Brain Structure and Function
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
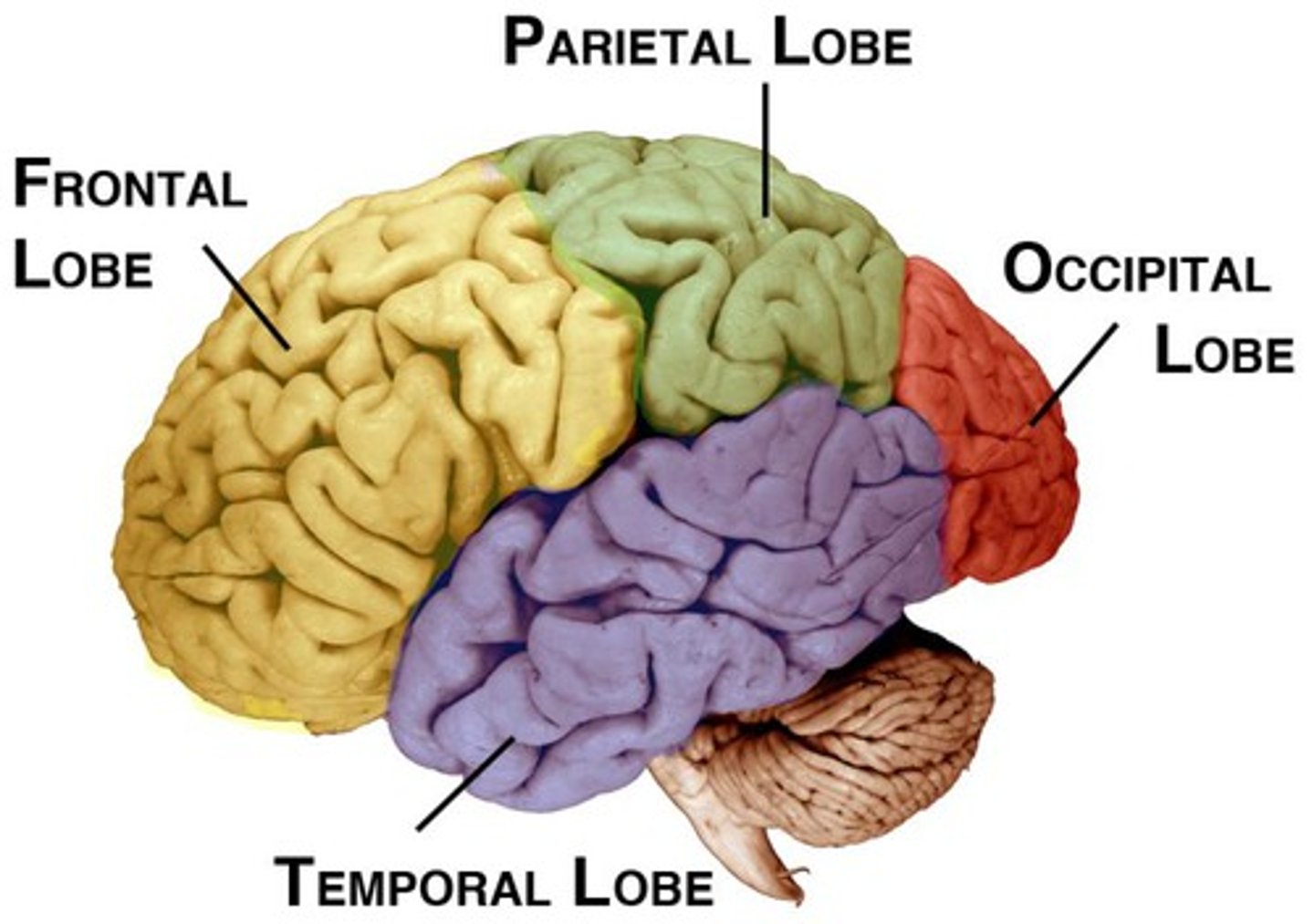
Lobes of the brain
There are 4 lobes in each hemisphere joined by the corpus callosum. They are:
Frontal
Pariental
Occipital
Temporal
Celebral Cortex
The outer layer/film (name means 'bark')
-role: memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, conciousness
-highest cognition levels
-folds contain <70% of human's braincells
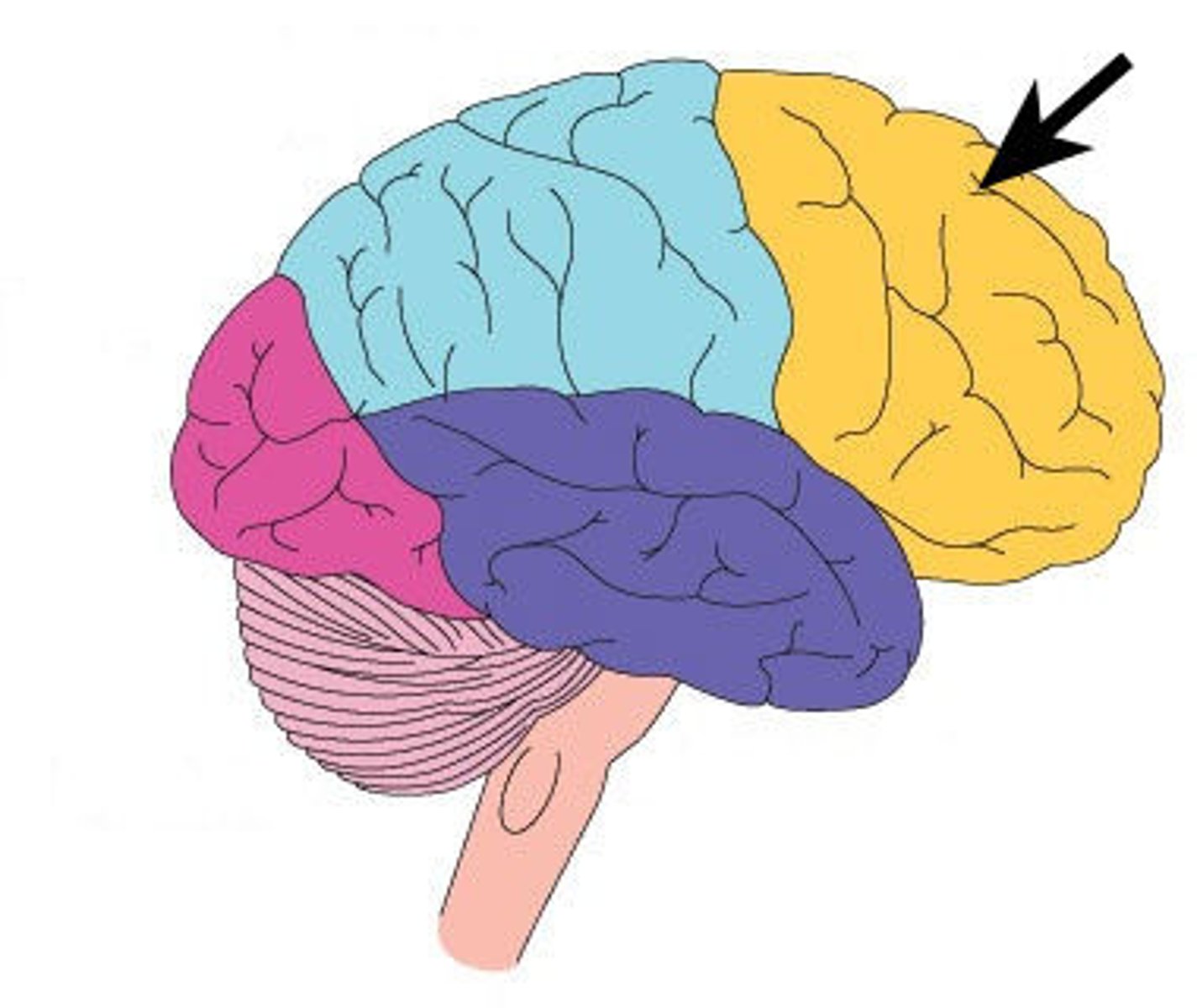
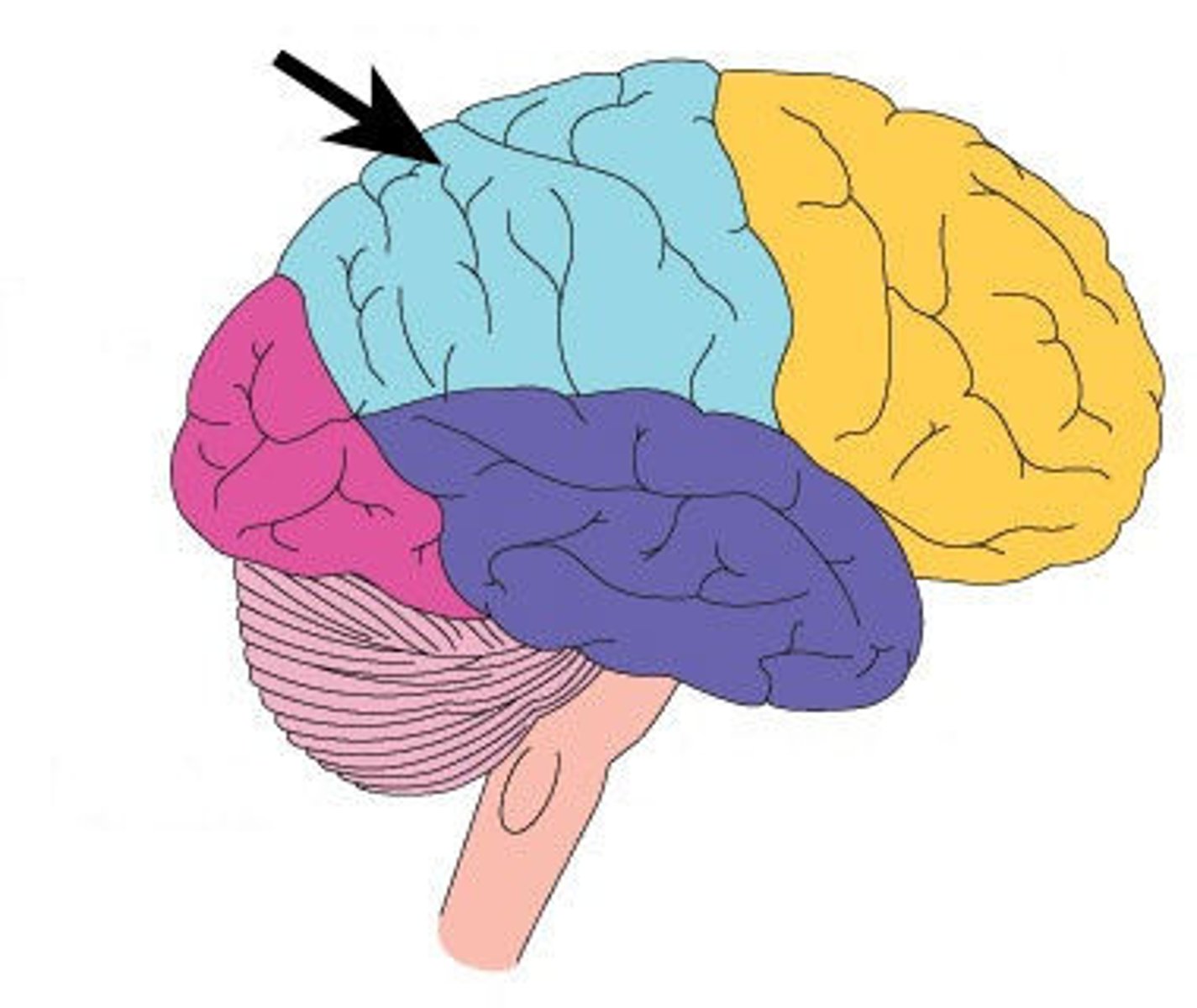
Frontal Lobe
-Role: reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement/control, emotions, problem-solving
-recognises future consequences of actions
-retains long-term memories
-primary motor cortex (op hemishpheres control op side)
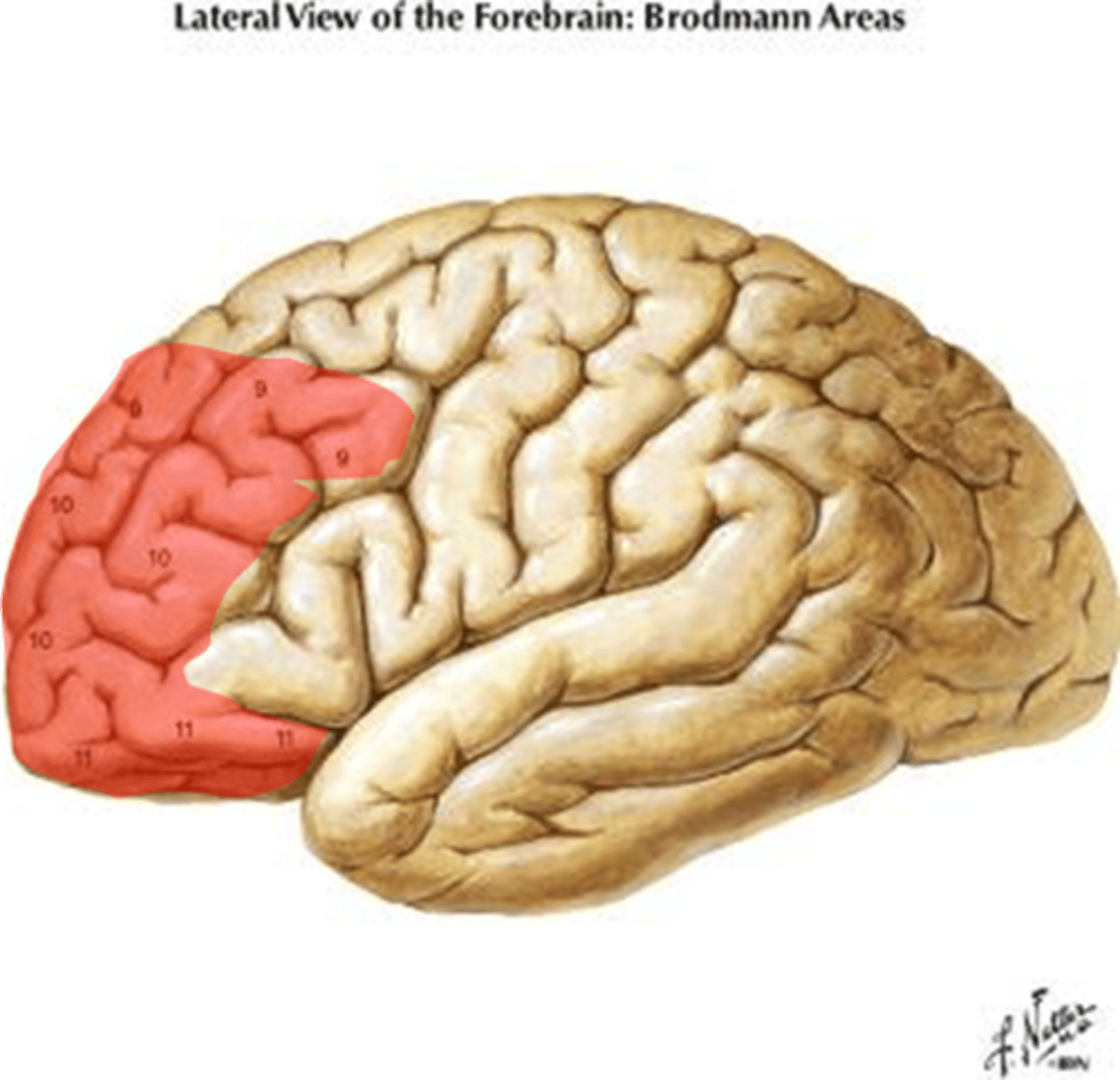
Prefrontal Lobe
-Role: executive functioning (plan, execute and carry out tasks), distinguish conflicting thoughts (determines good/bad, better/best)
-future consequences, social control
-?changes in personality? (found in key studies)
Pariental Lobe
-Role: integrates sensory info from different senses (modalities)
-sensory memory, visuo-spatial processing, touch pressure stimuli, temperature, pain.
-controls every sense BUT hearing
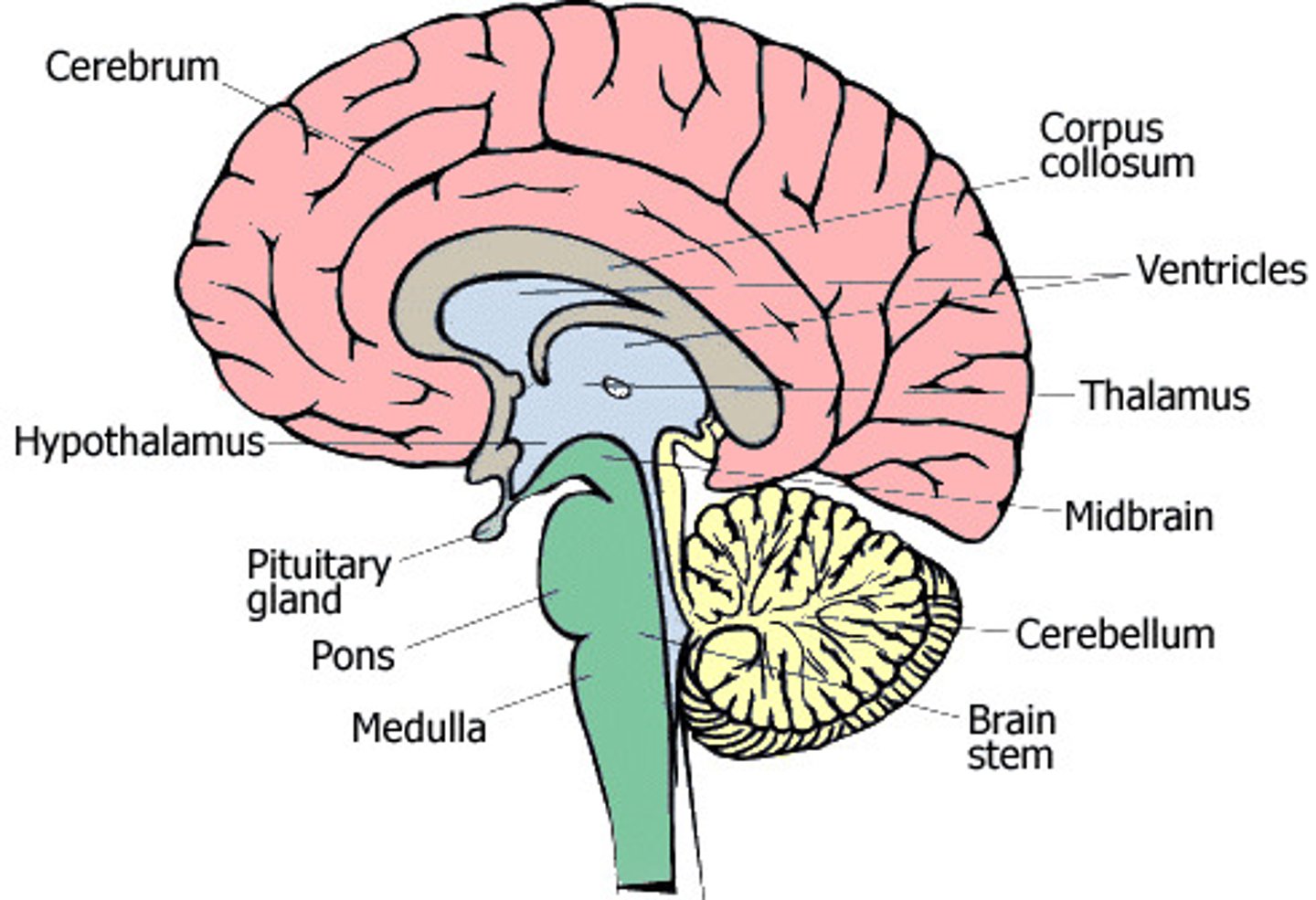
The Brain
-Centre of the nervous system in all vertebrates and most invertebrates
-<100billion neutrons
-linked w/10000 synaptic connections each
-cross wired
-corplus callosum joins hemispheres together
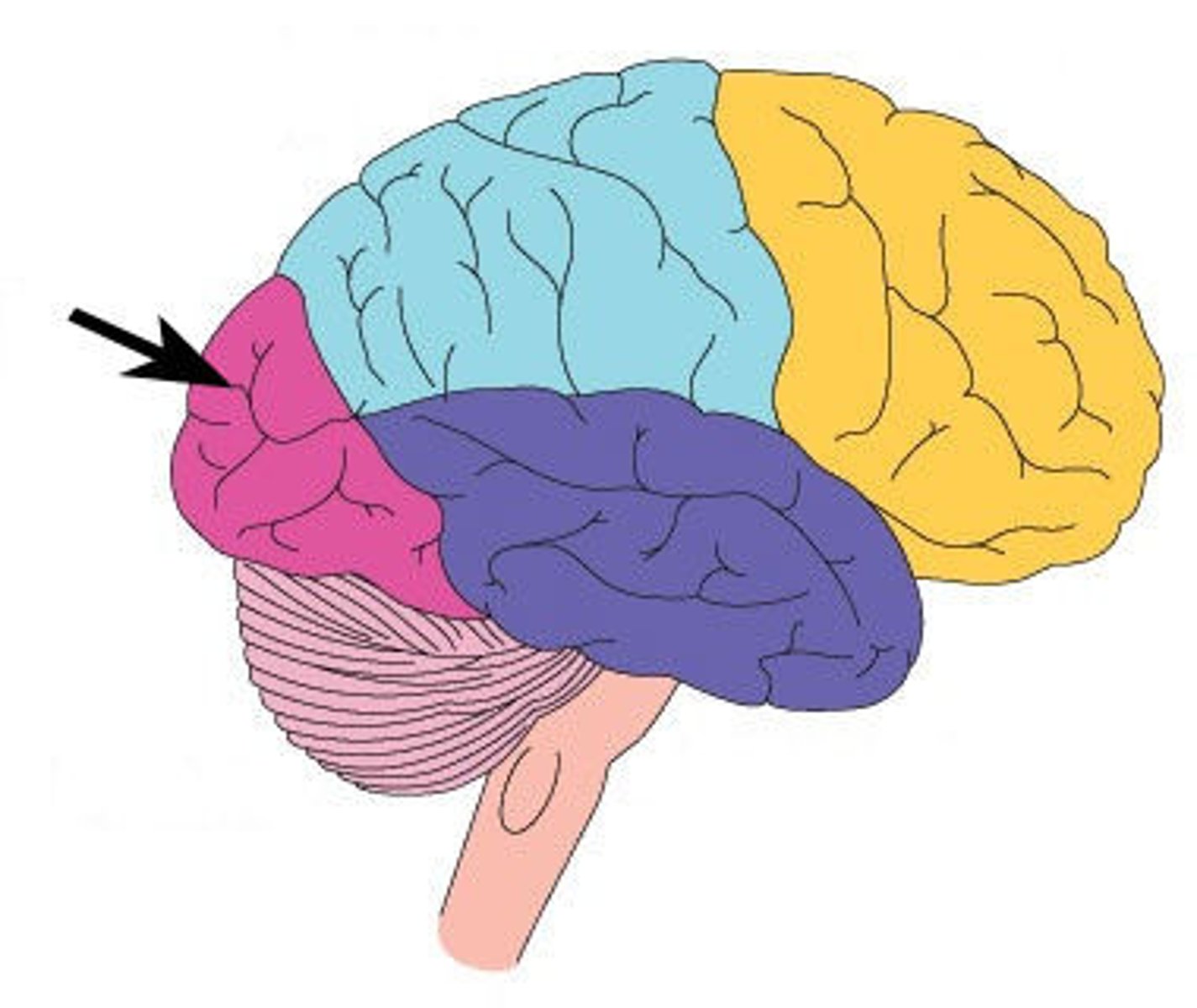
Occipital Lobe
Smallest true lobe
-Role: visual processing centre, vision & visual perception.
-50/50 split down eyeball for visual
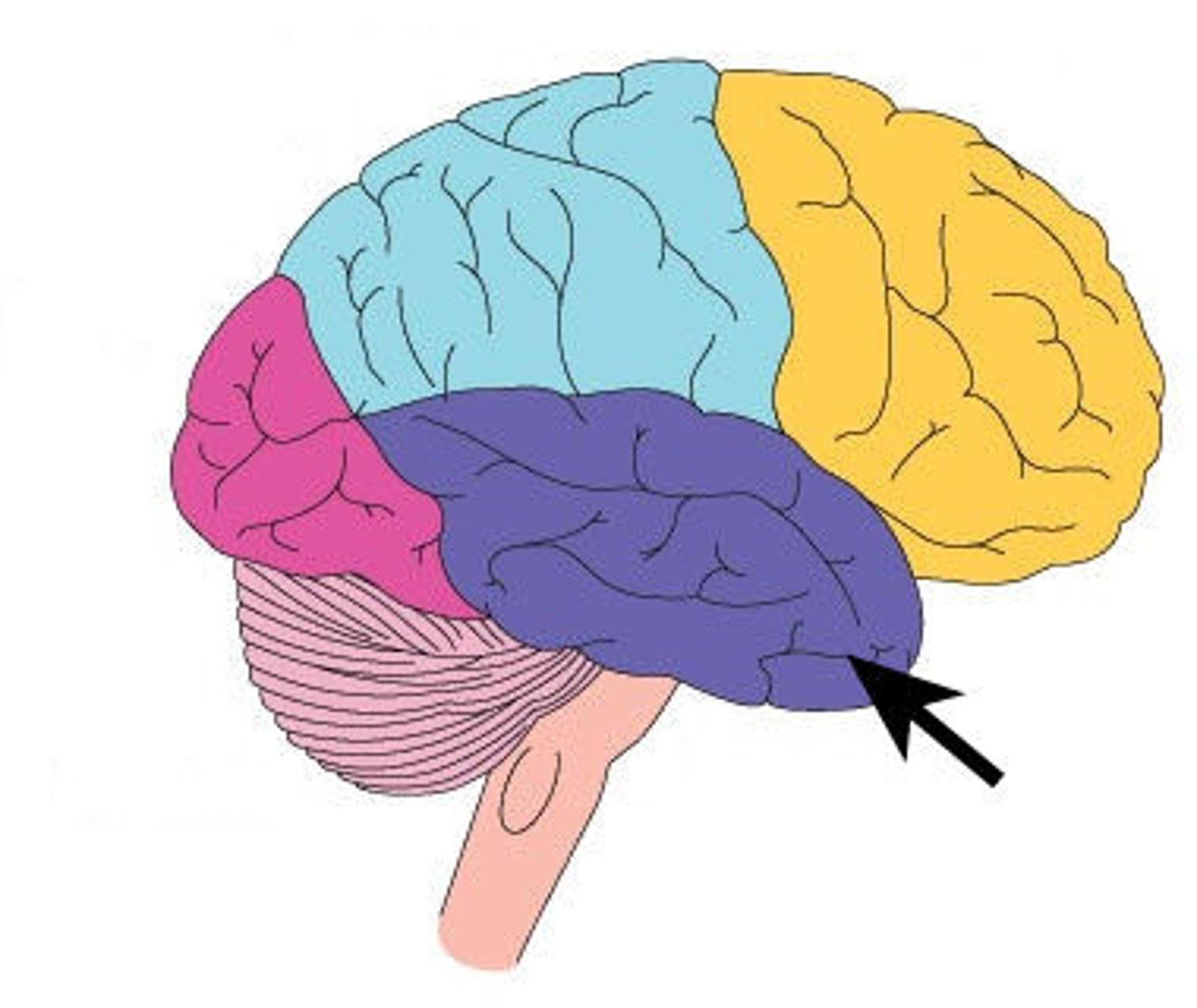
Temporal Lobe
Involved in speech, language, comprehension, memory, hearing and emotion control.
-contains the HIPPOCAMPUS
-if damaged, language difficulties, memory problems, and changes in emotional behaviour
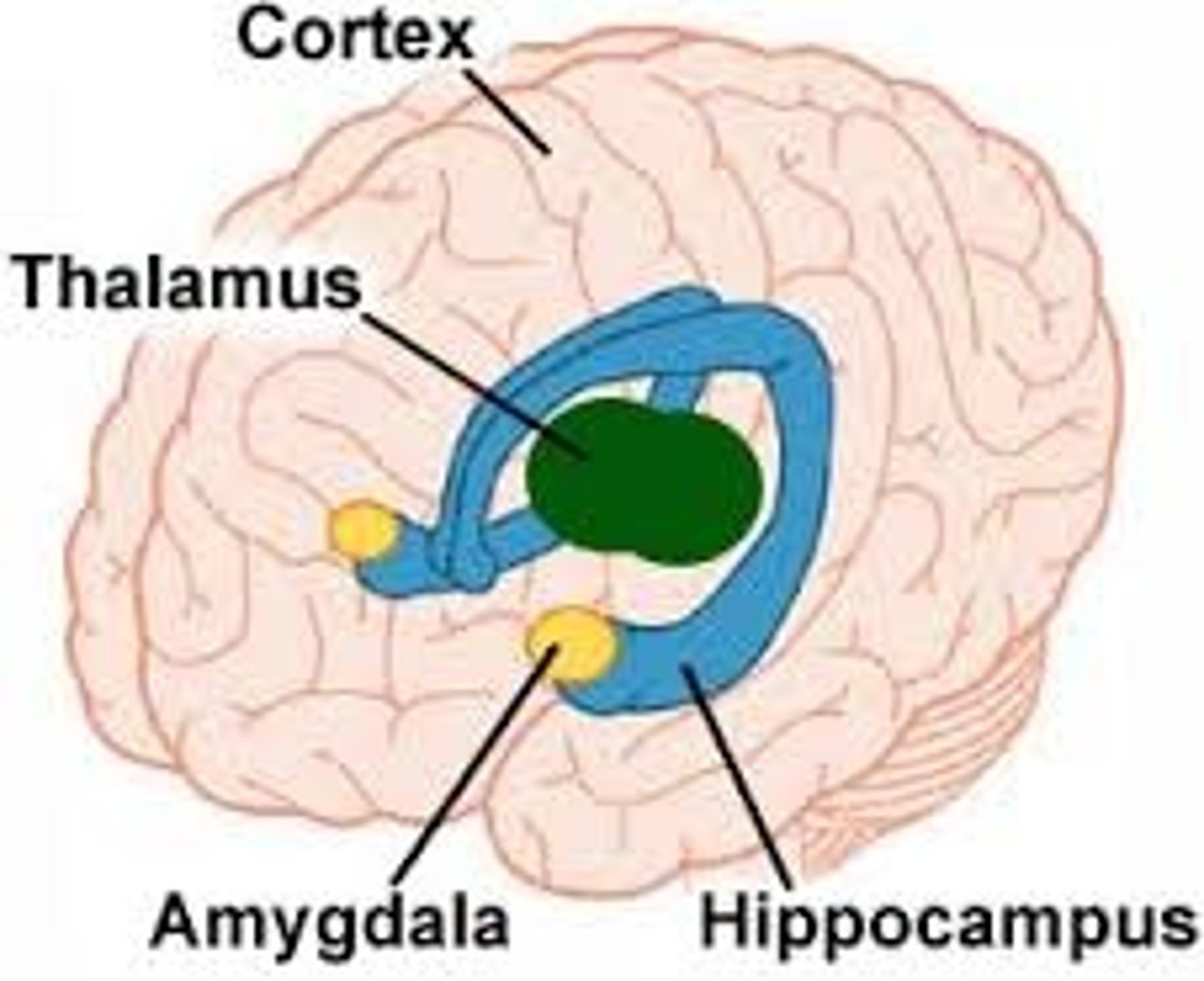
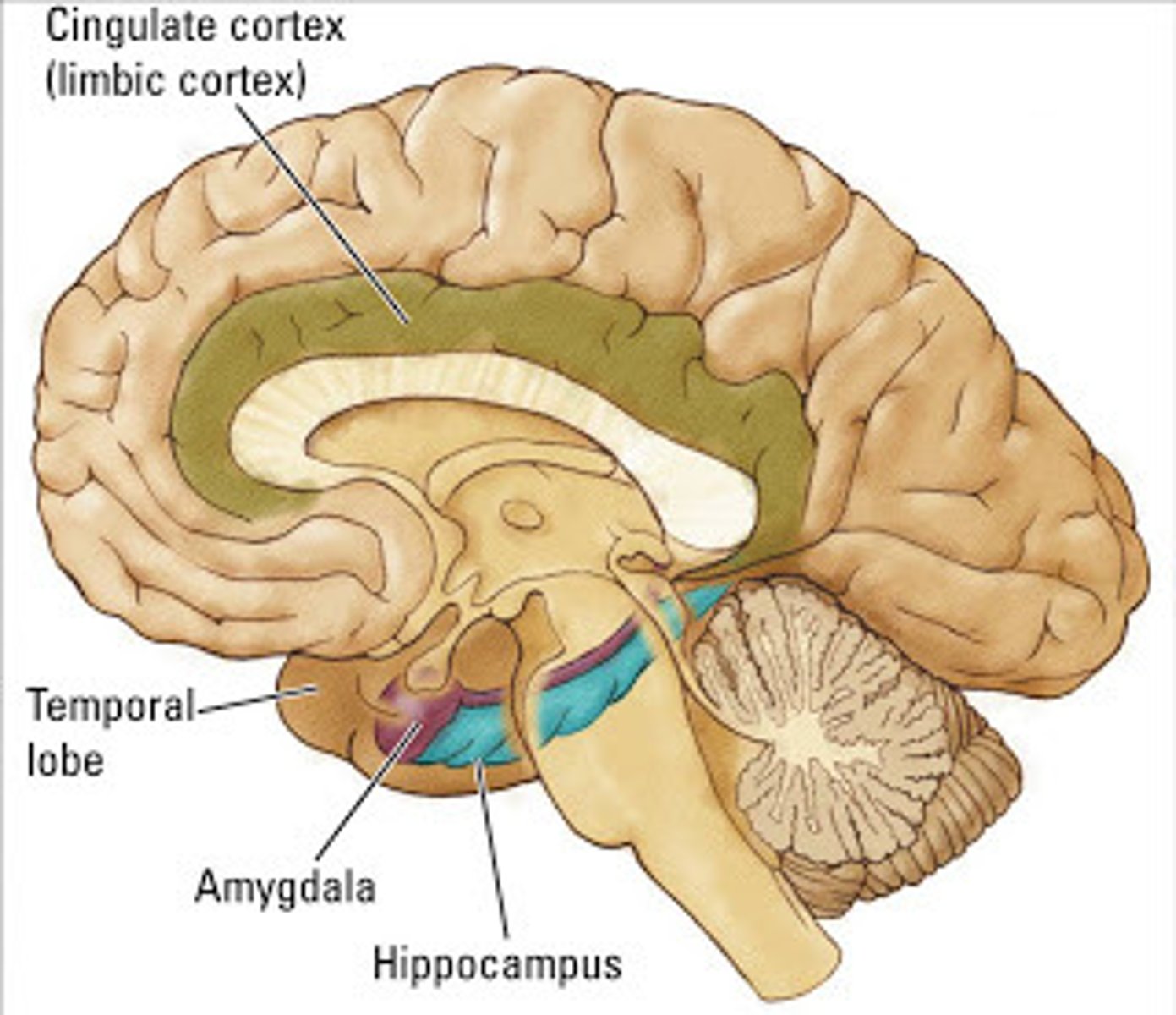
Limbic System
-Set of the brain structures including: hippocampus, amygdala, in the medial part of temporal lobe
-Emotion, behaviour, long-term memory and olfaction (sense of smell)
-Process centre-> know who you are/ fight/flight
-empathy learned here
-sociapathic behaviours if lack of movement here in MRI scan
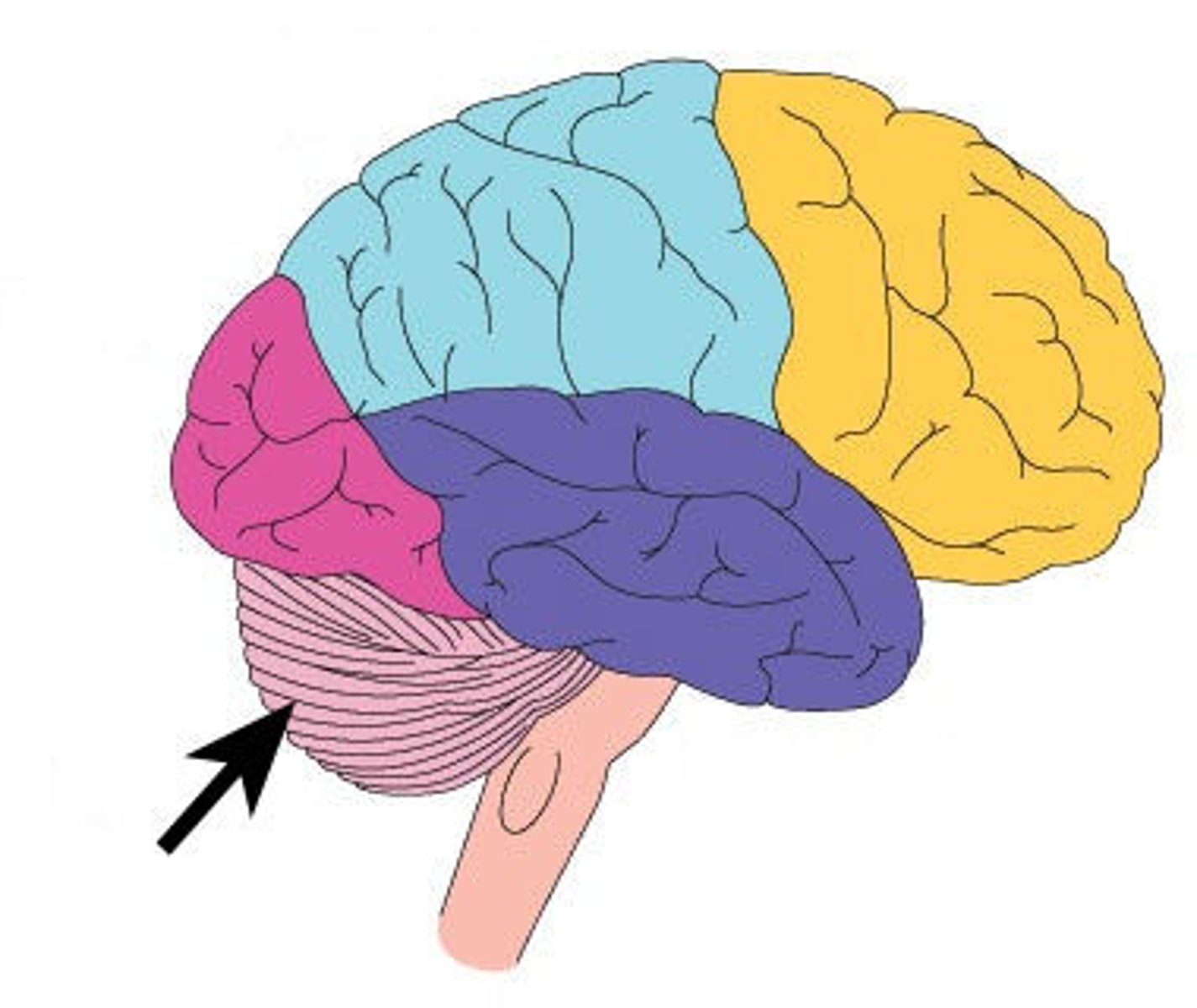
Cerebellum
The 'little brain' :>
-Sensory perception
-Coordination of voluntary movement
-Balance
-SOME speech and language
-many neural pathways linking the cerebellum w/ cerebral motor cortex
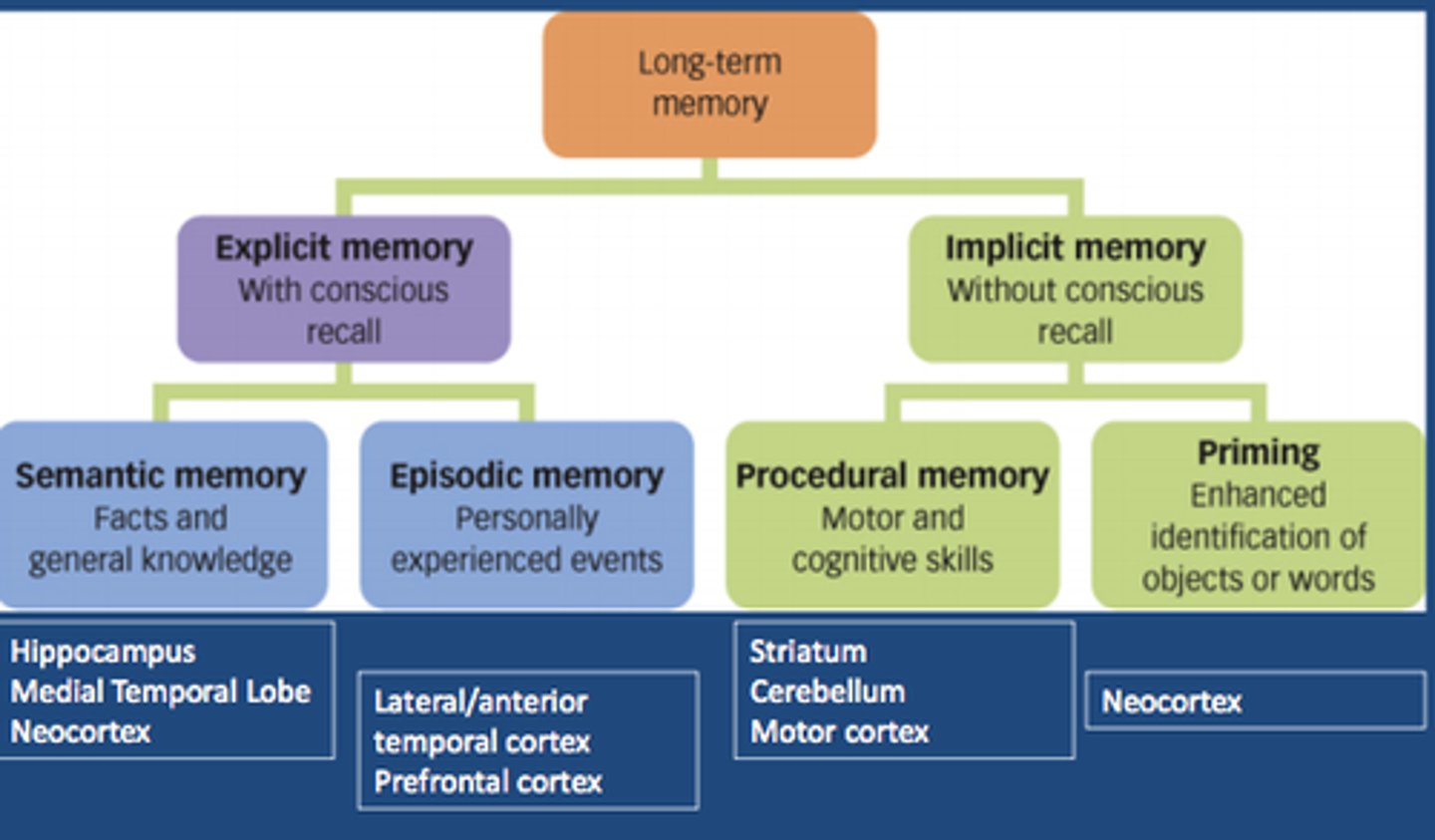
Hippocampus
-Responsible for declarative memory
-short term memory
-belongs to limbic system, plays central role in memory
-episodic memory
Declarative Memory
explicit/concious memory
-e.g. what you had for dinner on Sunday
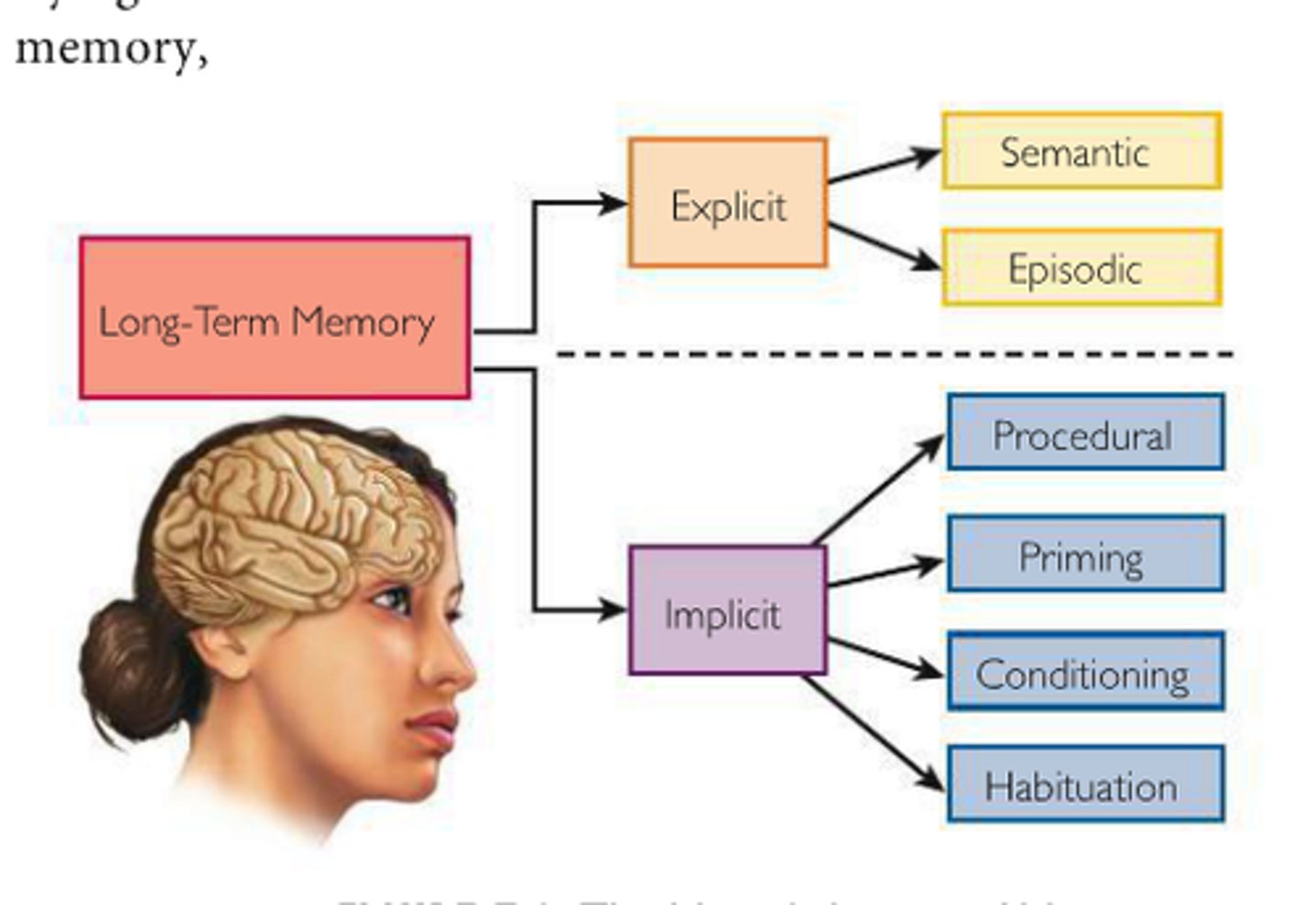
Episodic Memory
The collection of past personal experiences that occurred at a particular time and place
Hormones
chemical messengers released by endocrine glands into the bloodstream, influencing behaviour and bodily functions.
Hormones travel through the bloodstream, usually acting slowly whereas neurotransmitters act rapidly in synapsesbetween neurons.
how hormones influence behaviour
regulate mood, stress, memory, growth and metabolism by communicating with target organs and signalling messages to your body.
Cortisol
a stress hormone released by the adrenal glands in response to stress.
Functions of Cortisol in the body
To restore homeostasis and regulate our metabolism, immune response, and memory formation.
Newcomer et al. (1999)
Aim: To investigate how cortisol affects verbal declarative memory.
A double-blind, controlled experiment with 51 healthy adults (ages 18-30). Participants were randomly assigned into three groups:
1. High cortisol dose (160 mg/day) - mimicking major stress. 2. Low cortisol dose (40 mg/day) - mimicking mild stress. 3. Placebo (inactive) group.
A baseline test was conducted prior to testing. They took tablets, were given a verbal memory test, learning a comparable prose paragraph each day, over 4 days. Also tested on the 6th day to ensure no long-term effects.
High cortisol group performed significantly worse on memory tasks. Low cortisol group performed similarly to the placebo group.
Newcomer et al. conclusion
High cortisol levels impair memory recall, but moderate cortisol has no significant effect.
This suggests when people are highly stressed they may not recall information effectively. Prolonged high cortisol has also been shown to result in hippocampal atrophy (shrinkage) which leads to reduced acetylcholine receptors and impaired memory formation.
Practical applications of understanding hormones
important for almost all cells in the body to work. They influence the metabolism, memory, growth and many other functions. Some hormones affect almost all cells, others only target a small number of cells in specific organs. The study of hormones has led to enormous benefits to human health, social and economic progress, such as contraception, in vitro fertilization (IVF) and regulating hormonal imbalances.