Stream Study/Human Activity {Full} Vocabulary ~ Mrs. Bailey
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary terms related to stream studies and human activity, including definitions and important concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms

Pollution that enters a stream from one identified source, for example, from pipes.
Point Source Pollution
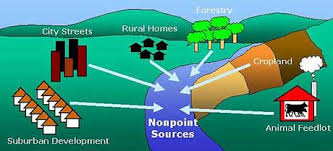
A wide-ranging source of pollution that is difficult to link to one source.
For example: runoff from fertilizer or oil from cars.
Non-Point Source Pollution
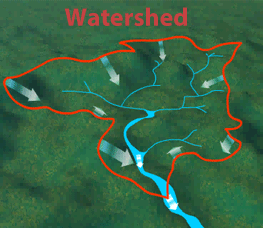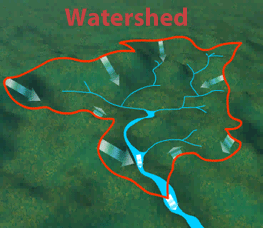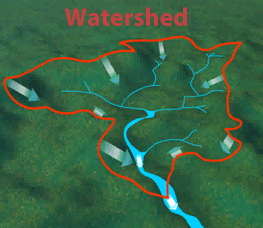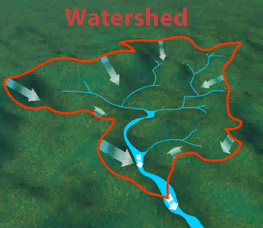
The area of land, including water, that drains into a larger body of water.
Watershed

An area of the stream where water bubbles over rocks.
Riffle

The bottom of a stream.
Substrate

Materials from living things or things that were once living, which are a natural part of a thriving ecosystem.
Organic Material

Water that is still or not moving.
Stagnant

Cloudy water, as a result of sediment being mixed or stirred up.
Turbid

When heavy rains cause pollutants to wash off the land and into a body of water.
Run-off
Studying living organisms to determine the quality or health of a stream or ecosystem.
The prefix "bio" means living
Monitor means to watch
Biomonitoring

Different forms of life living in an ecosystem.
Biodiversity
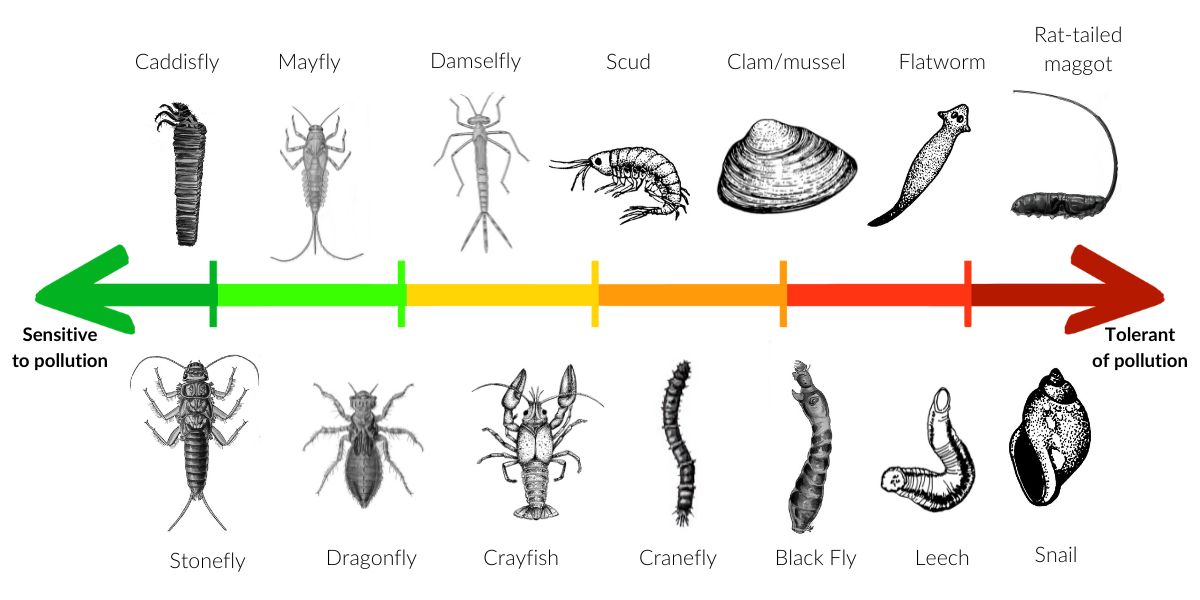
Bottom-dwelling organisms without a backbone that are large enough to see with the human eye.
Benthic Macroinvertebrates

Benthic macroinvertebrates that are extremely sensitive to polluted water.
Taxa 1

Benthic macroinvertebrates that are somewhat sensitive to polluted water.
Taxa 2
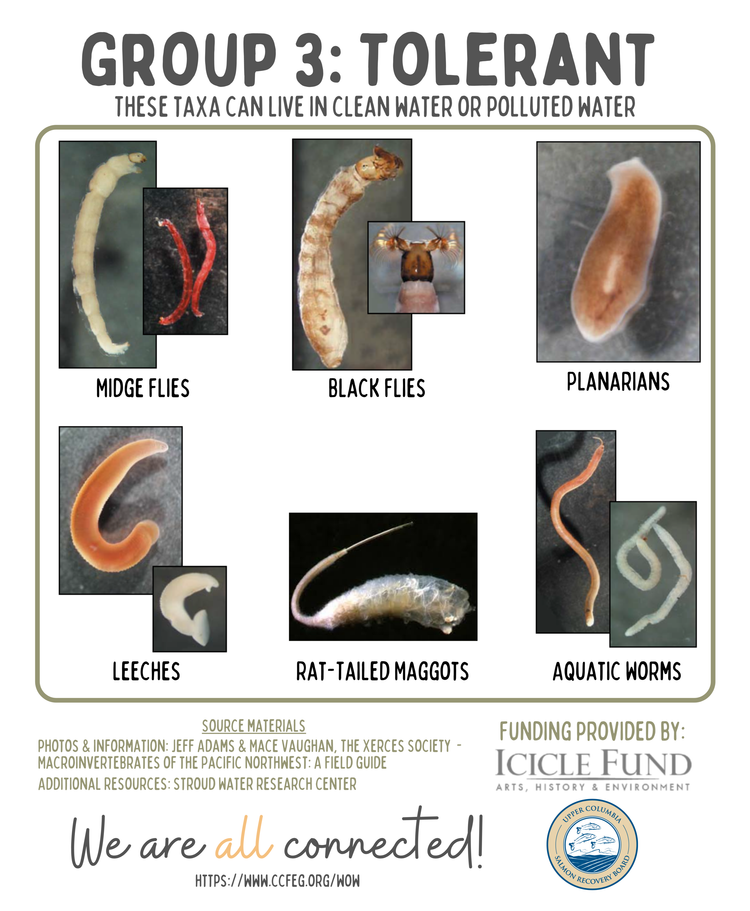
Benthic macroinvertebrates that are tolerant (can live/survive) of polluted water.
Taxa 3
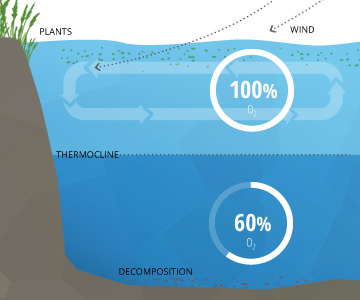
The amount of oxygen that is present in the water.
Dissolved Oxygen
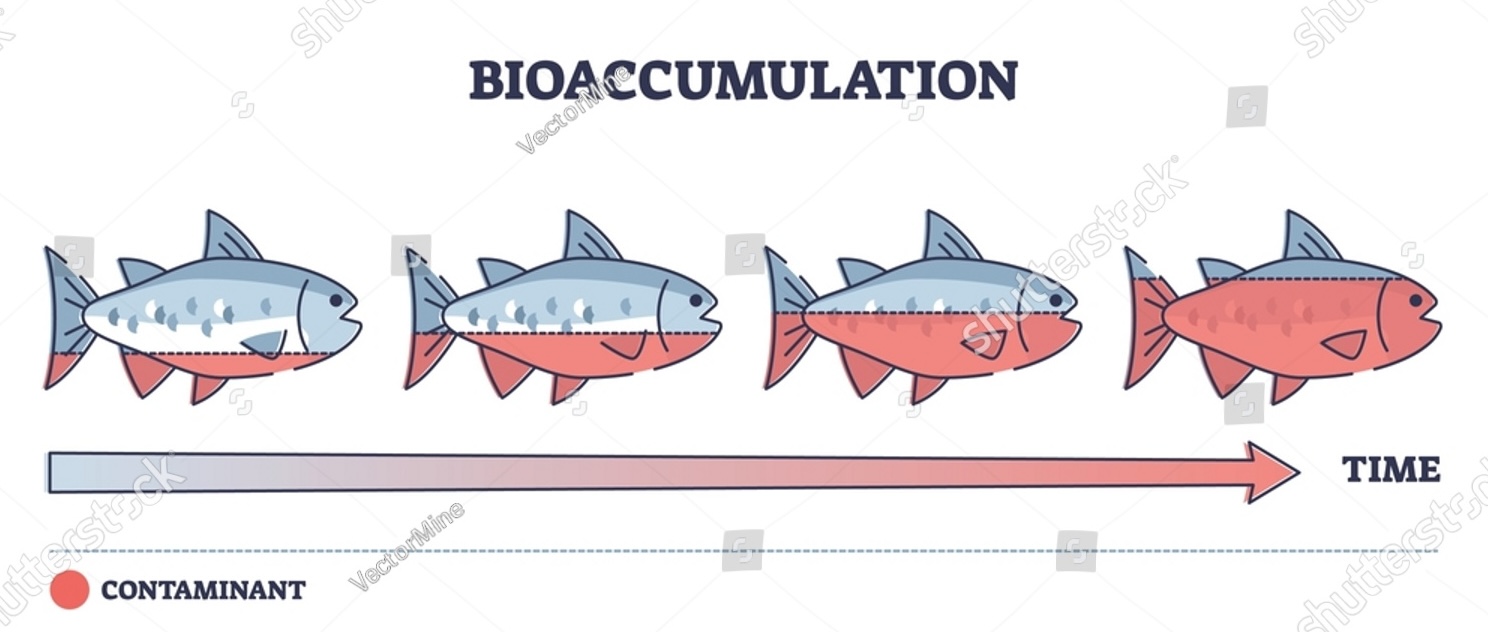
The build-up of a substance, usually a toxin, as it rises through a food chain.
Bioaccumulation
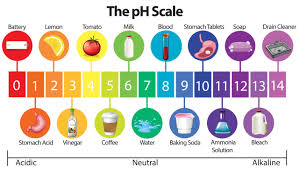
A measure of the acidity (acide) or alkalinity (base) of a solution.
pH

A harmful toxin, chemical, sediment, or bacteria material discharged (brought into)into the water, soil, or air.
Pollution
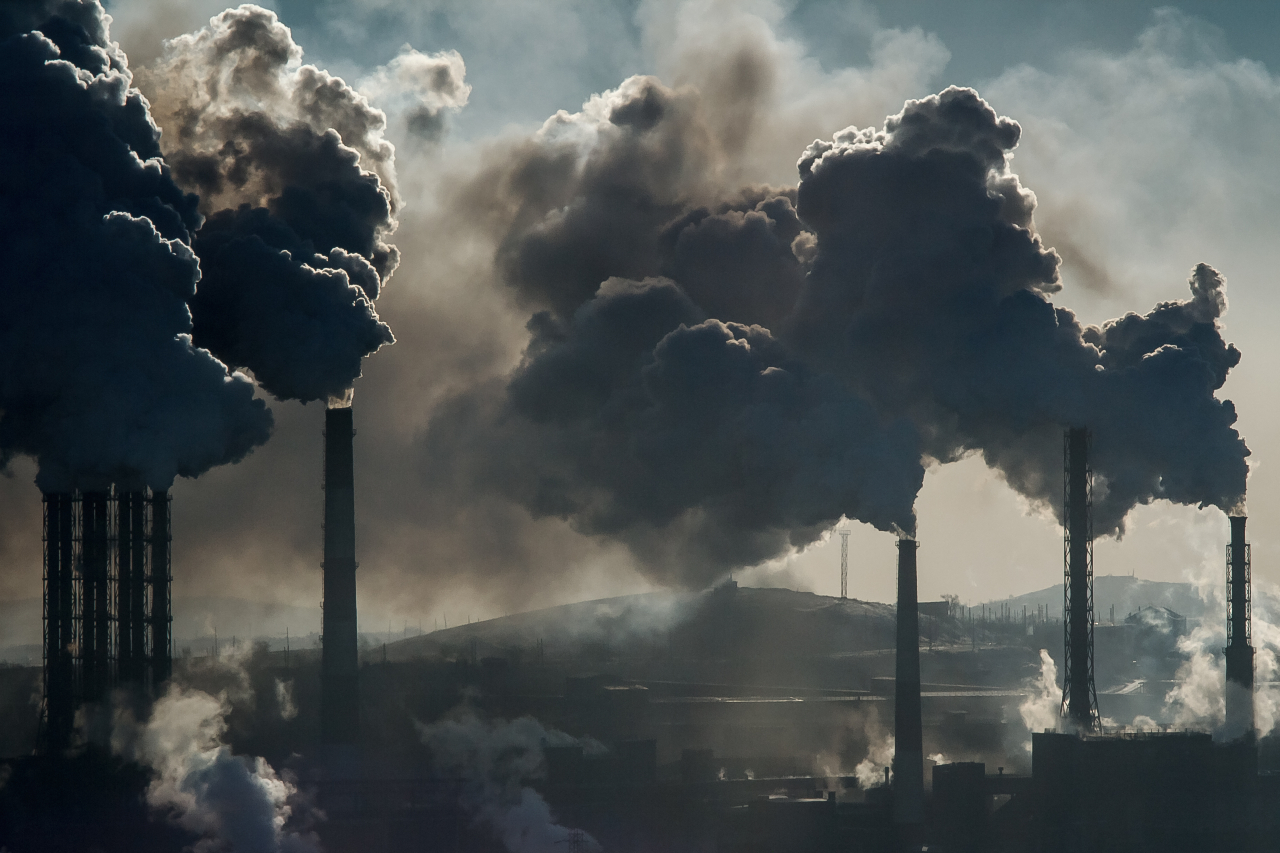

A substance that causes pollution.
Pollutant
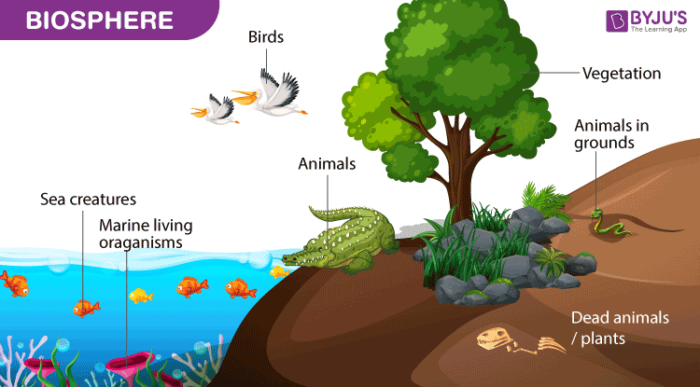
The thin layer of Earth extending from ocean bottoms to the highest mountaintops that contains all living organisms.
Biosphere
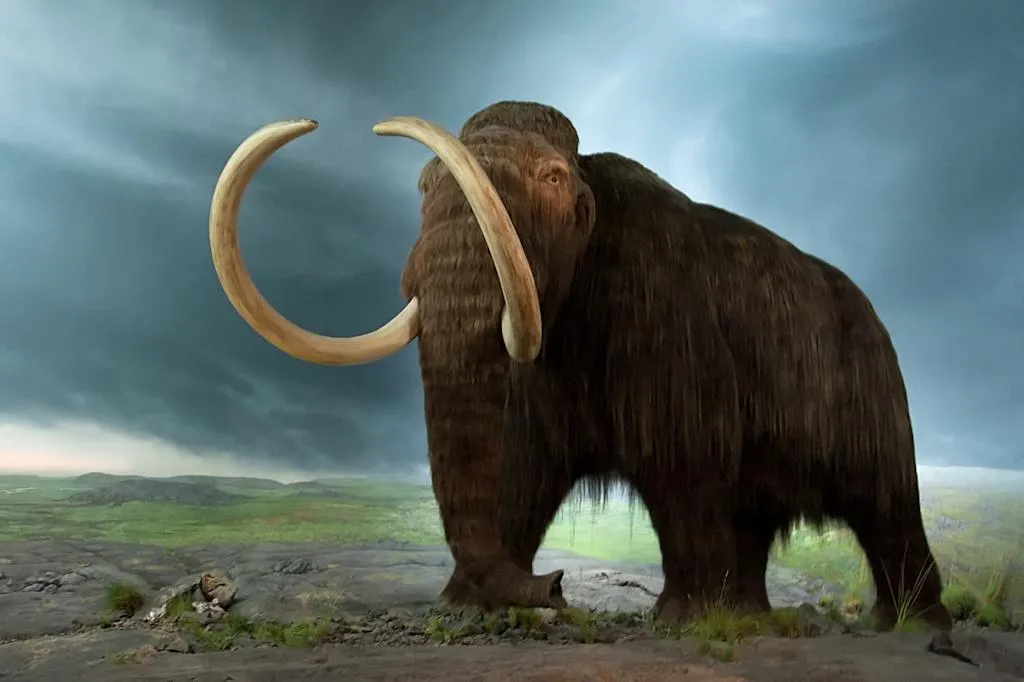

The complete disappearance of a species from Earth.
Extinction

An invasive, reed-like plant that indicates the presence of water and thrives in wetland areas.
Phragmites
A resource that can be replenished over time, for example, electricity from solar panels.
Renewable Resources

A resource that, once used up, cannot be replaced or used again, for example, fossil fuels.
Nonrenewable Resources

Using a resource without depleting it or permanently damaging it.
Sustainable
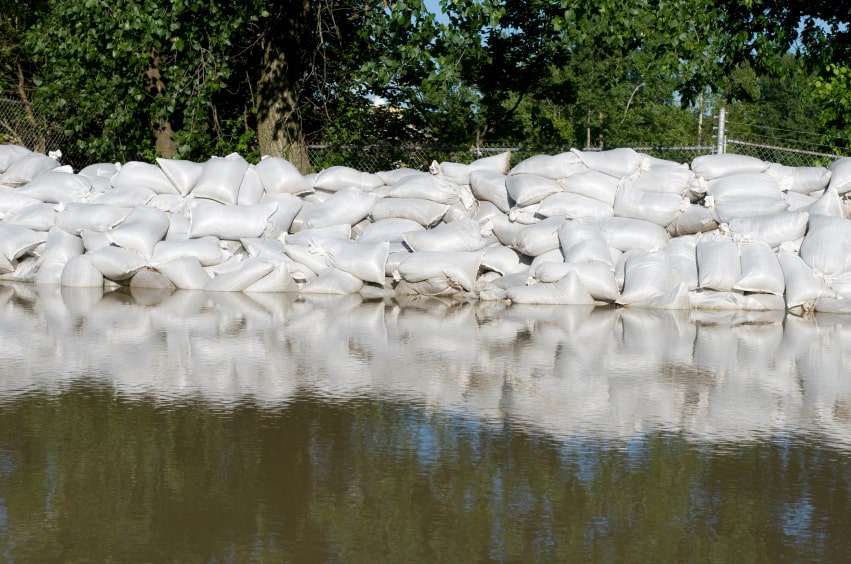

Making a problem less harsh or severe (minimizing it).
Example: placing down sandbags in an area to prevent or lessen flooding
Mitigate
Living or once-living things in an ecosystem, such as plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria.
Biotic
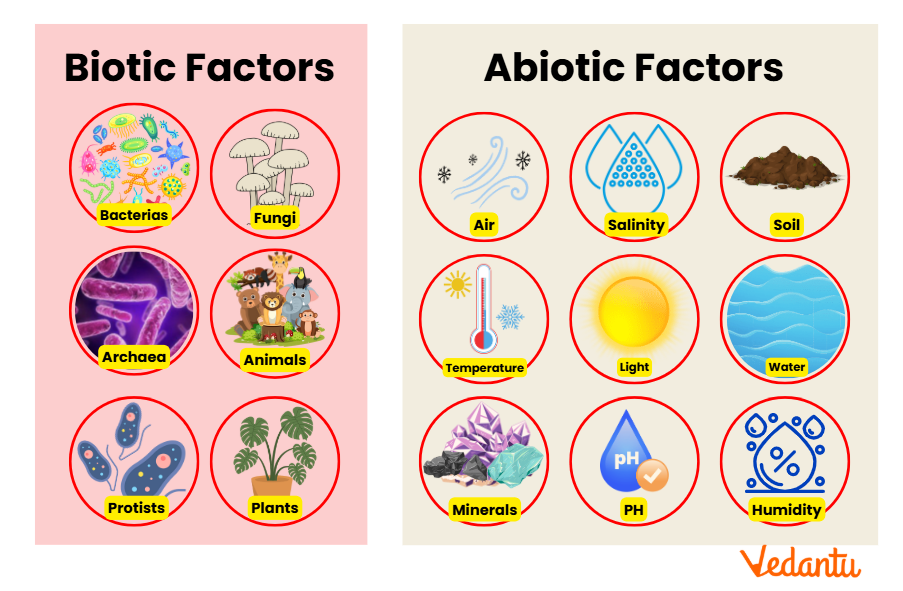
The non-living parts of an ecosystem, like sunlight, water, temperature, air, and rocks.
Abiotic
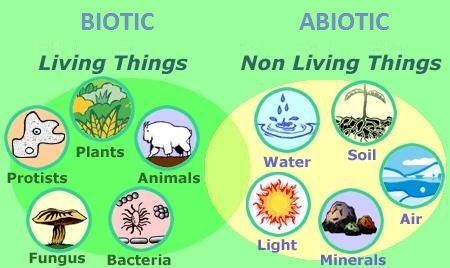
Biotic factors __________ (work together) with non-living, or abiotic factors to form a complete ecosystem.
interact