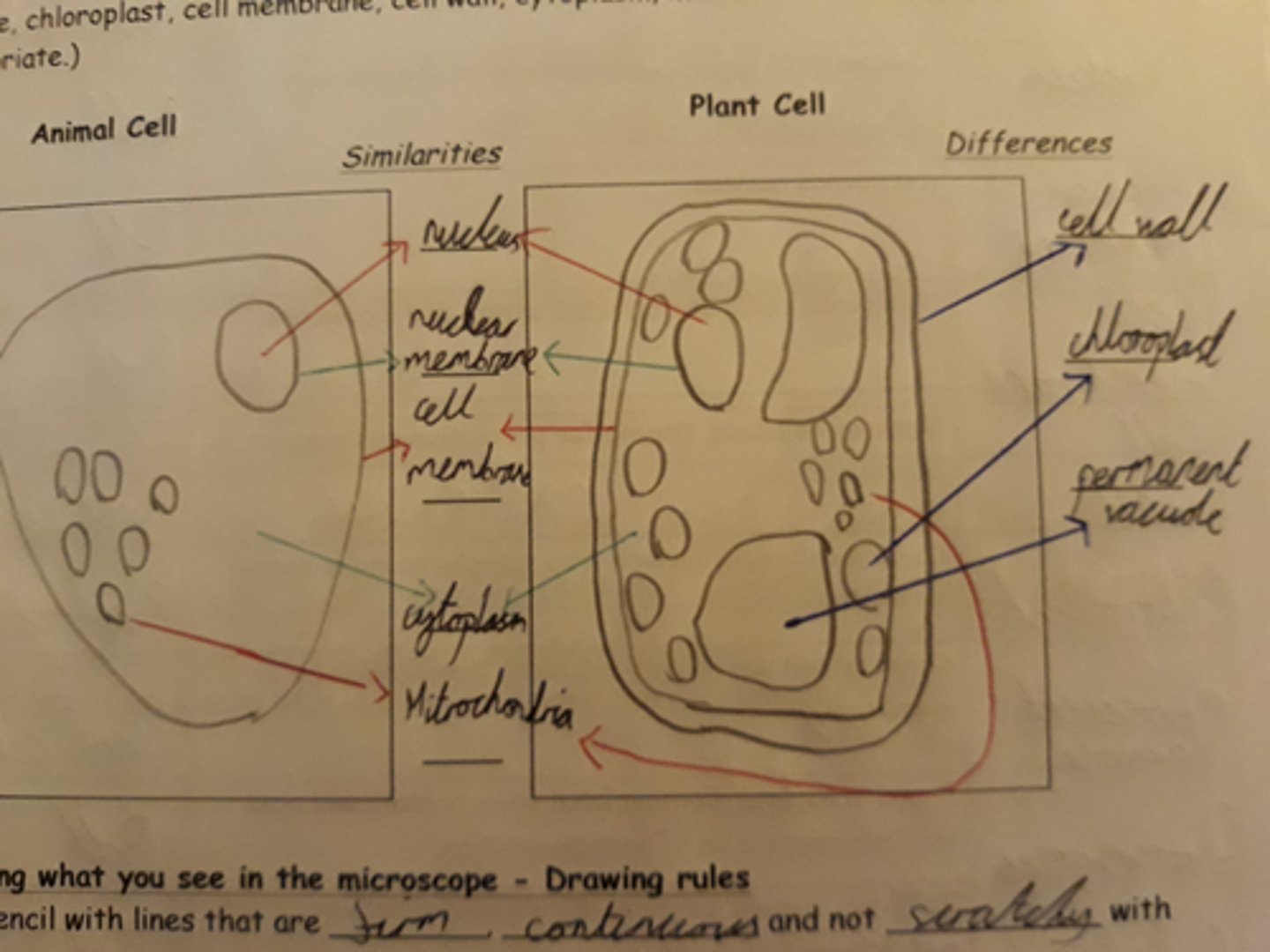
nucleus : contains genetic material
cytoplasm : site of chemical reactions, contains organelles and enzymes
cell membrane: controls what enters and leaves cell
mitochondria: site of aerobic respiration, providing cell with energy ('powerhouse of cell')
Ribosome- site of protein synthesis (transcription)
cell wall: provides cell support (made from cellulose)
permanent vacuole- contains cell sap
plant vs animal cell diagram
Define:
organelle
cell
organelle: a specialized structure found inside cells that carry out specific functions
cell: the basic functional and structural unit of life
define tissue
tissue: group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function
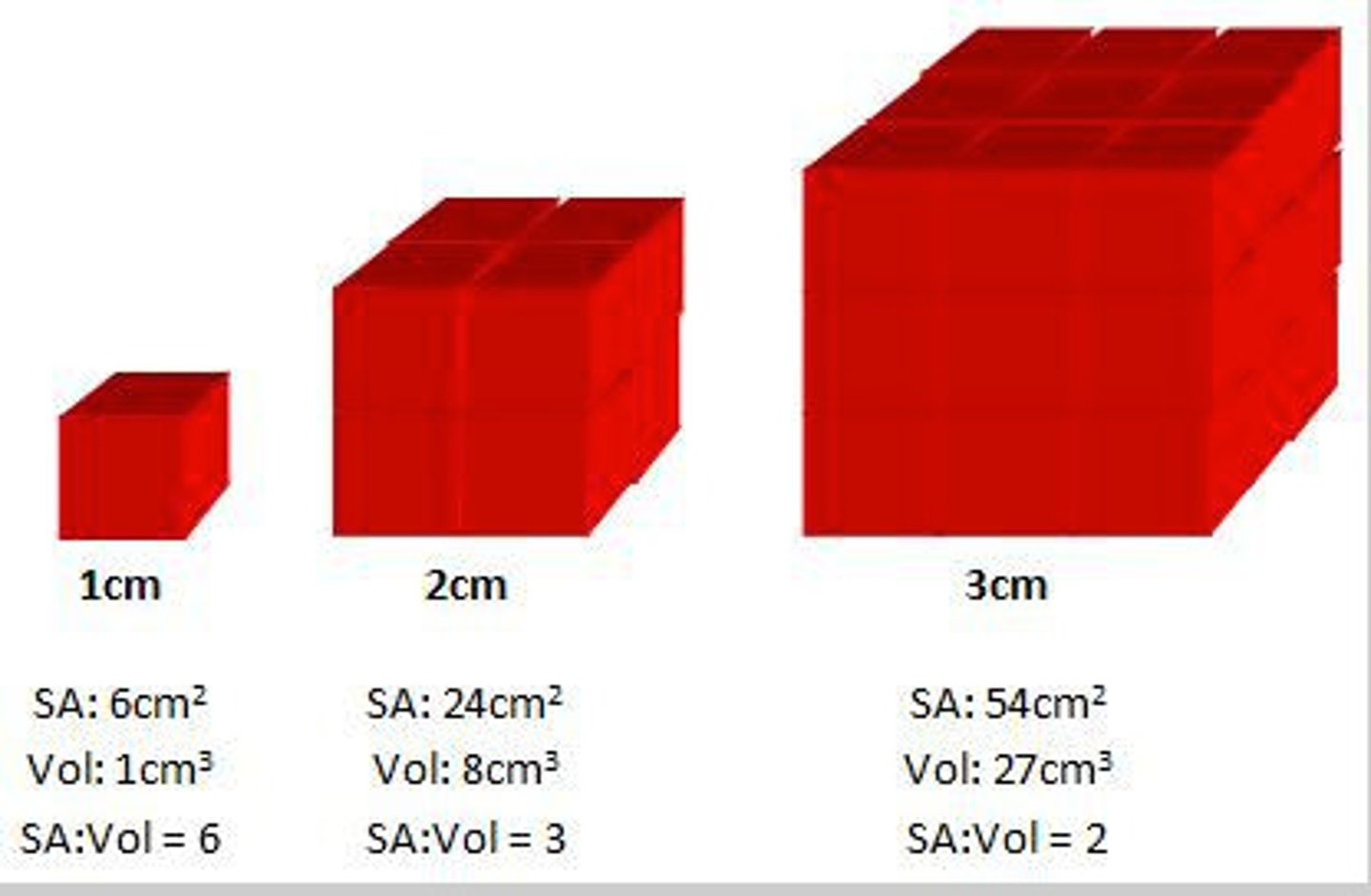
Surface area to volume ratio
- As an organism gets larger, SA:V ratio decreases (more increase in V, less increase in SA)
- so small organism = LARGE SA:V ratio
- small organisms like bacteria can rely on diffusion for exchange due to LARGE SA:V ratio.
- big organism = SMALL SA:V ratio
- for big organisms diffusion would be too slow due to SMALL SA:V ratio, so they have transport systems.
P.S - disadvantage of large SA:V --> more heat loss.
- so smaller organisms lose more heat, due to large SA:V
how fungi obtain food by saprotrophic nutrition?
- secretes digestive enzymes onto food
- for extracellular digestion
- then absorb the digested food
difference between eukaryotic organisms and prokaryotic organism
Eukaryotes: [yeast, plant, animal]
- has nucleus
- has organelles like mitochondria
- no plasmid
(can be unicellular or multicellular)
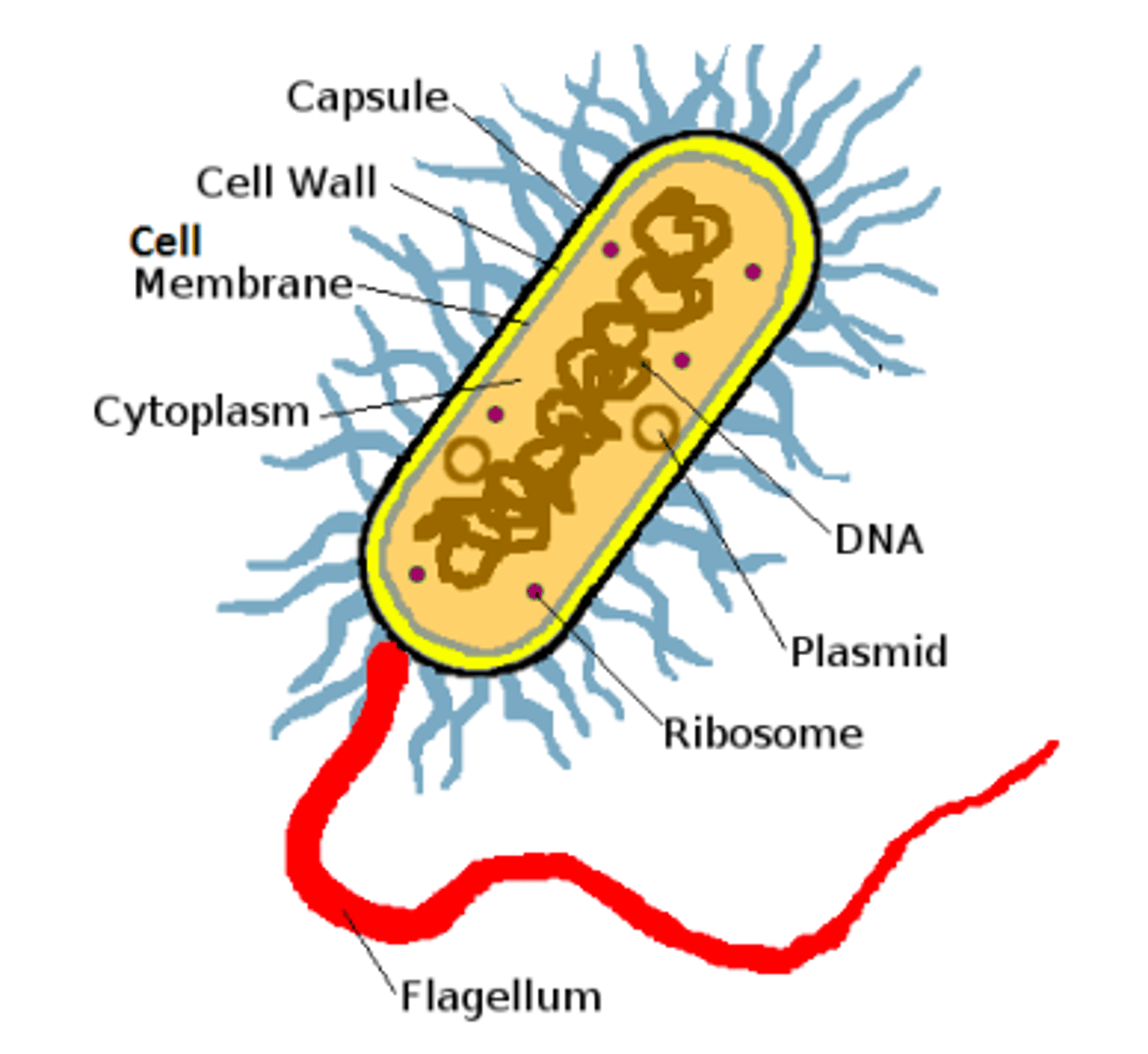
Prokaryotes: [bacteria]
- no nucleus
- no organelles
- plasmid present
(always unicellular)
define organ
define organ system
group of tissues working together to perform specific functions
group of organs working together to perform specific function
Define enzyme. How do enzymes work?
- Enzymes are biological catalysts
- that speeds up a reaction, without being used up
-each enzyme has a specific active site that fits a specific substrate like a lock and key
- when an enzyme and its substrate collide, an enzyme-substrate complex forms
effect of temperature and pH in enzyme activity
1) temperature:
- Increase in temp, increases enzyme activity/rate of reaction
- as K.E increases, more collision occurs (more es complex)
- above optimum temp, enzymes will denature, active site shape is altered
- so substrate no longer fit to active site, so rate of reaction decreases
-Decrease in temp decreases rate of reaction as enzymes are inactive(less K.E) (less collision)
- less ES complex formed
2) pH:
- pH above or below the optimum pH decreases enzyme activity
- if change in pH too large, enzyme denature
define antibiotic
Give an example.
medicines that kill bacteria.
e.g: penicillin
how is carbohydrate stored in fungi.
draw yeast cell ( yeast cell is unicellular btw)
- carb is stored as glycogen in fungi
[fungi have cell wall made of chitin ]
![<p>- carb is stored as glycogen in fungi</p><p>[fungi have cell wall made of chitin ]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/51528d4a-4be4-46ea-8dde-d5b8ec20ba5a.png)
draw bacteria diagram
protist vs bacteria
protist:
- nucleus present
- some got chloroplast
bacteria:
- nucleus absent
- no chloroplast
both can have flagellum
Give example of virus and its effect, in humans and plants.
Human: HIV, causes AIDS. (weaken immune system)
plants: tobacco mosaic virus, prevents formation of chloroplasts.
give example of a pathogenic protist and the disease it causes.
pathogenic protist: plasmodium
disease: malaria
Define partially permeable membrane
A membrane that only allows small molecules to pass through and does not let large molecules to pass through.
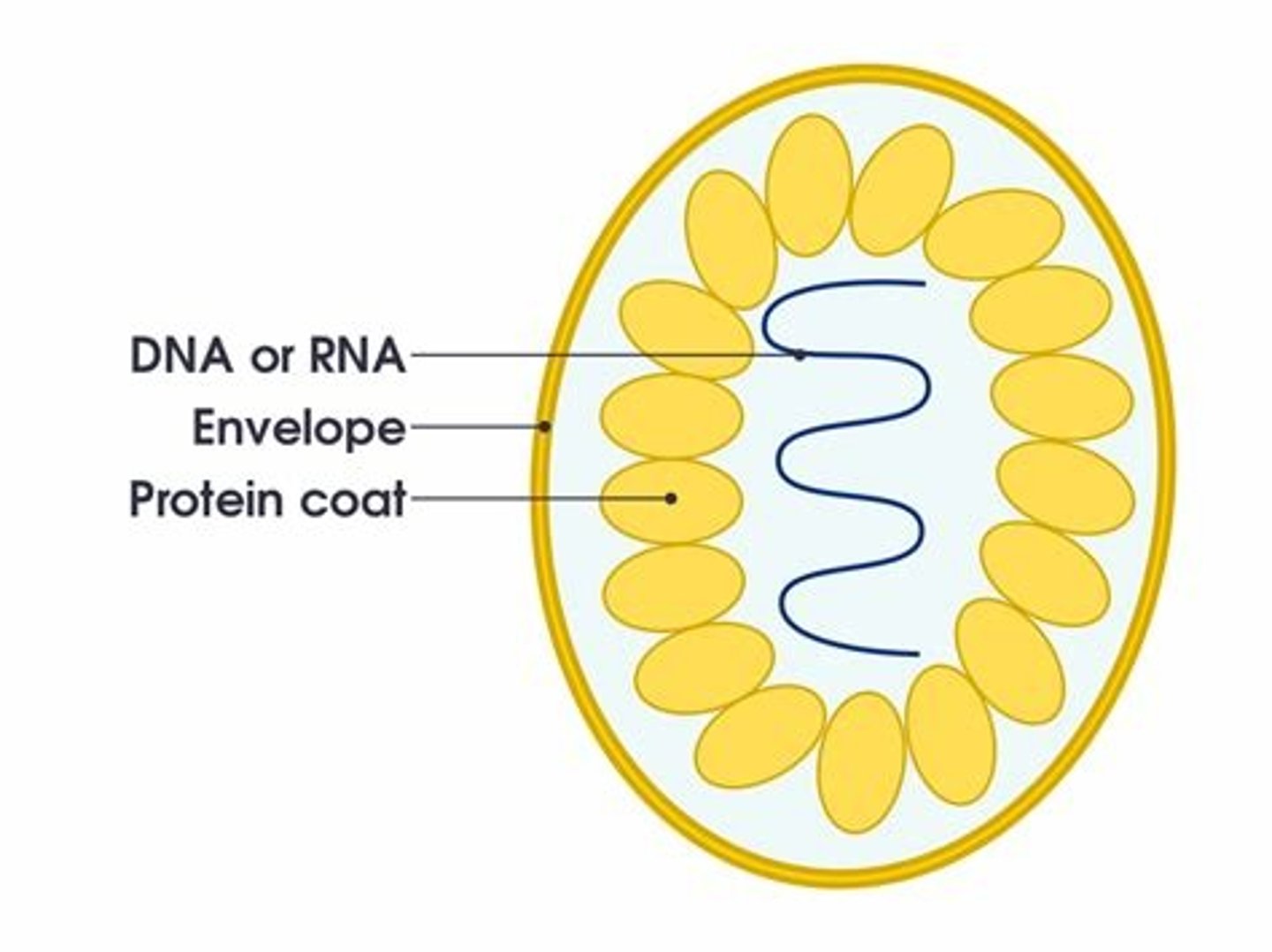
Features of virus
why are viruses not considered as living organisms?
virus:
- protein coat
- DNA
- they cannot reproduce without a host
- do not feed, respire or move etc.