ch7 membrane structure and function
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
the plasma membrane is the boundary that separates the ____ from its ____
living cell; nonliving surroundings
the plasma membrane exhibits selective permeability, which is what?
allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others
cell membranes are ____ ____ of lipids and proteins
fluid mosaics
_____, the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane, are ____ molecules, which contain ____ and ____ regions
phospholipids; amphipathic; hydrophobic; hydrophilic
the fluid mosaic model states that a membrane is a ____ structure with a "mosaic" of various _____ embedded in it
fluid; proteins
why do we die from dehydration?
water can not bring things to cells
Singer & Nicolson proposed what?
fluid mosaic model - membrane is mosaic of proteins dispersed/inserted into phospholipid bilayer w/only hydrophilic regions exposed to water
in the fluid mosaic model, the membrane contains multiple types of ____ sandwiched btwn two layers of ____
proteins; phospholipids
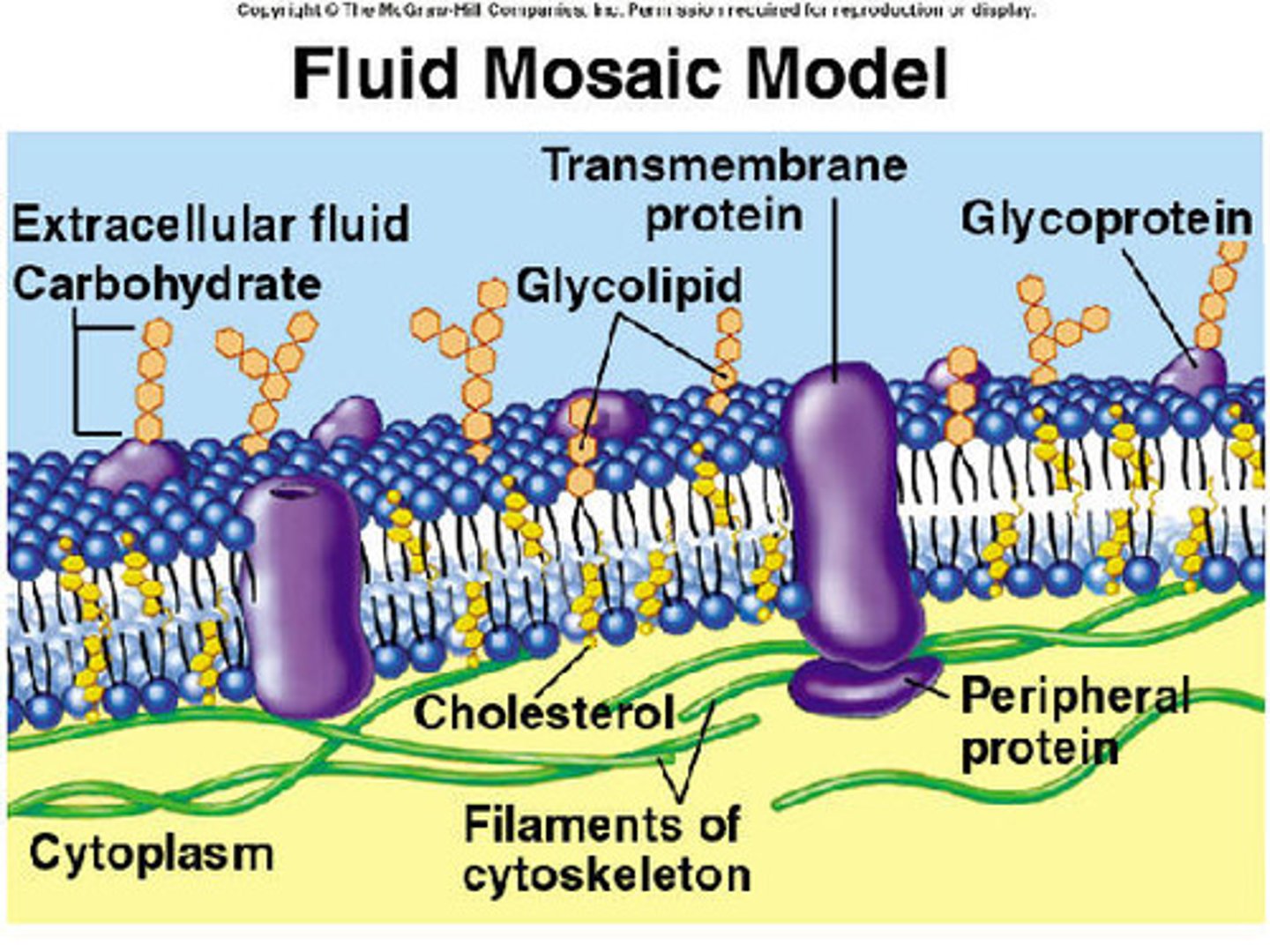
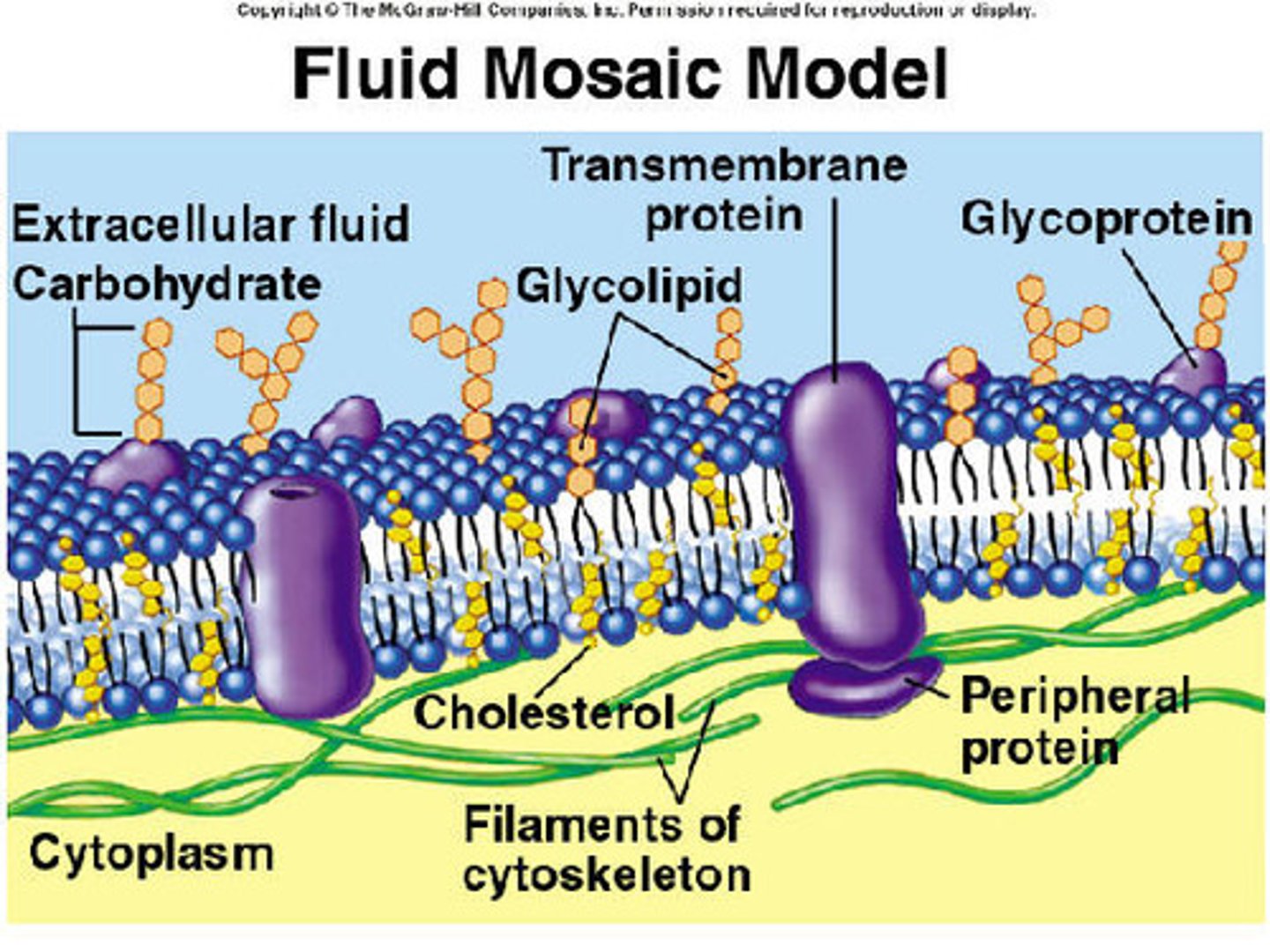
_____ form the basic structure of a cellular bilayered membrane, and ____ traverse through it
phospholipids; proteins
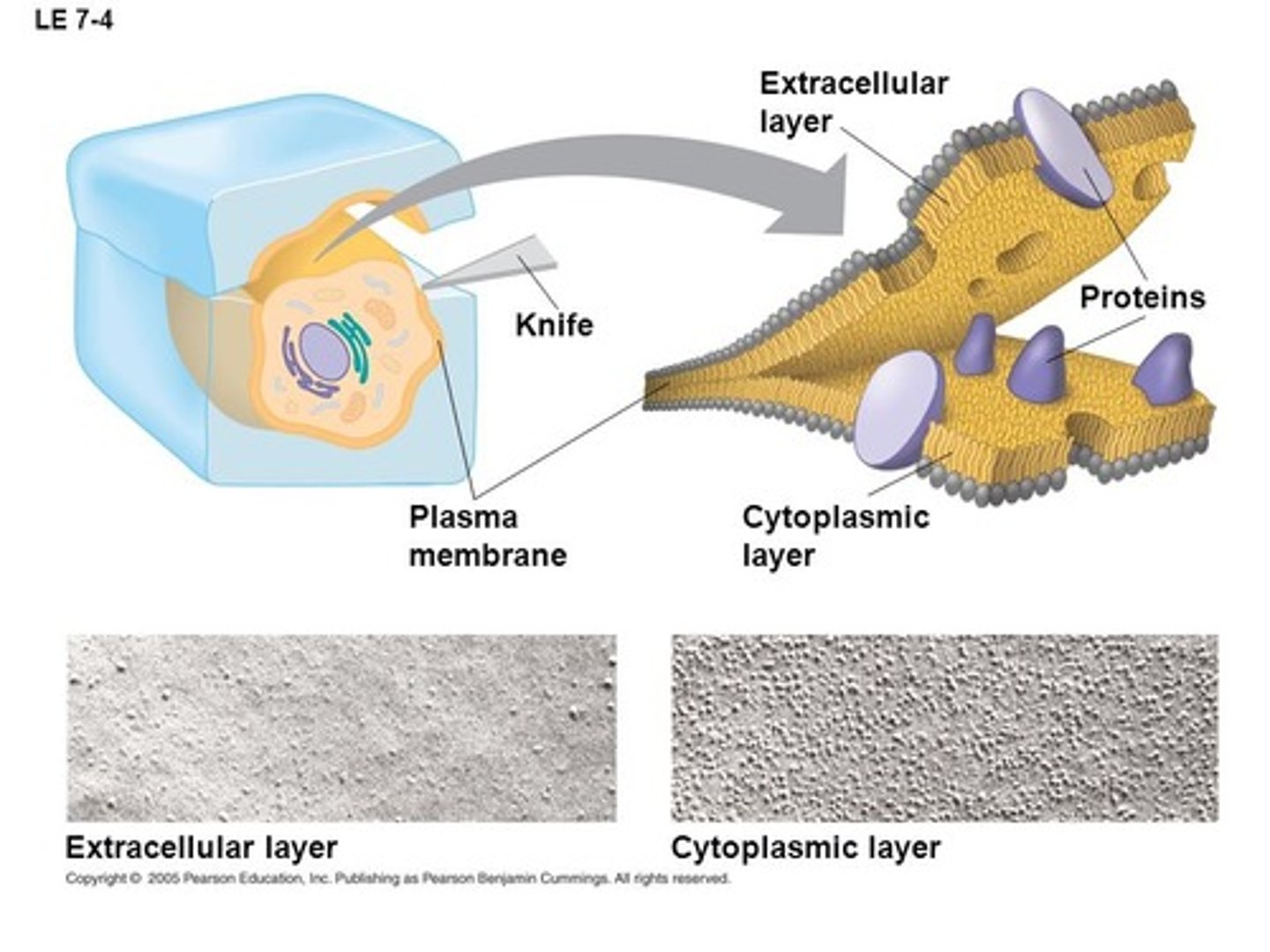
_____ studies of the plasma mem supported the fluid mosaic model. what do these studies include?
freeze-fracture; specialized prep technique that splits in middle of phospholipid bilayer
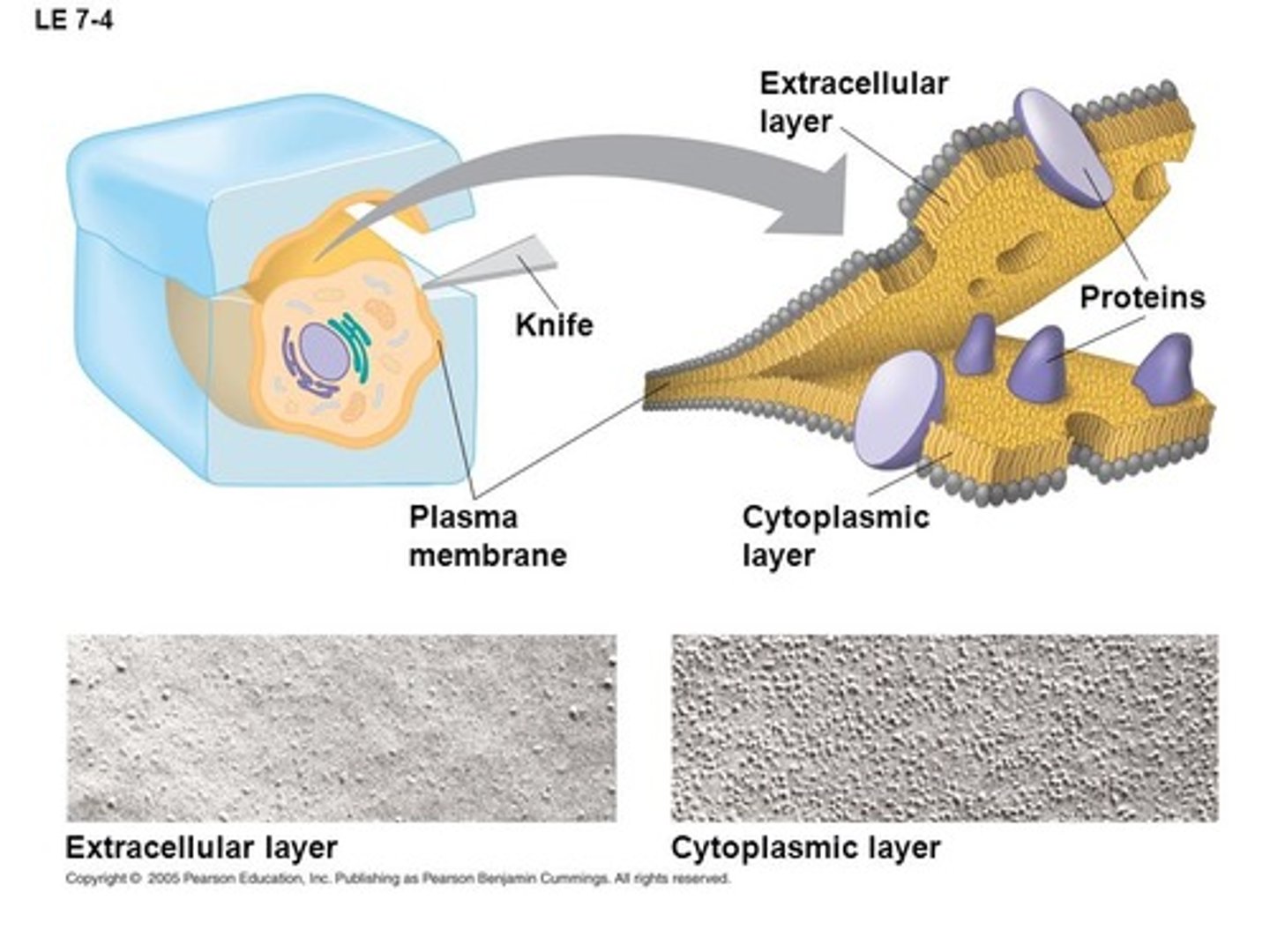
the extracellular layer of the fluid mosaic model has _____ proteins than the cytoplasmic layer
less
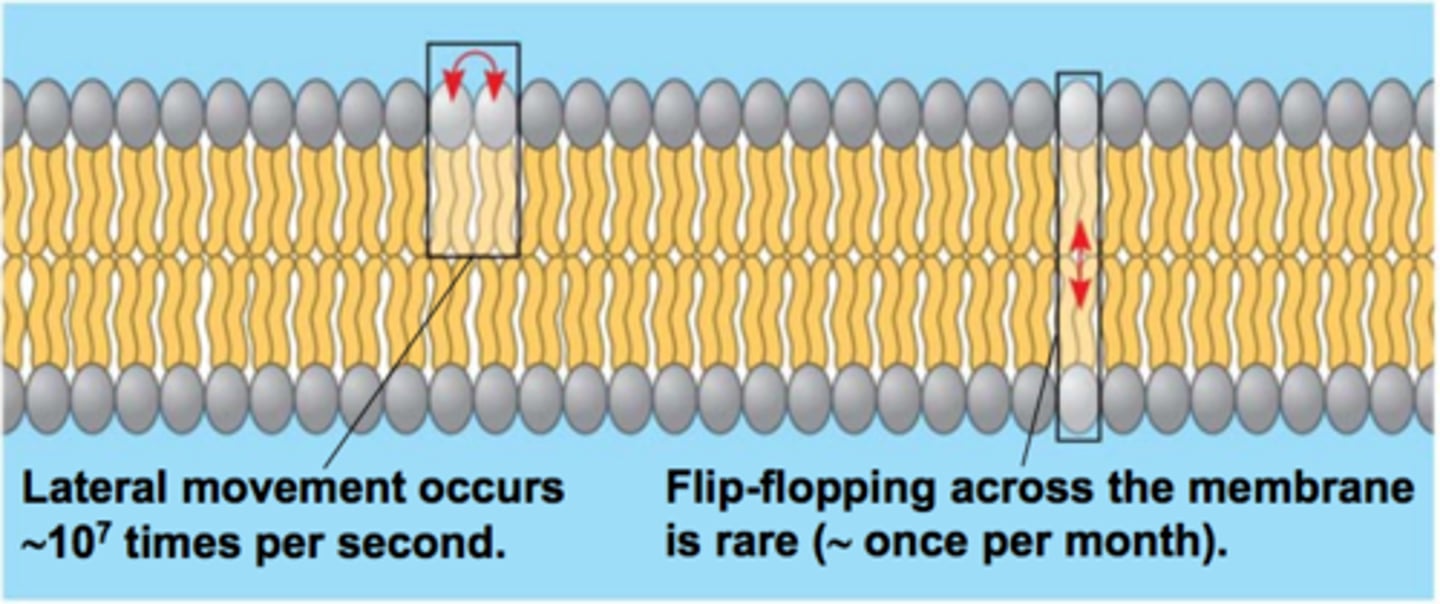
phospholipids in the plasma mem can ____ within the bilayer.
most lipids and some proteins ___ ___.
a molecule flip-flops transversely across the membrane _____
move
drift laterally
rarely
temperature affects membrane ____.
as temps cool, membranes switch from a ____ state to a ____ state
fluidity; fluid; solid
the temp that a membrane solidifies at depends on the types of ____ in the mem.
membranes rich in ____ are more fluid than those rich in ____
lipids
unsat fatty acids; sat fatty acids
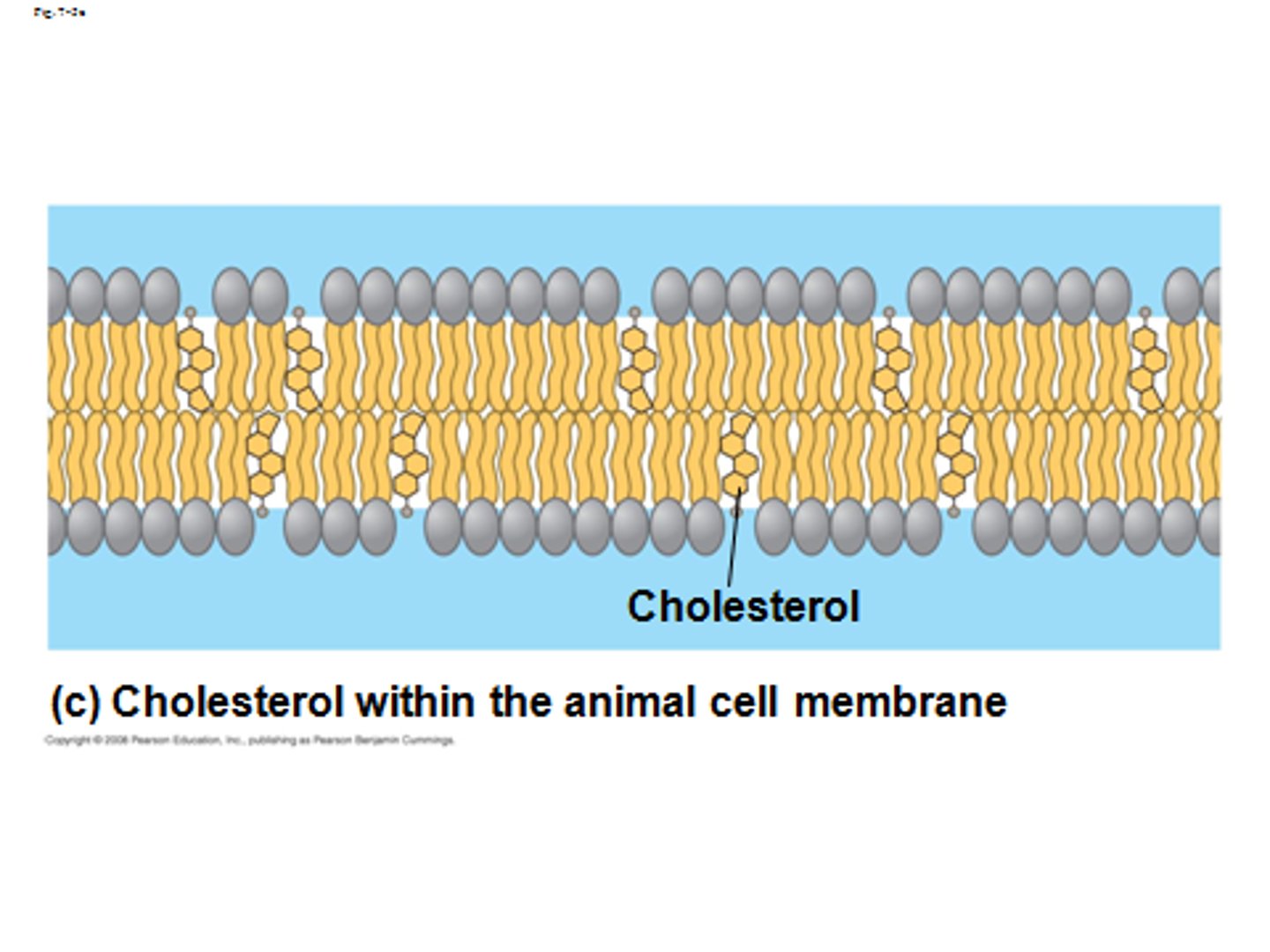
cholesterol effects at warm temps vs cool temps
warm:
restrains phospholipid movement
cool:
maintains fluidity by preventing tight packing
cell membranes must be fluid to ____; they are usually as fluid as _____
work properly; salad oil
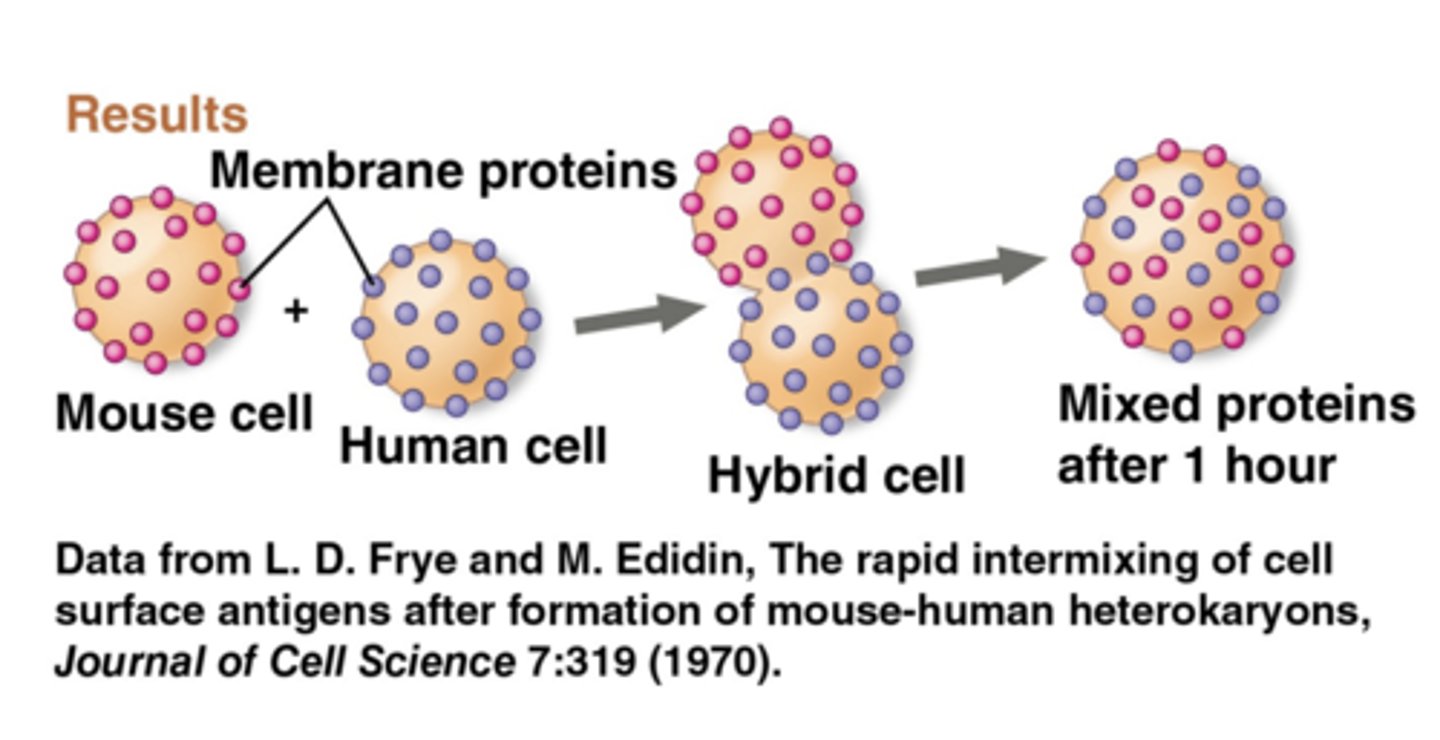
some proteins in the plasma mem can ____ within the bilayer. proteins are much ____ than lipids and move more ____
drift; larger; slowly
how did researchers investigate whether membrane proteins moved?
fused mouse cell + human cell and watched what happened to proteins from each cell
a membrane is a collage of different ____ embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer. these determine what?
proteins; membrane's specific functions
peripheral vs integral proteins
peripheral: not embedded (on top or bottom)
integral: penetrate hydrophobic core + span membrane
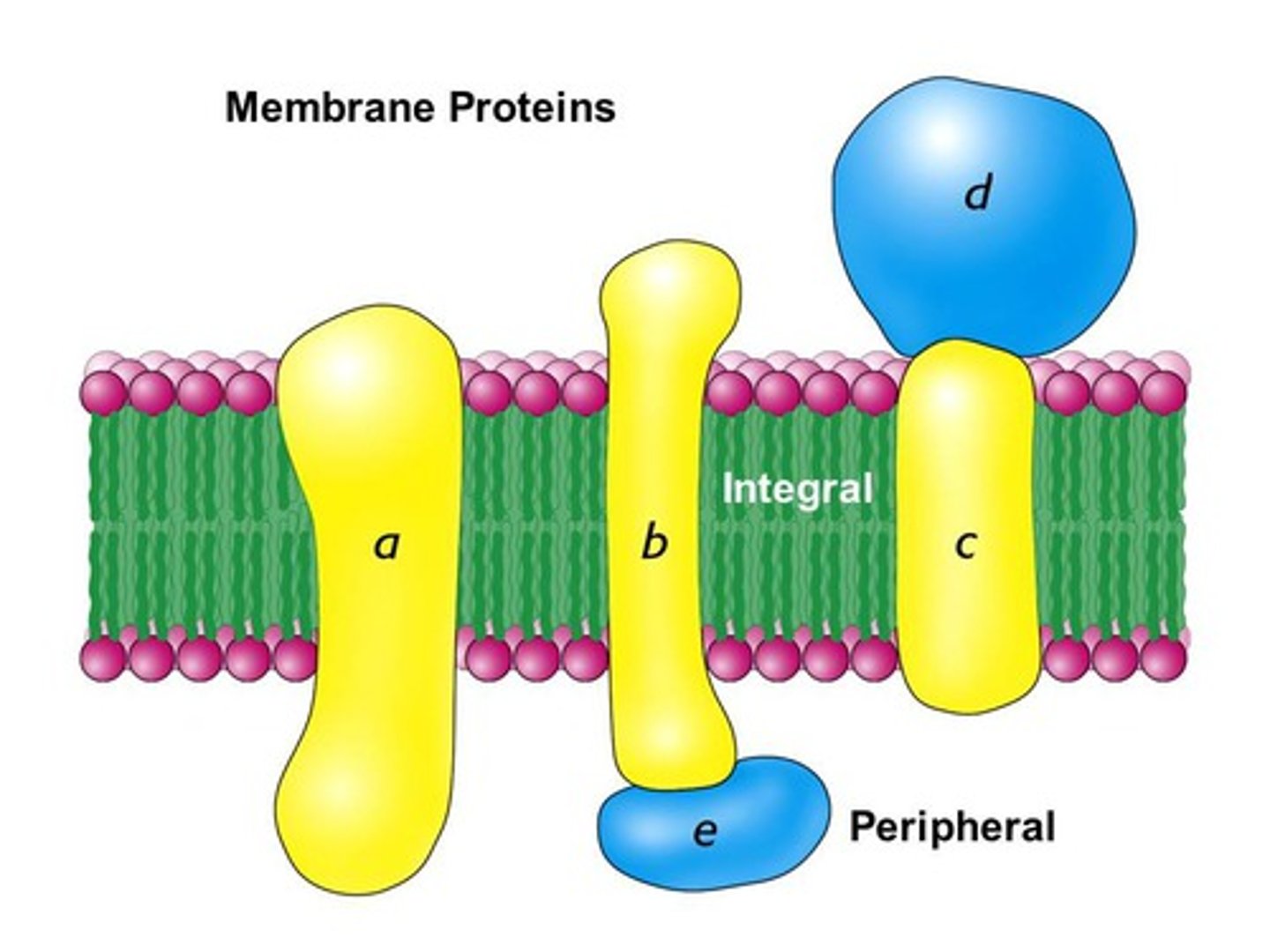
transmembrane proteins are integral proteins that:
span the membrane
the hydrophobic regions of an integral protein consist of 1 or more stretches of ______ coiled into ____.
nonpolar amino acids; alpha helices
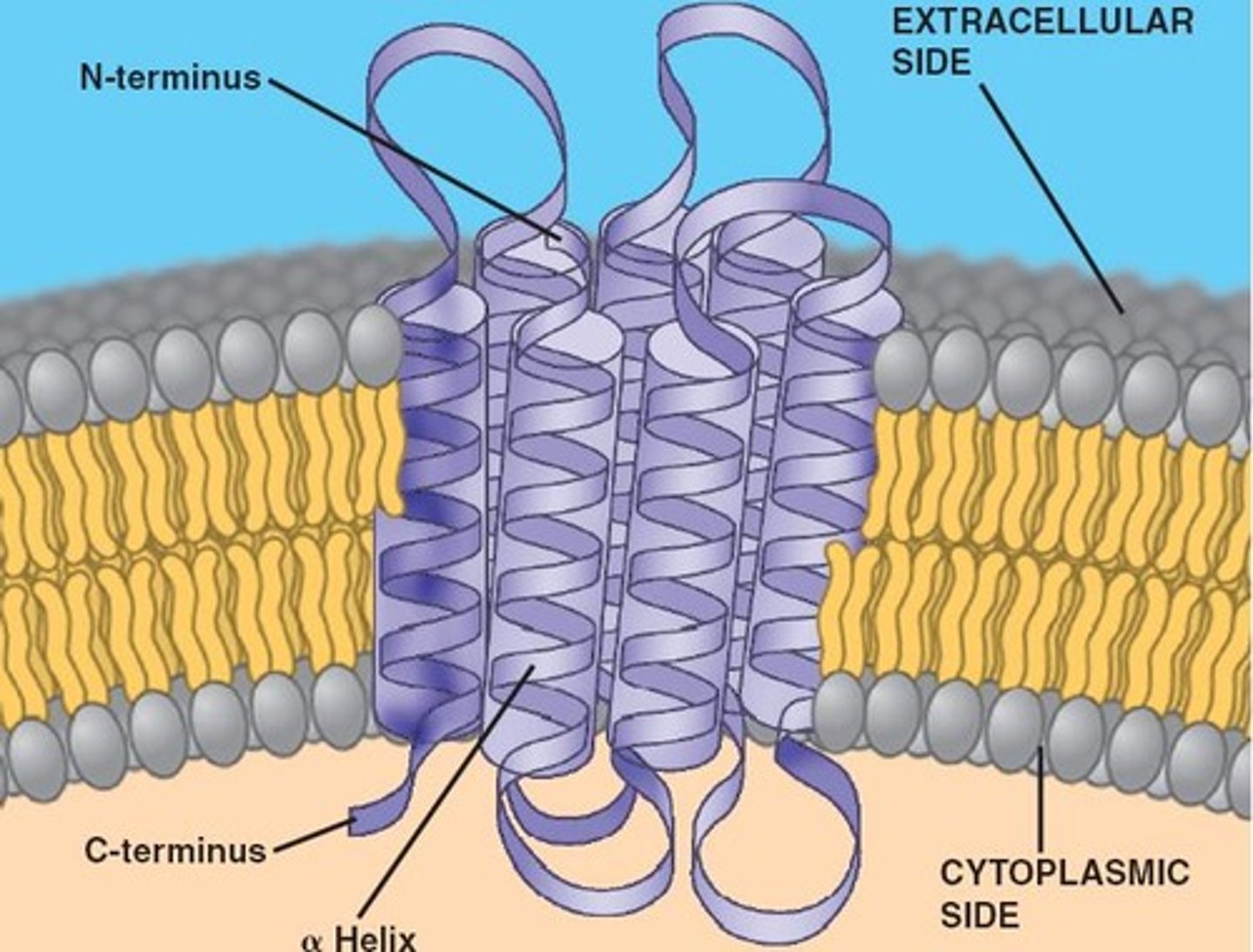
the ribbons of a transmembrane protein are _____. these allow:
hydrophilic; things to go in/out of the mem
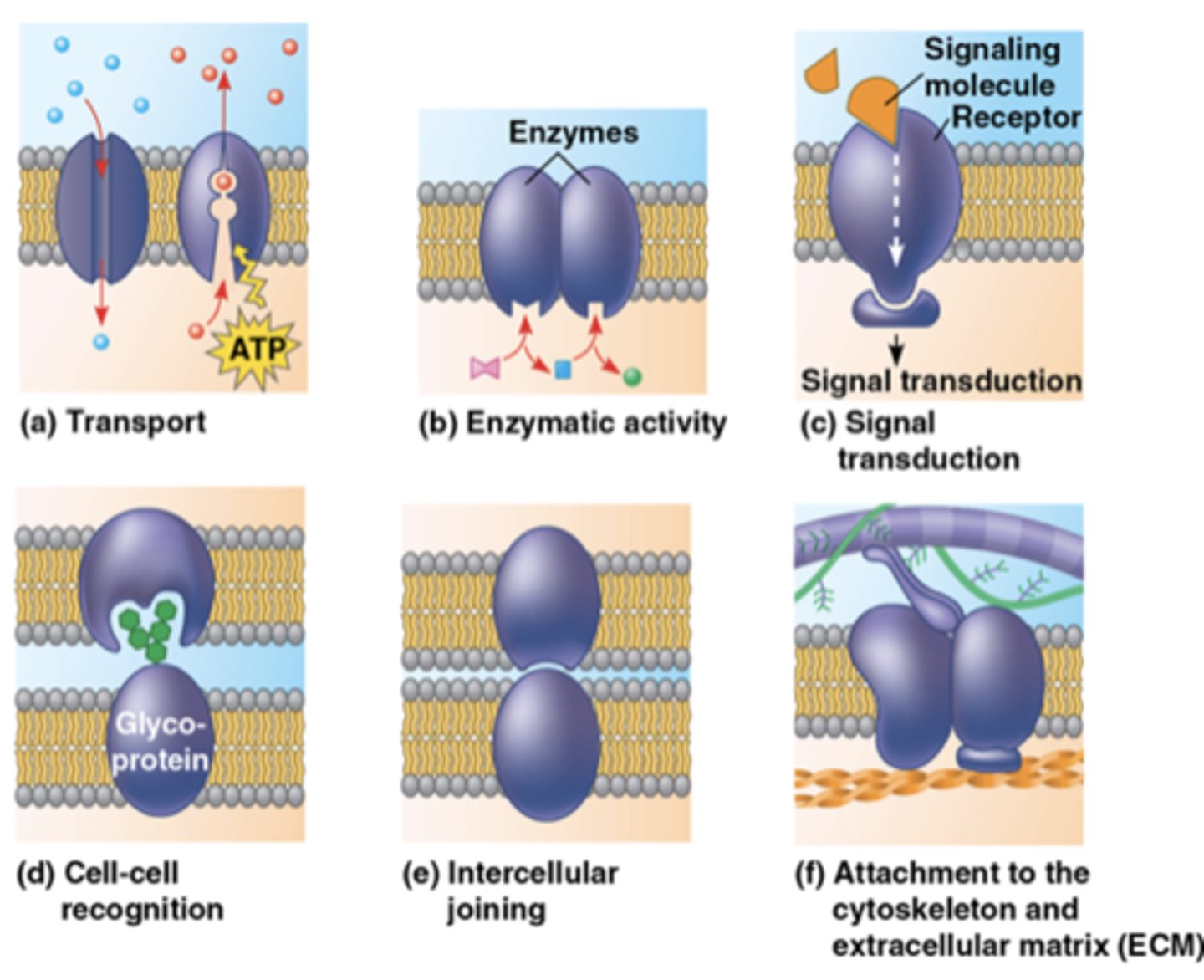
fave 3 major functions of membrane proteins + examples
1. transport
- Na/K pump (passage and gate)
2. signal transduction
- hormones (hits receptors in brain that make u tired)
3. cell-cell recognition
- WBCs recognize germ antigens
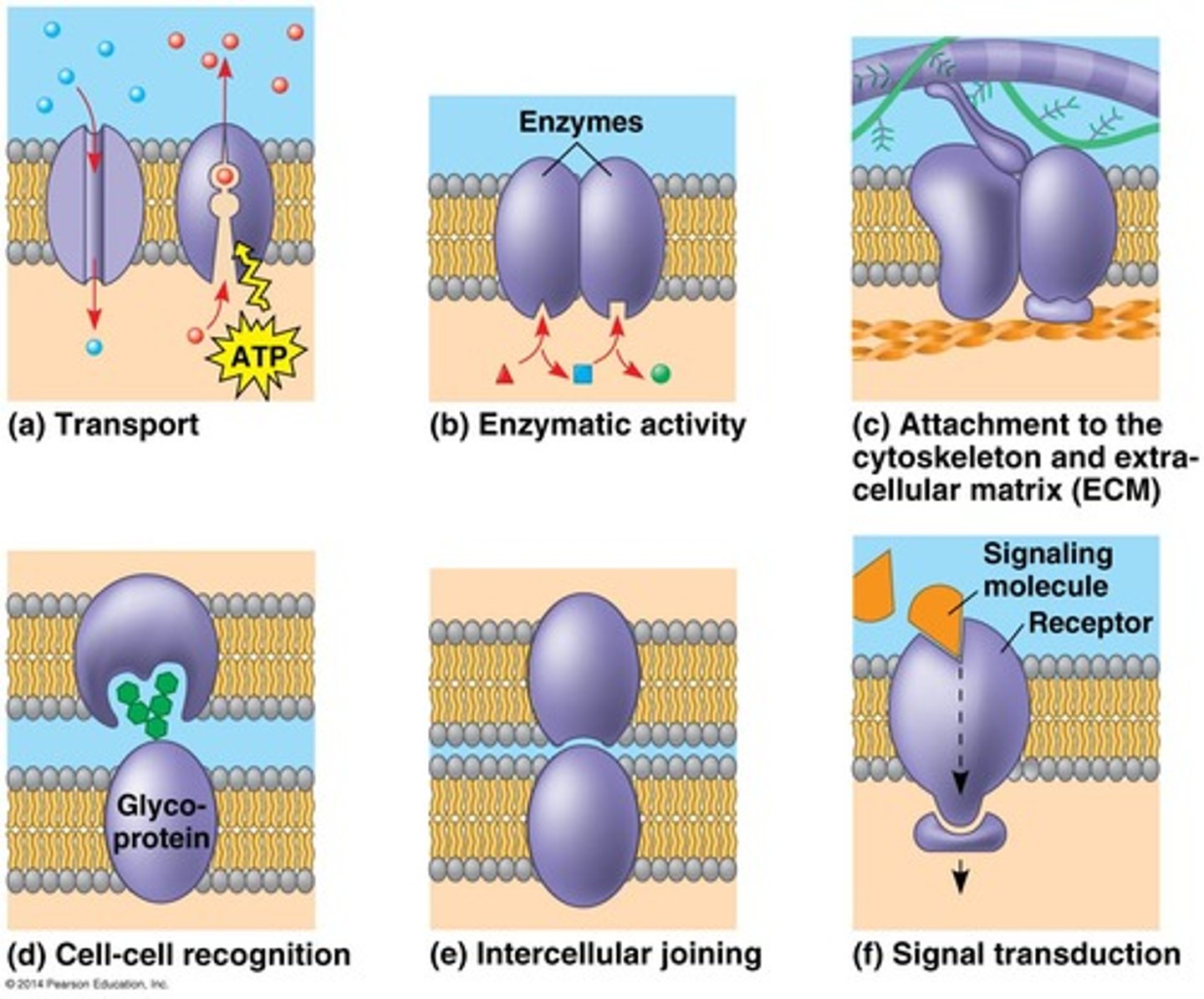
other 3 major functions of membrane proteins + examples
4. enzymatic activity
- adenylate cyclase catalyzes ATP to cAMP
5. intercellular joining
- desmosomes like cell buttons
6. attachment (to cytoskeleton and ECM)
- help things stick
how do cells recognize each other?
binding to surface molecules (membrane carbohydrates) on plasma membrane
membrane carbs may be covalently bonded to lipids (forming ____) or more commonly to proteins (forming ____)
glycolipids; glycoproteins
external carbs on the plasma mem ____ among species, individuals, and cell types in an individual
vary
2 distinct faces of membranes
inside (intracellular)
outside (extracellular)
the ____ distribution of proteins, lipids, and carbs in the membrane is determined when?
asymmetrical; membrane is built by ER and golgi
how do cells grow in size? stopping this process may be beneficial for who?
what cells grow faster than others?
vesicles from golgi merge with cell mem; ppl with cancer
cells that send things often (mucous membranes)
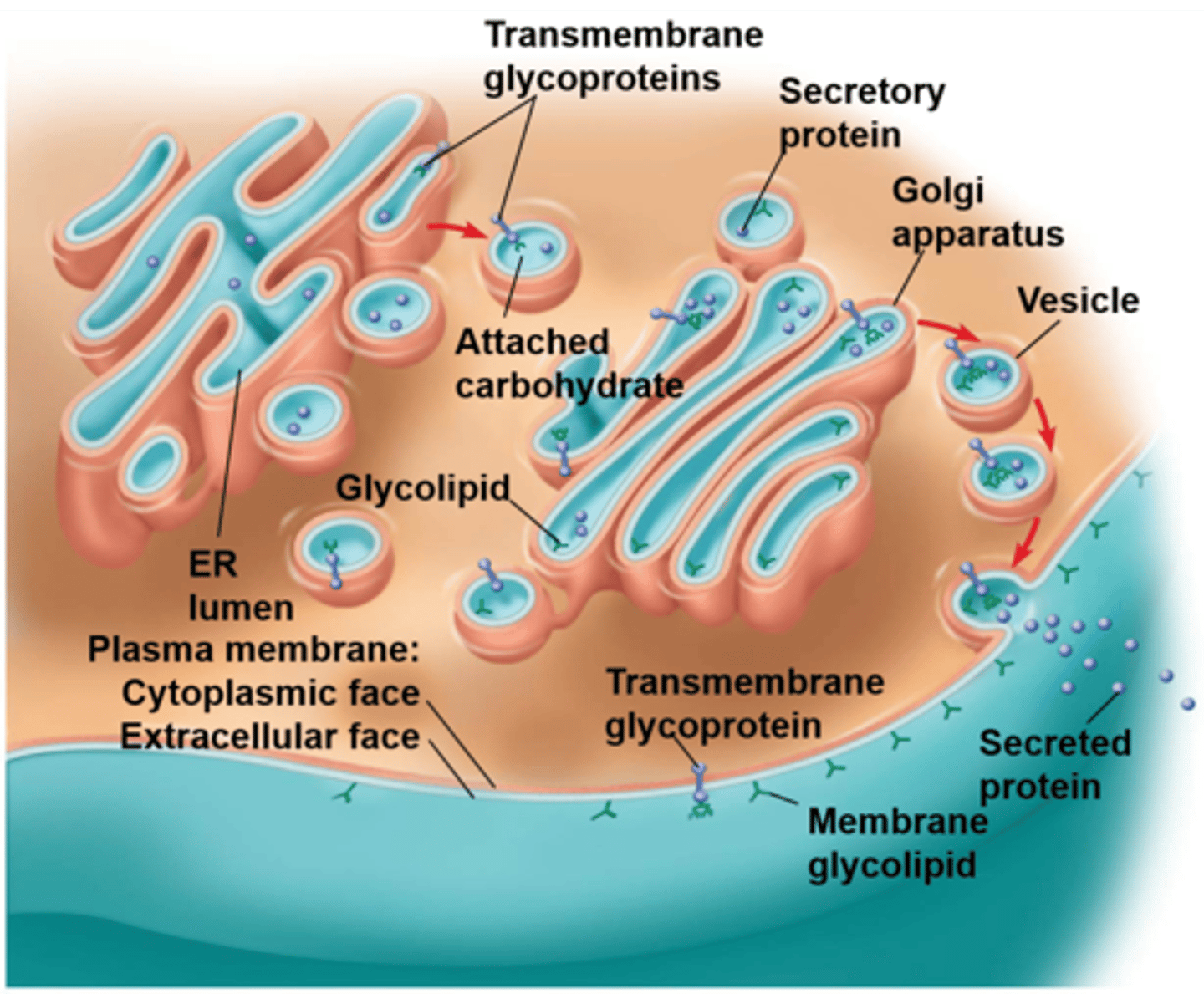
the plasma membrane controls what?
membrane structure results in ____ ___, which regulates the cell's ___ ___
exchanging materials btwn cell/surroundings; selective permeability; molecular traffic
do polar or nonpolar molecules cross the membrane readily?
nonpolar (hydrophobic): dissolve in lipid bilayer + pass thru easily
ex. hydrocarbons
polar: do not pass easily
ex. sugars
transport proteins allow passage of ____, ____ substances where?
hydrophilic, polar; across membrane
channel proteins vs carrier proteins
channel: hydrophilic channel/tunnel for molecules or ions
- like tunnels, limit shape of molecules that fit thru but do not change shape themselves
carrier: bind to molecules + change shape to shuttle them across membrane
- like gates, open/shut/open other way
a transport protein is ____ for the substance it moves.
ex. aquaporins are ____ proteins that facilitate the passage of ___
specific; channel; water
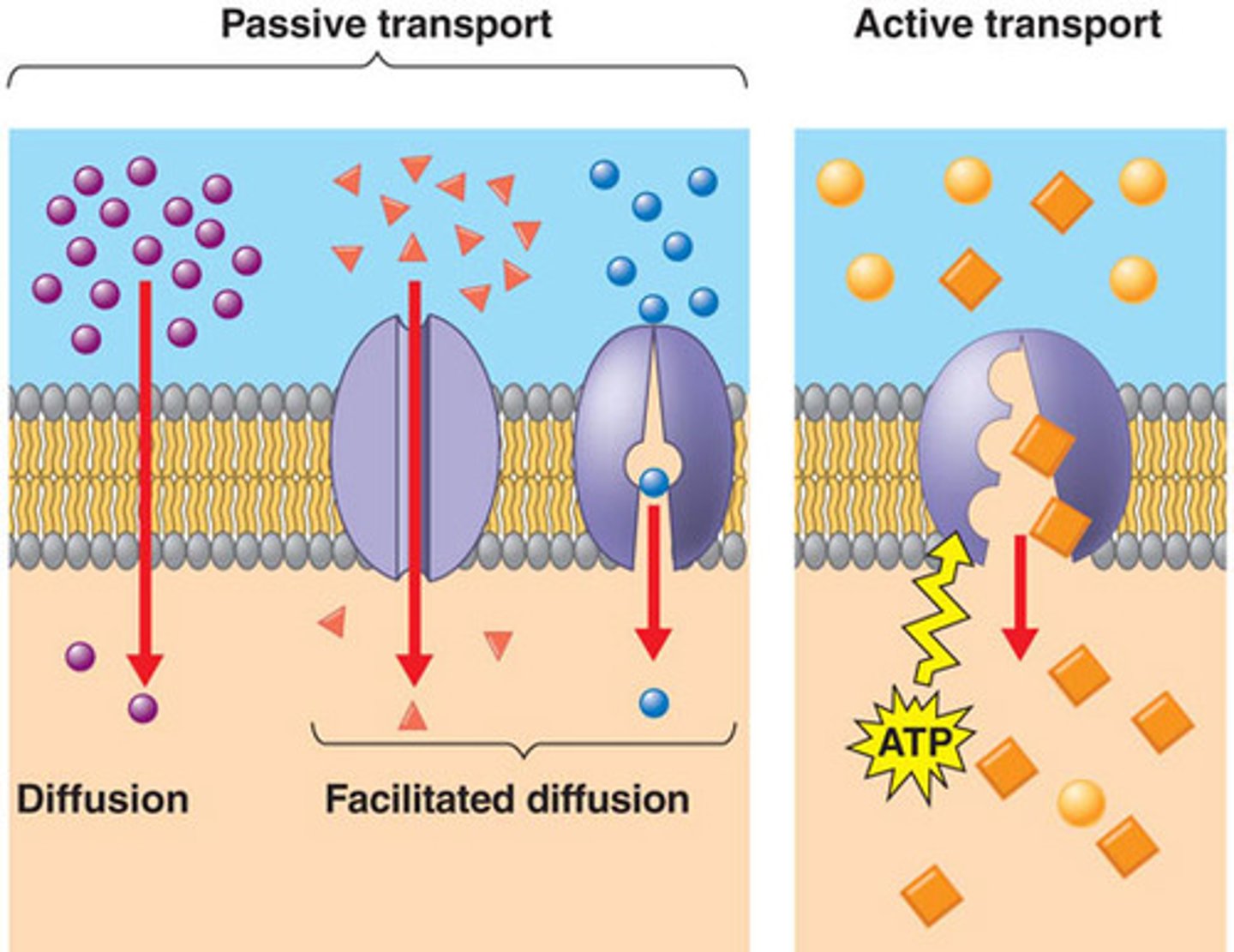
passive transport is ____ of a substance across a membrane ____ energy
diffusion; without
diffusion is the tendency for molecules to ______ into available space.
although each molecule moves randomly, diffusion of a ____ of molecules may exhibit a ____ movement in one direction
spread out evenly
population; net
what happens at dynamic equilibrium?
as many molecules cross one way as cross in the other
substances diffuse _____ (____) their conc gradient (the diff in ____ of a substance from one area to another).
is this passive or active transport? why?
down (high to low)
concentration
passive; requires no energy/work from cell
diffusion says if material can flow it flows from ____ conc to ___ conc until ____
high; low; equilibrium
diffusion of two substances occurs as ____ reactions until each reaches ____
separate reactions; dynamic equilibrium
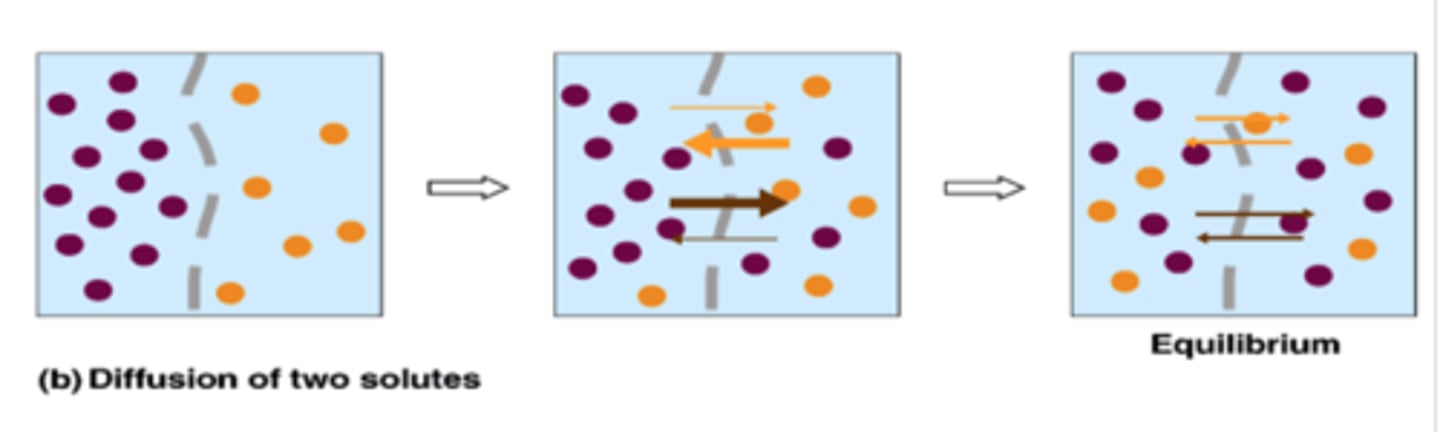
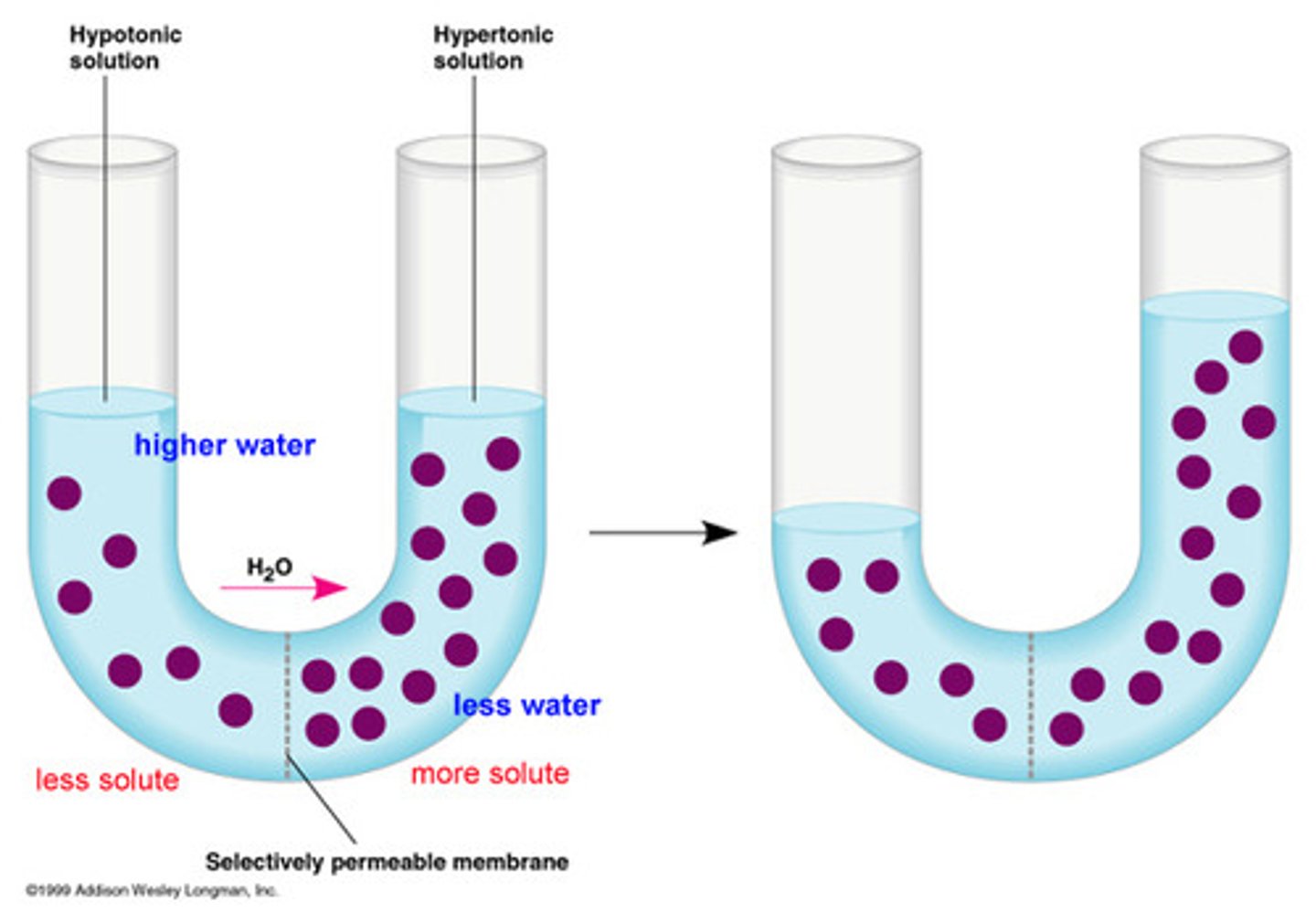
what is osmosis?
diffusion of WATER across selectively permeable mem
what is the direction of osmosis determined by?
diff in total solute concentration
how does water diffuse? what does this show?
from region of LOWER SOLUTE to region of HIGHER SOLUTE until equal conc of solute are on each side of membrane
- force of diffusion is greater than gravity
how to get a high concentration vs low concentration solution
HIGH: increase solute or decrease solvent
LOW: decrease solute or increase solvent
tonicity is the ability of a solution to cause a cell to:
gain/lose water
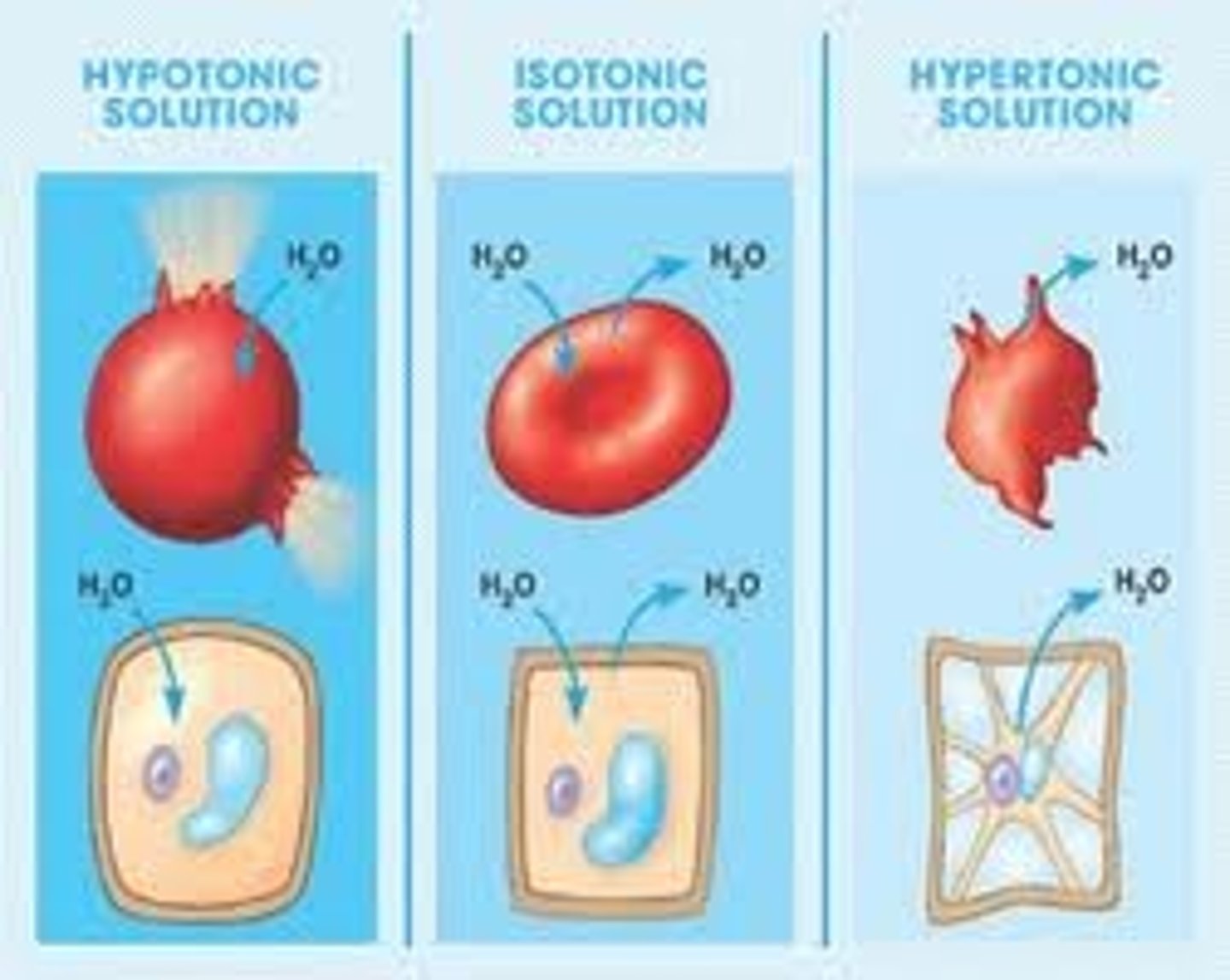
isotonic vs hypertonic vs hypotonic solutions
isotonic: solute conc. same inside/outside; no net movement
hypertonic: solute conc. GREATER outside than inside; cell loses water
hypotonic: solute conc. LESS outside than inside cell; cell gains water (hypo hippo)
____ and organisms without ____ have osmotic problems in hyper/hypotonic environments and must have adaptations for _____ (_____).
example?
animals; rigid cell walls
osmoregulation (control of water balance)
ex. Paramecium in hypotonic ponds have contractile vacuole to pump out water when it comes in
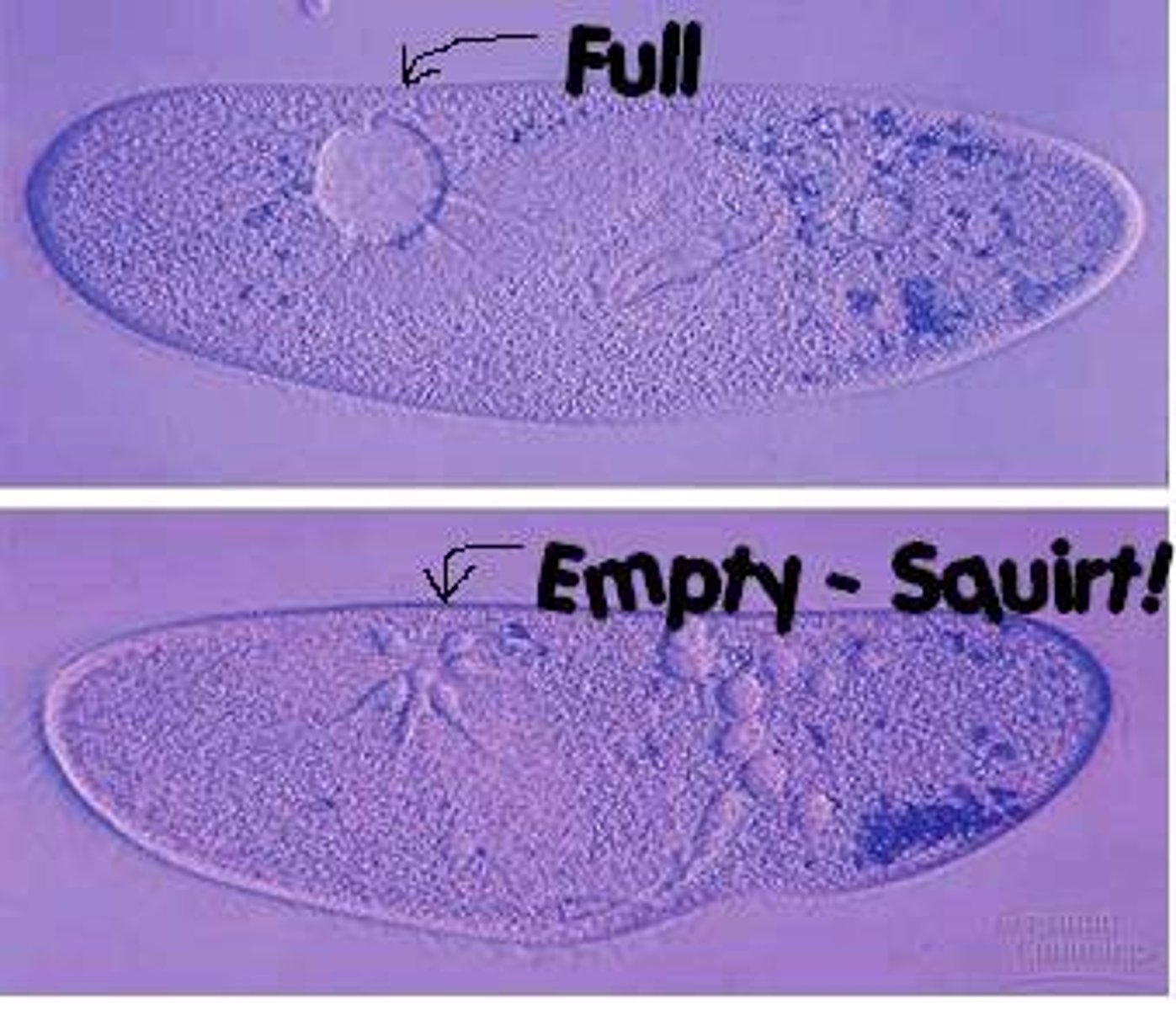
cell walls help maintain _____.
what happens to animal cells in hypo, iso, and hypertonic solutions?
water balance
animal: lysed, normal, shriveled
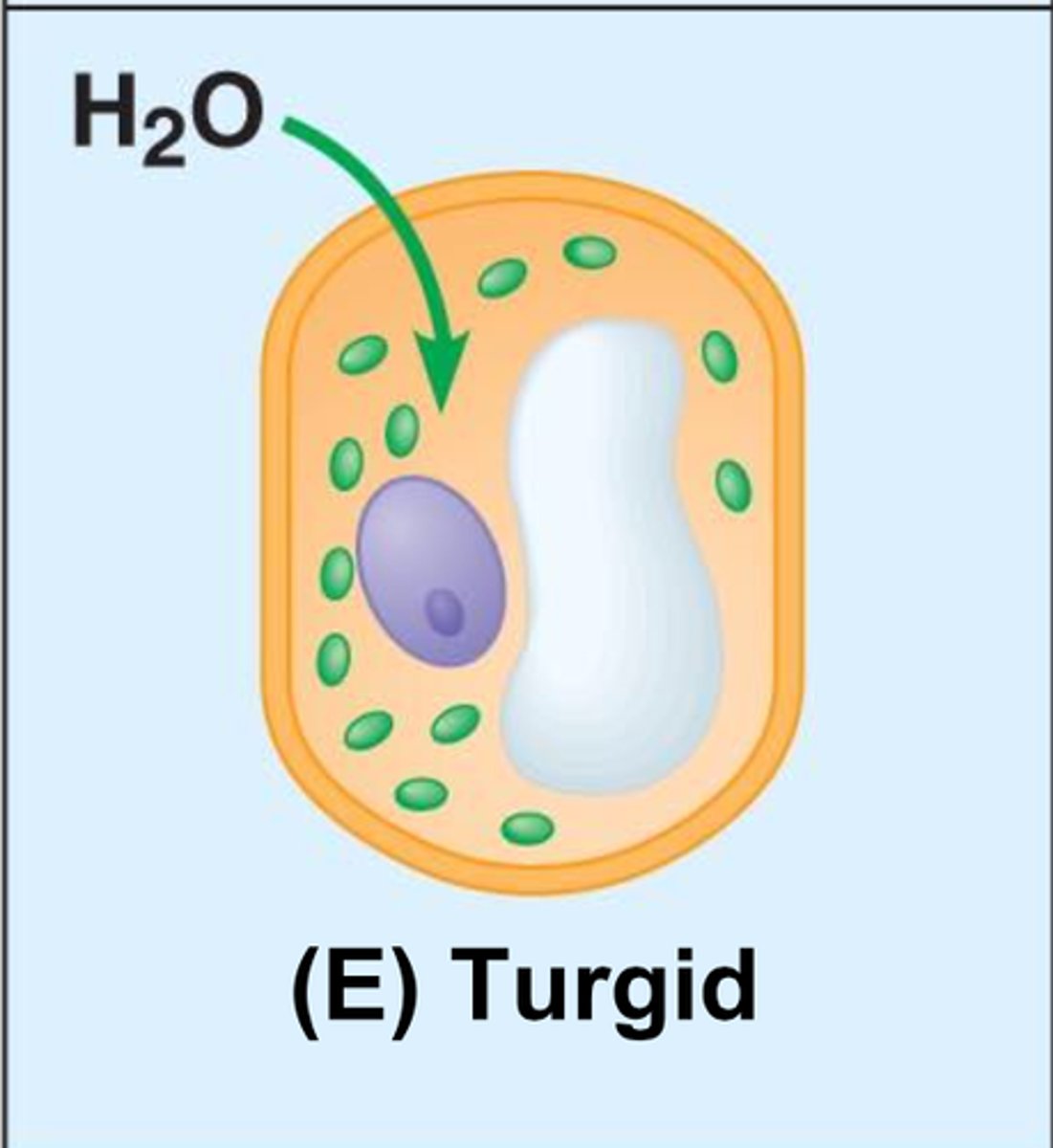
what happens to a plant cell in a hypotonic solution?
turgid (firm/normal)
- cell swells until wall opposes uptake
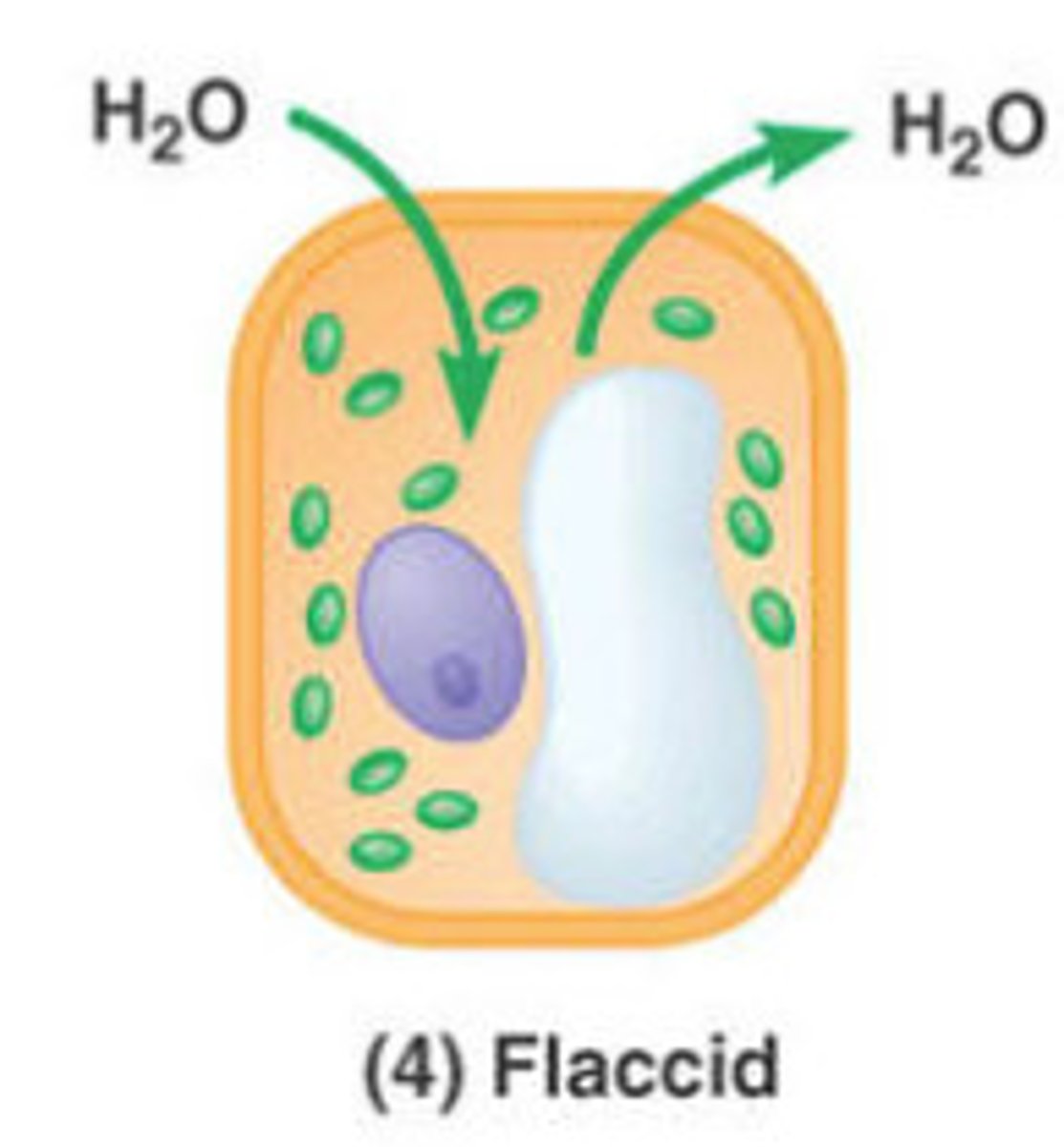
what happens to a plant cell in an isotonic solution?
flaccid (limp)
- no net movement of water into cell; plant may wilt
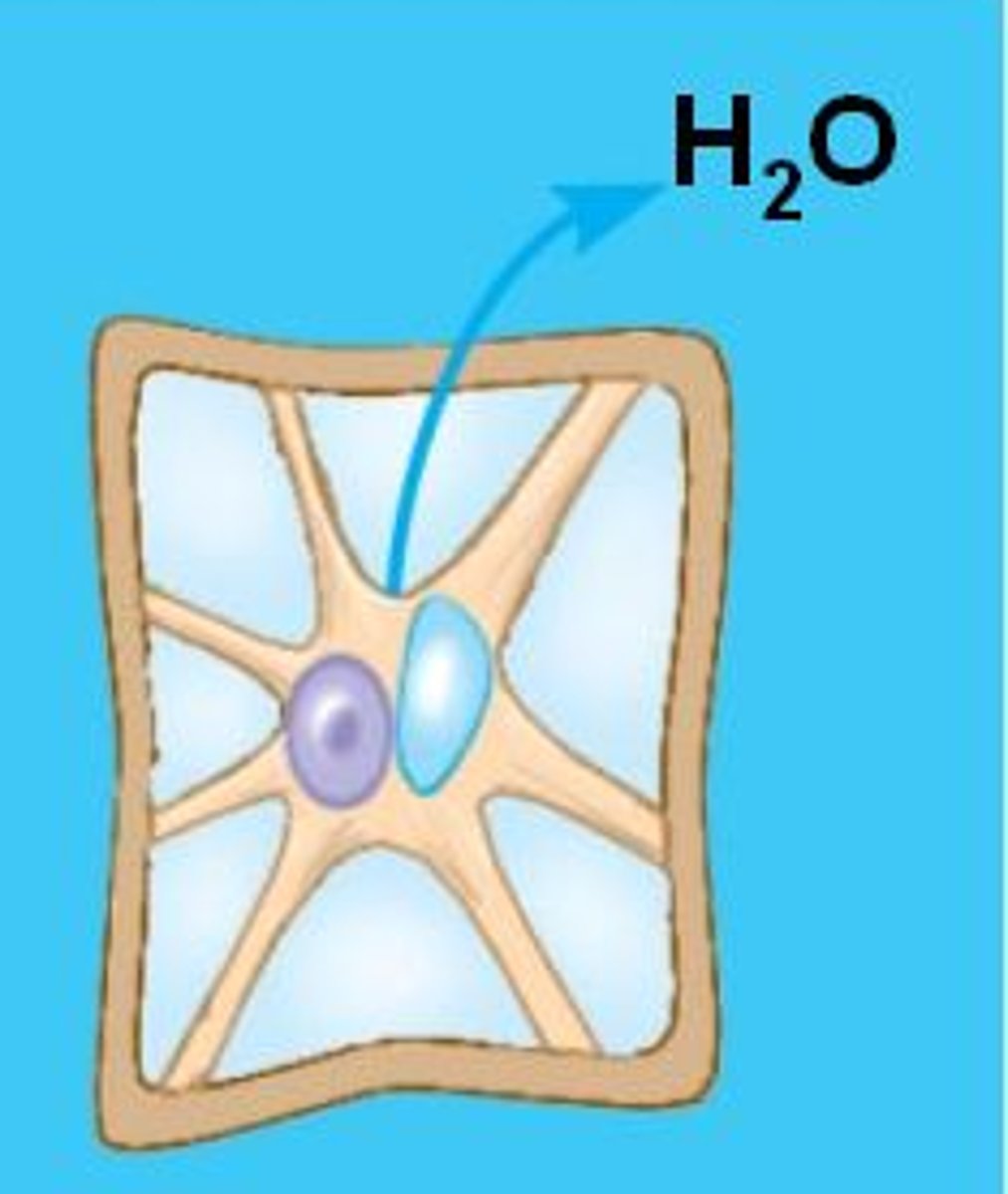
what happens to a plant cell in a hypertonic solution?
plasmolysis (lethal)
- mem pulls away from wall; cells lose water
facilitated diffusion is ____ transport aided by ____.
transport proteins ____ movement of molecules across membrane
passive; proteins
speed
channel proteins provide ______ that allow _____ molecules or ions to cross the membrane.
carrier proteins undergo a ____ in ___ that translocates the ____ across the membrane
corridors; specific
subtle change; shape; solute-binding site
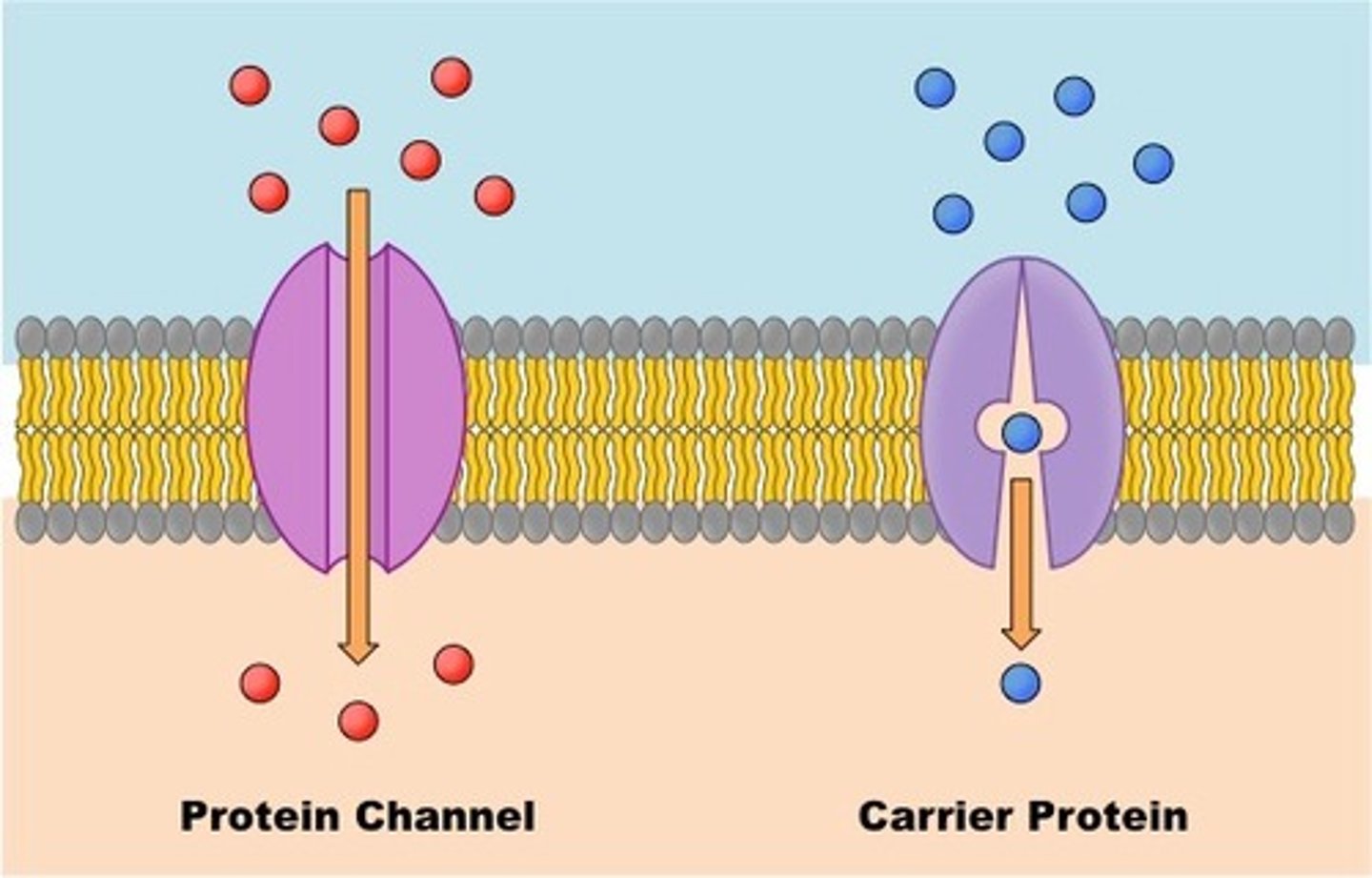
do channel proteins or facilitated diffusion carrier proteins require energy?
no; stuff moves based on diffusion
active transport uses ____ to move solutes ____ their gradients (___)
energy; against (low to high)
facilitated diffusion is still passive because the solute ____________.
moves down its concentration gradient
some transport proteins ____ in the membrane can move solutes against their conc gradients via ______, which requires _____/____
embedded; active transport; energy/ATP
the proteins that function for active transport are _____ proteins. ____ proteins CANNOT be used for active transport
carrier; channel
_____ is one type of active transport system. what are its 6 steps?
sodium-potassium pump
1. cytoplasmic Na bonds to pump
2. Na binding stimulates phosphorylation by ATP
3. phosphorylation causes protein to change conformation, releasing Na outside
4. extracellular K binds to protein, releasing phosphate
5. loss of phosphate restores protein's og conformation
6. K released inside, Na sites are receptive + cycle repeats
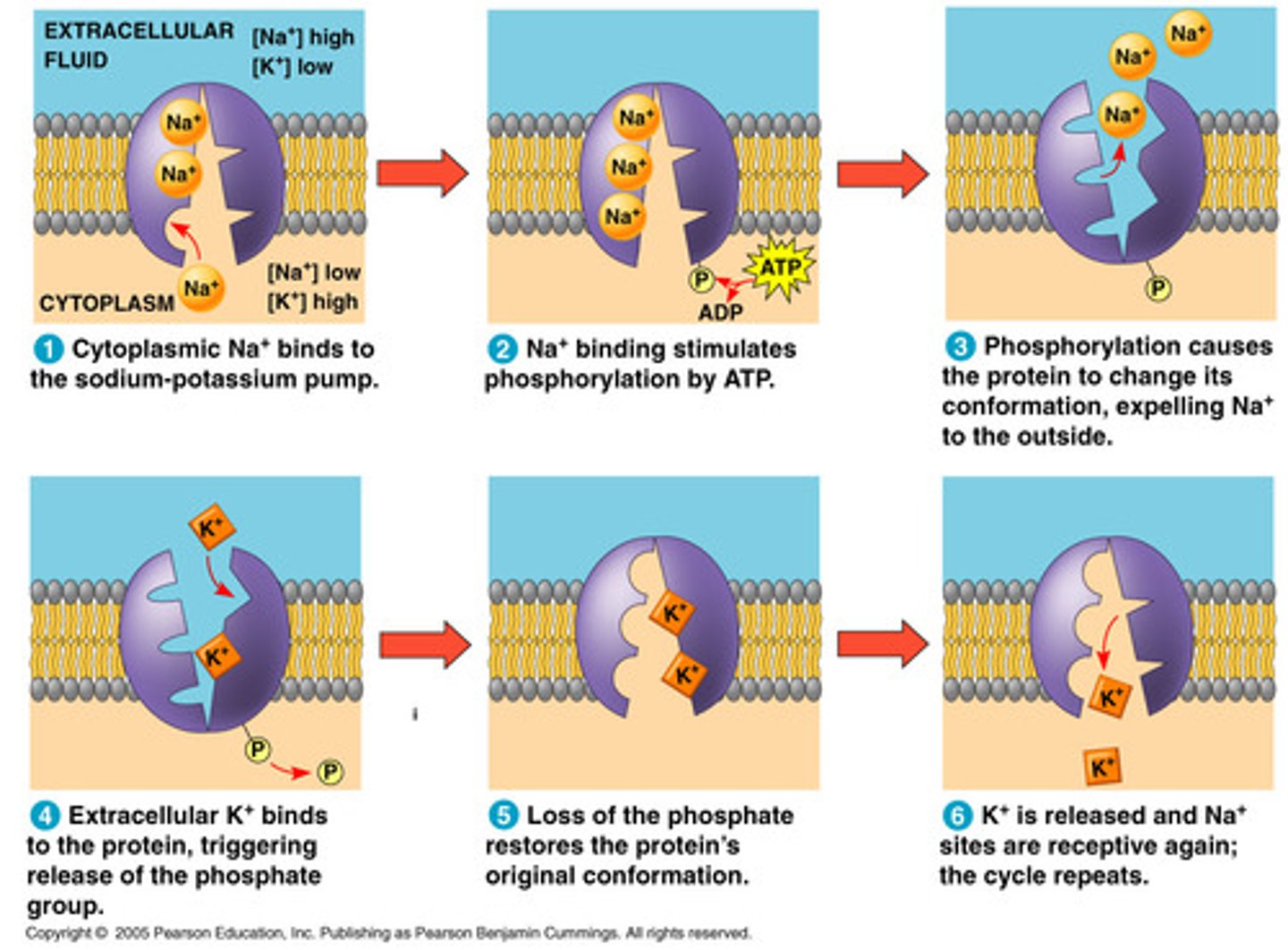
explain the conc in/out of the cell with a Na/K pump
Na high/K low outside cell
- pumps 3 Na out + 2 K in constantly
how is the Na/K pump related to charges?
- pump pumps chemicals to each side of mem + establishes electrochemical gradient which generates electricity
- Na/K both pos charged, but outside of cell is very pos and inside is very neg
- kind of makes a battery w/a pos end/neg end
- when a conductor connects these neg charges to the pos ones u create a current
- means ur cell mems have voltage (diff in charges) that are connected via stimulation
ex. touch sends signals to ur brain
what is membrane potential?
how does transport maintain membrane potential?
voltage/charge difference across a membrane
- ion pumps
passive diffusion review
high to low conc, no energy
ex.
- diffusion
- facilitated diffusion
--- channel proteins/carrier proteins
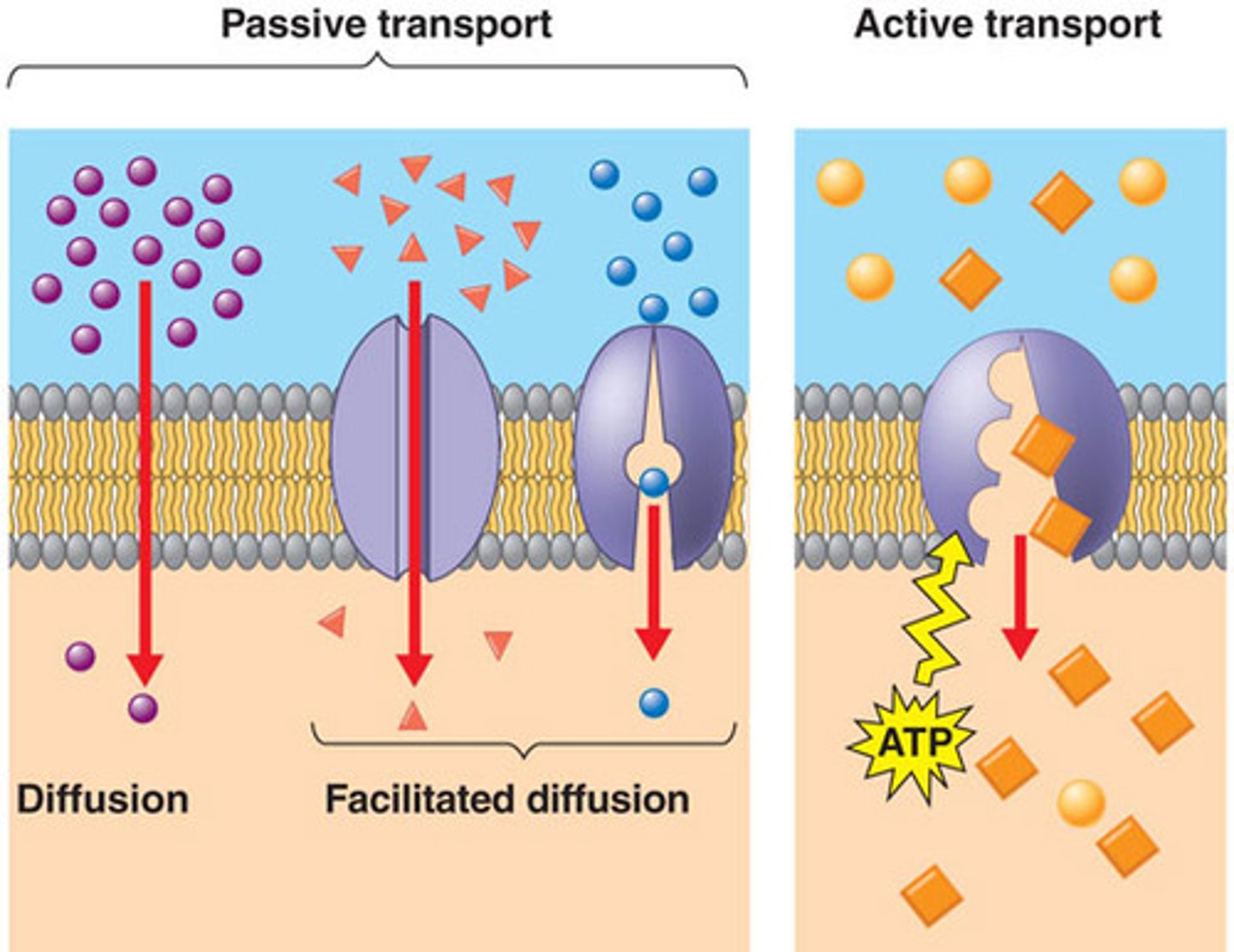
active diffusion review
low to high conc, uses energy
ex.
- carrier proteins
- pumps
what are the 2 combined forces (______) that drive the _____ of ions across a membrane?
(electrochemical gradient); diffusion
- chemical force (ion's conc gradient)
- electrical force (effect of membrane potential on ion's movement)
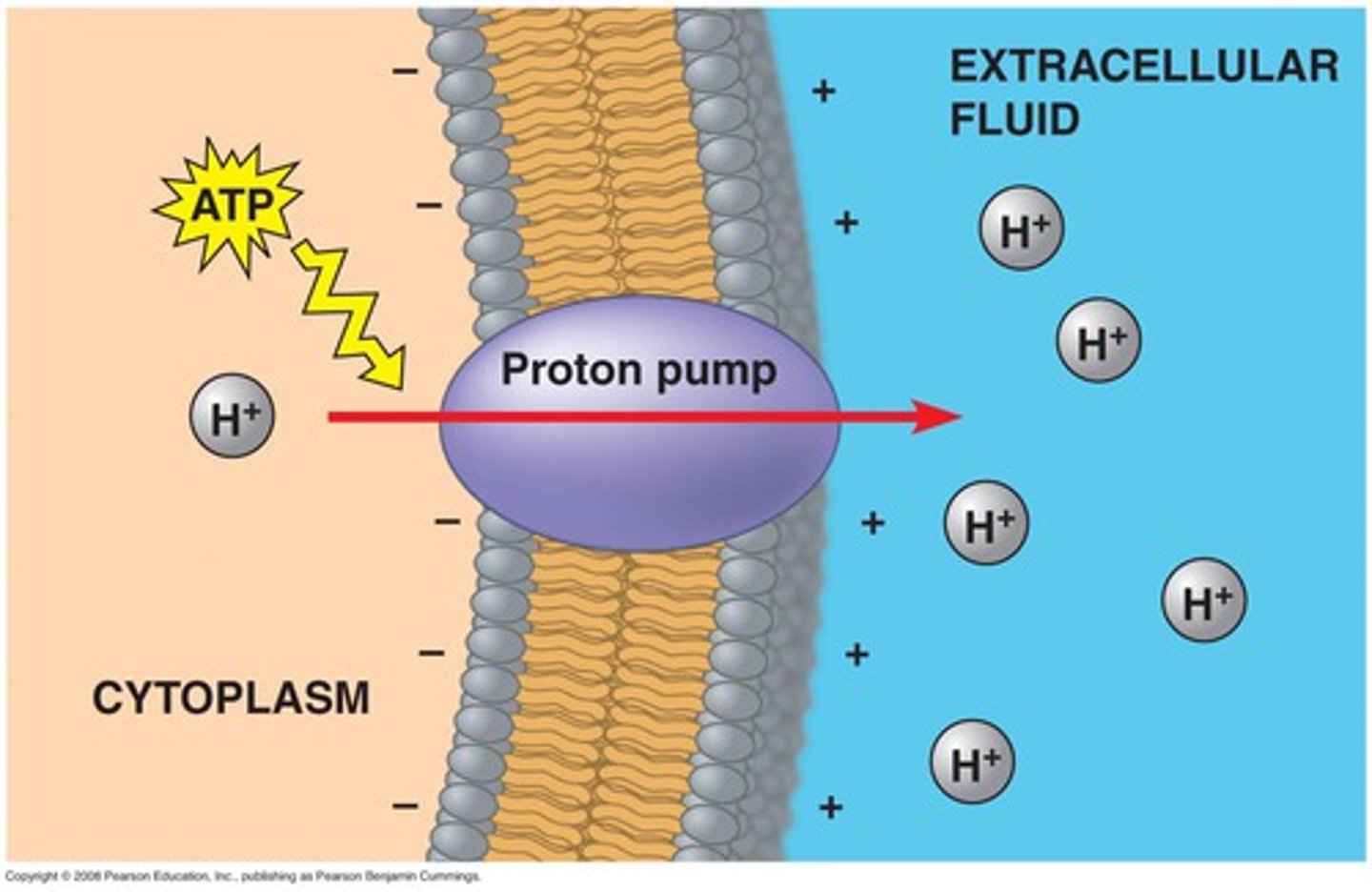
what is an electrogenic pump?
what is the main electrogenic pump of plants, fungi, and bacteria?
transport protein that generates voltage across membrane
- proton pump
explain what a proton pump does
- materials go in one direction, releasing H+
ex.
- stomach is acidic & H+ is released to incr. it (pos charge lowers pH)
- stomach receives alkaline food & H+ help to lower food pH similar to stomach
- if proton pumps are too active, stomach can be too acidic leading to digestion of ur own stomach (ulcers) or acid reflux
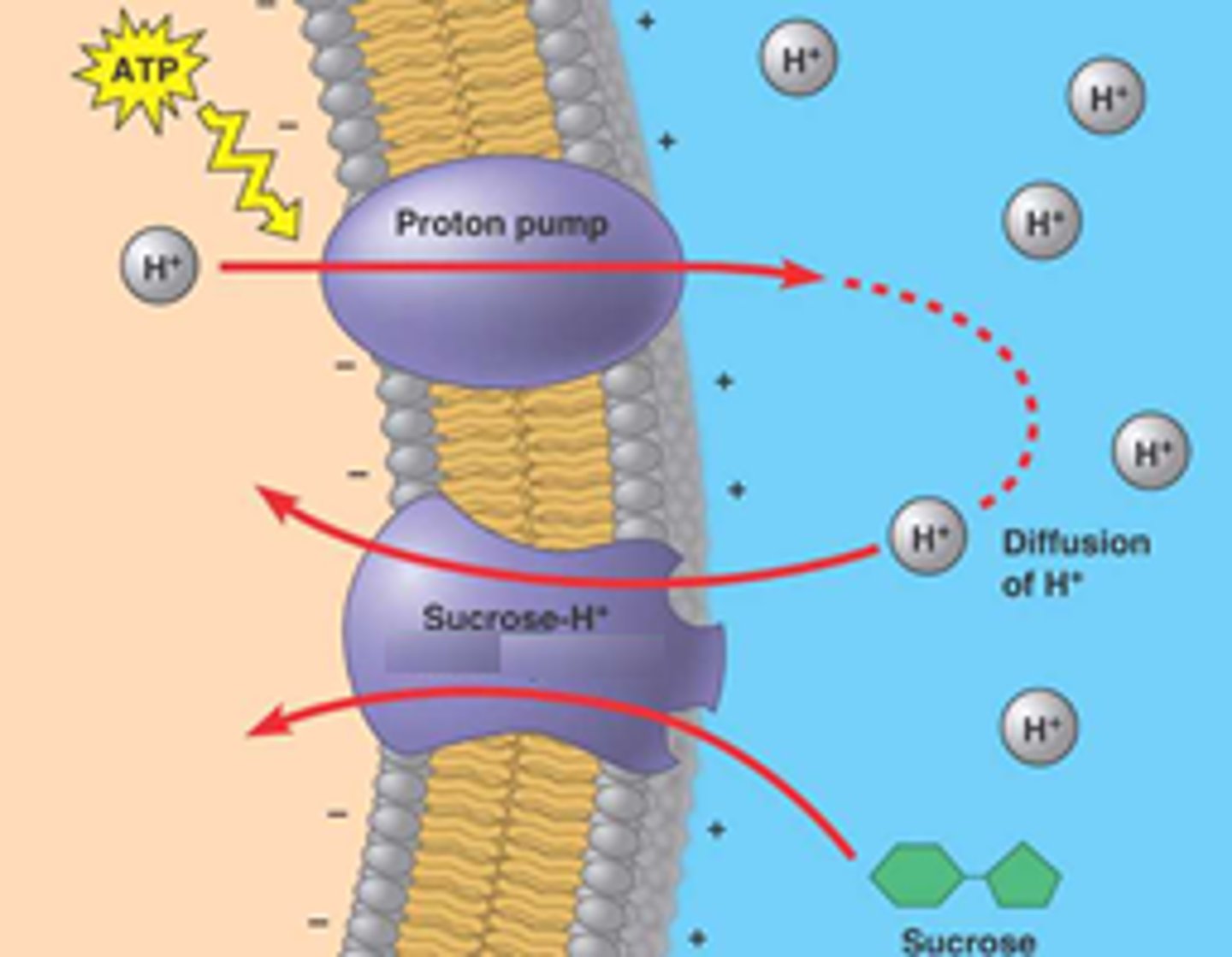
what is cotransport? when does it occur?
coupled transport by membrane protein
- occurs when active transport of a solute indirectly drives transport of another solute
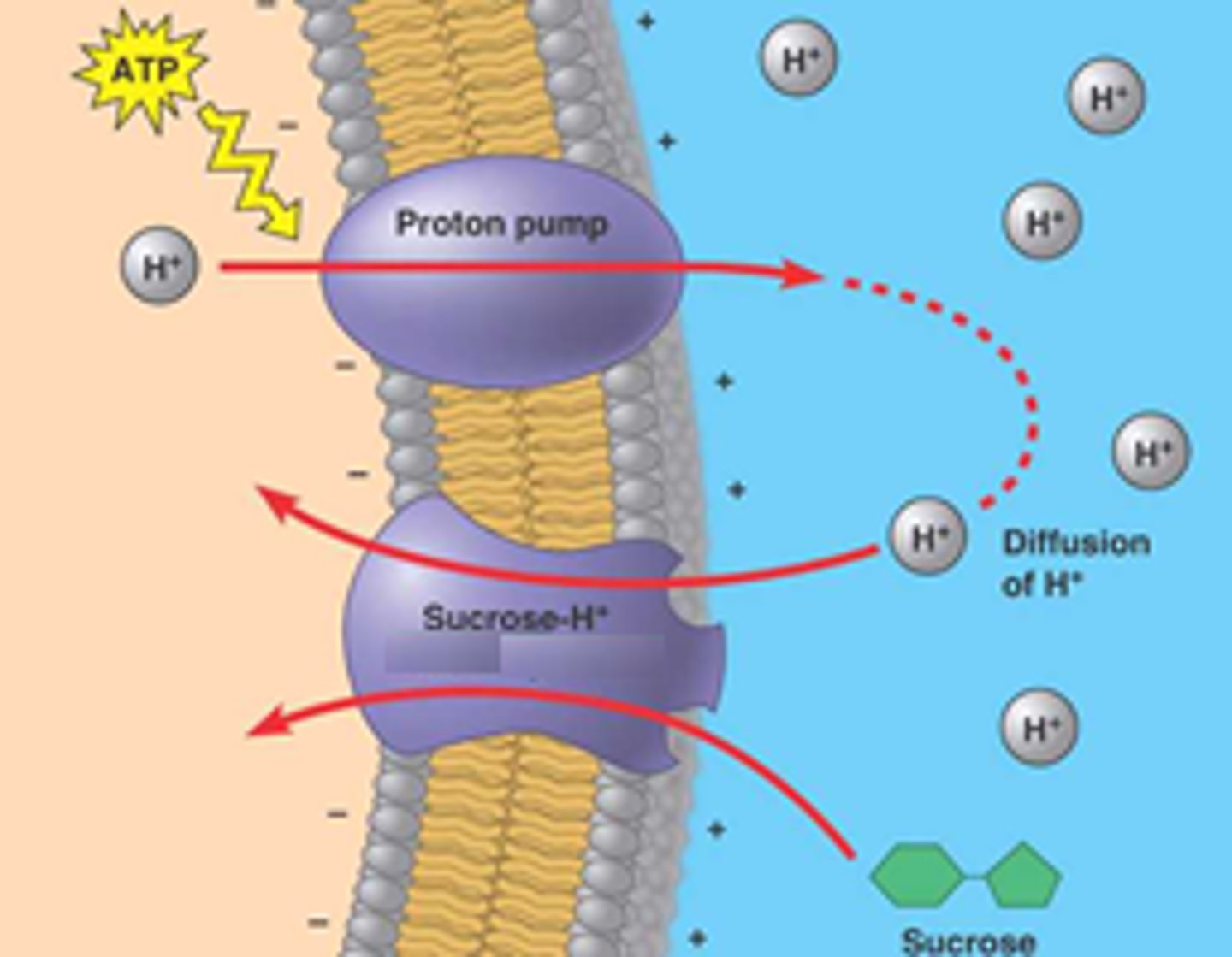
what is an example of cotransport?
- proton pump pumps out H+ which wants to come back to lower conc
- H+ links w/sucrose in sucrose-H+ cotransporter
-- lock/key system where both must bind to go into cell
plants use the gradient of H+ ions generated by ____ to drive ________
proton pumps; active transport of nutrients into cell
bulk transport across the cell mem occurs by ___ and __
exocytosis; endocytosis
small molecules/water enter/leave the cell through (2)
large molecules (polysaccharides/proteins) cross the mem via (1)
lipid bilayer or transport proteins
vesicles
many secretory cells use ____ to export their products. explain this process
exocytosis
- transport vesicles migrate and fuse to membrane and release their contents
_____ is a reversal of exocytosis, involving different proteins. explain this process
endocytosis
- cell takes in macros by forming vesicles from the plasma mem
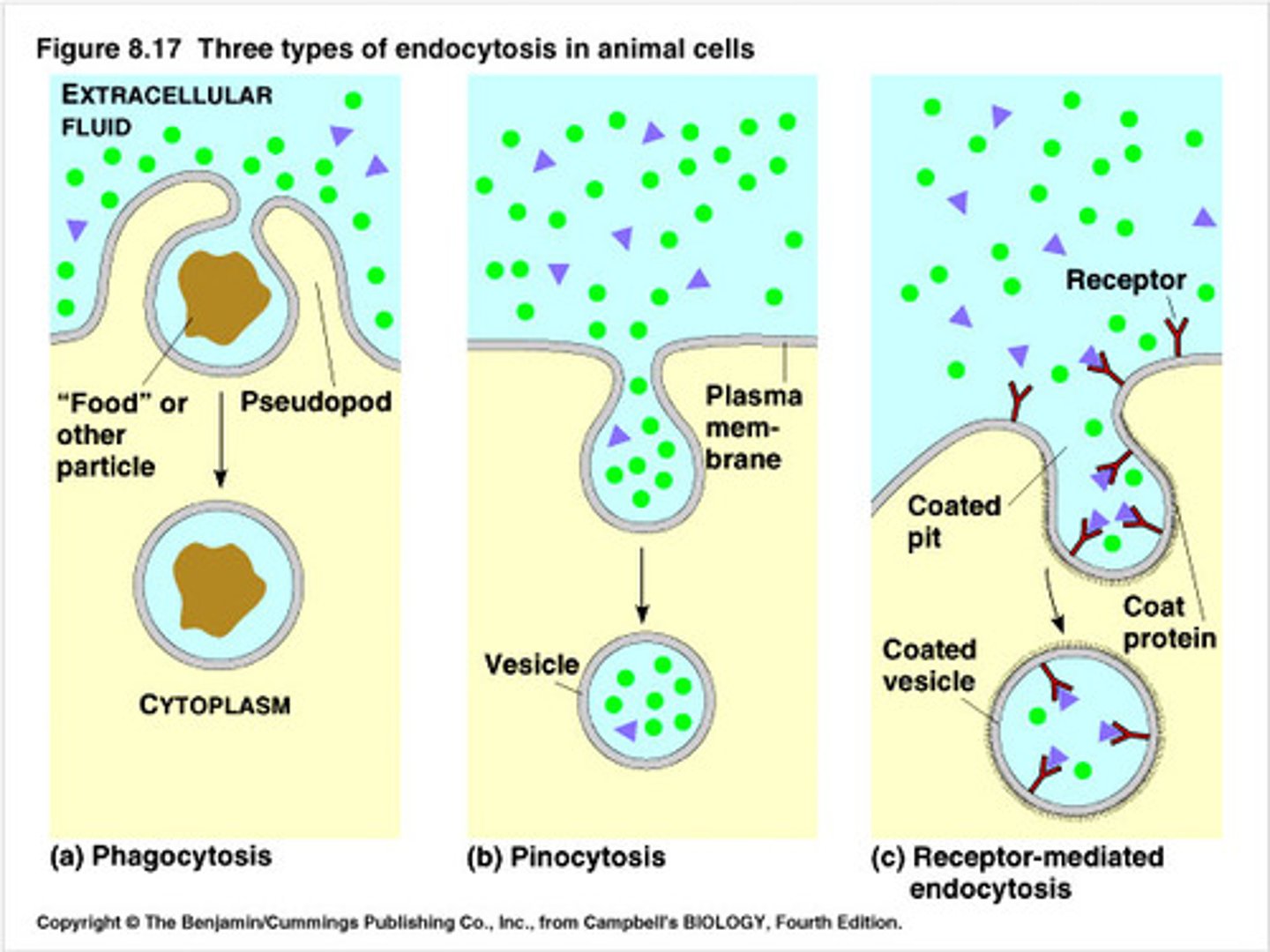
3 types of endocytosis
1. phagocytosis "cellular eating"
- cell engulfs particle in vacuole
2. pinocytosis "cellular drinking"
- cell creates vesicle around fluid
3. receptor-mediated endocytosis
- ligands bind to receptors + triggers vesicle formation
ex. viruses (keys) use receptors to get into cells