Ch 21: Circulatory System III
1/120
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
What are the efferent vessels?
Arteries
Which vessels carry blood away from the heart?
Arteries
What are the afferent vessels?
Veins
Which vessels carry blood toward the heart?
Veins
Which vessels are microscopic and connect small arteries to small veins?
Capillaries
In which vessels do gas exchange occur?
Capillaries
What is the term used to describe layers of arteries and veins?
Tunics
What is the inner layer of vessel wall that faces the lumen called?
Tunica interna
What lines the tunica interna?
Simple squamous epithelium
T/f: The tunica interna has a slick lining.
True
Which layer of the vessel wall has a selectively permeable membrane?
Tunica interna
What is the middle layer of the vessel wall called?
Tunica media
Which layer of the vessel wall is thick?
Tunica media
What does tunica media have within its wall (3)?
Smooth muscle, collagen, and elastin
Which layer of the vessel wall is responsible for vasoconstriction and vasodilation?
Tunica media
What is the outer layer of the vessel wall called?
Tunica externa
What is the tunica externa made of?
Loose connective tissue
Which layer of the vessel wall anchors the vessel to its surroundings?
Tunica externa
What is the term used to describe the network of small vessels that large vessels have?
Vaso vasorum
What are the resistance vessels?
Arteries
T/f: Arteries can withstand a high bp.
True
What are the biggest arteries called?
Conducting (elastic)
Which type of artery absorbs some pressure but also maintains it?
Conducting (elastic)
What is an example of a conducting artery?
Aorta
What type of artery is midsized?
Distributing
Which type of artery distributes blood to specific organs?
Distributing
What is an example of a distributing artery?
Femoral
What are the smallest arteries?
Resistance
How big are resistance arteries?
Less than 0.1 mm
What is the smallest example of a resistance artery?
Arterioles
Are resistance arteries named?
No
What is the term used to describe the short vessels linking arterioles and capillaries?
Metarterioles
Do elastic arteries have neurons?
Yes
What do elastic artery neurons sense?
Blood pressure and chemistry
What is the term used to describe baroreceptors in internal carotid artery wall?
Carotid sinuses
What nerve transmits signals to vasomotor and cardiac centers of the brainstem in carotid sinus?
Glossopharyngeal
What nerve transmits signals to respiratory centers of the brain in carotid bodies?
Glossopharyngeal
What is the term used to describe chemoreceptors near the branch point of the common carotid artery?
Carotid bodies
What is the term used to describe the chemoreceptors in the aortic arch?
Aortic bodies
What signal respiratory centers of the brain besides carotid bodies?
Aortic bodies
What are aortic bodies innervated by?
Vagus nerves
What division of the nervous system is the vagus nerve controlled by?
Parasympathetic
What are exchange vessels called?
Capillaries
What are exchanged between capillaries (3)?
Nutrients, wastes, and hormones
What makes up the capillary wall?
Endothelium and basal lamina
Name three routes through the capillary wall.
Intercellular clefts, filtration pores, and through endothelial cytoplasm
What are two ways through endothelial cytoplasm?
Transcytosis and diffusion
What is a means of getting through the endothelial cytoplasm for hydrophilic solutes?
Transcytosis
What is a means of getting through the endothelial cytoplasm for nonpolar solutes?
Diffusion
Fill in the blank: When a tissue is active, precapillary sphincters _____.
Relax and open
When precapillary sphincters relax, where does blood go?
Fills capillaries
Fill in the blank: When a tissue is inactive, precapillary sphincters _____.
Close
When precapillary sphincters close, where does blood flow?
From metarteriole to thoroughfare channel
When blood flows from metarterioles to thoroughfare channels what does it bypass?
Capillary bed
What are the holding tanks that contain most of the blood?
Veins
What are the capacitance vessels?
Veins
What are the smallest veins that are very porous and allow for exchange?
Postcapillary venules
What veins have smooth muscle in wall (tunica media)?
Muscular venules
What veins contain valves?
Medium
Why would some veins need valves?
Gravity
Which veins are individually named?
Medium veins
What veins have large lumens, very thin walls, and no smooth muscle?
Venous sinuses
Since venous sinuses have no smooth muscle what does that mean for vasomotion?
No vasomotion
Which veins have smooth muscle in all tunics?
Large
Where is most of the blood at rest?
Veins
What squeezes veins and forces blood through one-way valves toward heart?
Muscle
If you were in a cast how would that effect the skeletal muscle blood pump?
Get blood clots
What is the circulatory route from artery to capillary to vein called?
Simple path
What is a sequence of two capillary beds?
Portal system
Where are portal systems found?
Liver
Why does the liver have portal systems?
Extra filter
What is a vessel merger without intervening capillary bed?
Anastomosis
T/f: The pulmonary trunk is paired.
False
Where does the pulmonary trunk come from?
R ventricle
What type of blood do the pulmonary arteries carry?
Oxygen poor
T/f: Pulmonary arteries are paired.
True
Name the 5 vessels in the pulmonary circuit.
Pulmonary trunk, pulmonary arteries, lobar arteries, alveolar capillaries, and pulmonary veins
What type of blood do pulmonary veins carry?
Oxygen rich
T/f: Pulmonary veins are paired.
True
Name the three parts of the aorta.
Ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending aorta
Name three structures that make up the aortic arch.
Brachiocephalic a, L common carotid a, and L subclavian a
What does the Brachiocephalic a branch off into?
L common carotid a and L subclavian a
What two structures make up the descending aorta?
Thoracis aorta and abdominal aorta
What structures separates the thoracic aorta and abdominal aorta?
Diaphragm
Name the arteries that make up the circle of Willis?
Anterior cerebral a, anterior communicating a, posterior cerebral a, and posterior communicating a
Name the dural venous sinuses.
Superior sagittal, inferior sagittal, and transverse
What are the arteries of the thorax?
Brachiocephalic trunk, L common carotid, and L subclavian
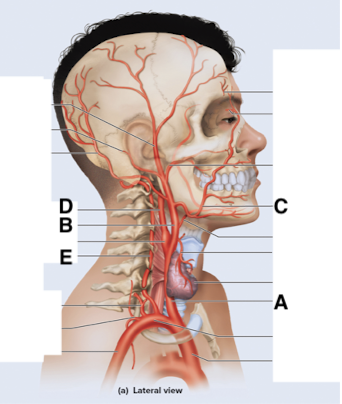
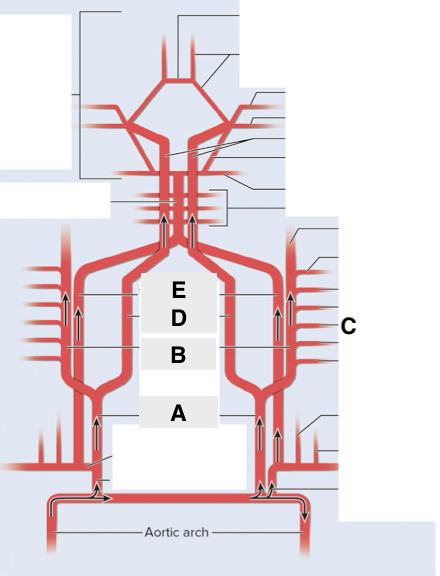
Name point A.
Common carotid a
Name point B.
External carotid a
Name point C.
Facial a
Name point D.
Internal carotid a
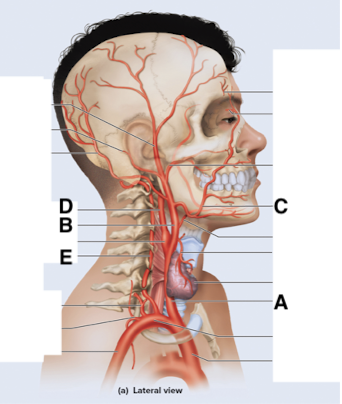
Name point E.
Vertebral a
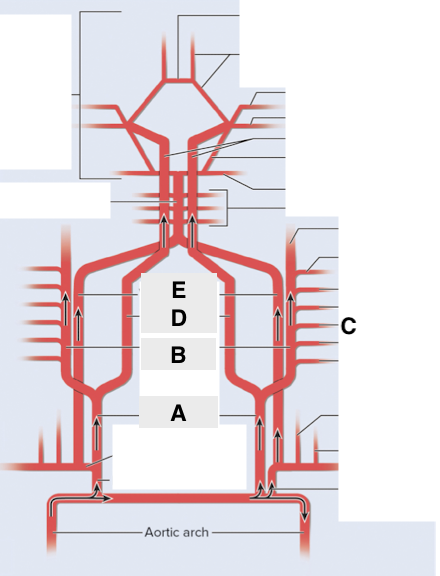
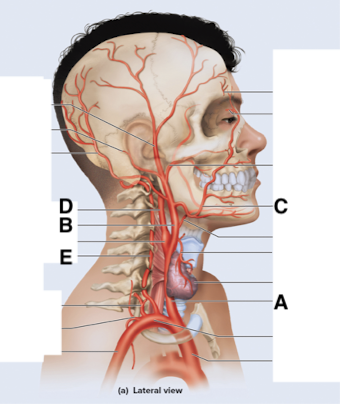
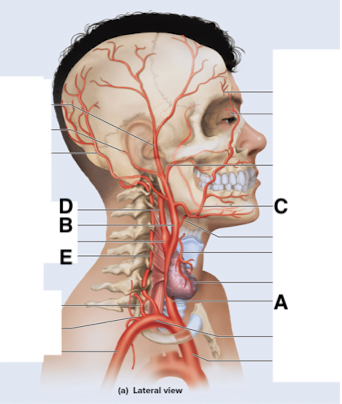
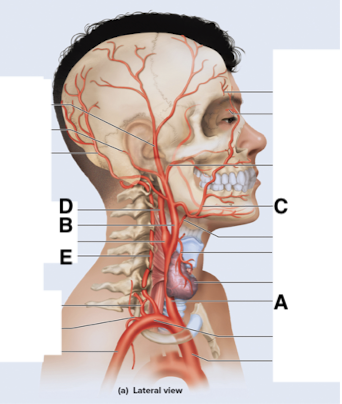
Name point A.
Common carotid a
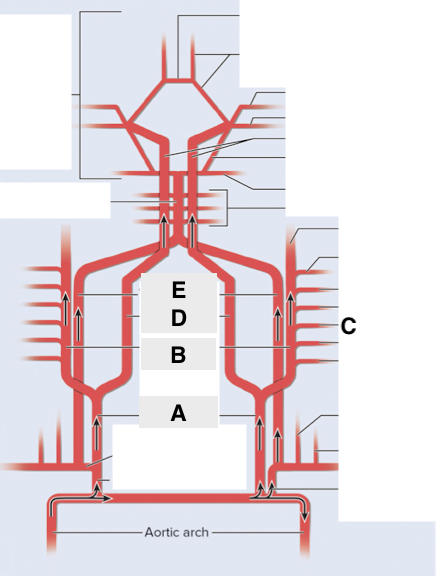
Name point B.
External carotid a
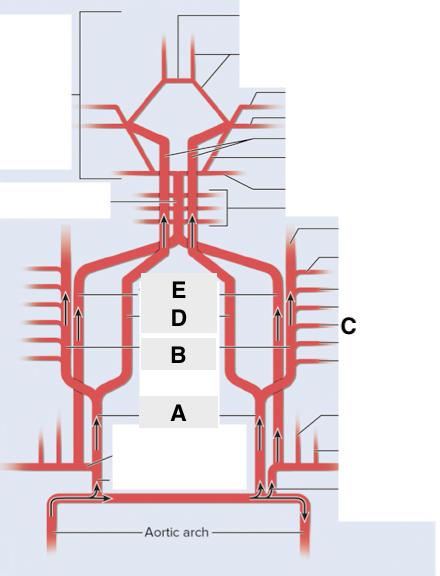
Name point C.
Facial a
Name point D.
Internal carotid a
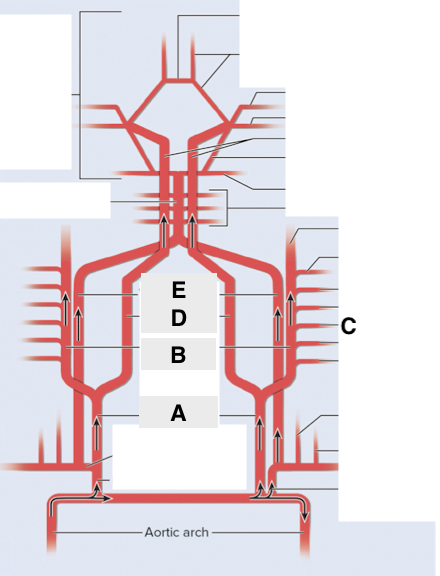
Name point E.
Vertebral a
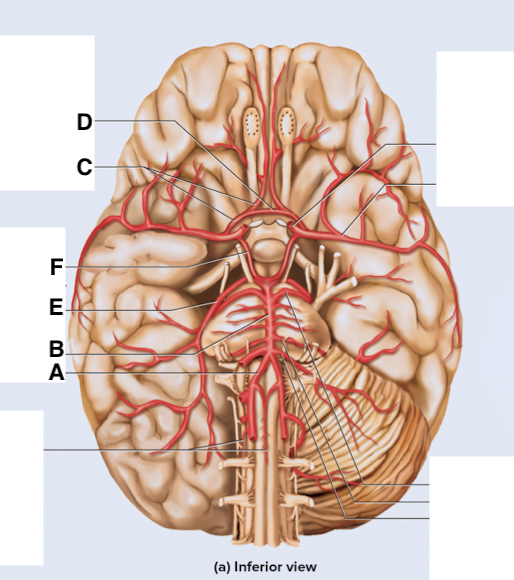
Name point A.
Vertebral a
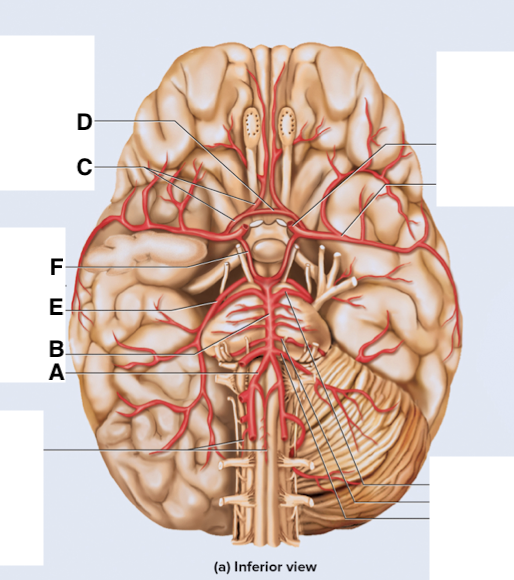
Name point B.
Basilar a
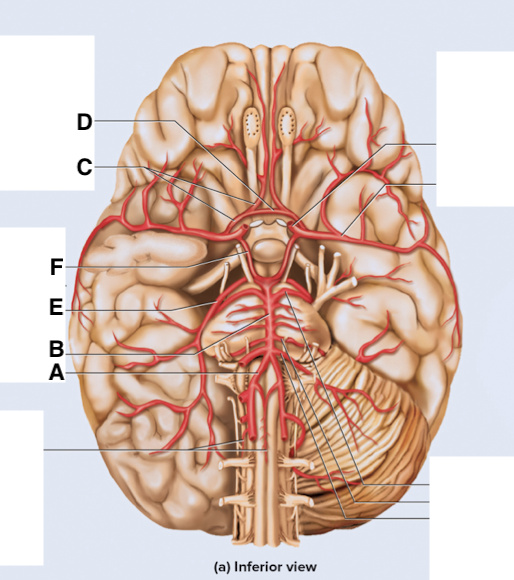
Name point C.
Anterior cerebral a