Peristalsis / how is food absorbed
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is peristalsis?
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that pushes bolus through the gut.
Where does peristalsis occur?
Peristalsis occurs in the oesophagus, stomach, and intestines.
How does bile move from the liver to the small intestine?
Bile is produced by the liver and sores in the gall bladder it passes down the bile duct into the small intestine.
What are the 2 functions of bile once it reaches the small intestine?
Neutralises the acid - providing alkali conditions
Emulsifies fat
Why is it important bile is alkaline
Because most enzymes work in an alkali pH
How does emulsification of fates increases digestion of lipids
Emulsification increases the surface area of fats, allowing lipase enzymes to act more effectively, thus enhancing lipid digestion.
Explain absorption in the small intestine
Digestion produces soluble substances like glucose, which are absorbed into the small intestine. The inside of the small intestine is covered in millions of tiny projections called villi. These increase surface area so that soluble substances diffuse into the blood.
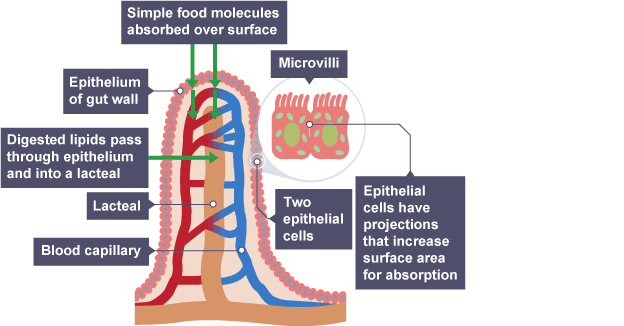
How is the small intestine adapted for this?
1. Thin lining to allow rapid diffusion
2. Large surface area caused by villi speeds up absorption and makes it more efficient
3. Good blood supply around villi takes away absorbed nutrients
Define absorption
The movement of digested small soluble food molecules through the wall of the small intestine into blood, occurs by diffusion.