L05 - The Nervous System (LHS)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions despite external changes.
Nervous System
The body system responsible for sensing changes in the environment, coordinating responses, and regulating physiology.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Comprised of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing and coordinating information.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Consists of signal-carrying nerves connecting the CNS to the rest of the body.
Brain
Organ responsible for learning, memory retention, balance maintenance, sensory information interpretation, and decision-making.
Neurons
Nerve cells that communicate with each other, with the brain containing an estimated 100 billion neurons.
Spinal Cord
Coordinates involuntary reflexes and serves as the main connection between the PNS and the brain.
Afferent System
Part of the PNS that receives sensory data from receptors and transmits it to the CNS for processing.
Efferent System
Part of the PNS that receives messages from the CNS and transmits them to effector cells to initiate actions.
Receptors
Sensory organs' components that detect environmental changes, with different receptors detecting various stimuli.
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary actions, while the Autonomic Nervous System regulates involuntary functions.
Glial Cells
Non-conducting cells of the nervous system providing support, myelin formation, and protection to neurons.
Nerve Cells (Neuron)
Conducting cells of the nervous system that transmit electrical signals throughout the body.
Dendrites
Branching extensions on neurons that receive signals from other neurons.
Axon
Long extension from the cell body transmitting signals to other cells, often covered by a myelin sheath.
Motor Neuron
Efferent neuron relaying information from the CNS to effectors like muscles, organs, or glands.
Sensory Neuron
Afferent neuron sensing information from the environment and relaying it to the CNS.
Interneurons
Neurons connecting sensory neurons to motor neurons within the body.
Myelin Sheath
Insulating layer around axons formed by glial cells, speeding up signal transmission.nucleus of Schwann cell
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Disease affecting the myelin sheath, leading to various symptoms like vision problems and paralysis. Fatigue, loss of balance, partial or compète paralysis, coordination, speech, bladder, bowel, short term memory issues
Astrocytes
Glial cells providing structural and metabolic support to neurons and regulating ion concentrations and neurotransmitters sweep up debris
Reflex Arc
Neural pathway controlling reflex actions, where the spinal cord initiates the response before the brain processes it. Since muscles work in opposing pairs the two signals are sent the first relaxes triceps the second engages biceps
Resting Potential
Neuron's stable negative charge inside compared to the outside, maintained by ion gradients and pumps.
Depolarization
The process of raising the membrane potential during an action potential in a neuron.
Nerve Impulse
The electrical signal that travels along a neuron.
Action Potential
The rapid change in electrical potential across a membrane as a nerve impulse is transmitted.
Repolarization
The phase during which the membrane potential of a neuron is restored after depolarization.
Na+/K+ Pumps
Proteins that help maintain the resting potential of a neuron by pumping sodium ions out and potassium ions in.
Refractory Period
The time following an action potential when a neuron is less sensitive to additional stimuli.
All-or-Nothing Response
The principle that an action potential either fires completely or not at all. Since action potential is all or nothing in response to stimulus. If threshold potential is not reached (-55mV) the méninge does nothing
Neuron rests at -70Mv
Much reach -55 Mv to trigger depolarization
Reaches peak turns into dépolarisation back to resting state
Between a refractory period occurs where the neuron is hyperpolarized
Impulse Propagation
The transmission of the nerve impulse down the axon. The action potential is generated at the axon hillock where an electrical current depolarizes the neighbouring region of the axon membrane
The impulse travels down the axon as each section of the mentante that reaches its action potential depolarixed the membrane downstream from it
Conduction Speed
The rate at which an action potential travels along an axon, influenced by axon diameter and myelination. The myelin sheath insulates the axon, nodes of rangier are gaps that allow space for ion exchange.
Synaptic Cleft
The small gap between the axon terminal of one presynaptic and the dendrite of another postsynaptic neuron where neurotransmitters are released.
Nerve impulse causes neurotransmitters to be released
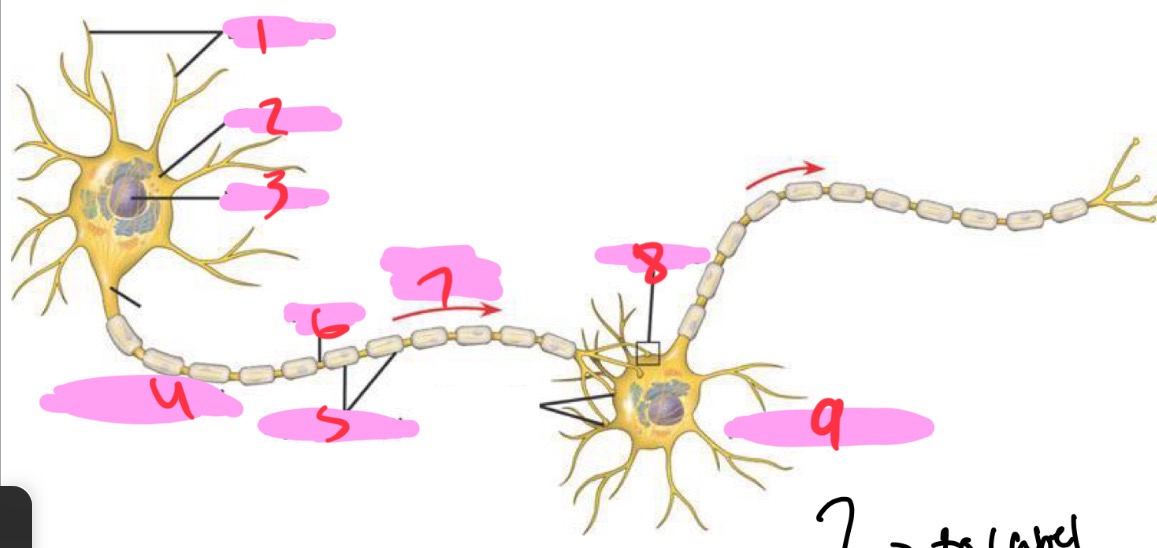
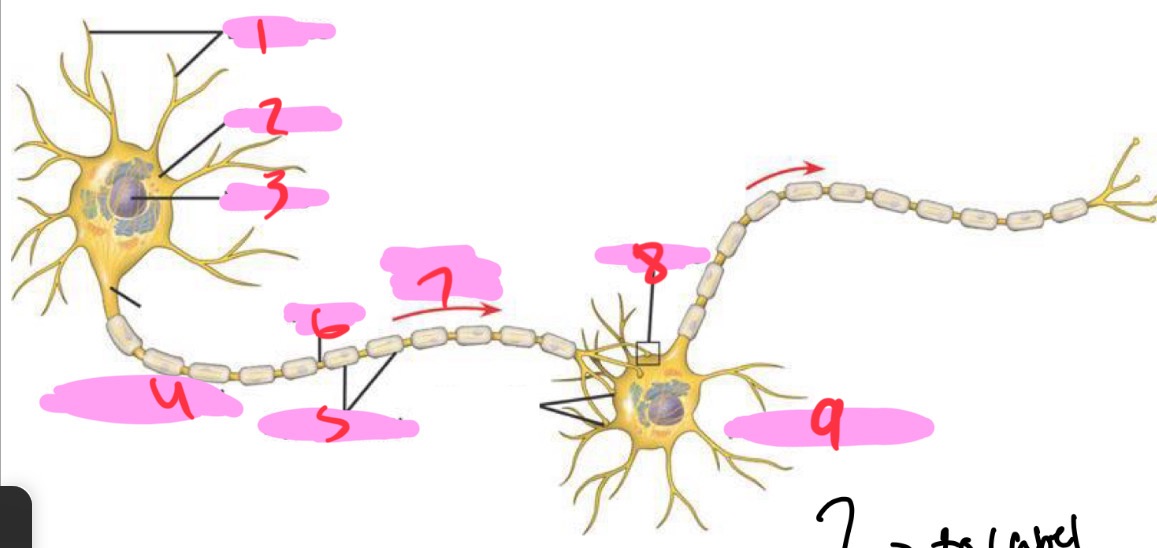
1 -Neuron
Dendrites
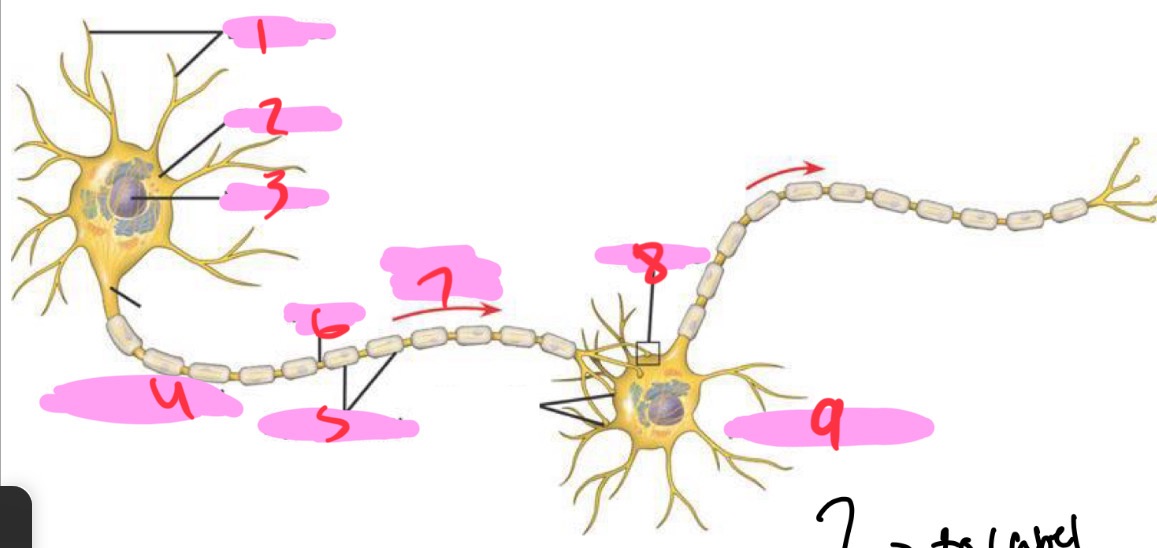
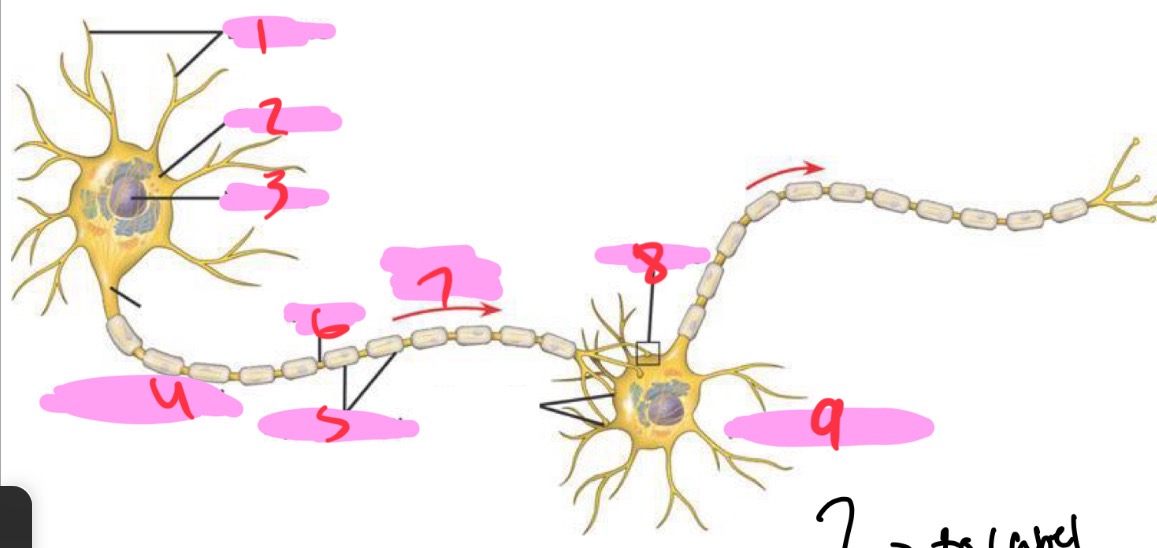
2 - Neuron
Cell body
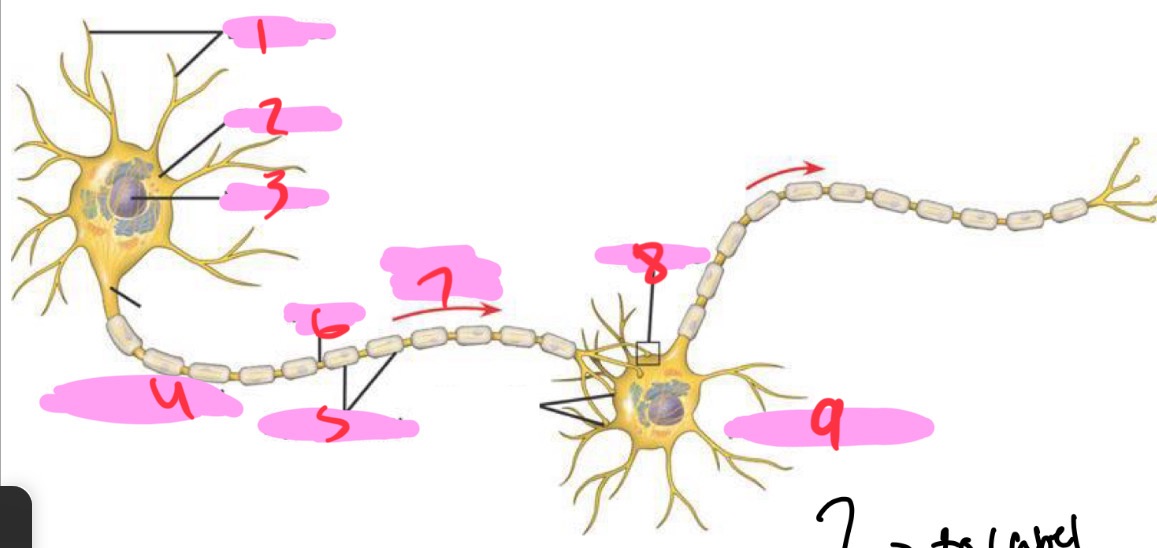
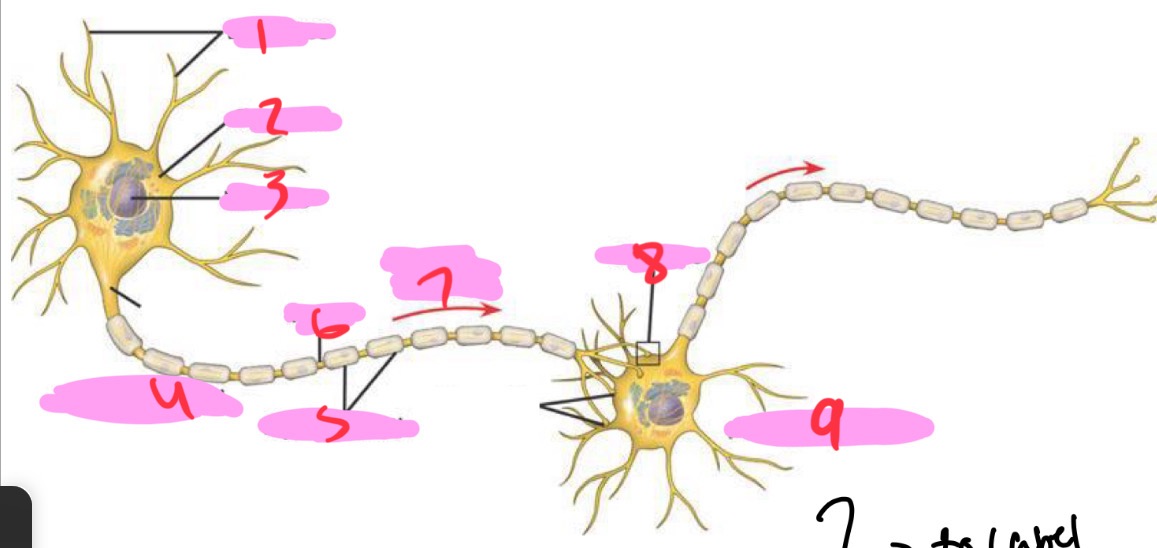
3 - Neuron
Nucleus
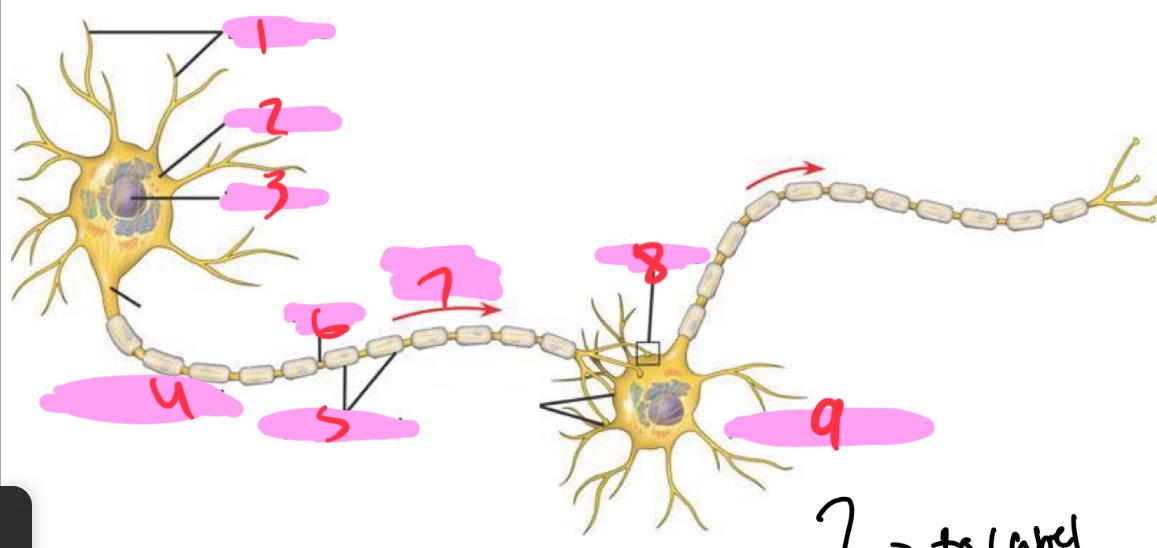
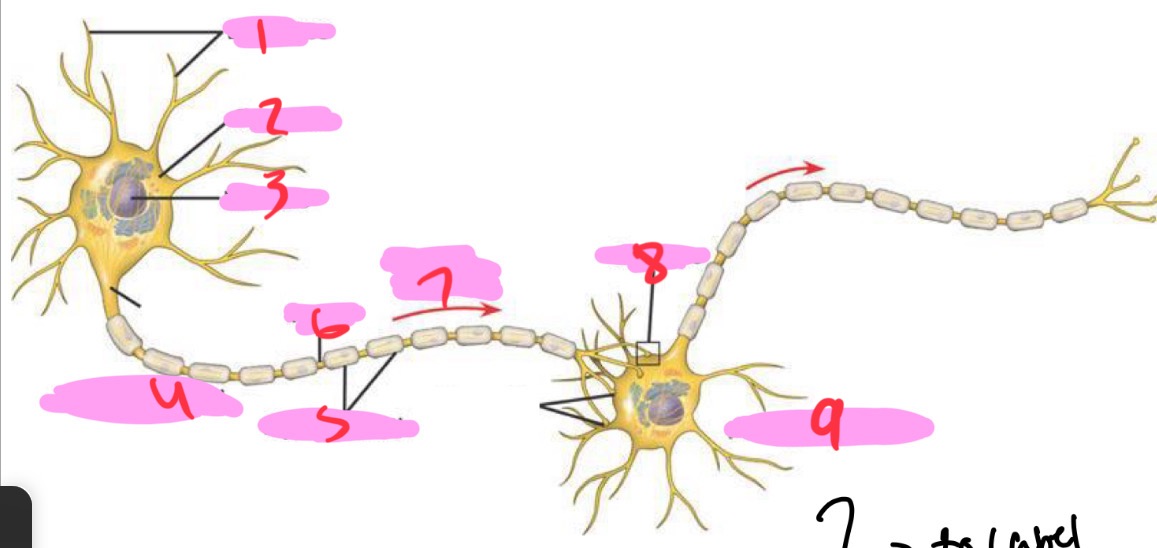
4 - Neuron
Presynaptic cell
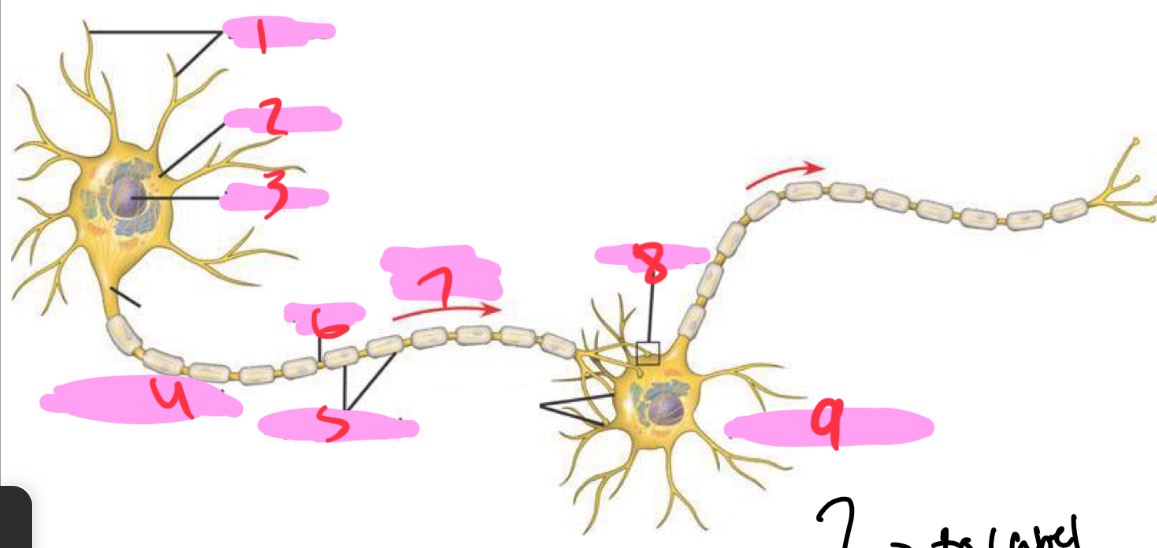
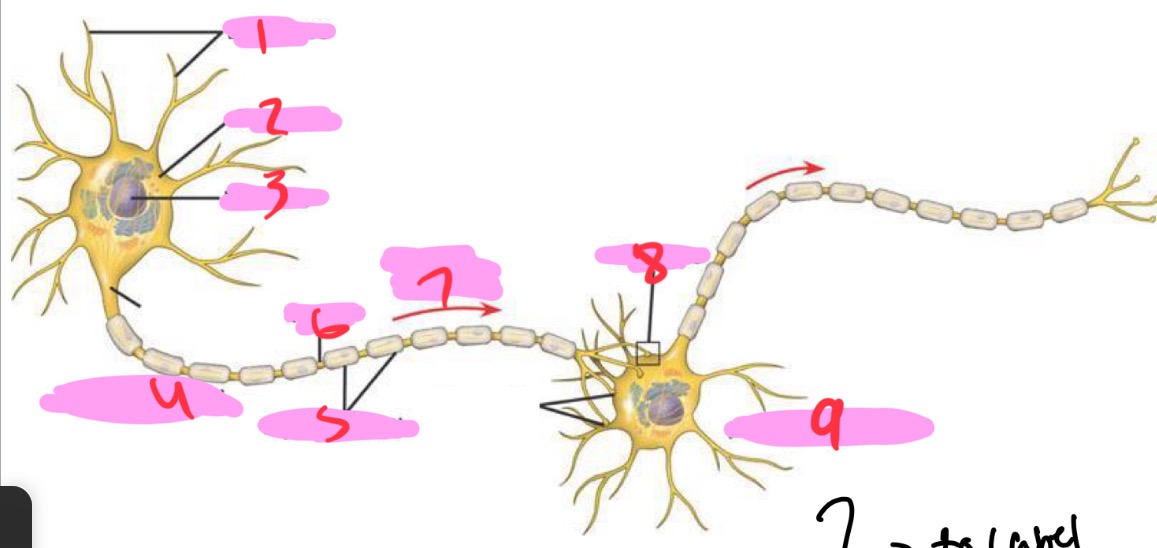
5 - Neuron
Myelin sheath
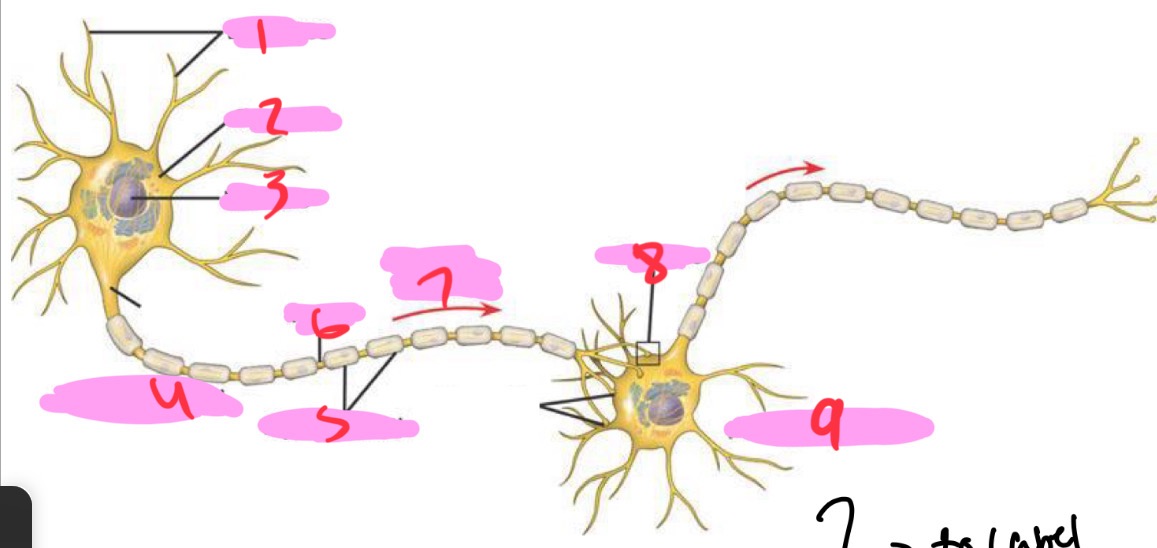
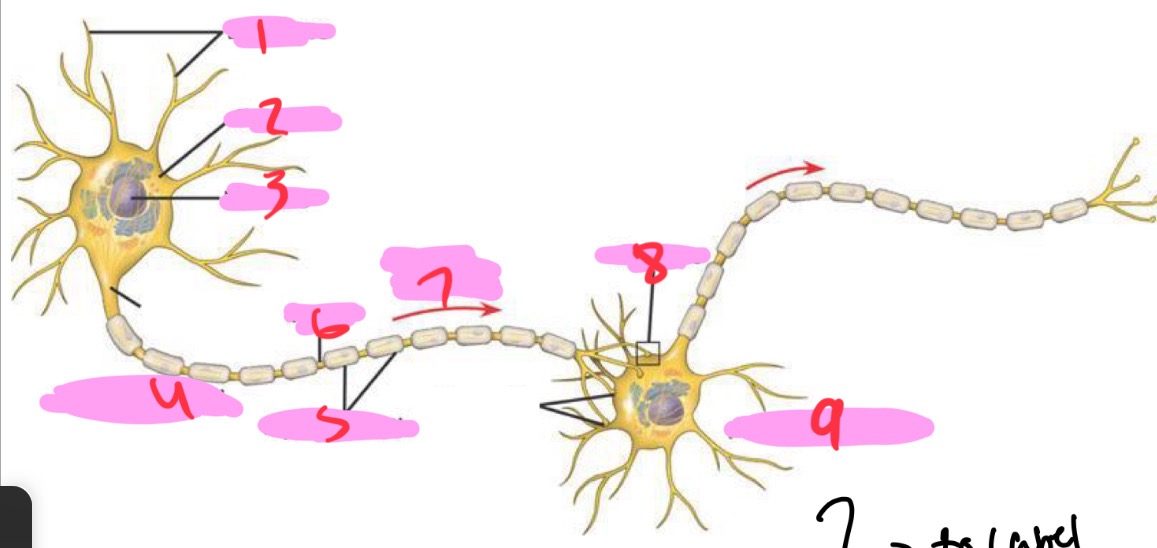
6 - neuron
Axon
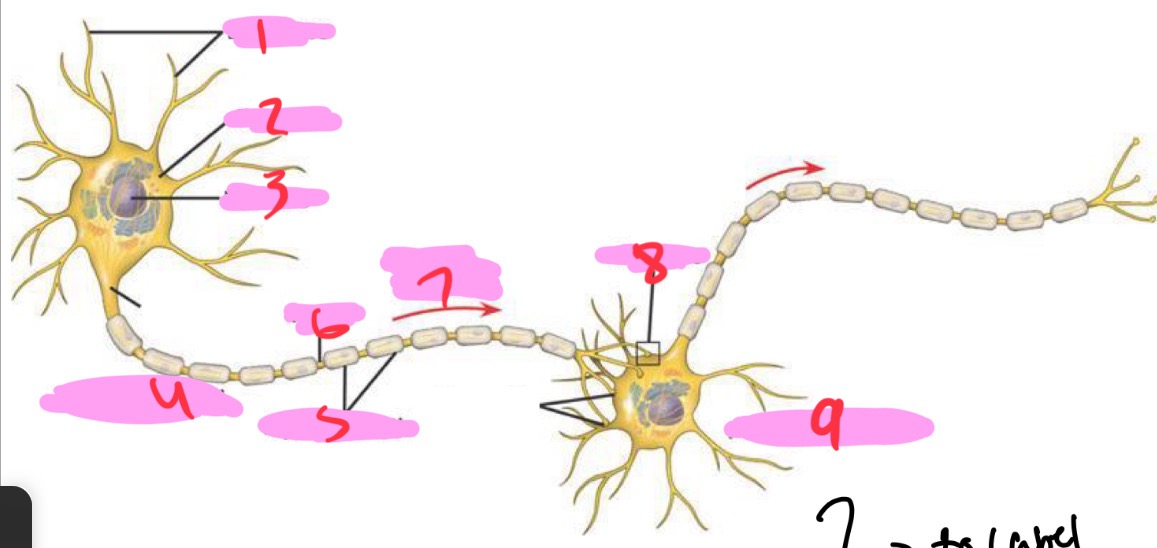
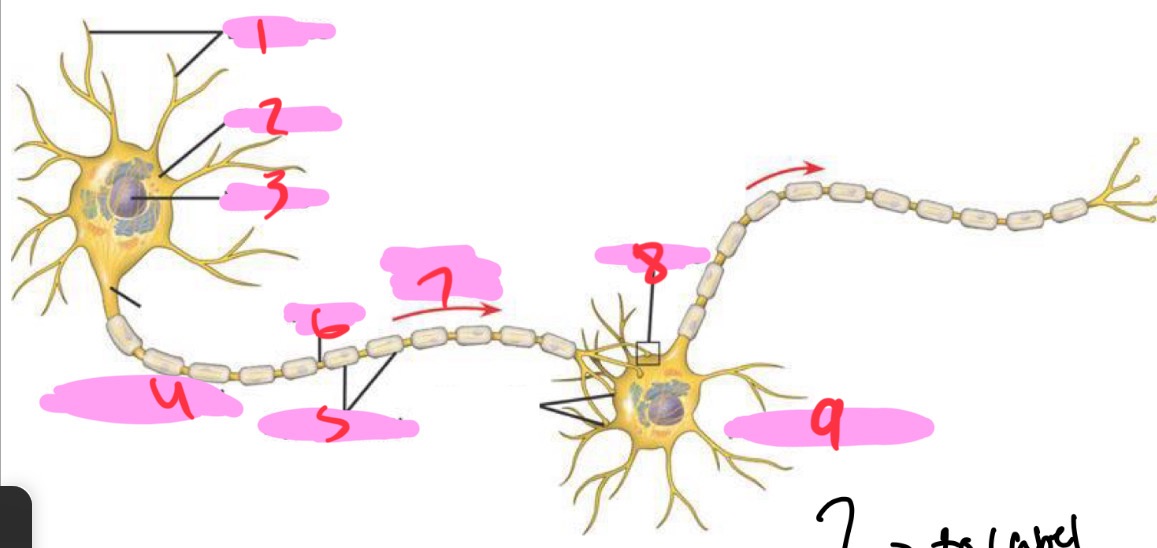
7 - Neuron
Signal direction
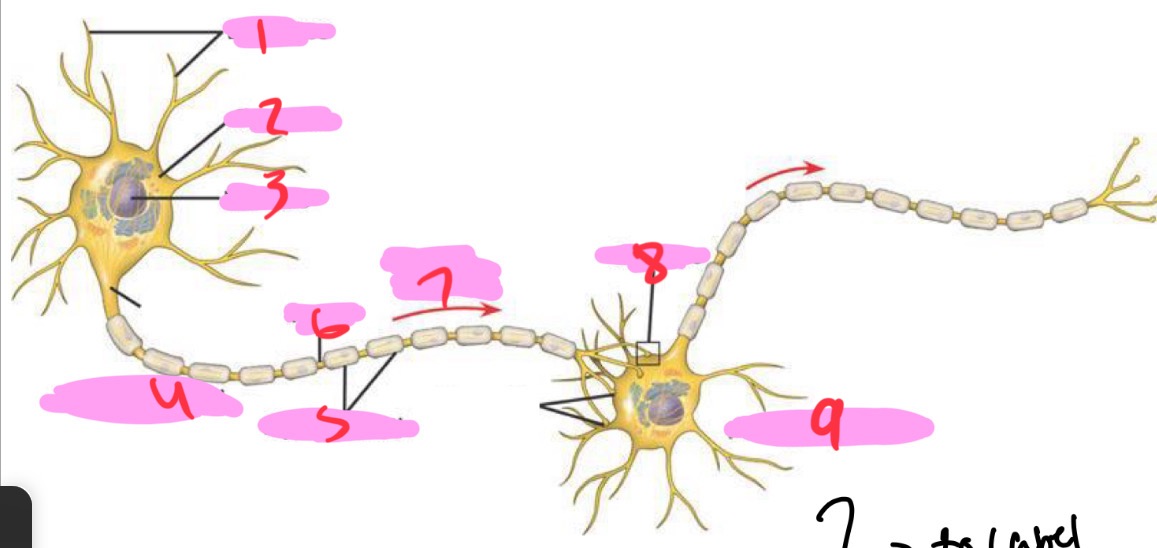
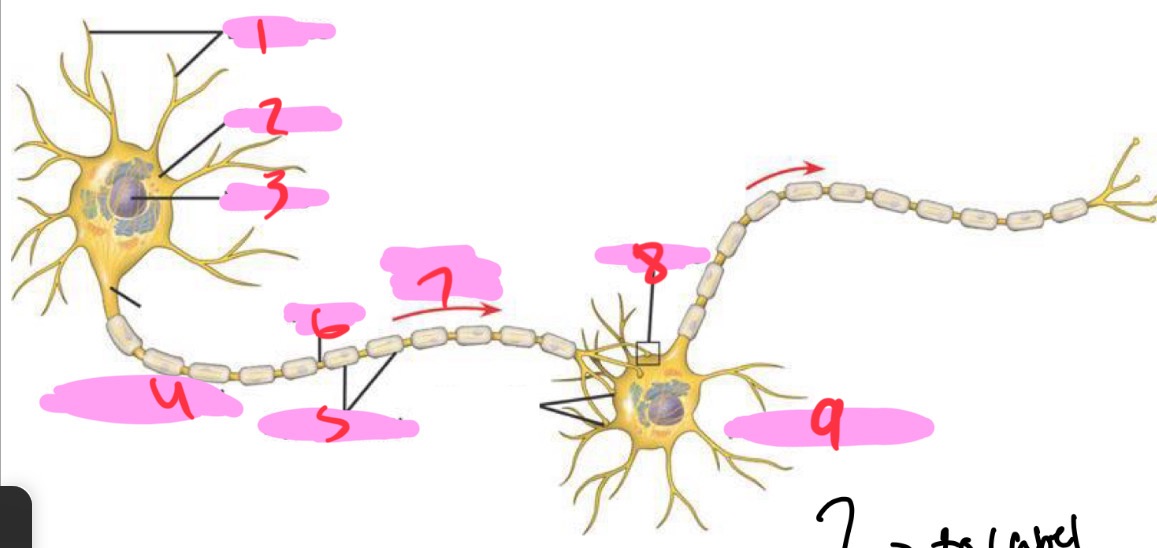
8 - Neuron
Synapse
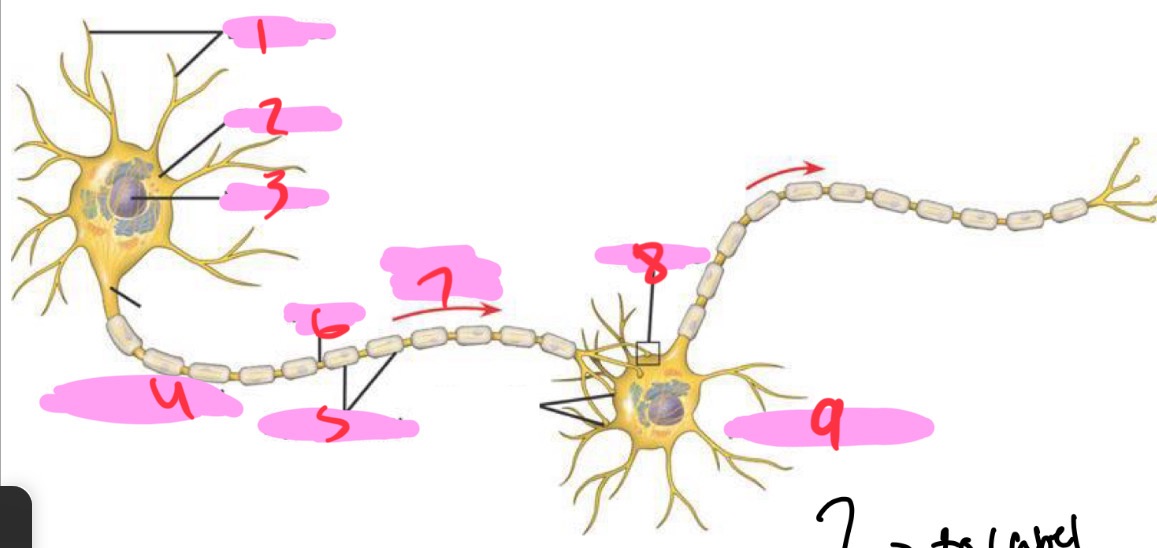
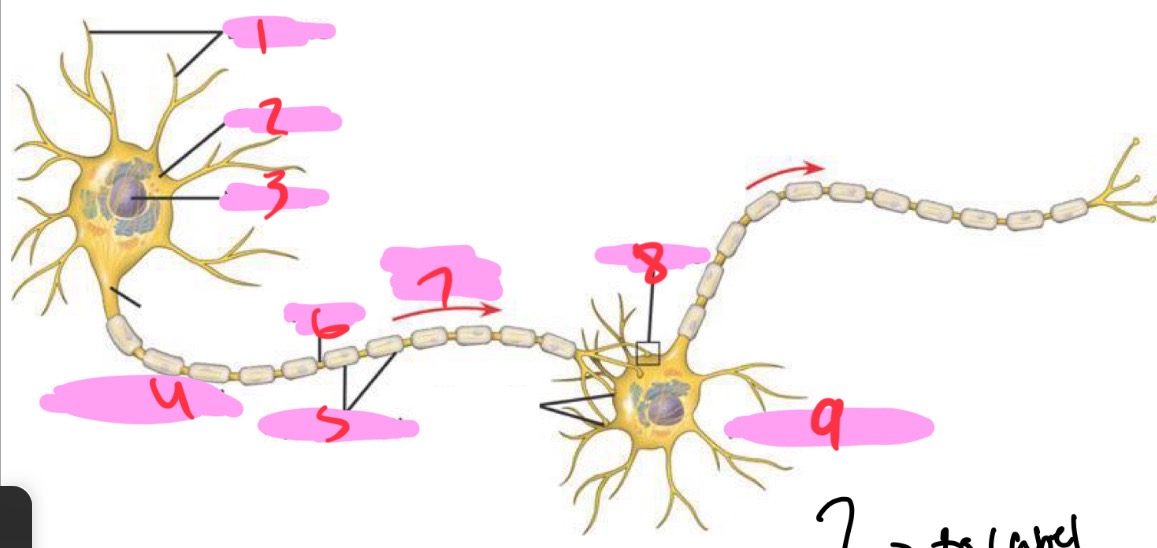
9 - Neuron
Postsynaptic cell
Oligodendrocyte
In the cns
Are glia that form myelin sheaths around the axons of many vertebrate neurons
Schwann cells
myelinating cell of the PNS and support cells
Synaptic cleft step 1
impulse from action potential opens ion channels for calcium ions
Synaptic cleft step 2
The increased calcium concentration in the axon terminal triggers release of neurotransmitters
Synaptic cleft step 3
Neurotransmitters released from its vesicle and crosses cleft and attaches to a protein receptor
Synaptic cleft step 4
Interaction of neurotransmitter and protein recoepr opens membrane ion channel for sodium
Synaptic cleft 5
Nt either degraded by an enzyme or taken back to presynatoc membrane by transporter or pump