Module 8 Animal Organs & Responses to Stimuli
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:27 PM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
centers, stimuli
Brain
➔ Controls every function in the human body (breathing, digestion, heart rate, etc.)
➔ Most hardworking organ; functions even when we are asleep (sleep ______)
➔ If we are braindead, other organs would still retain their basic functions but processing of _______ would not occur
➔ Controls every function in the human body (breathing, digestion, heart rate, etc.)
➔ Most hardworking organ; functions even when we are asleep (sleep ______)
➔ If we are braindead, other organs would still retain their basic functions but processing of _______ would not occur
2
New cards
oxygen, brain, beating, microcirculation
Heart
➔ In order for the body to function, it needs ______; oxygen is delivered to all parts of the body thanks to the heart
➔ ____ cannot function without the oxygen delivered to it through the pumping of the heart
➔ Even if you are braindead, your heart is still there for you
➔ Person only declared as dead if heart stops _______
➔ Important part of circulatory system: _______
➔ In order for the body to function, it needs ______; oxygen is delivered to all parts of the body thanks to the heart
➔ ____ cannot function without the oxygen delivered to it through the pumping of the heart
➔ Even if you are braindead, your heart is still there for you
➔ Person only declared as dead if heart stops _______
➔ Important part of circulatory system: _______
3
New cards
microcirculation
Circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ tissues.
4
New cards
homeostasis, electrolyte, hormones, red, bones, precise
Kidney
➔ Plays an important role in __________ by filtering out the wastes in our blood and regulating the fluid and ______ balance
➔ Produces ______ that control the blood pressure, produce ____ blood cells, and keep the ______ healthy and strong
➔ Very _____; reacts immediately to small changes regarding homeostasis in the body
➔ Plays an important role in __________ by filtering out the wastes in our blood and regulating the fluid and ______ balance
➔ Produces ______ that control the blood pressure, produce ____ blood cells, and keep the ______ healthy and strong
➔ Very _____; reacts immediately to small changes regarding homeostasis in the body
5
New cards
transplanted, regenerate, detoxify
Liver
➔ Can be donated or ___________ to others with little risk of harming the donor
➔ Can ________ for both the donor and receiver up to its original size in a short period of time
➔ Can ______ the body
➔ Can be donated or ___________ to others with little risk of harming the donor
➔ Can ________ for both the donor and receiver up to its original size in a short period of time
➔ Can ______ the body
6
New cards
glutathione, oxygen, radicals
➔ Produces one of the greatest antioxidants: __________; important to fight off reactive _______ species produced by the mitochondria due to leakage in ETC
➔ Glutathione produced by the liver inactivates free ______; free radicals affect the integrity of biomolecules and lead to various effects such as ageing
➔ Taking in glutathione affects its production by the liver, making it inefficient; this makes us susceptible to oxidative damages
➔ Glutathione produced by the liver inactivates free ______; free radicals affect the integrity of biomolecules and lead to various effects such as ageing
➔ Taking in glutathione affects its production by the liver, making it inefficient; this makes us susceptible to oxidative damages
7
New cards
glycogen
Liver
➔ Stores _______; can be utilized as a source of energy later on
➔ Stores _______; can be utilized as a source of energy later on
8
New cards
alveoli, phonation, initial, angiotensin
Lungs
➔ Responsible for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, particularly in the ______
➔ Acts as a generator to ________; supplies air to voicebox
➔ Acts as ______ barrier to outside environment; surface area of lungs is greater than that of the skin
➔ Produces certain important metabolites and enzymes (e.g., ACE or _________-converting enzyme)
➔ Responsible for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, particularly in the ______
➔ Acts as a generator to ________; supplies air to voicebox
➔ Acts as ______ barrier to outside environment; surface area of lungs is greater than that of the skin
➔ Produces certain important metabolites and enzymes (e.g., ACE or _________-converting enzyme)
9
New cards
first, pathogens, perspiration
Skin
➔ Protective layer; ____ line of defense
➔ Important for maintaining our immune system against invading _______
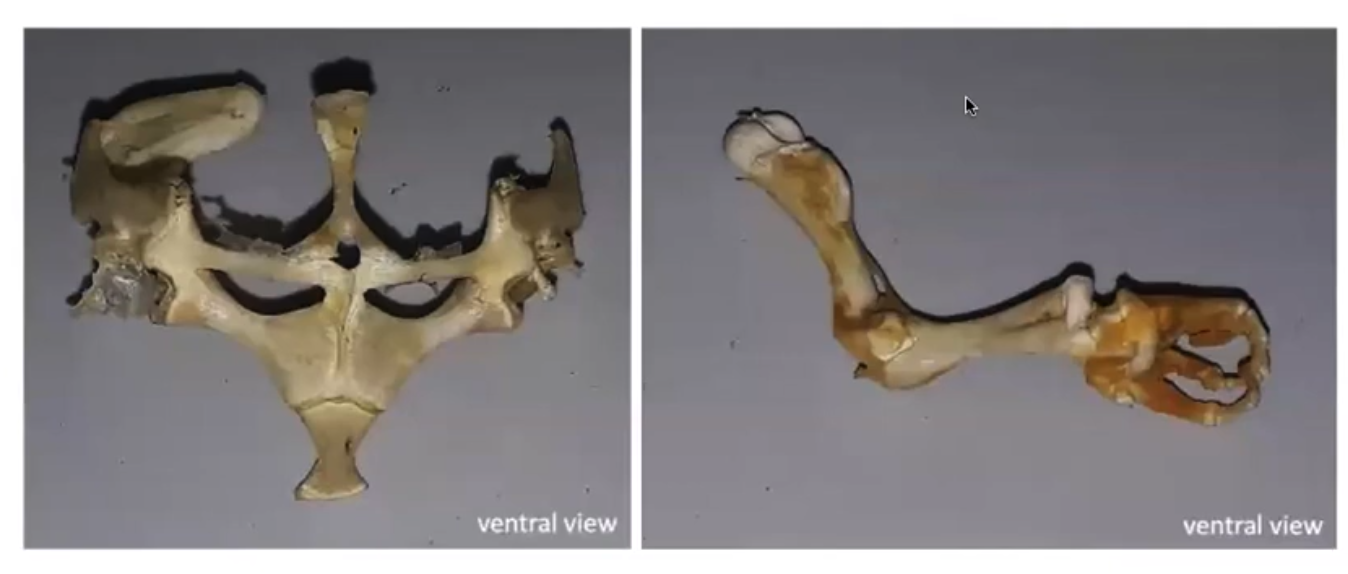
➔ Helps in maintaining homeostasis,
particularly during ________
➔ Protective layer; ____ line of defense
➔ Important for maintaining our immune system against invading _______
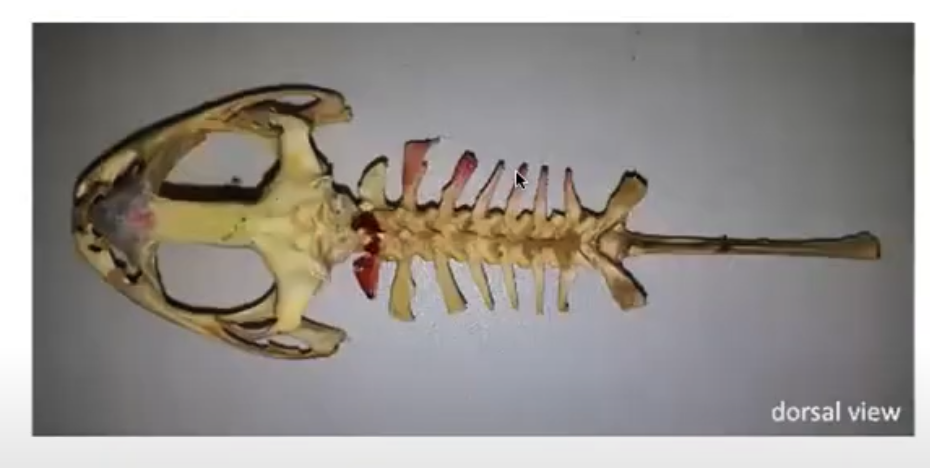
➔ Helps in maintaining homeostasis,
particularly during ________
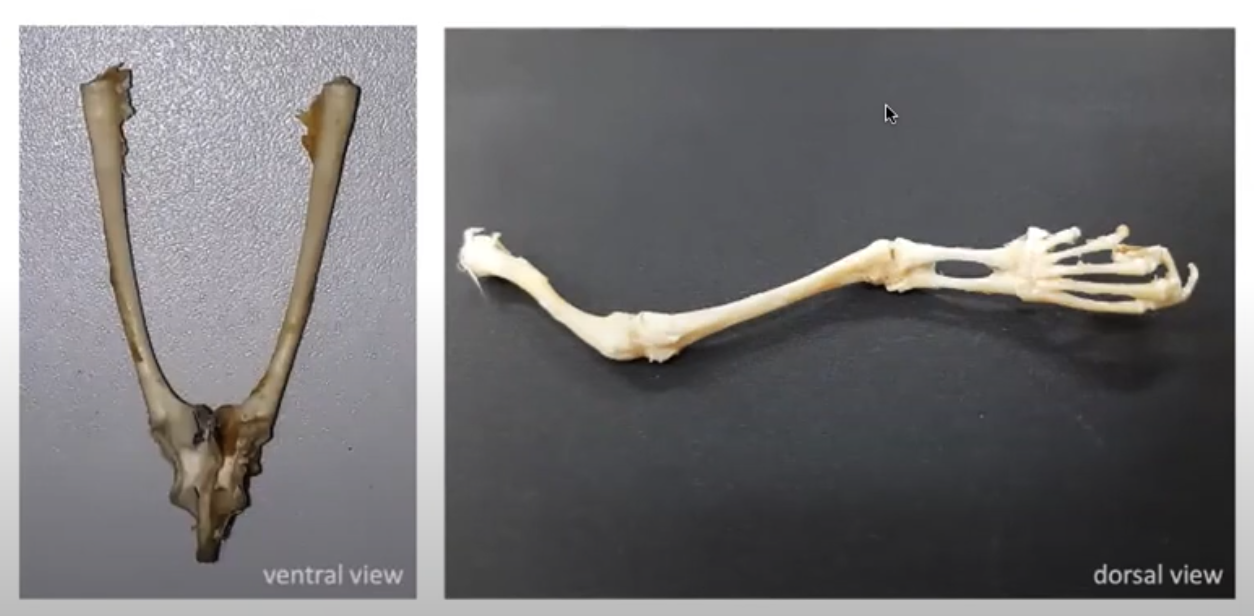
10
New cards
nutrients
Small intestine
➔ Responsible for absorption of ________; without this, we won’t be able to absorb and utilize them
➔ Responsible for absorption of ________; without this, we won’t be able to absorb and utilize them
11
New cards
Water
Colon
➔ _____ absorption; without it we would get dehydrated
➔ _____ absorption; without it we would get dehydrated
12
New cards
marrow, mineralizes, ions, interstitial, structural, internal
Bones
➔ Responsible for the production and maintenance of blood in the bone ______
➔ _________ itself and stores essential ____ like calcium within its ________ spaces
➔ ______ support; Without it, none of the other organs can organize themselves nor gain enough space to properly perform their functions
➔ Protects _______ organs
➔ Without this, we would have less motility
➔ Responsible for the production and maintenance of blood in the bone ______
➔ _________ itself and stores essential ____ like calcium within its ________ spaces
➔ ______ support; Without it, none of the other organs can organize themselves nor gain enough space to properly perform their functions
➔ Protects _______ organs
➔ Without this, we would have less motility
13
New cards
Animal organs concept map
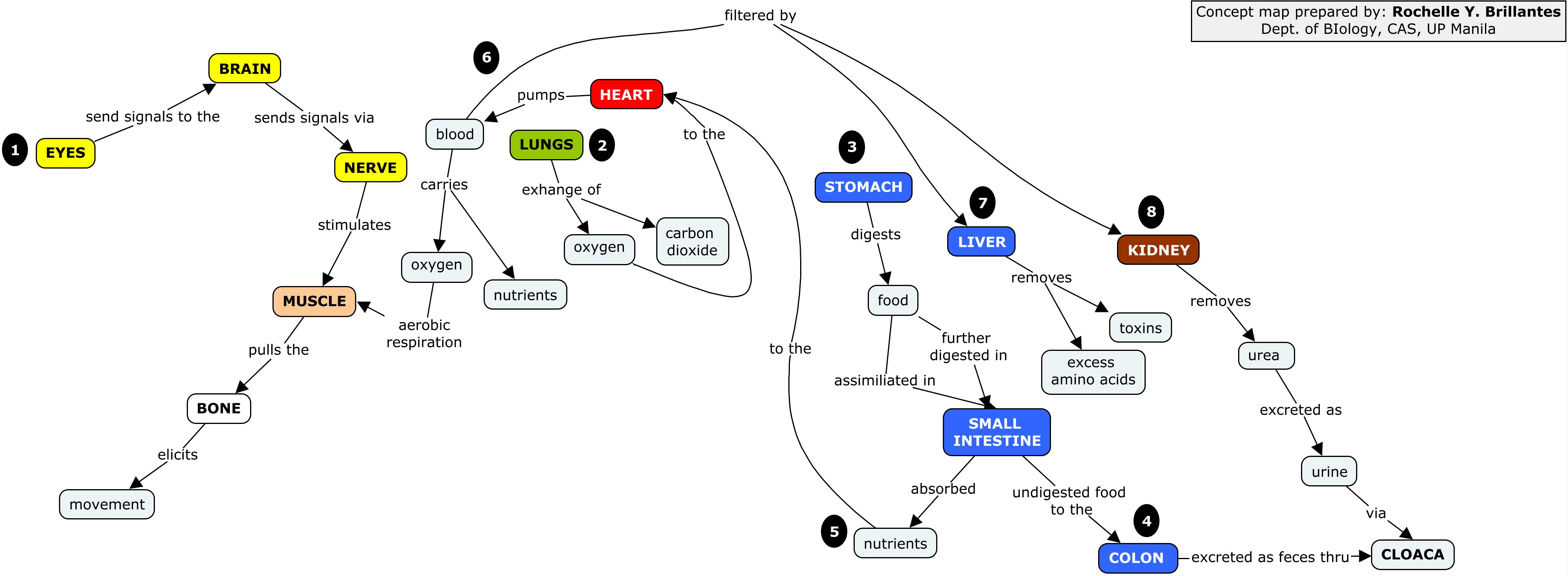
14
New cards
Endoskeletal system
- is an internal skeleton composed of hard, mineralized tissue that also enables movement by attachment to muscles
1. Invertebrate
2. Vertebrate
1. Invertebrate
2. Vertebrate
15
New cards
Invertebrate endoskeletal system
- Do not have true bones as vertebrates

16
New cards
Vertebrate endoskeletal system
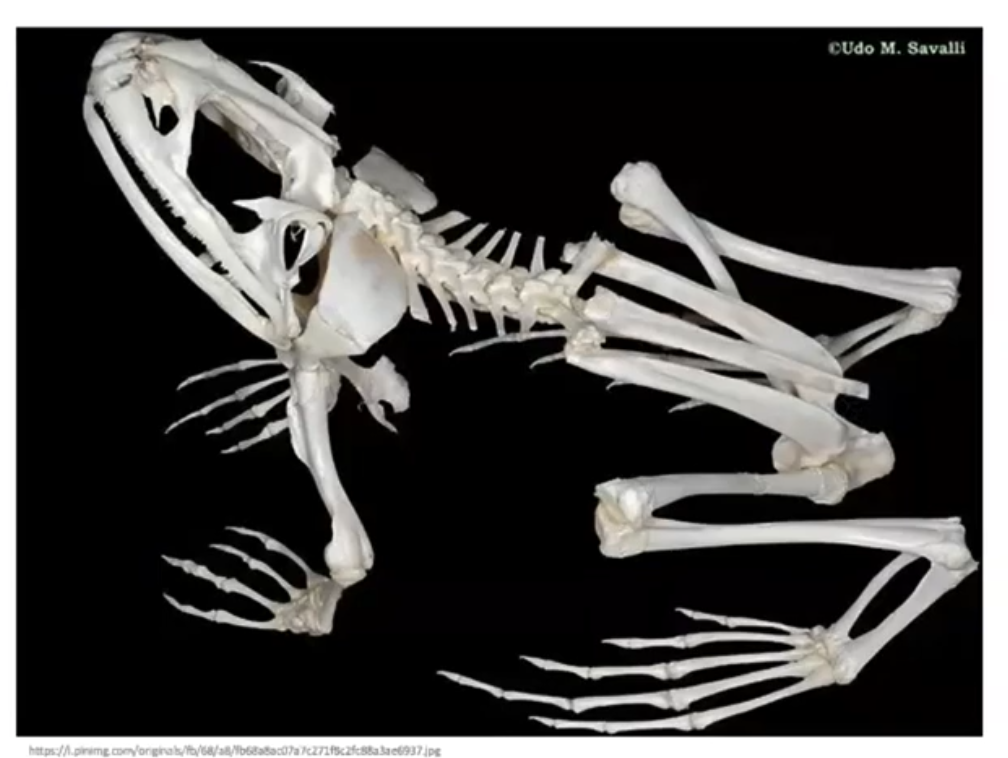
17
New cards
Axial
Vertebrate endoskeletal system
_______ skeleton
1. Skull
2. Vertebral column
_______ skeleton
1. Skull
2. Vertebral column
18
New cards
Appendicular
Vertebrate endoskeletal system
_______ skeleton
1. Pectoral girdle + Forelimb
2. Pelvic girdle + Hindlimb
_______ skeleton
1. Pectoral girdle + Forelimb
2. Pelvic girdle + Hindlimb
19
New cards
Muscular system
- is an organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle
- work with skeletal system to allow locomotion and motility
1. Invertebrate
2. Vertebrate
- work with skeletal system to allow locomotion and motility
1. Invertebrate
2. Vertebrate
20
New cards
Invertebrate muscular system
21
New cards
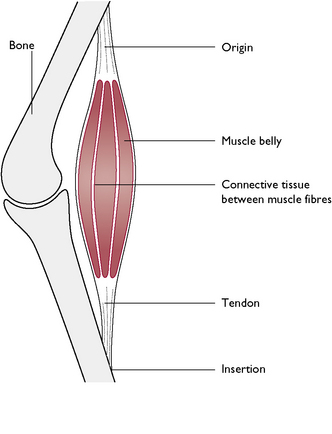
Vertebrate muscular system
Parts
1. Origin (fixed end)
2. Belly
3. Insertion (movable end)
Actions
1. Extension vs flexion
2. Adduction vs abduction
3. Elevation vs depression
1. Origin (fixed end)
2. Belly
3. Insertion (movable end)
Actions
1. Extension vs flexion
2. Adduction vs abduction
3. Elevation vs depression
22
New cards
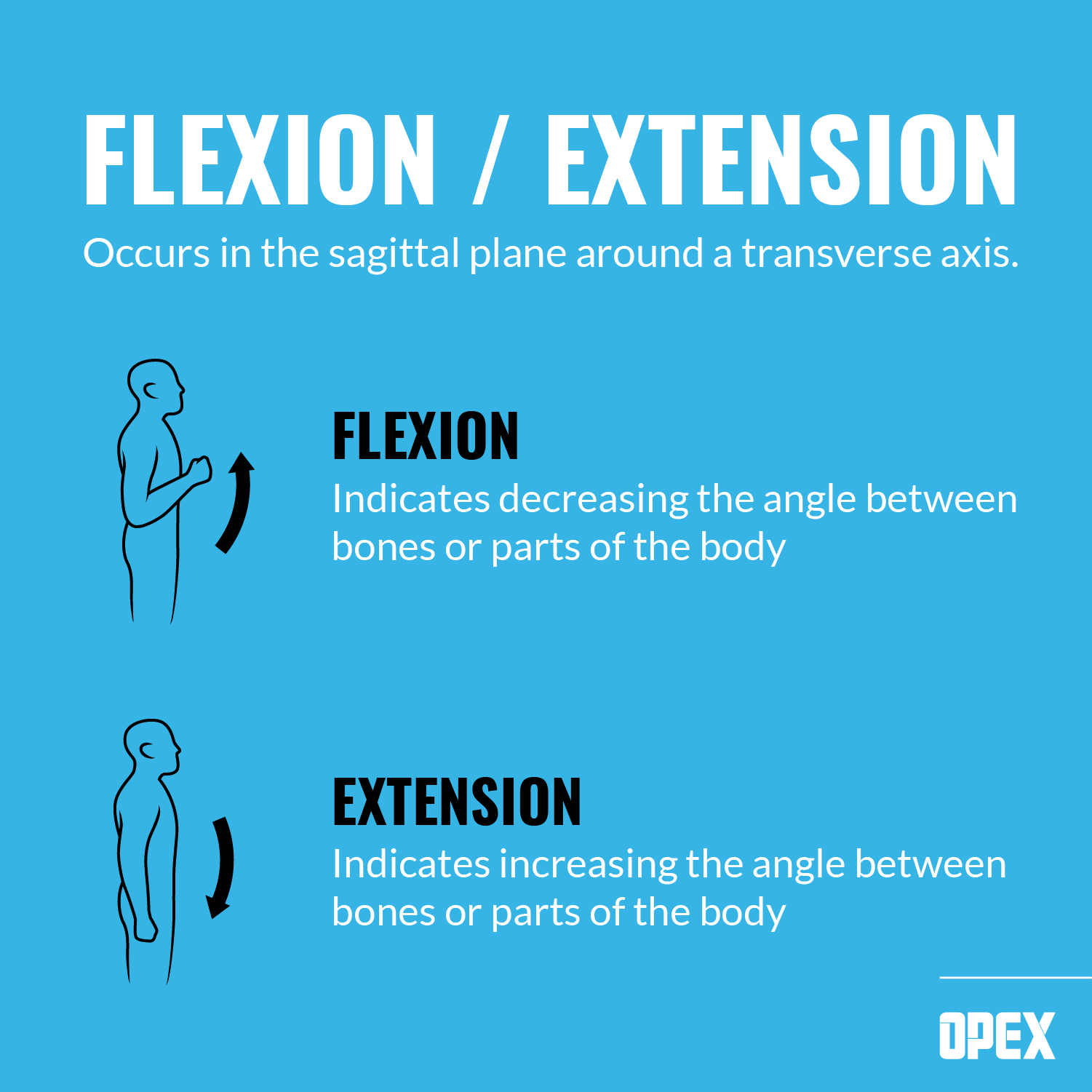
Extension vs flexion
23
New cards
Adduction vs abduction
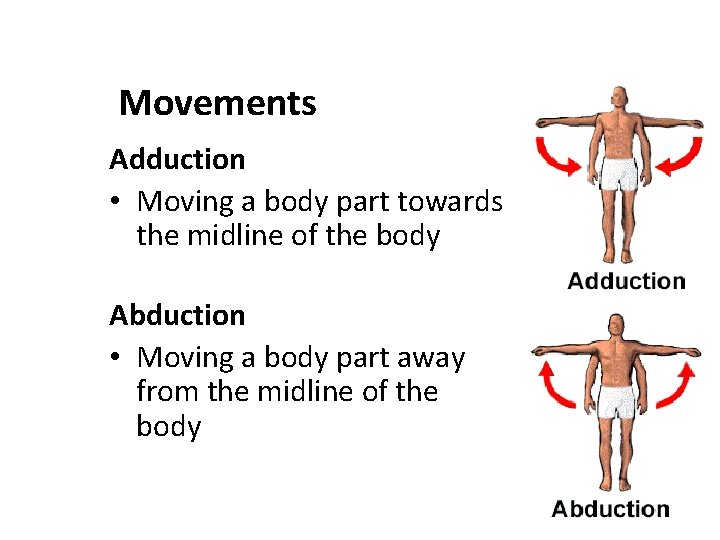
24
New cards
Elevation vs depression
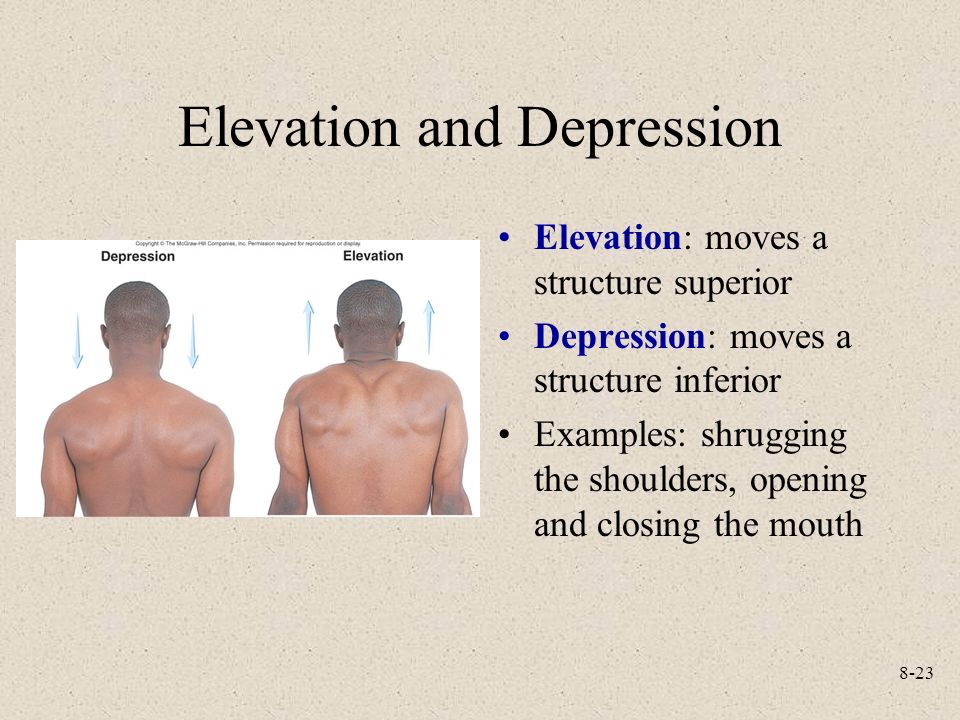
25
New cards
Digestive system
- consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion
1. Complete
2. Incomplete
1. Complete
2. Incomplete
26
New cards
Incomplete digestive system
- trematodes: is a class within the phylum Platyhelminthes. It includes two groups of parasitic flatworms, known as flukes
- digestive cavity with 1 opening only (mouth and anus)
- digestive cavity with 1 opening only (mouth and anus)
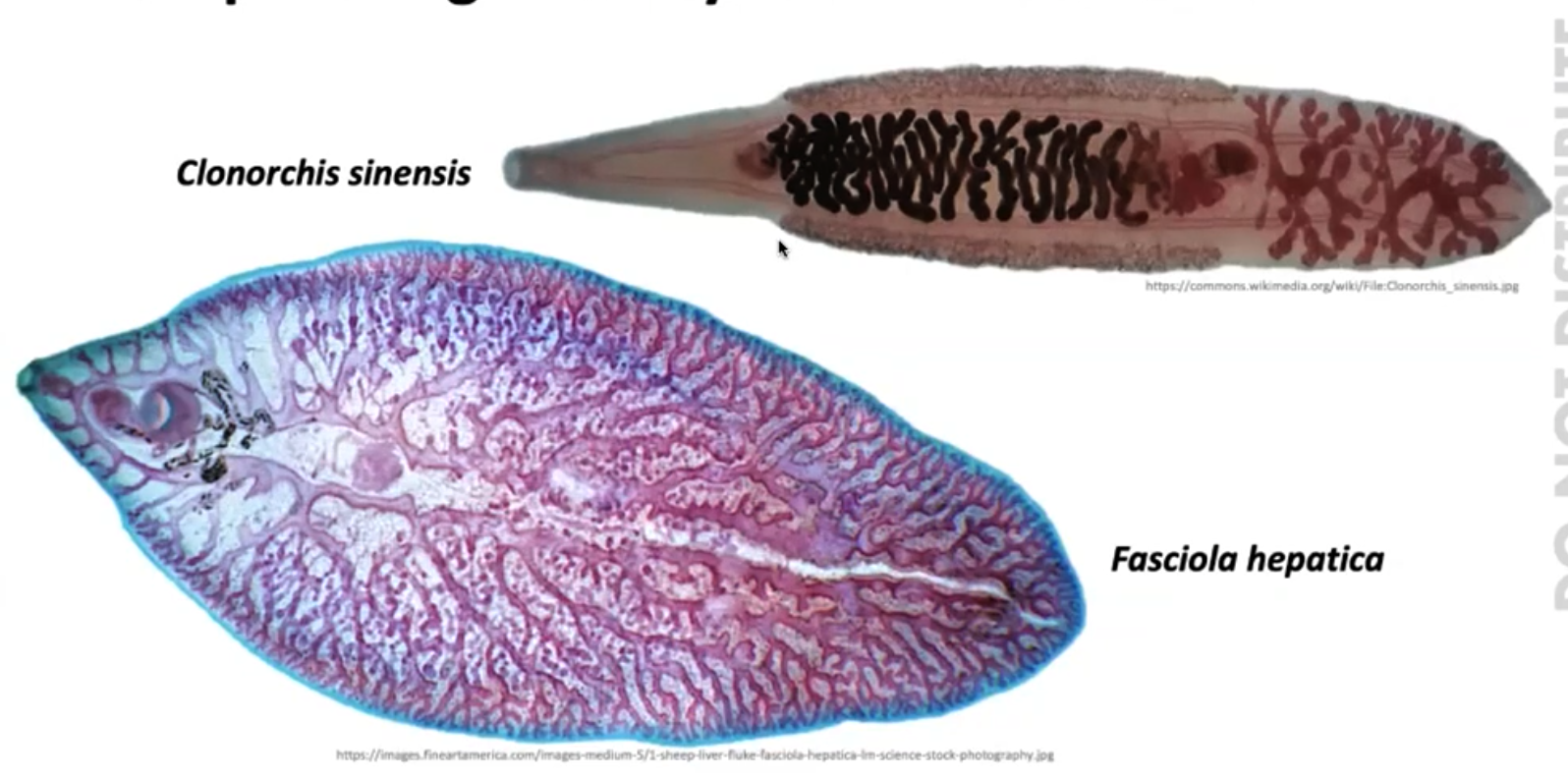
27
New cards
Complete digestive system
- consists of a digestive tract with 2 openings
28
New cards
Insects
Complete digestive system
1. Foregut
2. Midgut
3. Hindgut
1. Foregut
2. Midgut
3. Hindgut

29
New cards
Amphibians
Complete digestive system
1. Buccal cavity
2. Body cavity
1. Buccal cavity
2. Body cavity
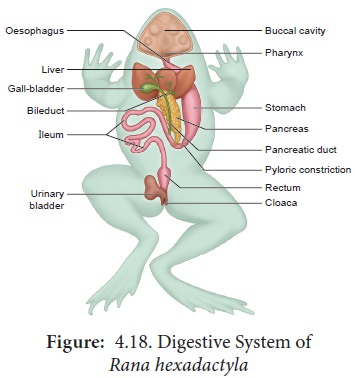
30
New cards
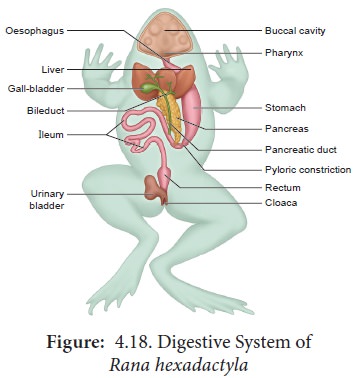
Toad digestive system
1. Esophagus
2. Stomach
3. Small intestine
4. Large intestine
5. Cloaca
2. Stomach
3. Small intestine
4. Large intestine
5. Cloaca
31
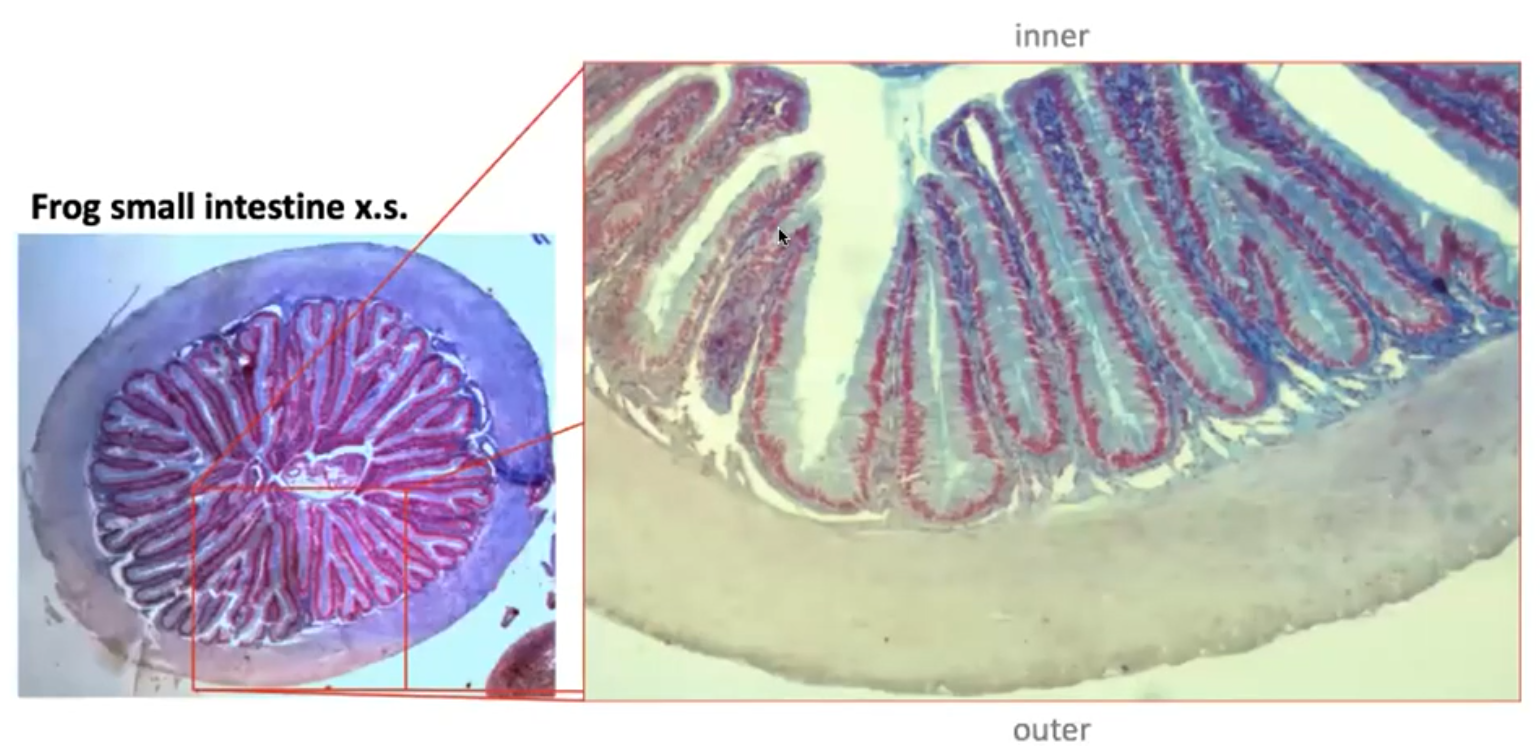
New cards
Frog small intestine
- Villus in inner
32
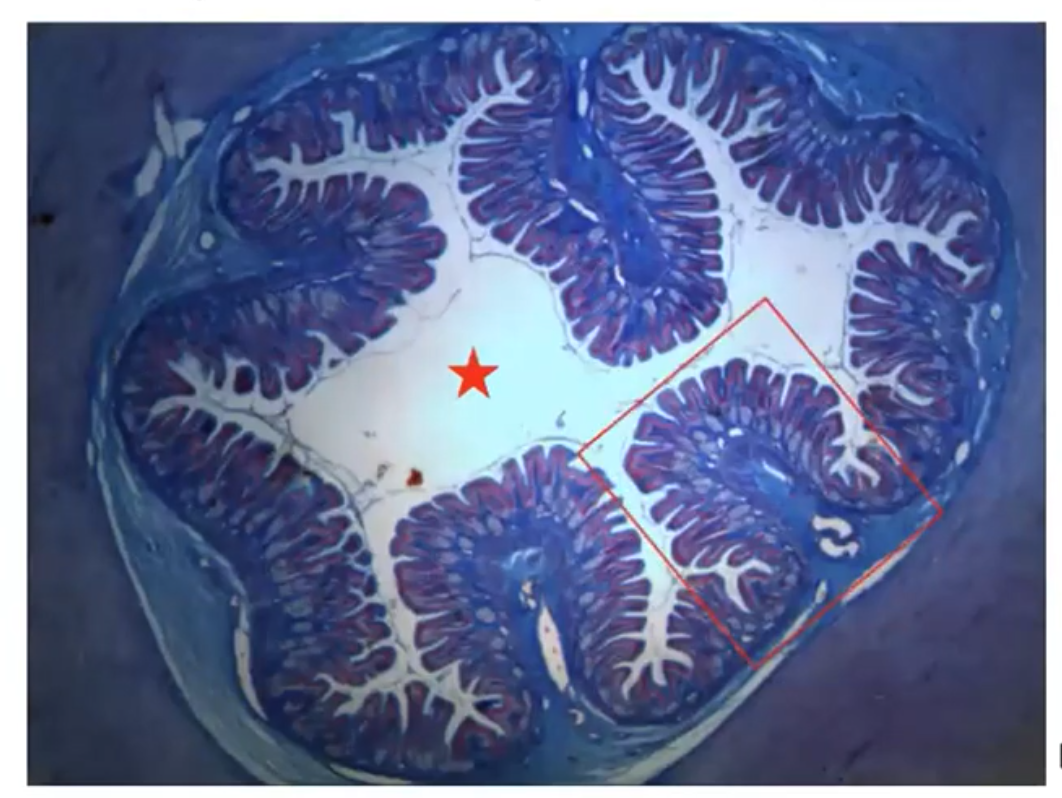
New cards
Frog stomach
- Columnar cells present for better absorption
33
New cards
Respiratory system
the system for taking in oxygen and giving off carbon dioxide; in terrestrial animals this is accomplished by breathing
1. Tracheal system
2. Gill system
3. Lung system
1. Tracheal system
2. Gill system
3. Lung system
34
New cards
Tracheal system
- insects and other invertebrates in phylum arthropoda
- openings in epidermis to allow gas exchange
- openings in epidermis to allow gas exchange
35
New cards
Gill system
- marine organisms
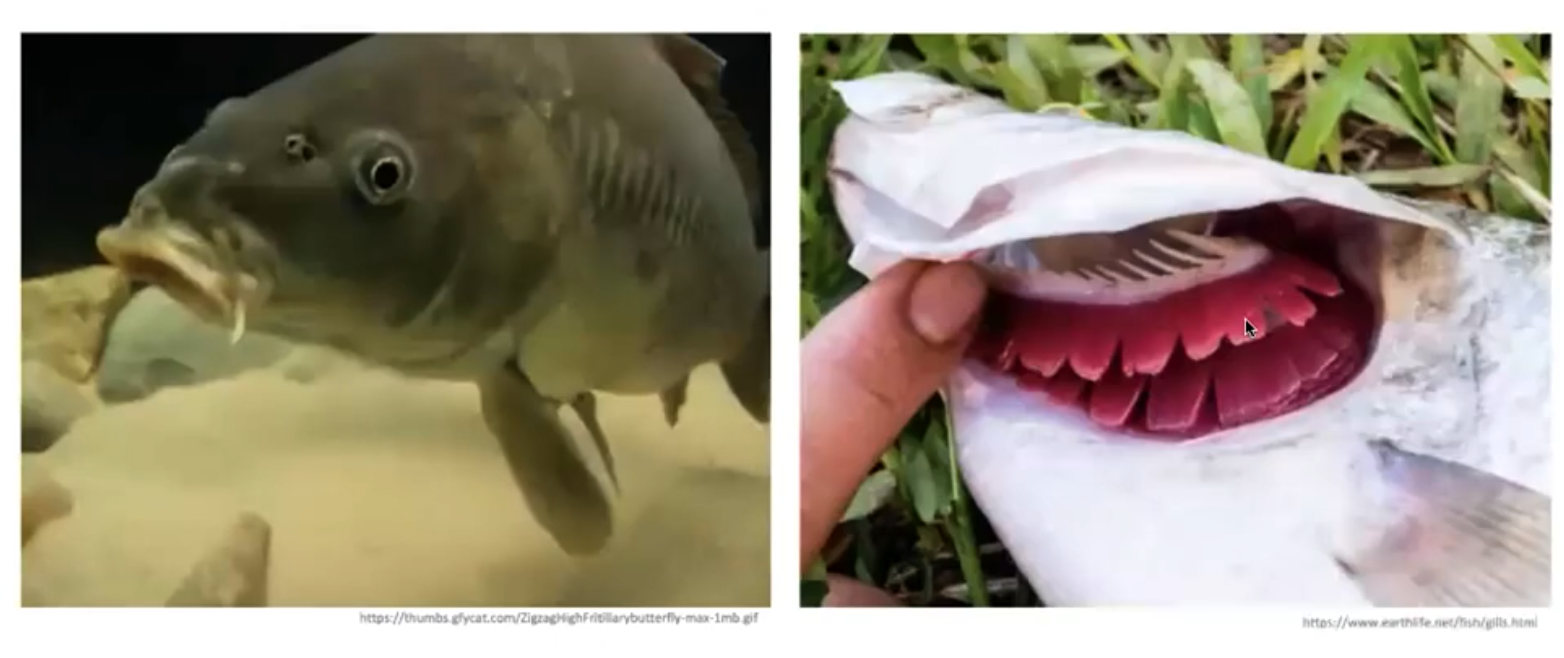

36
New cards
Lung system
- terrestrial organisms

37
New cards
Circulatory system
- is made up of blood vessels that carry blood away from and towards the heart.
1. Open
2. Closed
1. Open
2. Closed
38
New cards
Open circulatory system
- Arthropods, molluscs (except cephalopods)
- No vessels to contain the blood and flows freely through body
- Cockroach
- No vessels to contain the blood and flows freely through body
- Cockroach
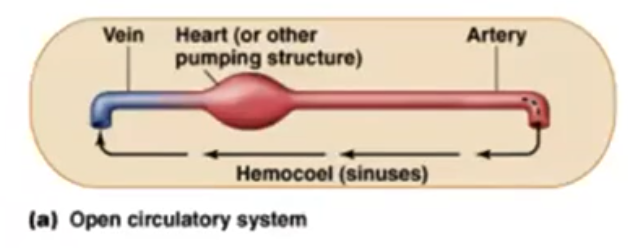
39
New cards
Closed circulatory system
- Arthropods, Cephalopods, Vertebrates
- Blood can flow through vessels inside the body (arteries and veins)
- Humans and toads
- Blood can flow through vessels inside the body (arteries and veins)
- Humans and toads
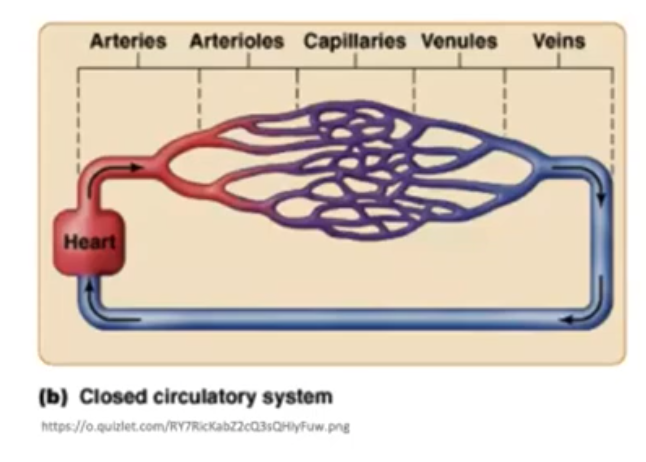
40
New cards
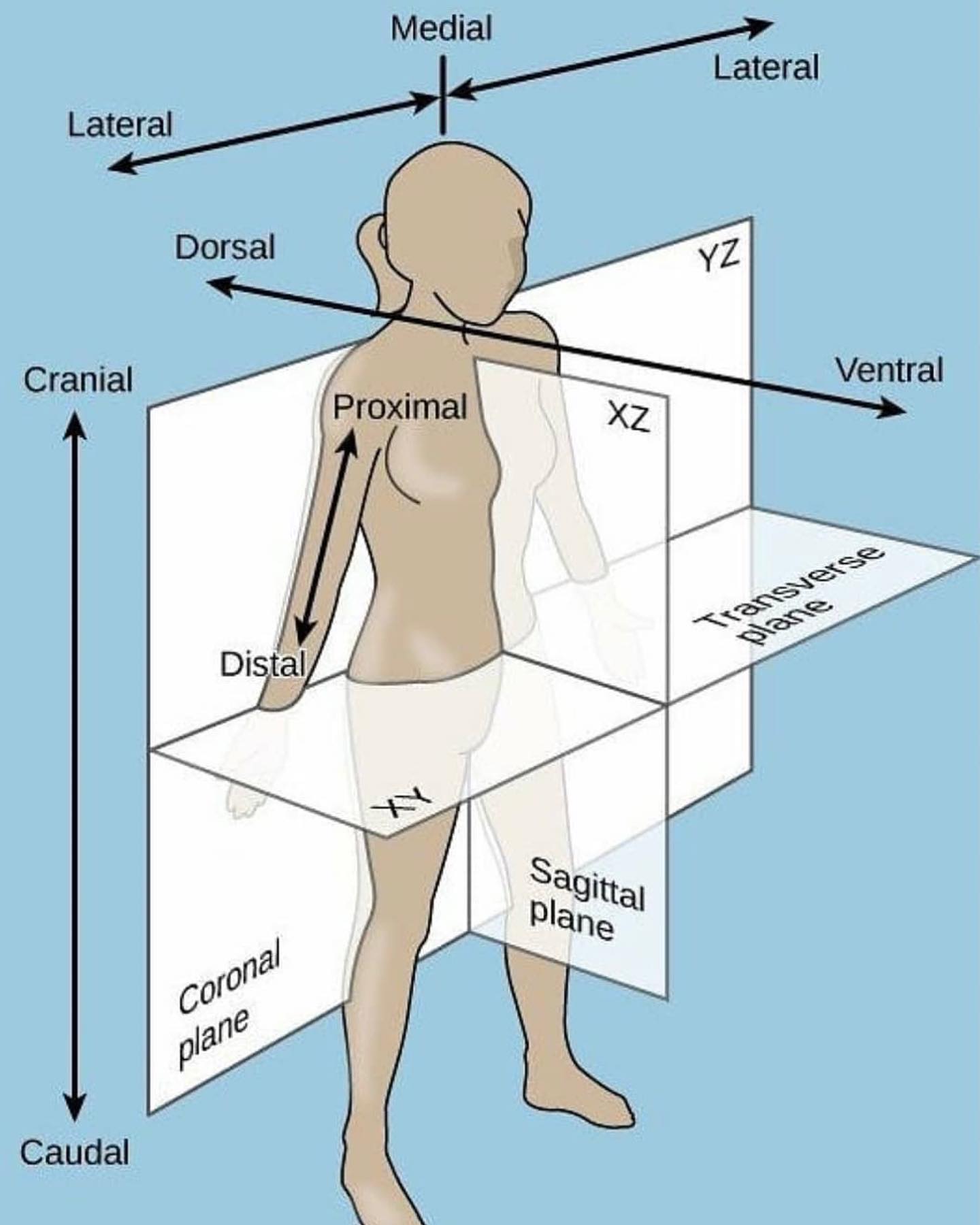
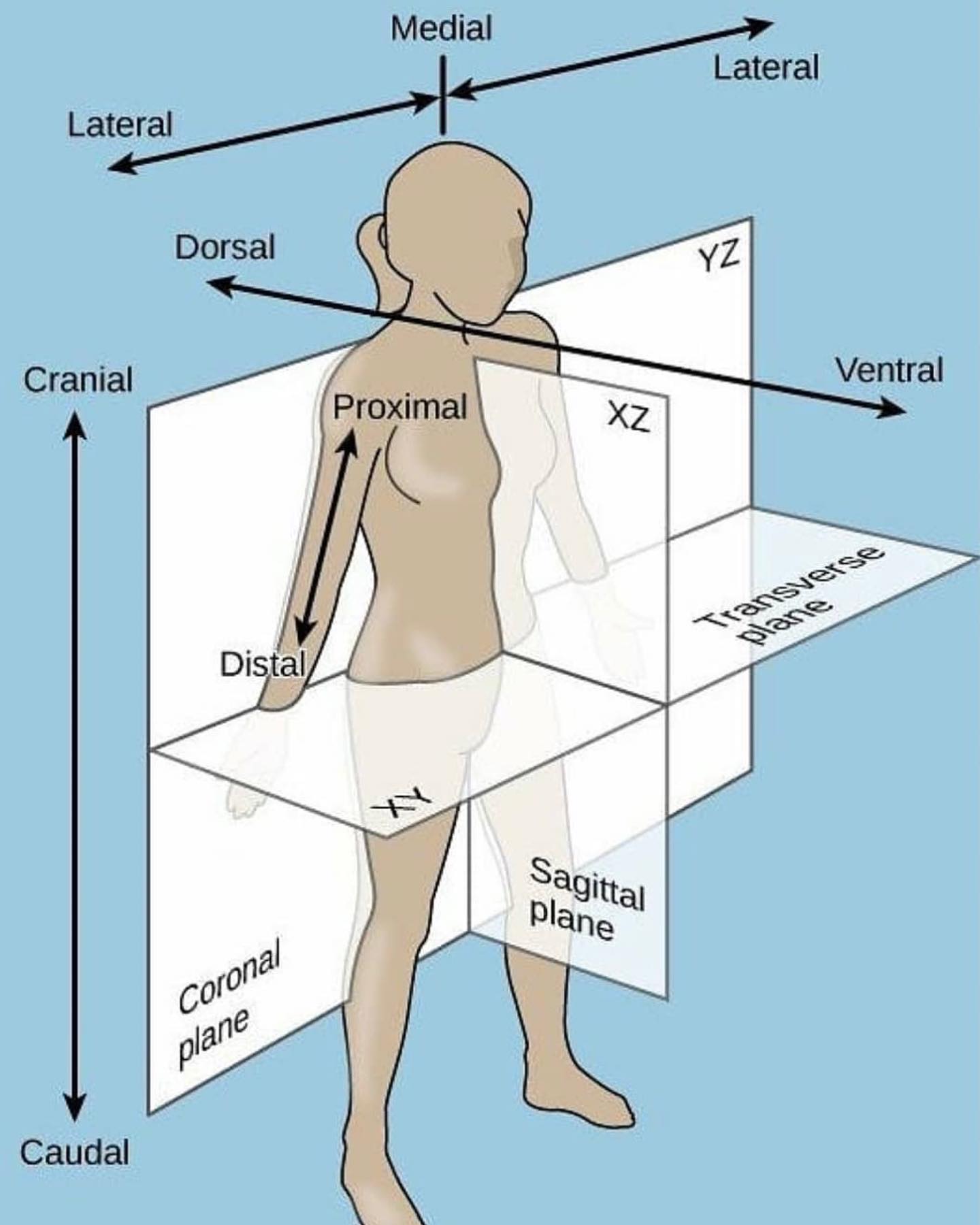
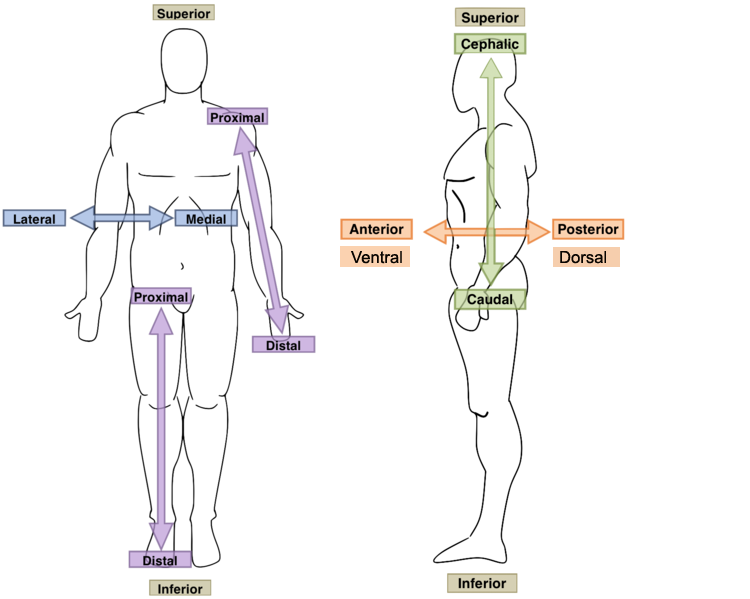
Coronal plane
- Anterior (Ventral)
- Posterior (Dorsal)
- Posterior (Dorsal)
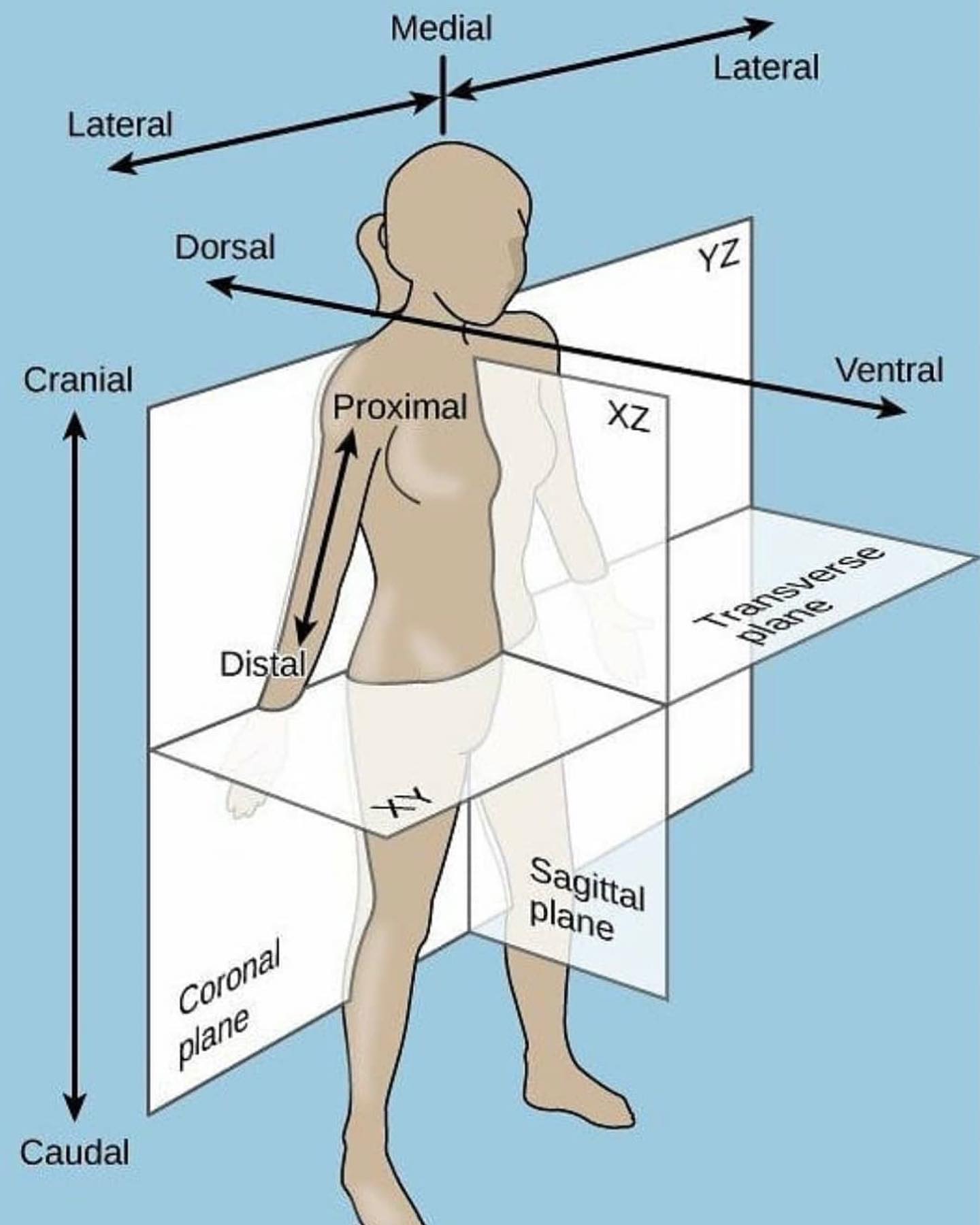
41
New cards
Sagittal plane
- Lateral (Sinister, dexter)
- Medial
- Medial
42
New cards
Transverse plane
- Cranial
- Caudal
- Caudal
43
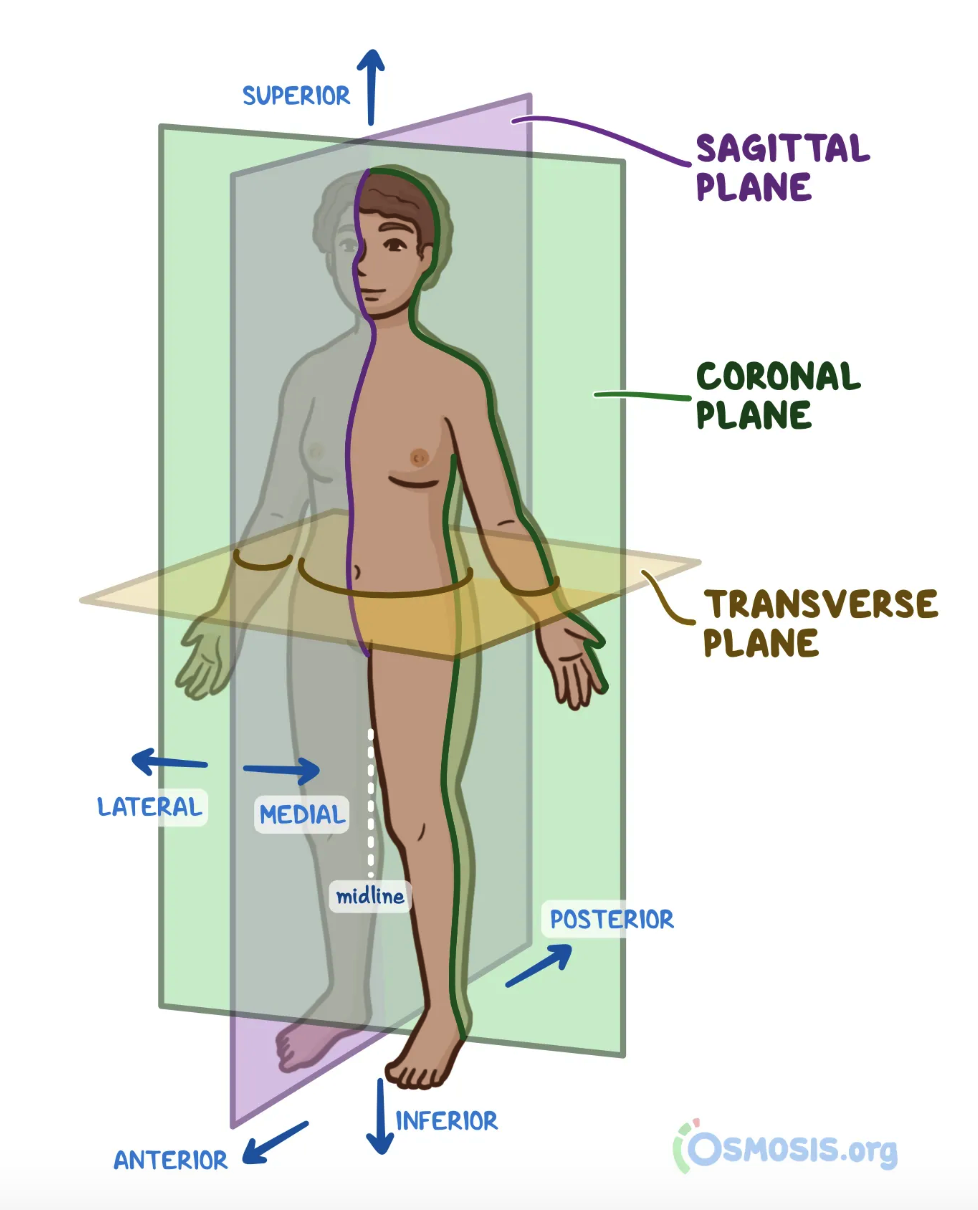
New cards
Anterior
- Toward the front
- nearer the front, especially situated in the front of the body or nearer to the head.
- nearer the front, especially situated in the front of the body or nearer to the head.
44
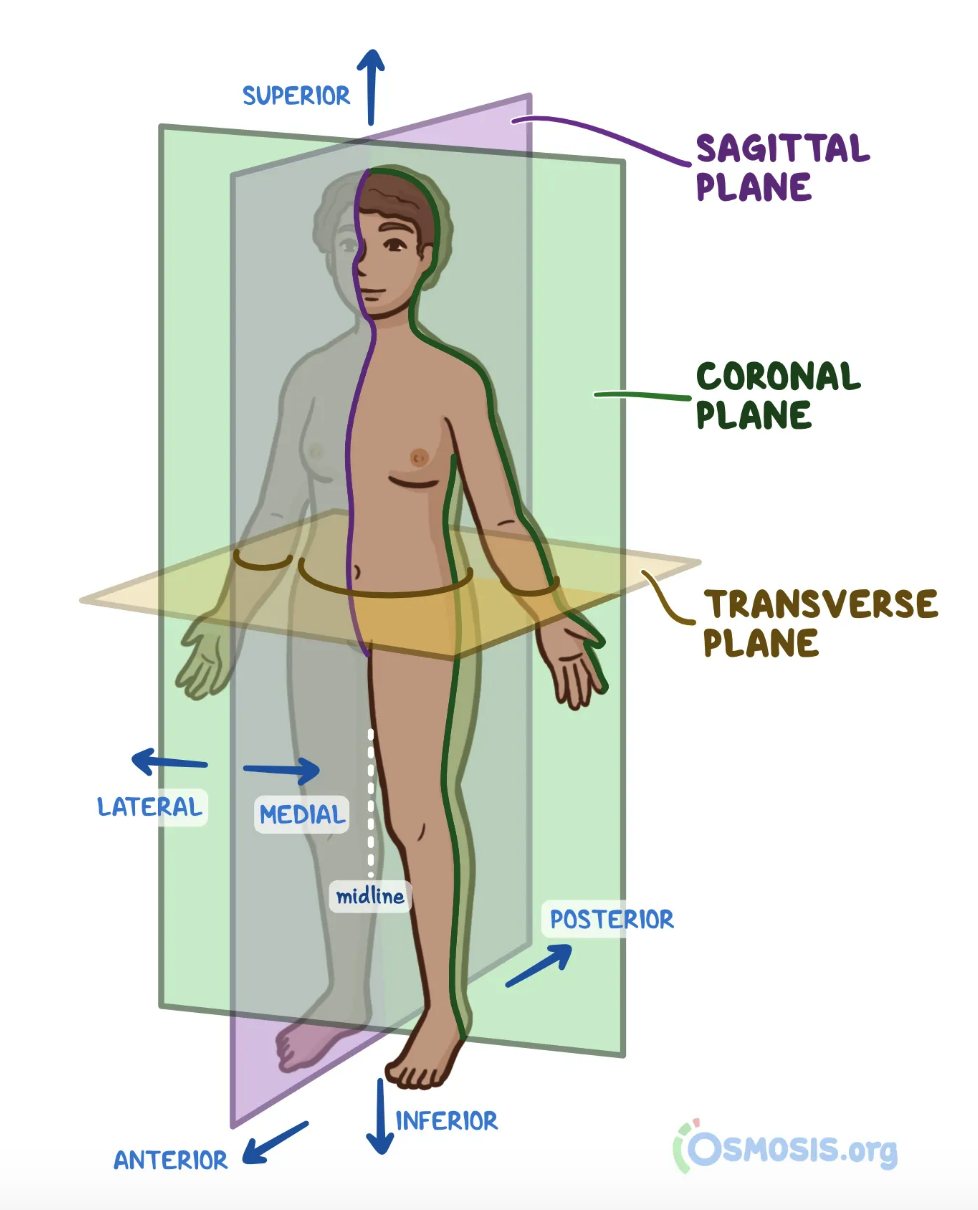
New cards
Posterior
- Toward the back
- further back in position; of or nearer the rear
or hind end, especially of the body or a part of it.
- further back in position; of or nearer the rear
or hind end, especially of the body or a part of it.
45
New cards
Dorsal
- Posterior
- of, on, or relating to the upper side or back of an animal, plant, or organ.
- of, on, or relating to the upper side or back of an animal, plant, or organ.
46
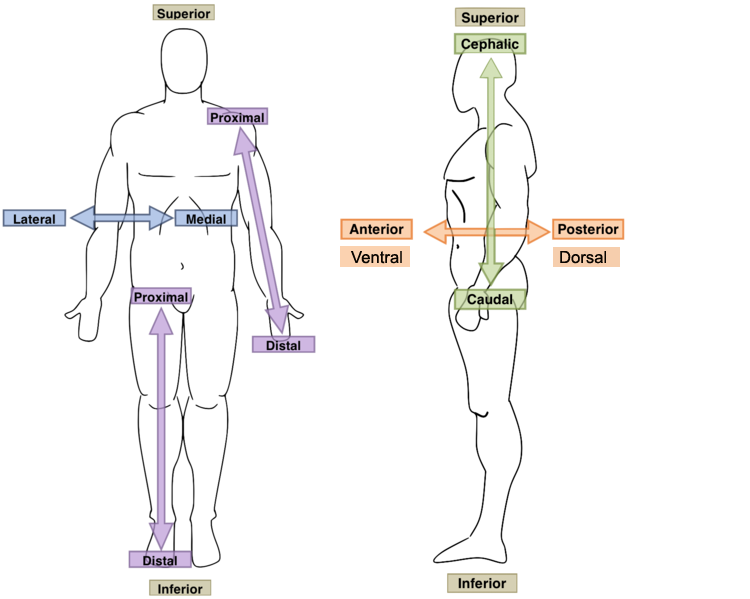
New cards
Ventral
- Anterior
- of, on, or relating to the underside of an animal or plant; abdominal.
- of, on, or relating to the underside of an animal or plant; abdominal.
47
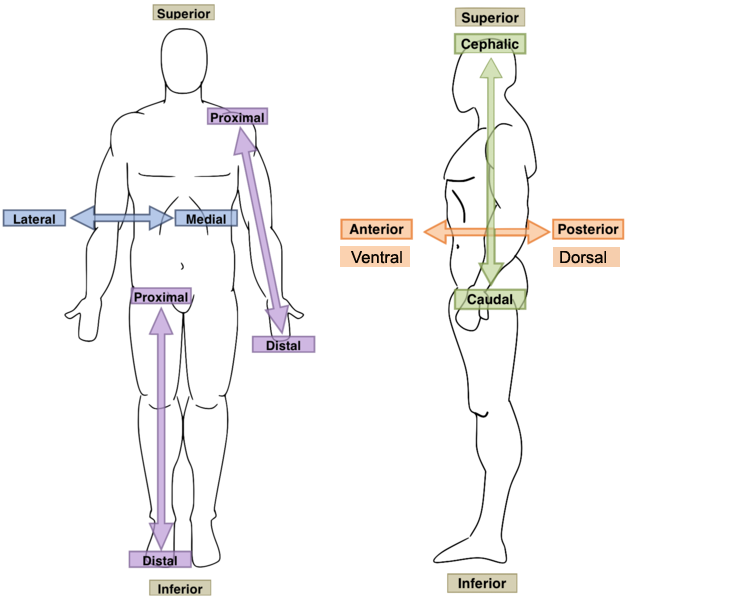
New cards
Proximal
- Toward a reference point (extremity)
- situated nearer to the center of the body or the point of attachment.
- situated nearer to the center of the body or the point of attachment.
48
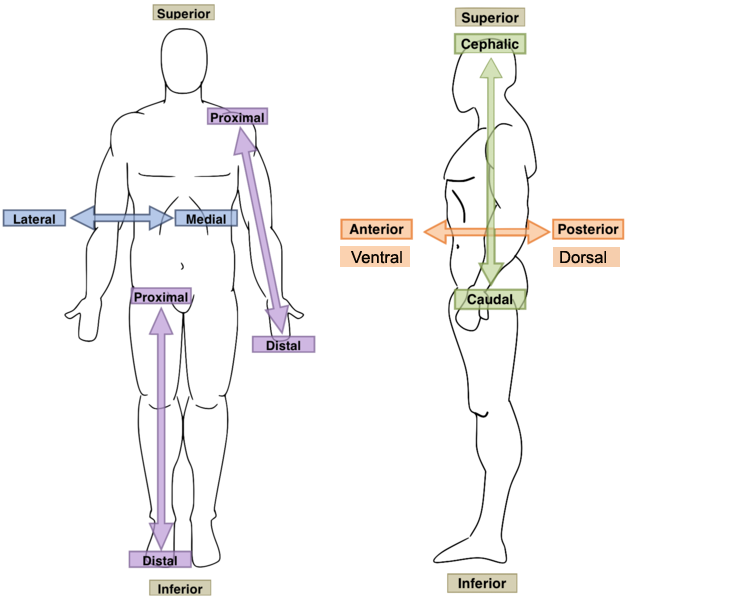
New cards
Distal
- Away from a reference point (extremity)
- situated away from the center of the body or from the point of attachment.
- situated away from the center of the body or from the point of attachment.
49
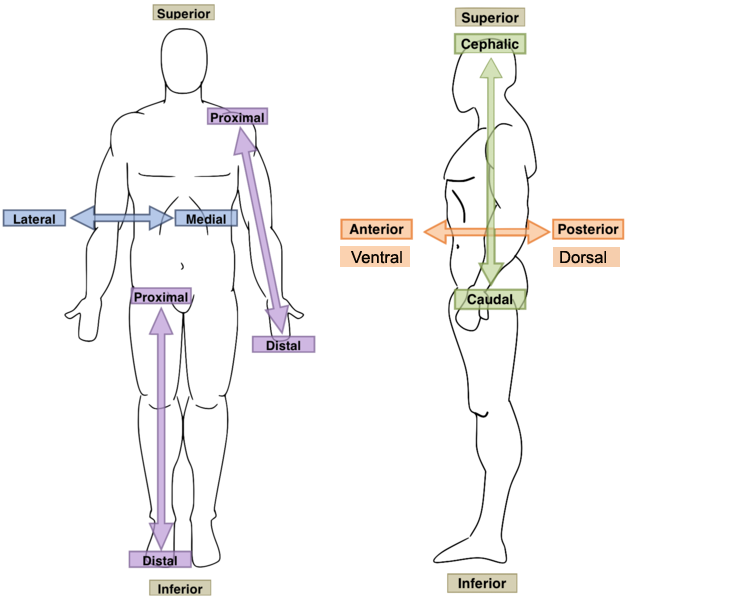
New cards
Cephalad/Cranial
- Head
50
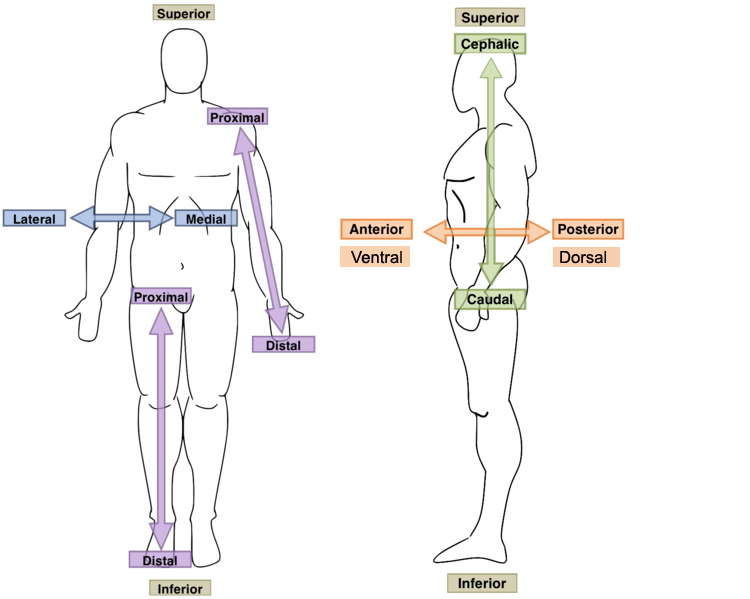
New cards
Caudad
- Tail, tail end
51
New cards
Form
1. Shape
2. Size
3. Surface Area
4. Volume
2. Size
3. Surface Area
4. Volume
52
New cards
Function
1. Locomotion
2. Thermoregulation
3. Substance exchange
4. Navigation
2. Thermoregulation
3. Substance exchange
4. Navigation
53
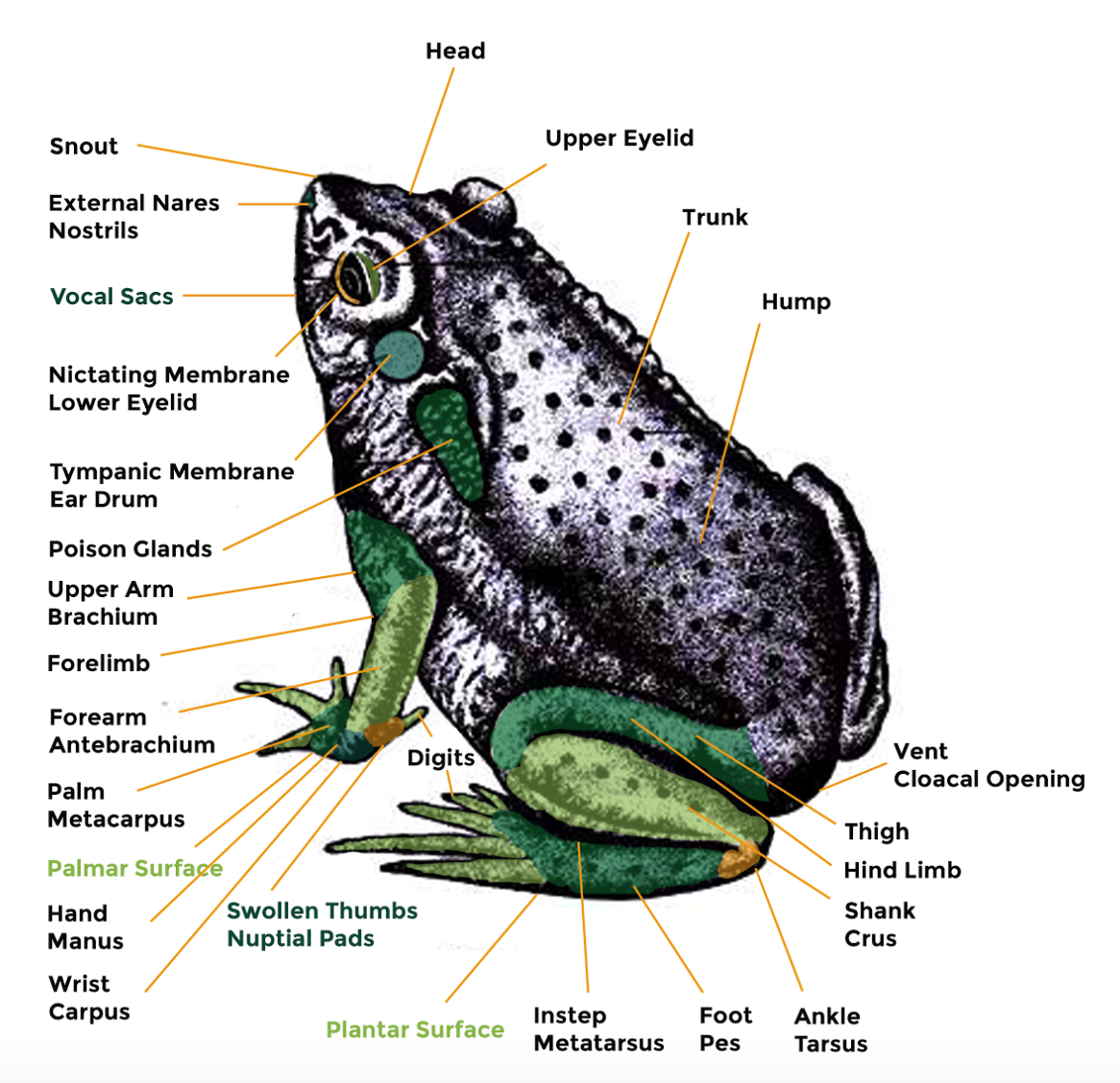
New cards
Male bullfrog external anatomy
54
New cards
moist, darker
Bull frog skin
- Is an amphibian so skin is smooth and _____
- _____ on dorsal side than ventral side
- Countershading
- Is an amphibian so skin is smooth and _____
- _____ on dorsal side than ventral side
- Countershading
55
New cards
Webbing, jump
Bull frog appendages
- 2 forelegs (4 toes), 2 hindlegs (5 toes)
- _____ between toes helps it swim through water
- Longer hind legs help it ____ on land
- 2 forelegs (4 toes), 2 hindlegs (5 toes)
- _____ between toes helps it swim through water
- Longer hind legs help it ____ on land
56
New cards
larger, nuptial, male
Frog sex
- Females (at least 7 in/18cm) are ____ than males
- Measured from head to backbone
- Enlarged thumb (_______ pad) in males and slender in females
- Only ____ frogs have sound producing vocal sacs
- Females (at least 7 in/18cm) are ____ than males
- Measured from head to backbone
- Enlarged thumb (_______ pad) in males and slender in females
- Only ____ frogs have sound producing vocal sacs

57
New cards
nares, 3
Bull frog nares and eyes
- External _____ are anterior to eyes
- Has 2 large bulging eyes each with ___ eyelids:
a. open and close for land
b. transparent membrane for swimming underwater (becomes cloudy)
- External _____ are anterior to eyes
- Has 2 large bulging eyes each with ___ eyelids:
a. open and close for land
b. transparent membrane for swimming underwater (becomes cloudy)
58
New cards
tympanic
Bullfrog hearing
- 2 ________ membranes (similar to human eardrum)
- Are larger in males (bigger than eyes) than in females (same size as eyes)
- 2 ________ membranes (similar to human eardrum)
- Are larger in males (bigger than eyes) than in females (same size as eyes)
59
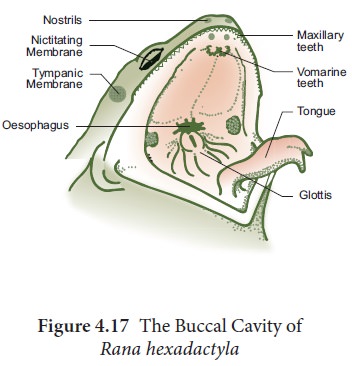
New cards
internal, Eustachian, esophagus, glottis
Bullfrog mouth
- Cut corners of the mouth to loosen the jaw
- Tongue is split in the middle and is attached towards the front of the mouth
- Nares open into the mouth cavity at the ________ nares
- Tiny teeth at the edge of the upper jaw for holding prey and near the internal nares
- ___________ tubes equalize pressure in the frog's ears while it is swimming
- _________ between tubes, leading mouth to stomach
- ____, below the mouth and opening of the trachea (epiglottis closes trachea when swallowing)
- Cut corners of the mouth to loosen the jaw
- Tongue is split in the middle and is attached towards the front of the mouth
- Nares open into the mouth cavity at the ________ nares
- Tiny teeth at the edge of the upper jaw for holding prey and near the internal nares
- ___________ tubes equalize pressure in the frog's ears while it is swimming
- _________ between tubes, leading mouth to stomach
- ____, below the mouth and opening of the trachea (epiglottis closes trachea when swallowing)
60
New cards
Parotid gland
- This gland contains bufotoxin, which is a neurotoxin. Be careful not to touch the excretions!
61
New cards
Hindlimb
- Each hind-limb consists of a thigh or femur, a shank or crus and a foot. While at rest most of the body weight is also displaced towards the hind limbs.
- This elongated hindlimb is responsible for the saltatory movement of toads.
- This elongated hindlimb is responsible for the saltatory movement of toads.
62
New cards
Pes
- The scientific term for the instep or the middle portion where the digits (toes) in the hindlimb are attached.
63
New cards
Tympanic membrane
- It functions much like our eardrum does –the tympanum transmits sound waves to the middle and inner ear, allowing a frog to hear both in the air and below water.
64
New cards
Forelimb
- They provide body support during sitting or walking, and absorbs impact forces during landing.
65
New cards
Nares
- Nares are another word for nostrils. - Toads have two types of nares: external and internal.
- These two types of nostrils work together to provide oxygen. In addition to nares, they can also breathe through their skin.
- These two types of nostrils work together to provide oxygen. In addition to nares, they can also breathe through their skin.
66
New cards
Eyes
- Unlike humans, toads do not have involuntary saccadic eye movements and they also cannot perform "tracking eye movements".
- The lack of saccadic eye movements forces the toad to hold its eyes in rigid positions.
- Therefore, it must decide whether the object is "prey" or "non-prey" before moving itself.
- The lack of saccadic eye movements forces the toad to hold its eyes in rigid positions.
- Therefore, it must decide whether the object is "prey" or "non-prey" before moving itself.
67
New cards
Digits
- The thumb of the male toad is larger than the female.
- This feature is because of nuptial pads, which help the male toads to cling on the back of the female toad during amplexus.
- This feature is because of nuptial pads, which help the male toads to cling on the back of the female toad during amplexus.
68
New cards
Manus
- The manus refers to the hands which is includes the wrist (carpus) or the portion next to the forearm, the palm or the broad middle portion, and the digits or fingers.
69
New cards
Dorsal
pertains to the back surface of the toad

70
New cards
Ventral
refers to the abdominal side of the toad

71
New cards
Lateral
is the side view of the toad.

72
New cards
Anterior
is towards the head part (cranial) of the toad
73
New cards
Posterior
is towards the tail part (caudal).
74
New cards
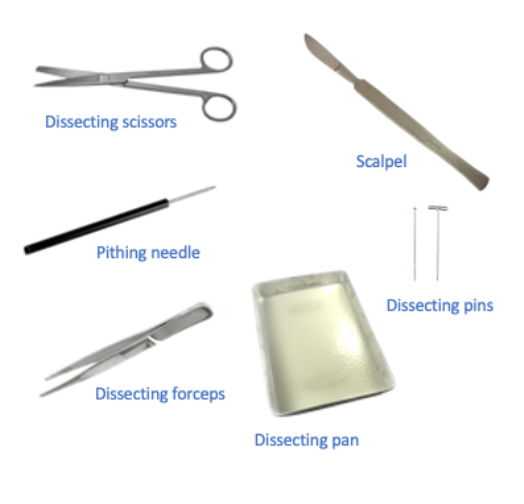
Dissecting tools

75
New cards
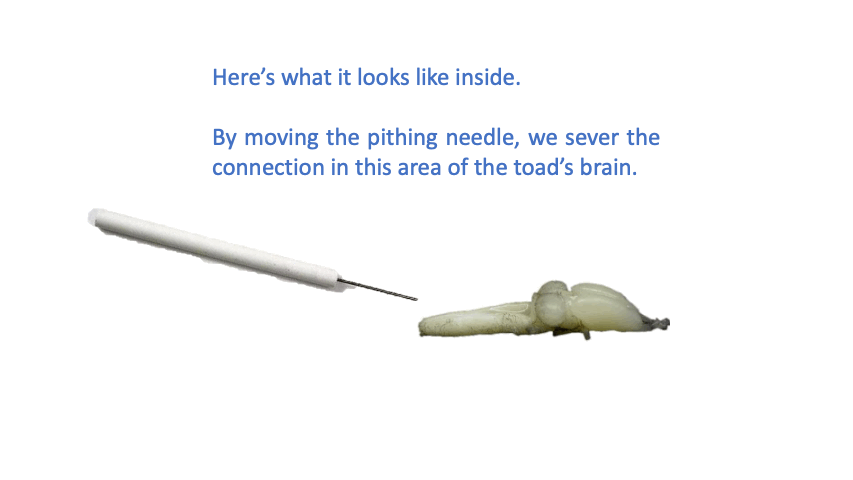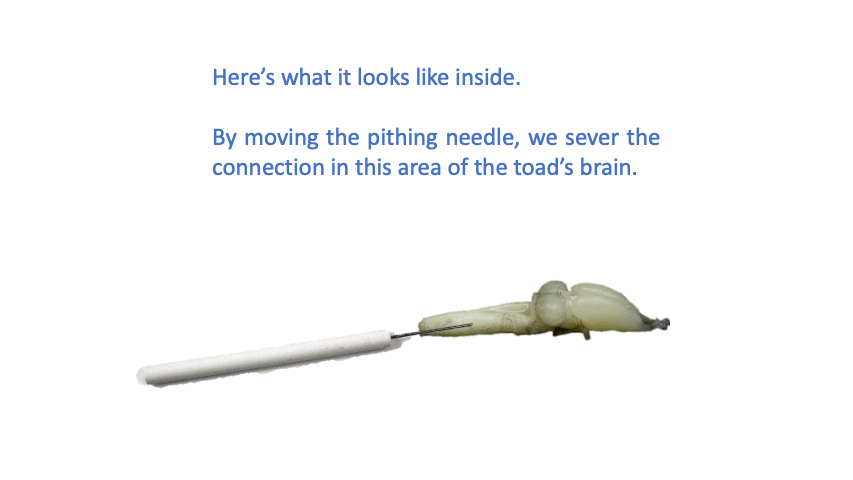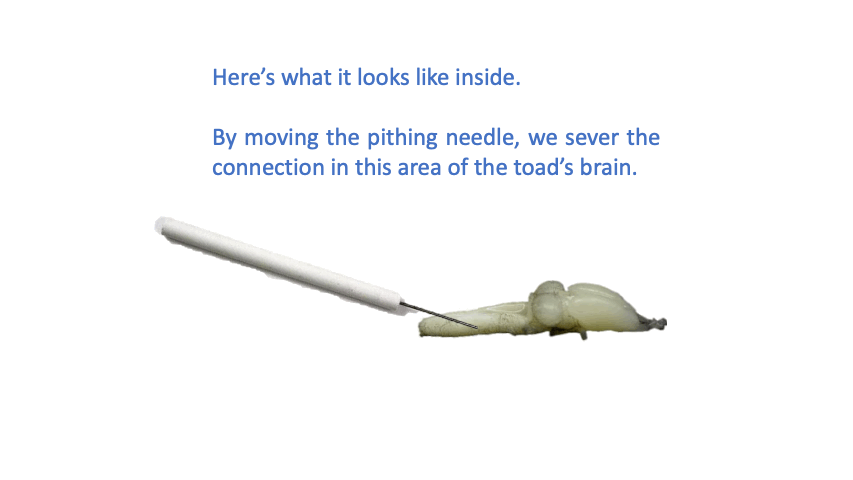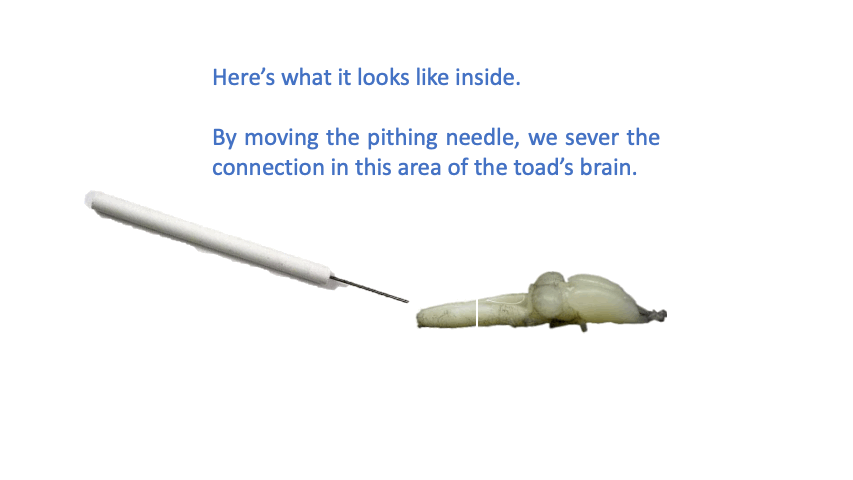
Pithing needle
- used to sever the connection between the brain and the spinal cord

76
New cards
Pithing
- term used in immobilizing the toad by severing the spinal cord
- we damage its spinal cord so that all sensory signals from the body will not be received and processed by the brain
- toad is still alive and breathing through its skin
- we damage its spinal cord so that all sensory signals from the body will not be received and processed by the brain
- toad is still alive and breathing through its skin
77
New cards
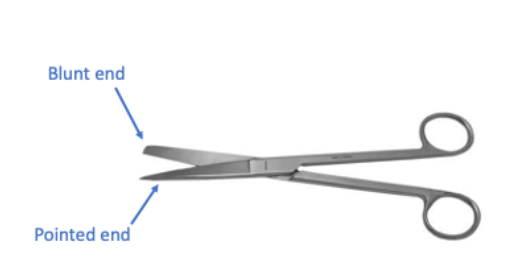
Dissecting scissors
- blunt end on top and pointed end at the bottom
78
New cards
Scalpel
- cut different parts of the body such as skin and muscle

79
New cards
Dissecting forceps
- helpful to grasp tissues and expose a particular area when cutting, mainly to prevent cutting ourselves

80
New cards
Dissecting pan
- aluminum tray filled with wax
- along with pins, used to stabilize the toad especially when observing its internal organs
- along with pins, used to stabilize the toad especially when observing its internal organs

81
New cards
Dorsal
- the great foramen is more accessible on the ______ side of the toad.
- this is where you are going to pith the toad
- this is where you are going to pith the toad

82
New cards
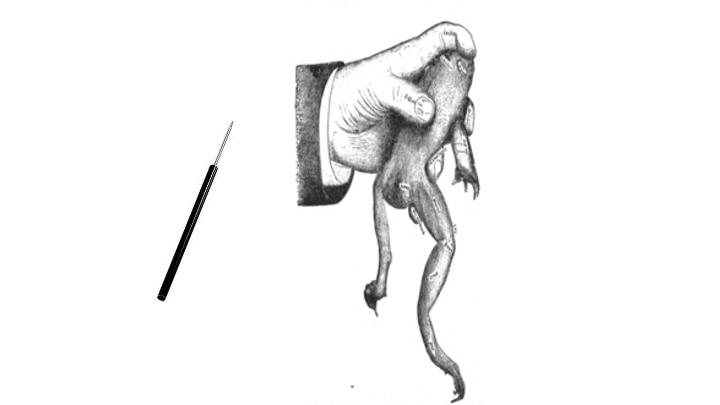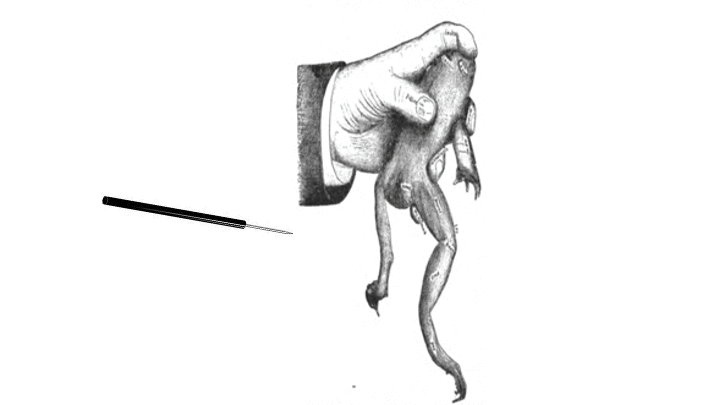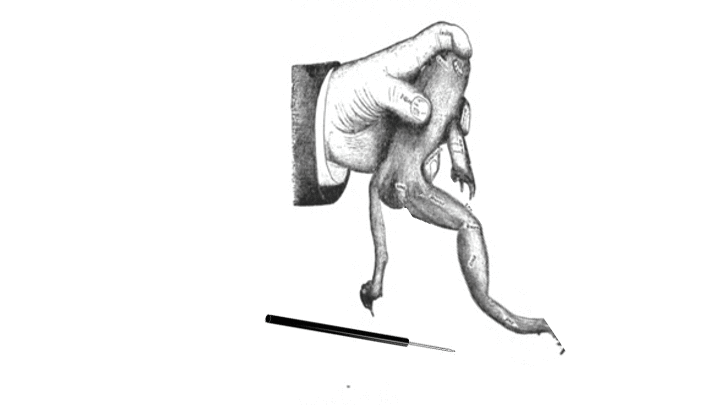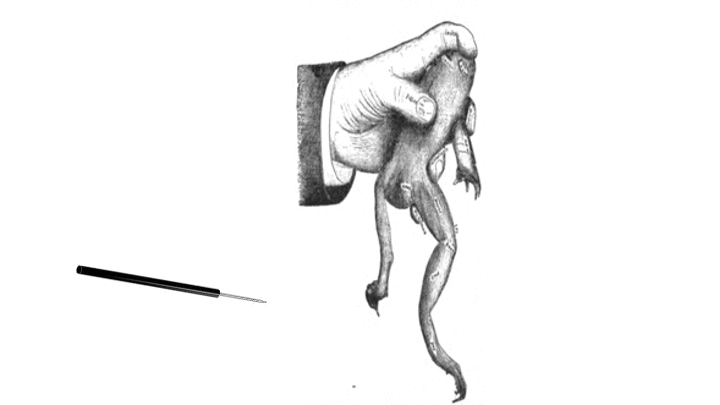
shank
- Poke the toad's _____ using the pithing needle to check if it demonstrates leg jerking
- pith the toad until the leg stops jerking
- pith the toad until the leg stops jerking
83
New cards
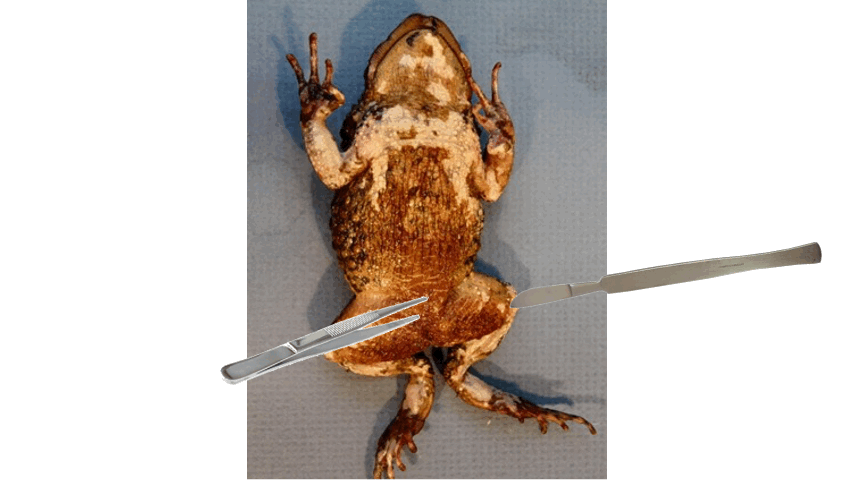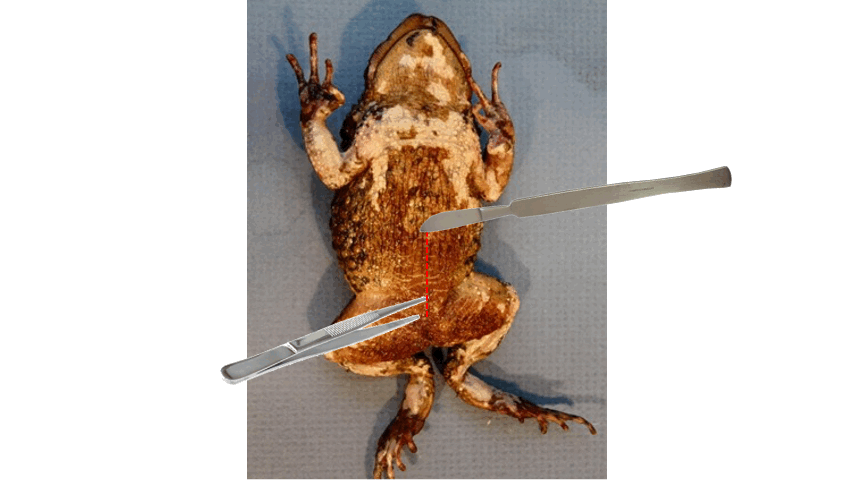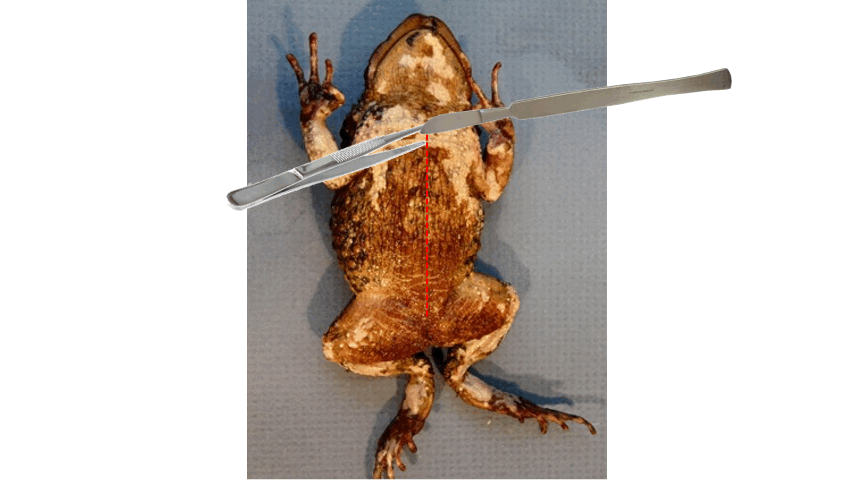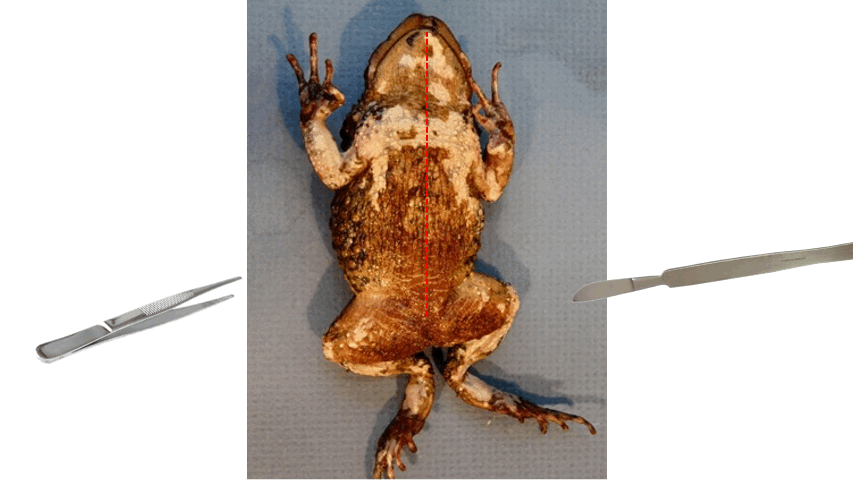
Ventral, posterior
- the best side to start skinning the toad is the ______ side
- typically loose skin is found on this side
- use scissors and scalpel to cut the skin, and forceps in grasping the skin
- point the scalpel upwards and cut from ________ to anterior end
- typically loose skin is found on this side
- use scissors and scalpel to cut the skin, and forceps in grasping the skin
- point the scalpel upwards and cut from ________ to anterior end
84
New cards
distal
- After cutting the toad's skin midsaggitally, extend the incision towards the ____ end of the three points, as shown in the figure below.
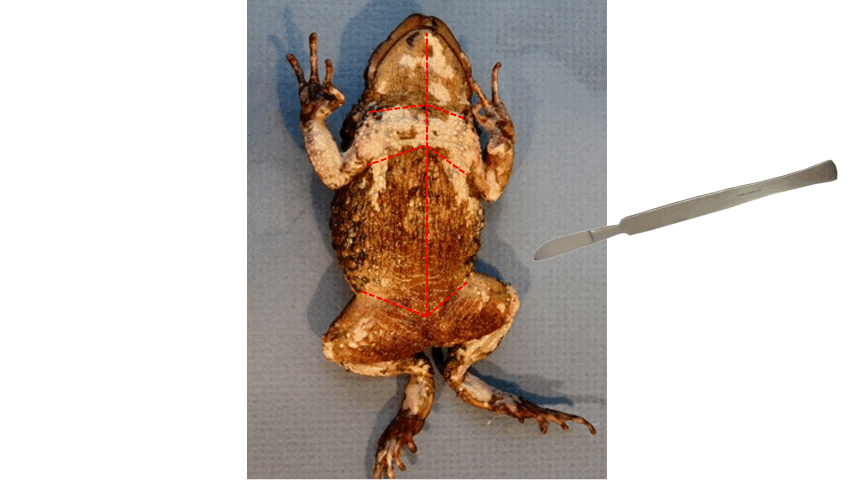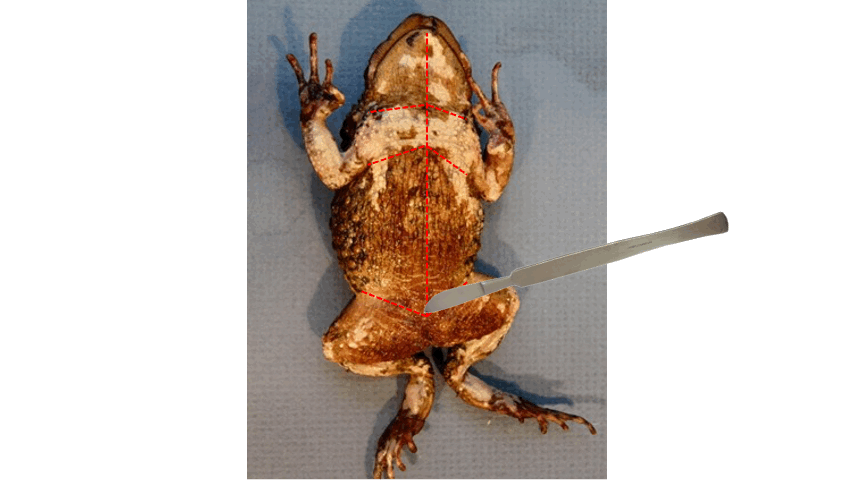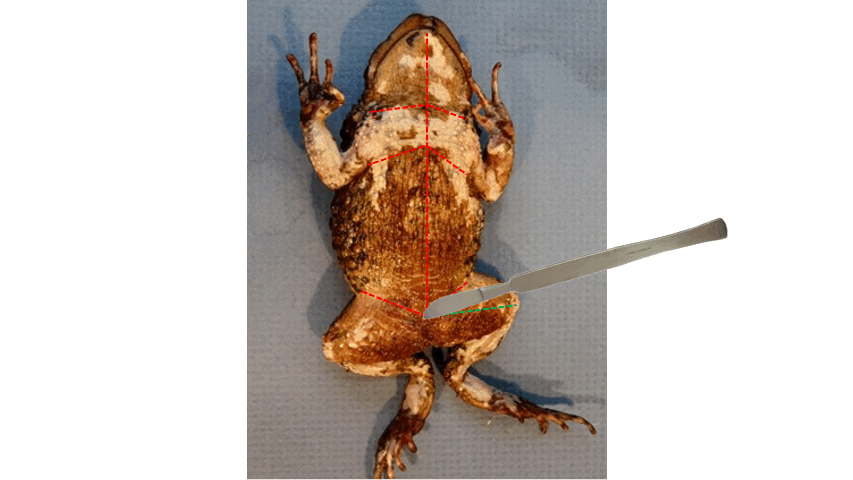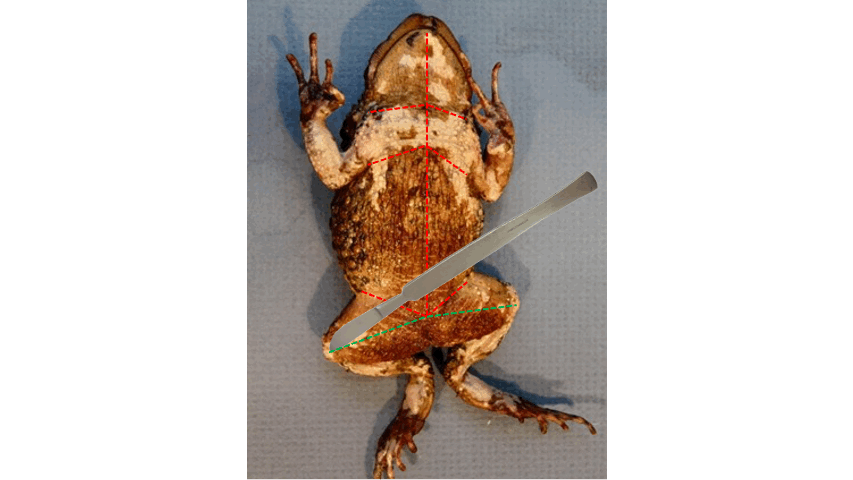
85
New cards
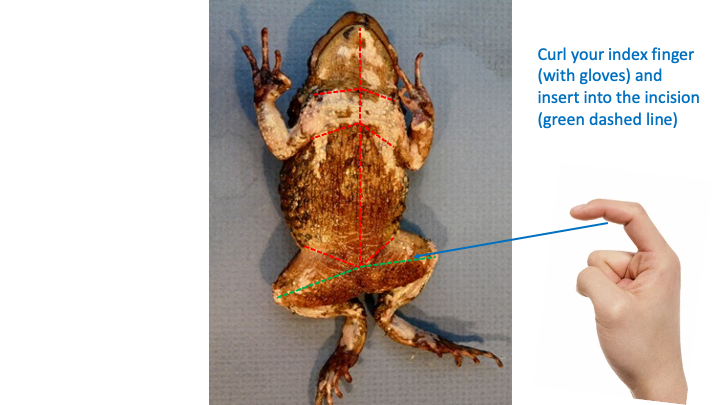
fingers
- separate the thigh skin using your ______.
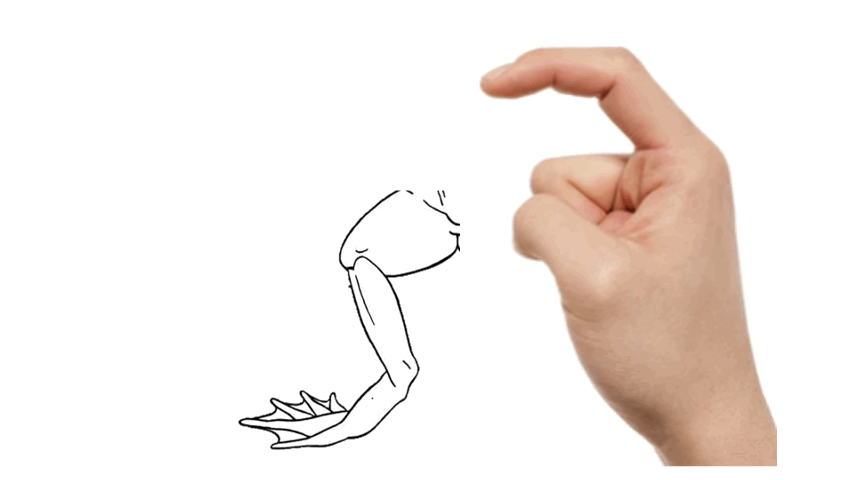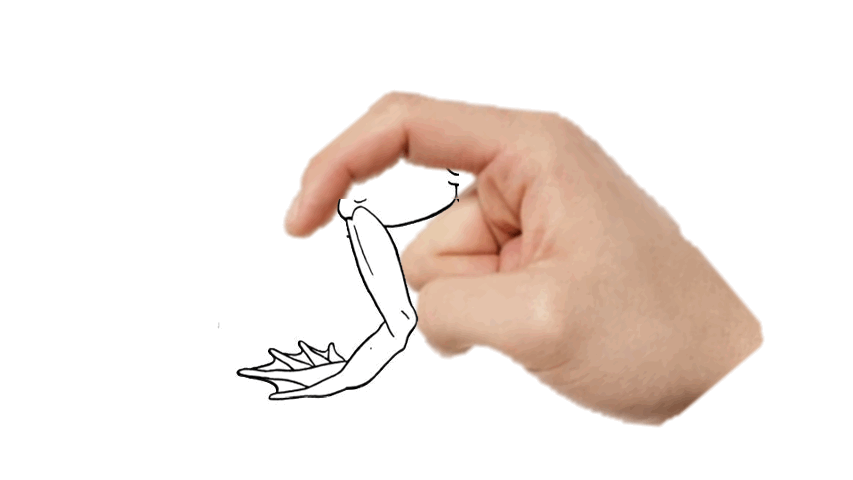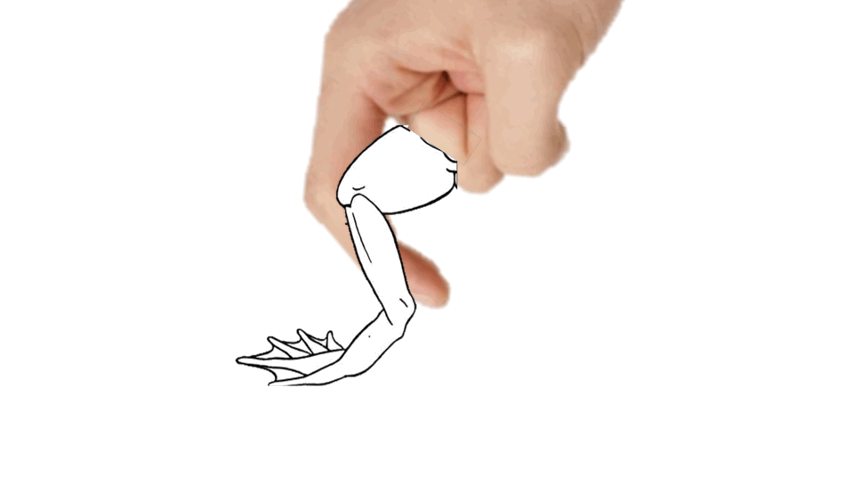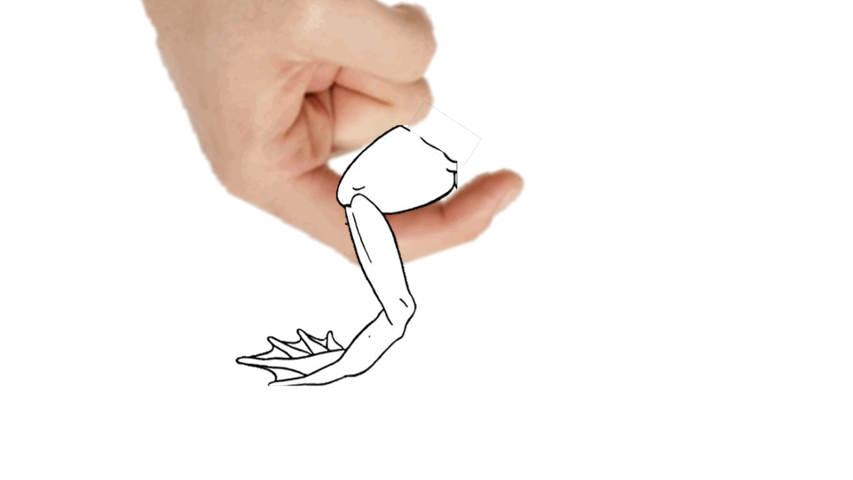
86
New cards
digits
- After pulling out the thigh from the skin, you can now simply remove the shank's skin by pulling it down towards the _____. This illustration is like pulling off your sock from your foot.

87
New cards
abdomen, attached
- To remove the skin on the _________ and lower jaw, simply flip the skin we cut awhile ago and use your scalpel or scissors to completely remove the skin on the throat and upper torso of the toad, as shown in the animation below.
- Keep the skin on the abdomen _______ to easily pull the skin when we deal with the backside of the toad.
- Keep the skin on the abdomen _______ to easily pull the skin when we deal with the backside of the toad.
88
New cards
Dorsal
- When dealing with the backside of the toad, in what view are we looking at the toad?
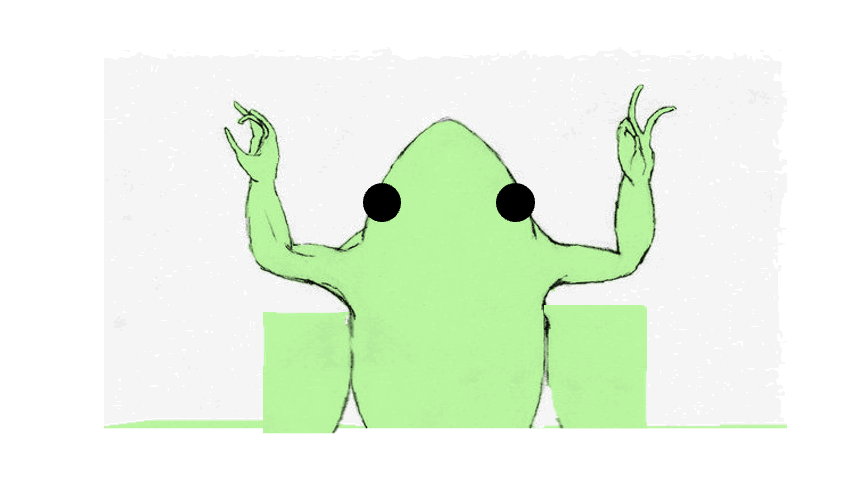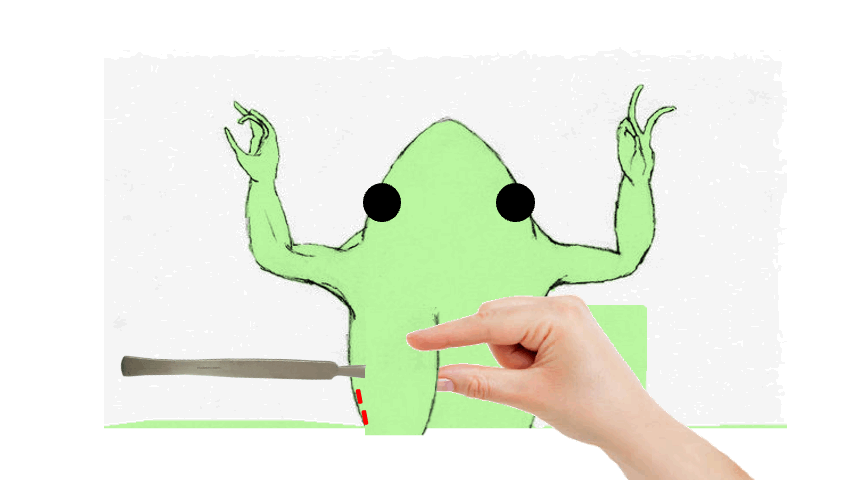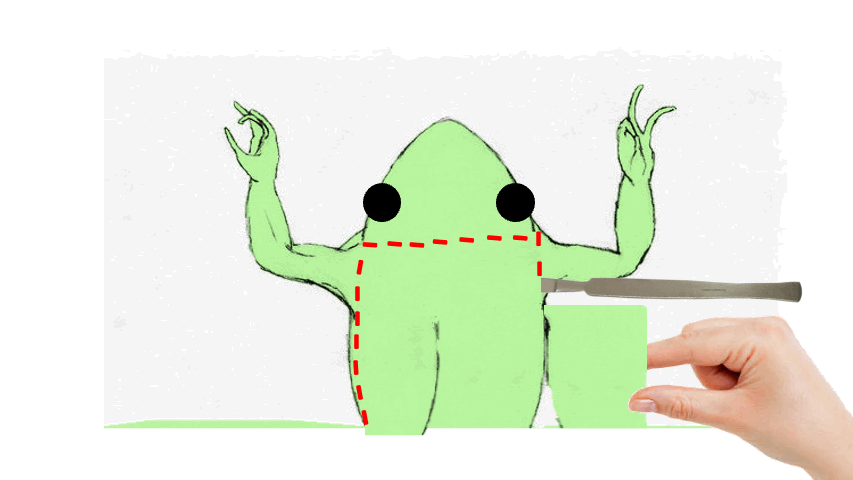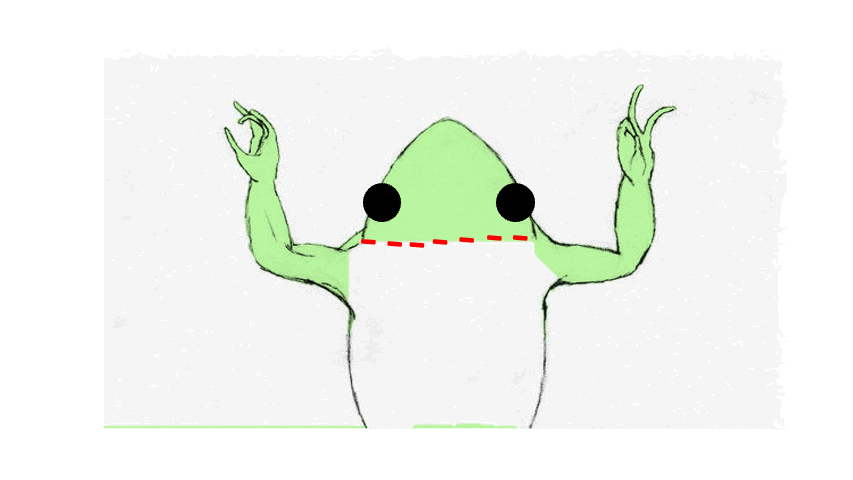
89
New cards
gloves
- Removing the skin on the upper limbs is similar with the lower limbs. We have to think that we are just pulling of a satin _____ from the toad's limbs.
90
New cards
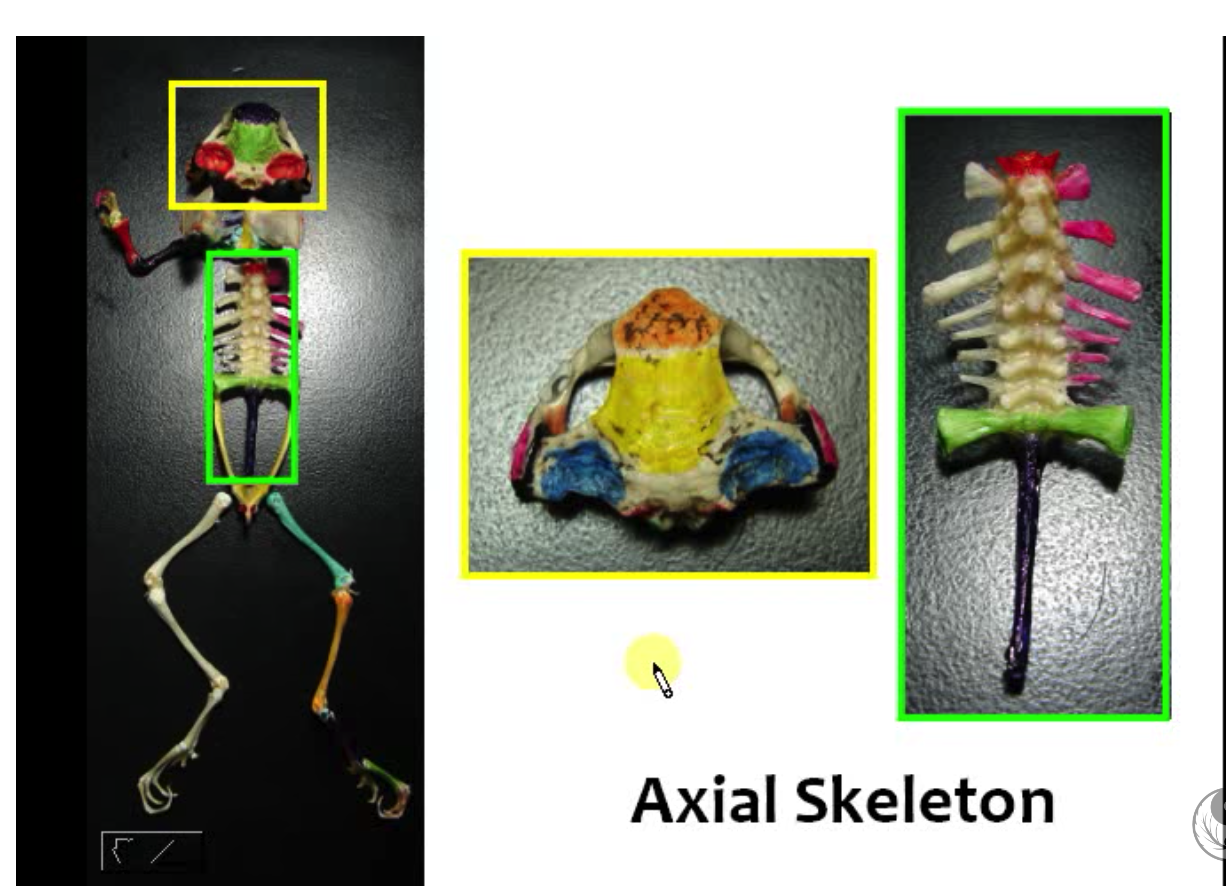
Axial Skeleton
- run along a straight axis
- framework bones to which the appendicular skeleton is attached
1. Skull (yellow)
2. Vertebrae (green)
- framework bones to which the appendicular skeleton is attached
1. Skull (yellow)
2. Vertebrae (green)
91
New cards
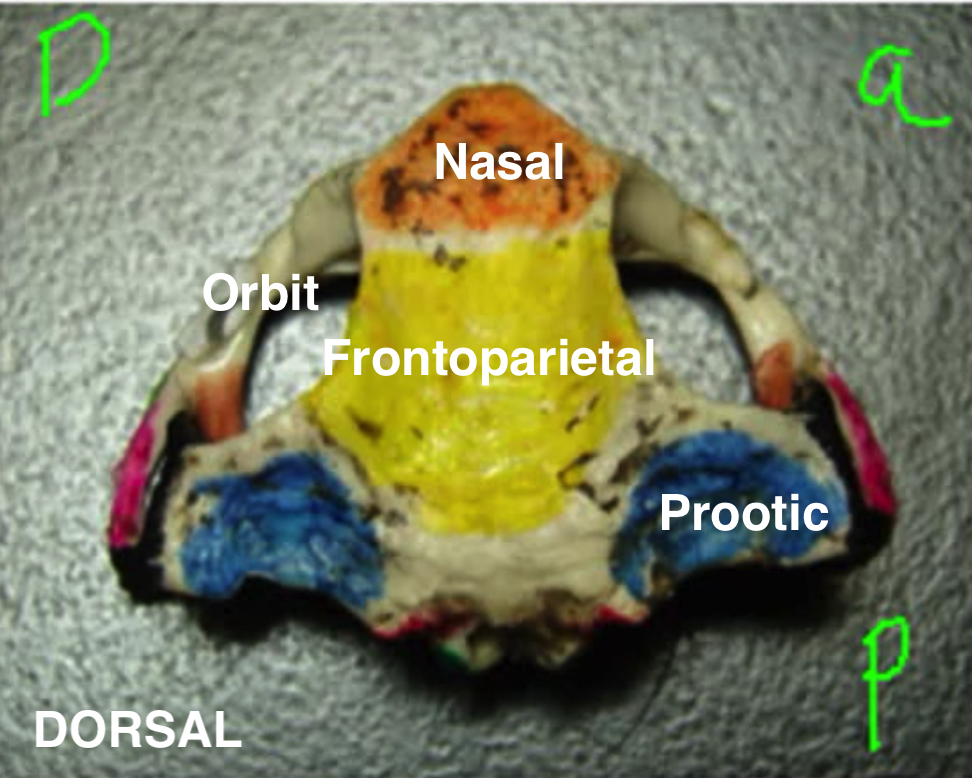
Skull dorsal
1. Nasal bone
2. Frontoparietal bone
3. Prootic bones
4. Orbit (eye sockets)
2. Frontoparietal bone
3. Prootic bones
4. Orbit (eye sockets)
92
New cards
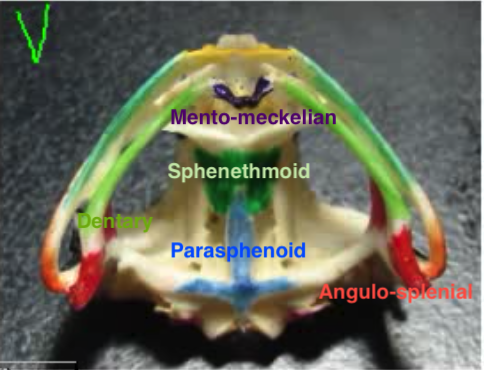
Skull ventral
1. Sphenethmoid
2. Parasphenoid
3. Angulo-splenial (attaches to quadratojugle)
4. Dentary (lower jaw)
5. Mento-meckelian
2. Parasphenoid
3. Angulo-splenial (attaches to quadratojugle)
4. Dentary (lower jaw)
5. Mento-meckelian
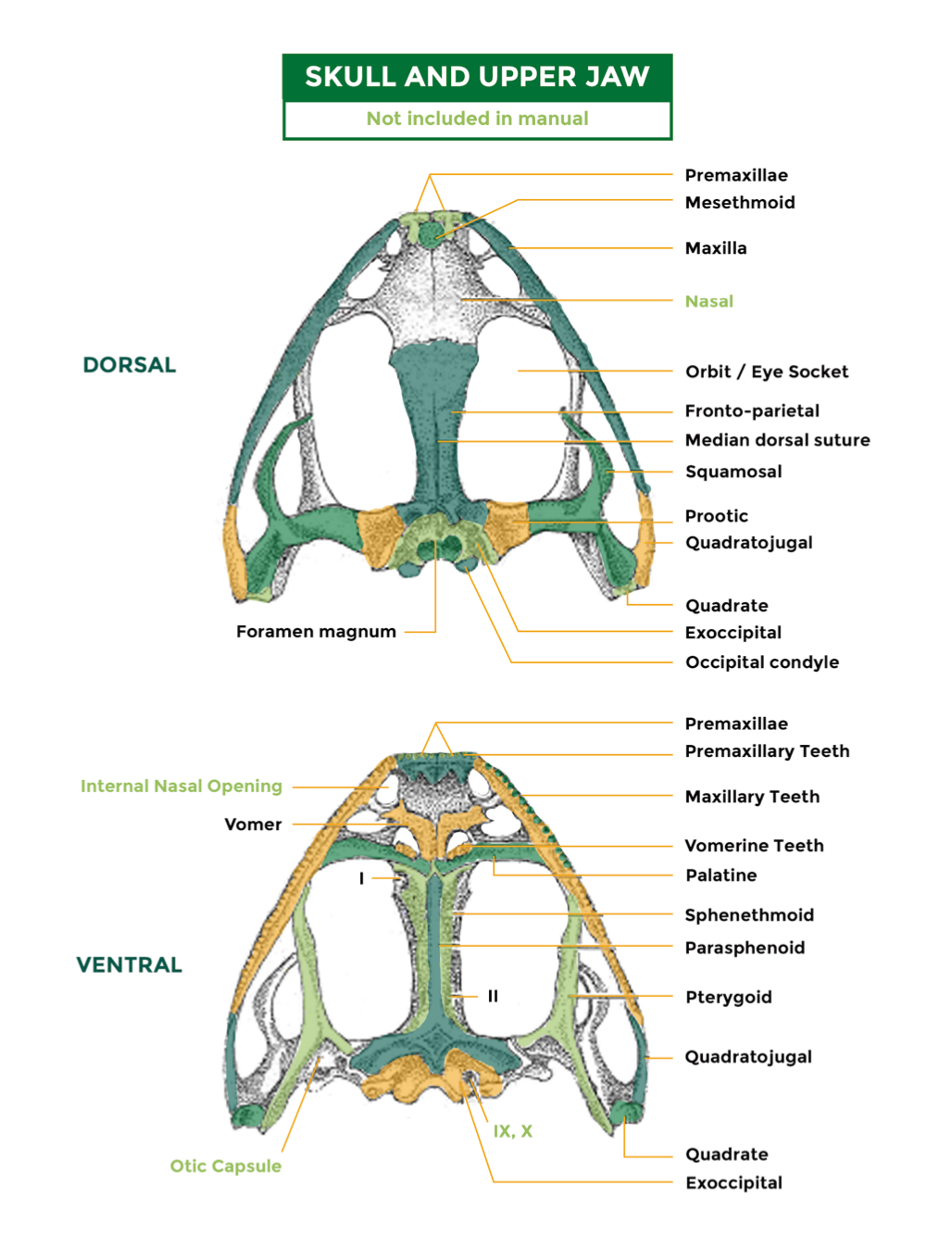
93
New cards
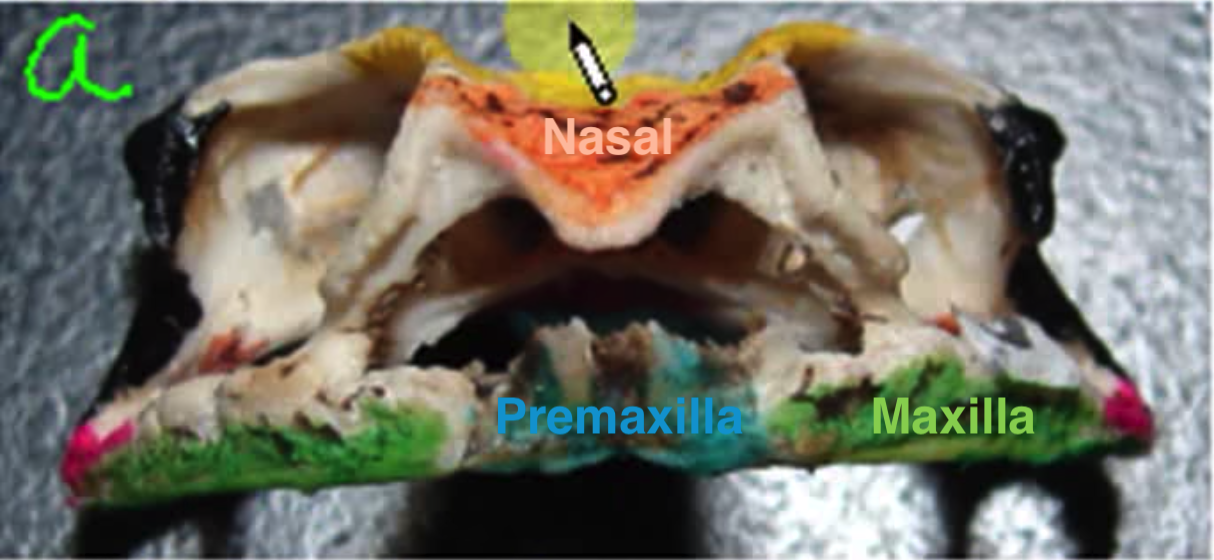
Skull anterior
Upper jaw
1. Premaxilla
2. Maxilla
1. Premaxilla
2. Maxilla
94
New cards
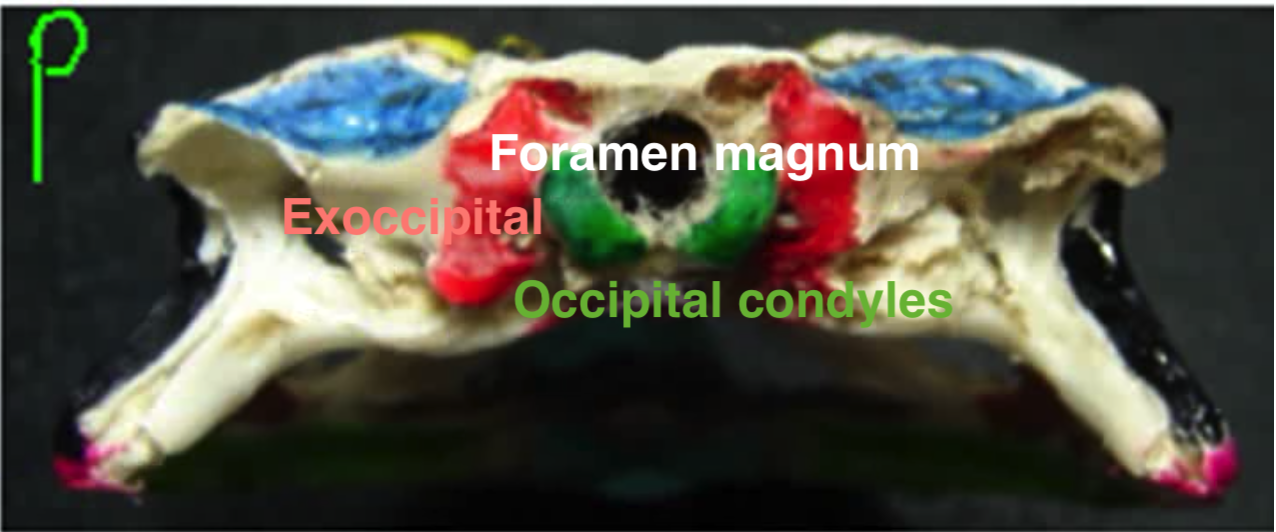
Skull posterior
1. Exoccipital
2. Occipital condyles
3. Foramen magnum (leads to brain, pithing rod)
2. Occipital condyles
3. Foramen magnum (leads to brain, pithing rod)
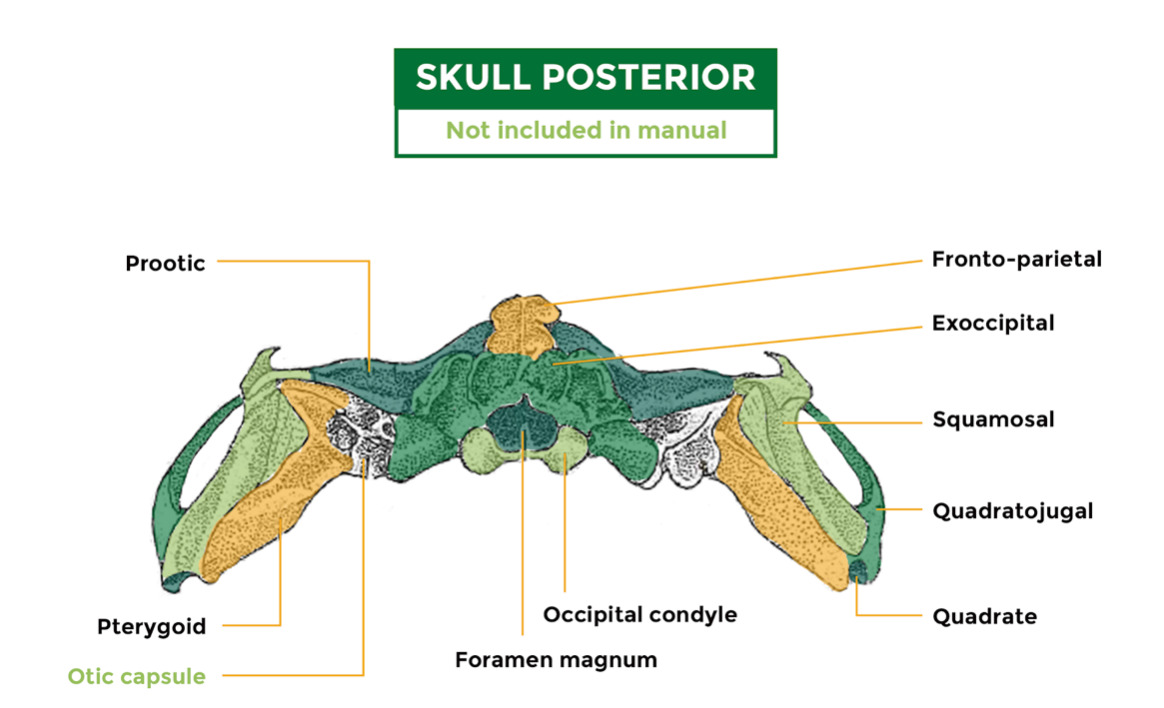
95
New cards
Skull lateral
1. Squamosal
2. Pterygoid
3. Quadratojugal
2. Pterygoid
3. Quadratojugal
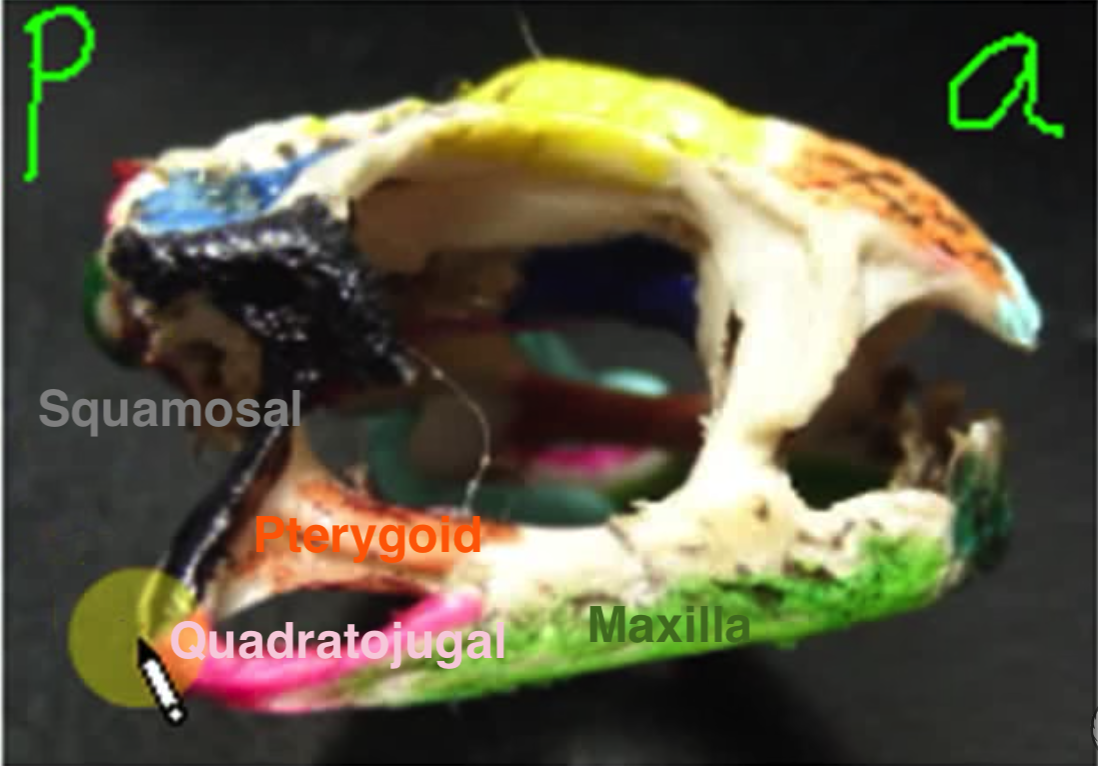
96
New cards
Vertebrae dorsal
- Has 10 segments
1. Atlas/Segment 1 (articulates with occipital condyles)
2. Segments 2-8 (typical vertebrate)
- Transverse processes (lateral projections)
3. Sacral vertebra/Segment 9 (most expanded transverse process)
4. Urostyle/Segment 10
1. Atlas/Segment 1 (articulates with occipital condyles)
2. Segments 2-8 (typical vertebrate)
- Transverse processes (lateral projections)
3. Sacral vertebra/Segment 9 (most expanded transverse process)
4. Urostyle/Segment 10
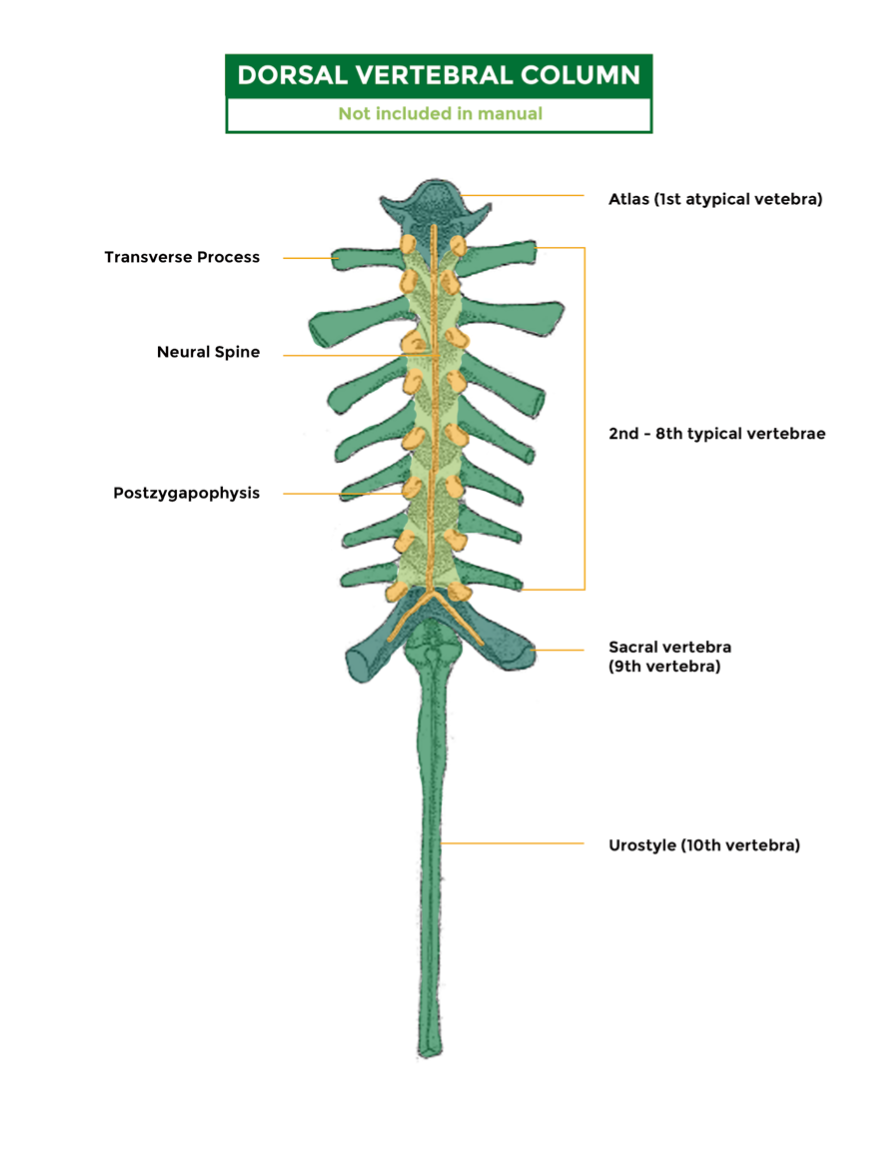
97
New cards
Appendicular skeleton
- from the word "append" meaning attach
1. Forelimb (and pecrotral girdle)
2. Hindlimb (and pelvic girdle)
1. Forelimb (and pecrotral girdle)
2. Hindlimb (and pelvic girdle)
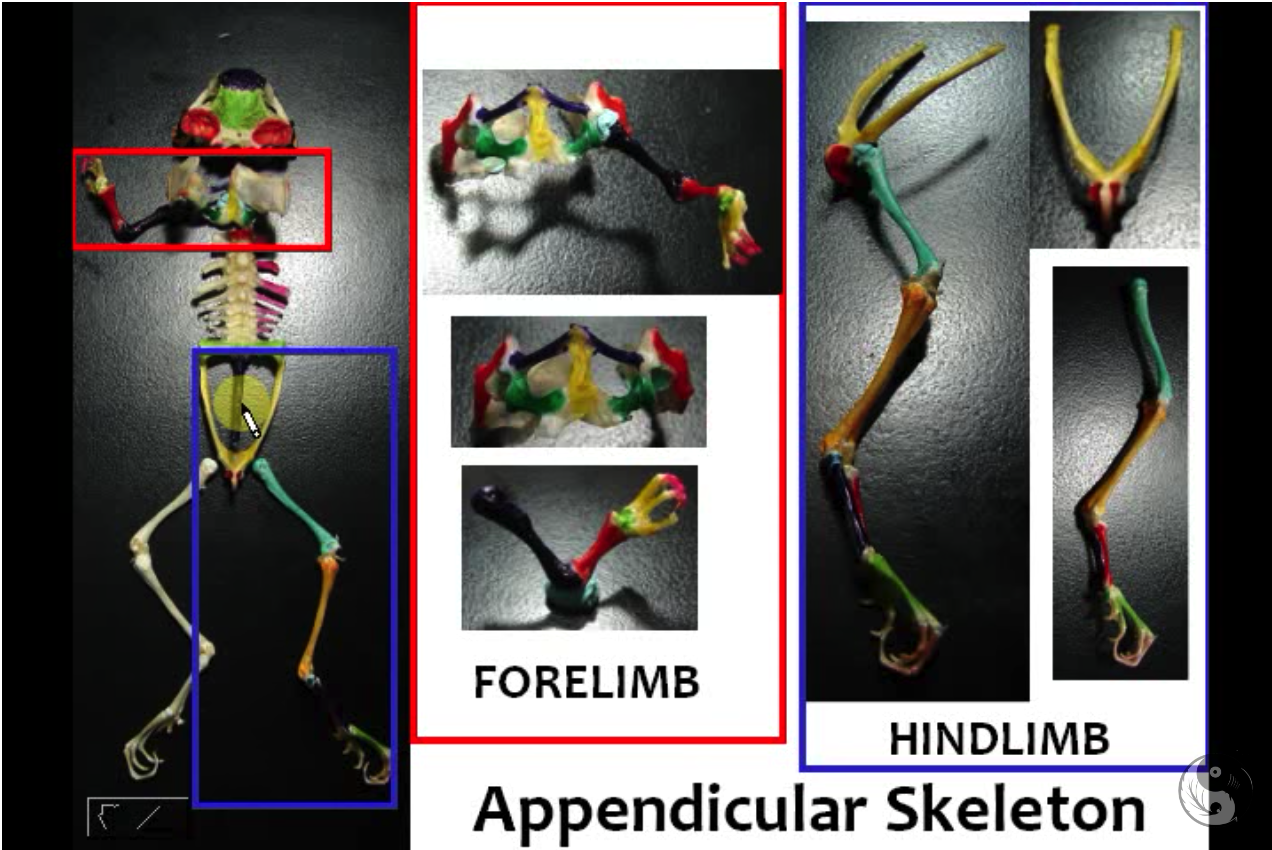
98
New cards
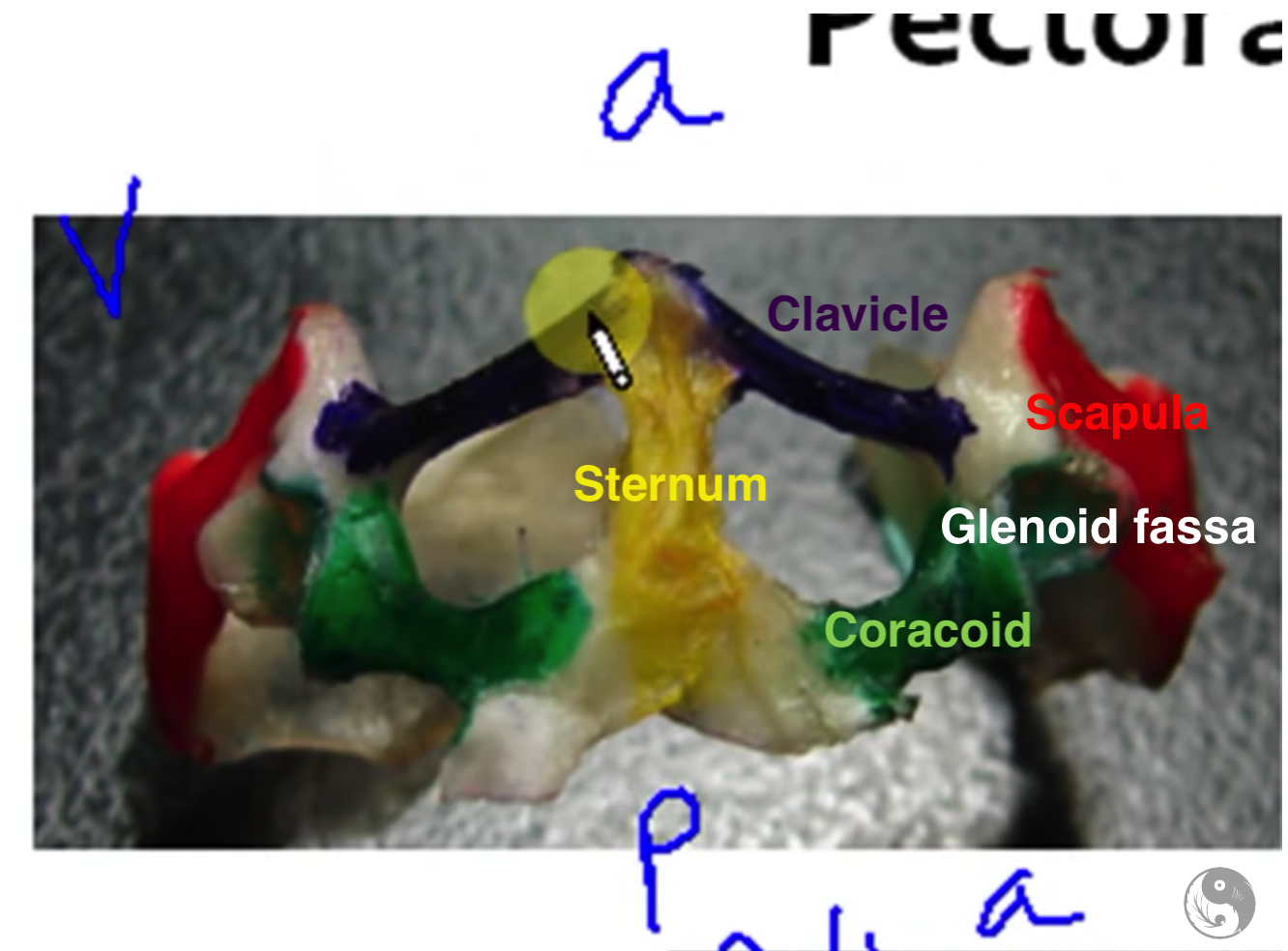
Pectoral girdle ventral
1. Clavicle
2. Sternum (breast bone)
3. Coracoid
4. Scapula
5. Glenoid fassa (socket to which arm is attached)
- clavicle vs coracoid (scapula is more interior and thinner)
2. Sternum (breast bone)
3. Coracoid
4. Scapula
5. Glenoid fassa (socket to which arm is attached)
- clavicle vs coracoid (scapula is more interior and thinner)
99
New cards
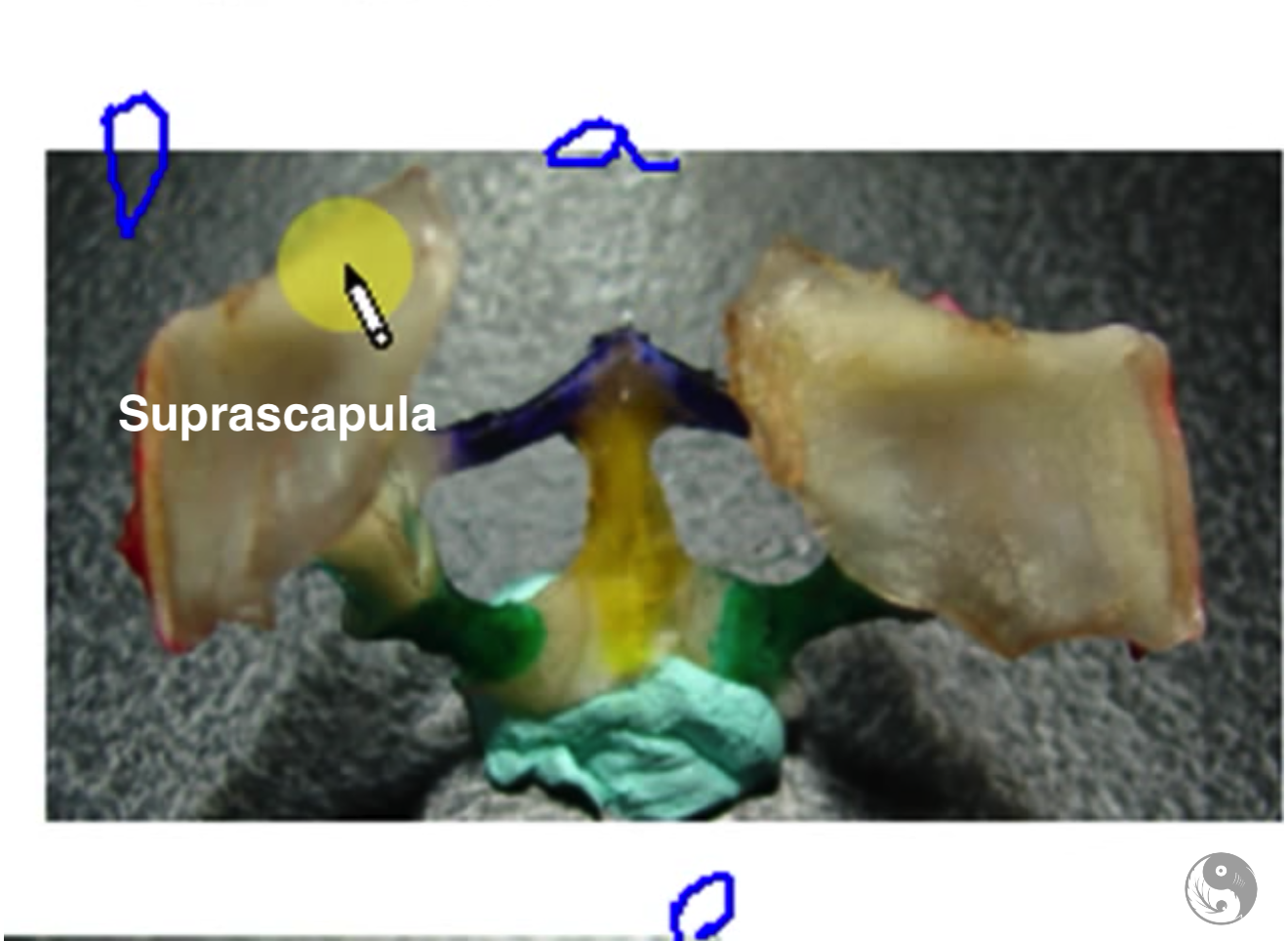
Pectoral girdle dorsal
1. Suprascapula (cartilegenous)
100
New cards
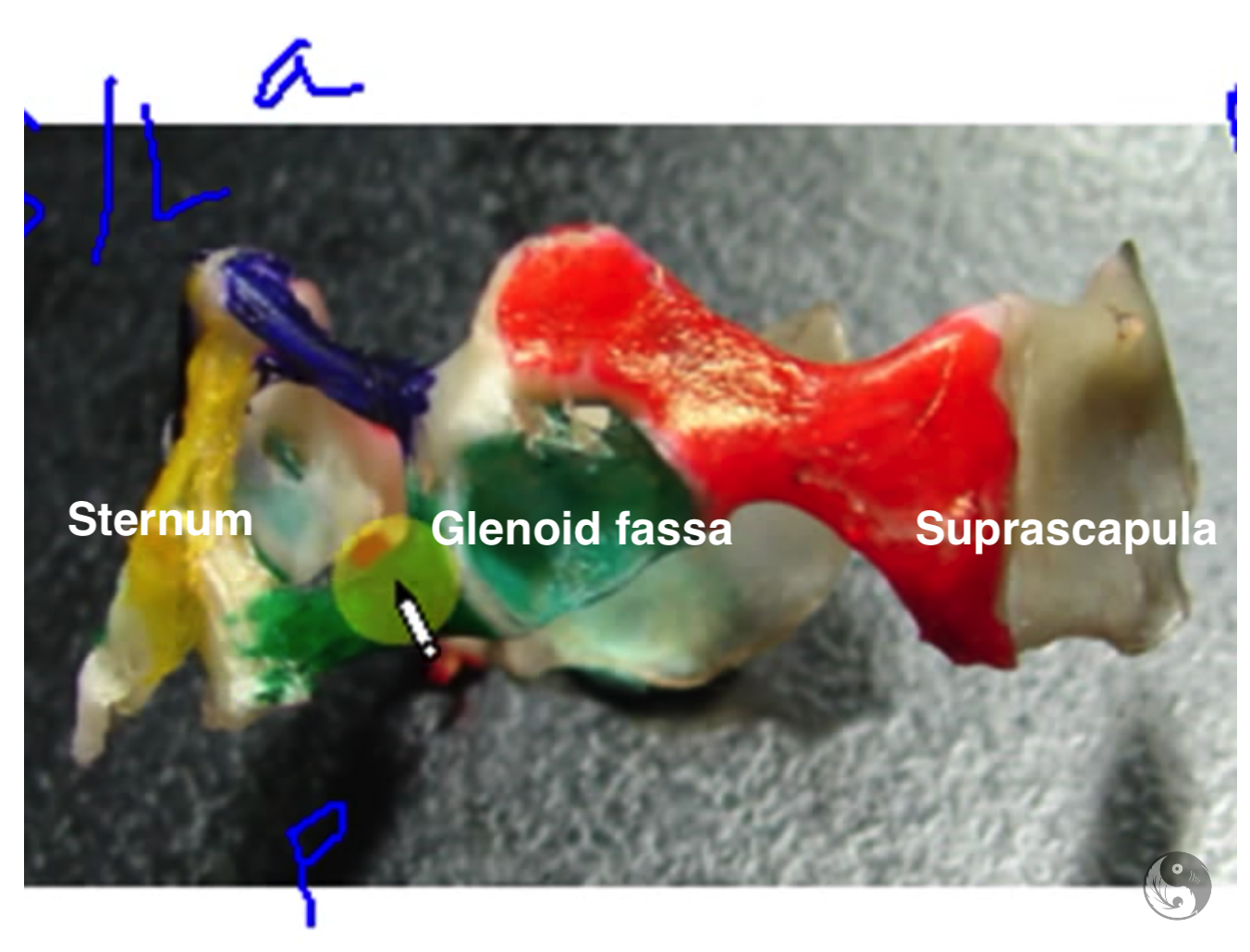
Pectoral girdle lateral
- not all pectoral girdle will look the same