Business Leadership 12: Unit 3 Planning and Controling
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
SMART Abbreviation Refers too..
1) Specific
2) Measurable
3)Attainable/Achievable
4) Realistic/Relevant
5) Timely
(S)MART
Specific: goal must be clear, well defined, detailed
S(M)ART
Measurable: define what signifies accomplishment of goals or progression towards goals, how is goal being tracked, milestones
SM(A)RT
Attainable: make sure goal is actually possible (time, ability, and resource wise)
SMA(R)T
Realistic: relevant to future plans, does it contribute to overall mission/visions
SMAR(T)
Timely: plans must have deadline, allows for sense of urgency
The Planning Process Steps
1) Define Objectives
2) Determine Where You Stand VS Objectives
3) Anticipate Future Events
4) Analyze and Chose Action Alternatives
5) Implement and Evaluate Results
Planning Process: Define Objectives
(Step 1) Identify desired outcomes, use SMART criteria
Planning Process: Determine Where You Stands VS Objectives
What strengths work in your favor, what weaknesses hold you back
**SWOT, BCG
Planning Process: Anticipate Future Events
Generate alternative scenarios, identify things that help or hinder progress towards objectives
Planning Process: Analyze and Chose Action Alternatives
evaluate possible actions, choose alternatives likely to accomplish objectives, select the best alternative given disadvantages vs advantages
Planning Process: Implement and Evaluate Results
measure progress towards objectives, do what the plan requires, evaluate results, take corrective actions and revise plans as needed
Benefits of Planning
1) Improved Flexibility
2) Improved Coordination and Control
3) Better Use of Time
Types of Plans
Short range, Long range, Operational, Single-use, Standing-Use
Short Range Plans
- less than a year
- exp: hire a new employee
Long Range Plans
- greater than 1 year
- exp: launch a new product
Operational Plans
Provide a clear understanding of how to complete day-to-day tasks
- ensure that individuals and teams are able to reach defined organizational objectives
Contingency Planning
the process of preparing alternative courses of action that may be used if the primary plans don't achieve the organization's objectives
Single Use Plans
- used only once
- created for unique situations
- exp: projects, budgets
Standing Use Plans
- designed to be used over and over again
- exp: policies, rules and procedures
Forecasting
Using current and past data to make informed decisions/predictions about the future
- Exp: how will products and services change in the future
Strategic Management Formula
Strategic Management (SM) = Strategic Formulation (SF) + Strategic Implementation (SI)
Strategic Management
Strategic management involves developing and implementing strategies to achieve an organization's long-term goals.
Strategic Formulation
creating a strategy, assessing existing strategies, organization, and environment to develop new strategies
Strategic Formulation Involves
- setting goals and objectives,
- determining mission + vision,
- conducting SWOT, BCG,
- contingency plan,
- planning tools (Gantt, budget)
Strategic Implementation
process of allocating resources and putting strategies into action
Strategic Implementation involves...
- hiring training
- tracking progress
-controlling
- implementing policies + procedures
- reflect + review
- big portion: results --> reflect and improve
Competitive Advantage
- comes from operating successful ways that are difficult to imitate
- smth that sets you apart from competition
SWOT Analysis
A study undertaken by organization to identify its internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external threat opportunities
Strengths (SWOT)
(Internal Positive Factors)
- what you do well
- internal resources
- advantages over competition
Weaknesses (SWOT)
(Internal Negative Factors)
- obstructions for competitive advantage
- areas of improvements, lacks
Opportunity (SWOT)
(External Positive Factors)
- opportunities in market or environment
- is perception of business positive
- ongoing or window for this opportunity
Threats (SWOT)
(External Negative Factors)
- existing, potential competitors
- risky factors beyond control
- unfavorable developments/trends
BCG Matrix
- analyzes businesses or products according to market growth rate and market share (on a four grid basis)
BCG Matrix Purpose
Helps companies decide what product to launch based on market, economy, + what products to get rid of
- also helps with resource allocation
Components of BCG Matrix
1) Question Mark
2)Star
3)Cash Cow
4) Dog

Question Mark (BCG)
"The Problem Child"
- High growth
- Low market share
--> a new product, introduction stage of product life cycle
- performance undetermined
Star (BCG)
- high growth and high market share
- high cash generation and consumption
- heavy investment
Cash Cow (BCG)
- Low growth and high market share
- foundation
- generate more cash than consumed, little investments + marketing needed
Dog (BCG)
- Low growth and low market share
- cash traps, high cost low output
- declining stage, costs business money
Product Life Cycle and BCG Matrix Location
1) Question mark = introduction phase
2) Star = Growth
3) Cow = maturity
4) Dog = decline
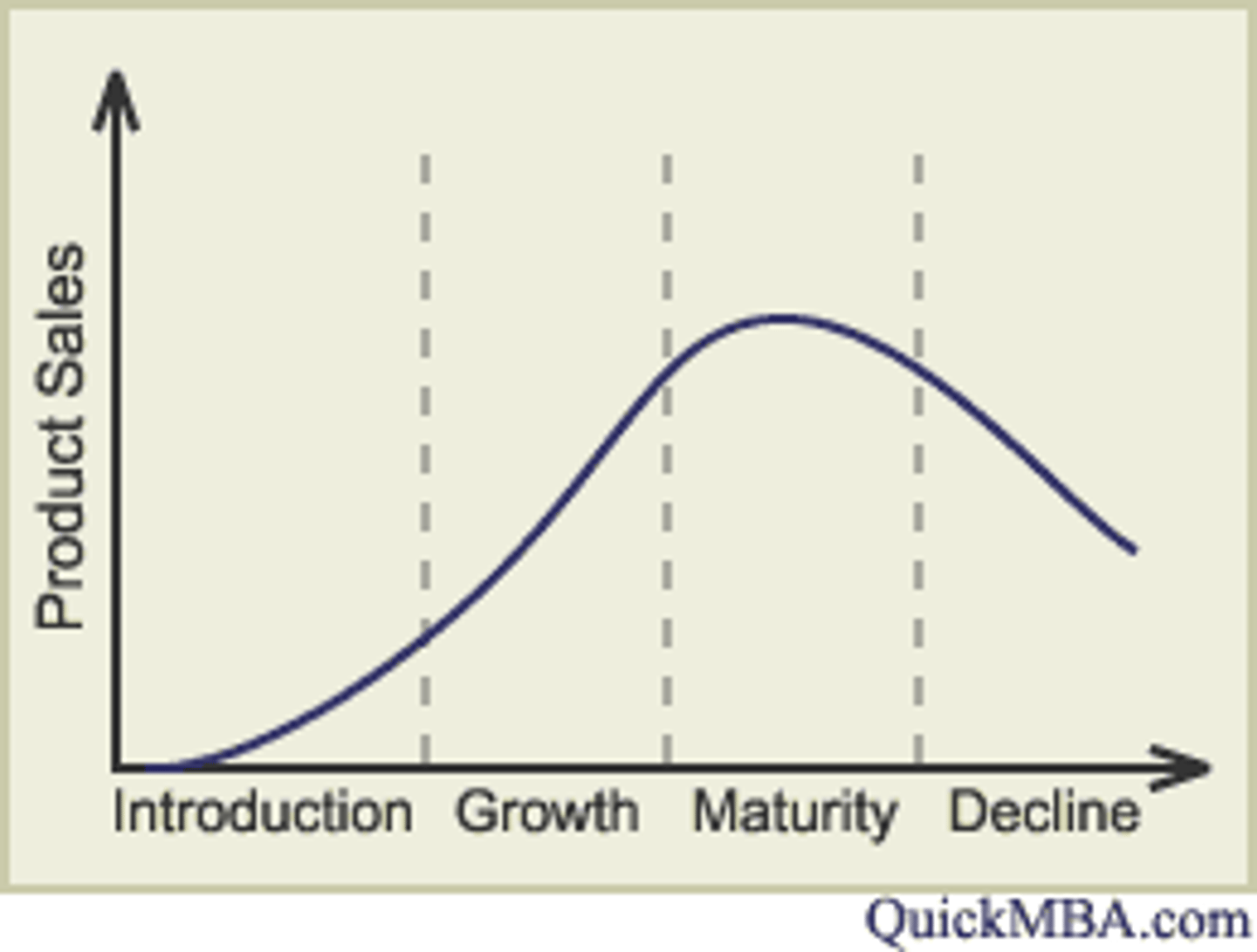
Steps in Control Process
1) Establish Performance Objectives and Standards
2) Measure Actual Performance
3) Compare Actual Performance with Objectives and Standards
4) Take Necessary Action
Control Process Step 1: Establish Performance Objectives and Standards
- Objectives: represent key desired results
- Standards and Measures: used to evaluate performance
Output Standard
measure performance results in terms of quantity, quality, cost of time
- results from effort
Input Standard
measures work efforts that go into a performance task
- effort put in
Control Process Step 2: Measure Actual Performance
- measure the performance efforts and results
- measurement must be accurate enough to differ between current and desired progress
- measure how much you over or underacheived
Control Process Step 3: Compare Results with Objectives and Standards
Compare objective with results
Control Process Step 4: Take Necessary Action
Focuses on differences between actual and desired performance
2 types of Exceptions: Problem Situations
performance is below expected levels
2 Types of Exceptions: Opportunity Situations
performance is above expected levels, learn what was done well --> can it be applied again
Discipline
act of influencing behavior through reprimand
Progressive Discipline
ties reprimands to the severity and frequency of the employee's infractions
Qualities of Progressive Discipline
1) Penalties very in accordance to severity and frequency of behavior
2) Use the least extreme disciplinary action possible
3) Follows a four step process, from least to most severe reprimands
Discipline must be _____ to be useful
handled in a fair, consistent, and systematic way
The Goal of Discipline
achieve compliance with organizational expectations through least extreme reprimands
A reprimand should be...
1) Immediate
2) Directed towards an action not personality
3) Consistently applied
4) Informative
5) In a supportive setting
6) Support realistic Rules
Why are control systems used
ensure things get accomplished, plans get followed, strategic direction continues, and organization objectives get met
Types of Controls
1) Feedforward
2) Concurrent
3) Feedback
Types of Controls: Feedforward
ensure directions and resources are right BEFORE the work begins
Types of Controls: Concurrent Controls
focuses on what happens DURING the work process
Types of Control: Feedback Controls
takes place AFTER an action is completed
Internal Control Strategy
occurs through self-discipline and self-control
Internal Control: Theory Y
Trust employees, believe they are motivated to do work, self-mediate, and self-correct/discipline
External Controls
occurs through direct supervision or administrative systems
External Control: Theory X
employees need direct supervision, managers do not trust employees
Gantt Chart
Visual representation of all the tasks in a project plotted against a timescale
Purpose of a Gantt Chart
Identify the minimum amount of time needed to complete a project
Advantage of Gantt Charts
- quick overview of large number of tasks and deadlines
- can help monitor progression against time
- delays can be calculated quickly
Disadvantage of Gantt Charts
- large-scale projects can end up hard to read
- each bar's length does not indicate complexity of tasks
Mission Statement
description of what an organization actually does/is
What to Consider When Creating a Mission Statement
- your customer base
- your products and services
- where you intend to operate
- who is this directed at (employee, customers, shareholders,)
Vision Statement
a company's road map, indicating both what the company wants to become and guides initiative towards growth
--> what you want to become