Unit 2.1 - Managers, Leadership and Decision Making
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Management
Planning, organising, directing and controlling all or part of a business
Leadership
Functions of ruling, guiding and inspiring other people within an organisation in pursuit of an agreed objective
4 basic functions of management
planning, organizing, directing, controlling
Planning
Looking into the future - may include
- Setting objectives and targets for the business for their area
- Conducting analysis to gather forecasts of key information such as: costs / revenues, incomes, competitors and prices
- Drawing up plans for functional areas within the business
(marketing, finance, HR and operations)
- Estimating the likely resource needs for the proposed plan
Organising
Assemble the resources that they need to carry out the actions set out as part of the planning process. (labour, capital etc)
Directing
Leading - Motivating and communicating with other employees to oversee their behaviour and ensure everyone is working towards the same goals.
Controlling
Setting standards using the company's objectives, and reviewing and reporting performance. This enables managers to identify areas of weakness and implement corrective action.
Ways managers may report on performance
Financial reports - are they on track to make the targeting level of profit?
Employee performance - are the workers productive?
Social performance - how ethical is the business?
Roles of management/managers overview
Planning - Setting objectives
Organising
Motivating (directing)
Communicating (directing
Measuring performance (monitoring)
Developing Employees
The 4 leadership styles
- Autocratic
- Democratic
- Laissez-faire
- Paternalistic
Autocratic leadership style
Leader believes information and decision making is best kep at the top of the organisation:
- Primarily one way communication (downards)
- Minimal delegation or decentralisation (one person has authority)
- Close supervision of employees
Authority
power or ability to carry through an action - typically decision making power in a business
Delegation
The passing authority down the organisational hierarchy - allowing others freedom to make decisions
Empowerment
Provide subordinates with the means to exercise power or control over their working lives
Decentralisation
Passing authority from the centre of the organisation to those working elsewhere in the organisation
Democratic leadership style
a style in which the nominal leader invites the group's participation in decision making:
- Delegates and decentralises
- Employees empowered
- Subordinates encouraged to contribute to decision making
Laissez-faire leadership style
a leadership style characterized by complete freedom for the group in making decisions:
- Leader has minimal input
- Employees are empowered to take majority of decisions
Paternalistic leadership style
leadership style where the leader makes a decision but takes into account the welfare of employees
- Dominant figure who decides what's best
- Leader makes decisions but may consult employees first
Benefits/when to use autocratic leadership
- When rapid decisions are needed
- Business is in crisis situation
- When it is important the same message is given out to everyone in the organisation
- When managers are responsible for a large number of unskilled employees
- When the manager holds the most expertise and experience
Drawbacks/when not to use autocratic leadership
- When making highly complex decisions requiring diverse knowledge and skills
- When leading self motivated employees
- When leading highly skilled employees
- In creative or innovative industries/parts of the business
- When junior employees are expected to develop a full range of managerial skills
Benefits/when to use democratic leadership
- Helps develop skills of subordinates
- Generally results in more highly motivated workforce
- Lower dependence on leader
- Gain more diverse and constructive ideas to aid decision making
- In globalised world it may allow for more responsive and varied decision making
- USeful when employees are highly skilled, creative or innovative
Drawbacks/when not to use democratic leadership
- Can slow down decision making if people opinions must be taken into account
- requires very good communication which may take time to develop
- May be less effective with large workforces especially if they are low skilled
When laissez-faire may be successful
- Manager or leader is one among a number of equals in terms of experience and qualifications
- Workforce is self-motivated and understands the role of managers
- Workforce understands and agrees with organisational objectives
Sometime laissez-faire leadership occurs due to lack of skills of the leader - can lead to organization lacking direction, coordination and planning if the above isn't present
Influences on style of leadership or management
- Type of labour force
- Nature of task
- TImescale of task or decision
- Personality of leader
- Tradition and history of a business
- Size of the business
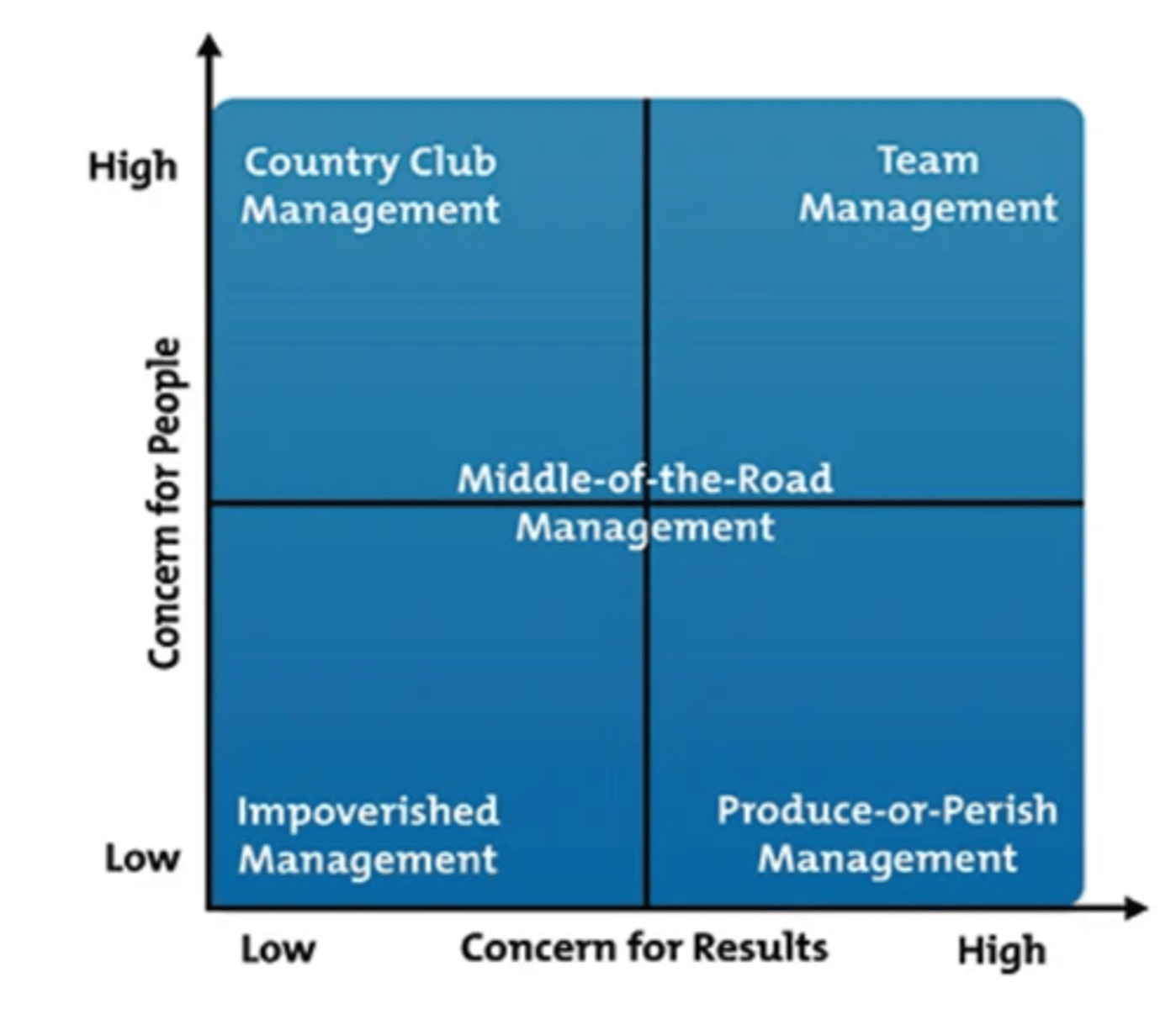
Blake mouton grid (last paper Y13 2024)
A framework used to identify a leader/managers behavioural style according to their concern for people vs concern for task production
5 sections of the blake mouton grid (last paper Y13 2024)
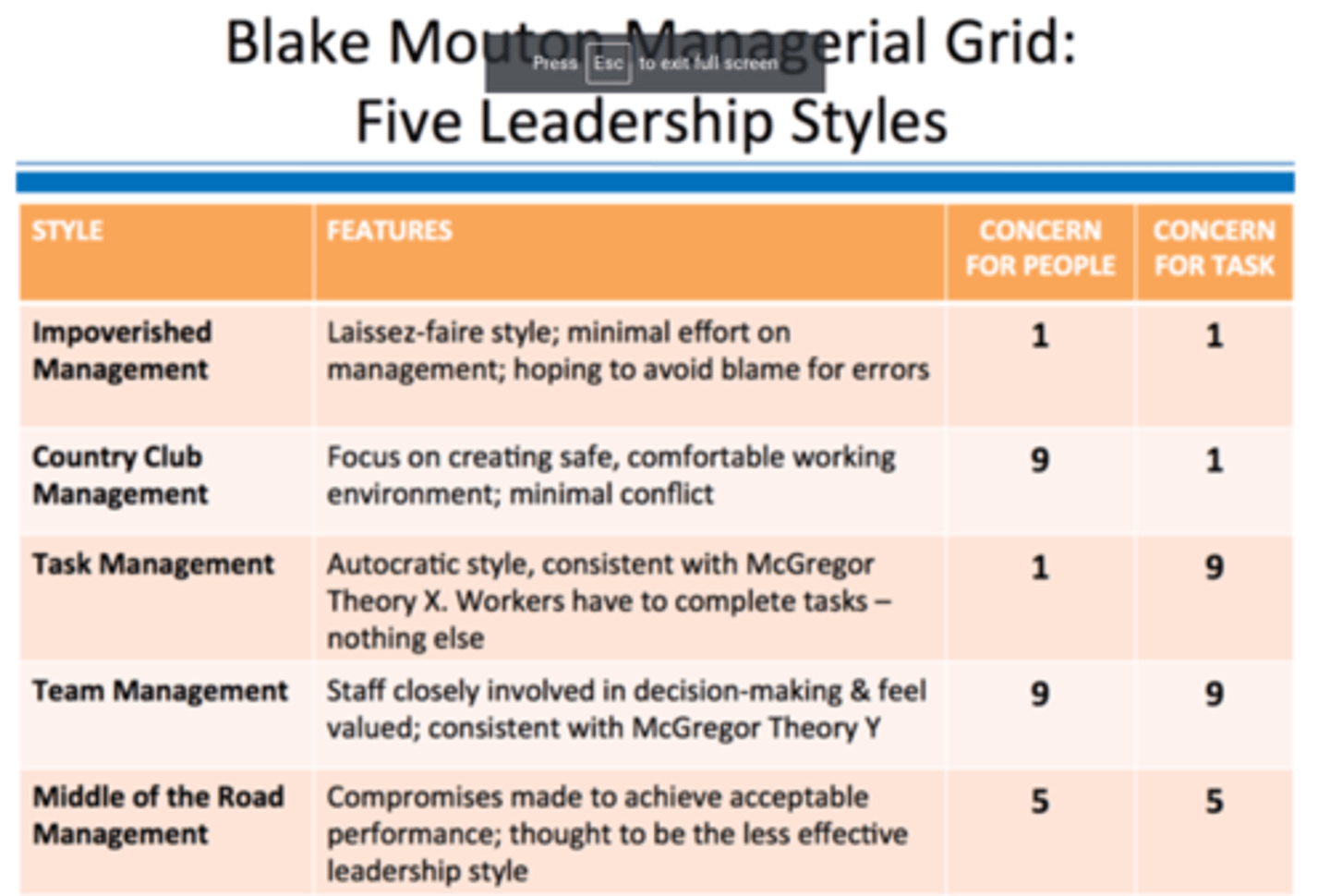
Country club - High concern for people, low concern for task
Team leader - High concern for people, high concern for task
Impoverished - Low concern for people, low concern for task
Produce or perish - low concern for people, high concern for task
Middle of the road - mid concern for both people and task
Blake Mouton grid - diagram (Last paper Y13 2024)
Blake mouton explanation grid - table (Last paper Y13 2024)
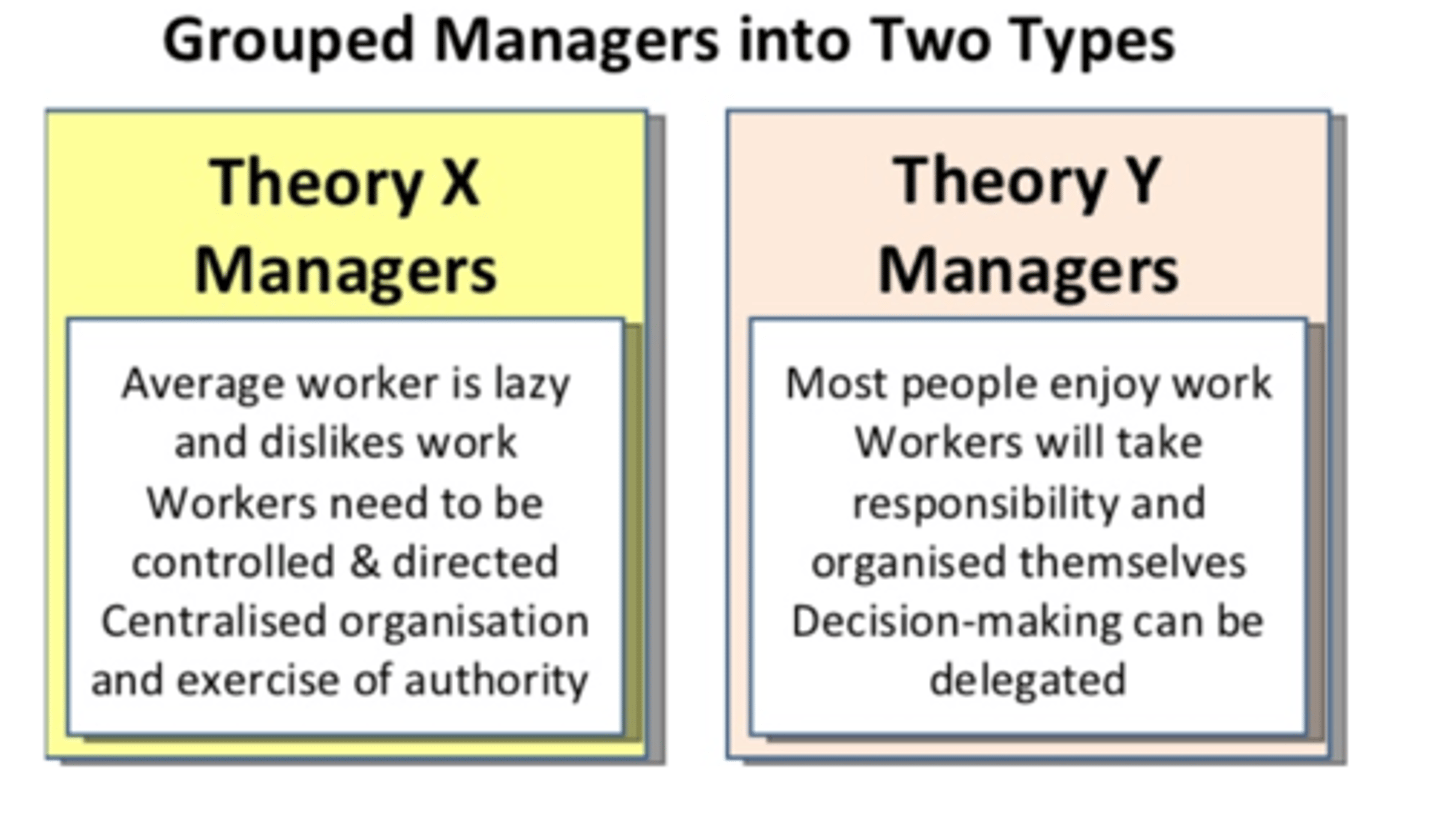
McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
Theory X - the assumption that employees dislike work, are lazy, avoid responsibility, and must be coerced to perform.
Theory Y - the assumption that employees are creative, enjoy work, seek responsibility, and can exercise self-direction.
Mcgregor's theory x and theory Y - visual aid
Productivity
output per unit of input - more productive when less inputs are needed to create one output
Labour productivity
Output per worker in a given time period i.e a worker makes 100 units an hour is more productive than a worker making 80 units per hour
Labour productivity formula
Output per period / number of employees per period
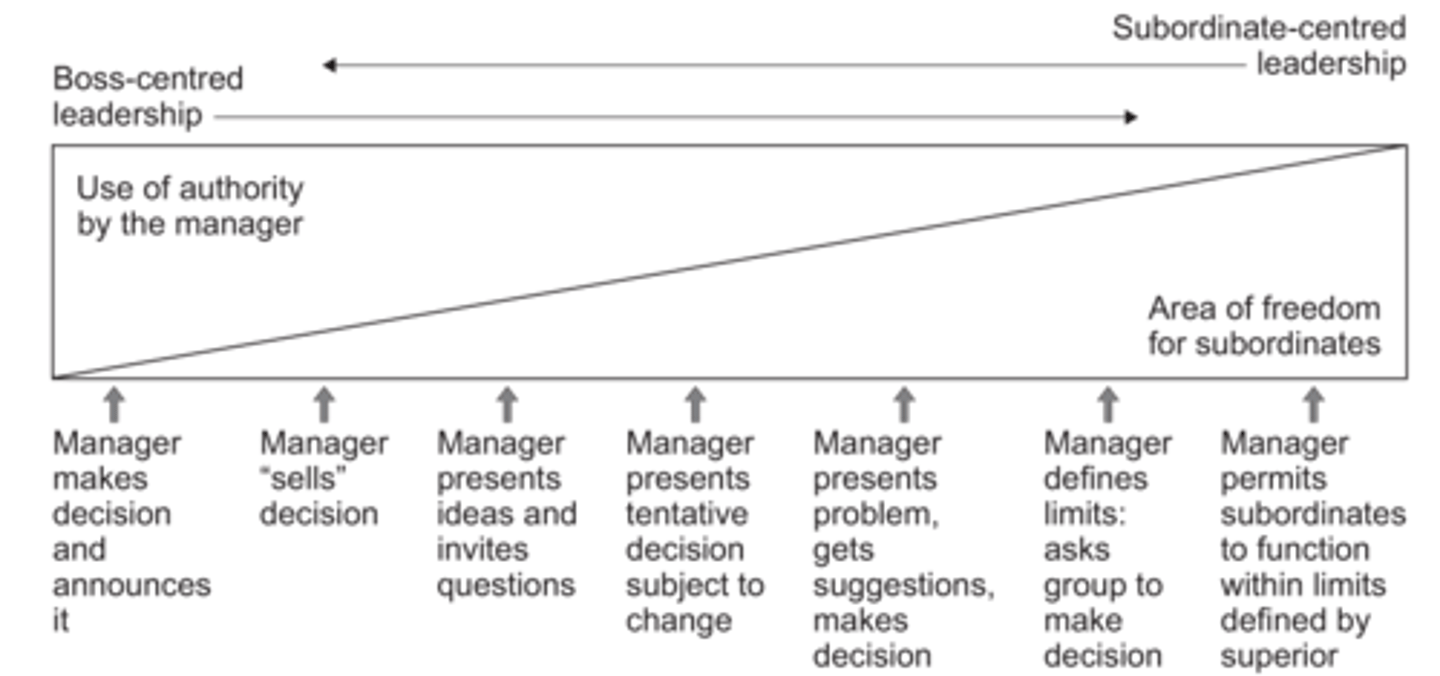
Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum
An analytical tool to assess management style based on amount of authority delegated by managers. Shows there is a range of style rather then simply authoritarian or democratic
Four main sections of Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum
Tell - Sell - Consult - Joins
Tell section of Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum
Manager makes decisions and tell staff about it, no delegation, similar to autocratic style of management
Sell section of Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum
Manager sells decision to staff - will retain decision making power, little delegation - may more paternalistic but still more autocratic
Consult section of Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum (3 parts of continuum)
- Manager present ideas and invited questions
- Manager presents tentative decision subject to change
- Manager presents problems, gets suggestions then makes decisions
Overall more delegation - getting more paternalistic and eventually democratic
Joins sections of the Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum (2 parts of the continuum)
- Manager asks group to make decision within limits they have set
- Manager allows workers to function and develop options and make decisions defined within limits of a senior manager
Overall now democratic and laissez faire - fare more freedom, delegation and subordinate centered
Tannenbaum Schmidt Continuum (Diagram)