Lecture 40 - Micelles and Micellar Behavior
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is a Micelle?
Thermodynamically stable aggregates of surfactant molecules
How are micelles formed?
Formed spontaneously under the right conditions
What are surfactants?
Is a molecule possessing a distinct polar head region, and a distinct non-polar hydrocarbon chain region
What is the size of surfactant micelles?
Small, generally 50-100 Armstrong in diameter, dependent on the surfactant
How do surfactant molecules behave in solution?
They exist in a dynamic equilibrium with other surfactant molecules that remain free in solution
What is the result of the dynamic equilibrium of micelles?
Because of that, they are being rapidly formed, falling apart and being reformed
The average lifespan of a single micelle is 10 milliseconds
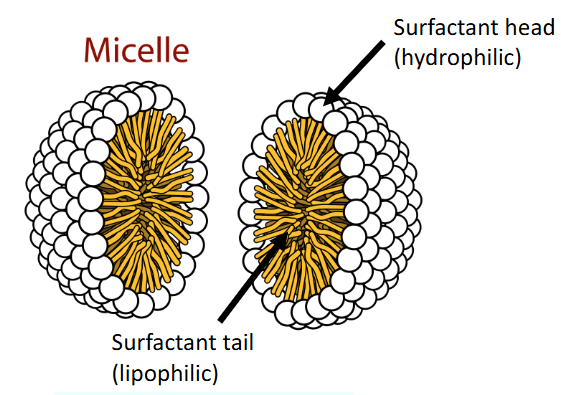
Hartley Surfactant Micelle model?
A micelle that has a spherical structure
Typical aggregation number is 50 or higher

Behavior of a hartley surfactant micelle in aqueous solution?
The polar head groups face outward towards the aqueous phase
The hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails face inward
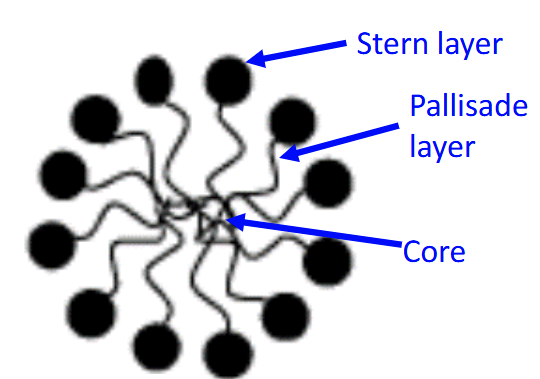
What are the three regions of a micelle?
The core, stern layer, and the palisade layer
Stern layer?
Is composed of polar head groups with tightly bound counter ions
Has full access to the aqueous environment
The core/Inner core?
Is composed completely of the hydrocarbon tails
No water access
The palisade layer?
Is located between the stern layer and the core
Composed of the first 3-5 carbon atoms from the stern layer
Has some limited water access
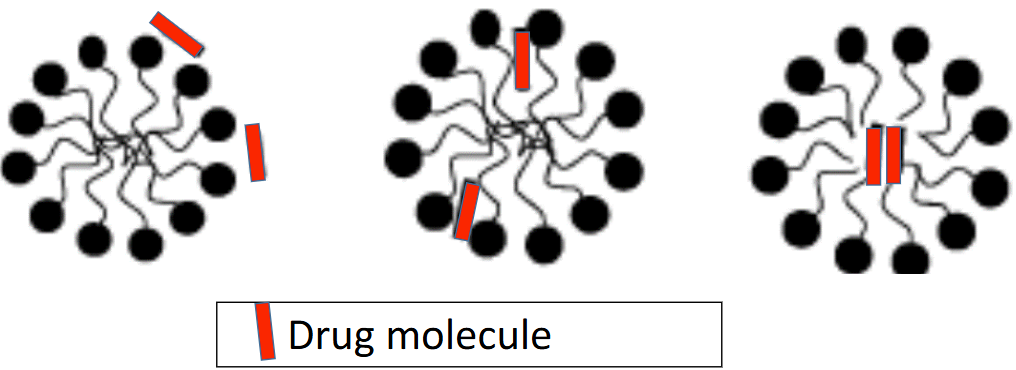
Why are the three regions of the micelle are important?
Between each layer, the micelle provides environments of varying polarity
Because these layers have different polarities, a drug molecule can go to the region that matches its polarity and then can be solubilized
Why do surfactant molecules have high interfacial tension in water?
The hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails have low affinity for water, creating a high energy interface with water
What do surfactant tails do in dilute solutions to reduce interfacial free energy?
They curl to reduce contact between the tail and water
To reduce the interface and the interfacial energy
Non-polar hydrocarbon tails come together, self associate, to form dimers/trimers to exclude water and decrease free energy
Not that efficient in decreasing the free energy
Why do surfactant molecules orient at the liquid surface?
They orient tails up, at the surface to minimize the increase in free energy with the increasing surfactant concentration
What happens after too many surfactant molecules go to the surface?
The surface is limited in area, so once saturated it cannot add more surfactant molecules
The excess molecules that do not have access to the surface undergo micellization
What happens to surfactant molecules at the liquid-air interface?
Polar heads interact with water → hydrocarbon tails stick out, lowering surface tension until the surface is saturated
What triggers micelle formation in solution?
Once the liquid surface is saturated with surfactant, excess molecules self-assemble into micelles
How do micelles form?
Hydrophobic tails are go inside, polar heads face outward, reducing contact with water
What is the critical micelle concentration (CMC)?
The surfactant concentration at which the surface is fully occupied and micelle formation begins; surface tension stops decreasing
What happens if more surfactant is added beyond the CMC?
More micelles form, but surface tension remains constant
Why does surface tension stop decreasing during CMC micelle formation?
Because there is no more room in the surface for surfactant molecules
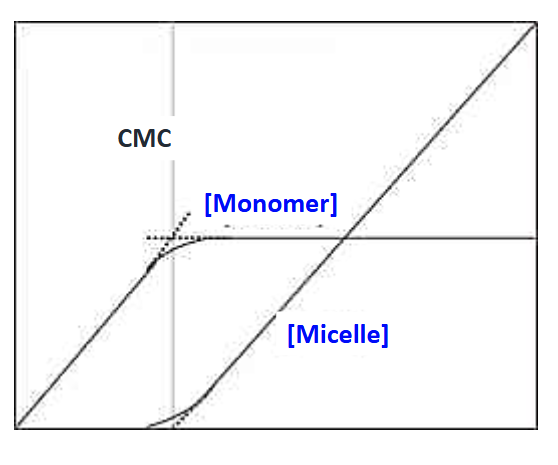
How does the concentration of surfactant monomers change as total surfactant concentration increases?
Monomer concentration increases until the CMC, then stays roughly constant as micelles form
How can the shape or structure of micelles change?
Micelle shapes and structures may change as surfactant concentration increases above the CMC
How does micelle formation affect drug solubilization?
This drug solubilization only occurs above the CMC
the solubilized drug concentration increases above the CMC
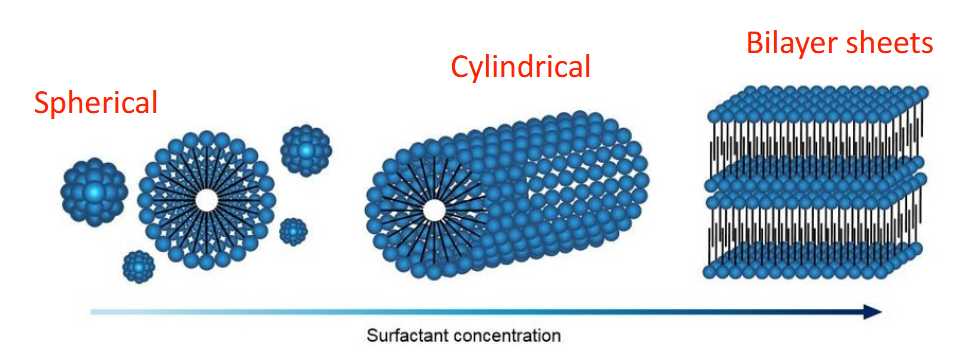
What affects the shapes of micelles?
Increasing the surfactant concentration, also increases the aggregation number making it difficult to accommodate more monomers in a given shape
so as the concentration increases the shape and structure changes as well
What factor affects micelle formation?
Its a spontaneous process, must be accompanied by a negative delta G
What favors micelle formation?
Reduced interfacial energy when hydrocarbon chains leave water
Increased entropy of water, when the HC chains are removed from water during micelle formation the additional water structuring is removed and entropy increases
Increased Delta S → Decreases Delta G
What opposes micelles formation?
Electrostatic repulsion between charged head groups, if the surfactant molecules are ionized
Loss of hydrocarbon chain mobility inside the micelle → entropy loss
Lower CMC?
Good! Makes easier micelle formation
How can surfactant charge and length affect CMC?
Uncharged is favored because there is no electrostatic repulsion
Long chain favored because more water get structured, leading to greater energy increase in system and greater driving force for micellization
How do electrolytes affect CMC?
Some counterions bind to the Stern layer partially neutralizing the polar head charges
decreasing the overall surface charge results in decreased repulsion
What happens when the counterions decrease overall surface charge?
The decreased repulsion leads to:
Decreased CMC with increasing salt concentration
Increased aggregations (larger micelles), number with increasing salt concentration
How does temperature affect CMC?
Increasing temperature decreases the hydration of the polar group, favoring micellization,
But it also causes disruption of the structured water surrounding the HC chains, opposing micellization
Why must the exact surfactant must be known for the effect of temperature on CMC?
Because the effect of temperature is unpredictable, the effect cannot be generalized and the exact surfactant must be known
What is micellar solubilization?
The spontaneous dissolution of a drug by reversible interaction with the micelles to form a thermodynamically stable solution
Why is micellar solubilization pharmaceutically important?
It allows the solubilization of poorly soluble drugs without the use of co-solvents
Do surfactant monomers solubilize the drug?
NO
Only the micelles formed from those monomers actually solubilize the drug
So no solubilization occurs before the CMC
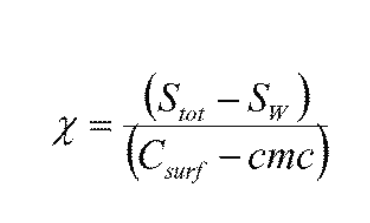
What does this mean?
X is how much drug 1 mole of micelles can solubilize
(Stot – SW) gives the amount of drug solubilized in the micelles
(Csurf – CMC) gives the amount of surfactant in the form of micelles