The Brain and Cranial Nerves
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
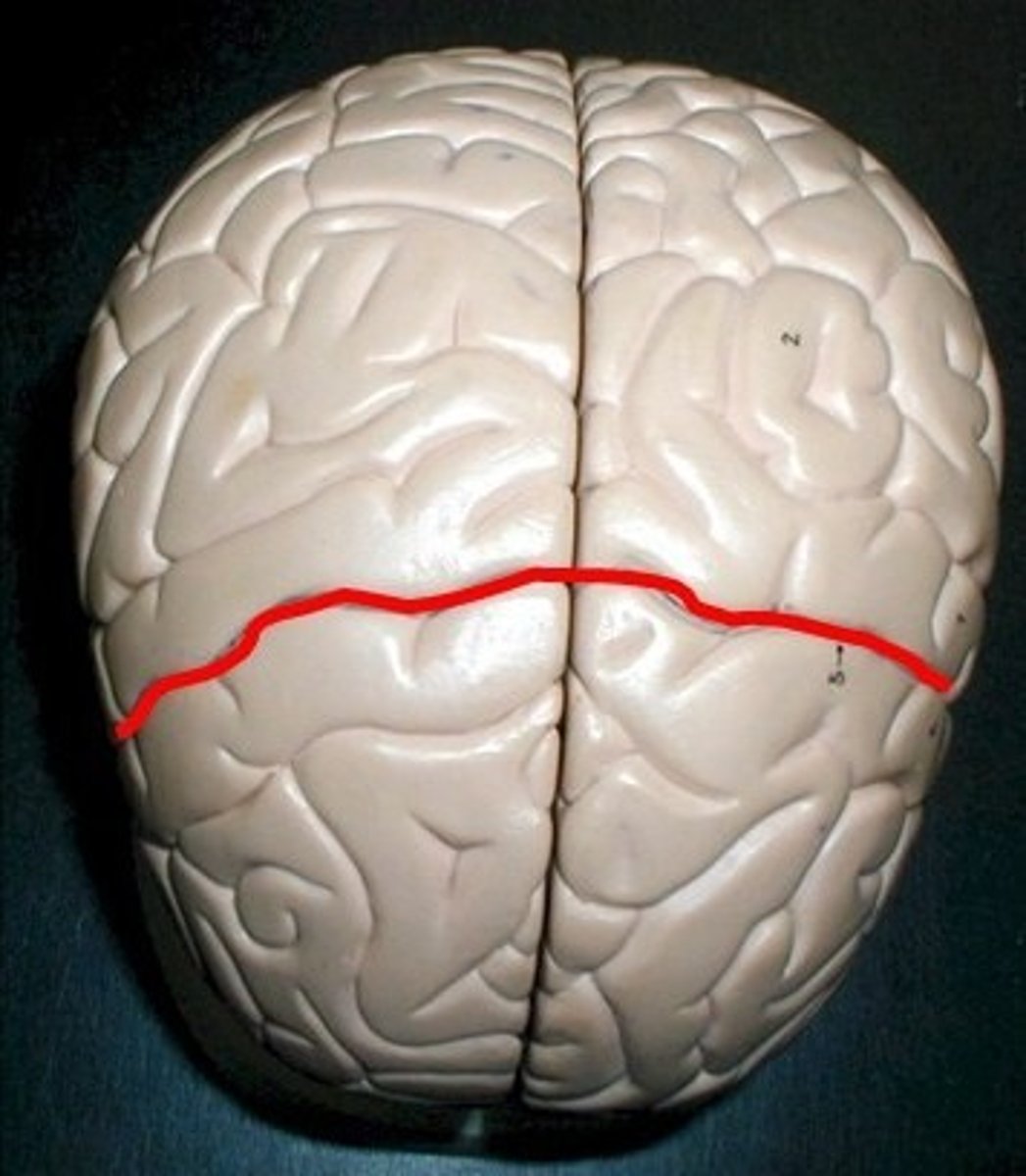
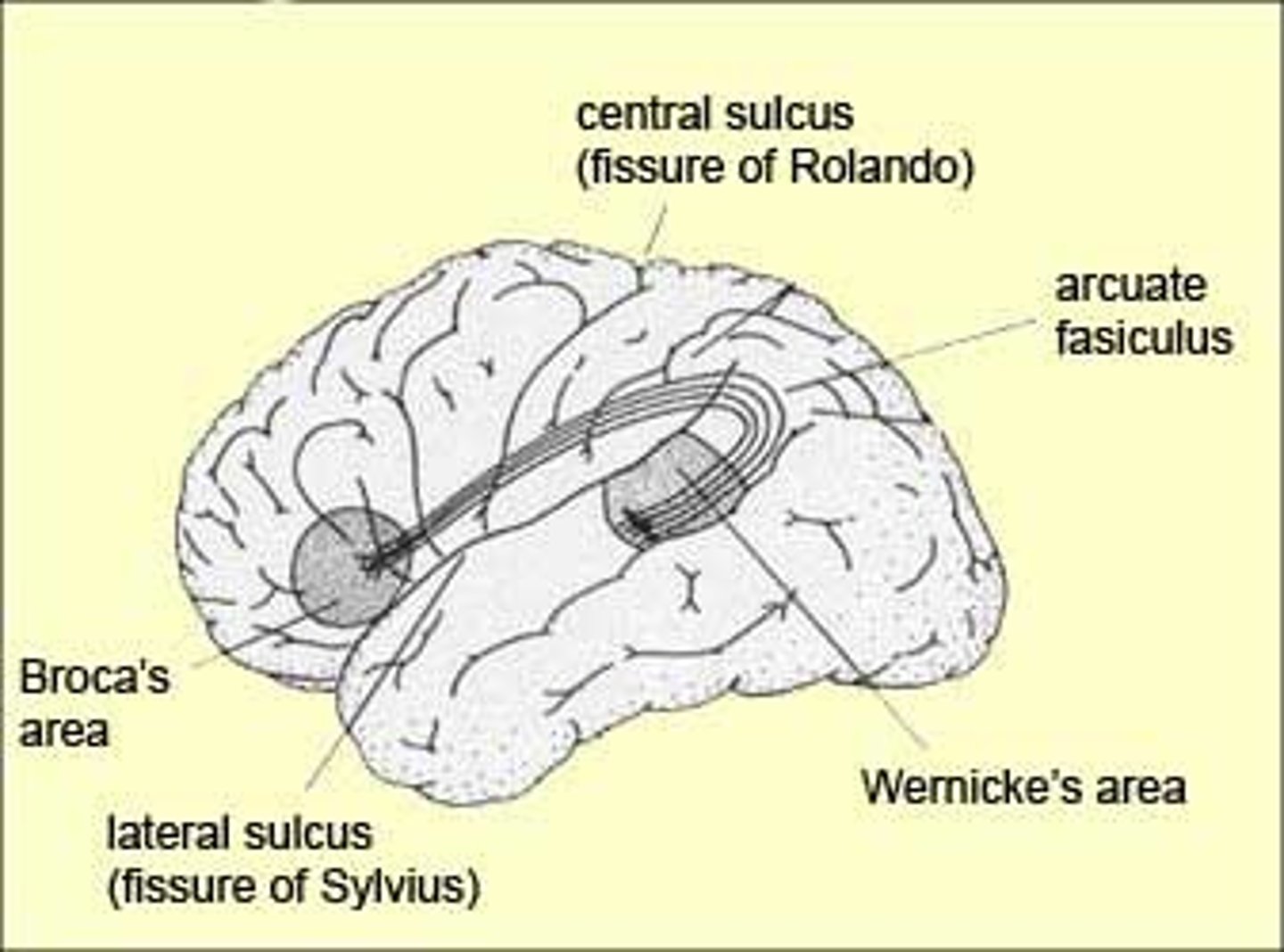
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes, longest continuous sulcus running to the lateral fissure
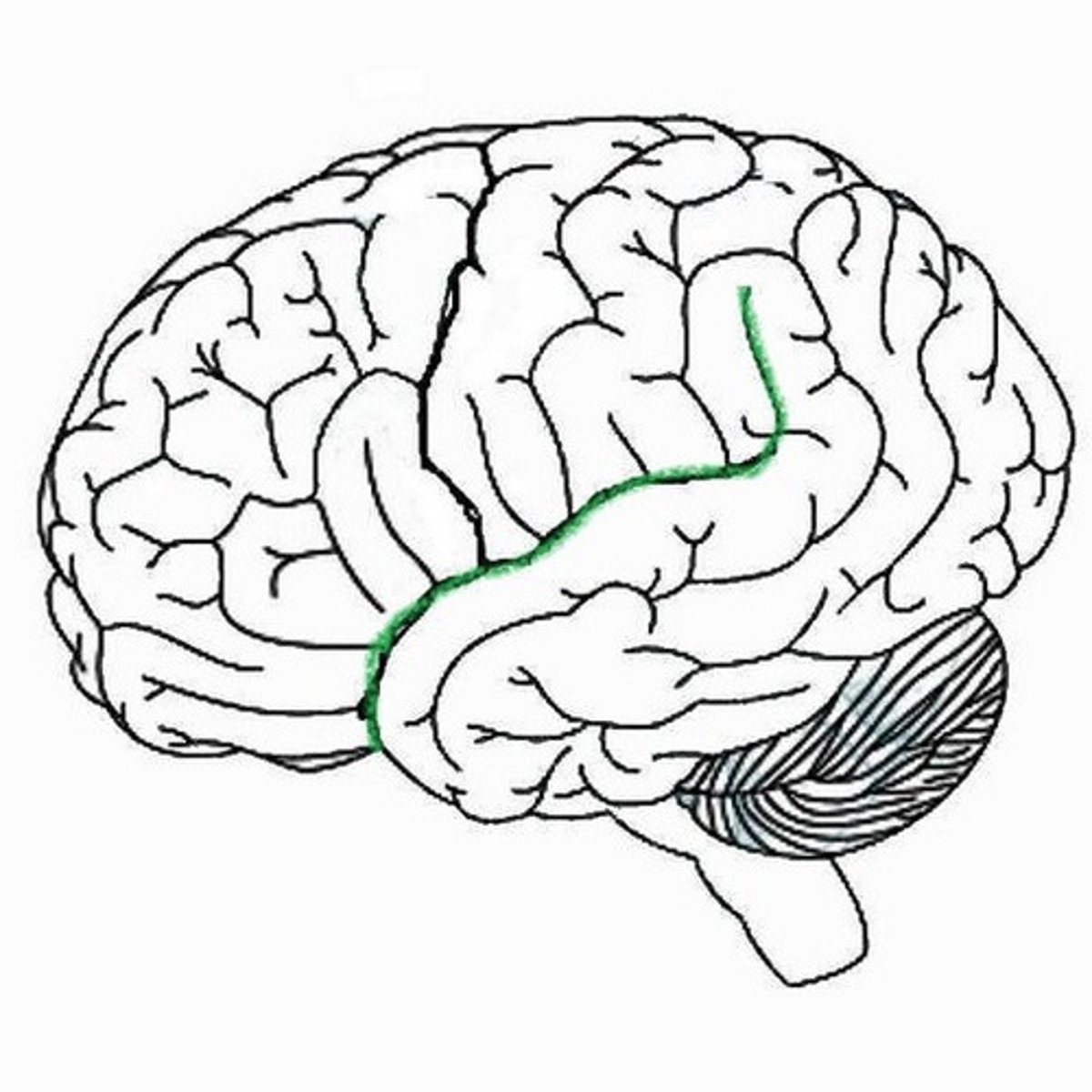
Sylvian fissure (lateral fissure)
separates frontal and parietal lobes from temporal lobe, deeper than a sulcus
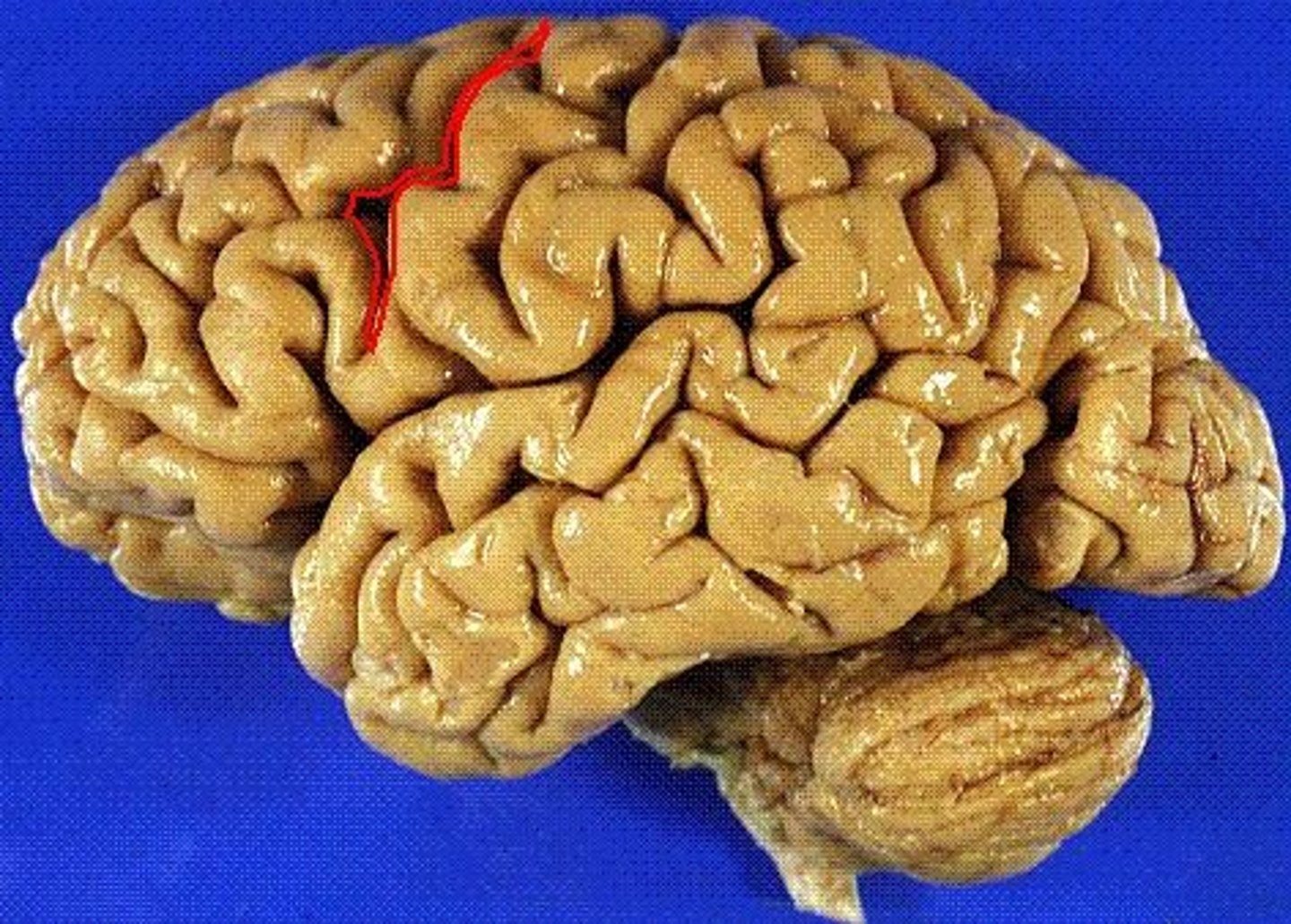
precentral sulcus
Separates the motor cortex from the premotor cortex
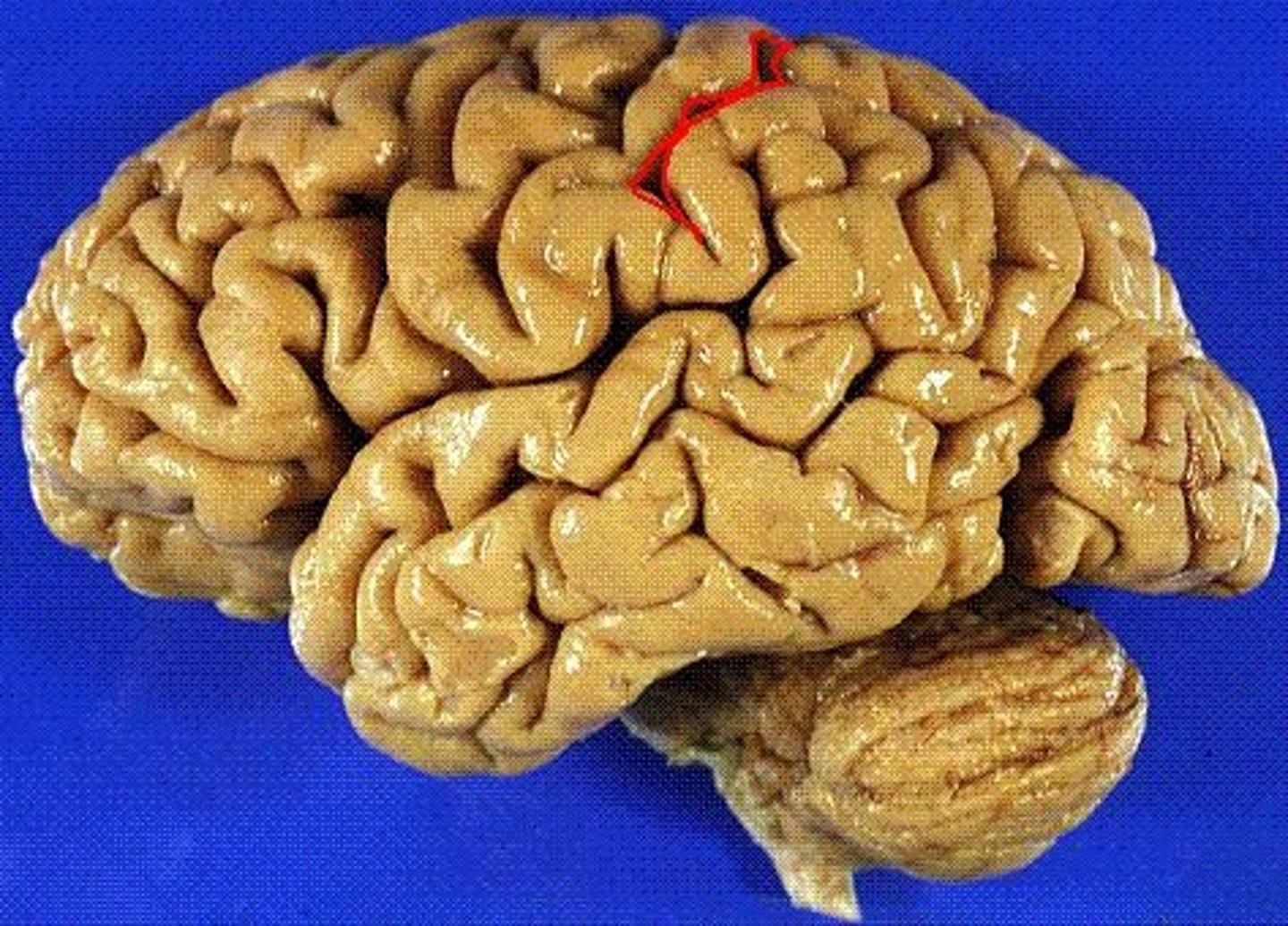
postcentral sulcus
Located immediately posterior to the central sulcus, contains the primary somasensory area of the cerebral cortex. Oraganized such that from medial to lateral it is legs, trunk, hands, face
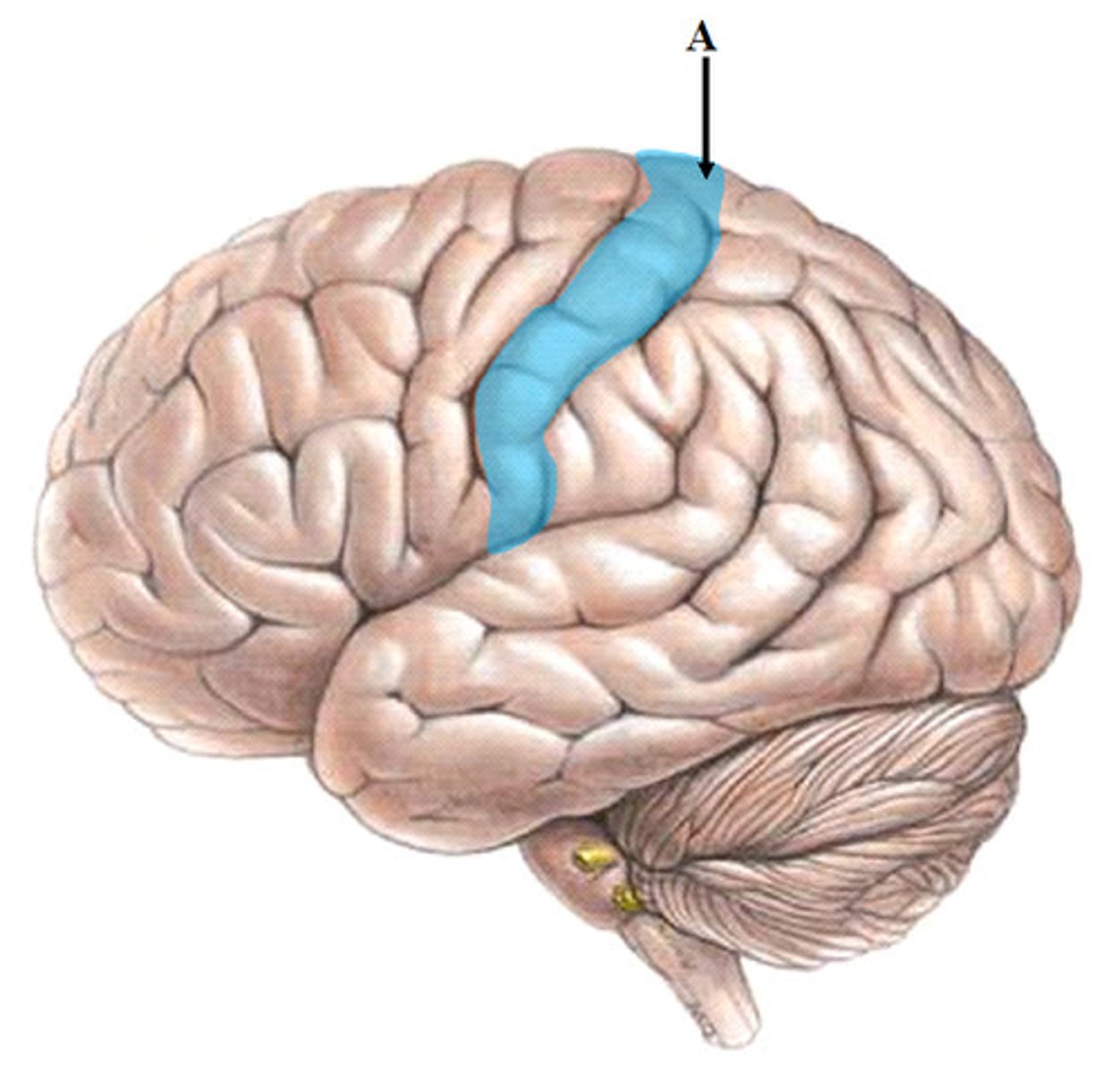
precentral gyrus
the strip of frontal cortex, just in front of the central sulcus, that is crucial for motor control
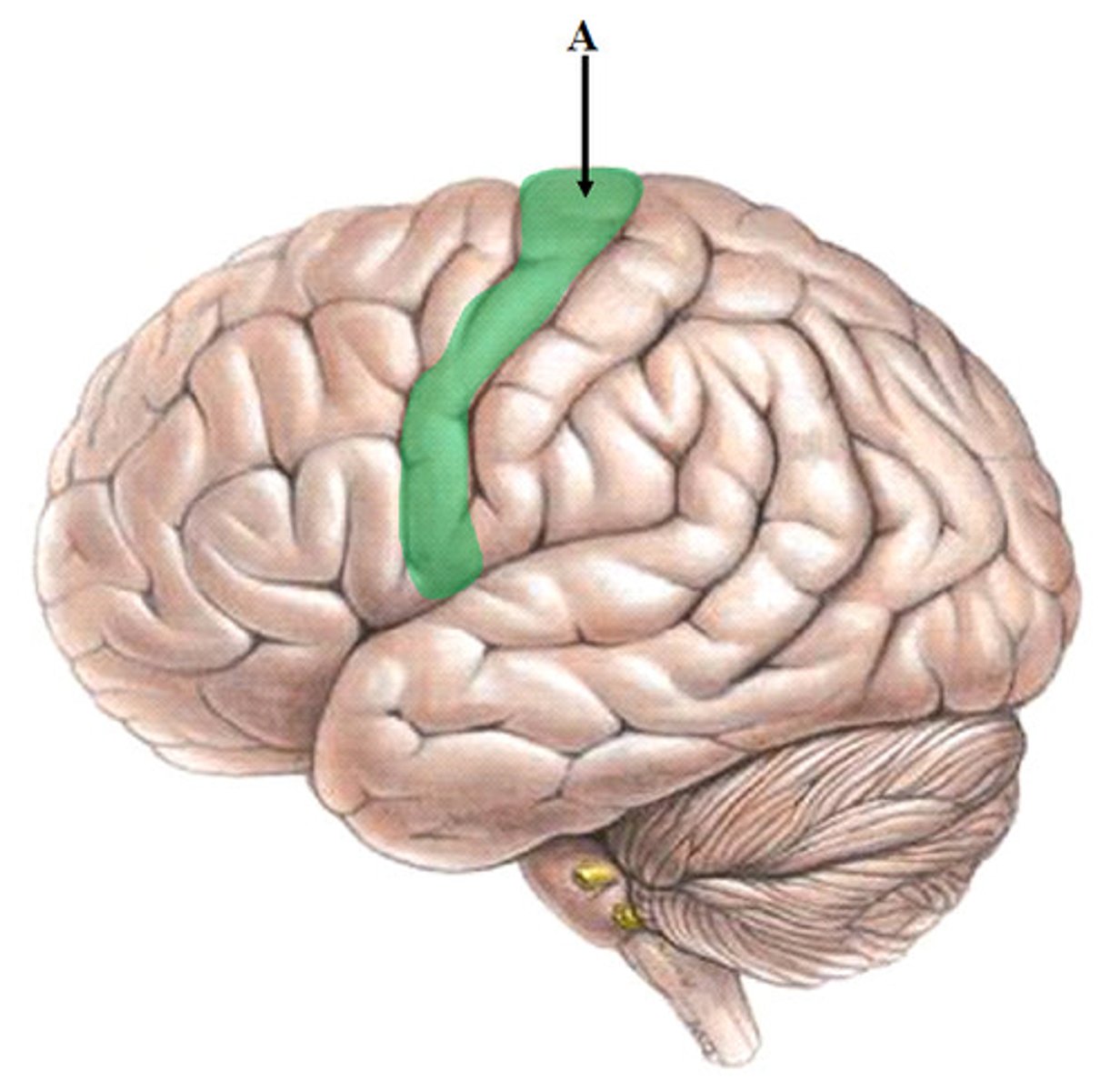
postcentral gyrus
the strip of parietal cortex, just behind the central sulcus, that receives somatosensory information from the entire body
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates parietal and occipital lobes
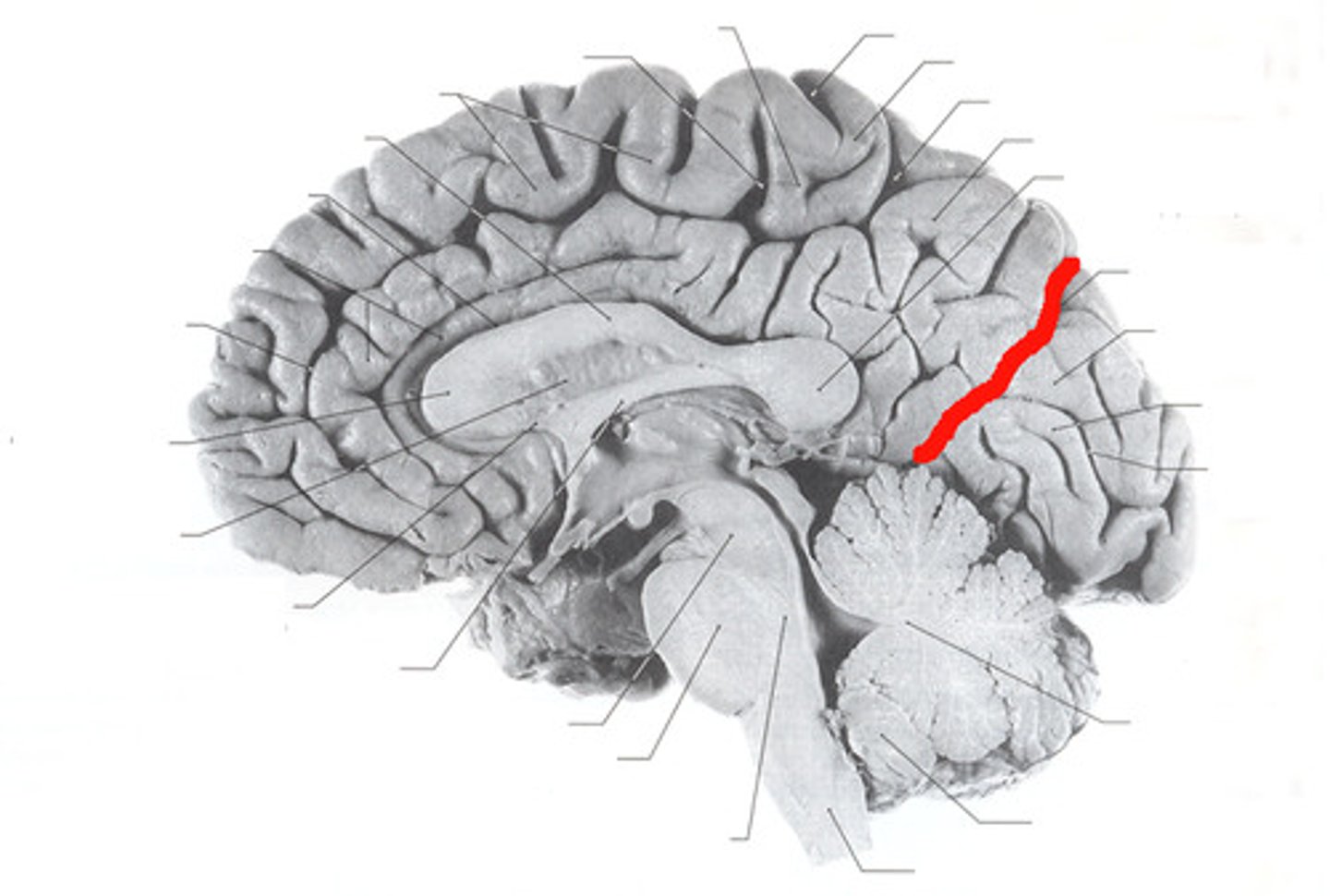
Pre-occipital notch
Divides Temporal and Occipital lobes
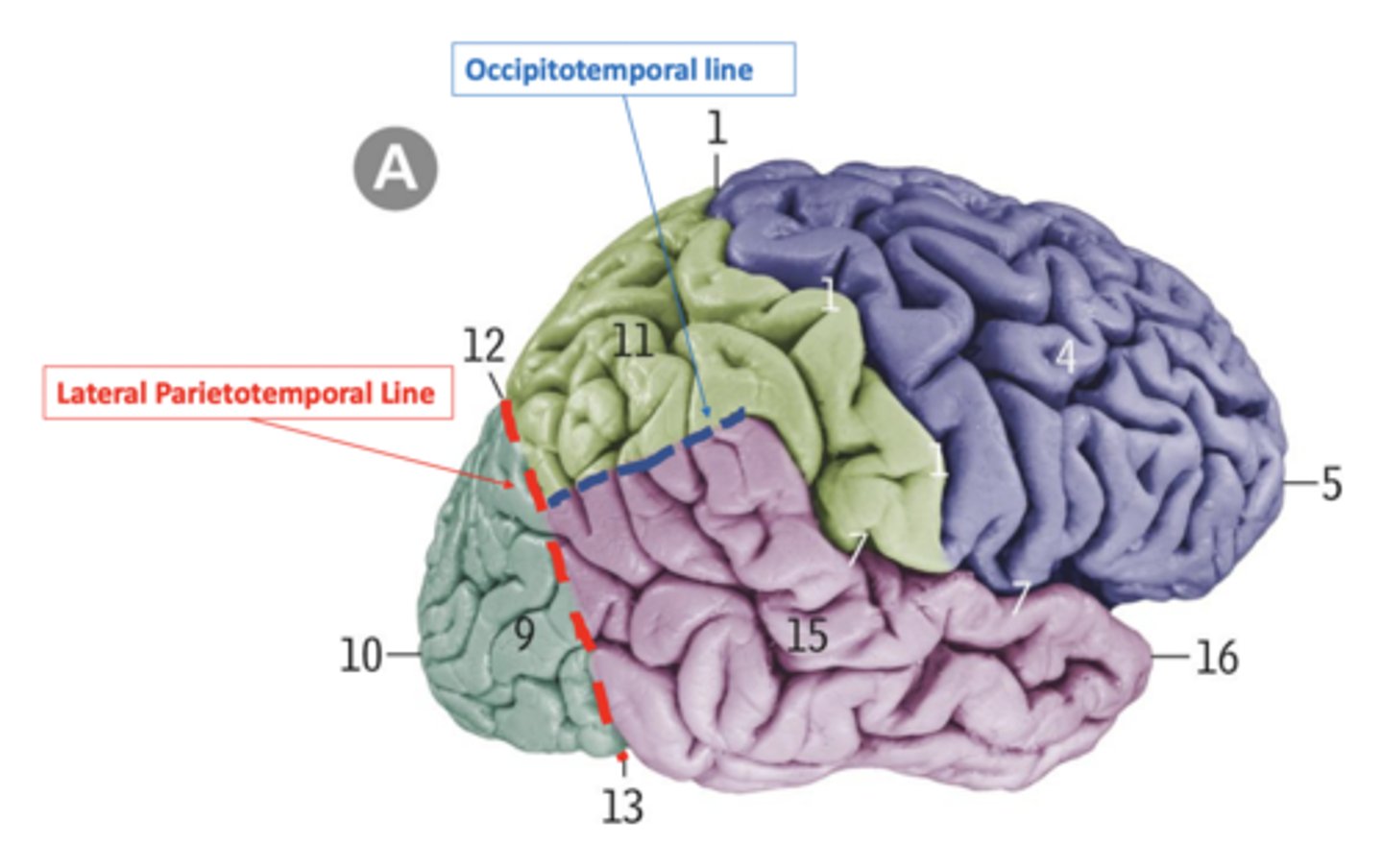
lateral parietotemporal line
imaginary line connecting the pre-occipital notch and parieto-occipital sulcus, separating the temporal and occipital lobes
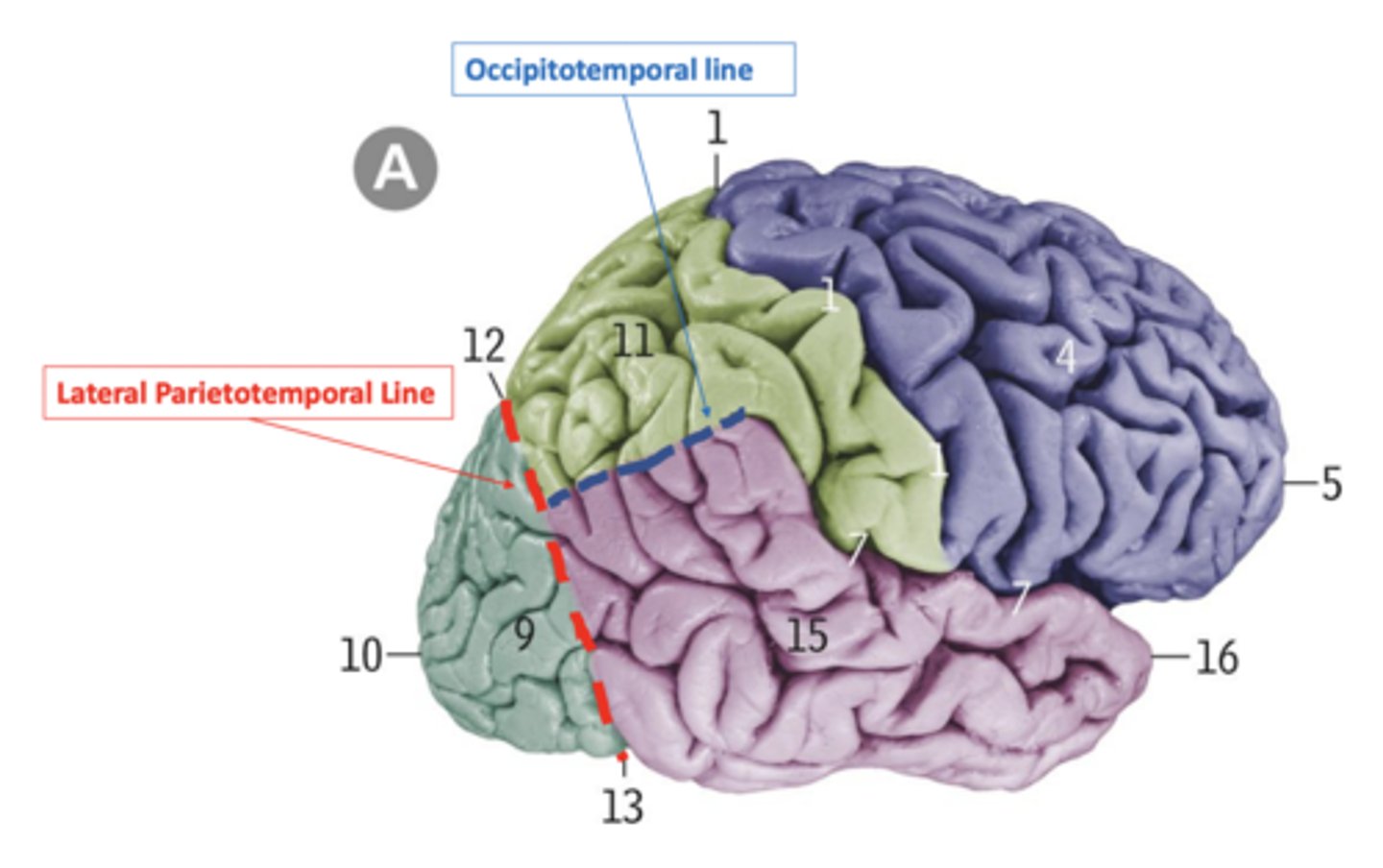
occipitotemporal line
imaginary line connecting the posterior margin of the Sylvian fissure with lateral parietotemporal line, separating the temporal and parietal lobes
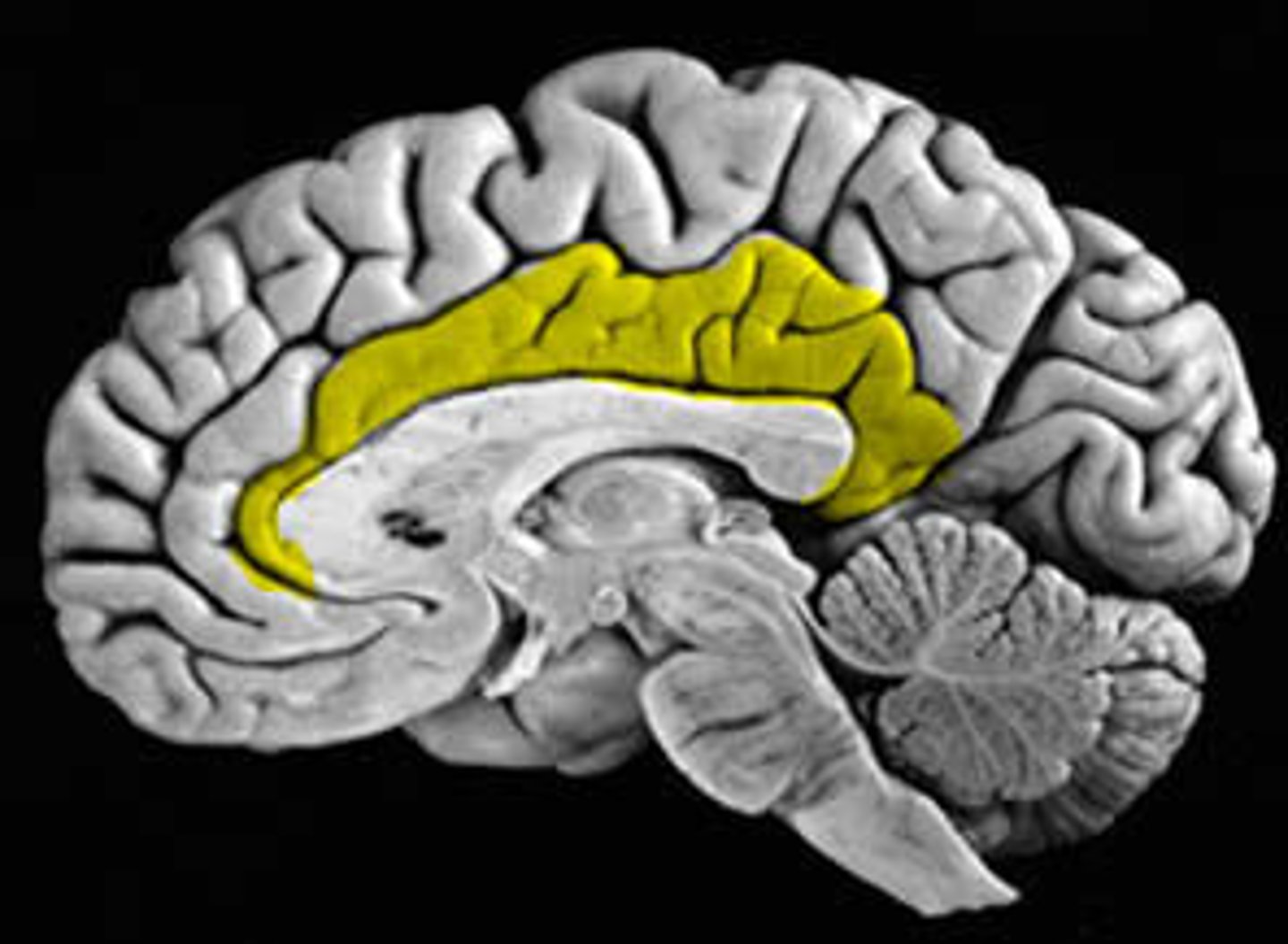
limbic lobe
located in the center of the brain beneath the other four cerebral lobes; influences unconscious instinctive behavior
cingulate sulcus
Separates frontal and parietal lobes from cingulate gyrus
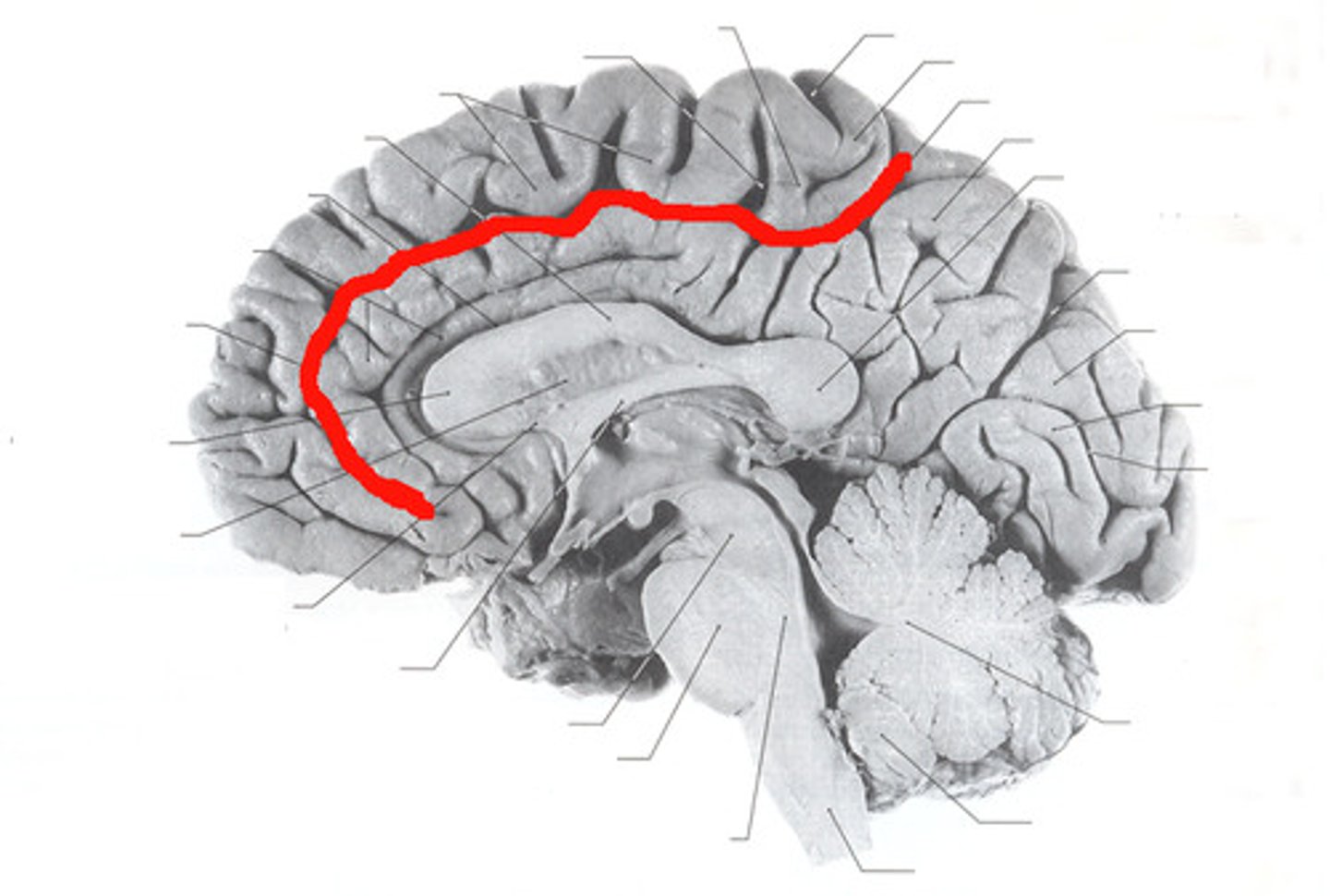
calcarine sulcus
separates the occipital lobe into superior and inferior halves
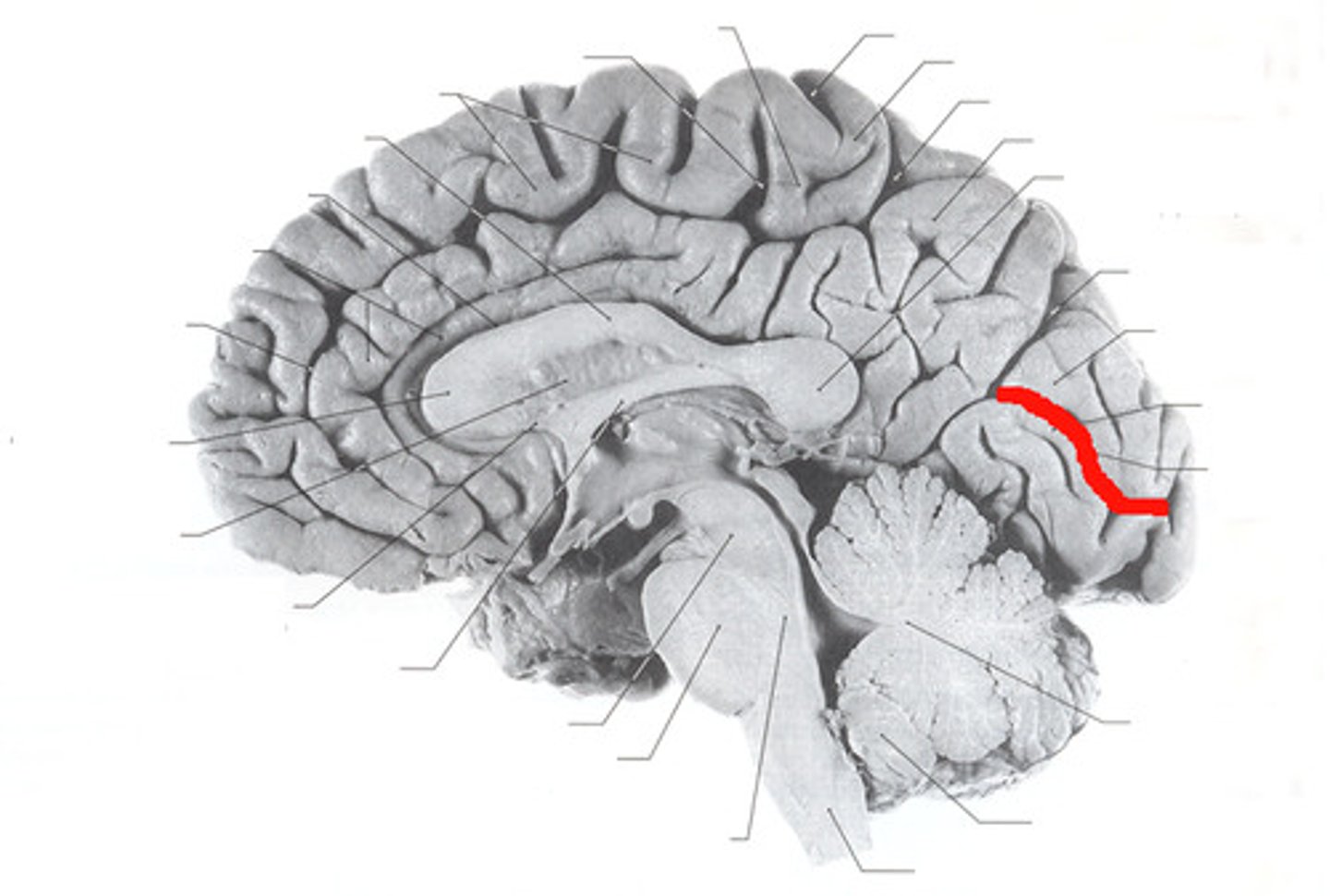
cingulate gyrus
a strip of limbic cortex lying along the lateral walls of the groove separating the cerebral hemispheres, just above the corpus callosum
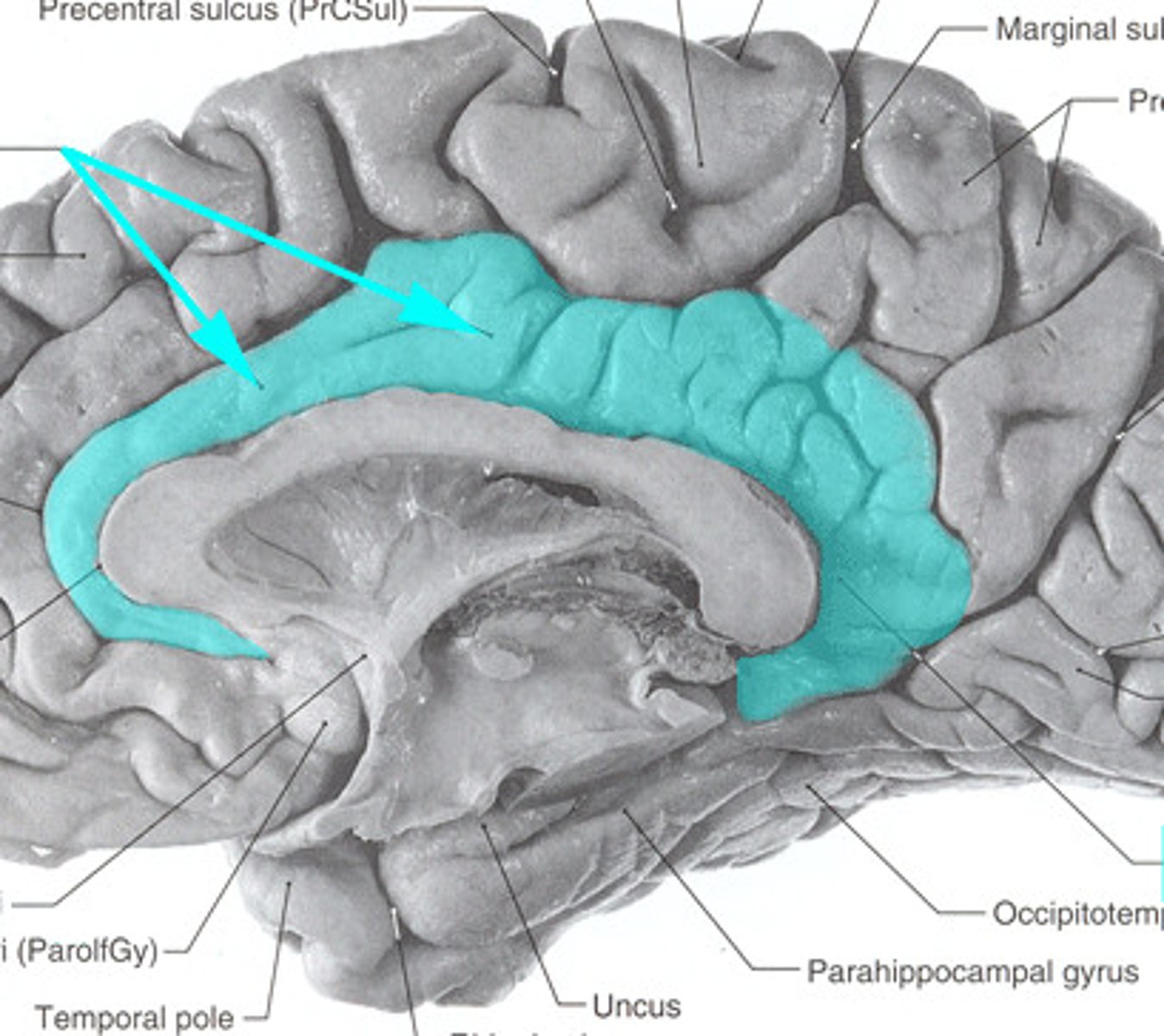
paracentral lobule
medial extension of the pre/post central gyri
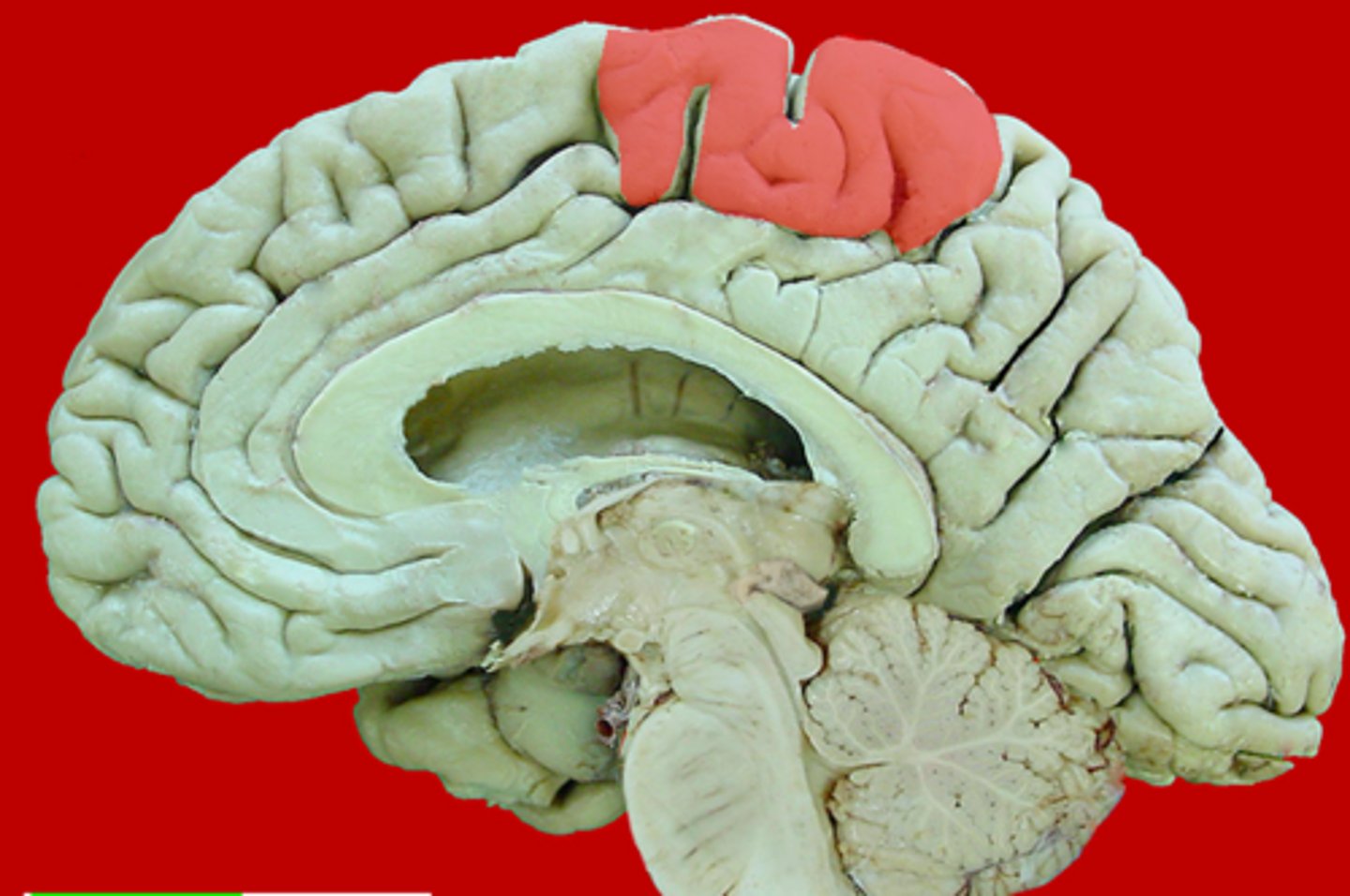
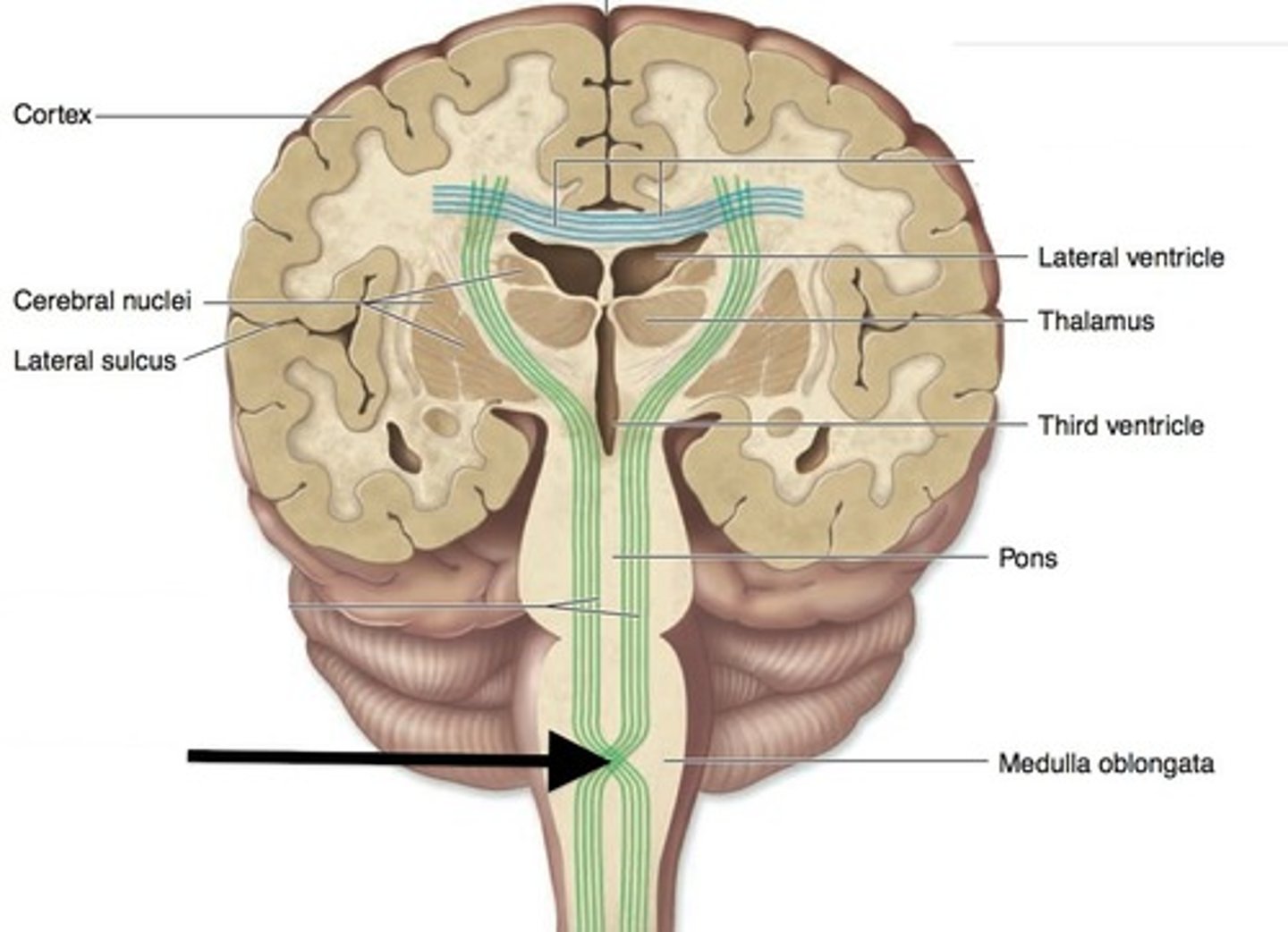
midbrain
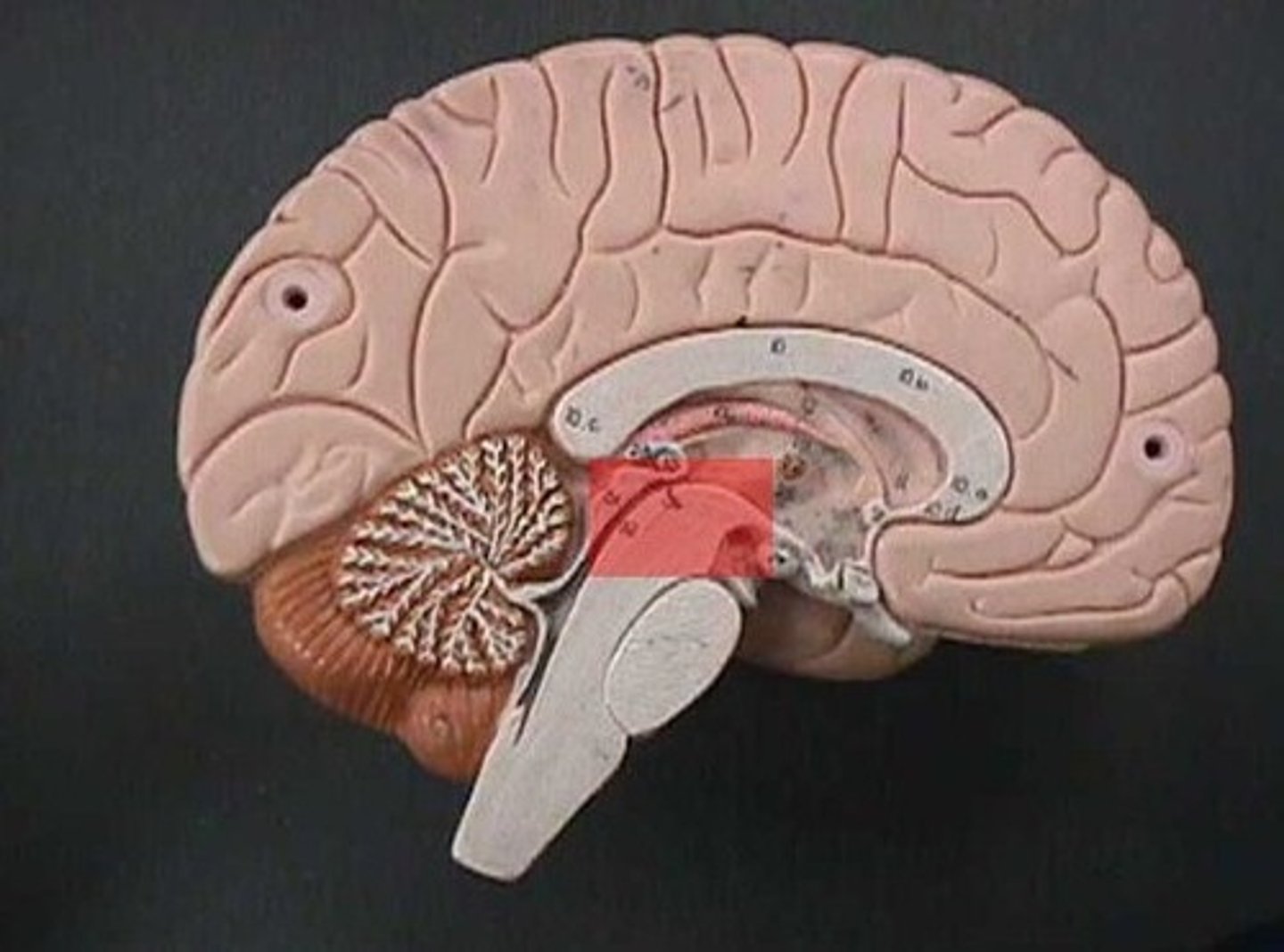
pons
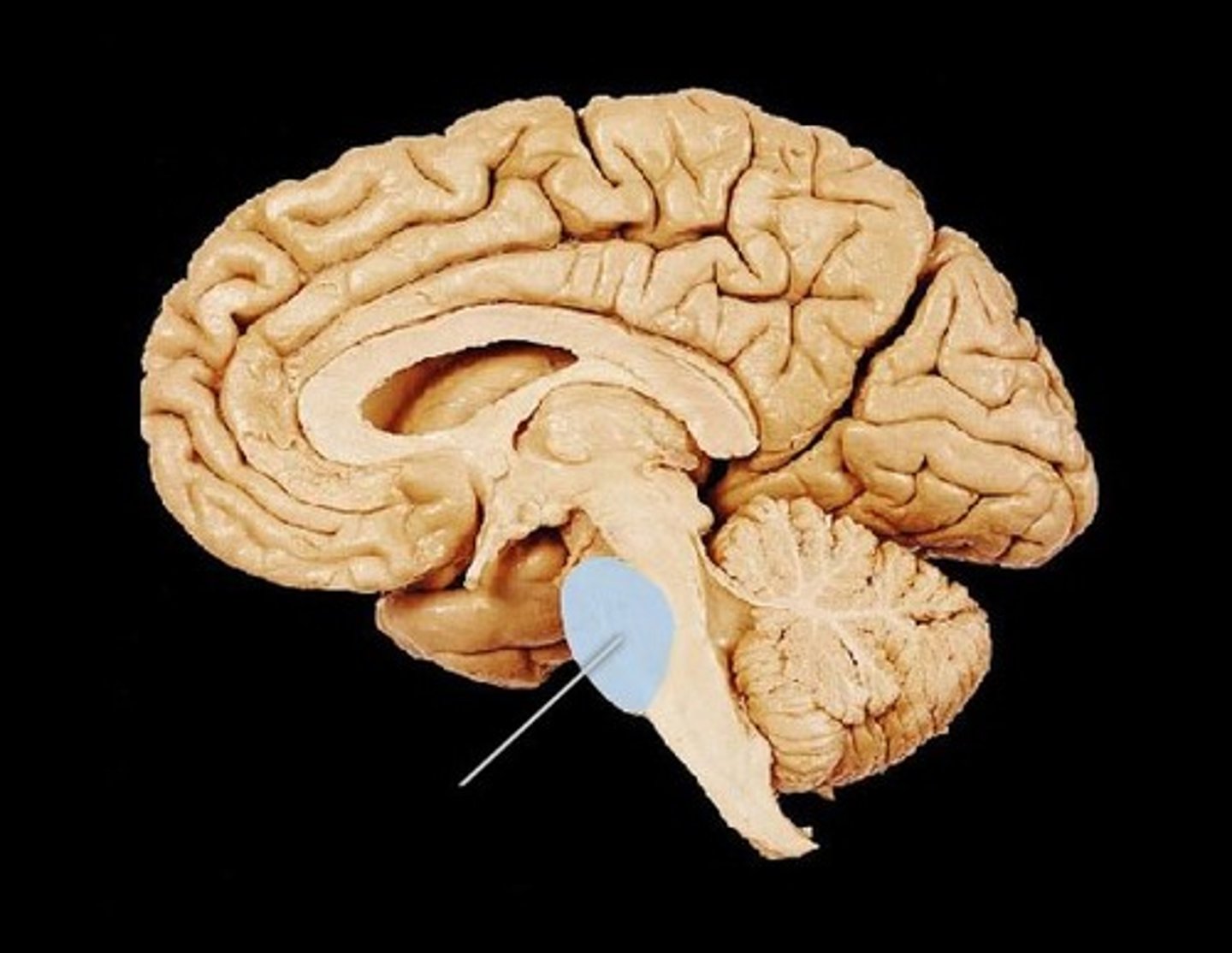
medulla oblongata
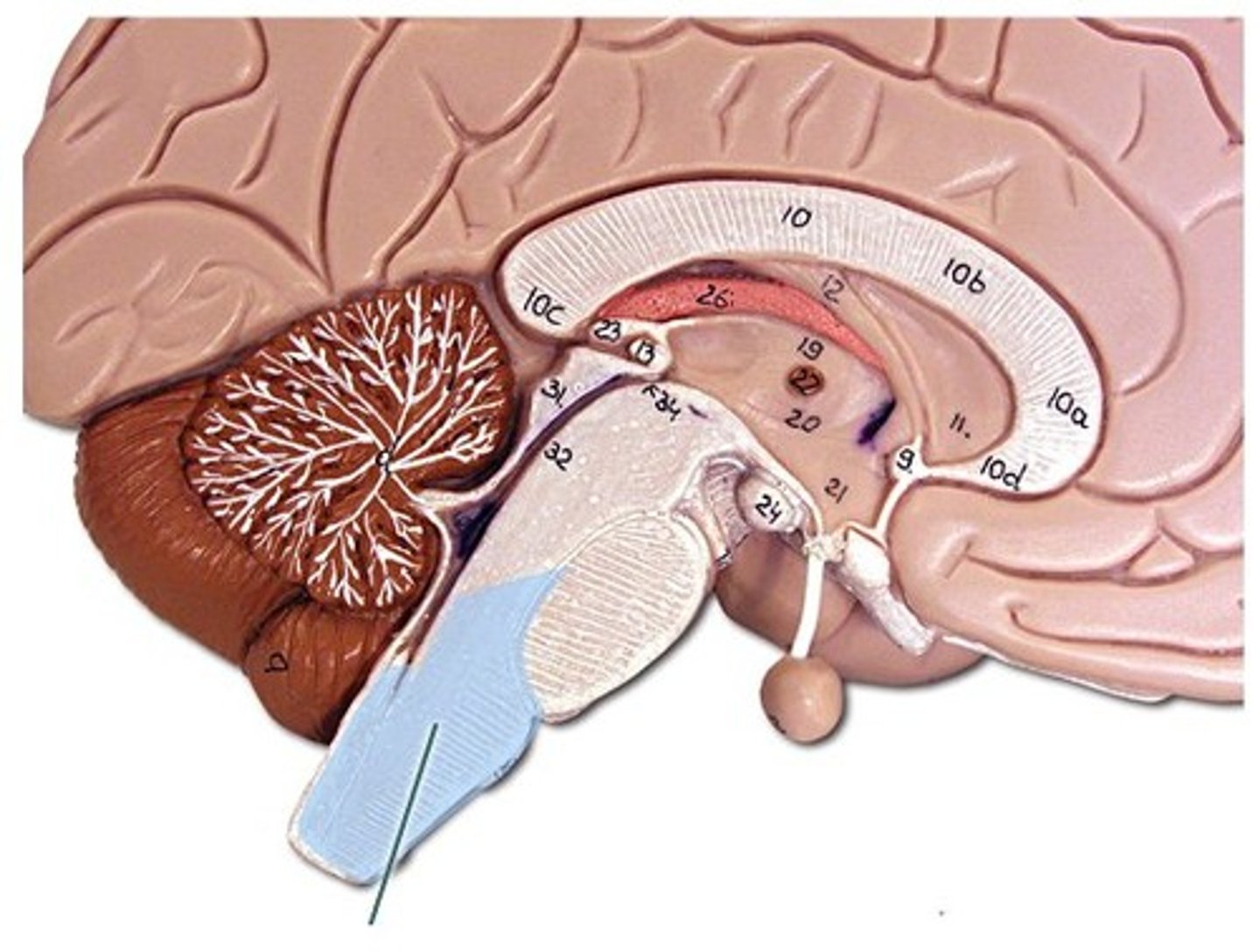
Which structures make up the brainstem?
midbrain, pons, medulla (cerebellum attached to it)
What are the major white matter tracts of the brain?
corona radiata, internal capsule, corpus callosum
corona radiata
- white matter within cerebrum that funnels axons (ex. corticospinal tract) to internal capsule
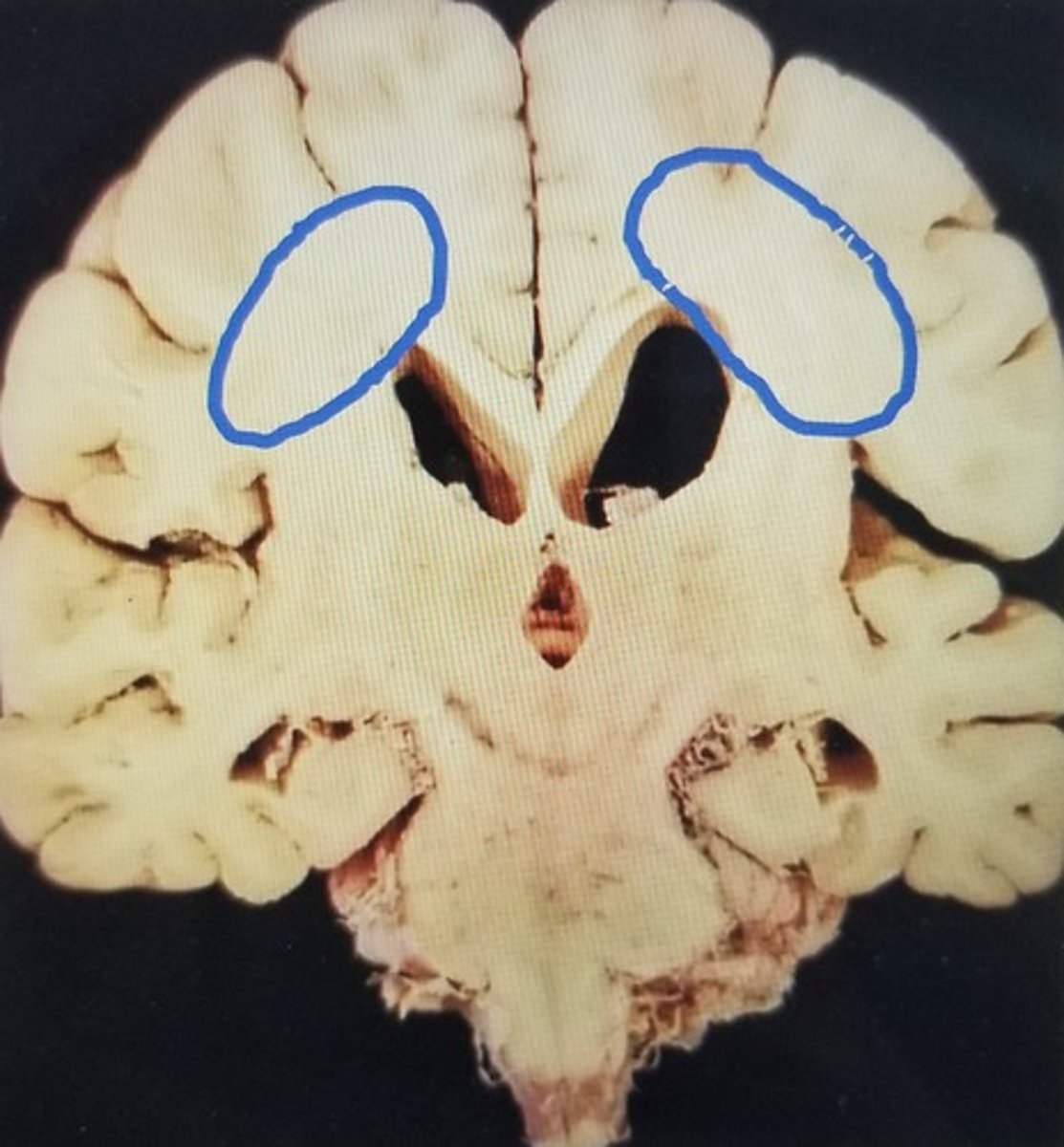
internal capusle
white matter tract that separates the lentiform nucleus from the thalamus and caudate nucleus
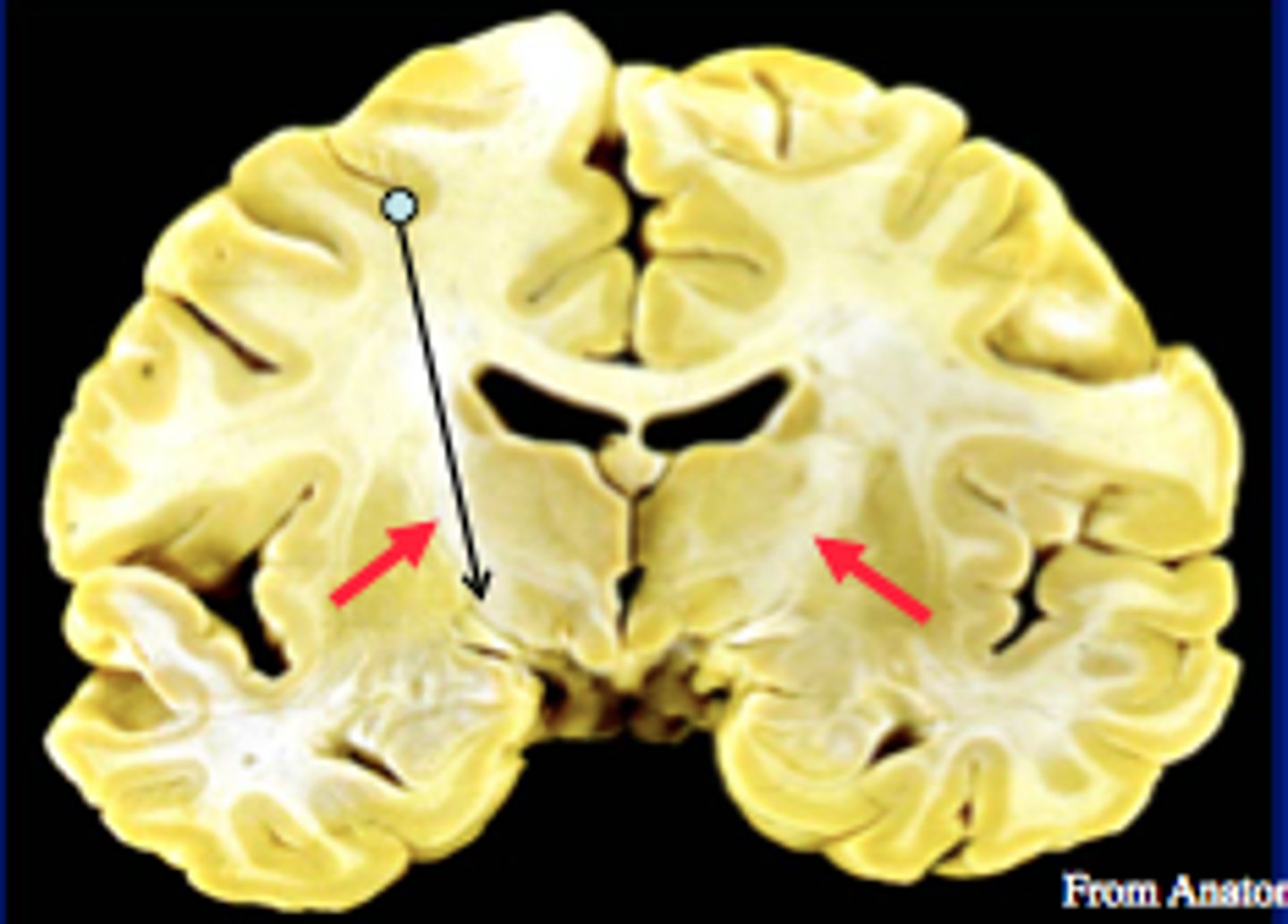
corpus callosum
white matter tract connecting the hemispheres and separating the deep brain nuclei from the cingulate gyrus
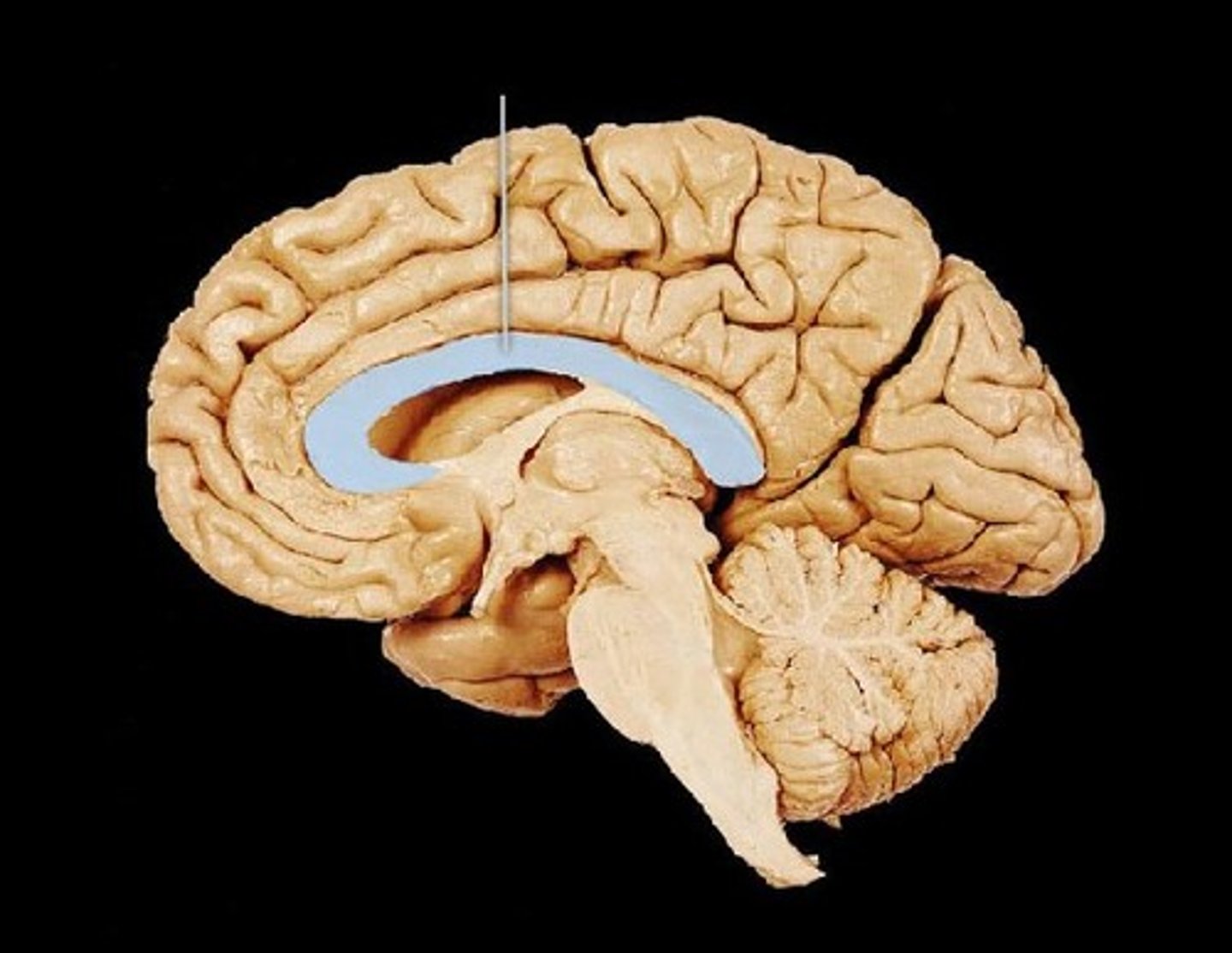
thalamus
most medial structure of the brain, paired bilaterally with a bridge and separation via the third ventricle
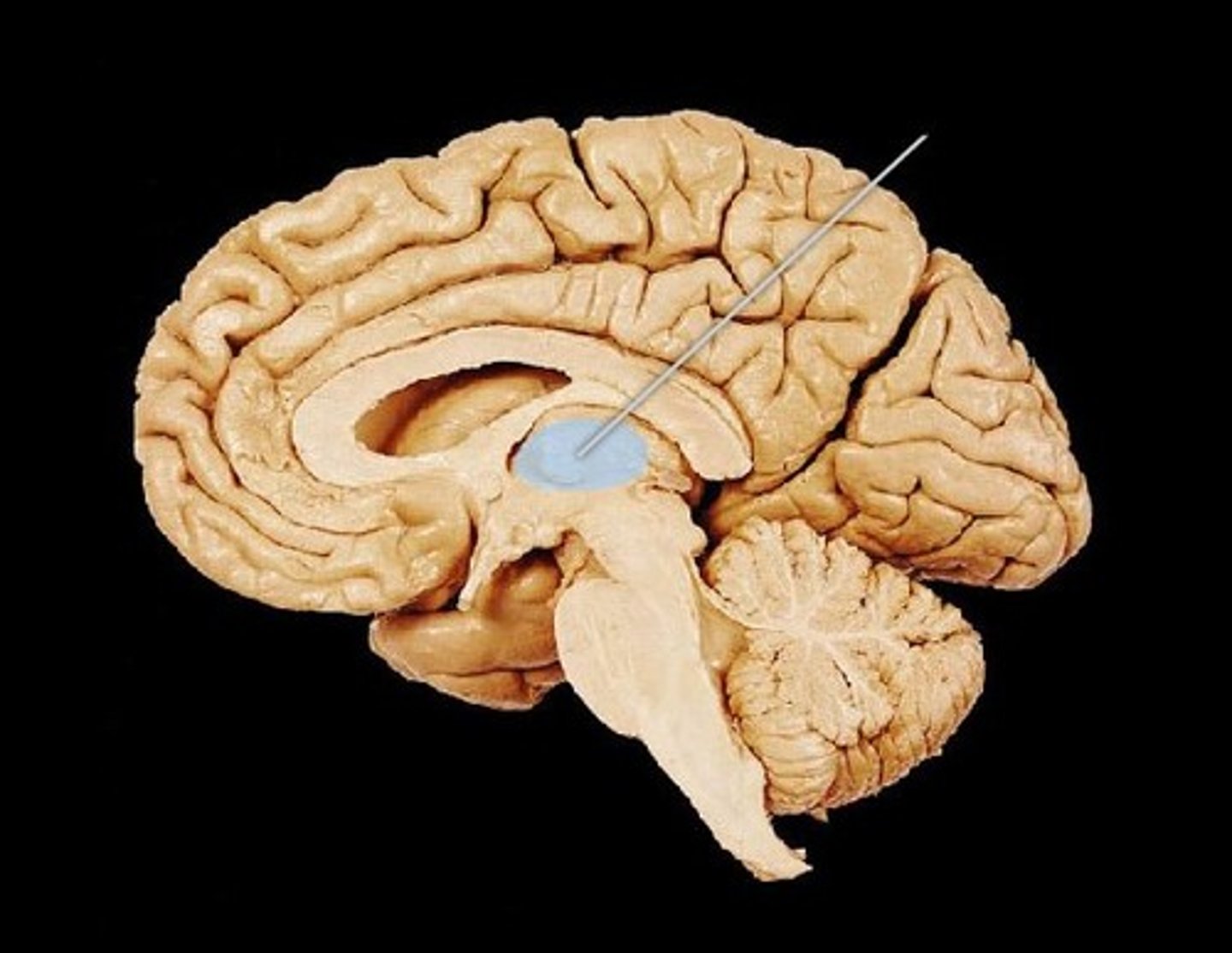
basal nuclei (ganglia)
structure consisting of the lentiform and caudate nuclei
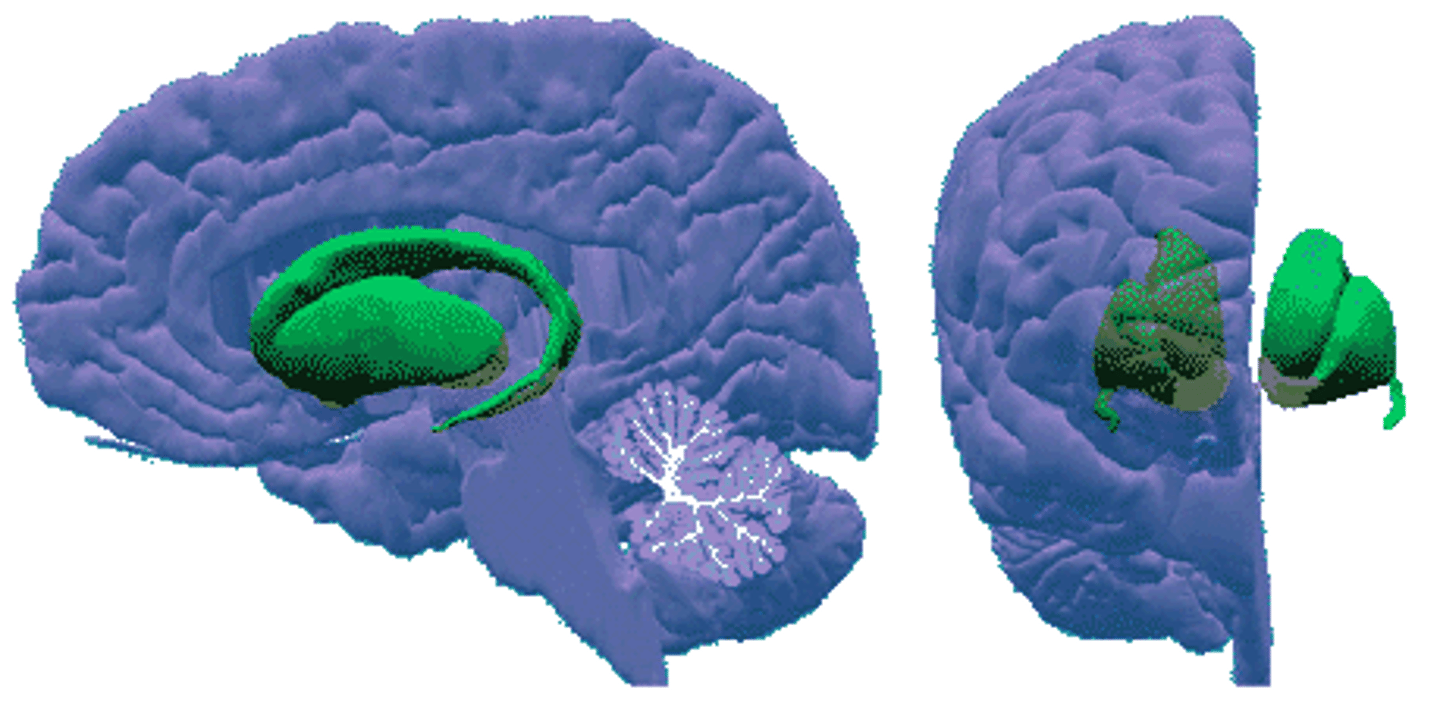
caudate nuclei
deep brain nuclei with a head and tail end, most lateral to the other basal nuclei
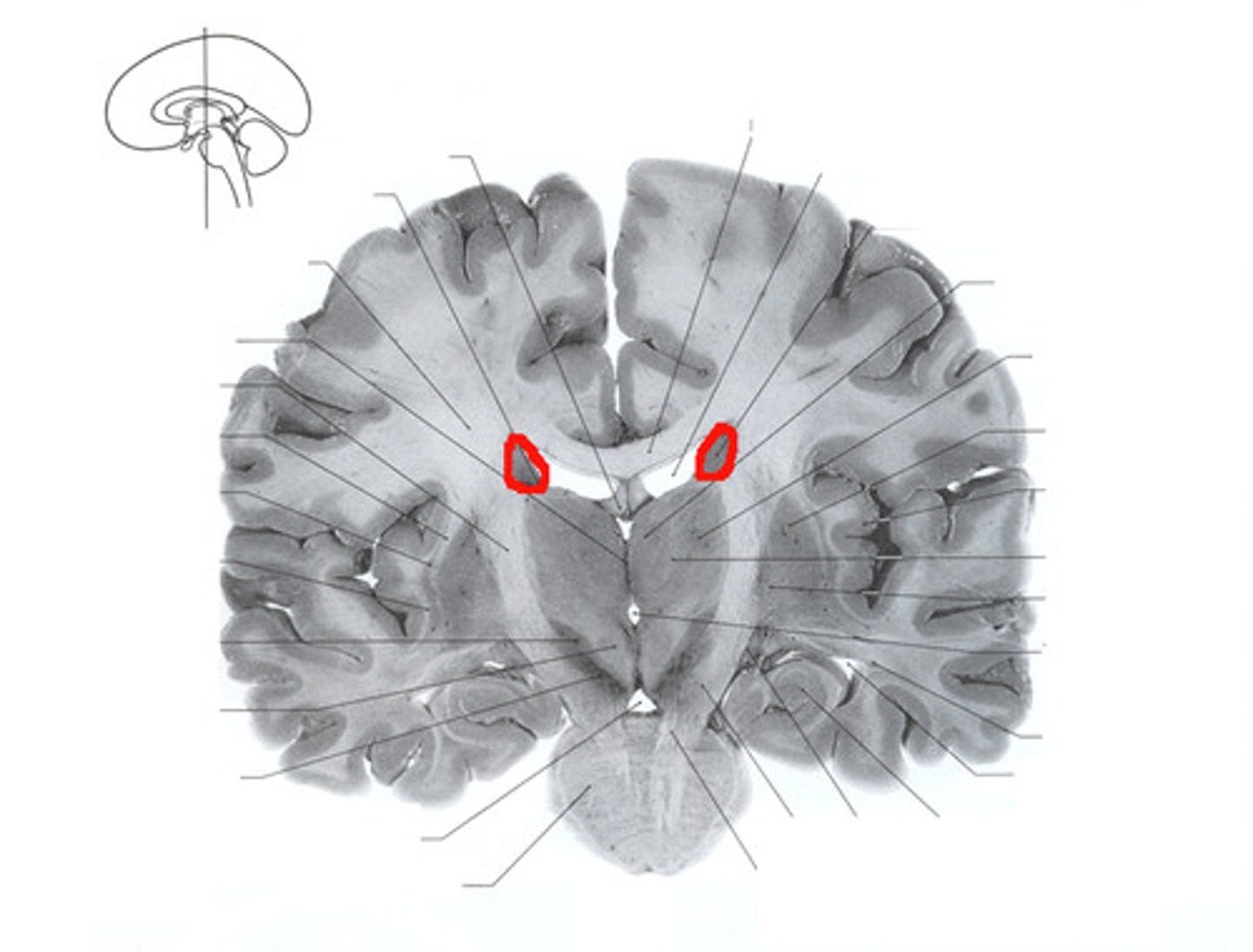
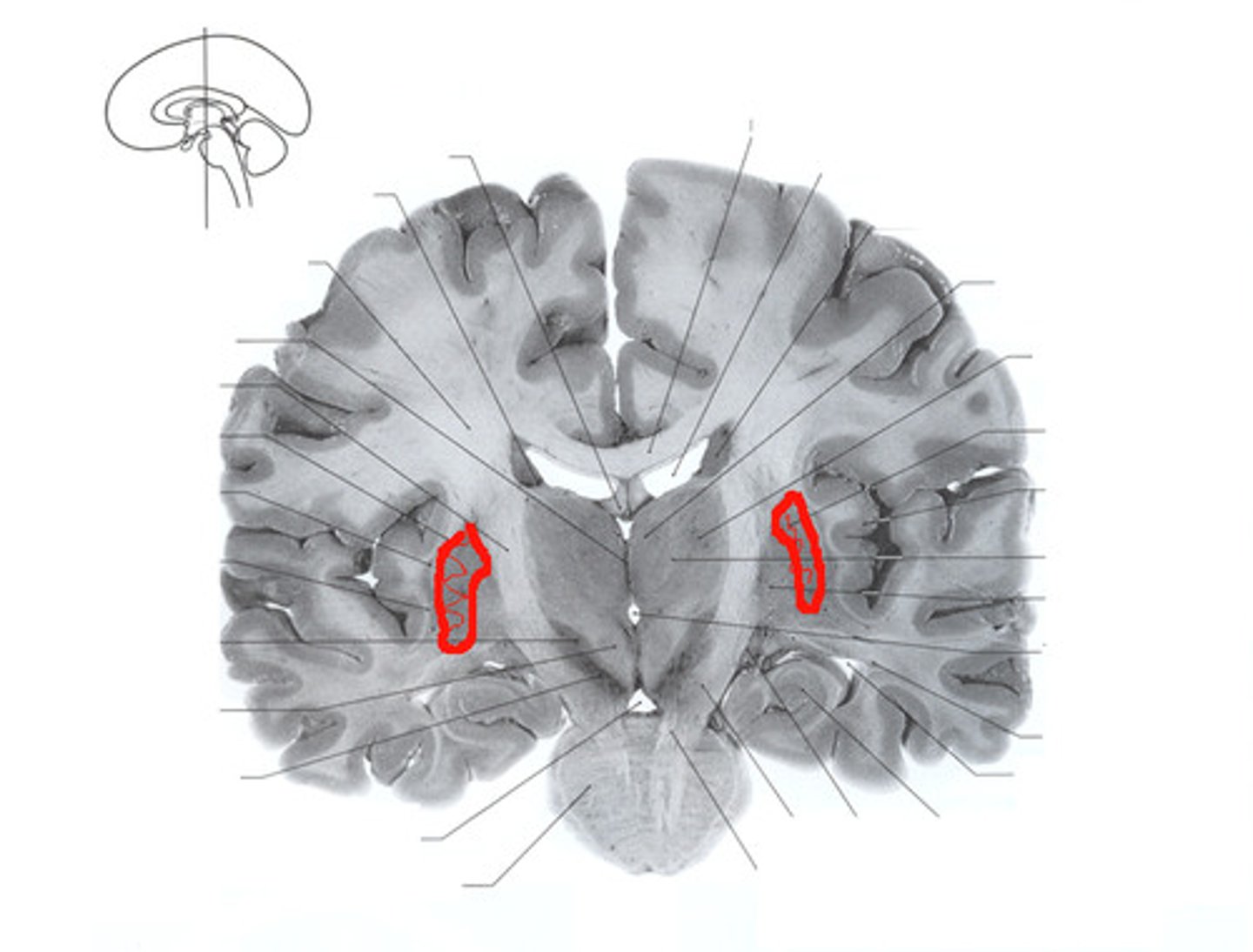
putamen
one of the basal ganglia
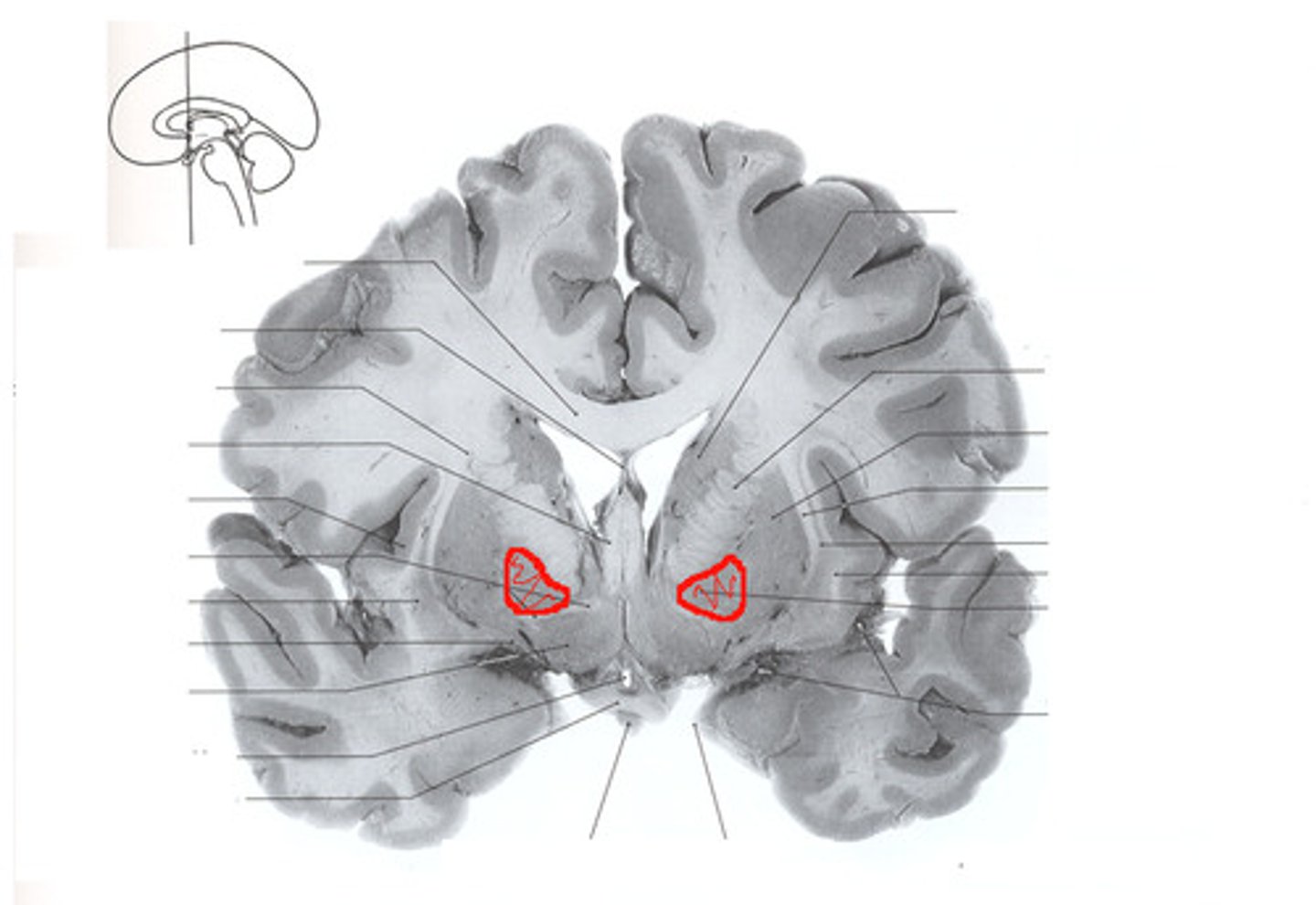
globus pallidus
most medial component of the basal ganglia
What structures are the deep brain nuclei?
thalamus, basal nuclei, caudate nuclei, putamina, globus pallidi
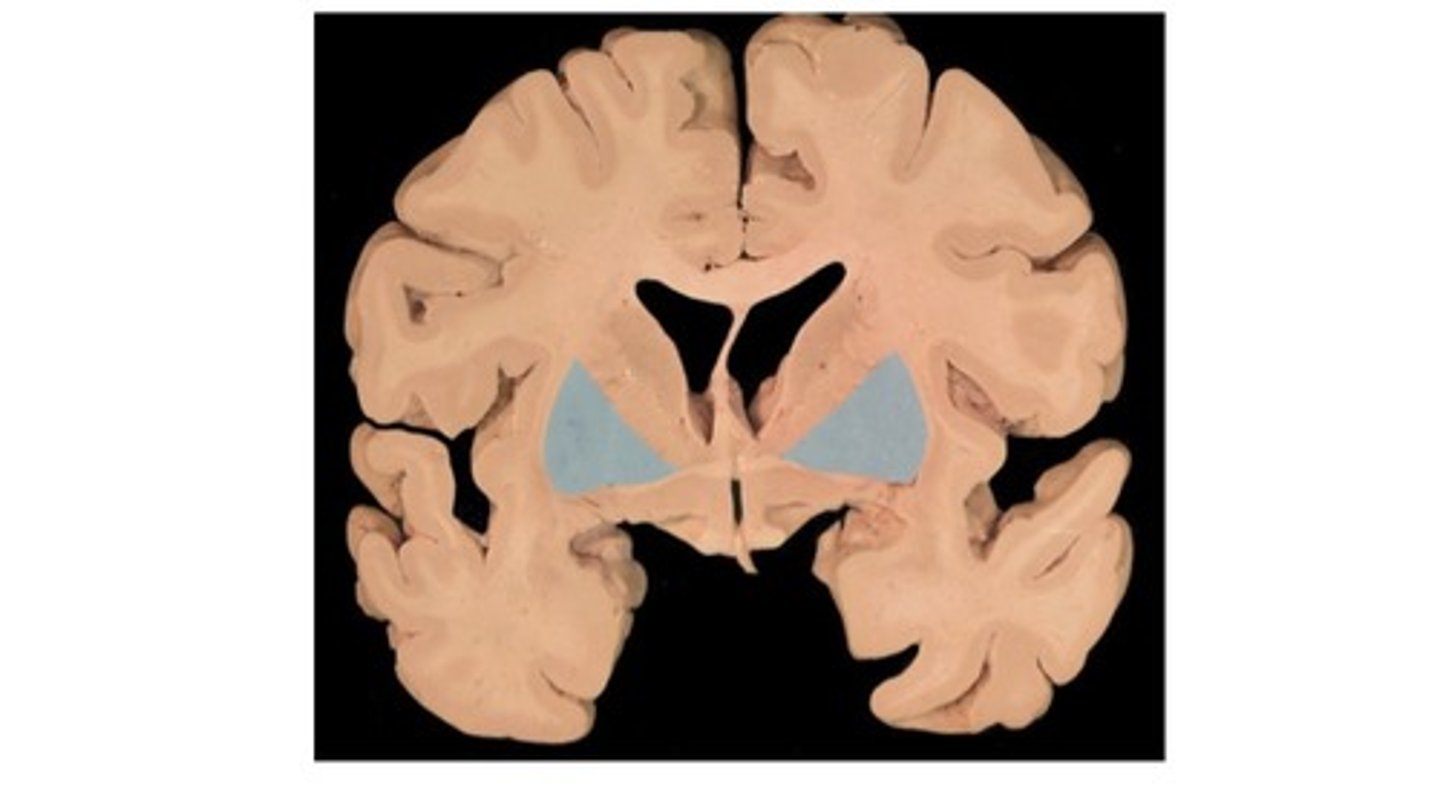
What is the lentiform nucleus?
putamen and globus pallidus
olfactory bulb (CN I)
sensory structure where axons of cranial nerve 1 synapse, resting on the cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone
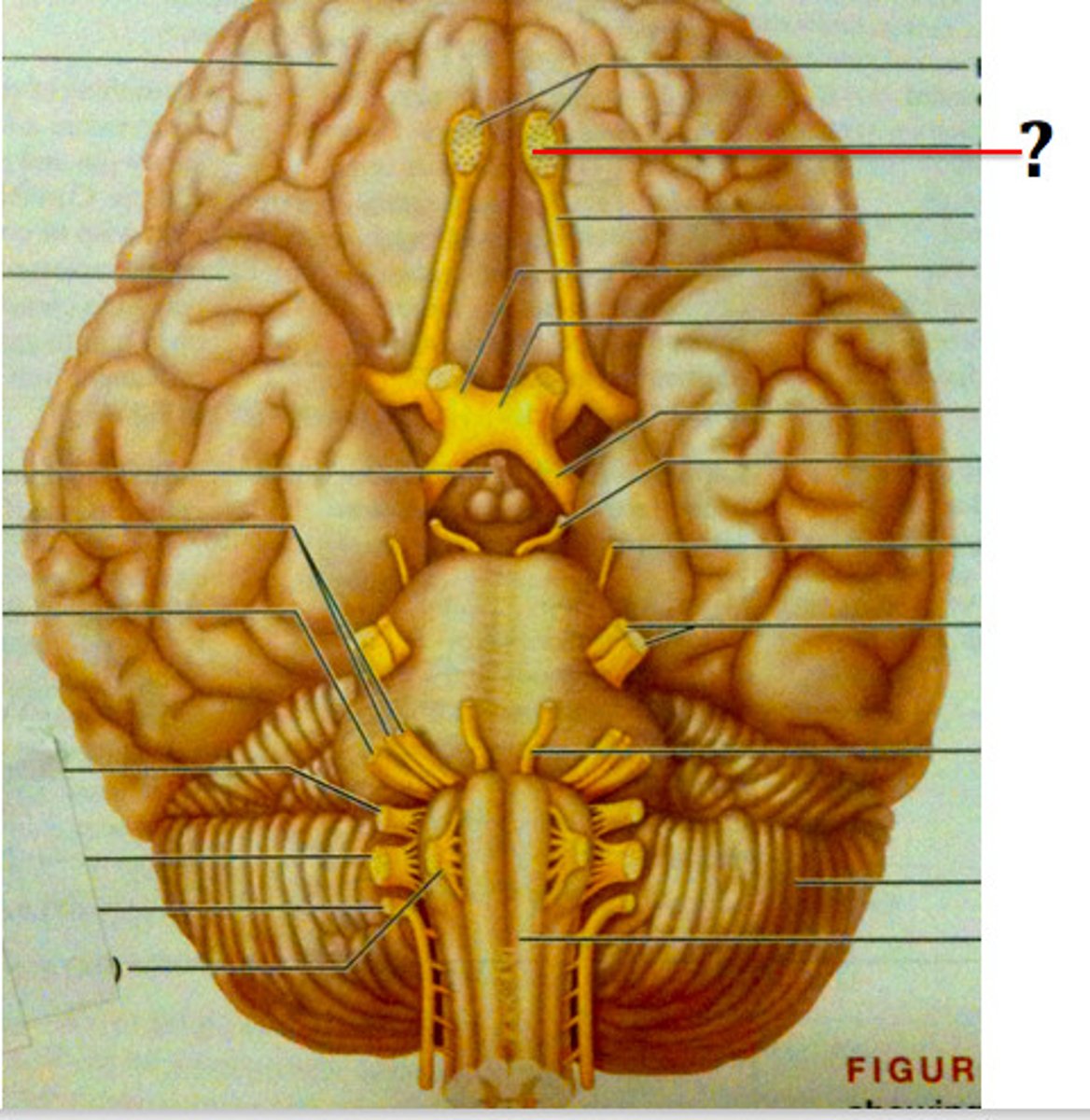
olfactory nerve
the nerve that carries smell impulses from the nose to the brain
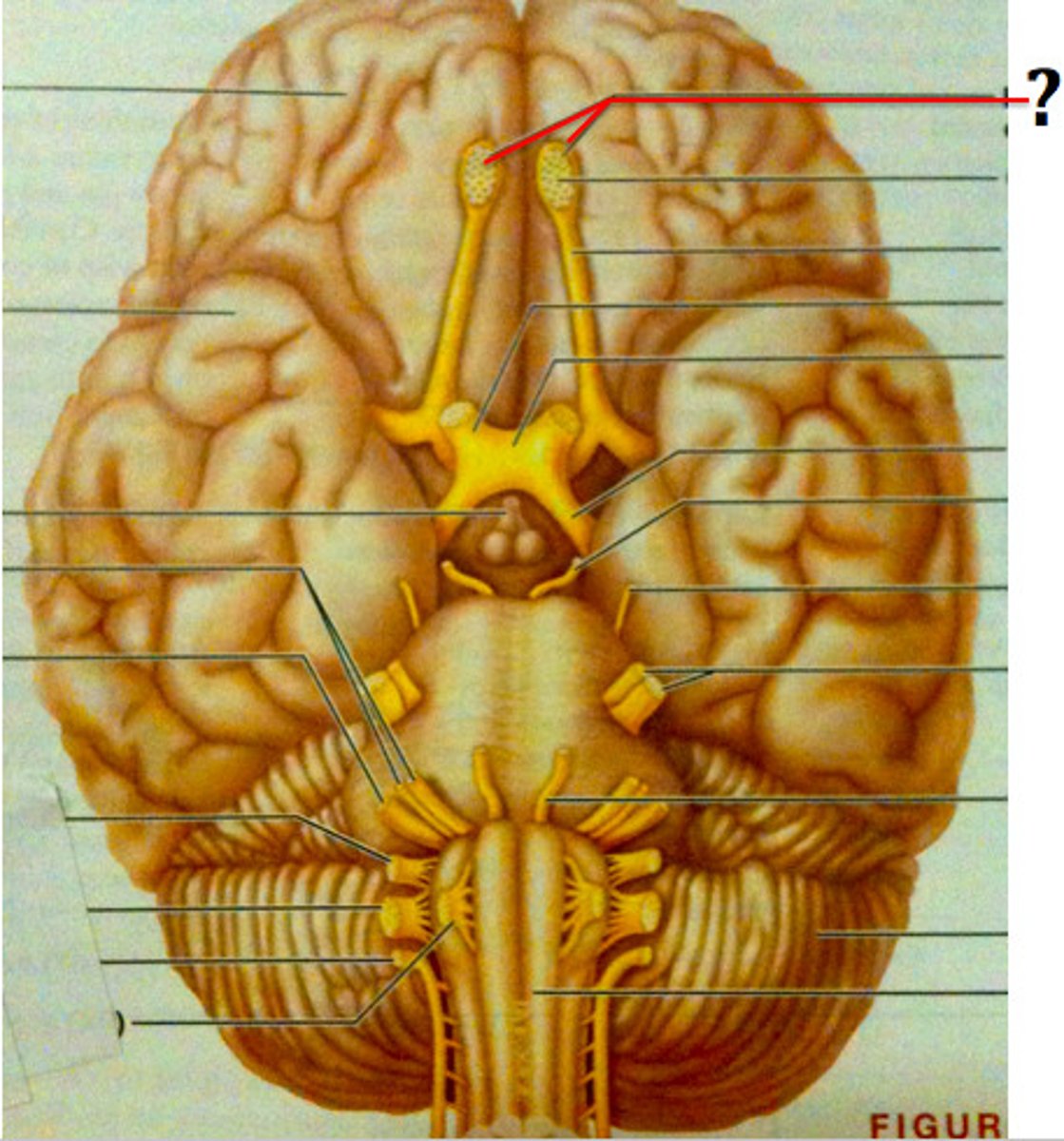
optic nerve (CN II)
sensory, vision
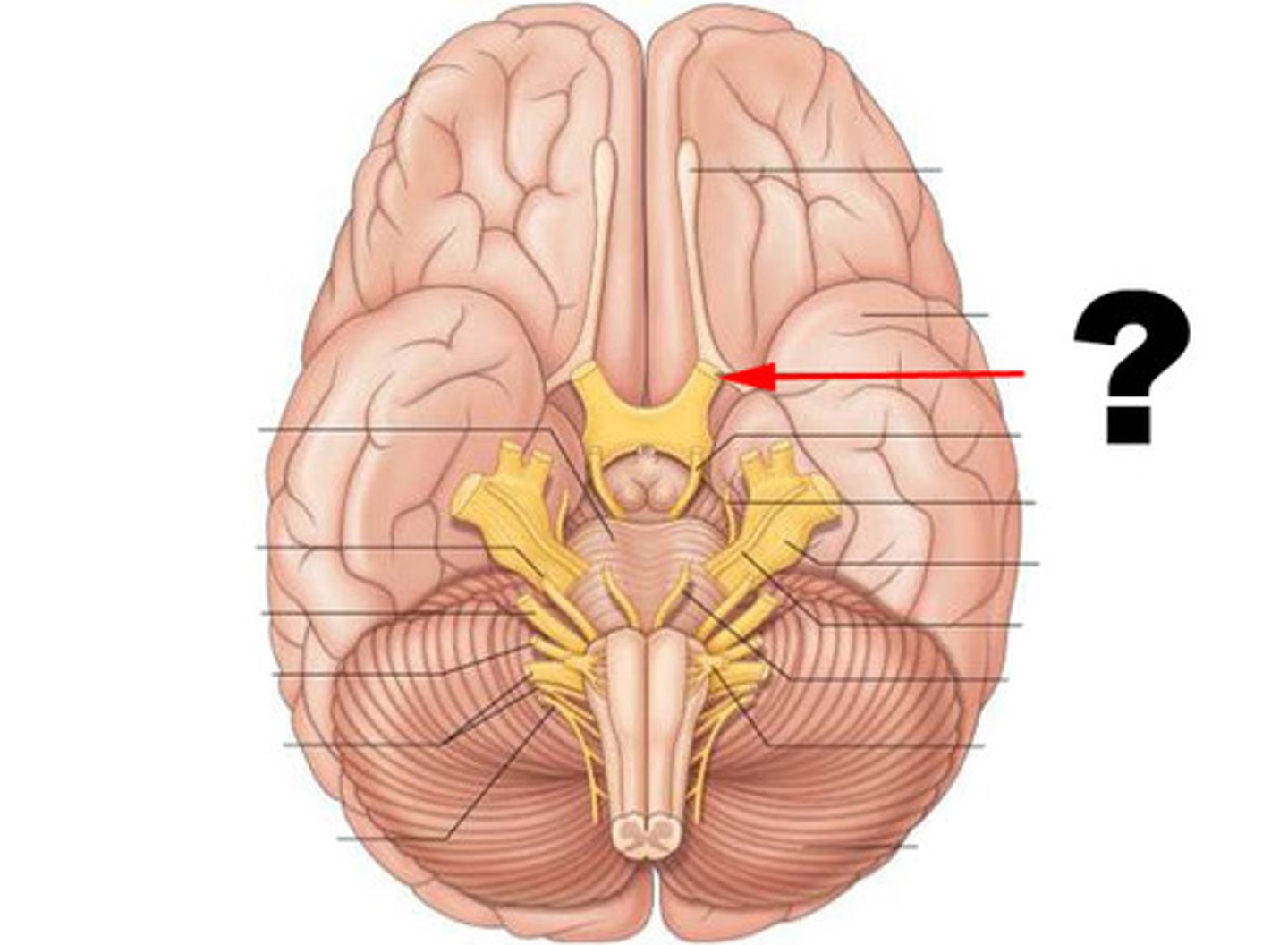
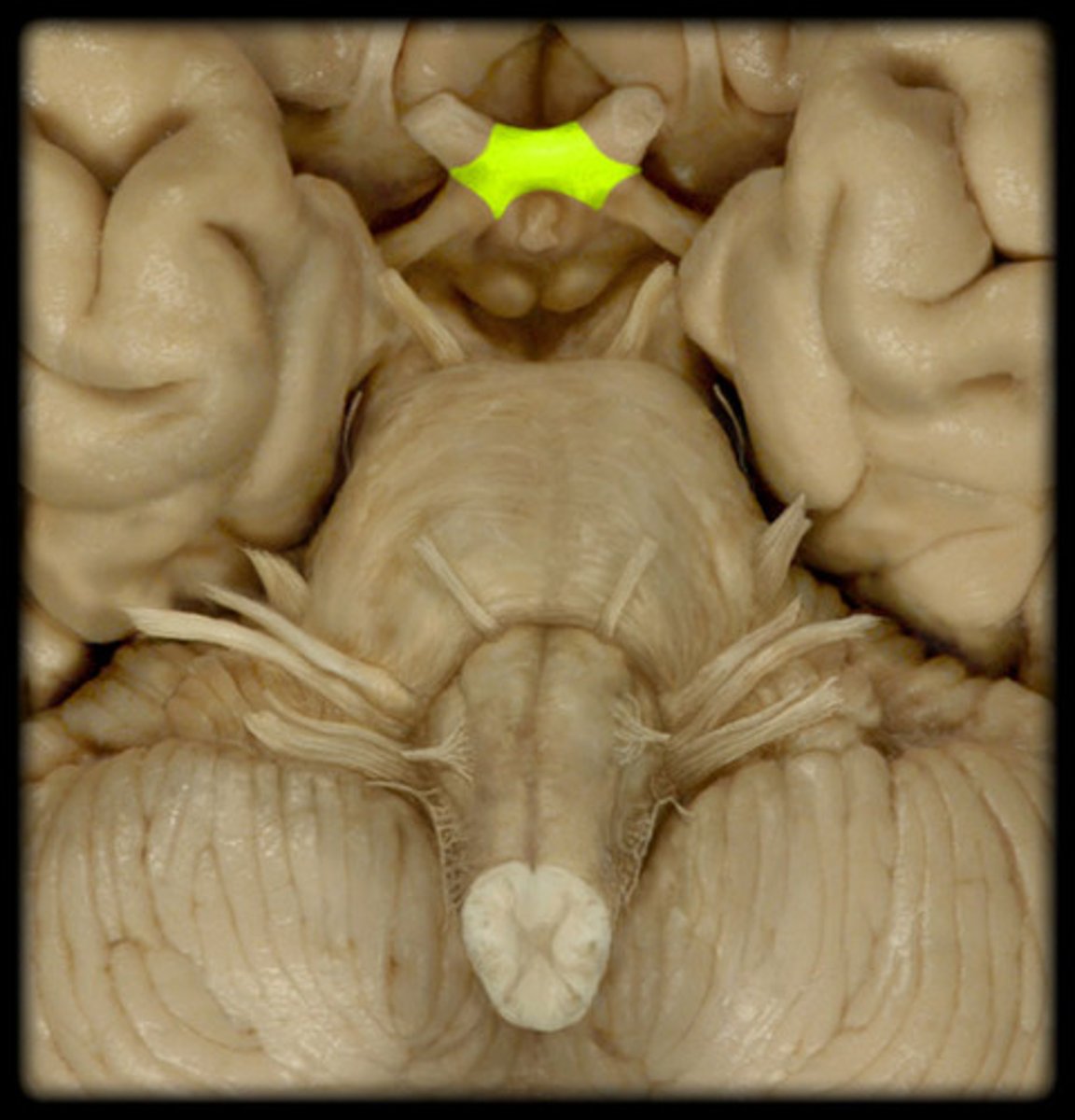
optic chiasm
point at which optic nerve fibers cross in the brain
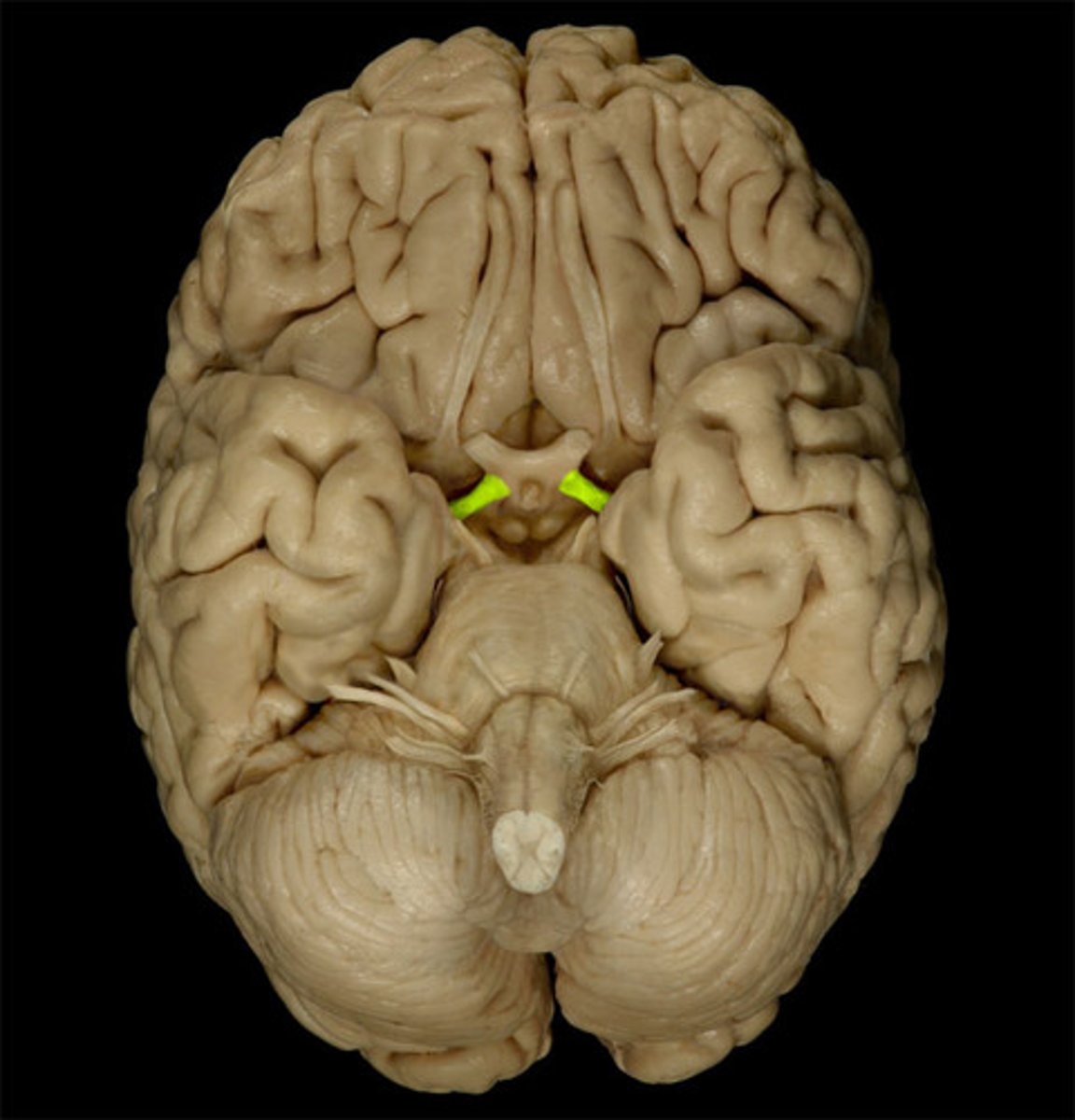
optic tract
leads from optic chiasma to terminate in lateral geniculate body of the thalamus
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
-motor only
-exits skull through superior orbital fissure
-innervates superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, inferior oblique, and levator palpebrae superioris with somatic motor fibers
-innervates smooth muscle of pupil and lens with parasympathetic fibers
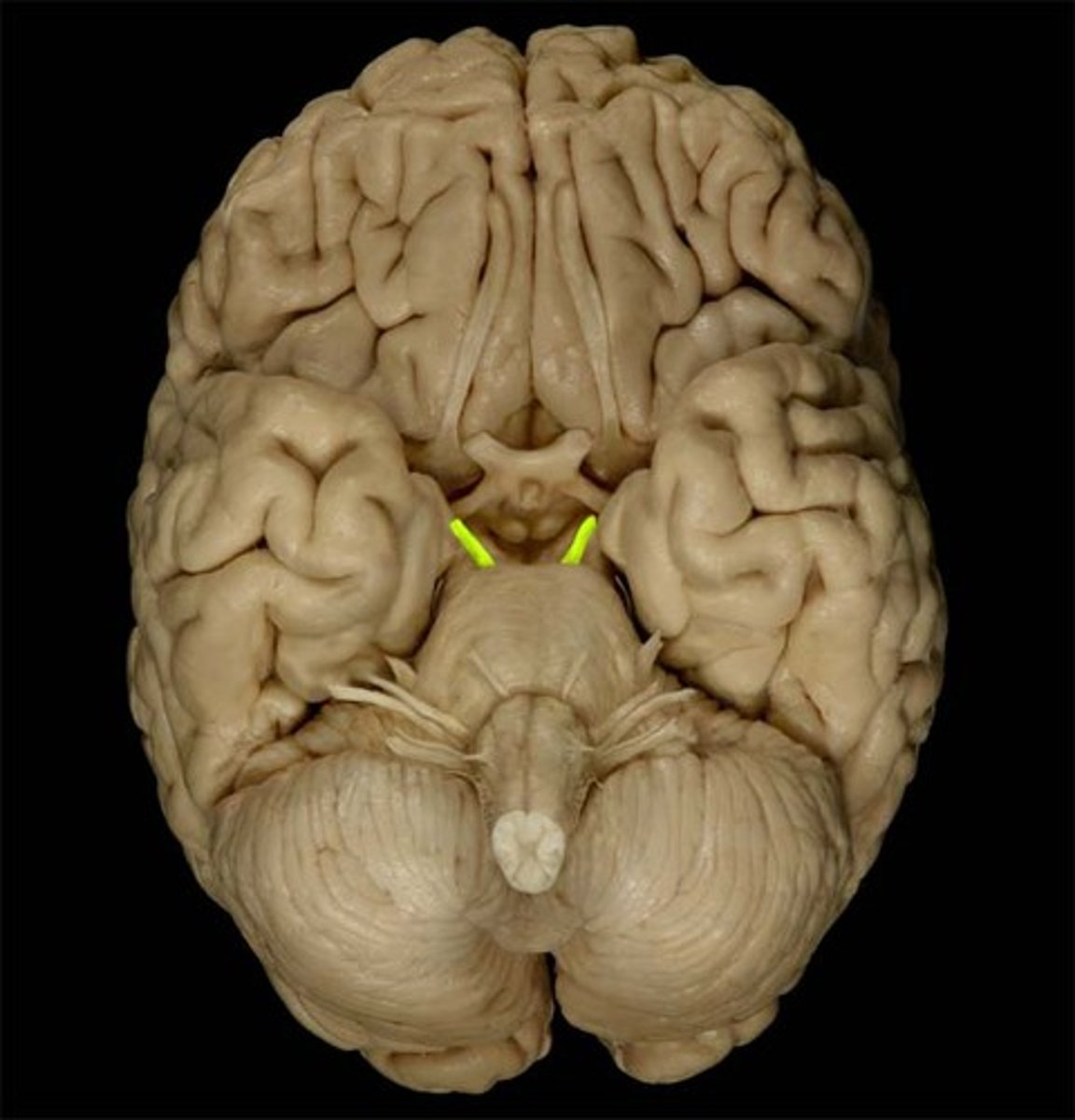
Trochlear nerve (CN IV)
innervates the superior oblique muscle, motor only
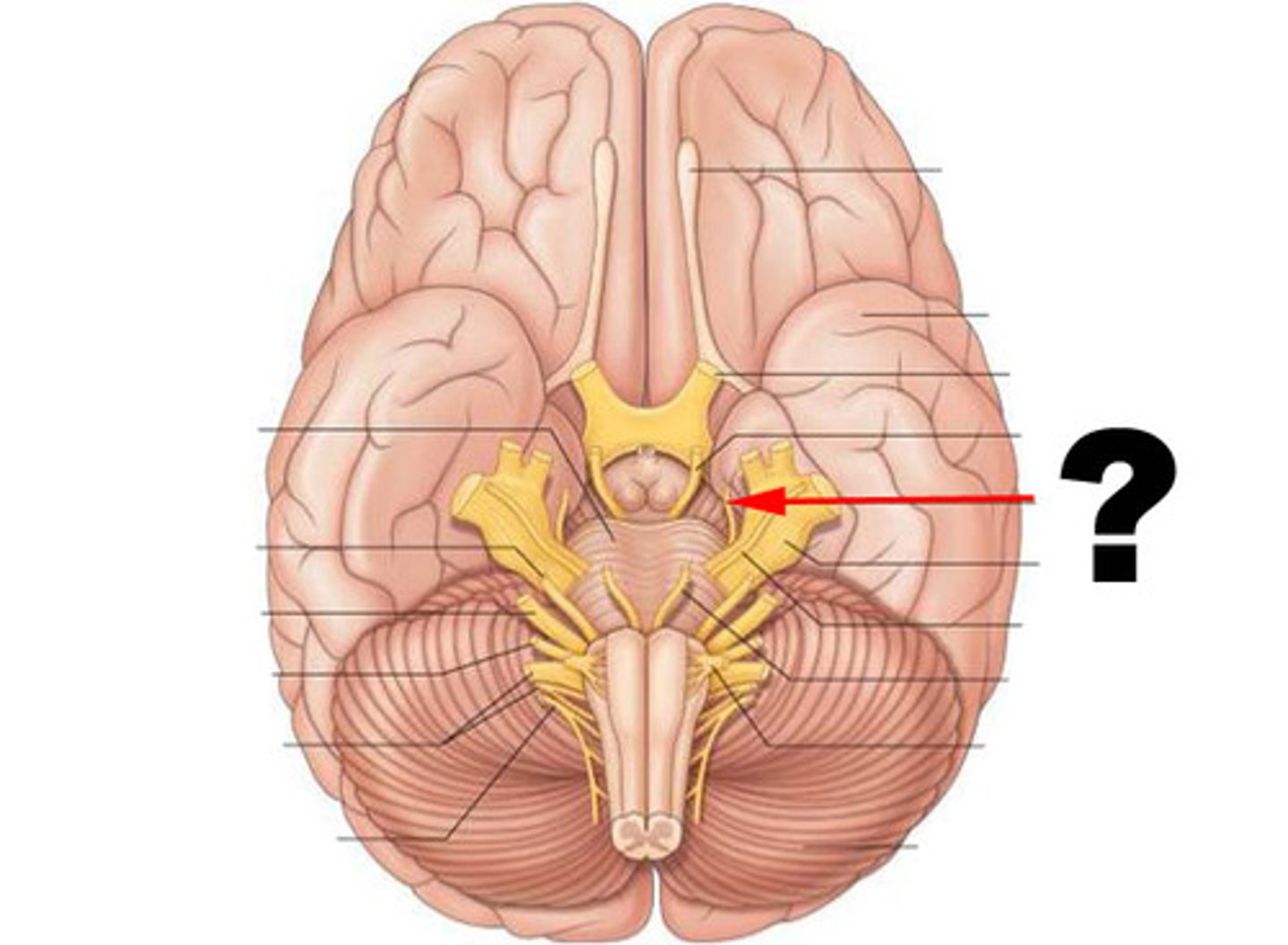
trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Somatic sensory nerve to skin over the mandible, temporal region, and anterior 2/3 of the tongue. It is sensitive to texture/irritants on the tongue and in the nasal cavity/eye as well.
Lingual nerve is the branch that controls touch for the tongue.
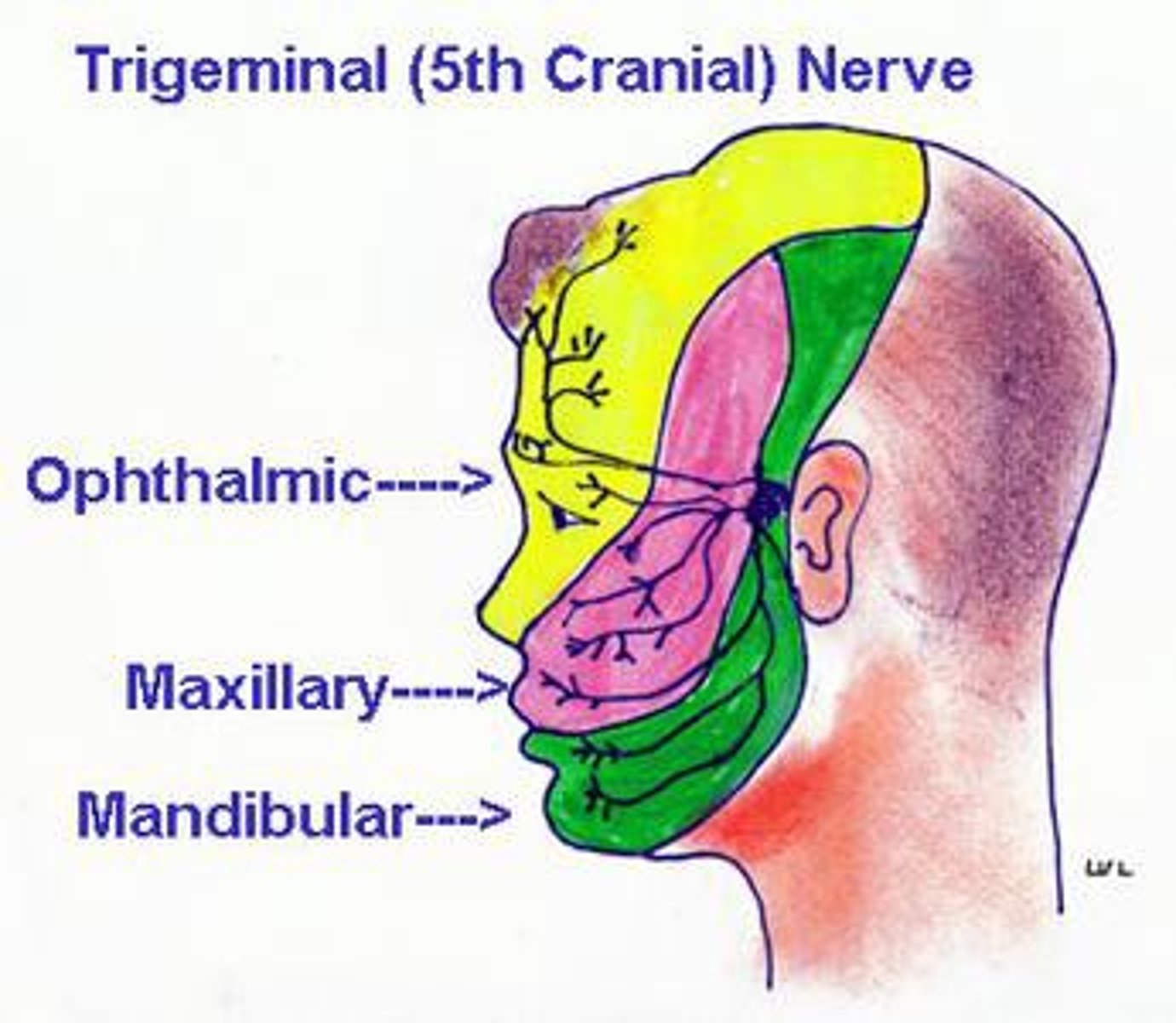
Opthalamic Nerve (CN V1)
Sensation to forehead, eyes and nose
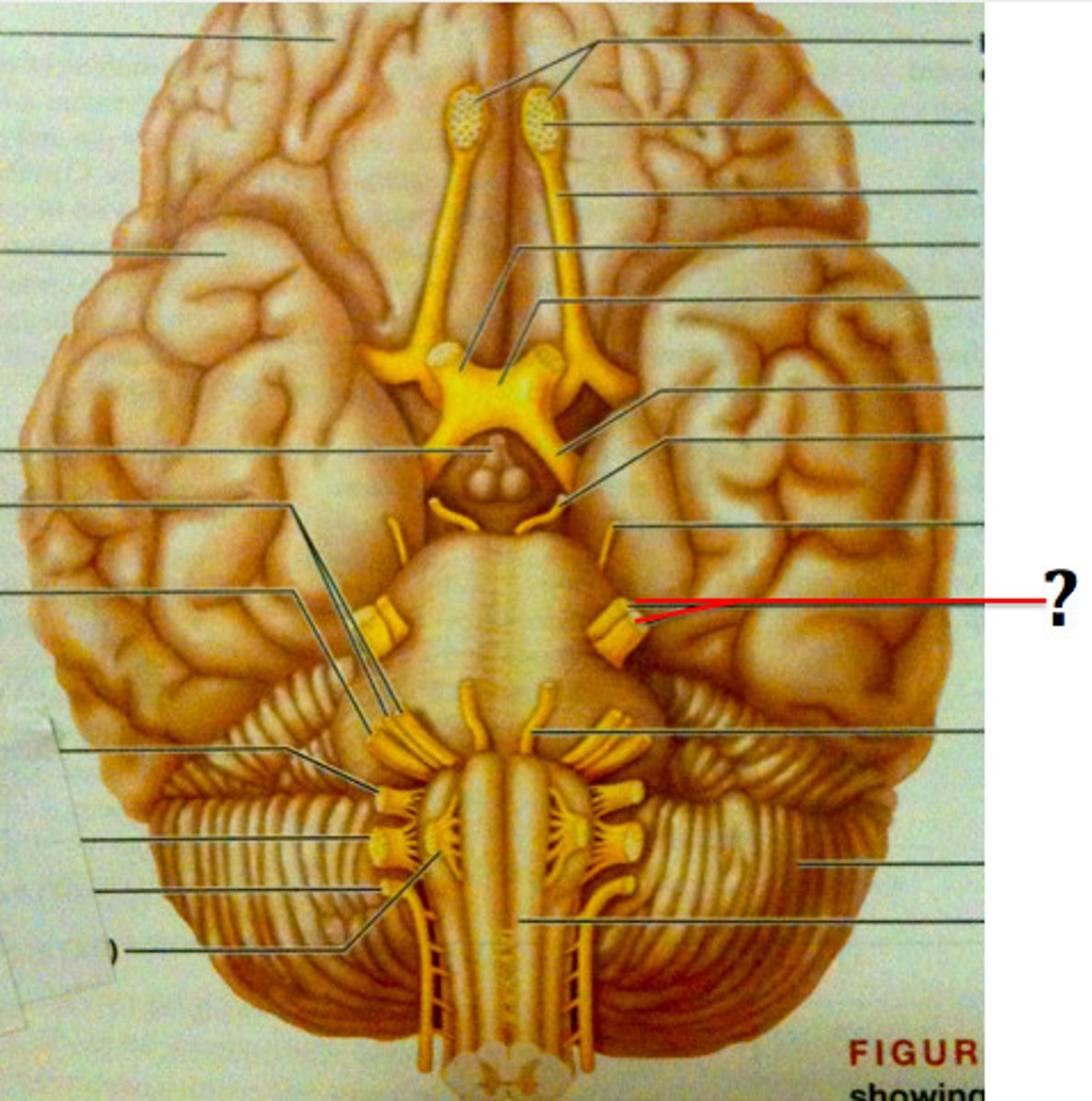
trigeminal ganglion
sensory ganglion that contributes sensory fibers to the trigeminal nerve
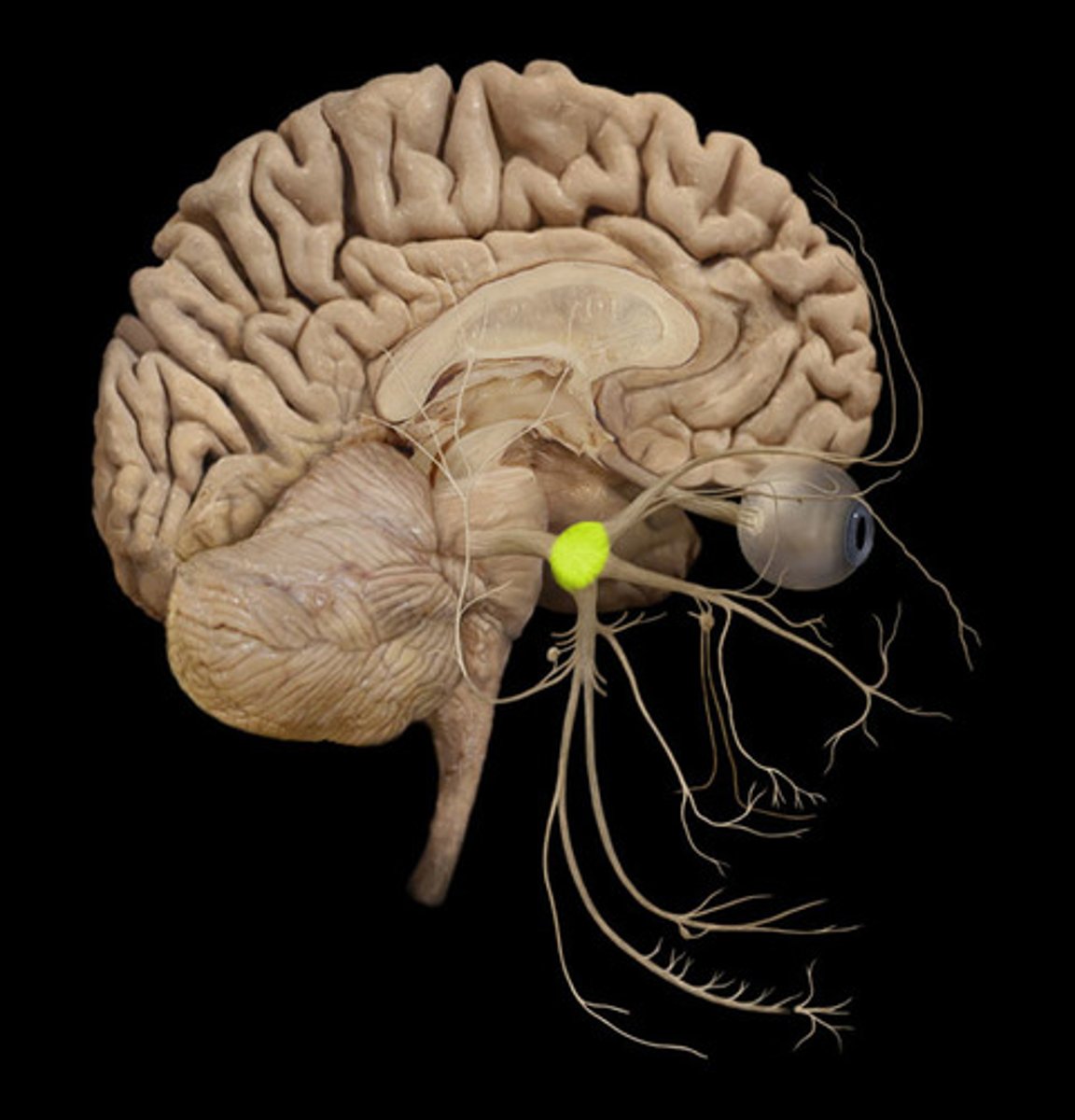
maxillary nerve (CN V2)
Branch of the fifth cranial nerve that supplies impulses to the upper part of the face.
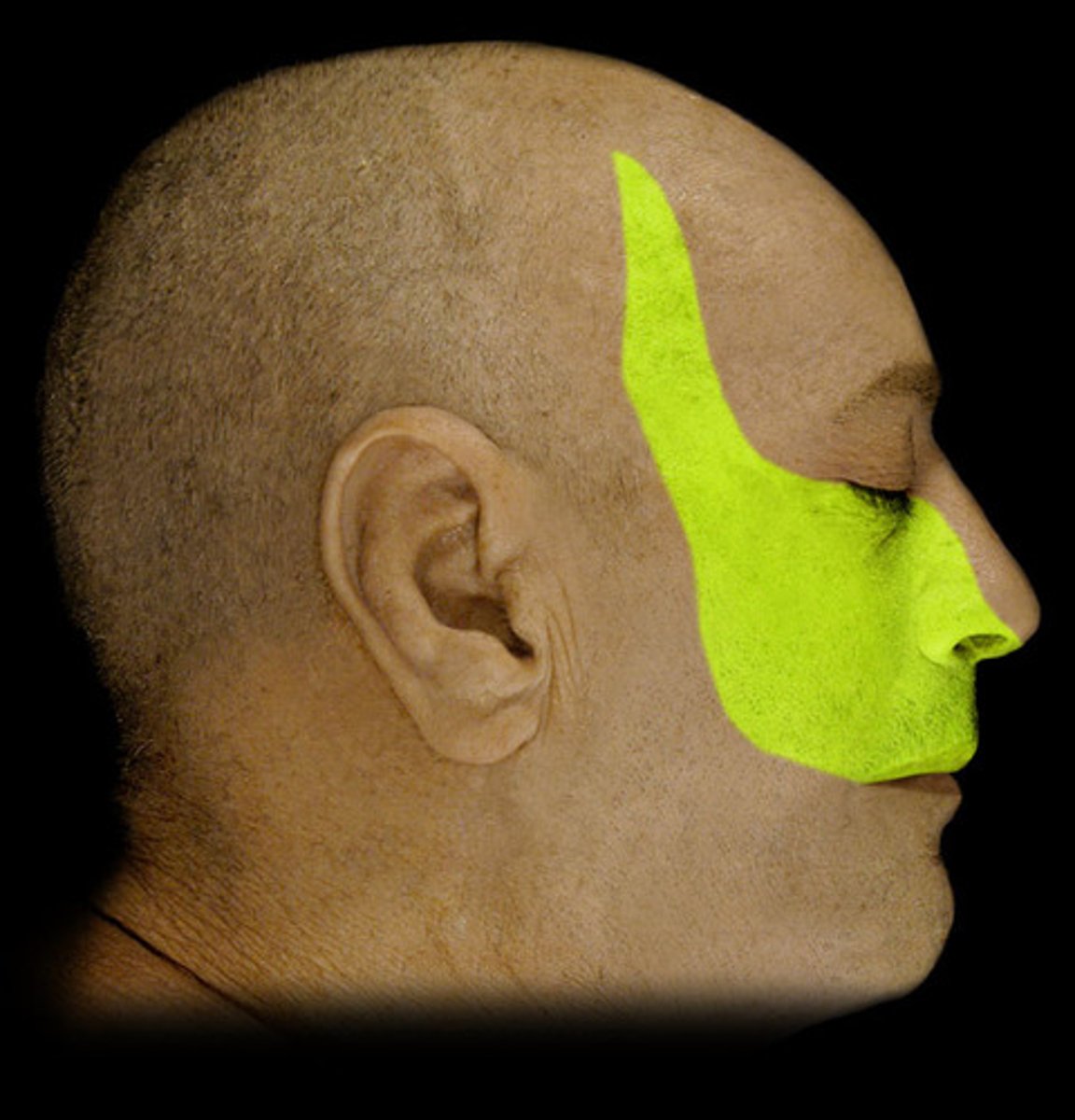
mandibular nerve (CN V3)
Affects the muscles of the chin, lower lip, and external ear.
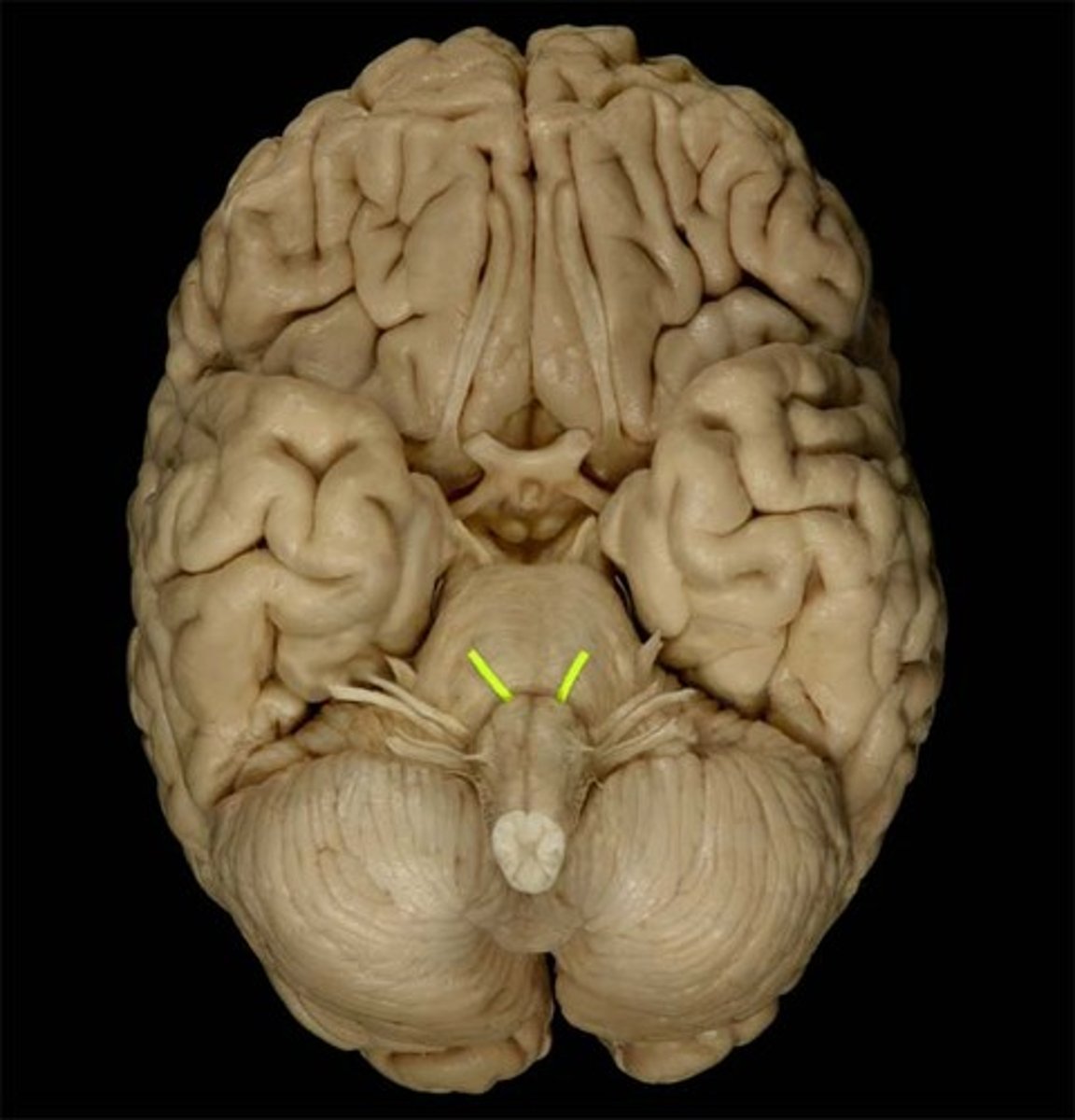
abducens nerve (CN VI)
eye movement laterally
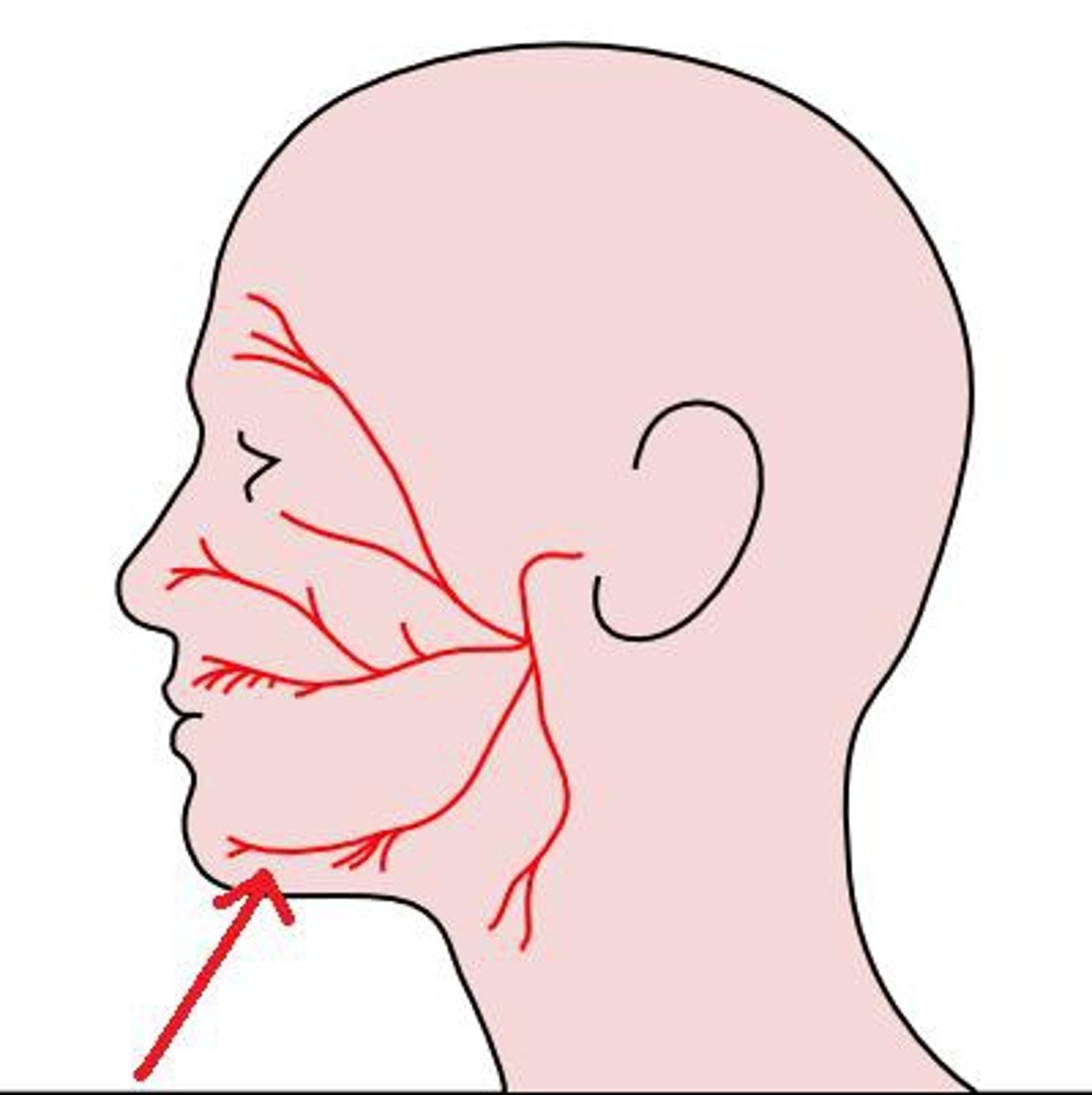
facial nerve (CN VII)
innervates muscles of facial expression
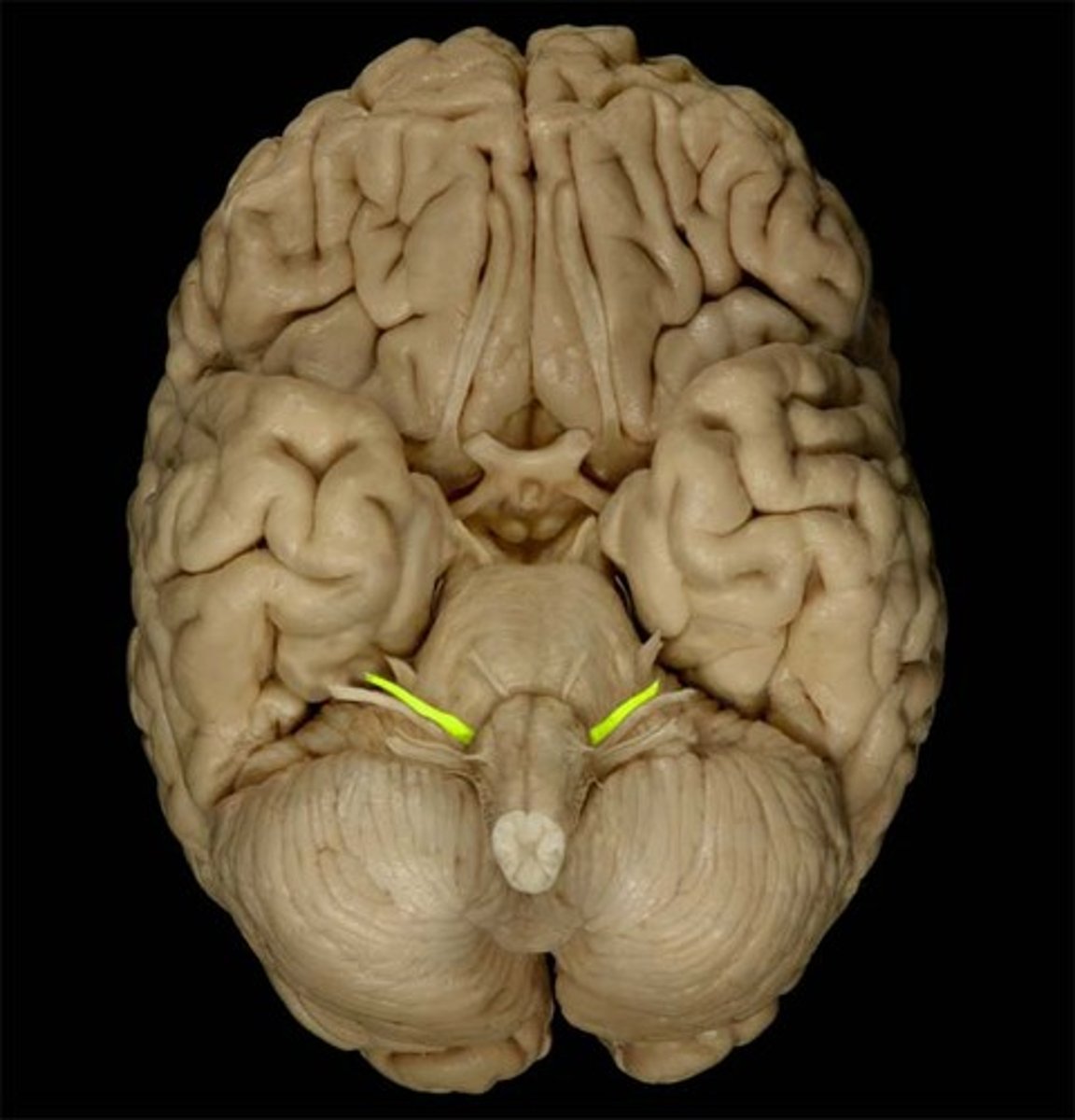
vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
sensory, hearing and balance
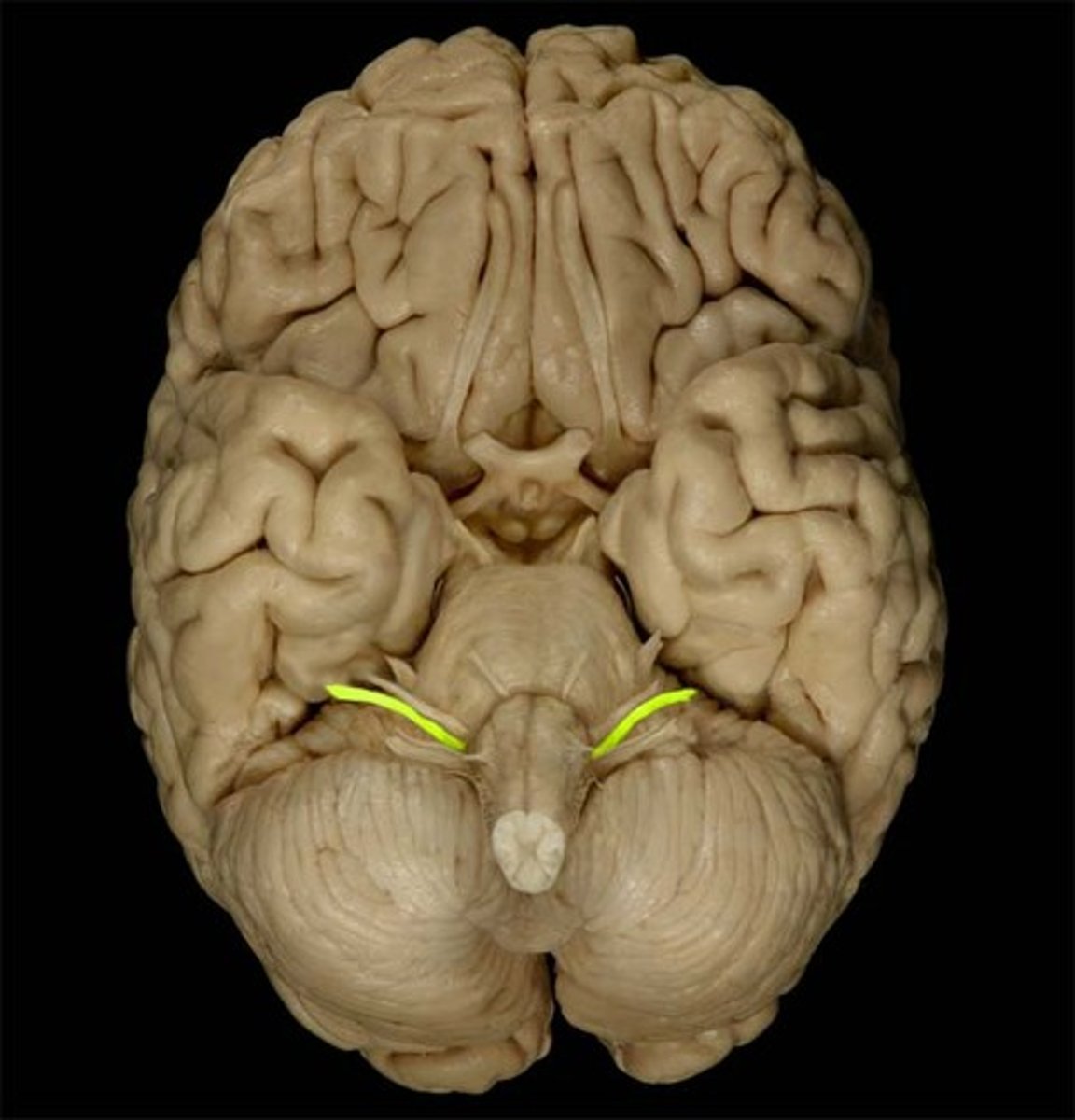
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
through jugular foramen, taste
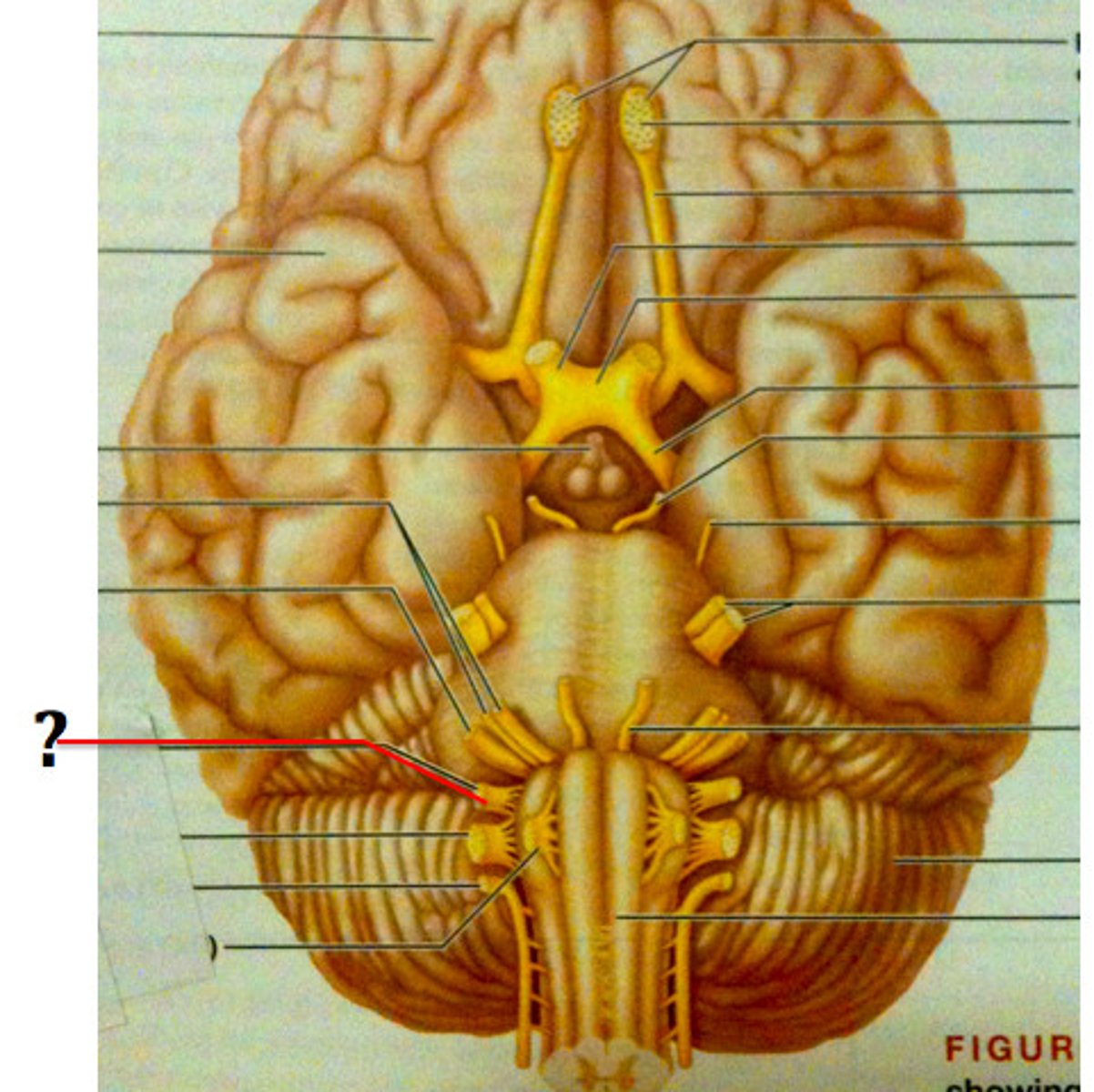
vagus nerve (CN X)
Cranial nerve exiting through the jugular foramen and innervating various regions of the body like the GI tract
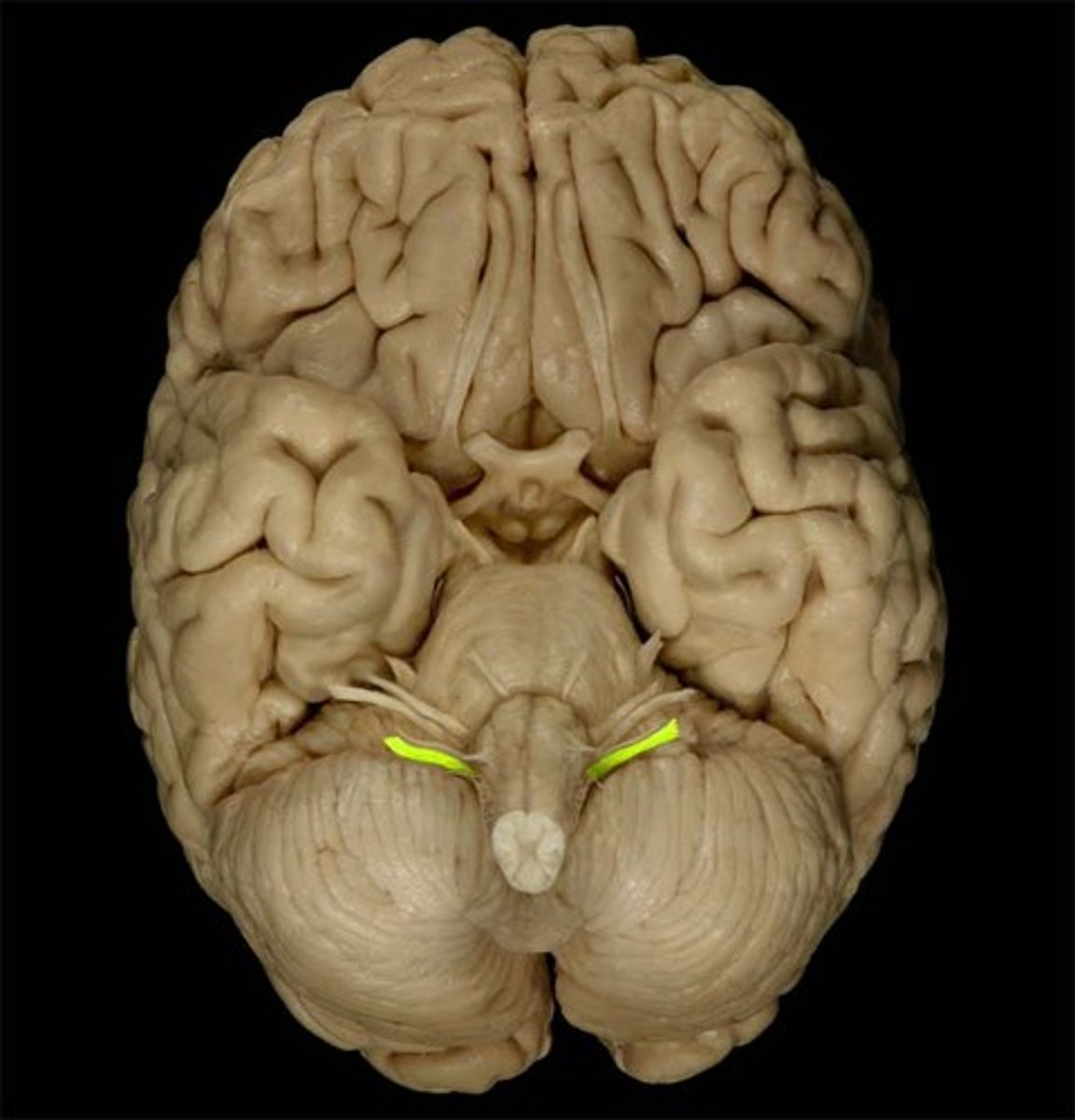
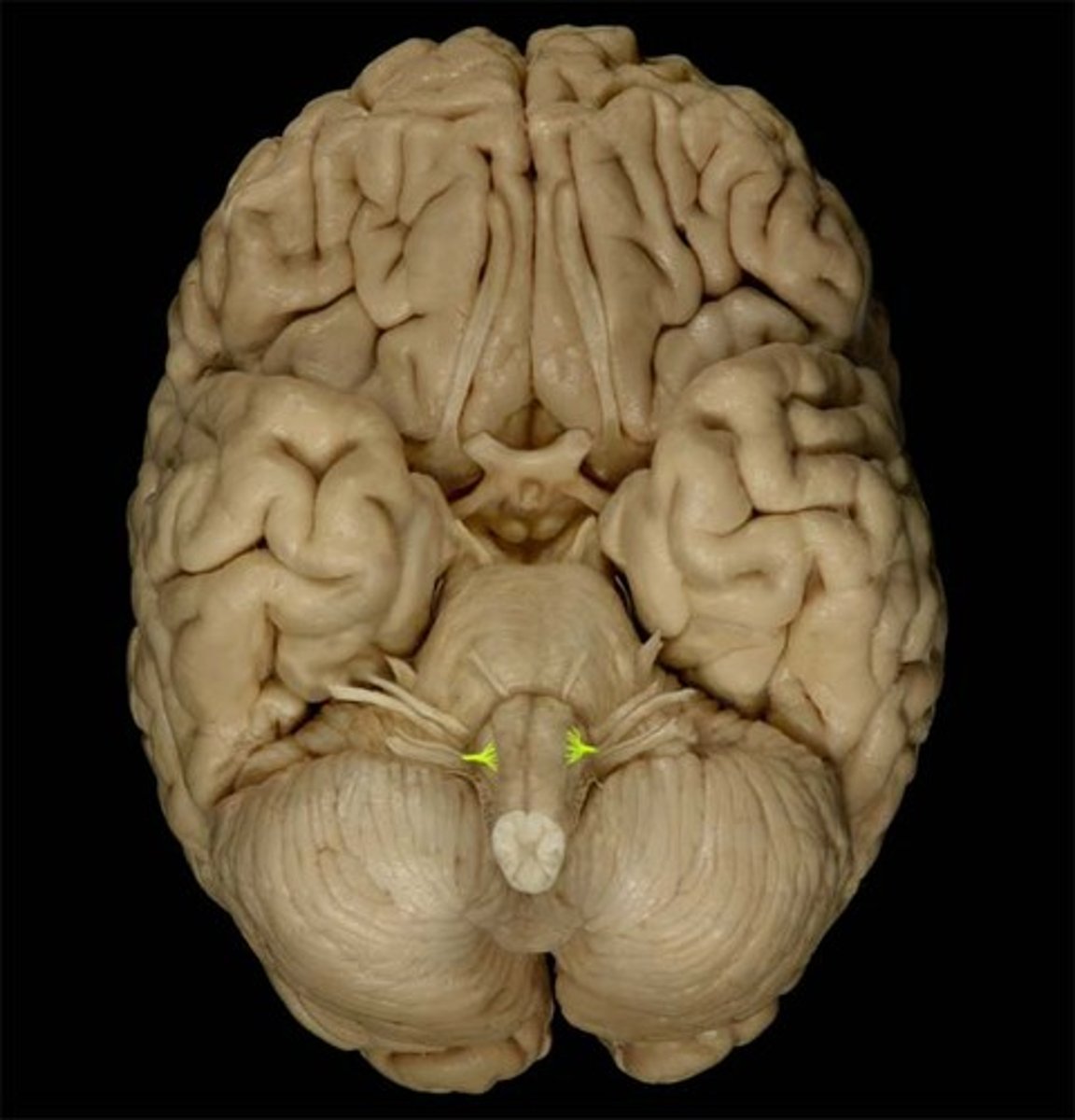
accessory nerve (CN XI)
innervation of trapezius
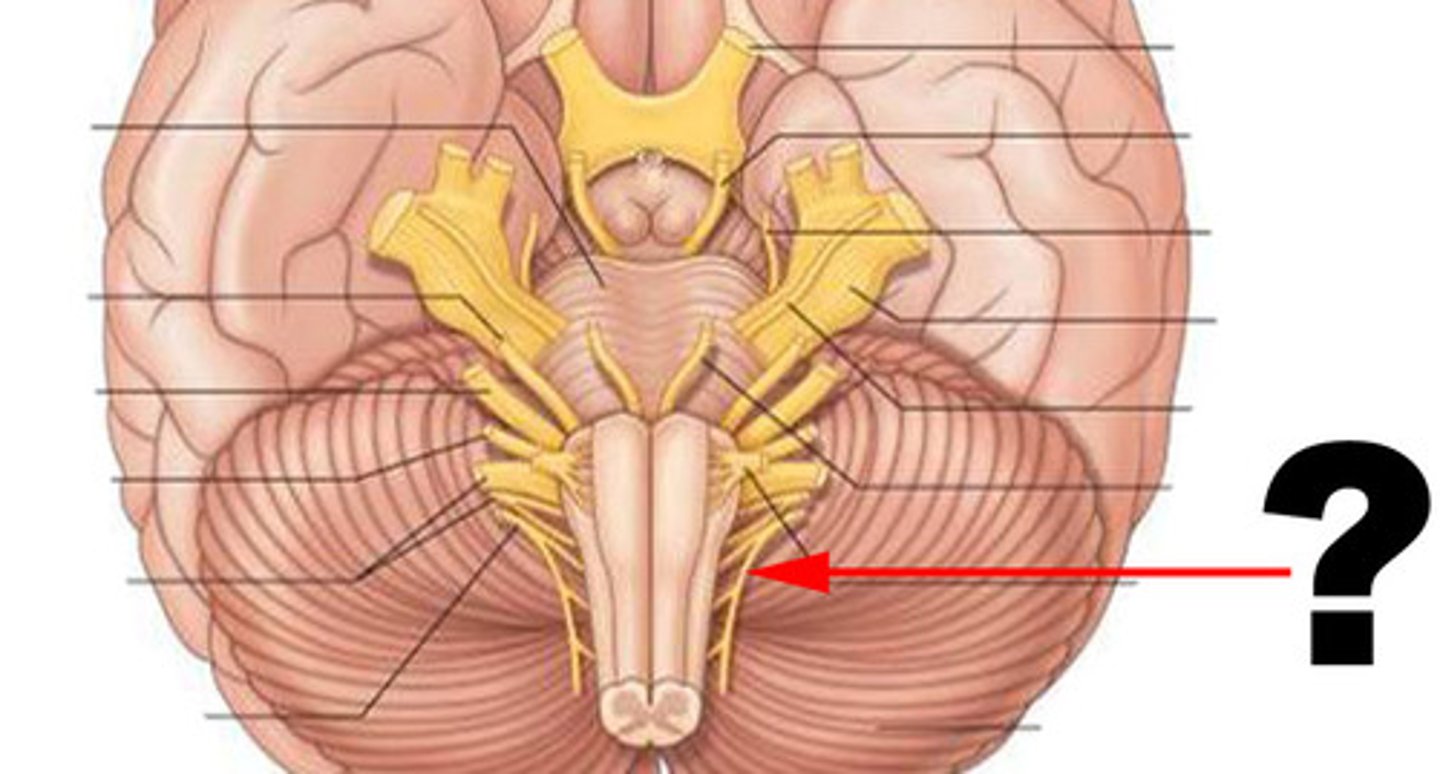
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
tongue movement
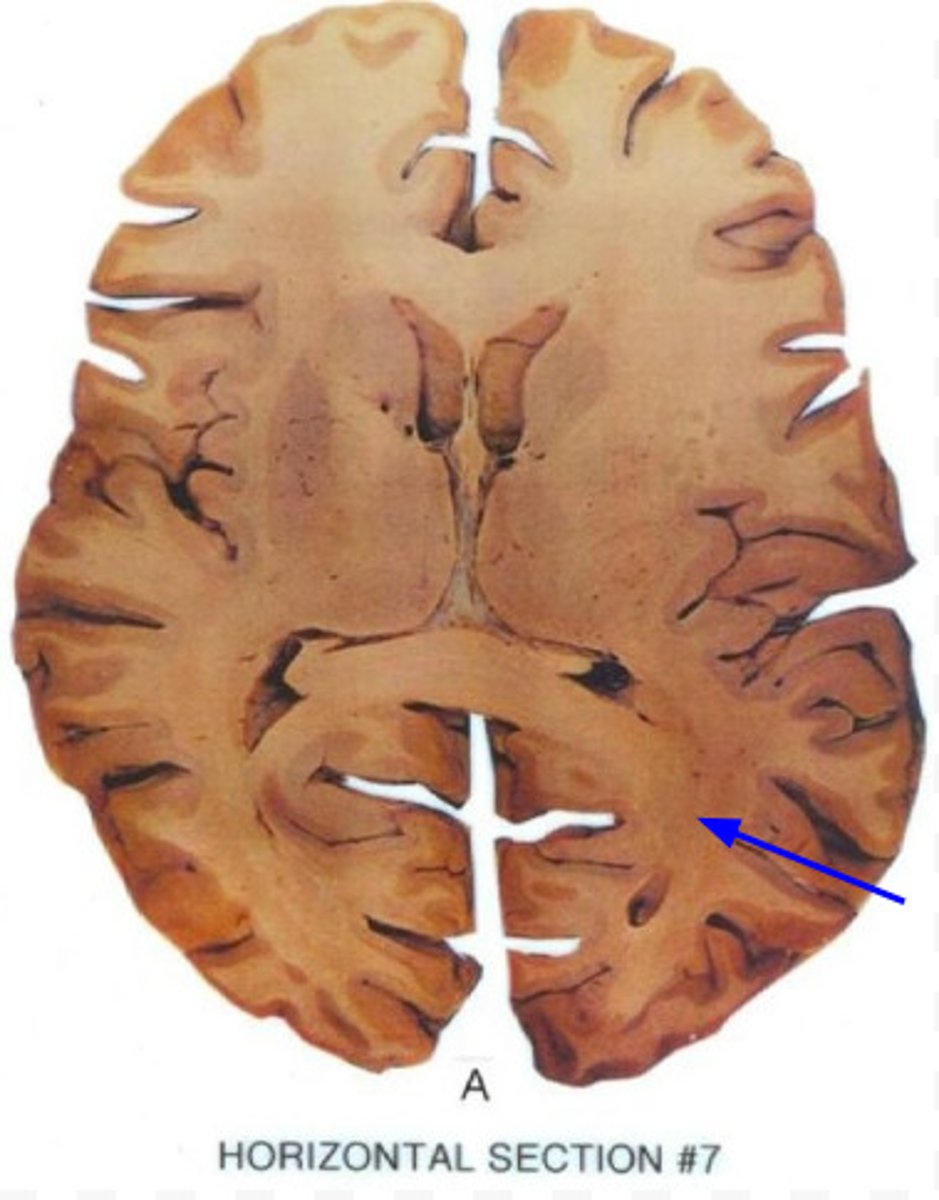
optic radiation
white matter axons from the lateral geniculate nucleus that terminate in the primary visual areas of the occipital cortex
comissural fibers
run horizontally and connect corresponding areas of gray matter in the two hemispheres, allowing the hemispheres to function together as a whole (includes the corpus callosum)
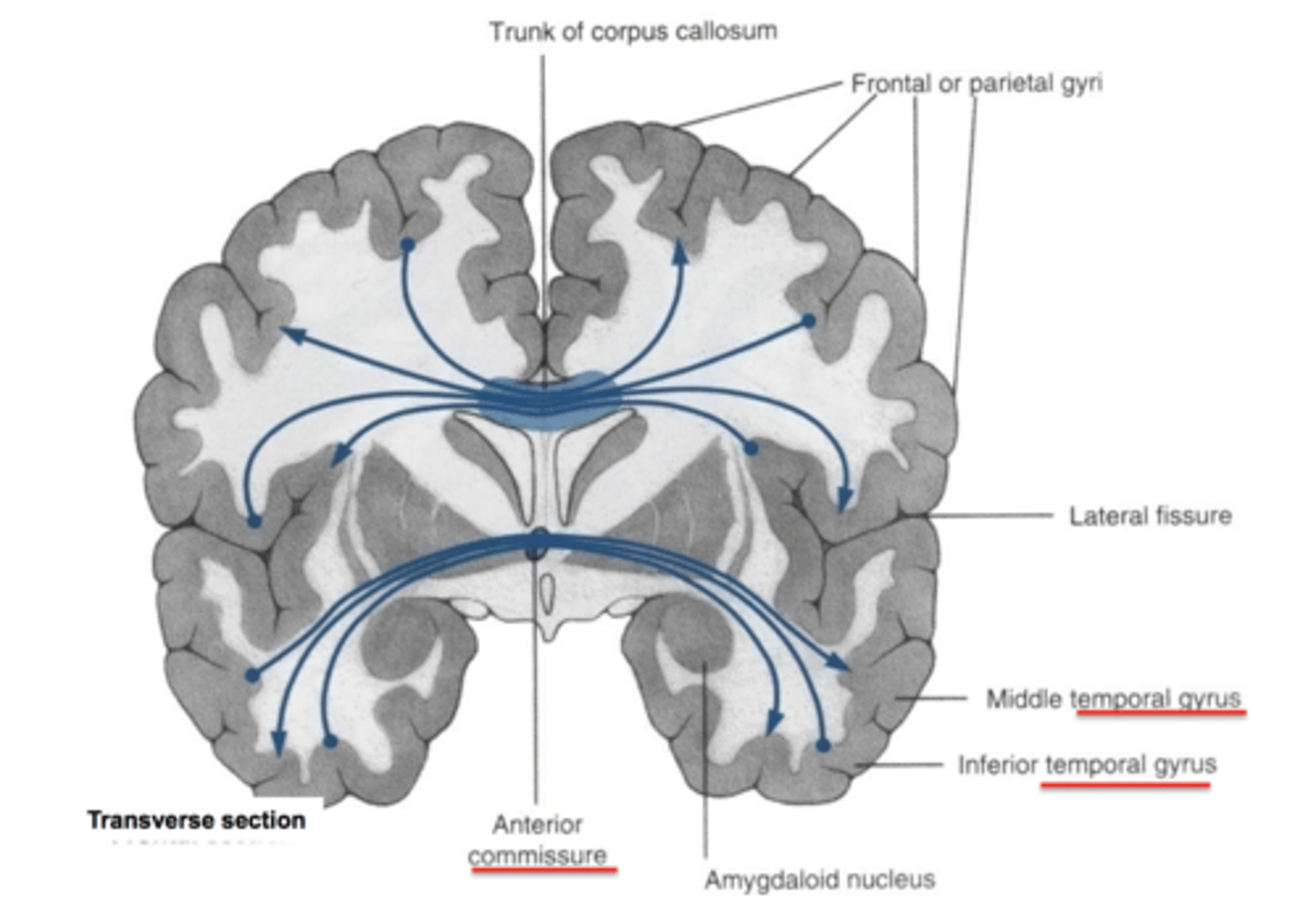
association fibers
connect different parts of the same hemisphere
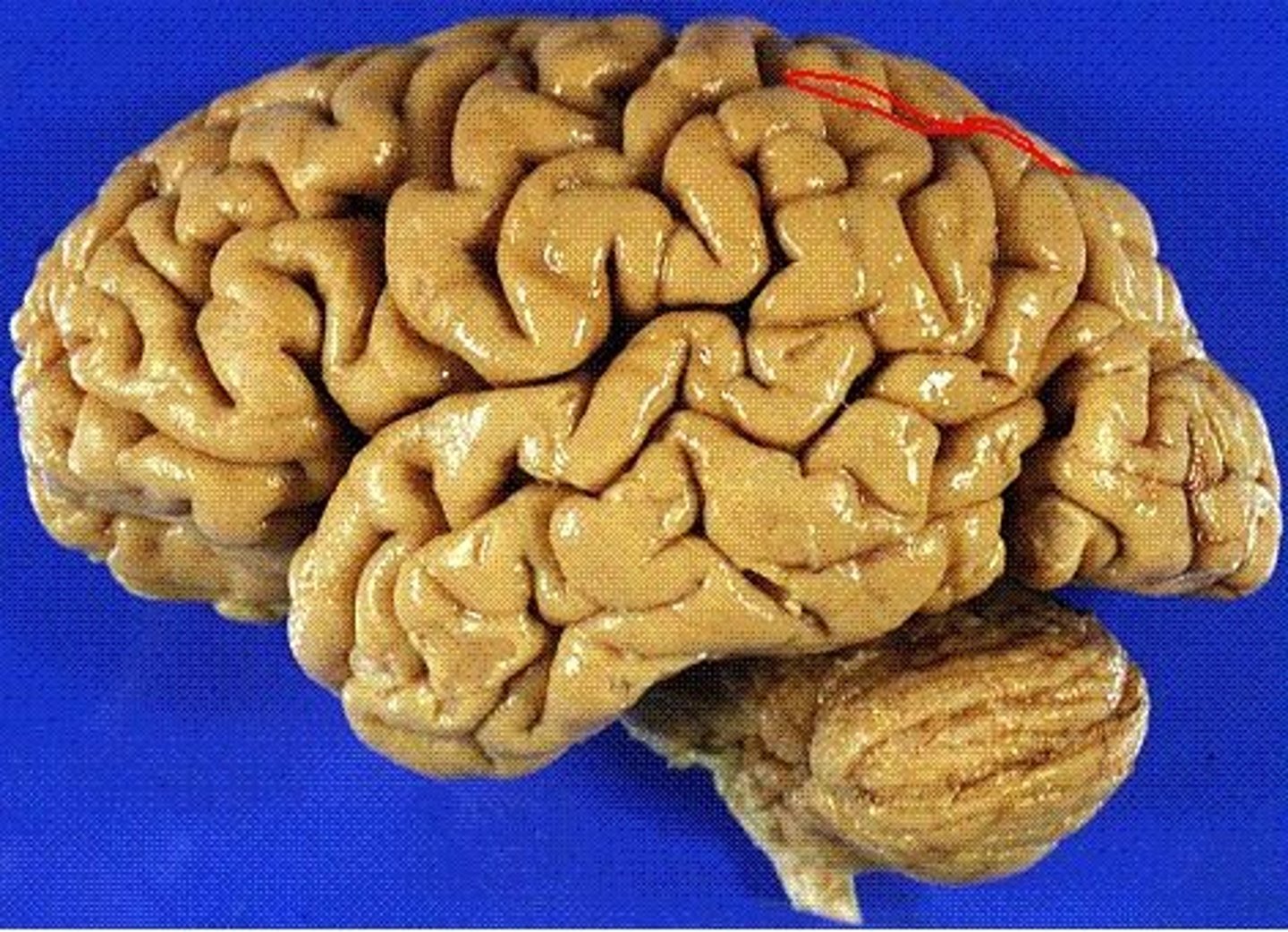
superior and inferior frontal sulci
Sulci separating the superior, middle, and inferior frontal gyri
intraparietal sulcus
Separates superior and inferior parietal lobules
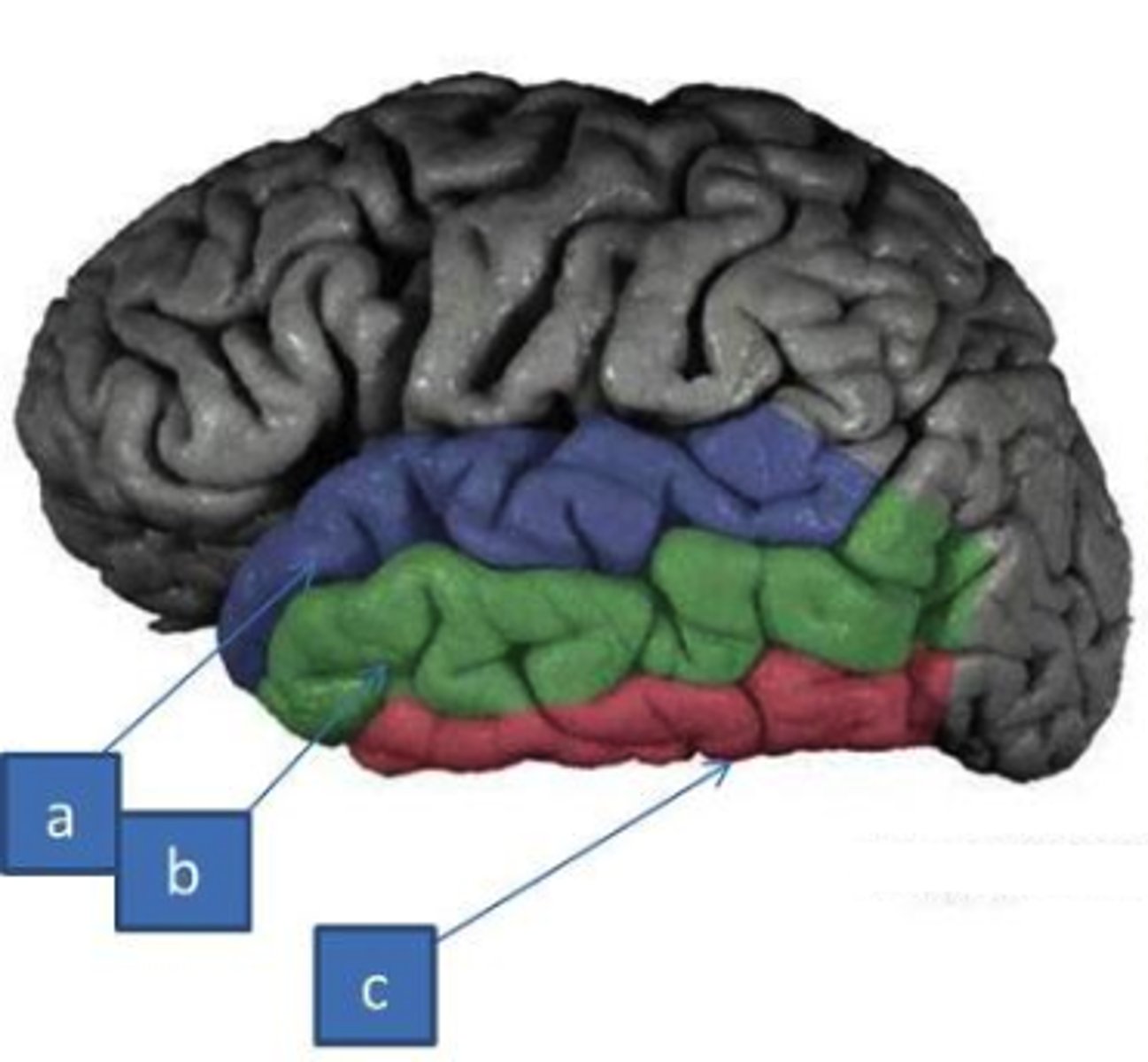
superior and inferior temporal sulci
divide the temporal lobe into superior temporal gyrus, middle temporal gyrus, and inferior temporal gyrus
collateral sulcus
separates parahippocampal gyrus from occipitotemporal gyri
occipitotemporal sulcus
separates inferior temporal gyrus from occipitotemporal gyrus
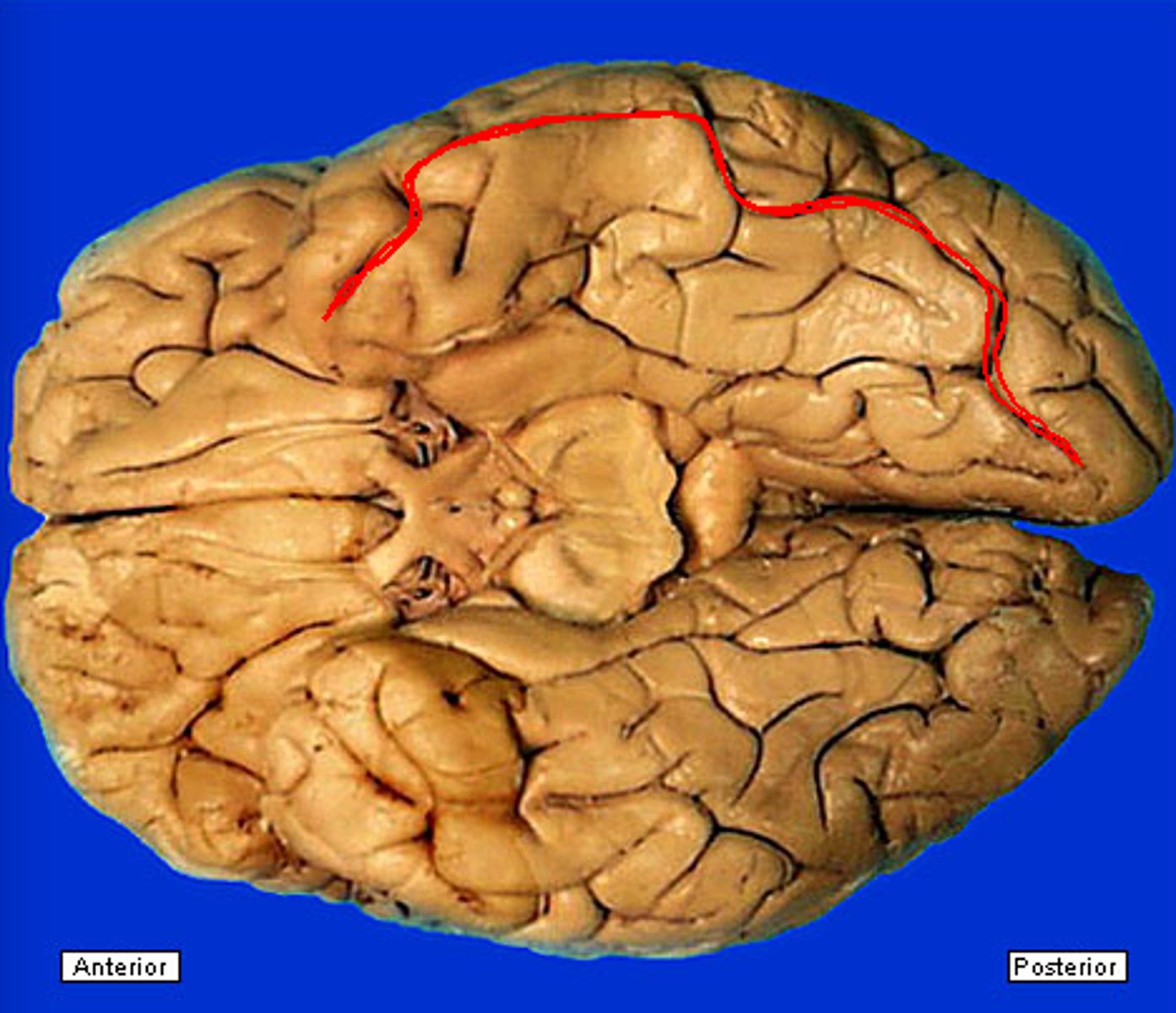
subparietal sulcus
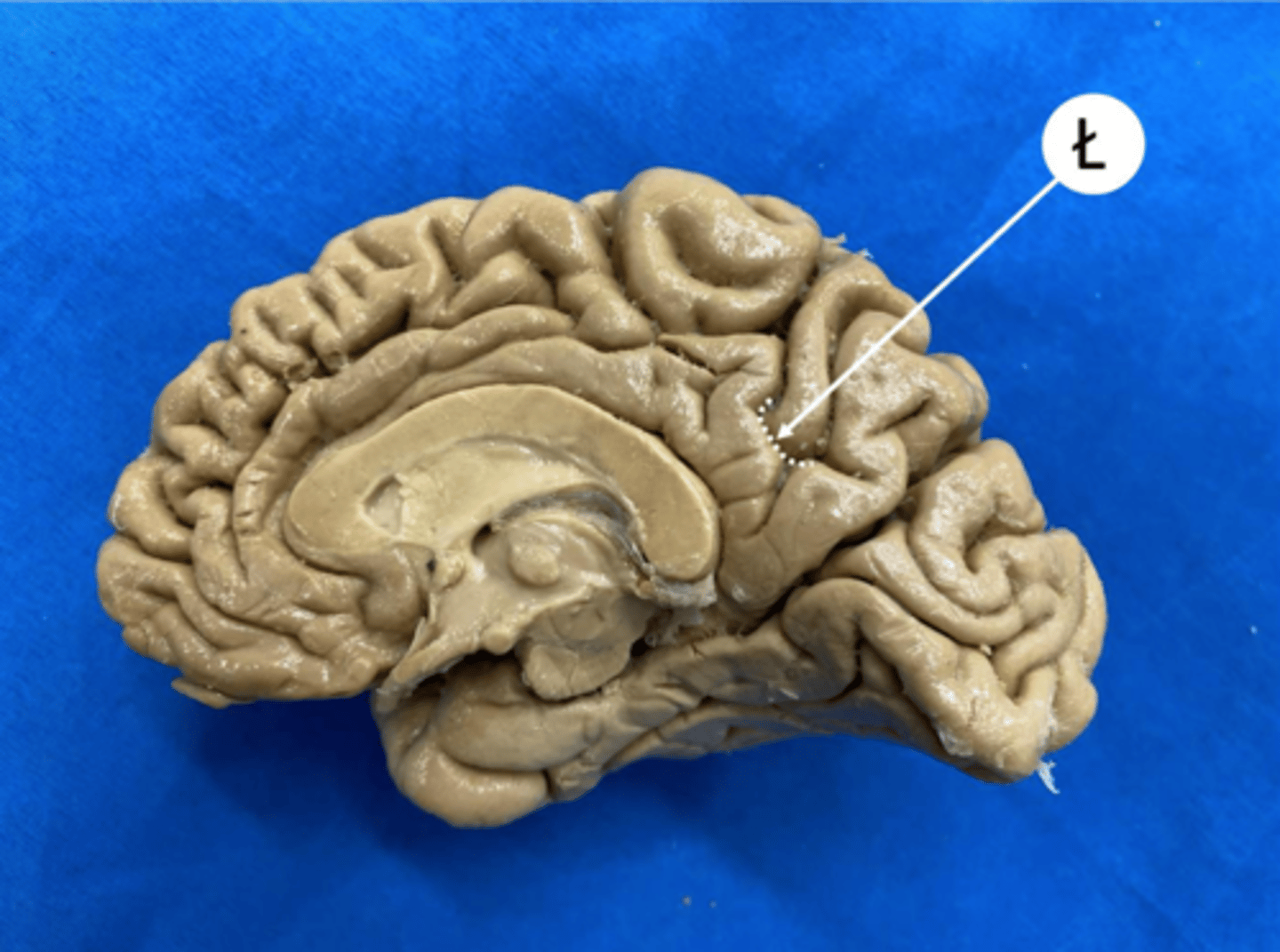
callosal sulcus
Separates cingulate gyrus from corpus callosum
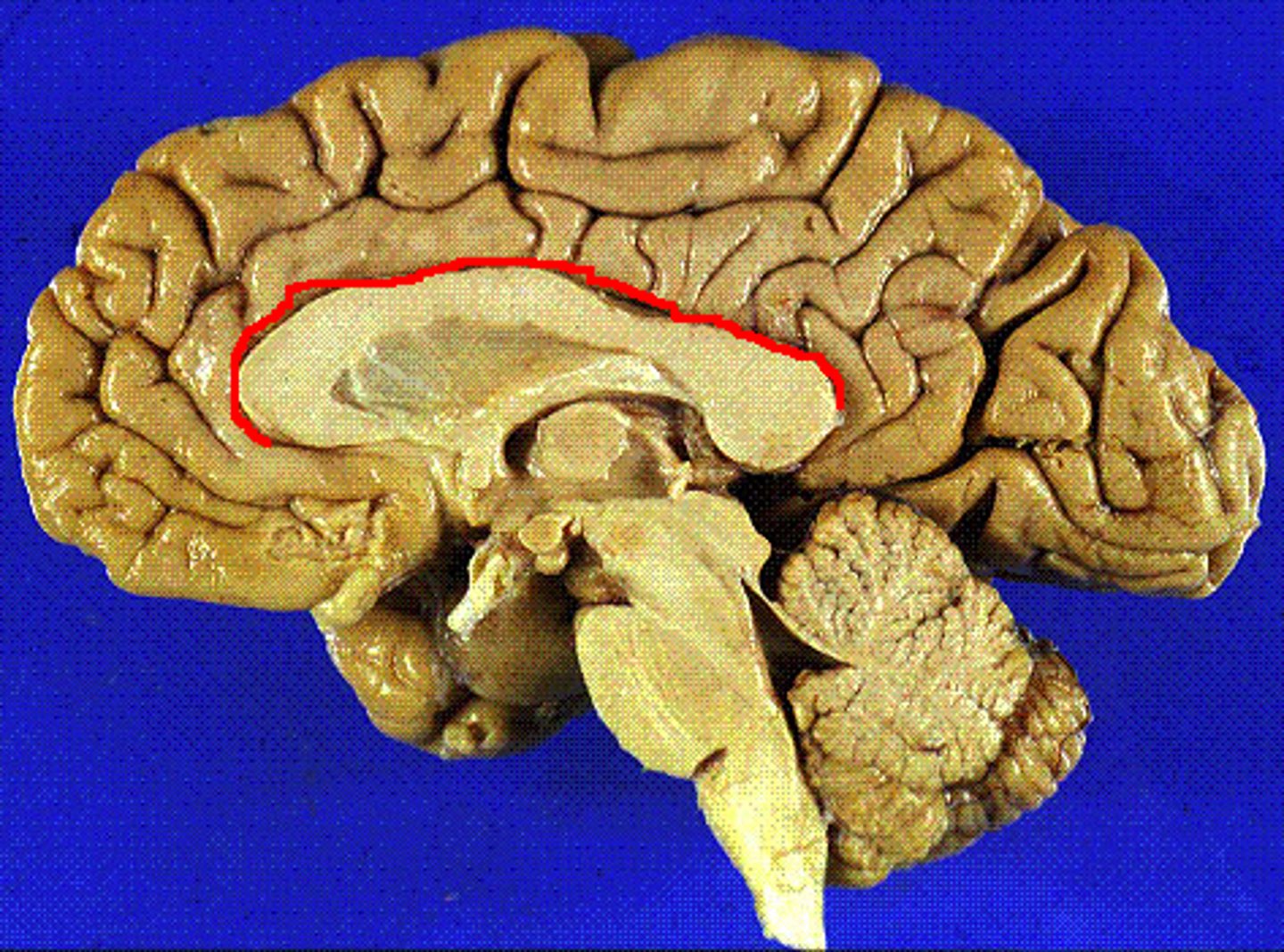
What is a tract?
collection of axons in CNS, AKA pathway or lemniscus
What is a nerve?
bundle of axons in PNS
What is a commissure?
any collection of axons that connect one side of the brain with the other side (cross midline) transversely in one spot
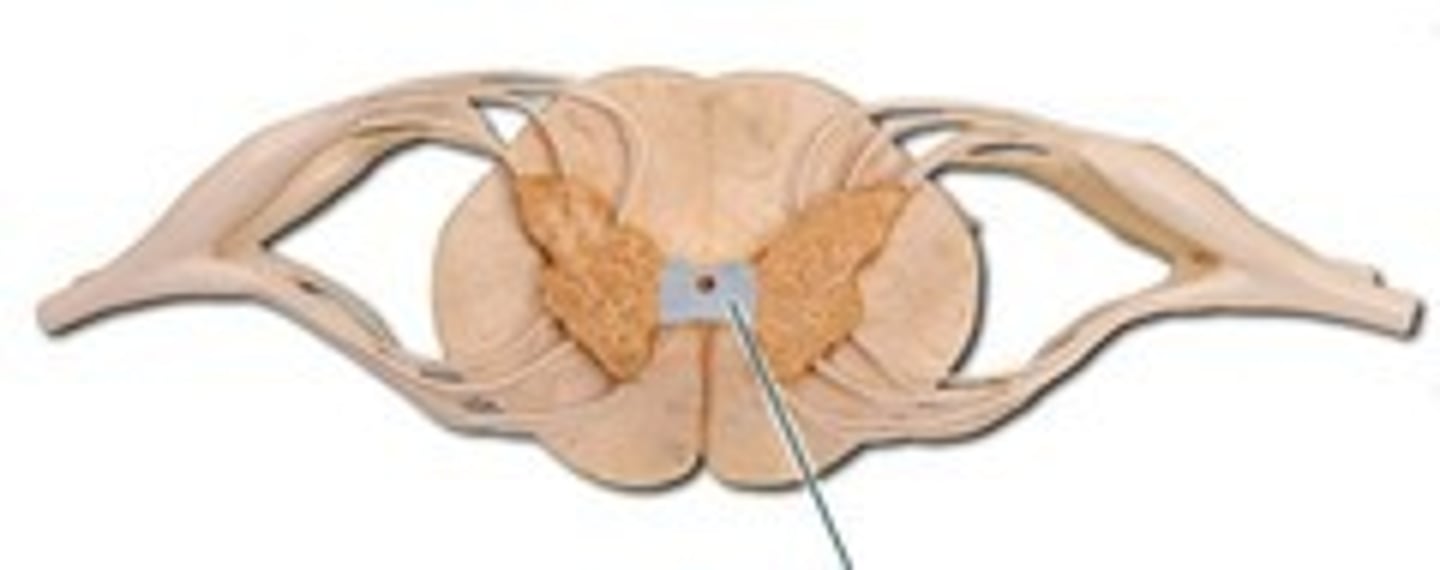
What is decussation?
crossing of the midline that occurs in many tracts so that brain senses and controls contralateral side of body (obliquely)
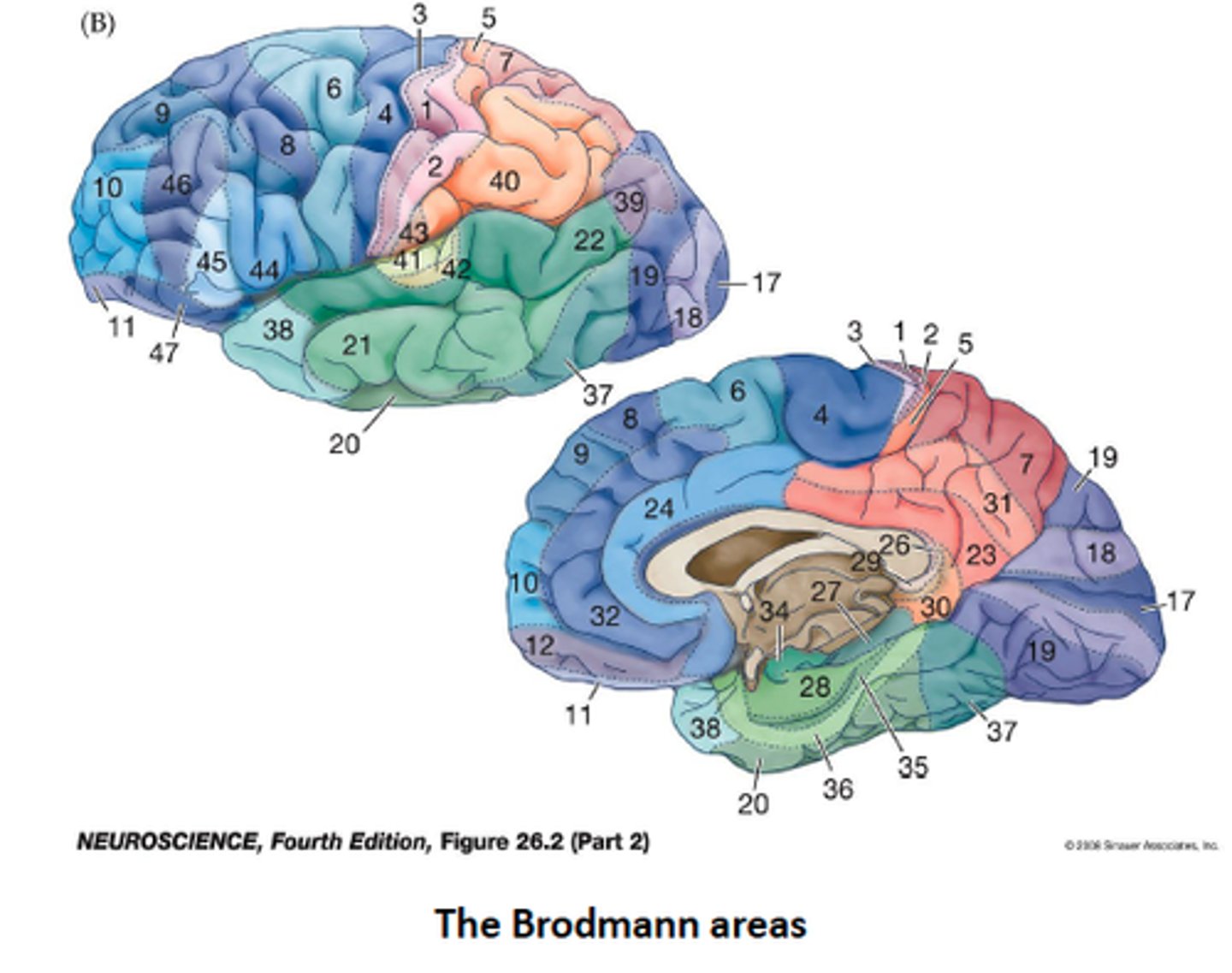
What are Brodmann's areas?
numbered regions of cortex that have been "mapped" to specific cognitive functions
What is multimodal association cortex?
involved in integrating functions from multiple sensory modalities, most of the cortex
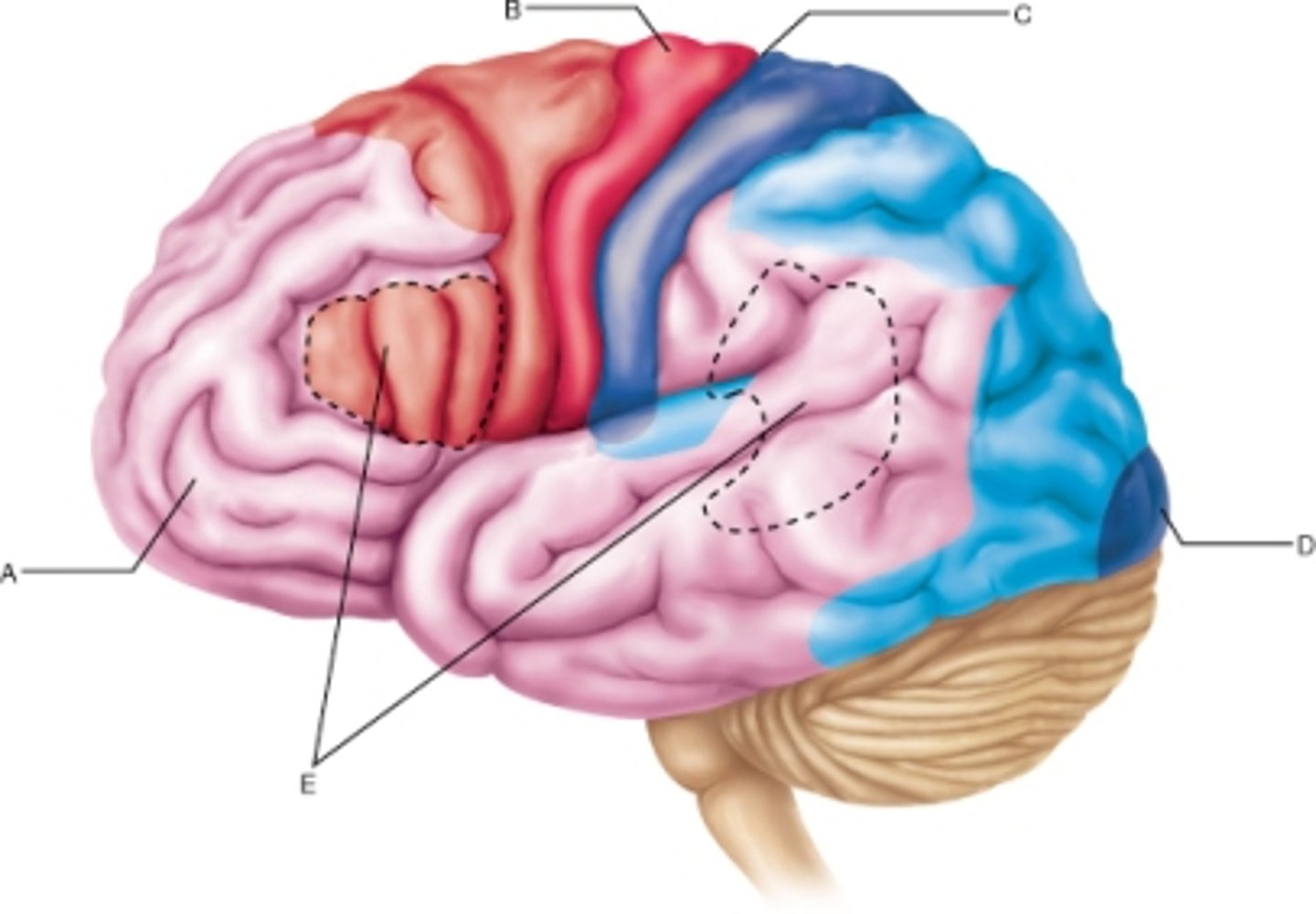
What is the difference between a primary cortex and a secondary cortex?
primary cortex has a specific, dedicated function. Secondary cortex has integrative roles (ex. premotor does planning, somatosensory association does context, importance of sensation)
What direction do commissural fibers run?
Left to Right and vice versa
What direction do projection fibers run? (corona radiata, internal capsule)
superior to inferior
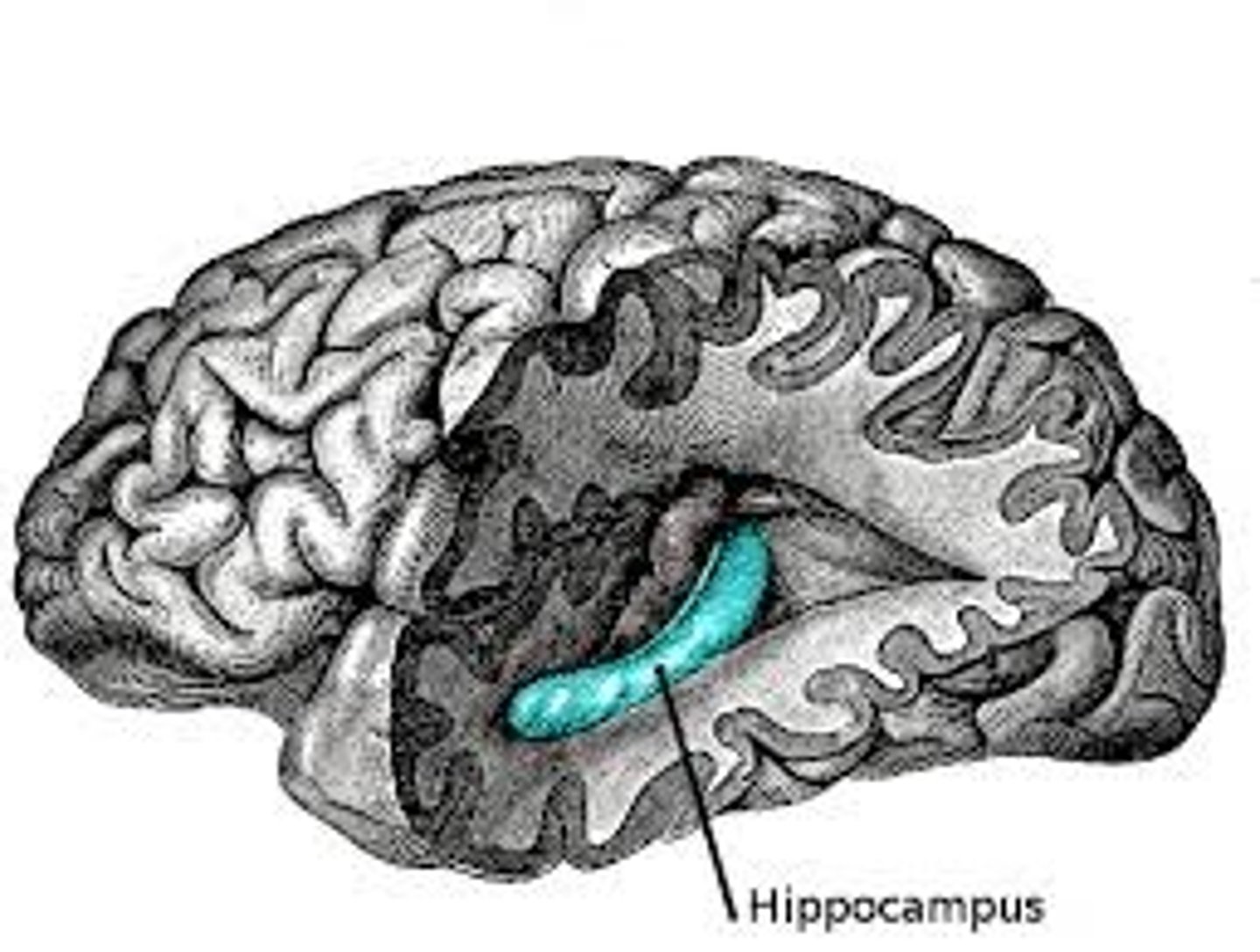
hippocampus
region of cortex with hippocampal nuclei embedded in it
Amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion.
What are the 2 main tracts that allow for motor control out of the M1?
1. lateral corticospinal tract (to spinal cord and skeletal muscles)
2. corticobulbar tract (to motor nuclei of cranial nerves)
Where does the lateral corticospinal tract decussate?
at the medulla
What is the laterality of motor pathways arising from M1?
the cortex controls the contralateral muscle, the nerve controls the ipsilateral muscle
What is damage to primary motor cortex referred to as and what is the effect?
an upper motor neuron lesion (UMNL) and there will be lack of movement in the contralateral side muscle
What is damage to a lower motor neuron called and what is the effect?
lower motor neuron lesion (LMNL) and will result in ipsilateral lack of movement
What are the differences between the motor and sensory homunculus?
the sensory homunculus has genitals on the most medial portion and intra-abdominal sensation on the most lateral part
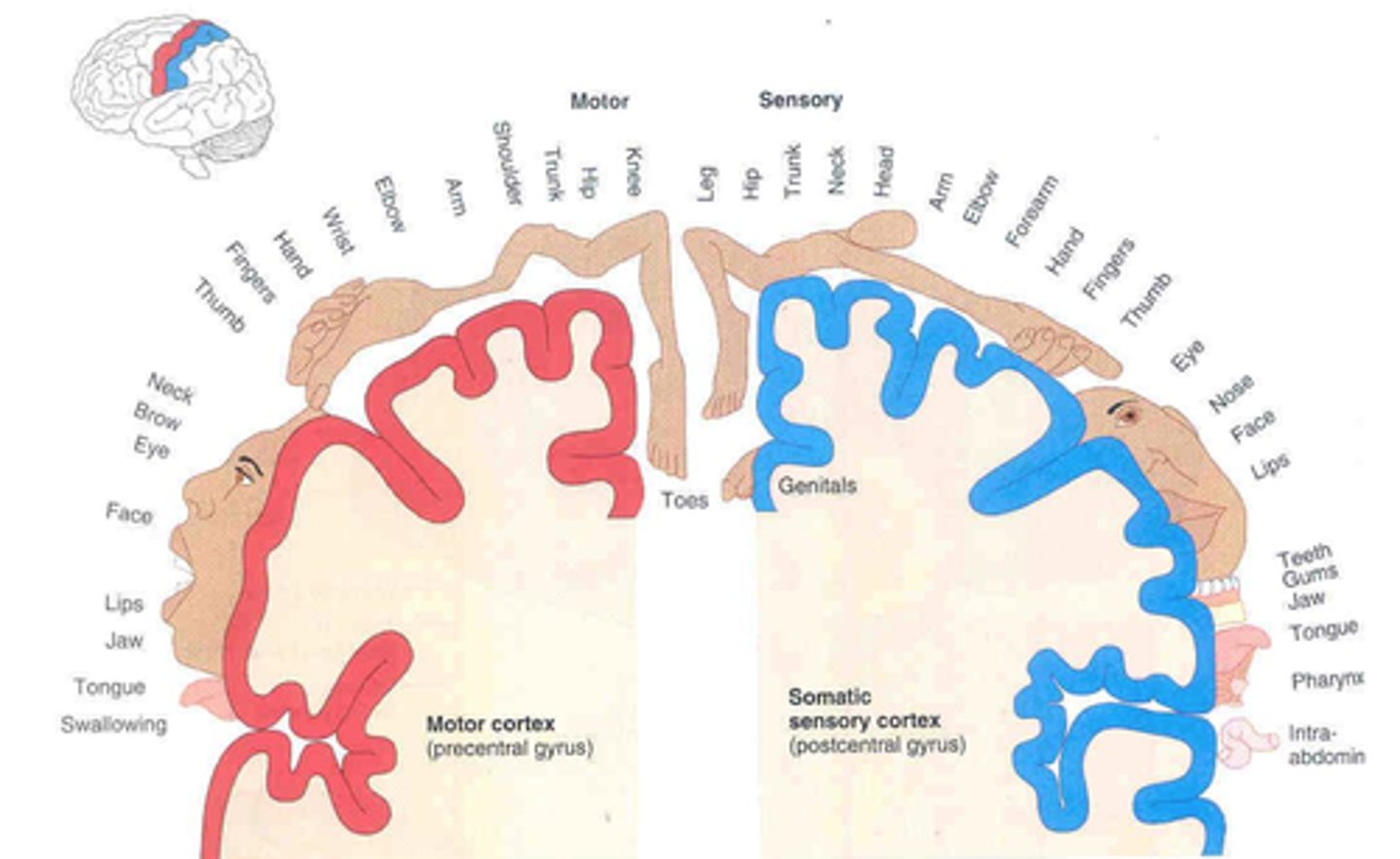
What are the main sensory tracts and what information do each carry?
1. dorsal column medial lemniscus for fine touch, proprioception, vibration
2. anterolateral/spinothalamic system, pain and temperature
- sensory input from cranial nerves enters either tract more laterally at the brainstem and synapse before their cortical areas in the thalamus
What area of the sensory pathway would you damage to have loss of sensation to the contralateral body area?
the sensory cortex that the body area mapped to
What area of the sensory pathway would you damage to have loss of sensation to the ipsilateral body area?
the sensory nerve supplying that body area