APP Key People and Their Contributions 2024-25
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Plato and Aristotle
- while Socrates and Plato believed knowledge is innate, Aristotle found it was best derived from systematic observation. SPA= Socrates, Plato and Aristotle

Charles Darwin
- studied the plants and animals of South America and the Pacific islands, and in his book On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (1859) set forth his theory of evolution. He was an English naturalist in that he studied the relationships between organisms and their environments.

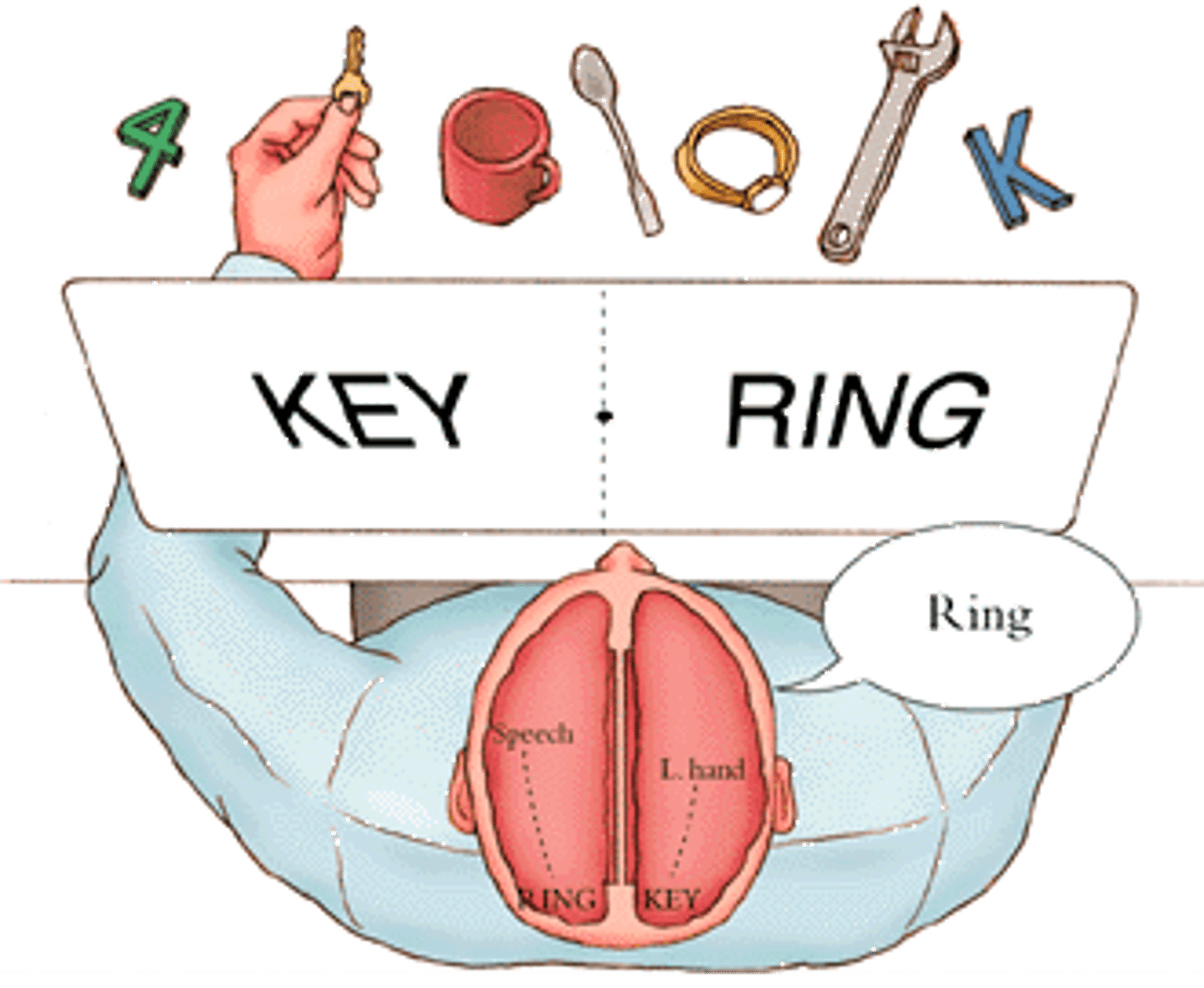
Roger Sperry and Michael Gazzaniga
- the researchers who adapted the split-brain testing techniques they developed in cats and monkeys for later use with split-brain, human patients to determine which hemisphere specializes in what.
Sigmund Freud
- the physician whose work focused on the unconscious causes of behavior and personality formation; founded psychoanalysis. He believed that dream were key to unlocking the unconscious.

Ernst Weber
- found difference threshold, or just noticeable difference, is the ability to detect the smallest change in a stimulus about 50% of the time. According to ___'s law, the just noticeable difference increases in proportion to the total intensity of the stimulus.

Gustav Fechner
- was Ernst Weber's student, and he formulated Weber's general statement of proportionality into a mathematical expression. Specifically, to be perceived as different, two types of stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage. So, it is sometimes called the Weber-Fechner Law.
Thomas Young and Hermann von Helmholtz
- discovered feature detector groups of neurons in the visual cortex that respond to different types of visual images.
David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel
- discovered feature detector groups of neurons in the visual cortex that respond to different types of visual images.
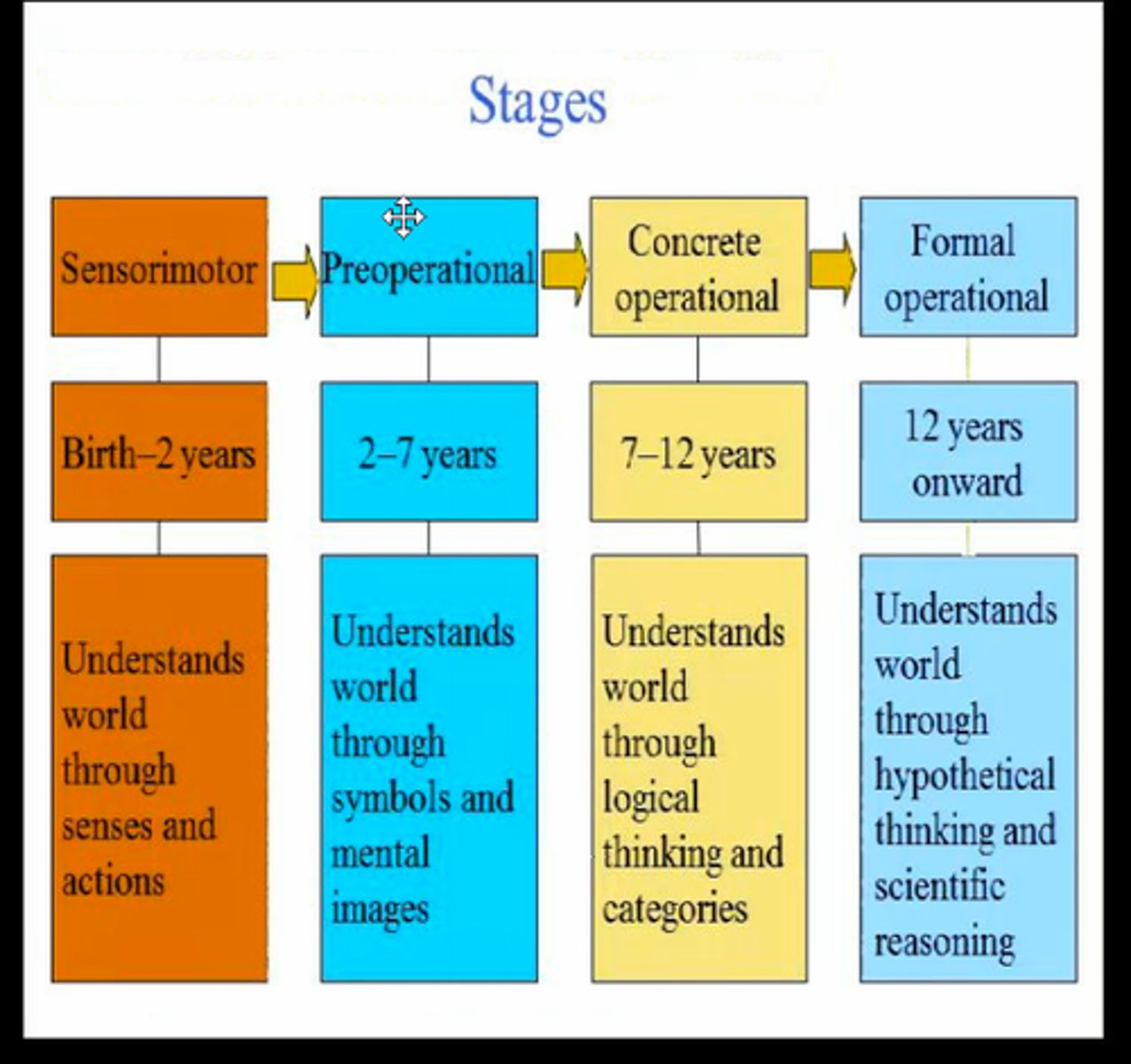
Jean Piaget
– known for his four-stage theory of cognitive development: i. sensorimotor, ii. preoperational, iii. concrete operational, and iv. formal operational. He said that the two basic processes work in tandem to achieve cognitive growth-assimilation and accommodation.
Robert Sternberg
- believe creativity has five components: expertise, imaginative thinking skills, venturesome personality, intrinsic motivation and a creative environment.
Wolfgang Köhler
- posited learning results from having an insight or figuring out a solution for their problems and applying it. He published a book called Mentality of the Apes in 1917 in which his experiments with chimps illustrated this process.

Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman
- worked together to study representativeness and availability heuristics to show how generally helpful heuristics can lead us to dumb decisions.
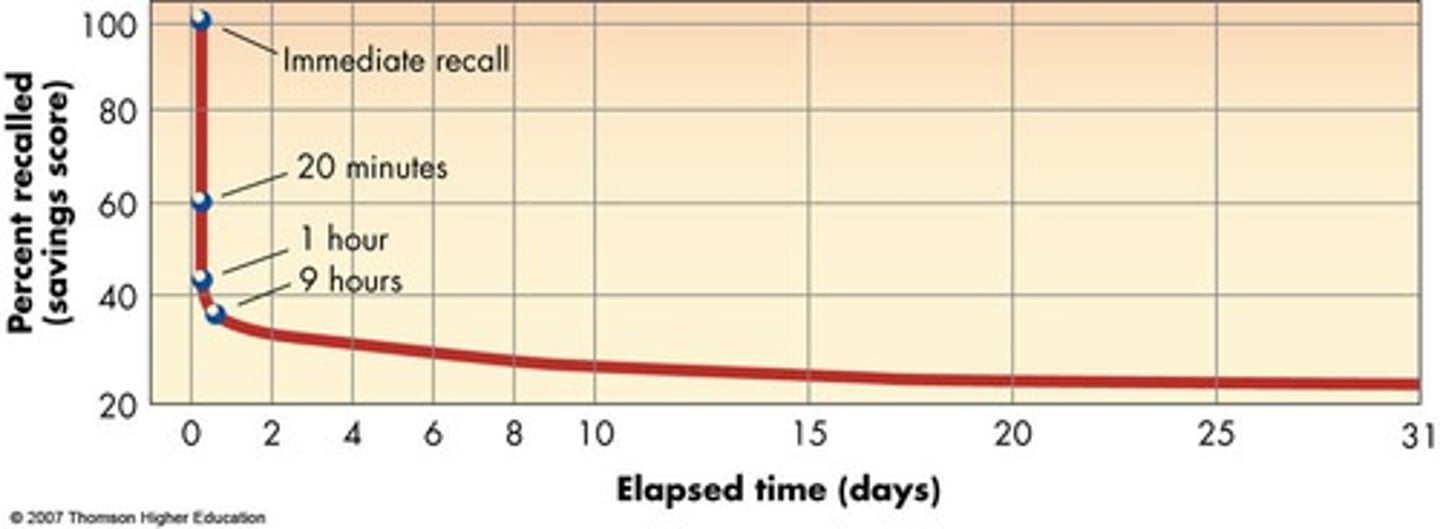
Herman Ebbinghaus
- the first person to study memory scientifically and systematically; used nonsense syllables and recorded how many times he had to study a list to remember it well.
Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin
- proposed the classic three-stage processing model of memory (sensory memory to short-term memory to long-term memory).
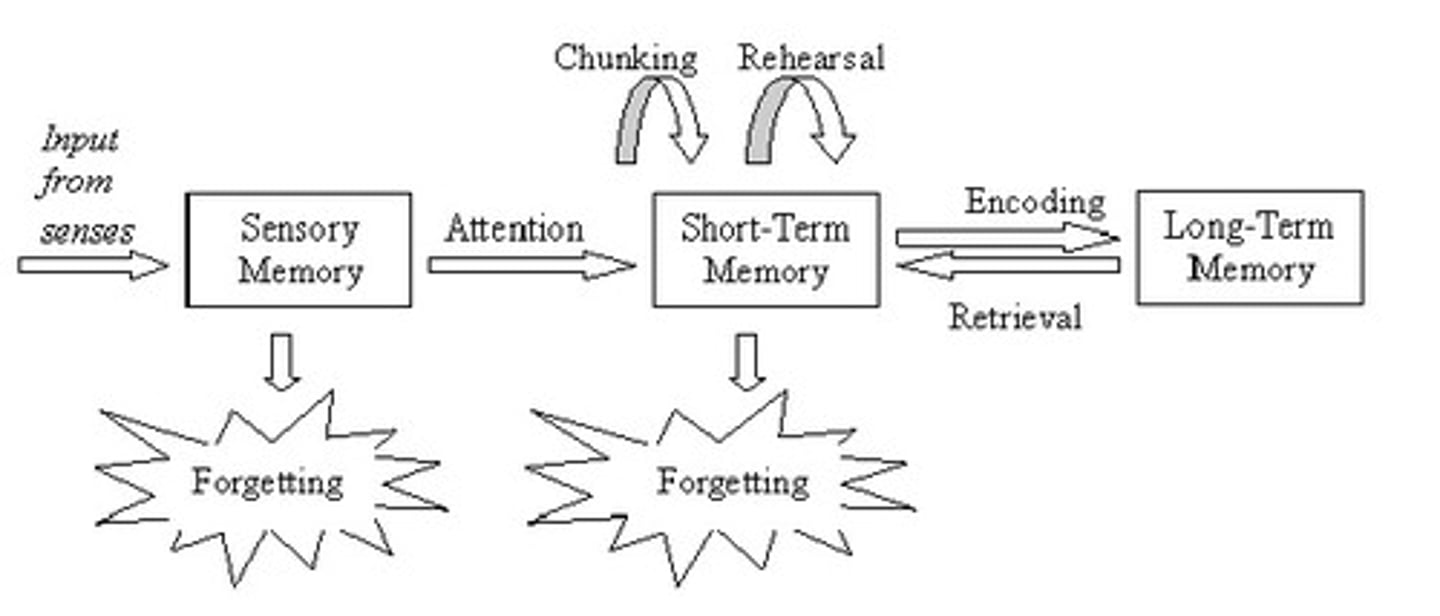
Eric Kandel
- studied the sea slug Aplysia and posited that learning and memory are evidenced by changes in synapses and neural pathways.

George A. Miller
- a psychologist who found that short term memory has the capacity of about seven (plus or minus two) items.

Steven Pinker
- argued that grammar is an innate algorithm evolved by natural selection. This innate phenomenon is influenced by a few cultural parameters to be set by language experience.
Carol Gilligan
- maintained that Köhlberg's work on moral development was developed by only observing boys and overlooked potential differences between the habitual moral judgments of boys and girls; girls focus more on relationships than laws and principles.

Elizabeth Loftus
- her research on memory construction and the misinformation effect created doubts about the accuracy of eye-witness testimony.
Carol Dweck
- explains why it's not just our abilities and talent that bring us success, but whether we approach them with a fixed or growth mindset.
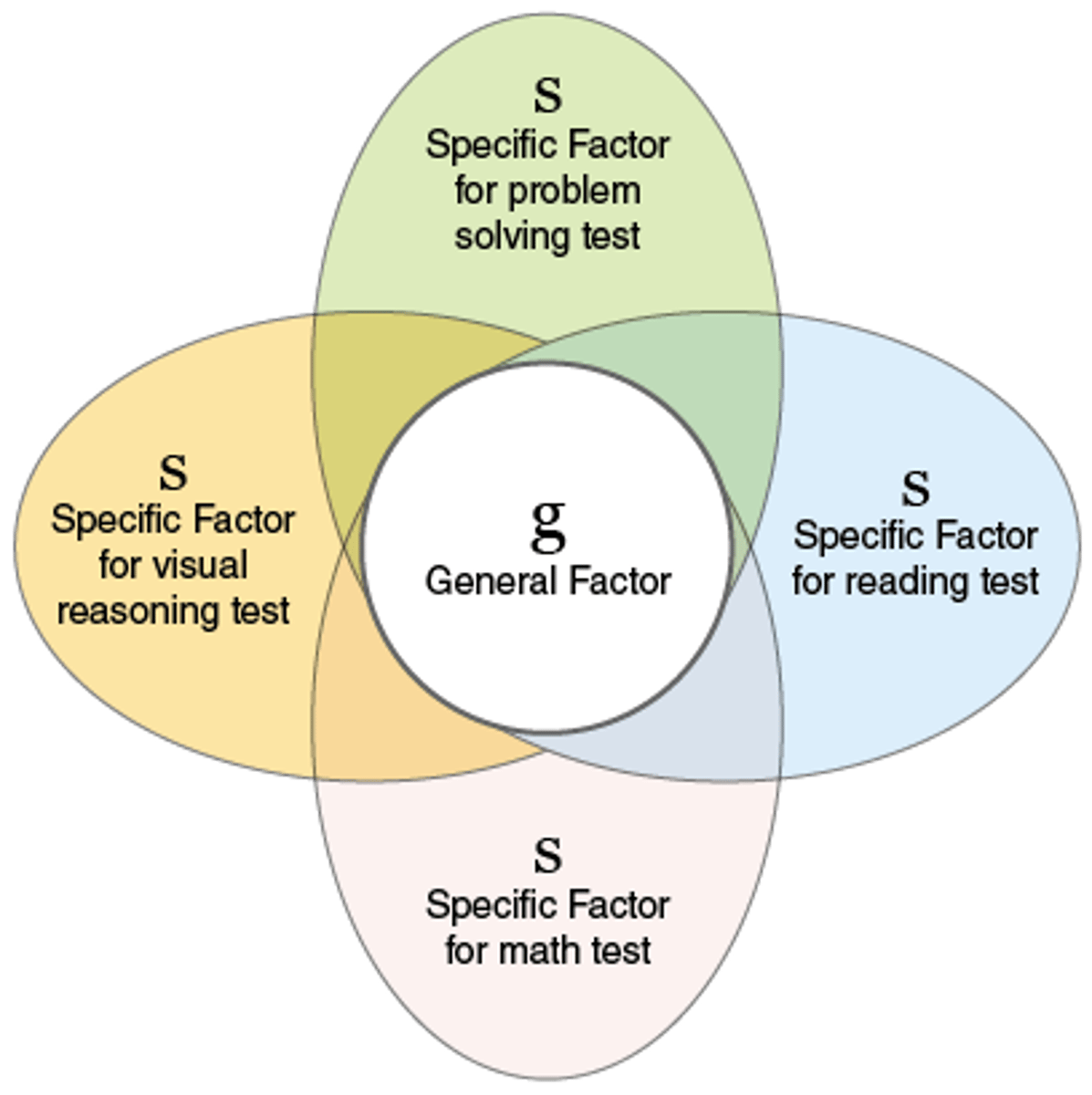
Charles Spearman
- found that specific mental talents were highly correlated, concluded that all cognitive abilities showed a common core which he labeled 'g' (general ability).
James Flynn
- documented the worldwide phenomenon that shows intelligence test performance has been increasing over the years. This rise is called the Flynn Effect.
L. L. Thurstone
- proposed seven clusters of primary mental abilities: word fluency, verbal comprehension, spatial ability, perceptual speed, numerical ability, inductive reasoning, and memory.
David Wechsler
- researcher that worked with troubled kids in the 1930's in NYC. He observed that many of these kids demonstrated a type of intelligence that was much different than the type of intelligence needed to succeed in the school system (STREET SMARTS). He created tests to measure more than verbal ability.
Raymond Cattell, John Horn and John Carroll
- theorized that our intelligence is based on g as well as specific abilities, bridged by Gf and Gc (fluid and crystallized intelligence).
Lewis Terman
- revised Binet's IQ test and established norms for American children; tested group of young geniuses and followed in a longitudinal study that lasted beyond his own lifetime to show that high IQ does not necessarily lead to wonderful things in life.

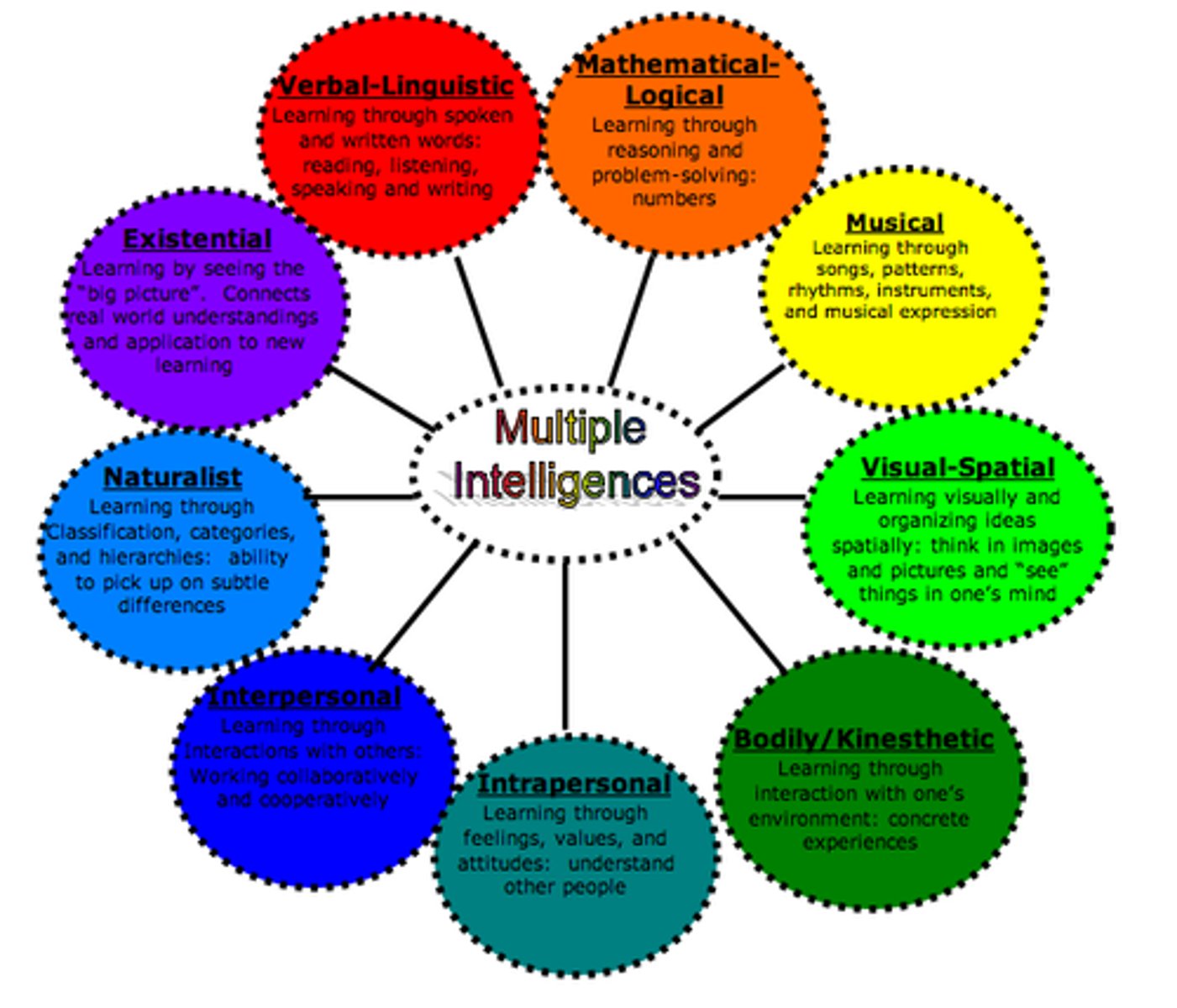
Howard Gardner
- devised theory of multiple intelligences: logical-mathematic, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, intrapersonal, linguistic, musical, interpersonal, naturalistic.
Alfred Binet
- pioneer in intelligence (IQ) tests, designed a test to identify slow learners in French schools.

Francis Galton
- maintained that personality and ability depend almost entirely on genetic inheritance. He compared monozygotic and dizygotic children to support his conclusions.
Alfred Kinsey
- published a series of reports which described common sexual behaviors in the US. They were controversial due to his methodology and conclusions.
Alice Eagly
- proposed that when there is a mismatch between the stereotype regarding someone's social group (e.g., female stereotype) and the value of their success in another social role (e.g., leadership), prejudice arises. That is, it is as if there is some exclusivity regarding one's social group; one cannot belong simultaneously to two different (stereotypically conflicting) groups.
Leon Festinger
- studied and demonstrated cognitive dissonance.
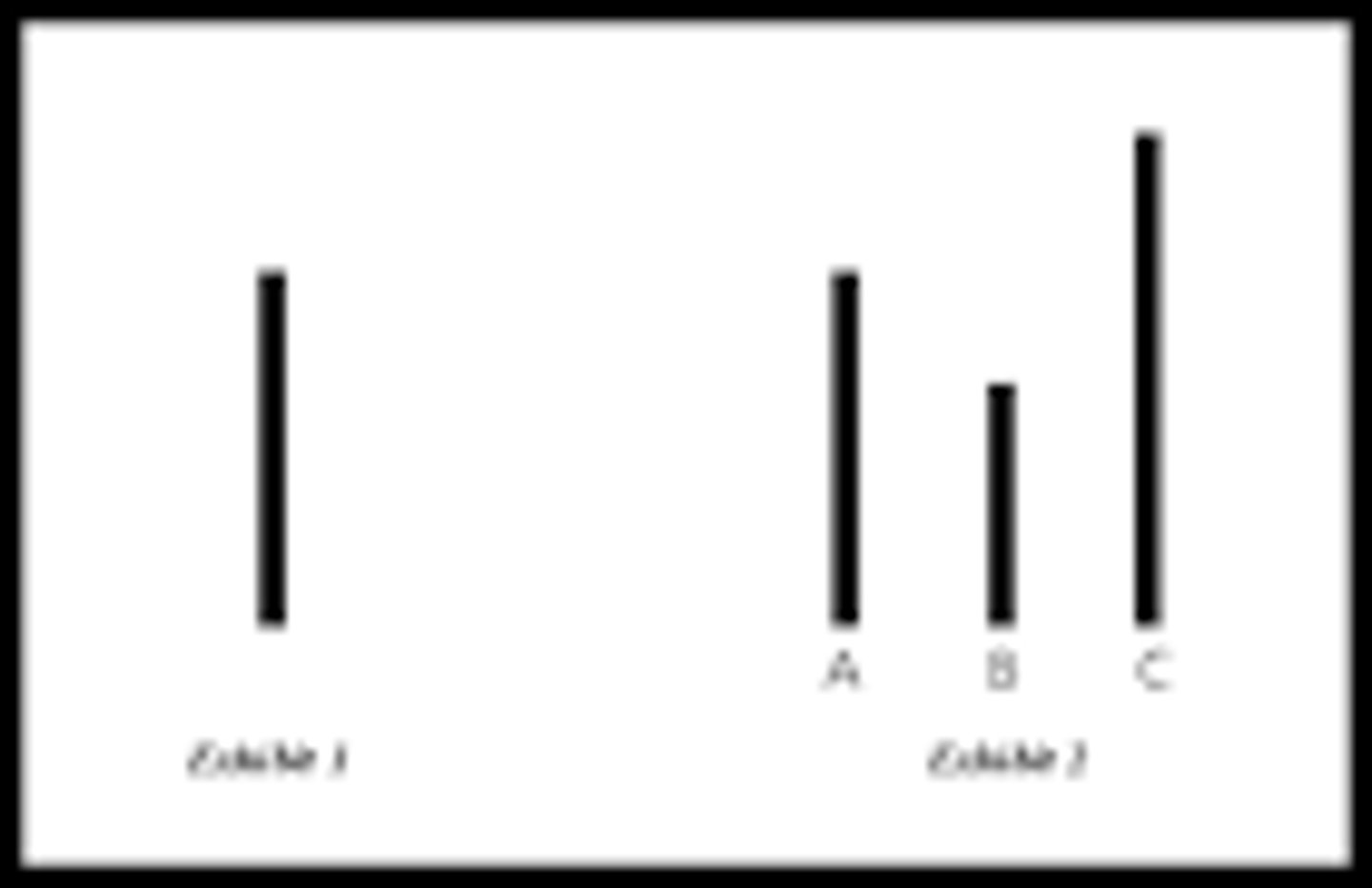
Solomon Asch
- studied conformity; in his famous study in which participants were shown cards with lines of different lengths and were asked to say which line matched the line on the first card in length. Some participants unknowingly chose the wrong answer simple because other said it was correct.
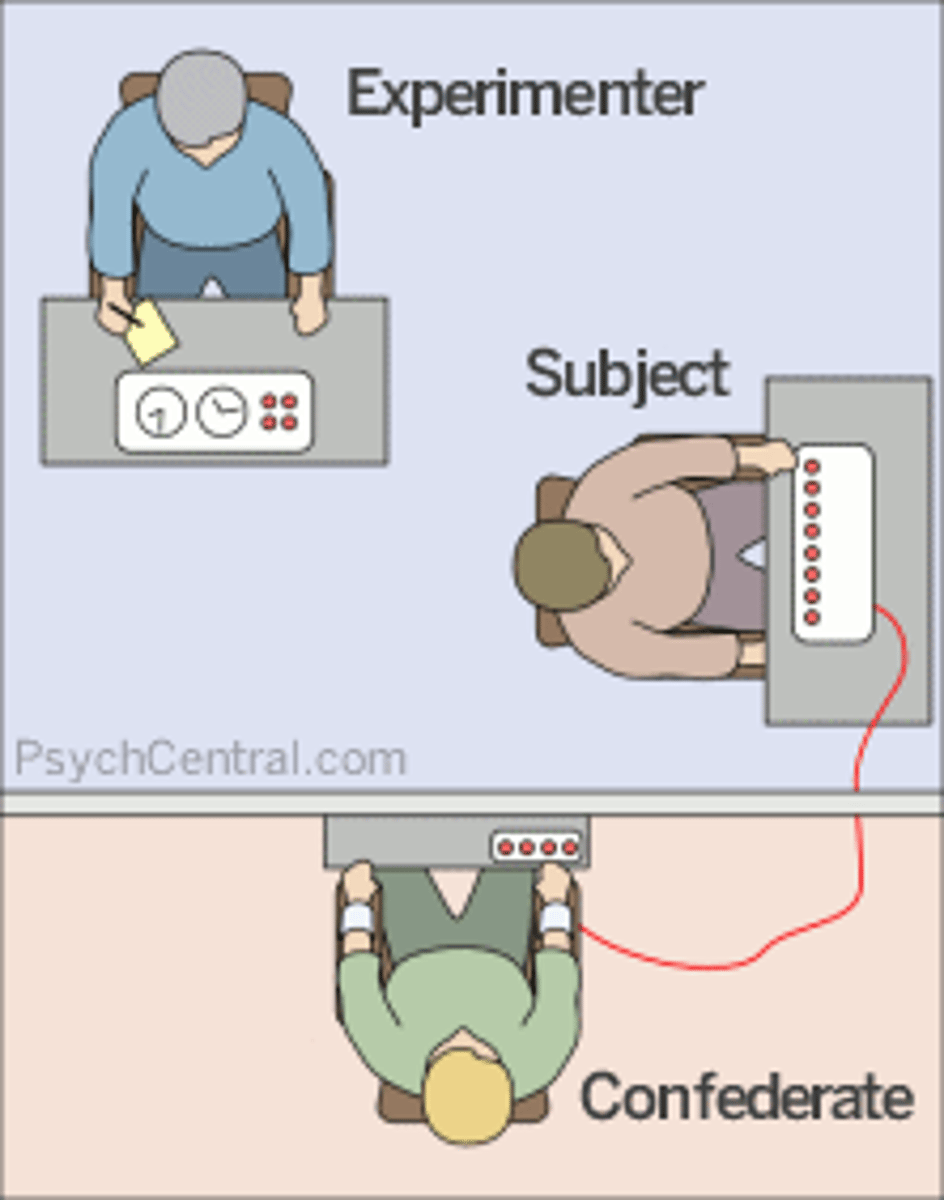
Stanley Milgram
- studied obedience to authority; he had participants administer what they believed were dangerous electrical shocks to other participants; wanted to see if Germans were an aberration or if all people were capable of committing evil actions.
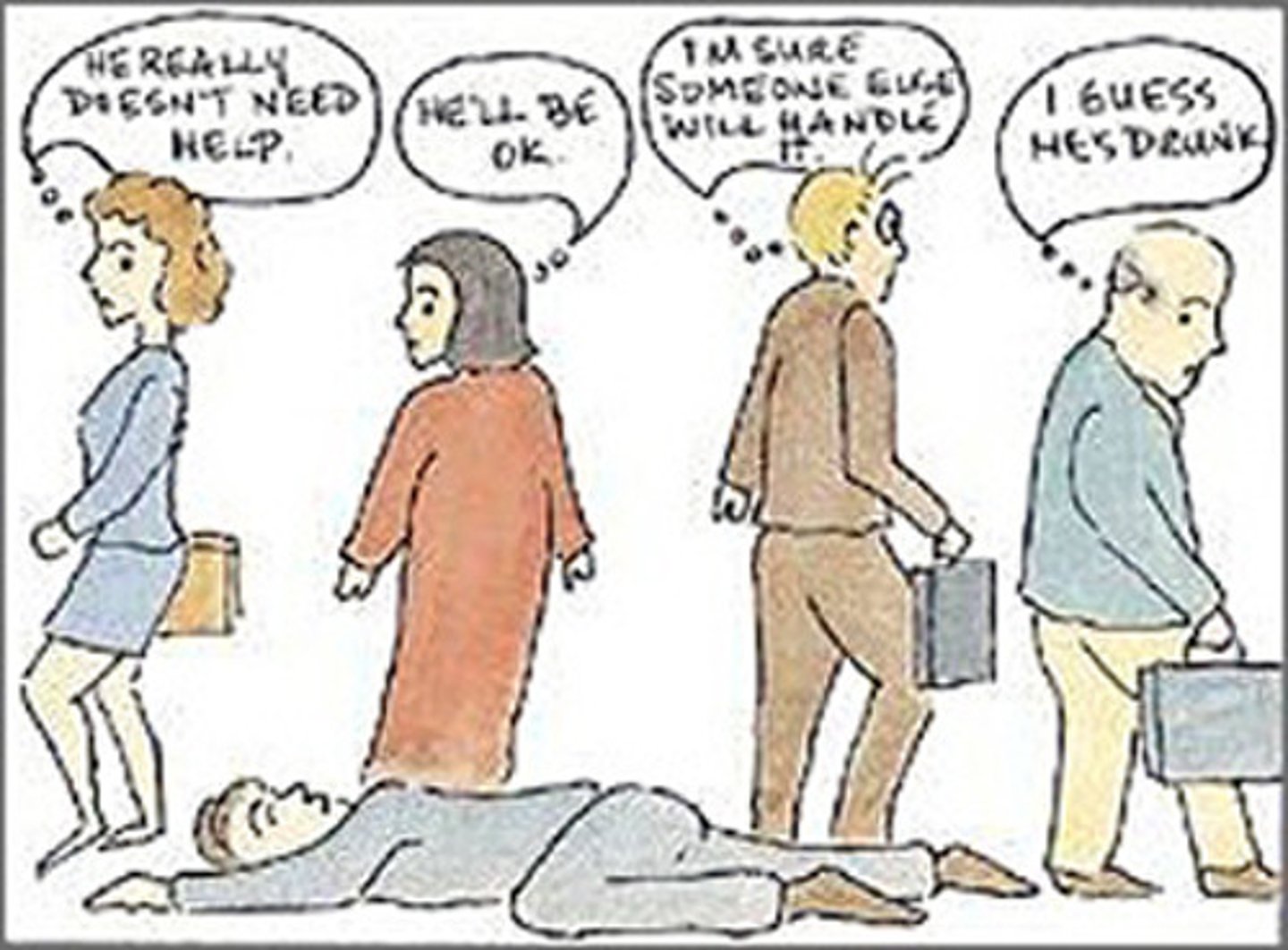
Bibb Latané and John Darley
- psychologists who researched the circumstances that determine when a bystander will intervene on behalf of another person.

Sigmund Freud
- Austrian physician whose work focused on the childhood experiences and unconscious causes of behavior and personality formation; founded psychoanalysis.
Alfred Adler
- Neo-Freudian; introduced concept of "inferiority complex" and stressed the importance of birth order.
Karen Horney
- neo-Freudian, psychodynamic; criticized Freud, stated that personality is molded by current fears and impulses, rather than being determined solely by childhood experiences and instincts, neurotic trends; concept of "basic anxiety."

Carl Jung
- proposed and developed the concepts of the extraverted and the introverted personality, archetypes, and the collective unconscious.
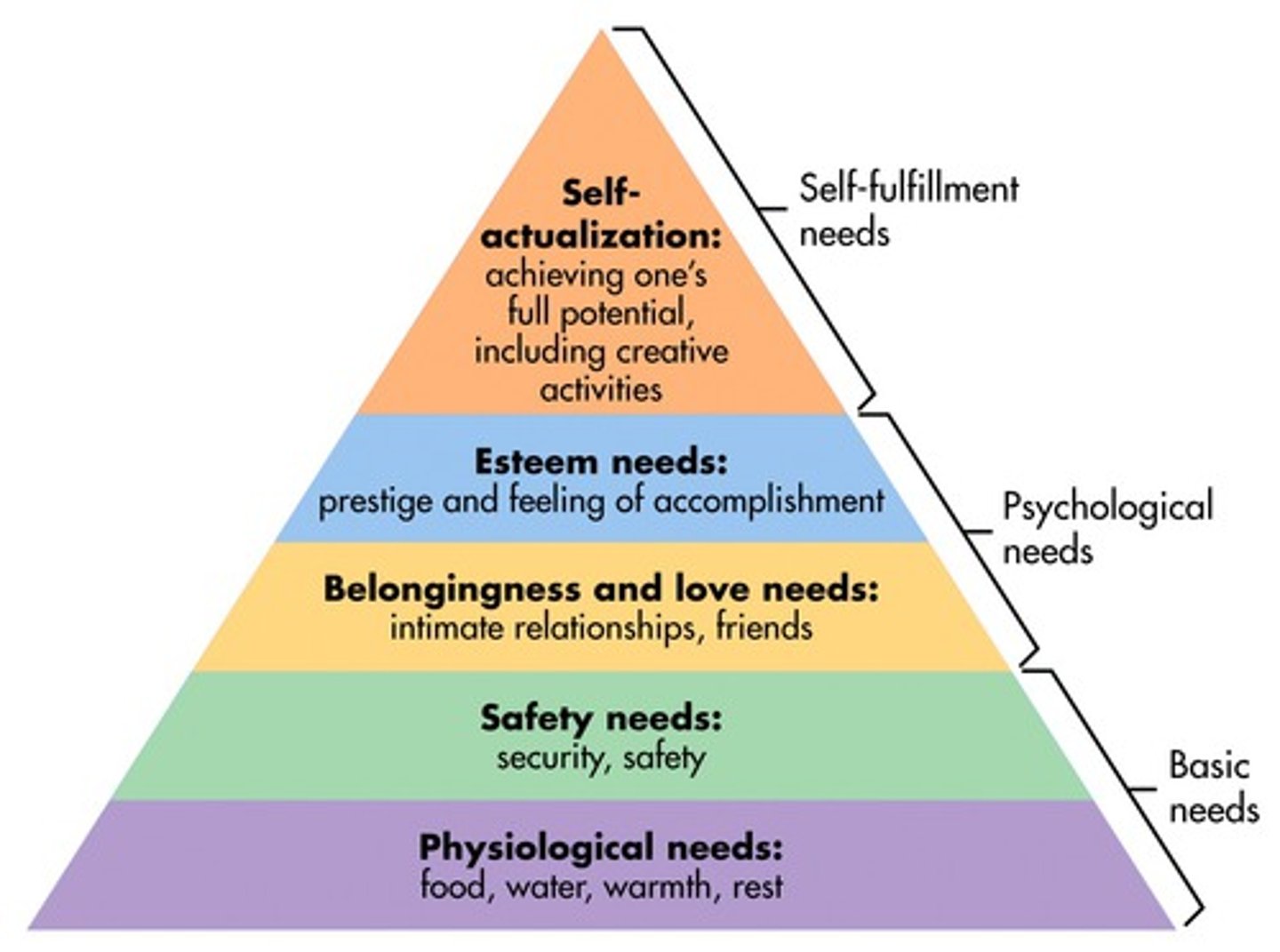
Abraham Maslow
- a humanistic psychology who found the hierarchy of needs-needs at a lower level dominate an individual's motivation as long as they are unsatisfied; self-actualization, transcendence.
Carl Rogers
- founded person-centered therapy, theory that emphasizes the unique quality of humans especially their freedom and potential for personal growth, unconditional positive regard, fully functioning person.
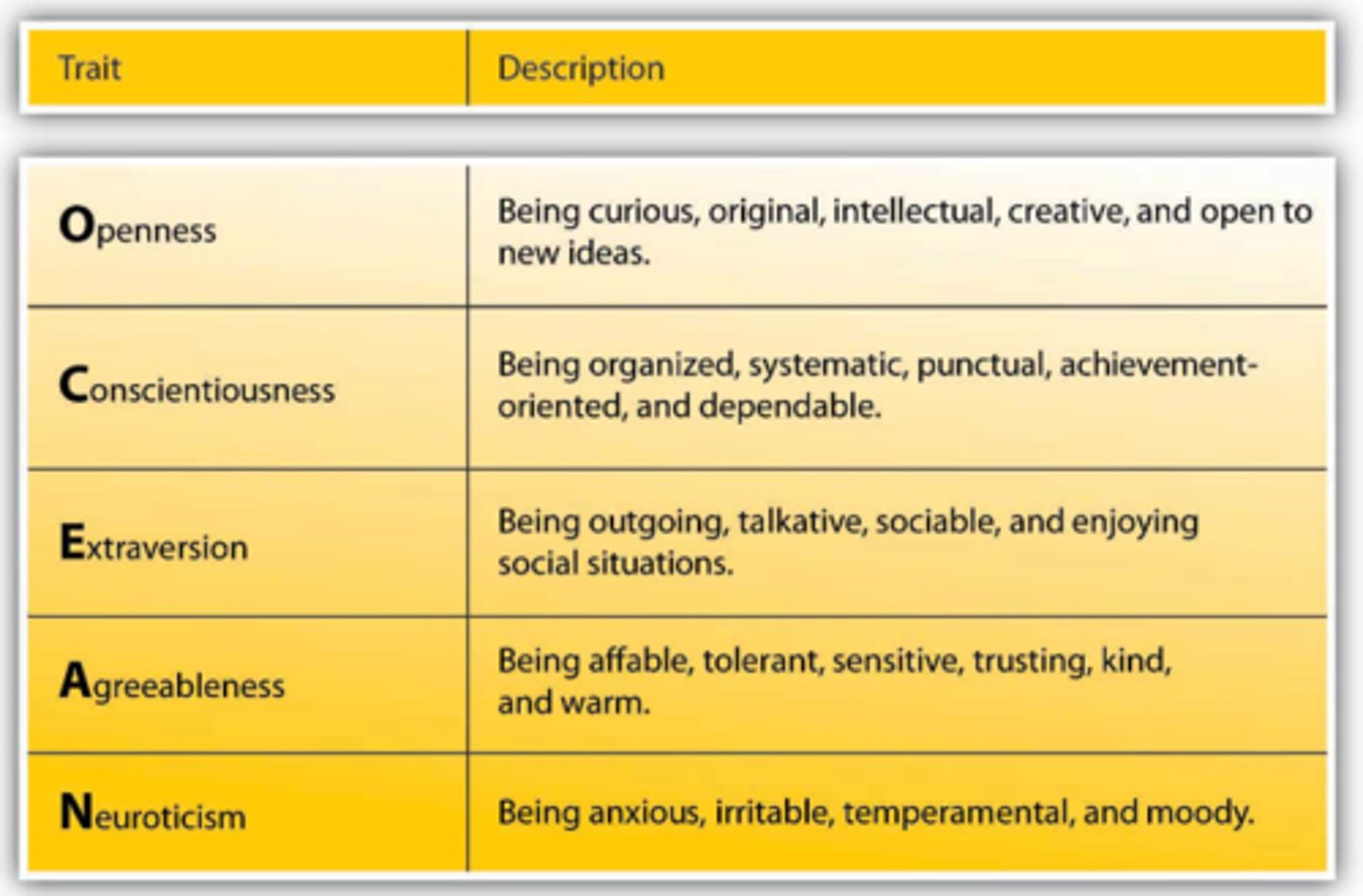
Paul Costa & Robert McCrae
- creators of the Big Five Trait Theory (CANOE: conscientiousness, agreeableness, neuroticism, openness to experience, and extraversion).
Albert Bandura
- pioneer in observational learning (AKA social learning), stated that people profit from the mistakes/successes of others; Studies: Bobo Dolls-adults demonstrated 'appropriate' play with dolls, children mimicked play.
William James
- founder of functionalism; studied how humans use perception to function in our environment. Wrote the first psychology textbook The Principles of Psychology.
Walter Cannon
- believed that gastric activity as in empty stomach, was the sole basis for hunger; Studies: inserted balloons in stomachs. He coined the term homeostasis.
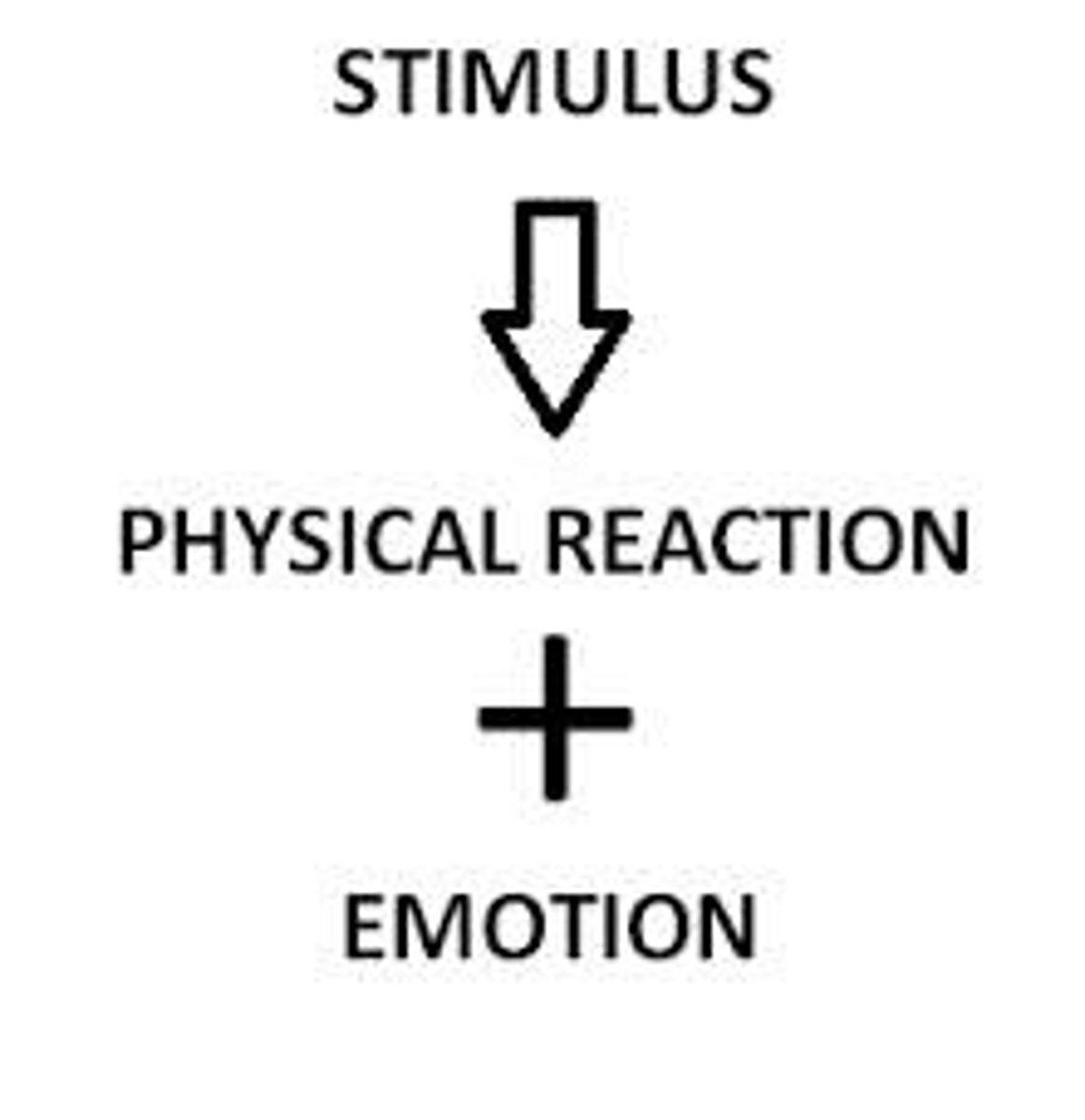
Stanley Schachter
- stated that in order to experience emotions, a person must be physically aroused and know the emotion before you experience it.
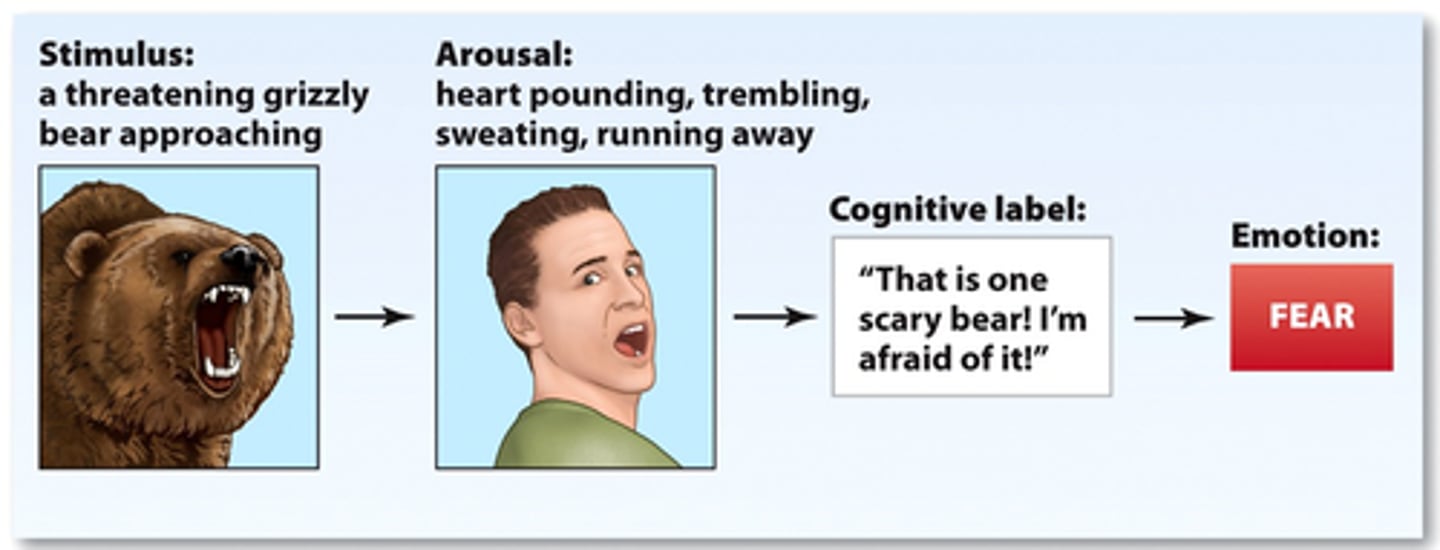
Robert Zajonc
- believes that we invent explanations to label feelings.
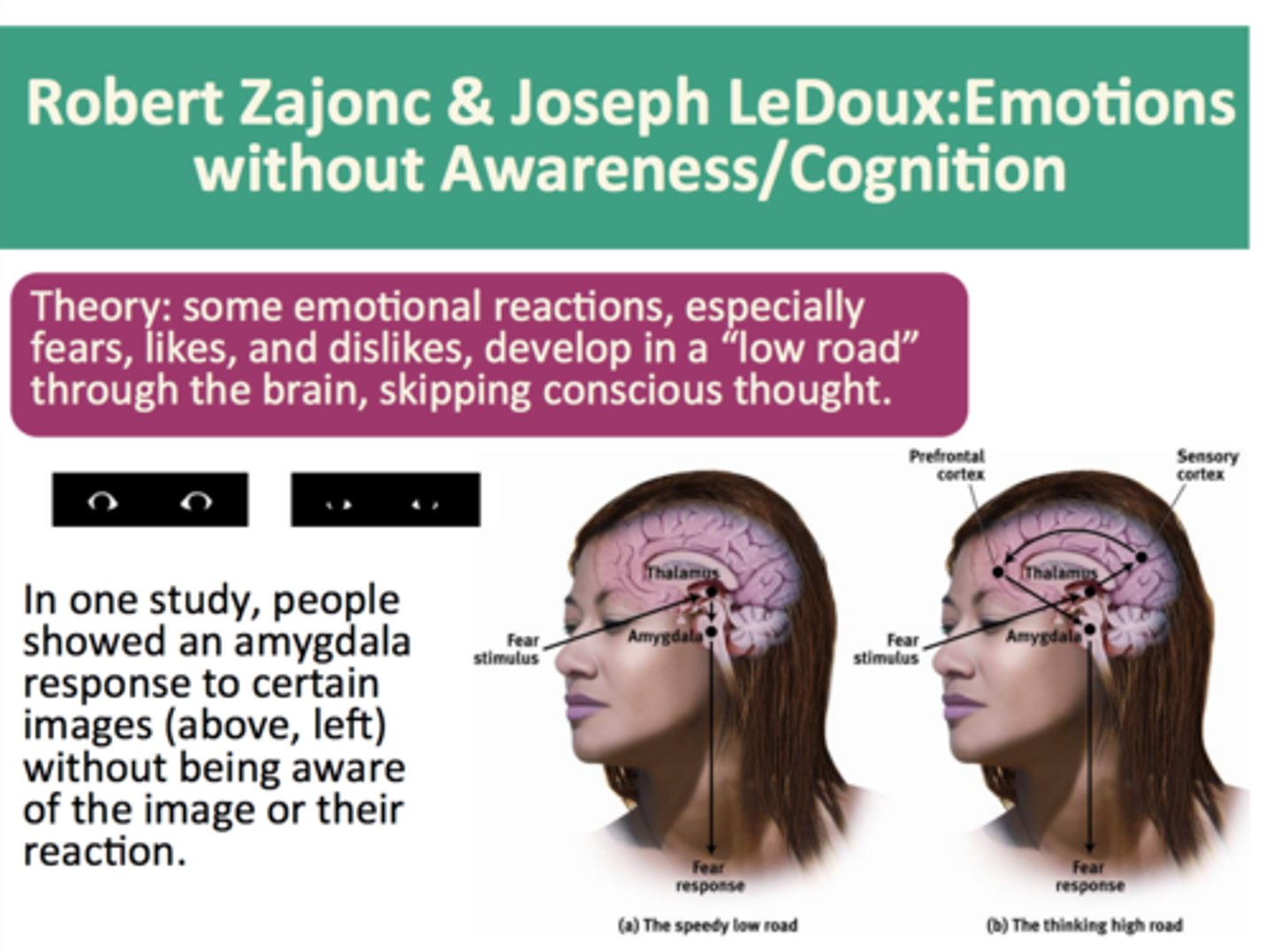
Joseph LeDoux
- proposed that the amygdala serves as a "hub" of rapid emotional response, especially to sensory input involving threat.
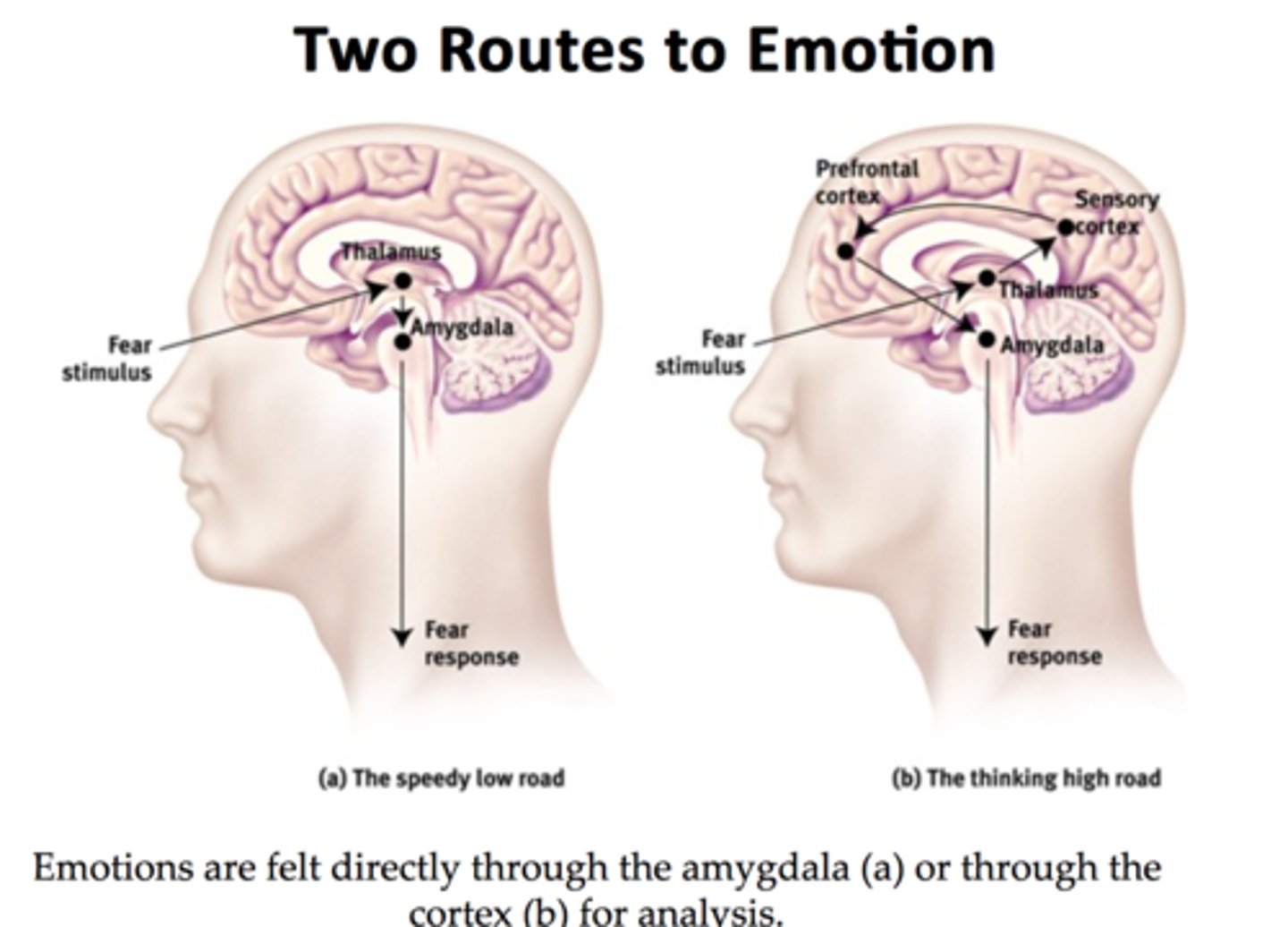
Richard Lazarus
- concluded that some emotional responses do not require conscious thought.
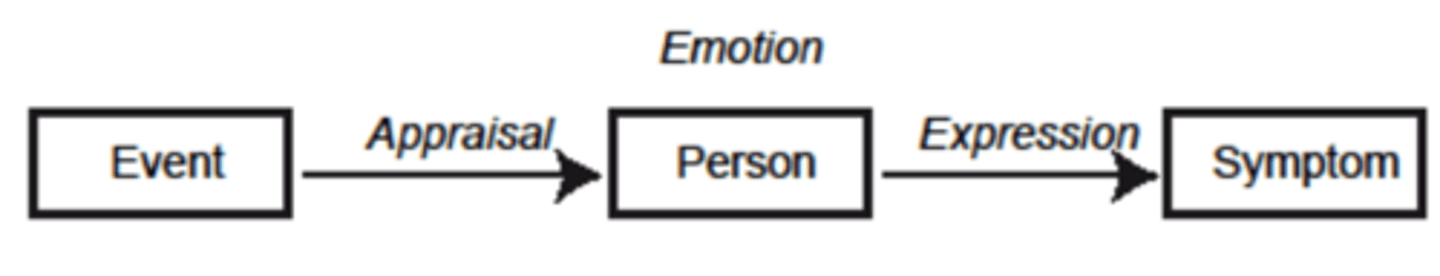
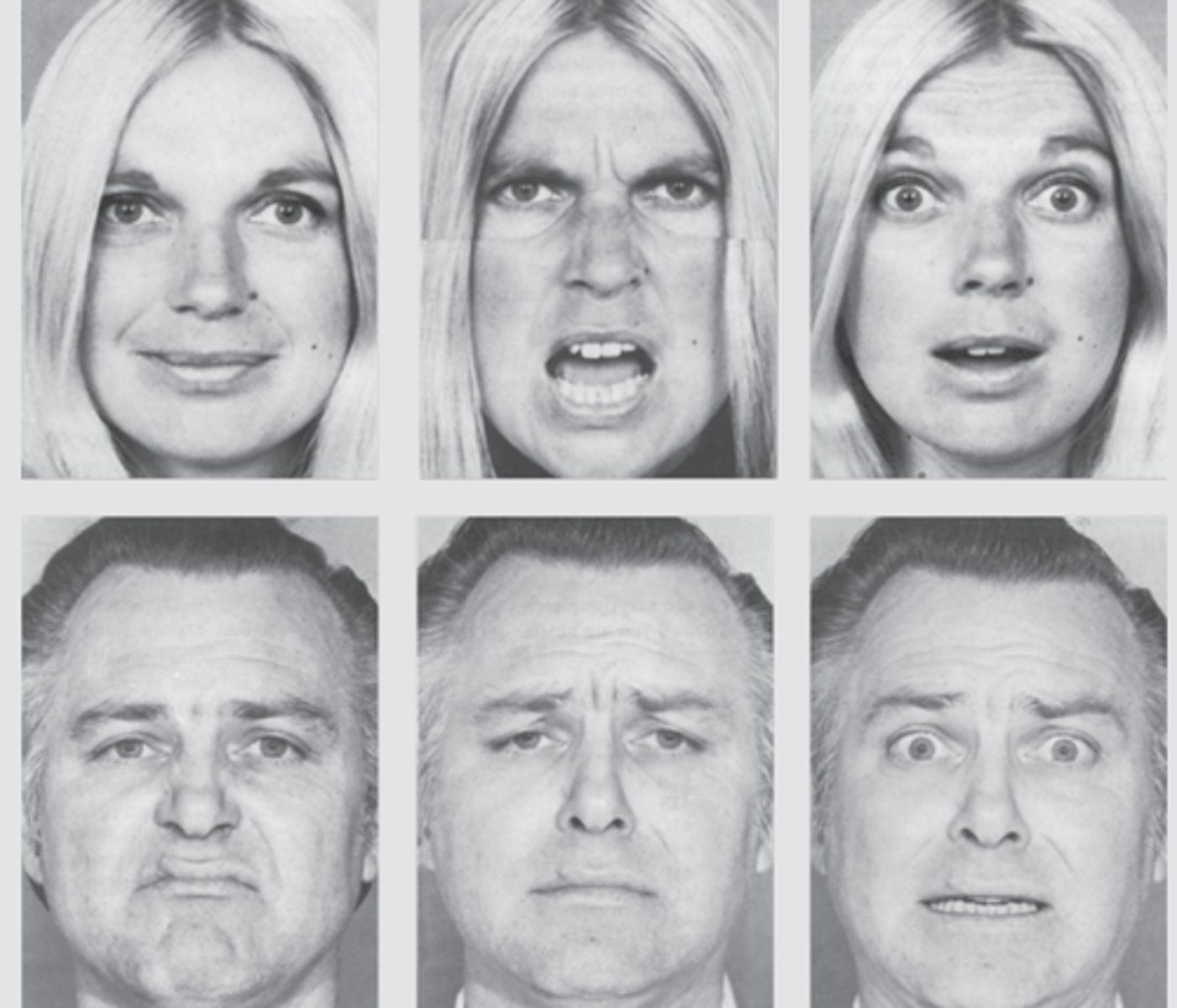
Paul Ekman
- found that facial expressions are universal.
