OIA1011 DIFFUSION & EFFUSION
1/13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Definition of Diffusion
Mixing of substances due to molecular motion.
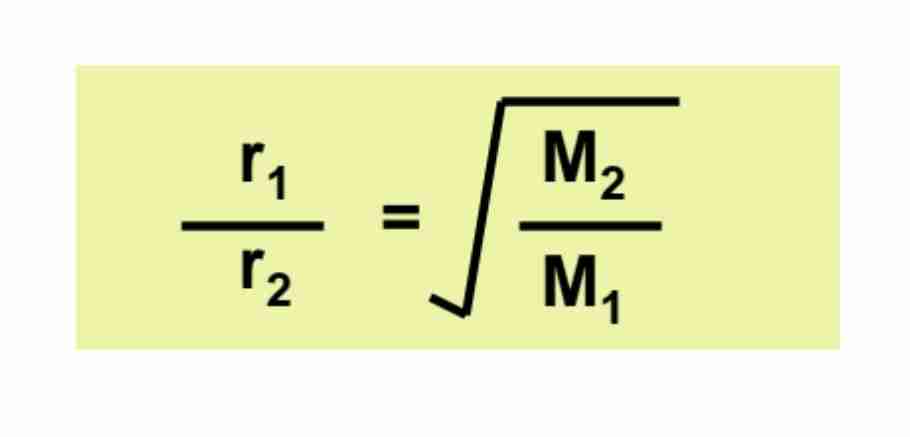
Graham’s Law of Diffusion
Given Temperature & Pressure are constant, rates are inversely proportional to square root of molar mass.
Definition of effusion
Gas escapes through a small hole without collisions (e.g., punctured tire).
Example of Effusion
Hydrogen effuses faster than carbon dioxide due to lower molar mass.
Effect of Temperature
Higher temperatures increase diffusion and effusion rates.
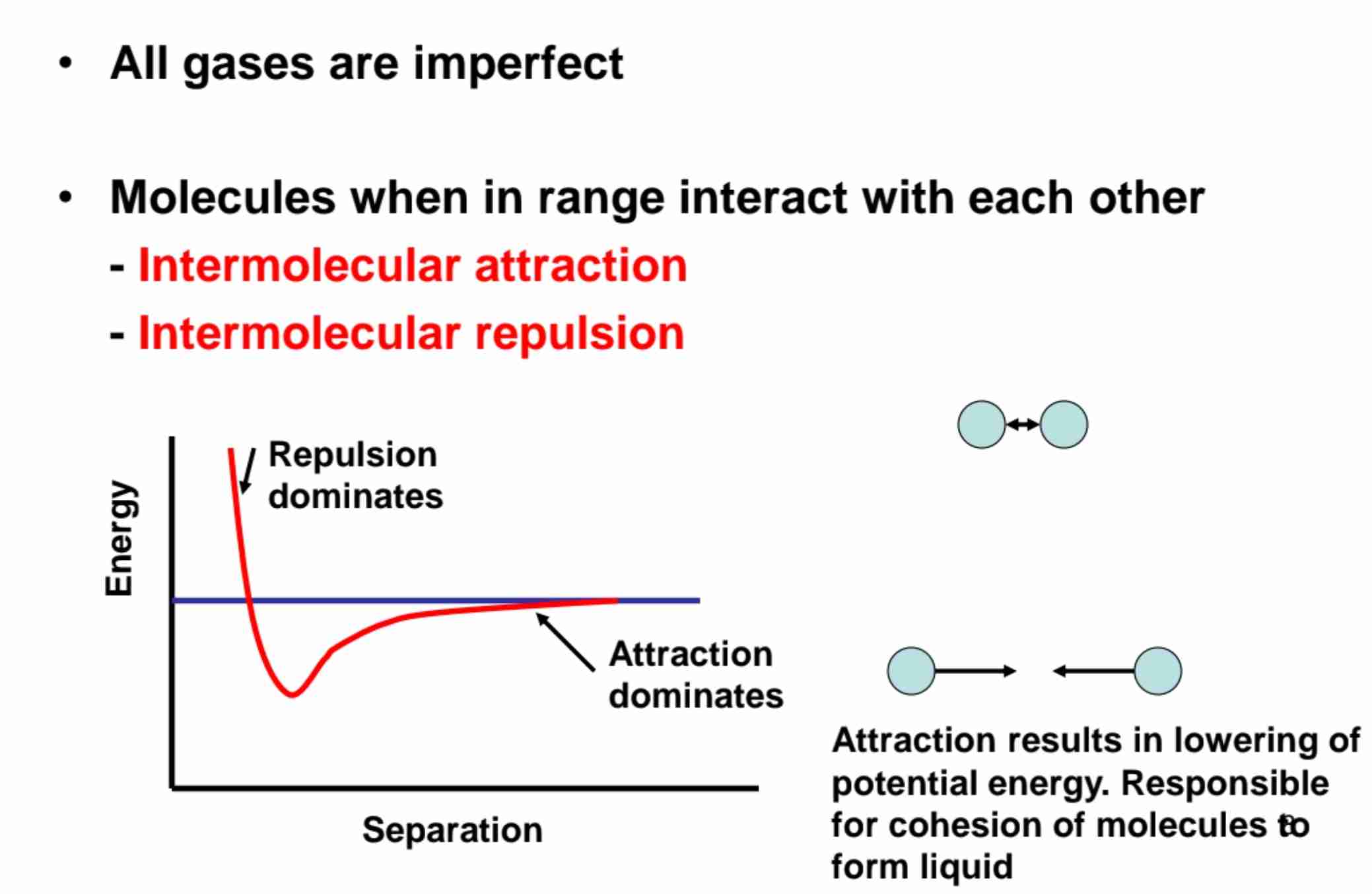
Real Gases and Imperfections
Deviations from ideal gas behavior arise due to intermolecular forces.
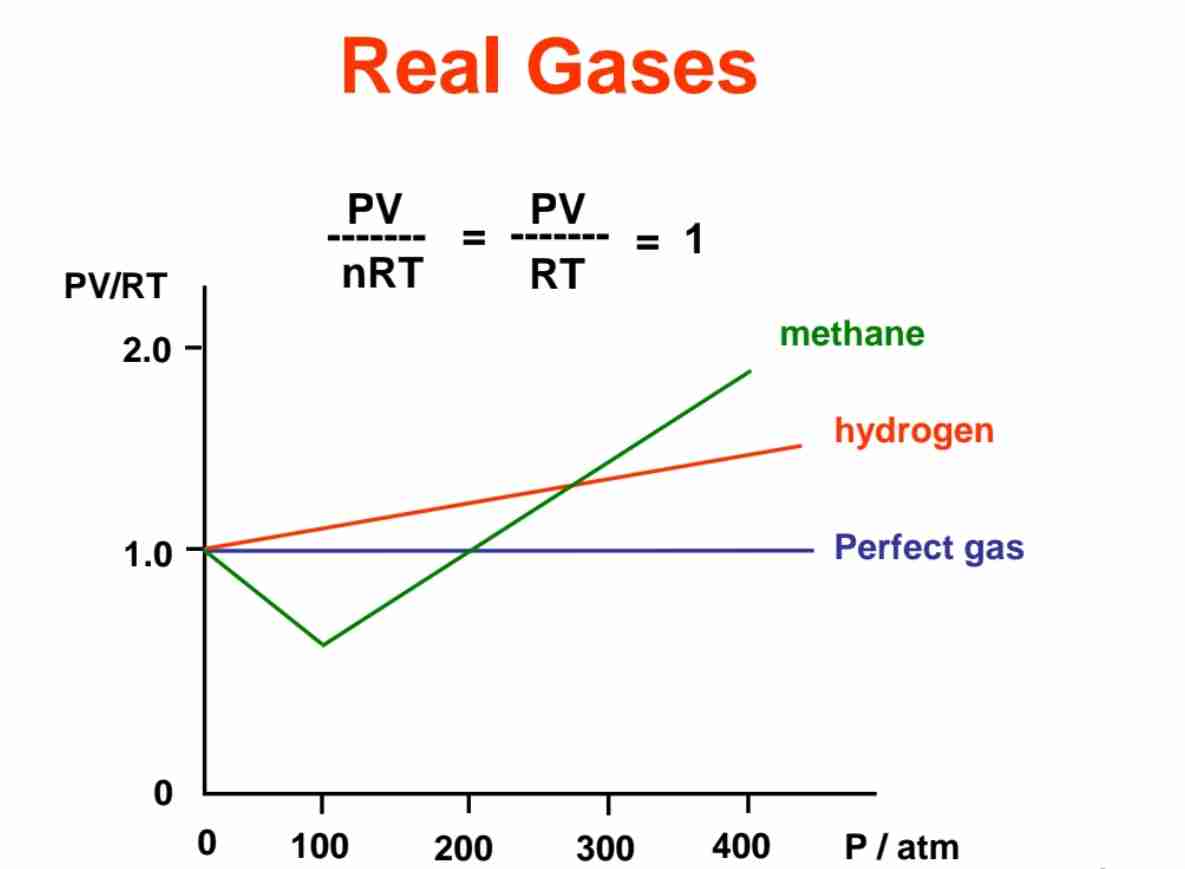
Why real gases possess non-ideal behaviour (e.g. PV/RT not equal to 1)?
Ideal gas equation, PV = nRT
Ideal gas condition: molecules don’t attract/repel each other & volume gas negligible compared w/ volume container.
For real gas, PV/RT <1, curve of methane & PV/RT >1, curve of hydrogen deviate & not follow ideal gas behaviour.
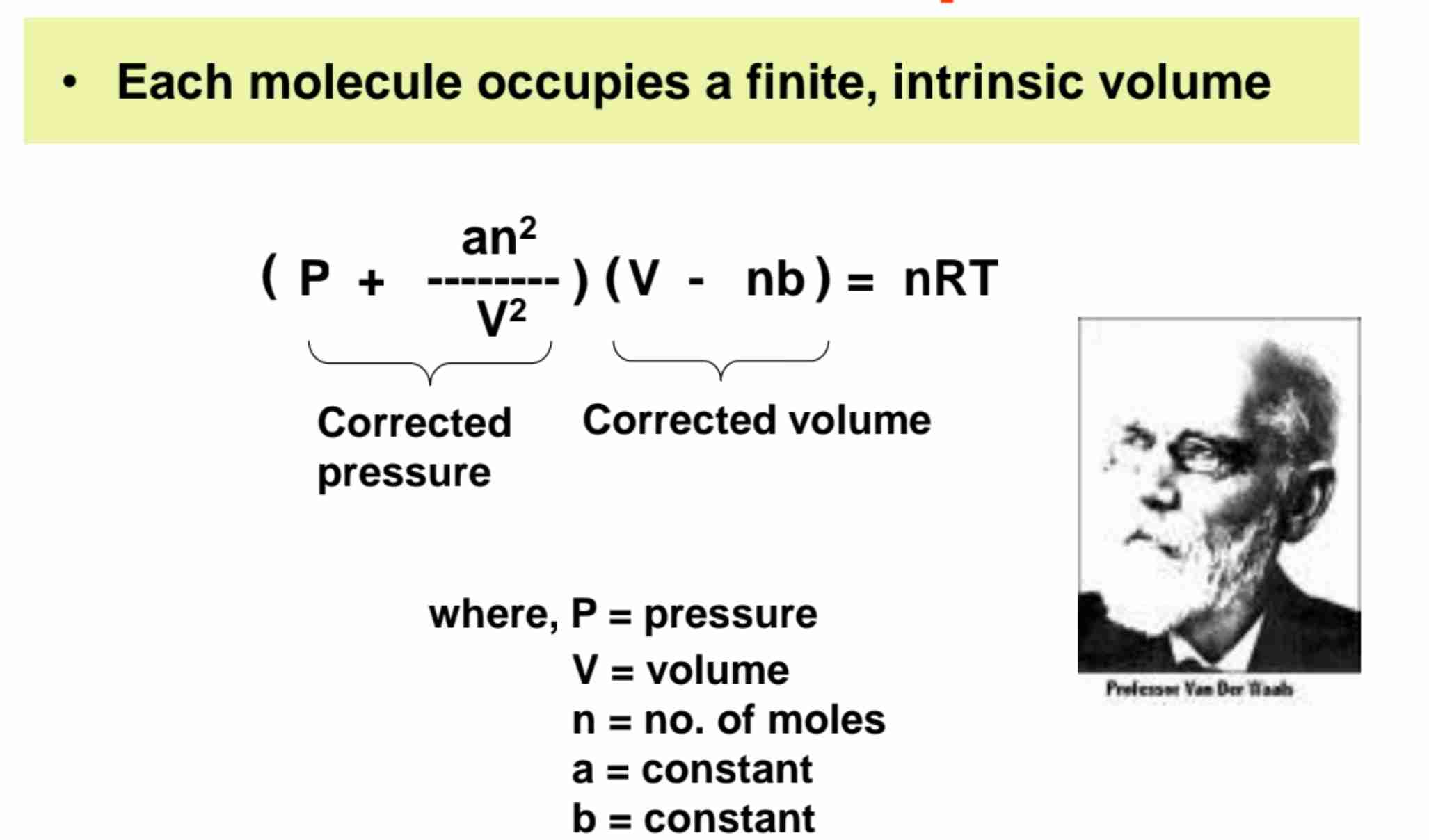
Van der Waals Equation
Corrected the Ideal Gas Law Equation PV = nRT
(P + an²/V²) X (V - nb) = nRT
Applications of Graham’s Law
Gas separation techniques like isotope enrichment.
Impact of Molar Mass on Diffusion
Lighter gases diffuse/effuse faster than heavier ones.
Practical Example of Diffusion & Effusion
Perfume spreading in a room demonstrates diffusion.
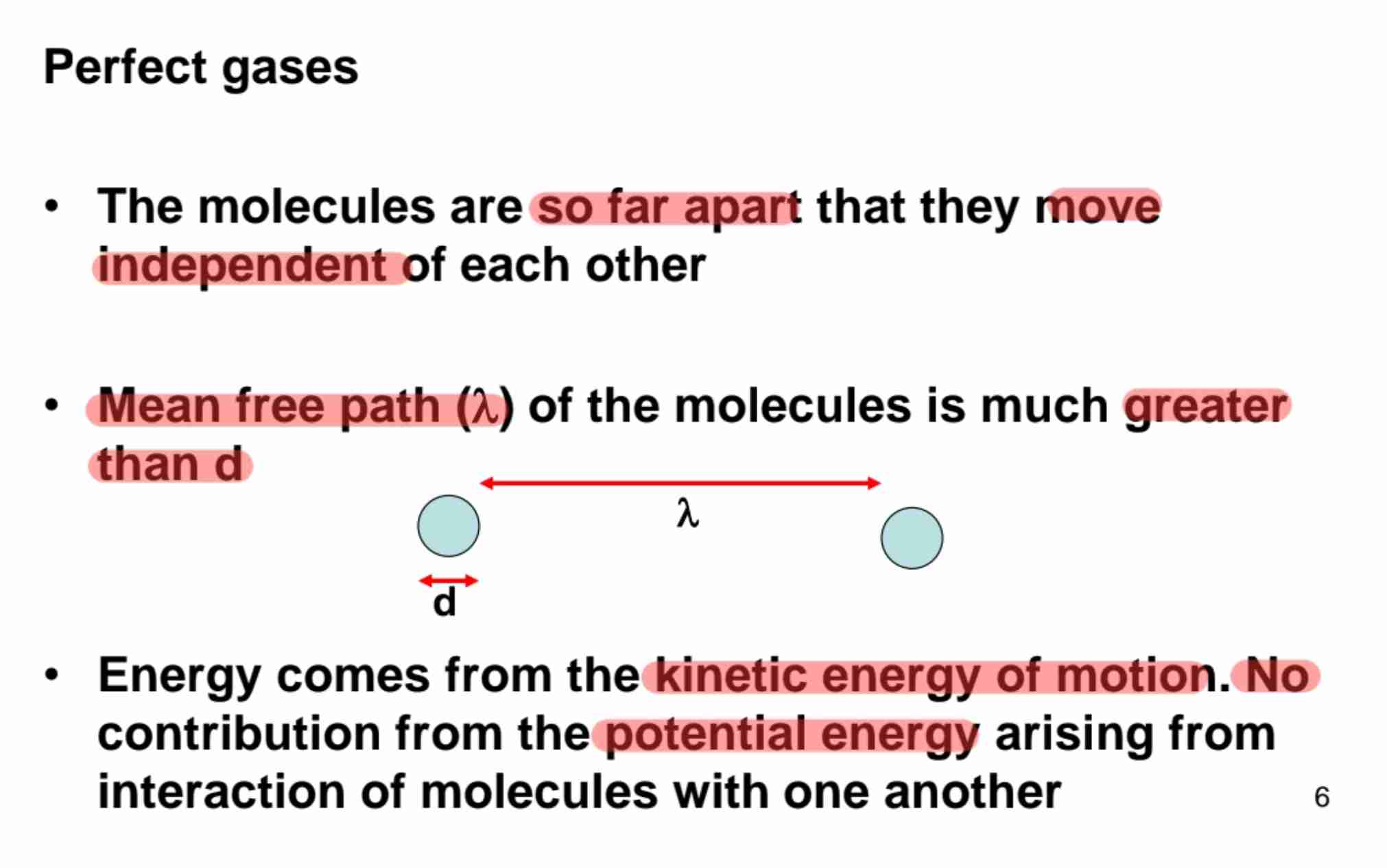
Assumption of Ideal Gas
Molecules far apart that each move independently, mean free path (lambda) /distance of molecules much greater than diameter (d) & energy comes from kinetic energy of motion that no contribution from potential energy from interaction of molecules.
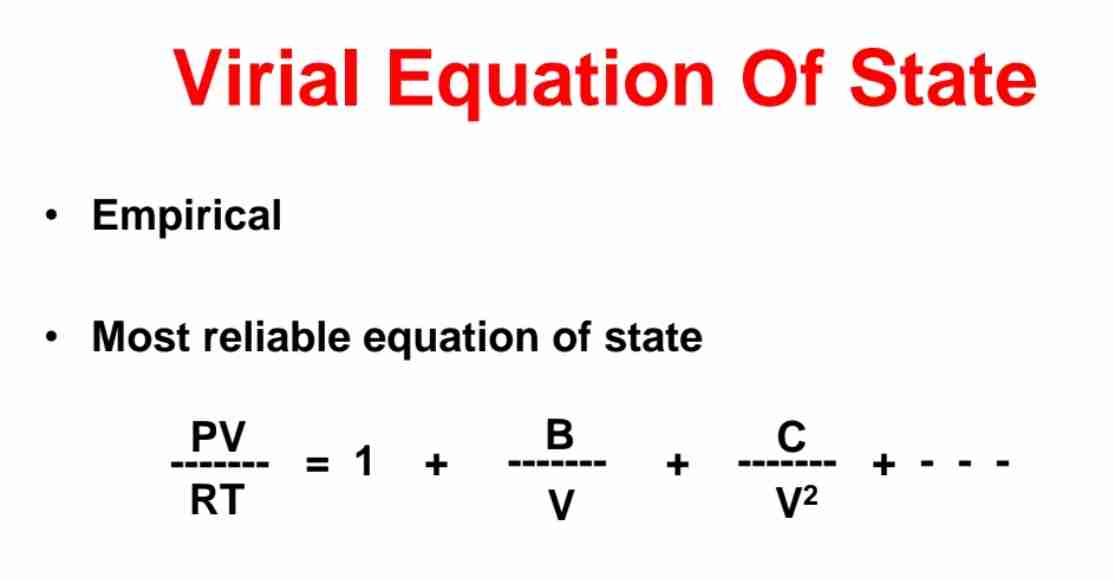
Viral Equation of State
PV/RT = 1 + B/V + C/V² + …
Explain Interaction of Intermolecular Forces
When molecules closer to each other, force of attraction stronger until reaches minimum distance, which is represented by the lowest point of graph.
However, molecules won't contact.
Any closer beyond minimum distance will cause molecules to repel as attraction force too weak to attract.
Electrons exert greater repulsion force to each other compared to attraction force exert by protons.