Electric Circuits and Current (W1.2/2.1 - Chapter 1)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what does q represent? what are its units?
q reps charge → amount of elec responsible for electric phenomena
measured in coulombs (C)
what does i rep? what are its units?
i reps current → the rate of the flow of electric charge over a time interval / past a certain pt
measured in amperes (A)
current exists in or through an elem and is represented as a VECTOR (has mag and dir)
flow of current is CONVENTIONALLY REPRESENTED as a flow of POSITIVE charges (even though electric current is actually made up of electrons which are negatively charged)
what is the relationship between current (i) and charge (q)?
i = dq/dt (so q = the integral of i)
1A = 1C/1s (a coulomb over a second)
current = the rate of flow of electric charge over time
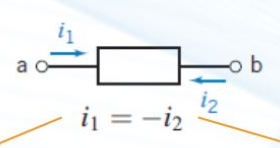
explain all the variables in this image.
i1 = first current = rate of flow of elec charge from terminal a to terminal b (note: terminal = node)
i2 = second current = rate of flow of elec charge from terminal b to terminal a
and i1 = -i2 because they are going different directions
direct current (dc)
current of CONSTANT magnitude
see image
rep by a capital I (instead of i)
two main types of currents
direct current (dc)
time-varying current (or non-constant current or alternating current → ac)
linear, sinusoidal, exponential
REMEMBER: current i = 0 for t < 0 (because a current can’t exist in negative time)
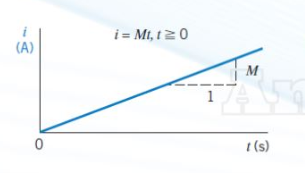
case 1 of non-constant current - linear/ramp
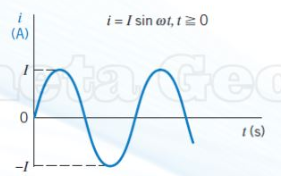
case 2 of non-constant current - sinusoidal
I = the max/min current (A)
omega symbol (the weird w) = angular freq = 2*pi*f
t = time (s)
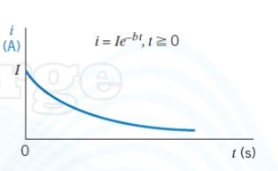
case 3 of non-constant current - exponential
I = max current, only decreases from here.
t = time (s)
-b = has to be neg so that the exponential is a decay
rule for converting units
constant value * given prefix/wanted prefix
what does v rep? what are its units?
v reps voltage → work (en) required/needed to move a unit pos charge from the neg terminal to the pos terminal
in other words, it’s the “pressure” needed to move current from one point to another (pushes current through the wire)
measured in volts (V)
voltage exists ACROSS an elem, has mag and polarity (dir)
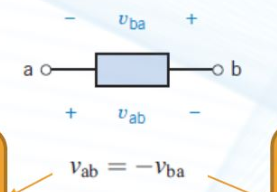
explain the image
vab = voltage at term a wrt term b (POS TERM IS ALWAYS WRITTEN FIRST)
vba = voltage at term b wrt a (pos term is once again written first)
vab = -vba (because they have oppo polarity, and the en required to move a unit pos charge from b to a is the negative en req to move a unit pos charge from a to b
what is the relash b/w voltage, charge, and work?
v = dw/dq (since voltage boils down to work needed per charge)
1V = 1J/1C
what does p rep? what are its units?
p reps power → rate of supplying or receiving power over a time interval
measured in watts (W)
what is the relash b/w power (p) and other electric variables (v, i, q, w)
p = dw/dt (rate of work / time) = dw/dq (formula of v) x dq/dt (formula of i) → p = vi → 1W = 1V * 1A
therefore, w = integral of p (dt) with 0 as the lower bound since you can’t have neg t (time)
power supplied vs power received
for power received, the current heads into the POS TERM
for power supplied, the current heads into the NEG TERM
power received = -power supplied

how do you know from a diagram of an elem in an elec circuit that the current (i) and voltage (v) adheres to PASSIVE CONVENTION?
when the current enters the circuit elem at the POS VOLTAGE TERMINAL → this is also interpreted as POWER RECEIVED by the elem rather than power being supplied (which means the elem is giving away power)
how do you verify if all the values/polarity of a diagram of a circuit with multiple elems are correct?
check if the sum of all power received is = 0
rmbr to convert power supplied values to power received
rmbr to check that the elem adheres to passive convention
if the sum = 0, then the diagram may or may not be correct (would need to be further verified by hand but this is irrelevant in terms of theoretical calculations)
if the sum ≠ 0, then the diagram is definitely incorrect.
the relash b/w charge (q) and electrons (e)
one electron contains 1.602 × 10-19 C (coulombs) of NEGATIVE charge
therefore, one C = 6.24 × 1018 electrons