Biochem Lab Spectro and Centrifuge (Buhay ay di karera)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is centrifugation? What particles typically become sediments?
The spinning of stuff at high speed (generation of centrifugal force), to separate components of a mixture by means of their size, shape, or viscosity of a medium, and density of a particle.
Denser particles
What is centrifugal force?
the apparent force pushing a body outward from the center of a curved path, but it is a fictitious force, not a real one, experienced in a rotating reference frame. It is the result of inertia, where the object's tendency to move in a straight line feels like an outward push.
Principles of centrifugation
Can be refrigirated depending on sample stability and machine model to prevent sample degredation
can work under vacuums typically those who reach high speeds
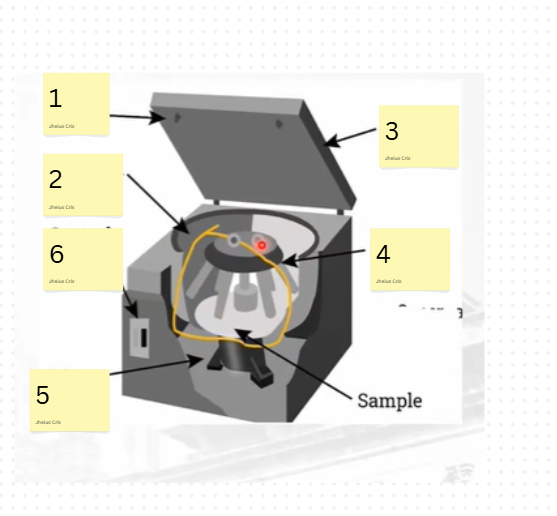
label the parts
Latch
Chamber
Lid
Rotor
Motor
Control
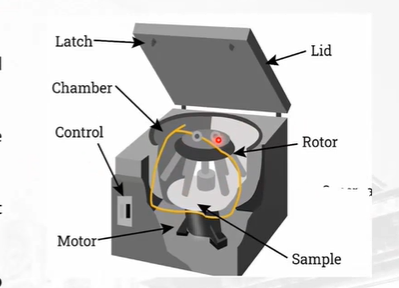
What do you call the rotating part of that holds the tubes and spins?
Rotor
What do you call the part that powers the rotor to generate centrifugal force?
Motor
What are the containers that securely hold on to the sample in the rotor?
Sample Holder/Buckets
What connects the rotor to the motor to transfer rotational force?
Spindle
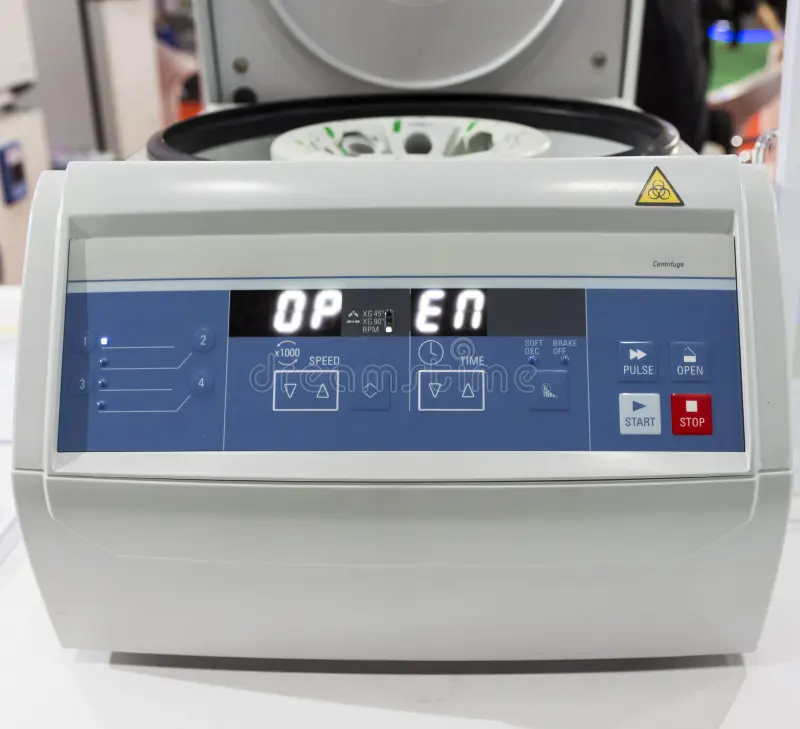
The part of the machine that allows users to set parameters like speed, time, and temperature?
Control Panel

Part of the machine that Maintains low temperatures during operation in refrigerated centrifuges?
Refrigeration System
The part of the machine that covers the chamber and prevents operation or opening during spinning?
Lid and Safety Lock

What is the outer shell that protects internal components and supports the device?
Chassis or Housing
Two classifications according to rotor
Horizontal / Swing-Bucket Rotor
Fixed-Angle Rotor
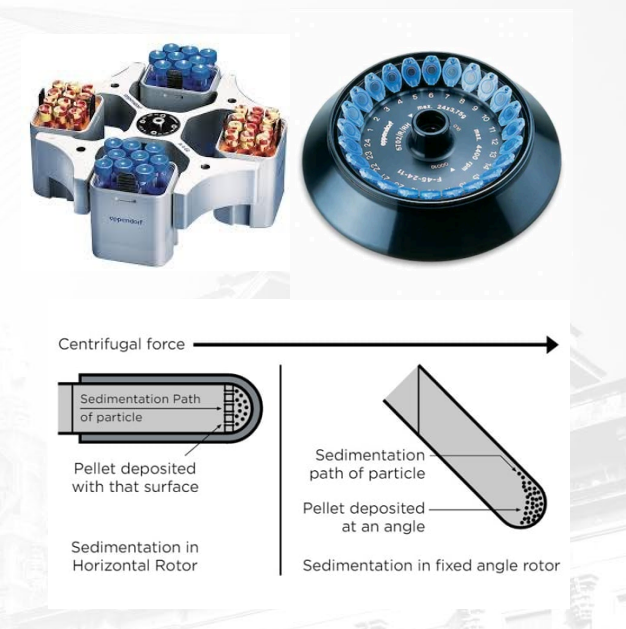
What is a Horizontal/ Swing Bucket Rotor and its functions?
Buckets swing out horizontally during spinning, ideally used for the separation of multiple components according to density (density-gradient centrifugation)
This method is ideal for separating multiple components in a single sample, such as blood cells, organelles, or DNA, as it produces a sharp and well-defined separation.
What is a Fixed-Angle Rotor and its functions?
Holds tubes at a fixed angle, suitable for fast pelleting of particles
This type of rotor is particularly effective for collecting a small, dense pellet from a large volume of liquid, such as bacteria, yeast, or cell debris.
What is RPM (revolutions per minute)?
– The speed at which the rotor spins and is also the number of times the centrifuge rotor spins in one minute. It's a straightforward measure of rotational speed.

What is RCF (relative centrifugal force)?
the force applied to a sample during centrifugation, expressed as a multiple of the Earth's gravitational force (g)

What determines how quickly the rotor speeds up or slows down, allowing gradual acceleration/deceleration to protect fragile samples and prevent tube damage?
Acceleration/Deceleration Ramp
Typical units of time and temperature
Time= Minutes
Temp.= Celsius
Do’s in operating centrifuge?
Use the appropriate centrifuge tube
Pre-cool centrifuge and rotor if applicable
ensure the correct rotor is used and installed properly
Balance the load in the rotor
Don’ts in using a centrifuge
Leave the centrifuge unattended if not at maximum speed or running smoothly
Ignore the safety features
What are colorimetric assay?
the process that measure the light absorbed by the substance, in the visible or UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum, using an ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometer
What is spectrophotometry
used to measure the amount of light transmitted through a sample at a given wavelength
The colors of the visible light spectrum
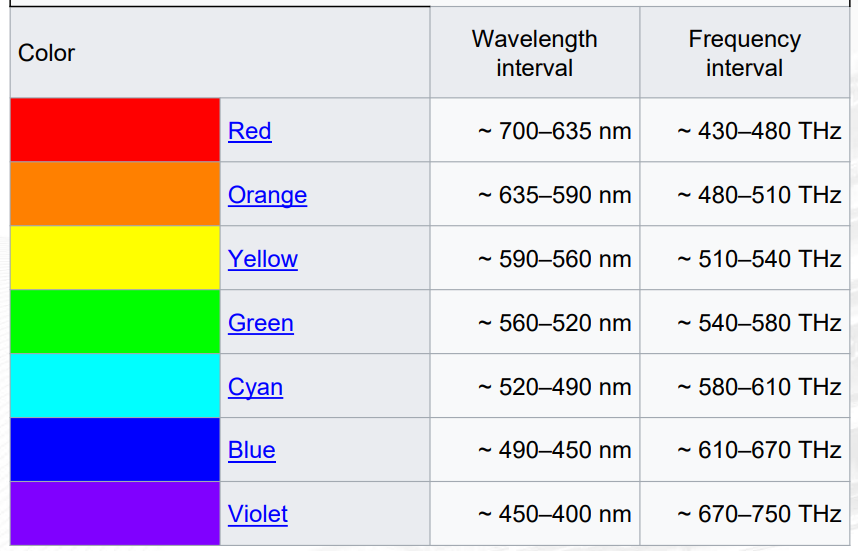
Part of the spectrophotometer that Emits a broad range of light used to illuminate the sample
Light Source
Part of the spectrophotometer that selects a specific wavelength of light from the white light source
Monochromator
Part of the spectrophotometer that holds the sample in a transparent container for light to pass through
sample compartment (cuvette)
Part of the spectrophotometer that measures transmitted light and displays the corresponding absorbance or transmittance
Detector and Readout
What is the formula for transmittance?
Incident light (before) / Transmitted light (after)
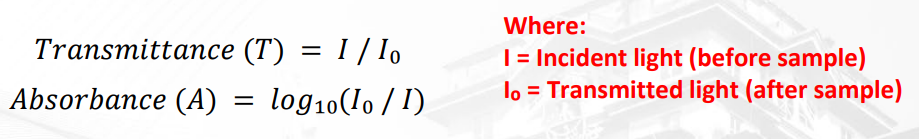
what is the formula for absorbance?
Log 10 (Transmitted (after) / Incident (after) )
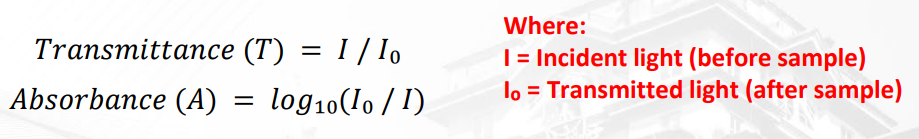
Most commonly used type of spectrophotometer in biochemical analysis?
microplate spectrophotometer
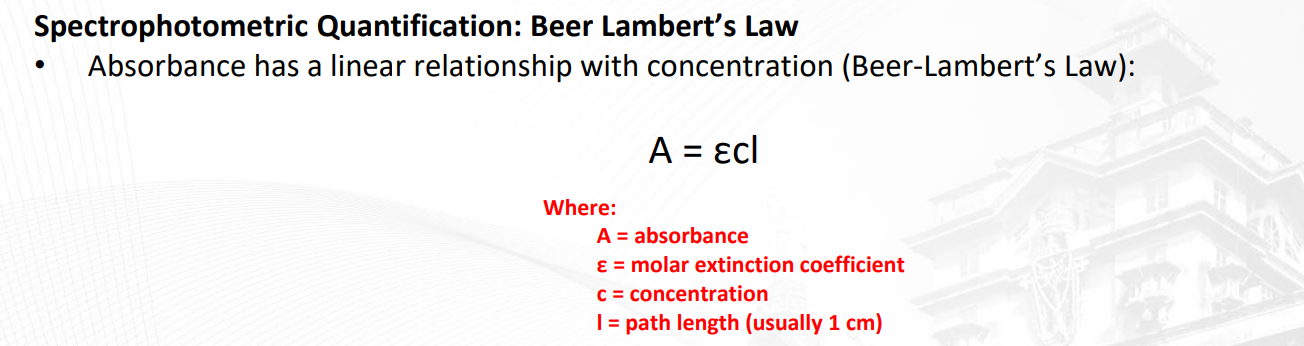
Describe the relationship of absorbance and solution concentration
Linear / Direct

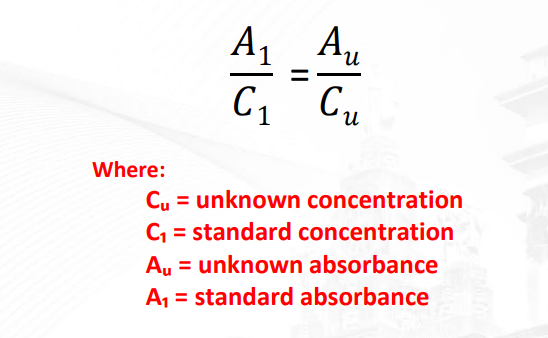
proportion/solution used to estimate the concentration of the unknown given a known concentration
A over C
What is a Spectrophotometric Calibration Curve and how is it used to determine the unknown concentration of a substance?
also known as a Standard Curve is a graph that helps you find the concentration of an unknown sample. You first create the curve by measuring the absorbance of several solutions with known concentrations. You then plot these absorbance values (y-axis) against their corresponding concentrations (x-axis) and draw a straight line through the points.
Picture ni Master Yoda
