Estrogens/Progestins
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
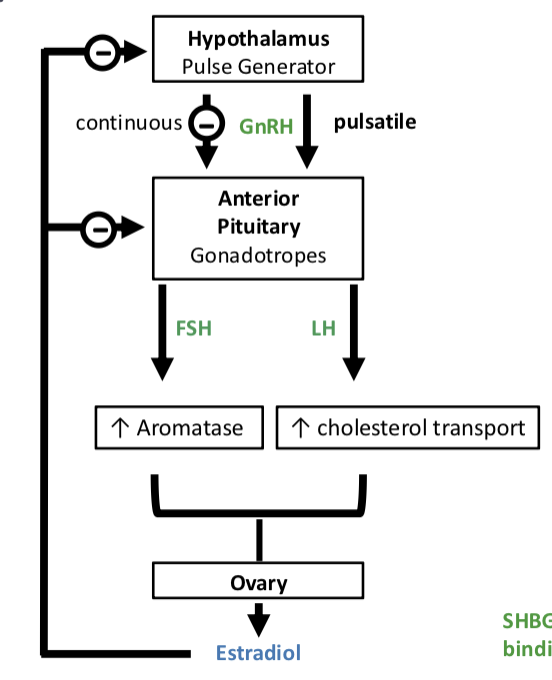
Estrogen Synthesis and Secretion
the hypothalamus releases ______, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release ______ and _______
________ GnRH release maintains normal pituitary stimulation, while ________ GnRH leads to receptor desensitization and suppression of FSH/LH
LH increases ______ ______ —> increase in ______ precursors
FSH stimulates ______ activity which converts androgens into ______
three estrogens produced by aromatase activity —>
the ______ ______ is responsible for high affinity binding to estrogen receptors
______ inhibits FSH and LH
GnRH, LH, FSH
pulsatile, continuous
cholesterol transport, androgen
aromatase, estradiol
estradiol, estrone, estriol
phenolic ring
progesterone
Sources of Estrogen in Different Physiological Stages
In premenopausal women, the main source of estrogen is the ________.
In postmenopausal women and men, the primary site of estrogen synthesis is ________ tissue.
In postmenopausal women, ________ produced by the ________ ________ is converted to estrogens in adipose tissue.
In men, ________ precursors and ________ are converted to estrogens in adipose tissue.
During gestation, large quantities of estrogen are produced by the ________ unit.
In this process, the ________ ________ produces androgen precursors that are transported to the ________, where they are aromatized to ________.
ovary
adipose
DHEA, adrenal cortex
androgen, testosterone
fecoplacental
fetal adrenal, placenta, estriol
Estrogen Receptor MOA
ERs exist as ______ stabilized by HSPs in the ______
ERs then ______
ERs interact with coactivators —>
two receptor types —>
monomers
dimerize
agonist OR antagonist
ERa, ERB
ERa is expressed abundantly in —> (4)
female reproductive tract —> uterus, vagina, ovaries, and mammary glands
hypothalamus
endothelial cells
vascular smooth muscle
ERB is expressed in:
high expression —> ______ and ______
lower expression —> (4)
prostate, ovaries
lung, brain, bone, and vasculature
Estrogen Physiological Effects —> (4)
female development
bone
cardiovascular
CNS
Estrogen Physiological Effects —> Female Development
changes in females at ______
______/______ of vagina, uterus and fallopian tubes
______ & ______ of breast tissue
______
most of the changes in organs during the ______ ______
puberty
growth, development
enlargement, differentiation
libido
menstrual cycle
Estrogen Physiological Effects —> Bone
______ bone mineral density & ______ of epiphyses
increase ______ production
decrease ______ number and activity
increase, closing
osteoblast
osteoclast
Estrogen Physiological Effects —> Cardiovascular
beneficial effect on blood lipids by decreasing ______ and increasing ______
promotes vasodilation by stimulating endothelial production of ______ ______
estrogen enhances blood coagulation by:
increasing production of coagulation factors in the ______
decreasing levels of anticoagulation factors such as ______, ______, and ______
increase ______
mild ______ and ______ retention
LDL, HDL
nitric oxide
lipid
Protein C, S anti-thrombin
fibrinolysis
sodium, water
Estrogen Physiological Effects —> CNS
stimulates ______ —> hormone involved in stress regulation
enhances ______ activity, promoting a sense of ______ in women
CRH
SNS, well-being
Therapeutic Uses —> (4)
primary female hypogonadism —> due to estrogen deficiency
contraception
endometriosis, dysmenorrhea
menopause and hormone replacement
Menopause and Hormone Replacement
______ of menstrual cycle and ______ in estradiol levels
______ years of age
common signs and symptoms of menopause include:
______ (vasomotor symptoms)
______
______ and ______ disturbances
______ of estrogen-dependent tissues
increase risk of ______ and ______
increase ______ risk
______/cognitive difficulties
cessation, decline
45-60
hot flashes
sweating
irritability, sleep
atrophy
osteoporosis, bone fractures
cardiovascular
memory loss
Postmenopause Hormone Replacement Goals
reduce ______ symptoms —> hot flashes
HRT helps ameliorate atrophy of ______-dependent tissue
prevent bone loss associated with ______
1st line-therapy —> ______
adequate intake of ______ and _______
vasomotor
estrogen
osteoporosis
biphosphonates
calcium, vitamin D
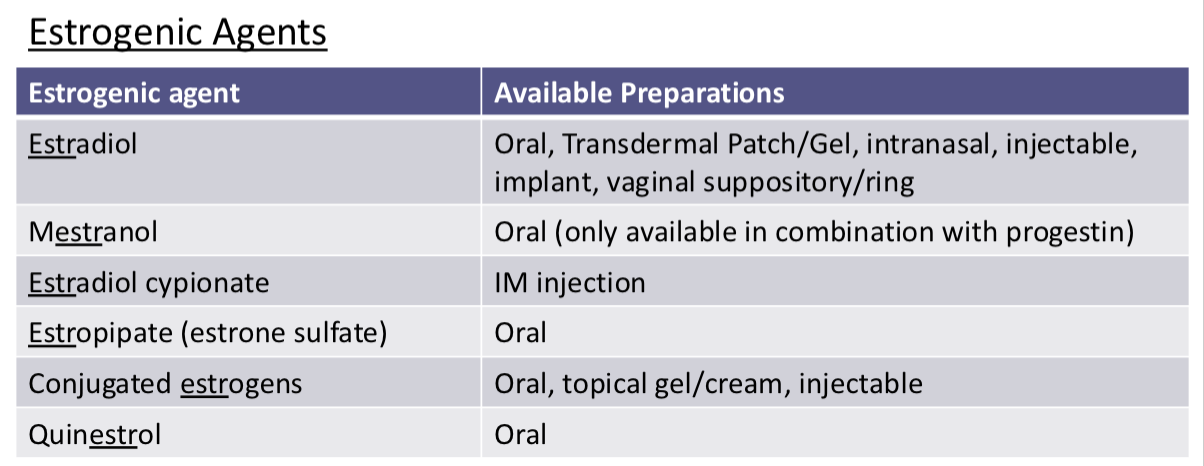
Estrogen Preparations
Pharmacokinetics:
readily absorbed from ______ sites
______ application is sufficient to produce systemic effects
after absorption, ______ metabolism can be significant
all
topical
hepatic 1st pass
Estrogen Adverse Effects
large doses of estrogen can cause ______ and other ______ side effects
large doses may also cause ______ retention
increases the risk for ______ and ______
can cause ______ bleeding
Carcinogenic Concerns:
used by ______ women —> increases ______ cancer (5-15x)
in women with an intact uterus, estrogen replacement therapy should be combined with ______ to decrease cancer risk
do not use in ______-dependent cancers
contraindicated in ______
increases the risk of cancer in ______ offspring
______ ______ in male offspring
has no proven efficacy in pregnancy disorders
nausea, GI
fluid
DVT, PE
uterine
postmenopausal, endometrial
progestin
estrogen
pregnancy
female
genital teratogenesis
Anti-Estrogens Therapeutic Uses —> (3)
breast cancer
osteoporosis
infertility
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
SERMs have selective beneficial estrogenic actions in the ________, ________, and ________.
SERMs have anti-estrogenic actions in the ________ and maybe the ________.
Examples of SERMs include:
→ ________, ________, and ________.
bone, brain, liver
breast, endometrium
Tamoxifen, Toremifene, Raloxifene
SERMs —> Tamoxifen
______ has similar actions
educes ______ tumor size and number
stimulates ______ cell proliferation —> increases the risk of ______ ______ by 2-fold
blocks bone ______
decreases total ______ and ______, but causes no increase in HDL or triglycerides
increases the risk of ______ and ______ by 2-3 fold
______ bioavailable and has a ______ half-life
requires ______ weeks to reach steady-state levels
metabolized by _______, producing a potent active metabolite
drug ______ and enzyme ______ can alter effectiveness
primarily used to treat ______ ______
toremifene
breast
endometrial, endometrial carcinoma
resorption
cholesterol, LDL
DVT, PE
orally, longer
3-4
CYP2D6
interaction, deficiency
breast cancer
SERMs —> Raloxifene
activates ______ in bone —> blocks ______ resorption
decreases total ______ and ______ but does not increase ______
reduces proliferation in ______ breast cancer
does not stimulate ______ cell proliferation
increases the risk of ______ and ______ by 3-fold
increases ______ flashes and ______ cramps
______ absorption after oral administration
metabolized in the ______ and eliminated in the ______
primarily used to treat ______ ______
ER, bone
cholesterol, LDL, HDL
ER+
endometrial
DVT, PE
hot, leg
rapid
liver, feces
post-menopausal osteoporosis
Estrogen Receptor Antagonist —> Fulvestrant
binds ER with ______ affinity than estradiol
represses ______ _______
increases ______ ______
primarily used to treat ______ breast cancer
monthly ______ injections
side effects: ______ symptoms
greater
gene transcription
ERa degradation
tamoxifen-resistant
IM
menopausal
Estrogen Receptor Antagonist —> Clomiphene
blocks ______ in the ______, preventing the normal ______ ______ inhibition by estrogen
increases ______ and ______
increases ______
primarily used to treat _______
well absorbed and bioavailable with ______ administration
ER, pituitary, negative feedback
LH, FSH
ovulation
infertility
oral
Estrogen Synthesis Inhibitors
the three main aromatase inhibitors are ________, ________, and ________
primarily used to treat ______ cancer
often used as ______ or ______ line therapy after ______
compared to tamoxifen:
no increase in ______/______ cancer
no increase in ______ and ______ risk
increased ______ ______
no beneficial effect on ______ ______
exemestane, anastrozole, letrozole
breast
first, second, tamoxifen
endometrial/uterine
DVT, PR
hot flashes
bone density
Progesterone MOA and Physiological Effects
MOA similar to ______ complex
mediated by two receptor subtypes:
______ —> mediates the stimulatory activities of progesterone
______ —> strongly inhibits PR-B actions and inhibits ______ of other steroid receptors
estrogen-ER
PR-B
PR-A, transcription
Progesterone Physiological Effects —> Female Reproductive Effects
______ development
maturation and ______ changes in ______ following ovulation
helps maintain ______ by suppressing ______ and ______ contractility
breast
secretory, endometrium
pregnancy, menstruation, uterine
Progesterone Physiological Effects —> Carbohydrate Metabolism
increases ______ insulin and the ______ response to glucose
promotes ______ storage
basal, insulin
glycogen
Progesterone Physiological Effects —> Cardiovascular/Renal
competes with ______ for the ______ receptor
decrease in ______ reabsorption and a compensatory increase in ______ release
increases ______ levels and causes a modest reduction in ______
aldosterone, mineralcorticoid
sodium, aldosterone
LDL, HDL
Progesterone Physiological Effects —> CNS
______ —> temperature regulating center
increase in ______ temperature during ______
alters regulatory centers by increasing ______ ______ ventilation
has ______ and ______ effects on the CNS
hypothalamus
body, ovulation
carbon dioxide
depressant, hypnotic
Progestins Therapeutic Uses —> (2)
hormone replacement therapy
contraception
Progestin Agents
______ —> agents similar to progesterone
examples —> (4)
______ —> agents similar to 19-nortestosterone
examples —> (3)
______ —> agents similar to 19-norgestrel
examples —> (3)
pregnanes
progesterone, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, megestrol acetate
estranes
norethynordel, norethindrone, norethindrone acetate
gonanes
desogestrel, L-norgestrel, norgestimate
Progestins — PK
well absorbed by any ______
T1/2 in plasma —> ~______ minutes
metabolized in ______
route
5
liver
Progestins — Adverse Effects —> (7)
depressant and hypnotic actions
irregular menstrual bleeding
weight gain
mood changes
decreased bone mineral density
decreased HDL and increased LDL
androgenic effects —> acne and hirsutism