Vet A&P Skeletal
1/367
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
368 Terms
5 functions of skeletal system
support
locomotion
protection
storage
haemopoiesis
The skeletal system acts as an internal _____ upon which the body is built
scaffold
The skeletal system provides ____ for muscles, which operate a system of levers (___) to bring about locomotion
attachment, bones
The skeletal system ____ the underlying soft parts of the body
protects (brain encased in skull)
The skeletal system acts as a store for essential minerals ____ and _____
calcium and phosphate
_____ tissue forming the ______ manufactures the blood cells
haemopoietic, bone marrow
7 types of bones
long, flat, short, irregular, sesamoid, pneumatic, splanchnic
long bones have a shaft containing a ______ filled with bone marrow
example: ____
medullary cavity
limb bones (femur, humerus), metacarpus, metatarsus, phalanges
flat bones have an outer layer of ____ bone and inner layer of _____ bone
example: ___
compact, cancellous/spongy
bones of the skull, scapula, ribs
T/F: Flat bones have no medullary cavity
True
short bones have an outer layer of ____ bone and core of _____ bone
example: ___
compact, cancellous/spongy
carpal and tarsal bones
T/F: short bones have a medullary cavity
False
irregular bones have a similar structure to ____ bones, but a less uniform shape and are ___
example: ___
short, unpaired
vertebrae
sesamoid bones develop within a _____ that runs over an underlying bony prominence
example: ____
tendon
patella associated with stifle joint
sesamoid bones serve to change the ____ at which the tendon passes over the bone and ____
angle, reduce wear and tear
pneumatic bones contain ____ known as _____ that have the effect of ___
example: ___
air-filled sacs, sinuses, reduce weight
maxillary and frontal bones
splanchnic bone develops in a ____ and is ____ to the rest of the skeleton
example: ____
soft organ, unattached
os penis
the process by which bone is formed is ___
ossification
in ____ ossification there is no cartilage template or model
intramembranous
in intramembranous ossification ___ lay down bone between ___
osteoblasts, two layers of fibrous connective tissue
flat bones of the skull are formed by ____ ossification
intramembranous
____ ossification involves the replacement of a ___ model within the embryo by bone
endochondral, hyaline cartilage
long bones of the limb develop by ____ ossification
endochondral
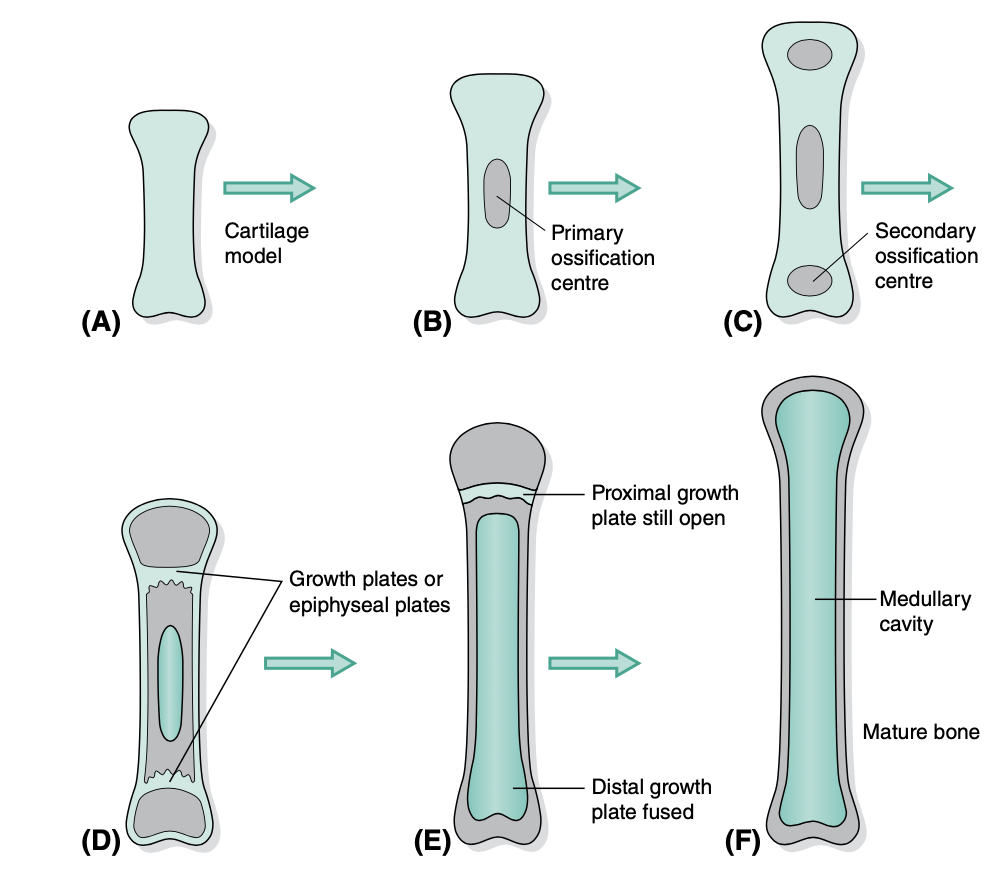
steps of endochondral ossification
cartilage model develops within embryo
Primary center of ossification appears in the diaphysis (shaft)
Secondary center of ossification appears in the epiphysis (end)
osteoclasts remove bone from center to form marrow cavity. osteoblasts continue laying bone in outer edges
growth/epiphyseal plate (narrow band of cartilage) appears between diaphysis and epiphysis
when the animal has reached final size, the ____ is replaced by bone and growth will no longer be possible
growth/epiphyseal plate
limb deformaties can occur when a _____ is abnormal or damaged by trauma
growth plate, causes bone to stop growing and shorten
carpal valgus and carpal varsus
angular limb deformaties (outward or inward twisting of paw)
bulldog and shihtzu bred to have this confirmation
articular projections
head, condyle, trochlea, facet
articular depressions
fovea, glenoid cavity, notch
non-articular projections
process, tuberosity, tubercle, spine, crest, neck, linea
non-articular depressions
fossa, foramen, canal
trochanter
LARGE non-articular projection for attachment of muscles on femur
tuberosity (tuber)
LARGE non-articular projection for attachment of muscles
tubercle (tuberculum)
SMALL non-articular projection for attachment of muscles
trochlea
articular grooves in long bone that allow tendons to act as pulleys
head
articular spherical projection for articulation with another bone
condyle
articular cylindrical projection for articulation with another bone
epicondyle
projection on lateral edge above condyle
facet
flat articular surface
foramen (pl. foramina)
opening for passage of blood vessels and nerves
fossa
hollow depression
head, neck, shaft
describe parts of long bone
tendon
connects muscle to bone
ligament
connects bone to bone
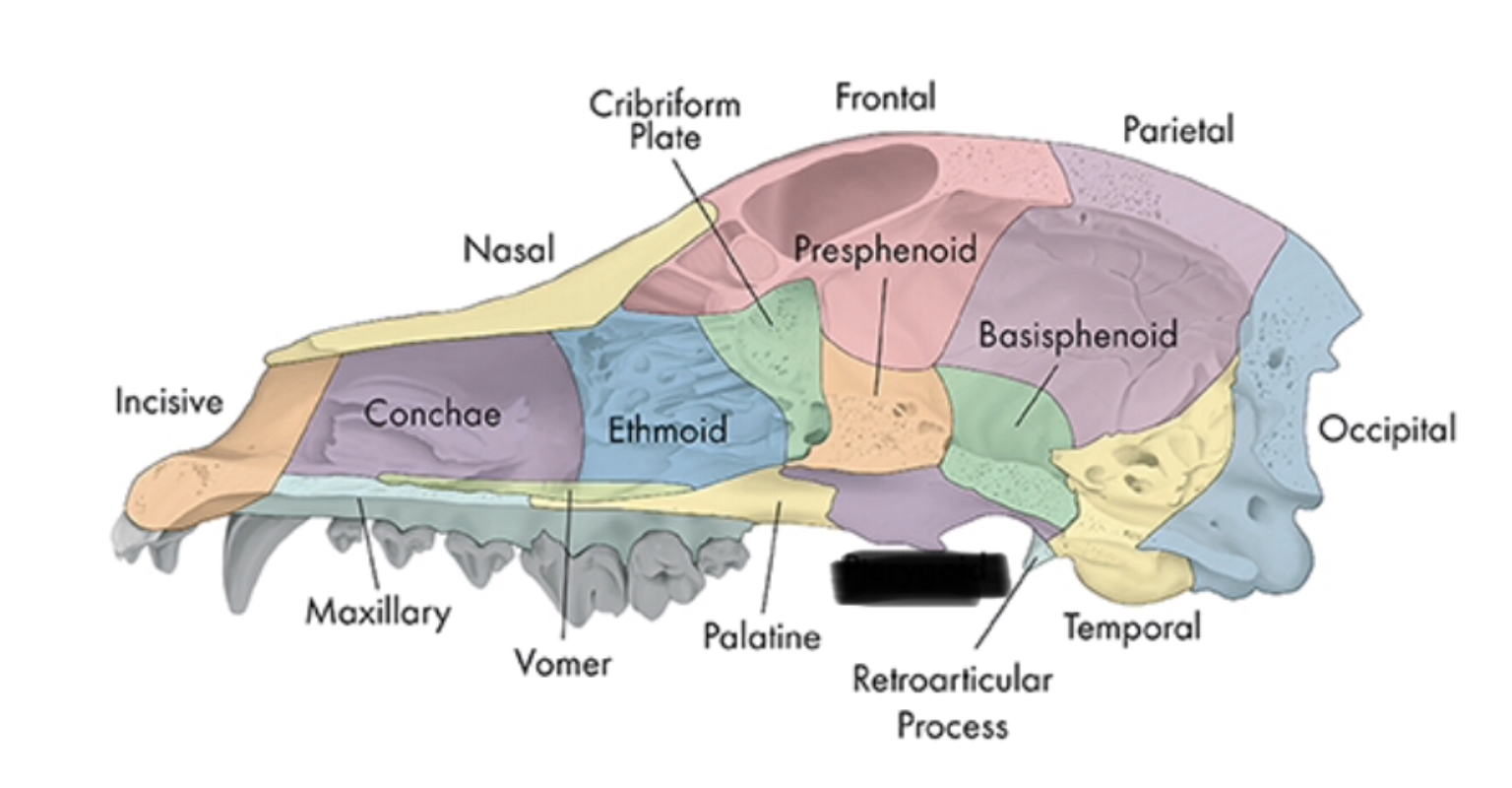
bones of the head (4)
skull, nasal chambers, mandible, hyoid apparatus
6 functions of the skull
house and protect brain
house sense organs (eye, ear, nose, tongue)
house and provide attachment for digestive system (teeth, tongue)
provide attachment for hyoid apparatus and muscles of mastication and facial expression
provide bony cavity through which air can enter body
communicate (muscles of facial expression)
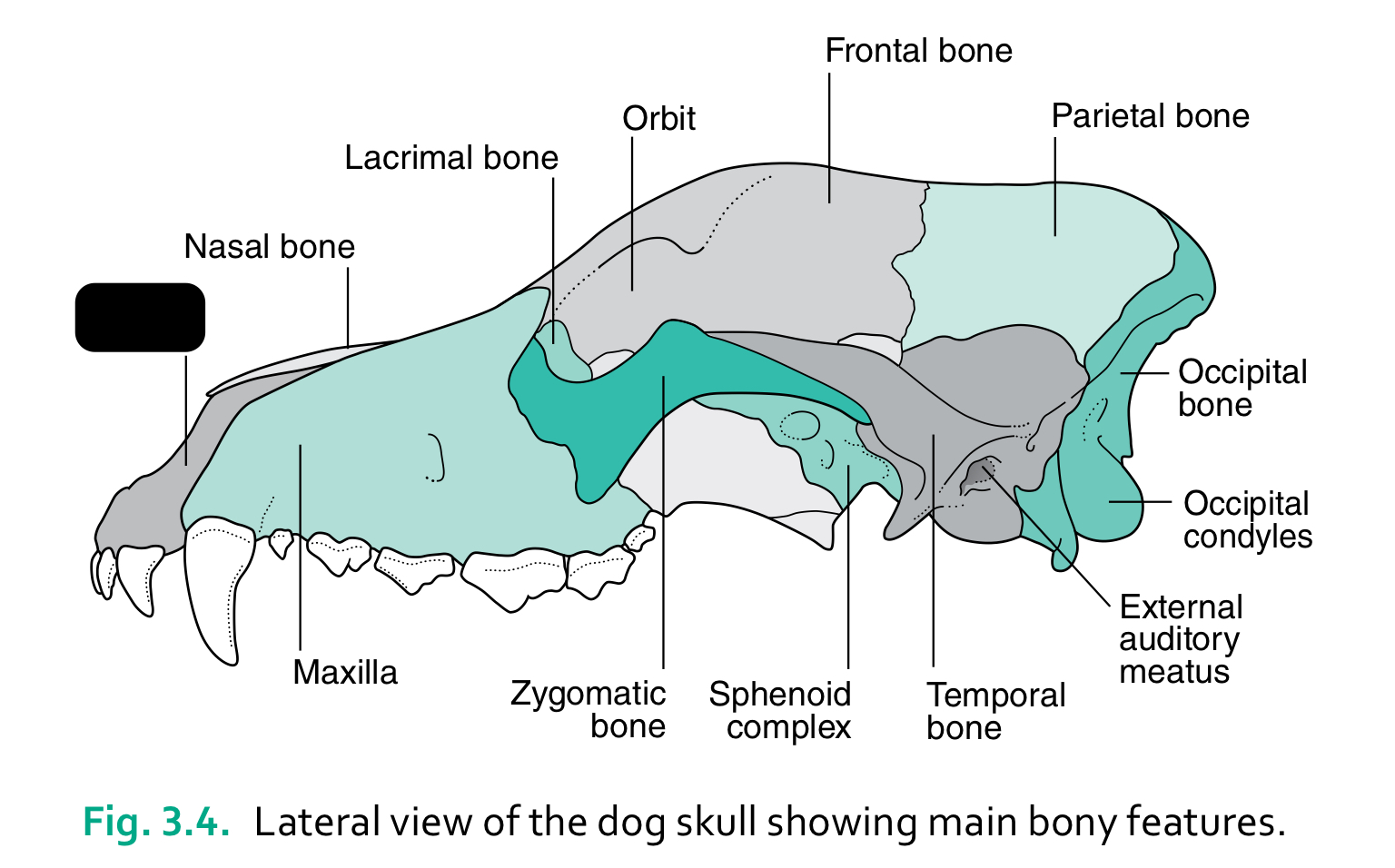
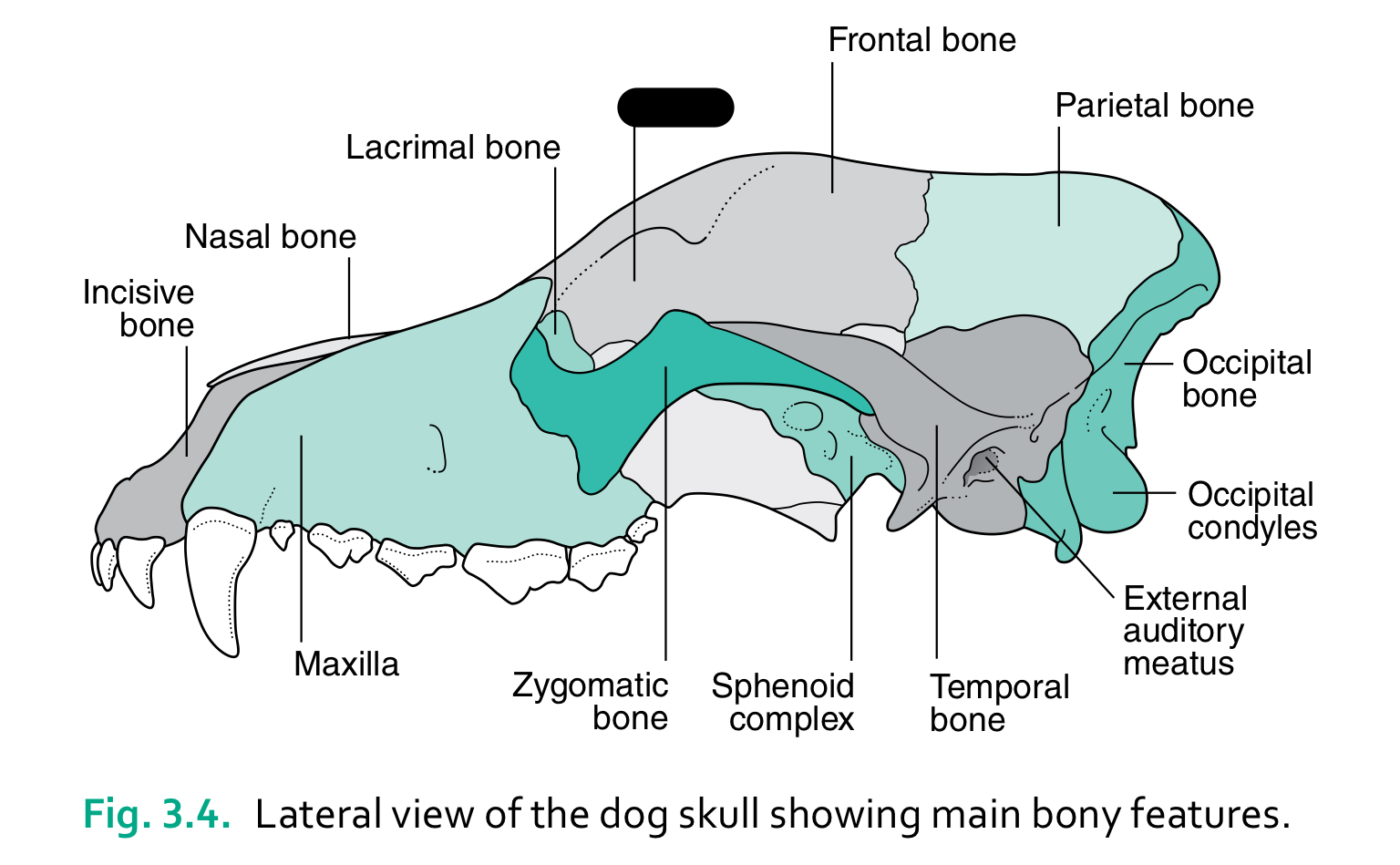
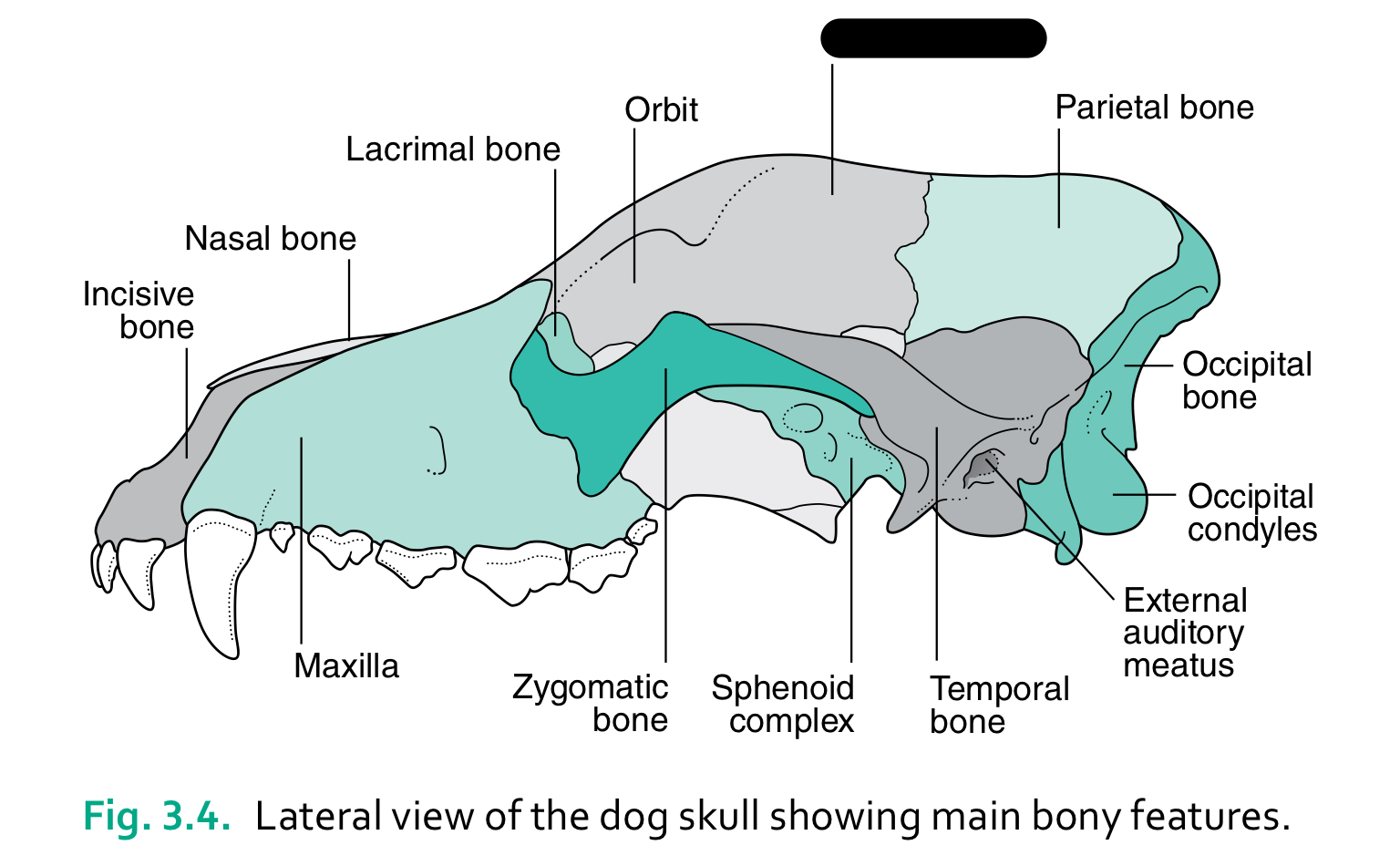
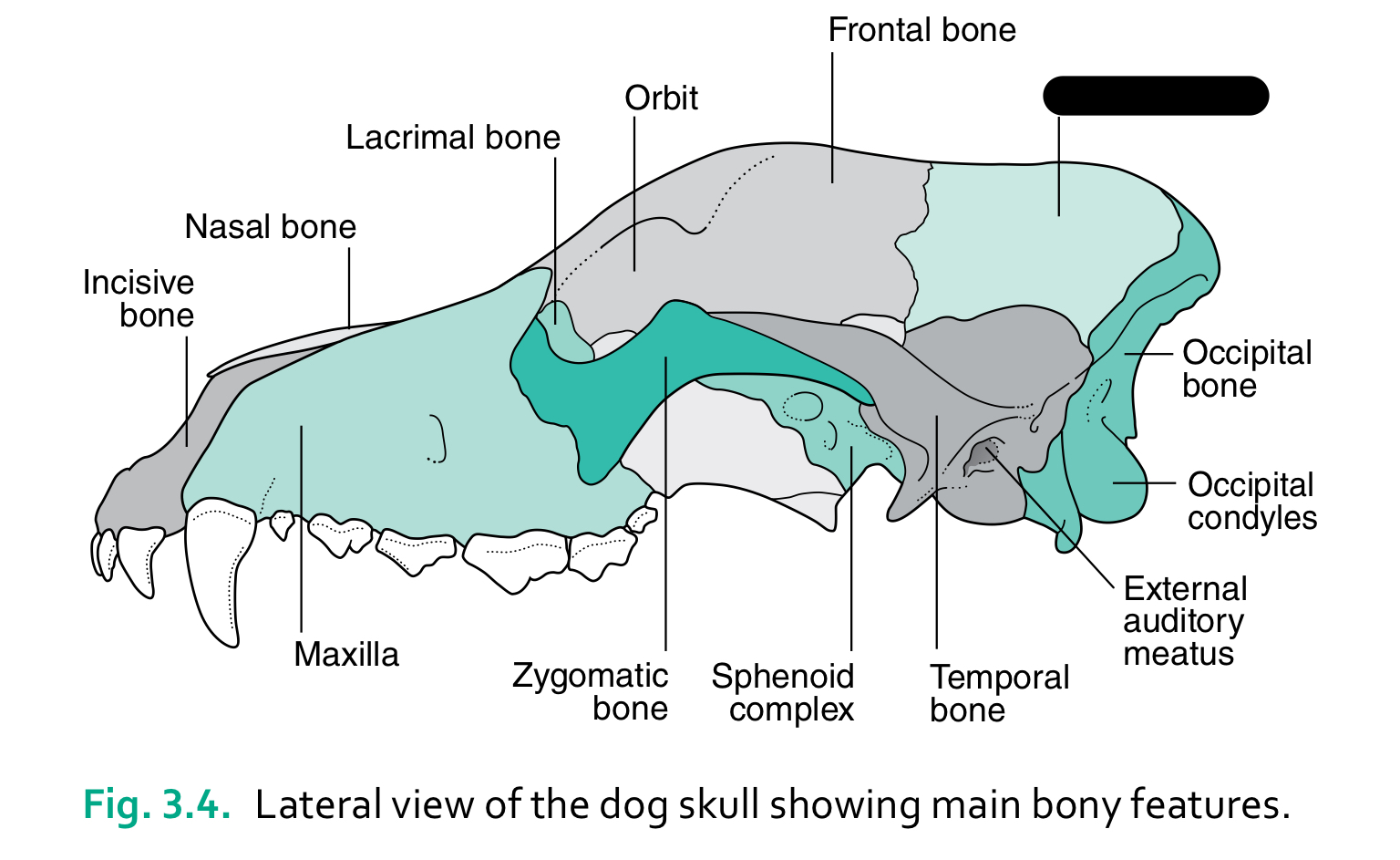
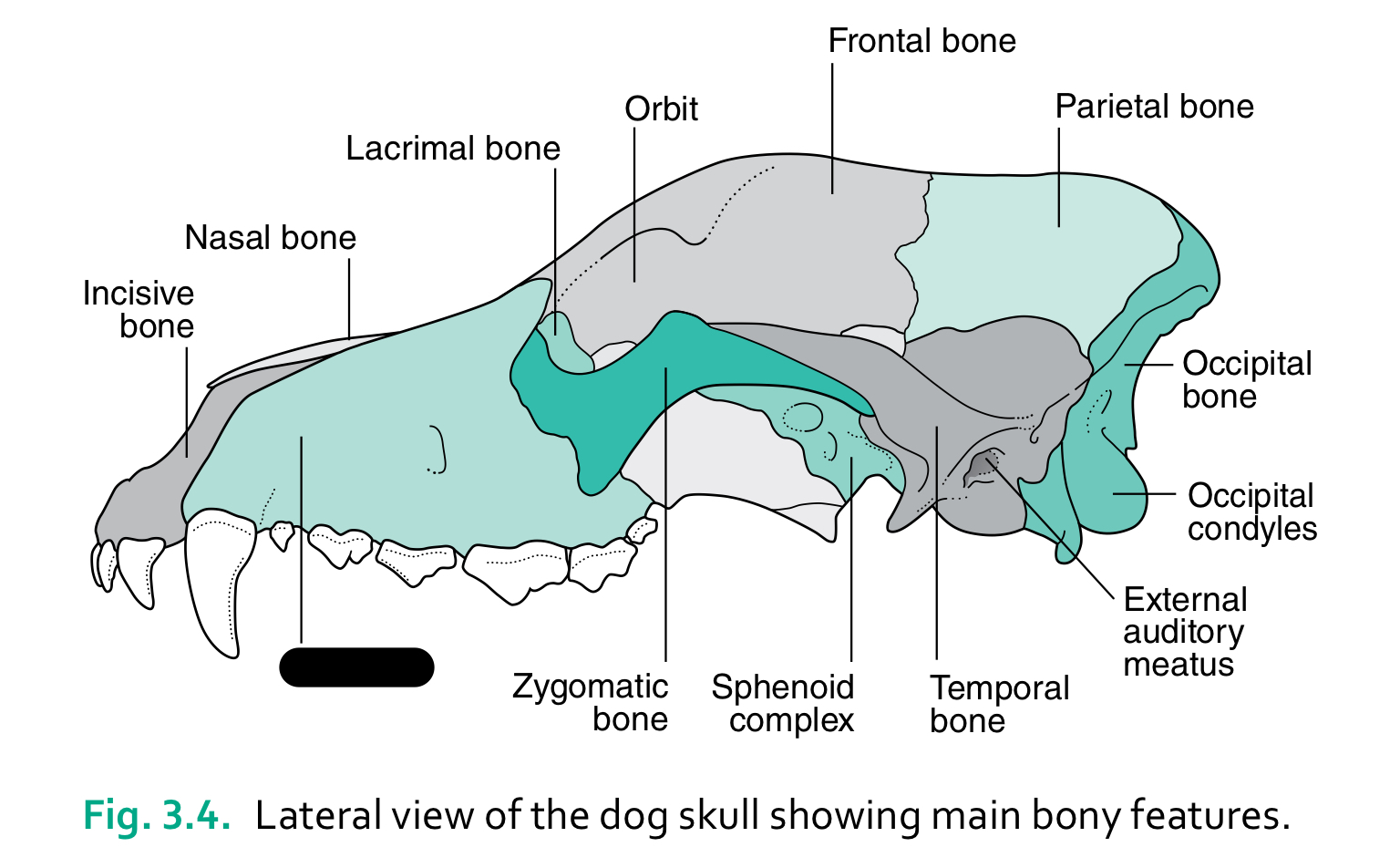
incisive bone
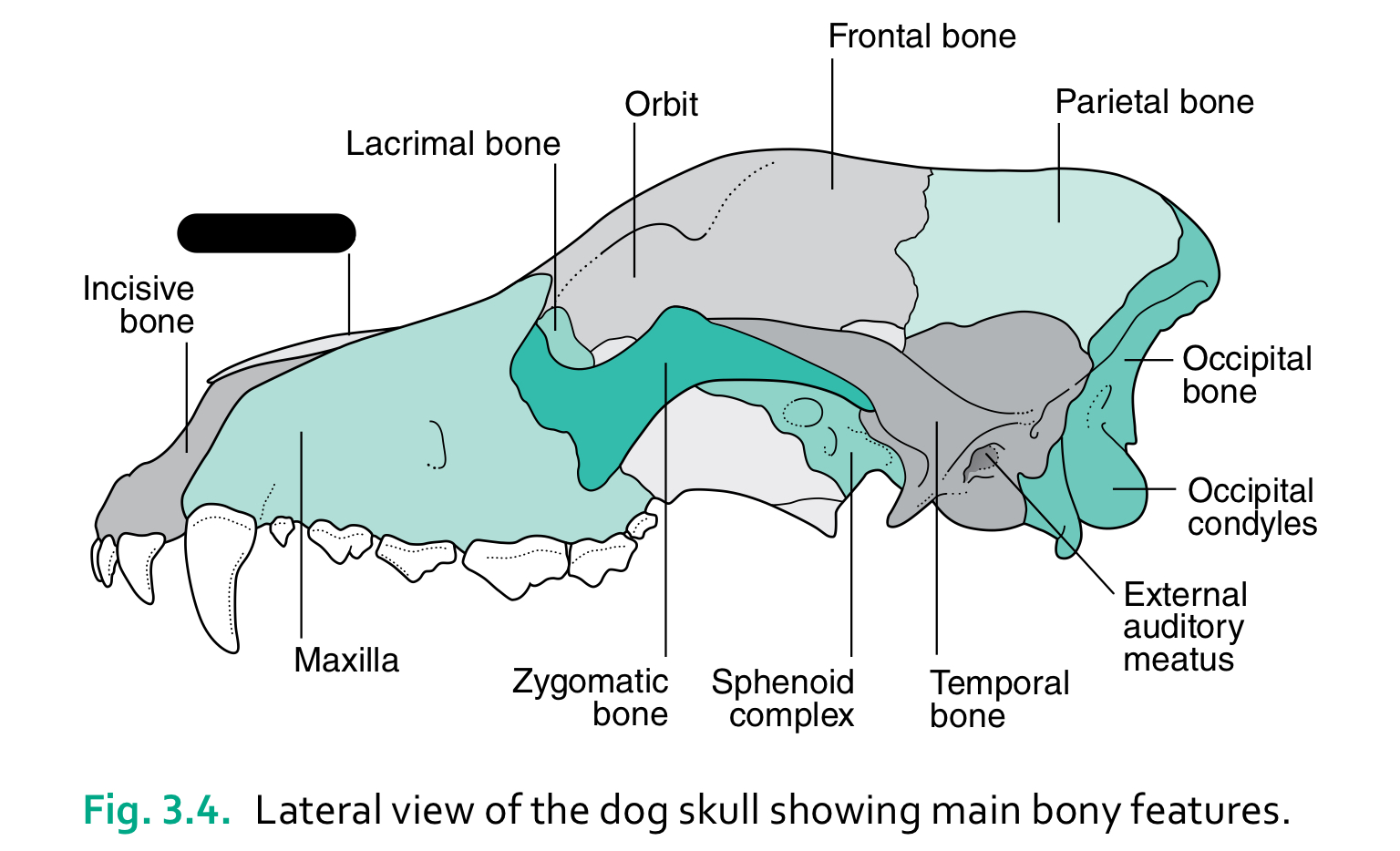
nasal bone
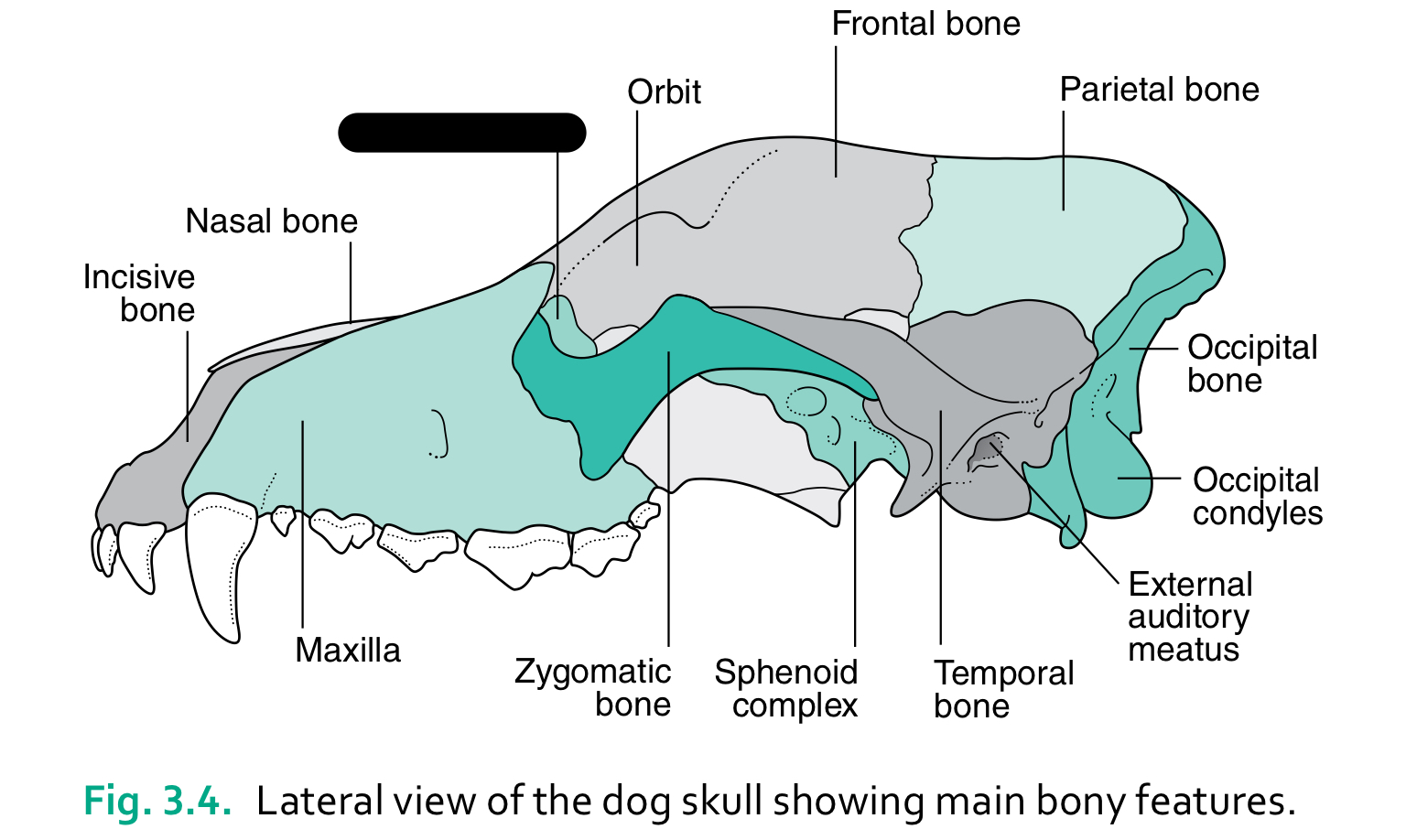
lacrimal bone
orbit
frontal bone
parietal bone
maxilla
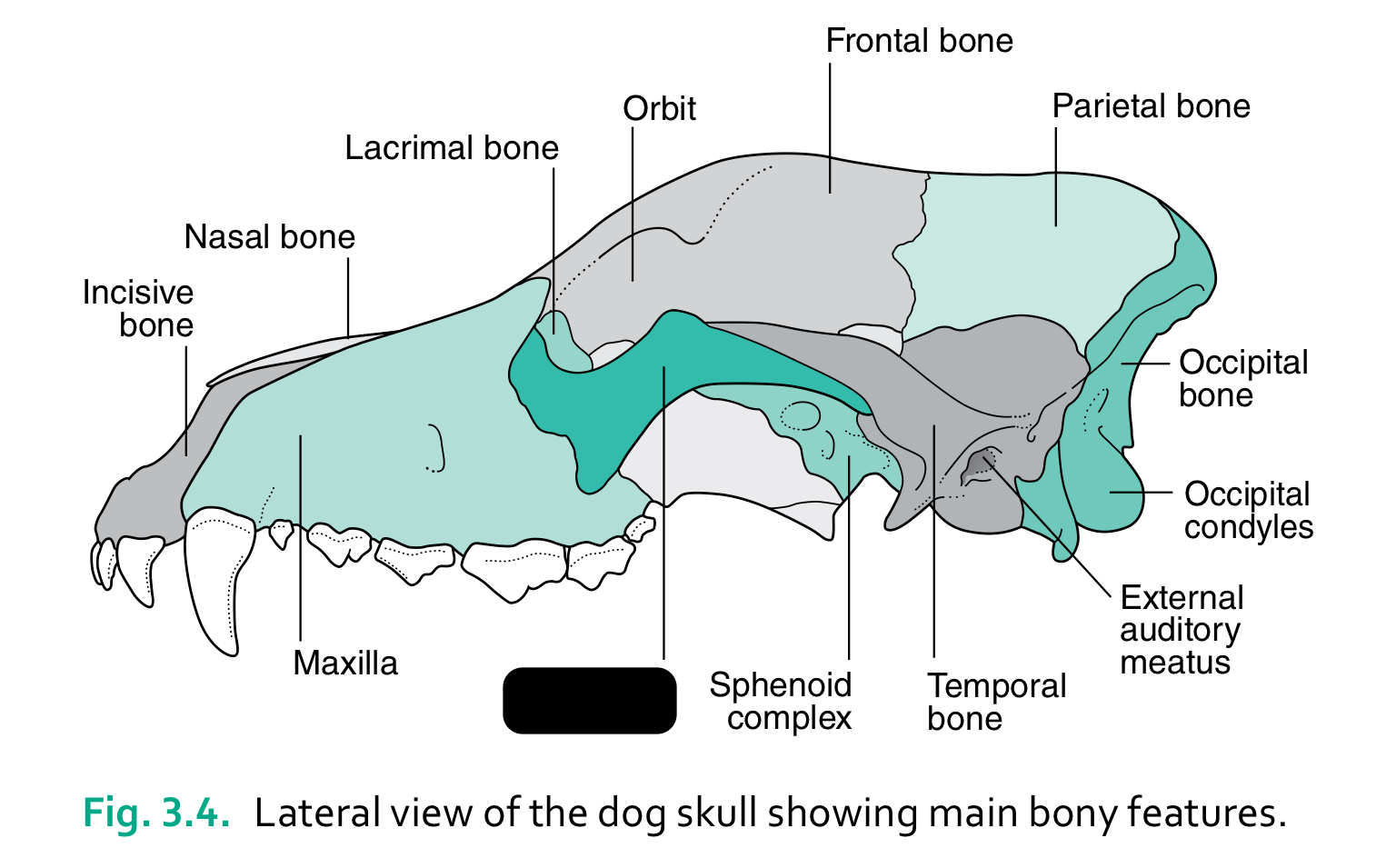
zygomatic bone
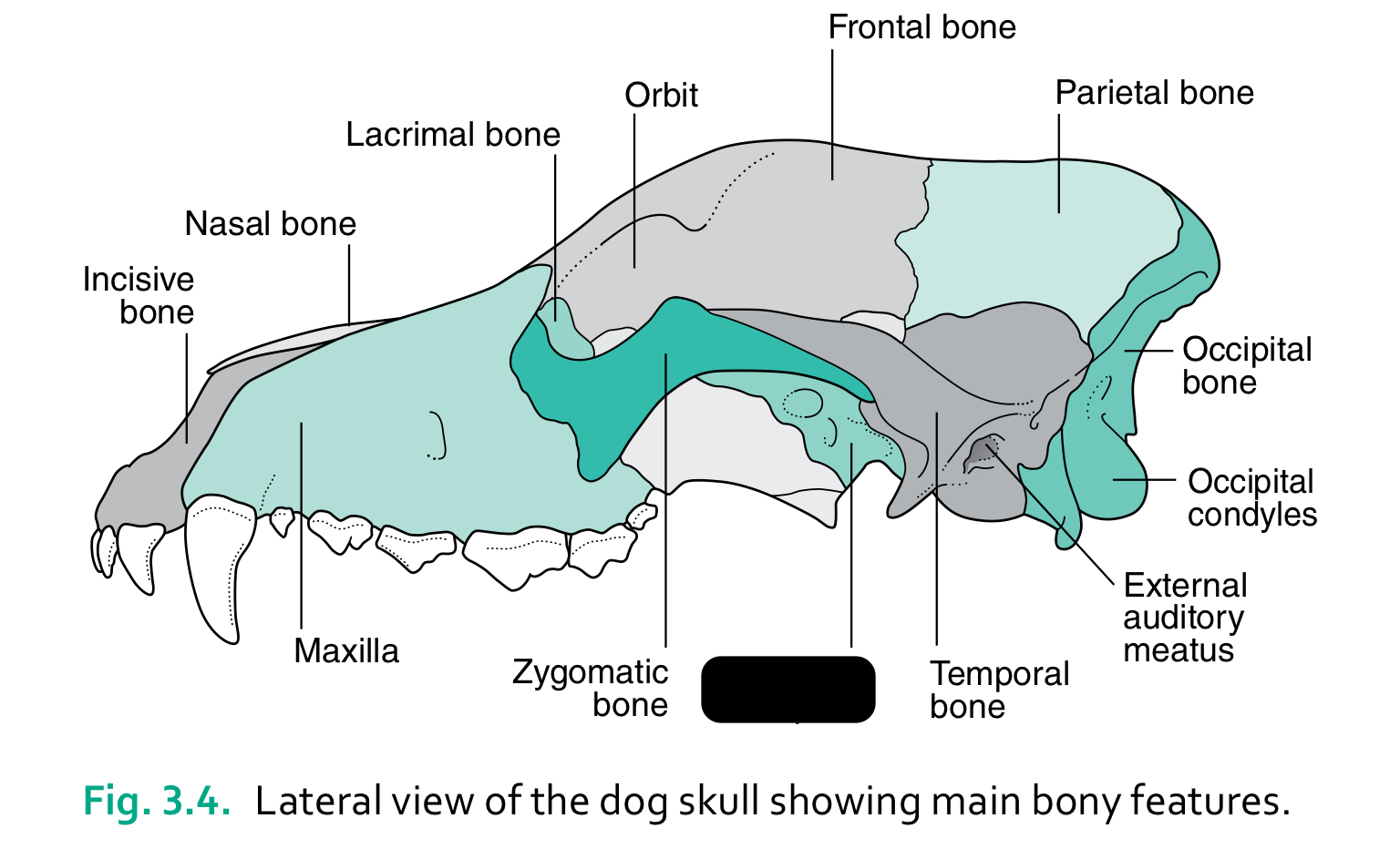
sphenoid complex
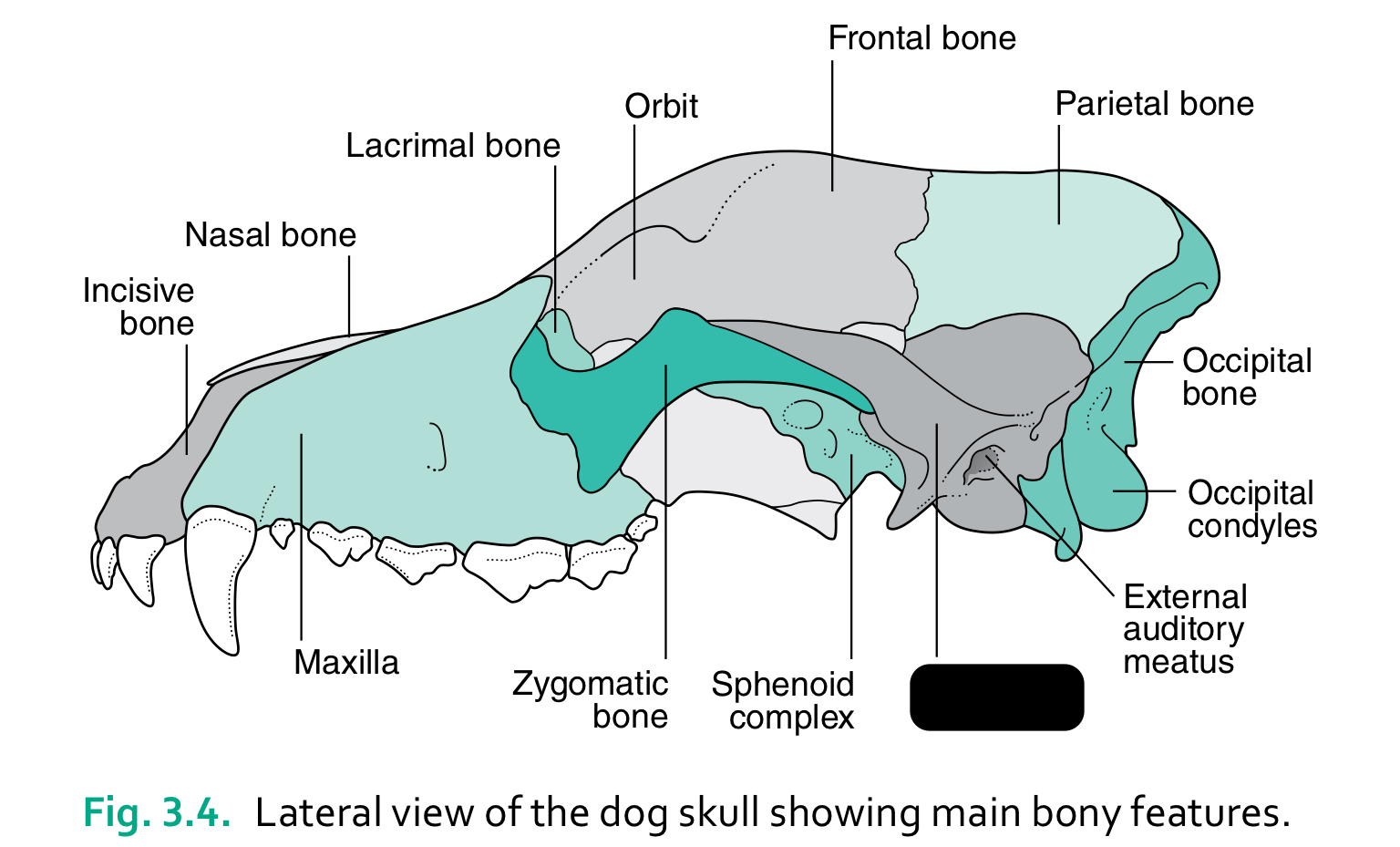
temporal bone
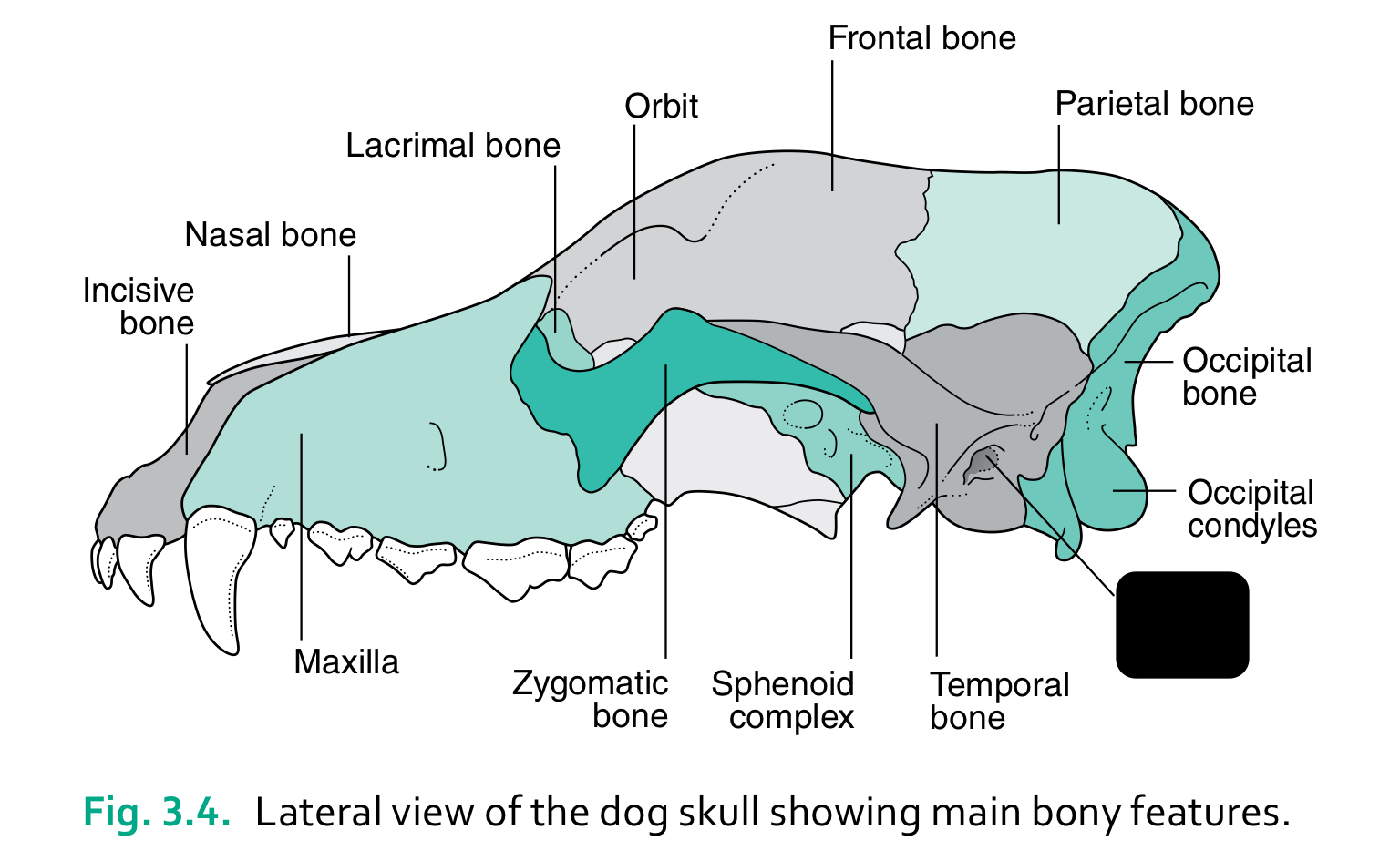
external auditory meatus
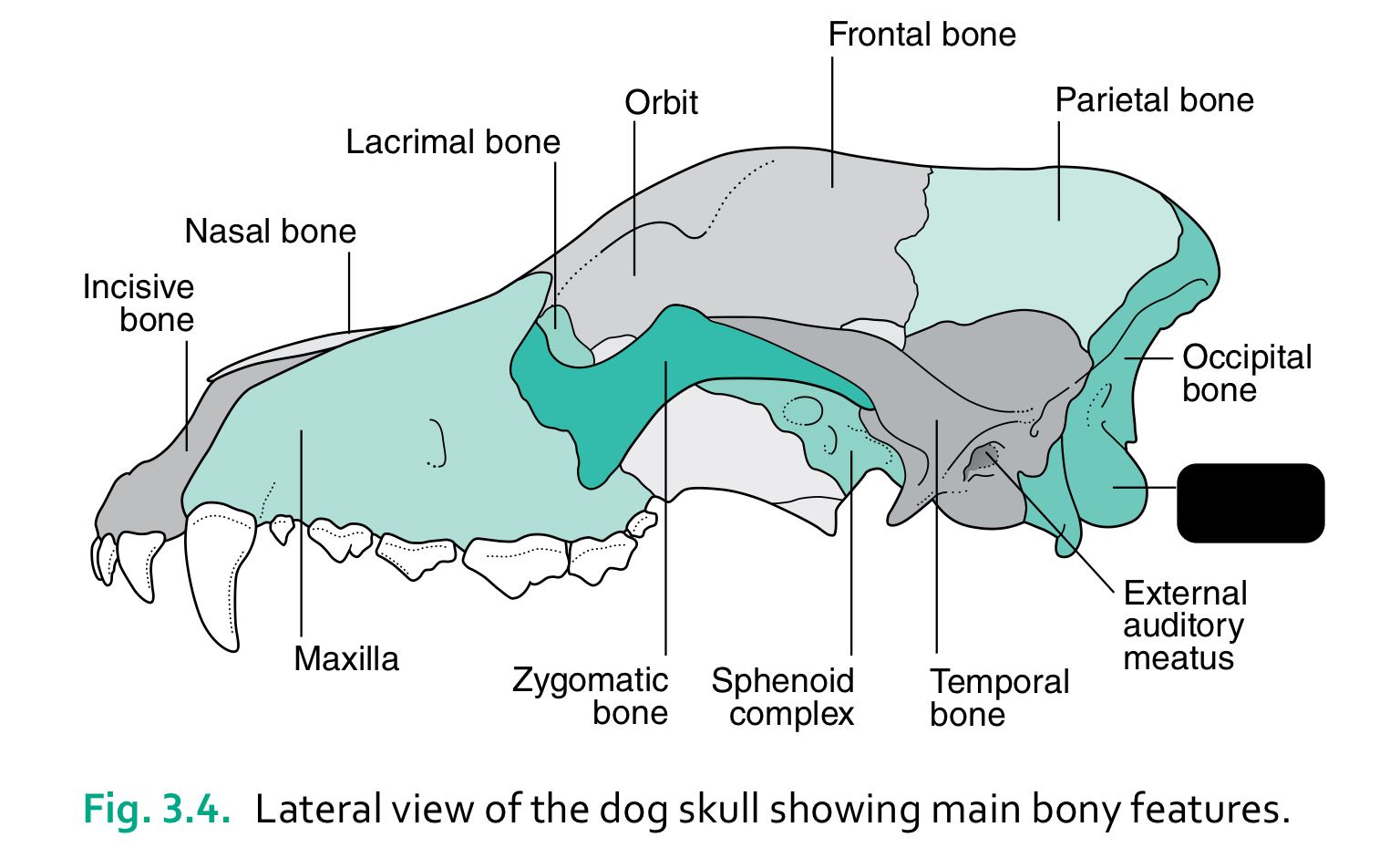
occipital condyles
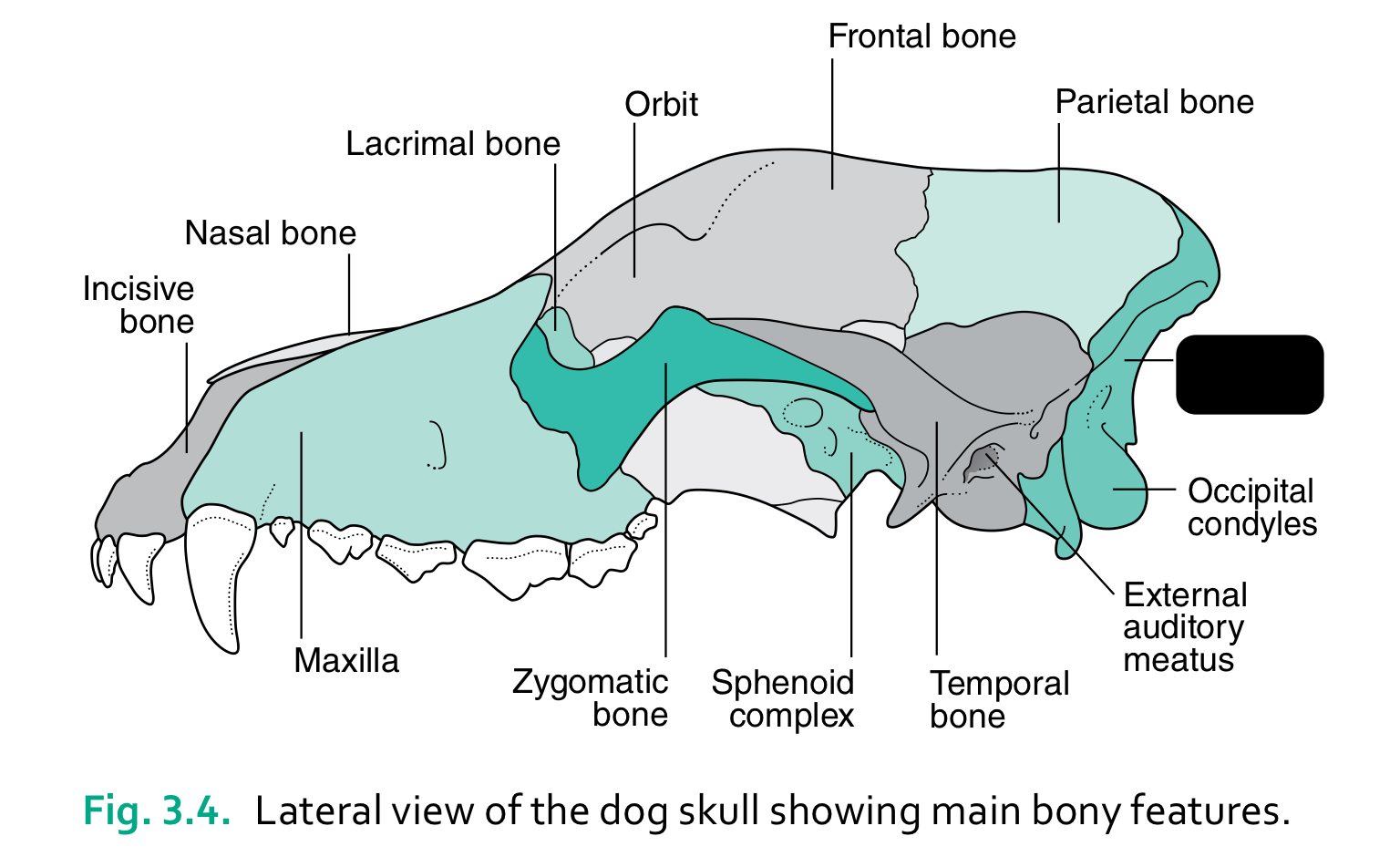
occipital bone
the caudal part of the skull where the brain sits is the ____
cranium
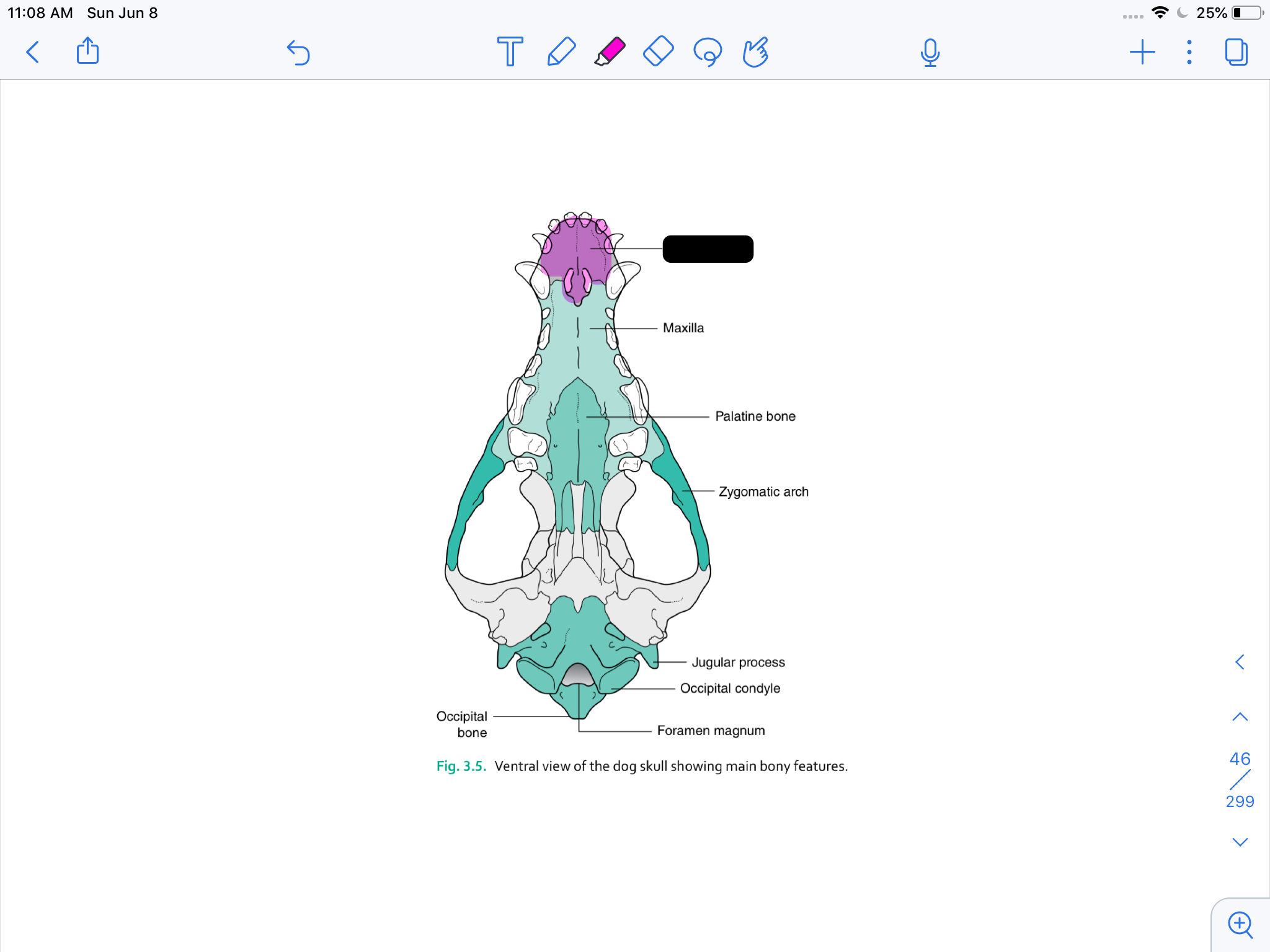
incisive bone
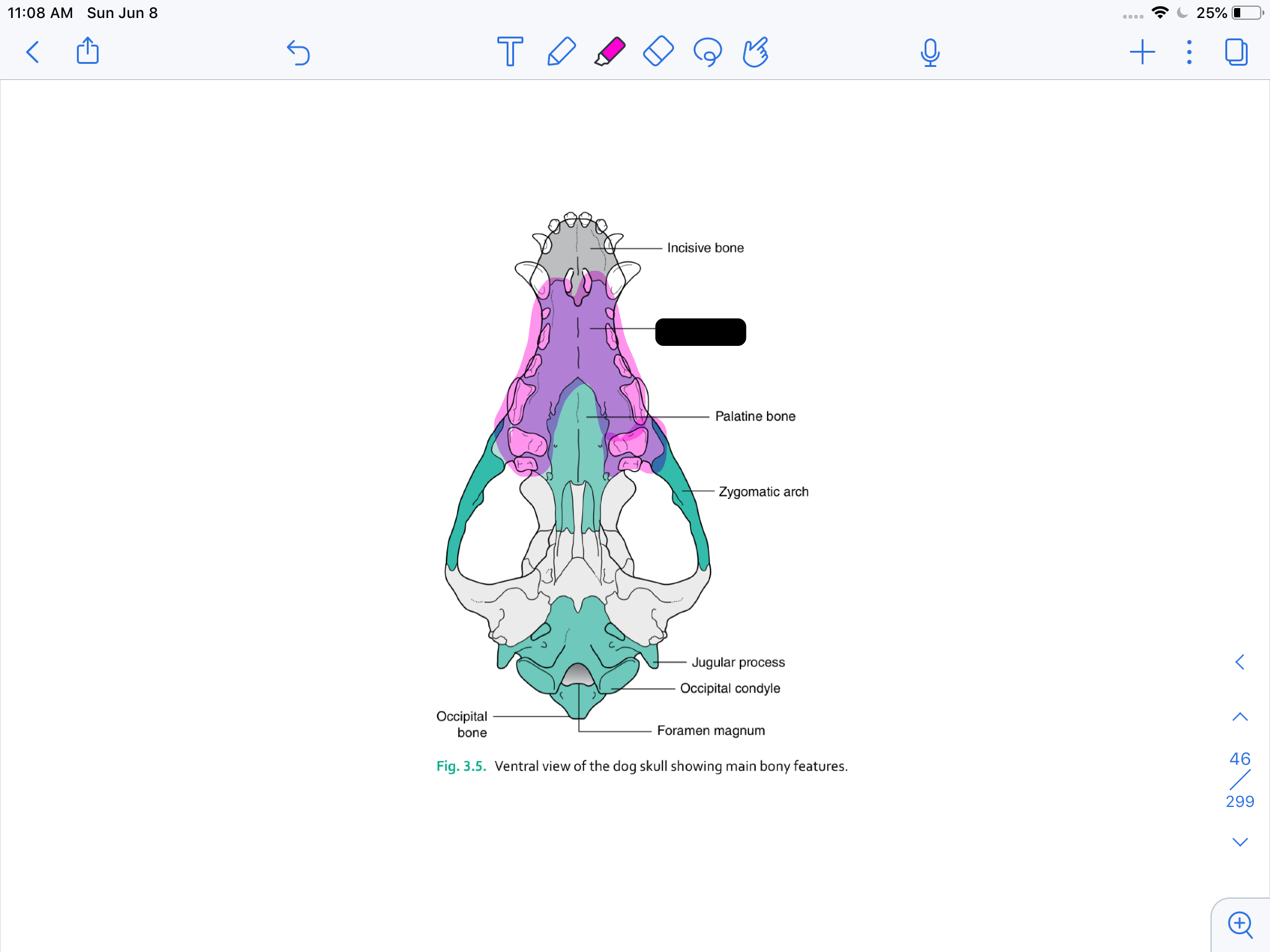
maxilla
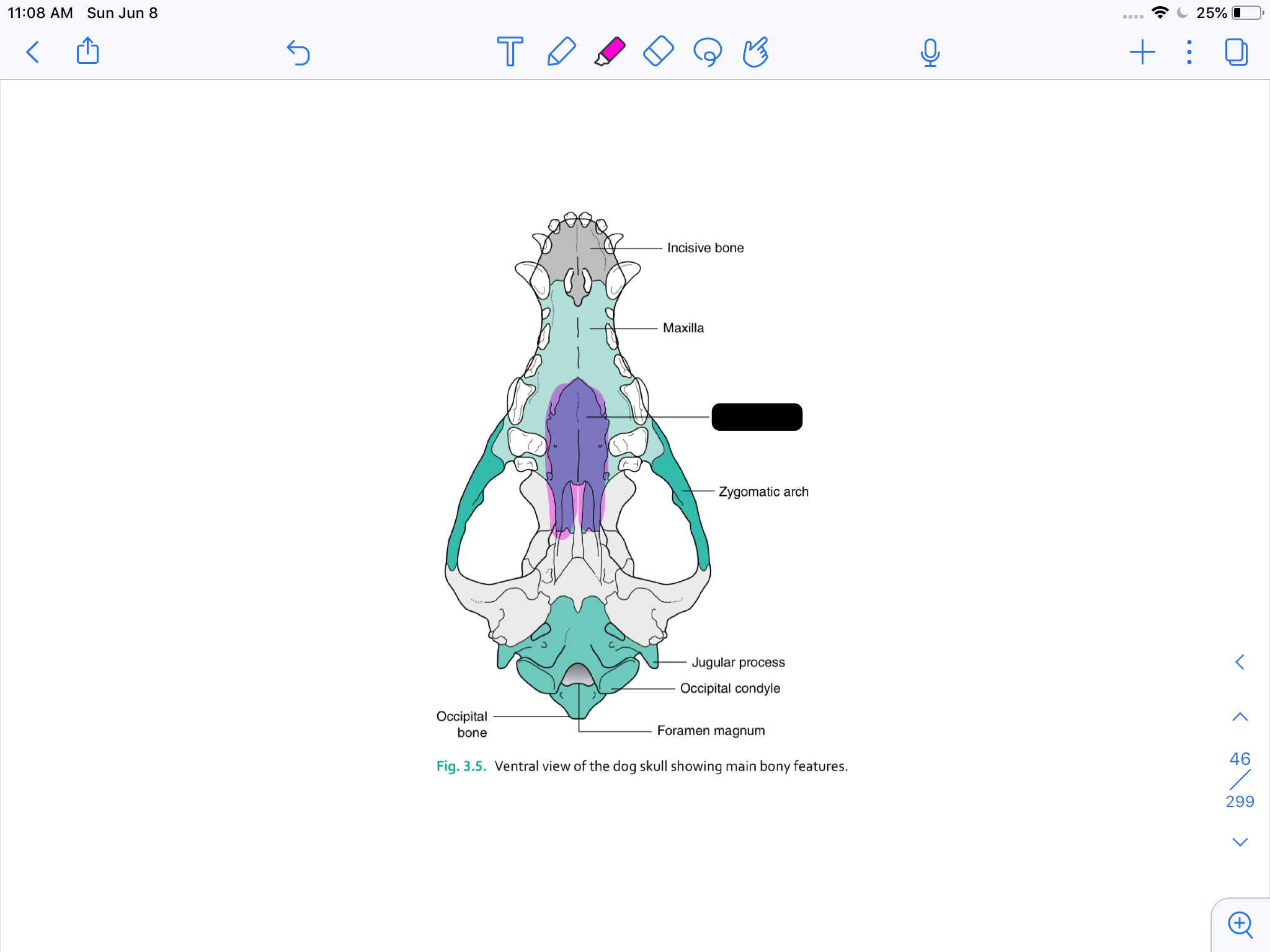
palatine bone

zygomatic arch
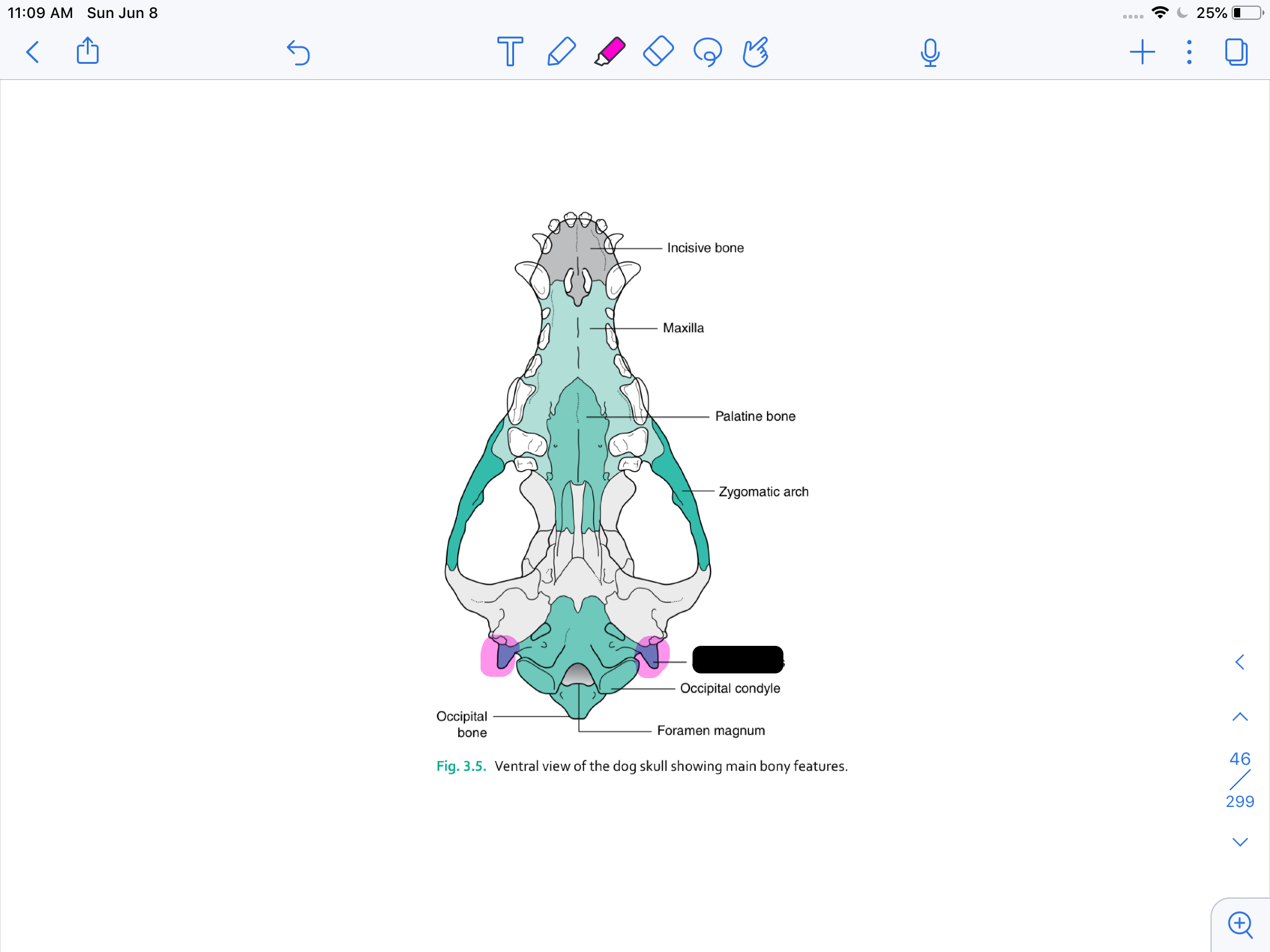
jugular process
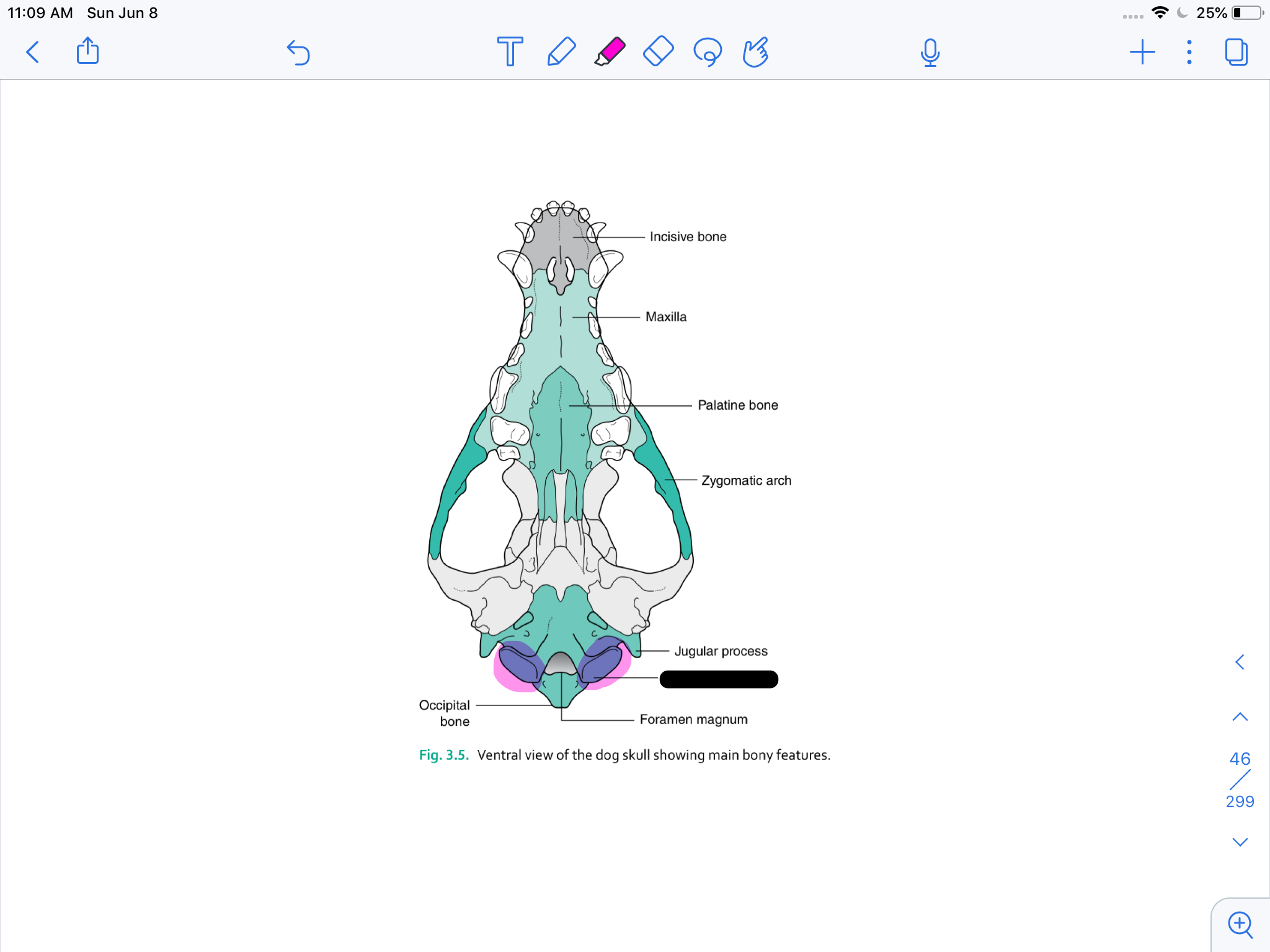
occipital condyle
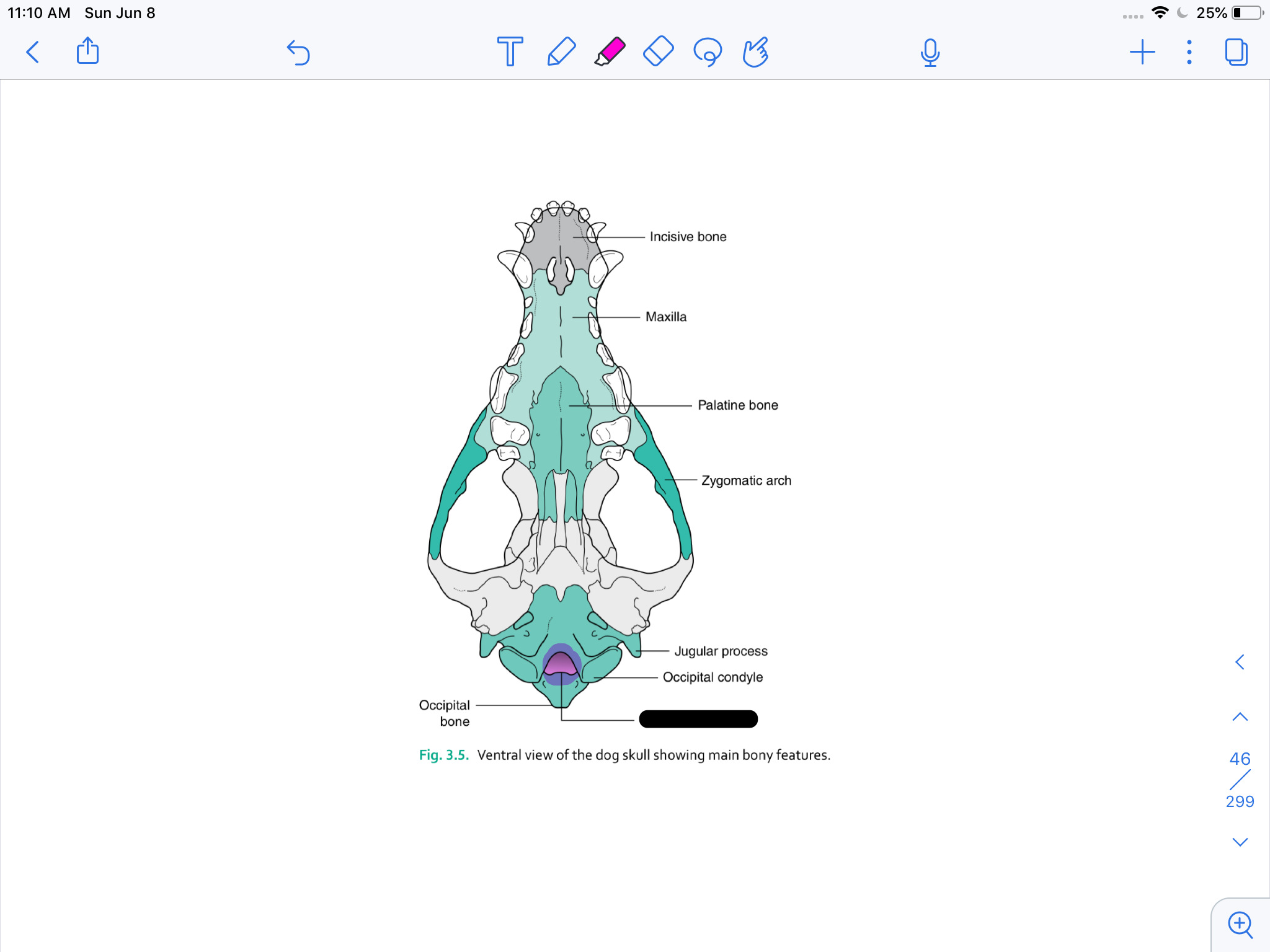
formamen magnum
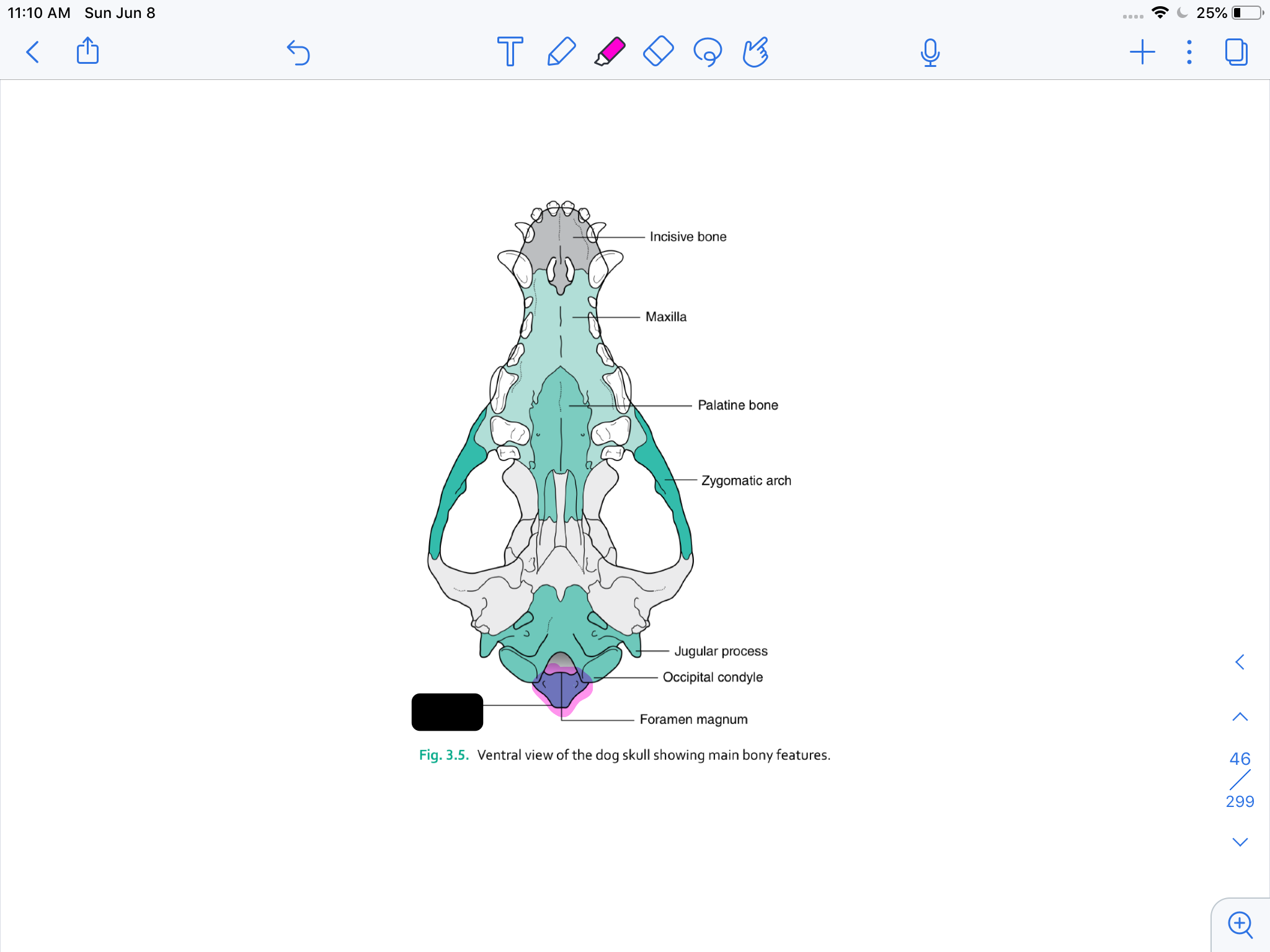
occipital bone
the ____ in the ___ bone house the structures of the middle ear
tympanic bulla, temporal
the ____ opens into the tympanic bulla of the temporal bone
external acoustic meatus (ear canal)
the ___ articulate with the first cervical vertebra (atlas)
occipital condyles
the ___ forms the floor of the cranial cavity and has many foramina
sphenoid
the ___ is a ridge of bone on the skull prominent in muscular breeds
sagittal crest
poor development of the skull can result in ____, causing herniation of the ___ through foramen magnum
small cranium (insufficient to accommodate size of brain), cerebellum
hydrocephalus
fluid on the brain
syringomyelia
fluid filled cavities of the spine
ataxia
uncoordinated gait
the nasal chamber is divided by a cartilaginous plate called the ____
nasal septum
many bones of the skull are joined together by fibrous joints called ____ that allow for ____
sutures, growth and expansion
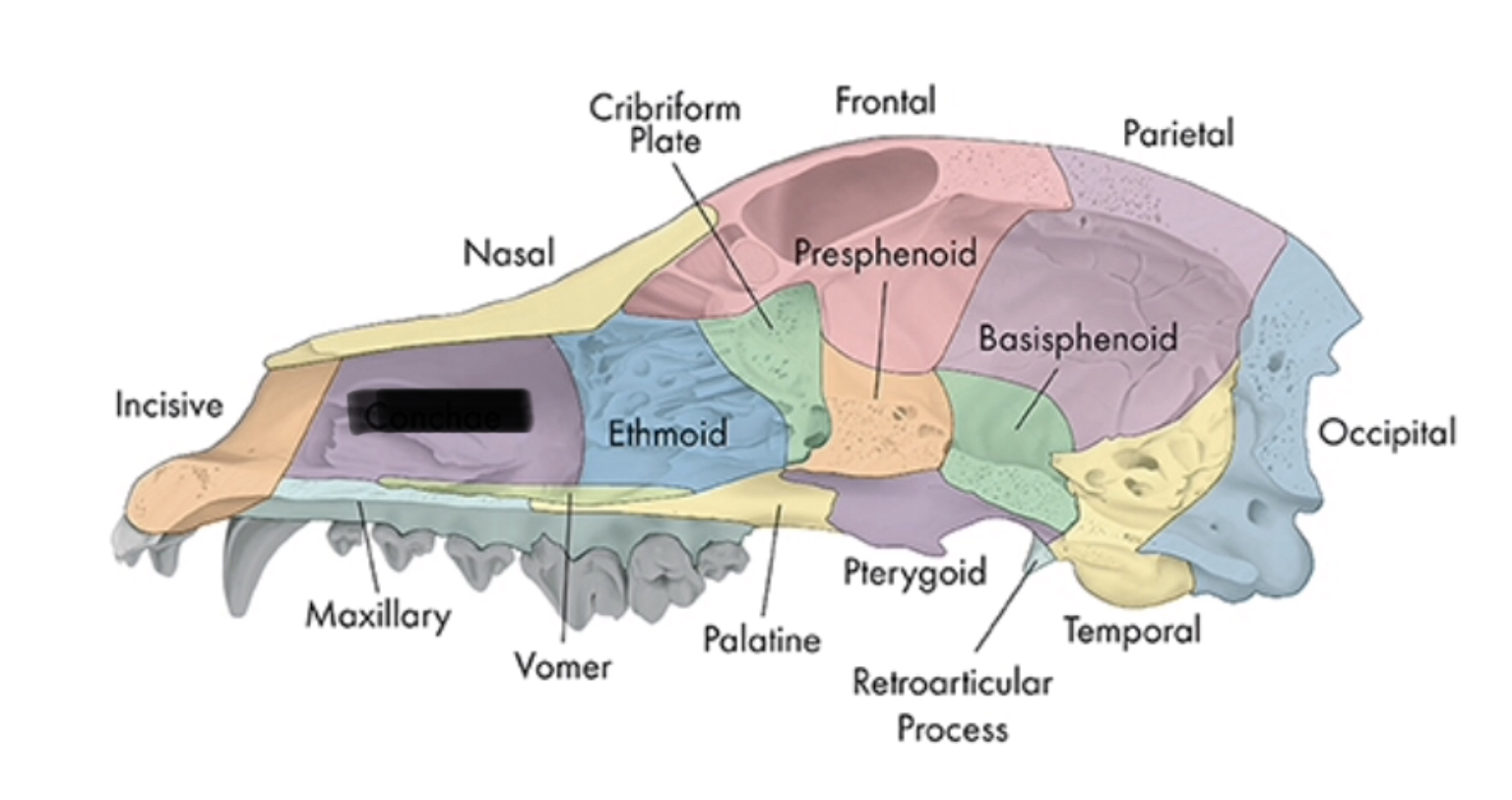
nasal conchae
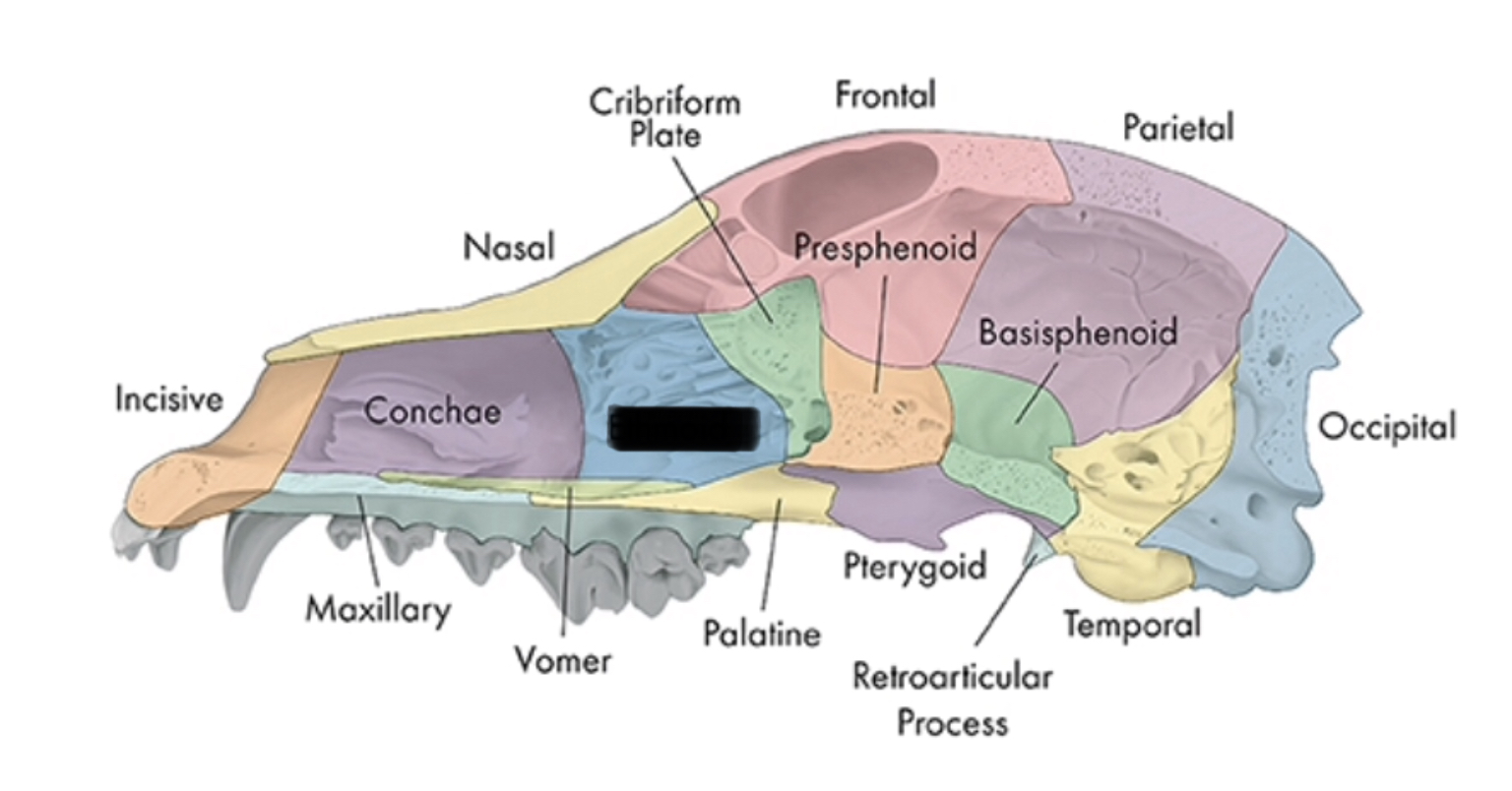
boundary between nasal and cranial cavities
ethmoid
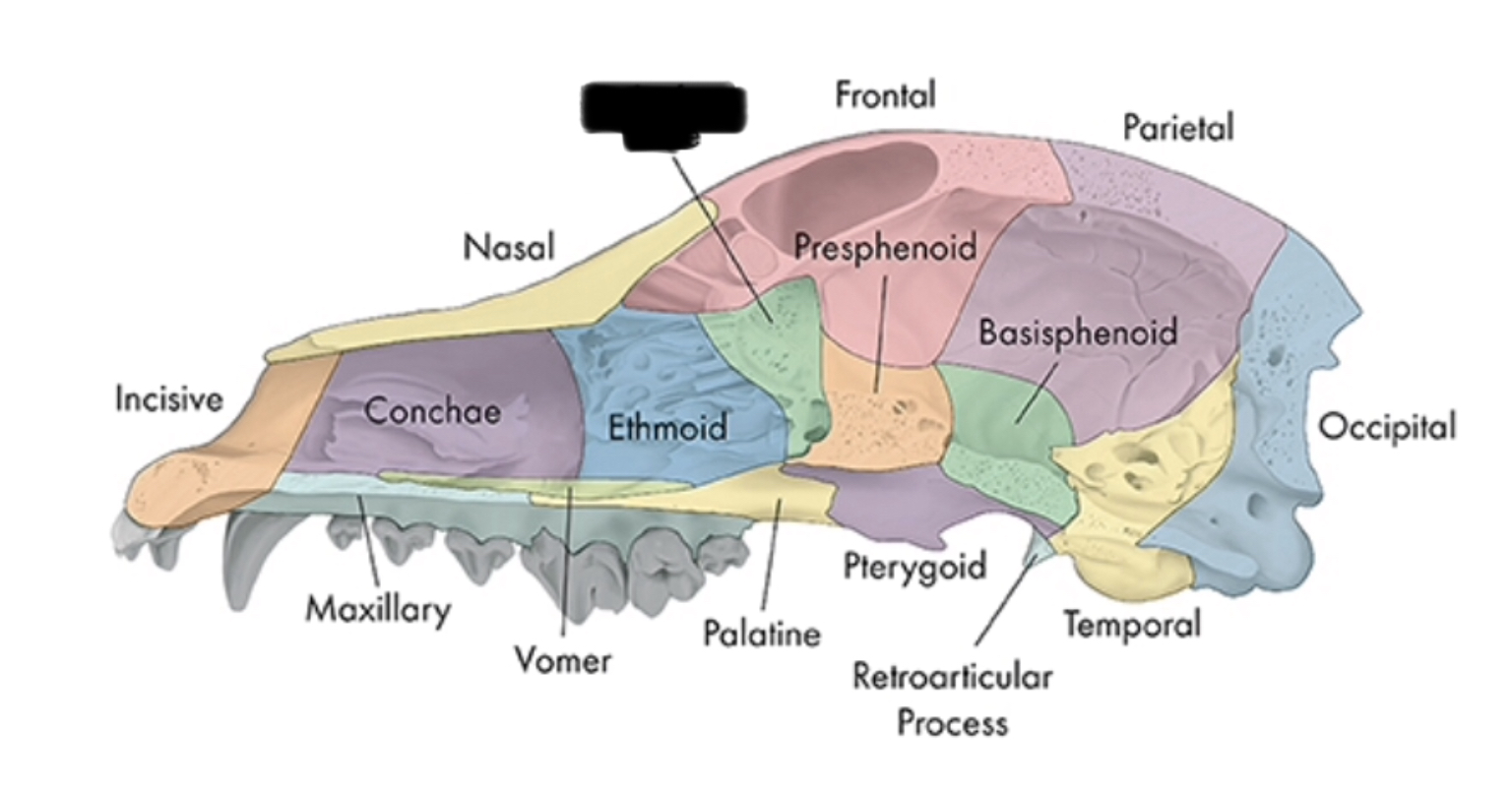
olfactory nerve passes
cribiform plate
pterygoid
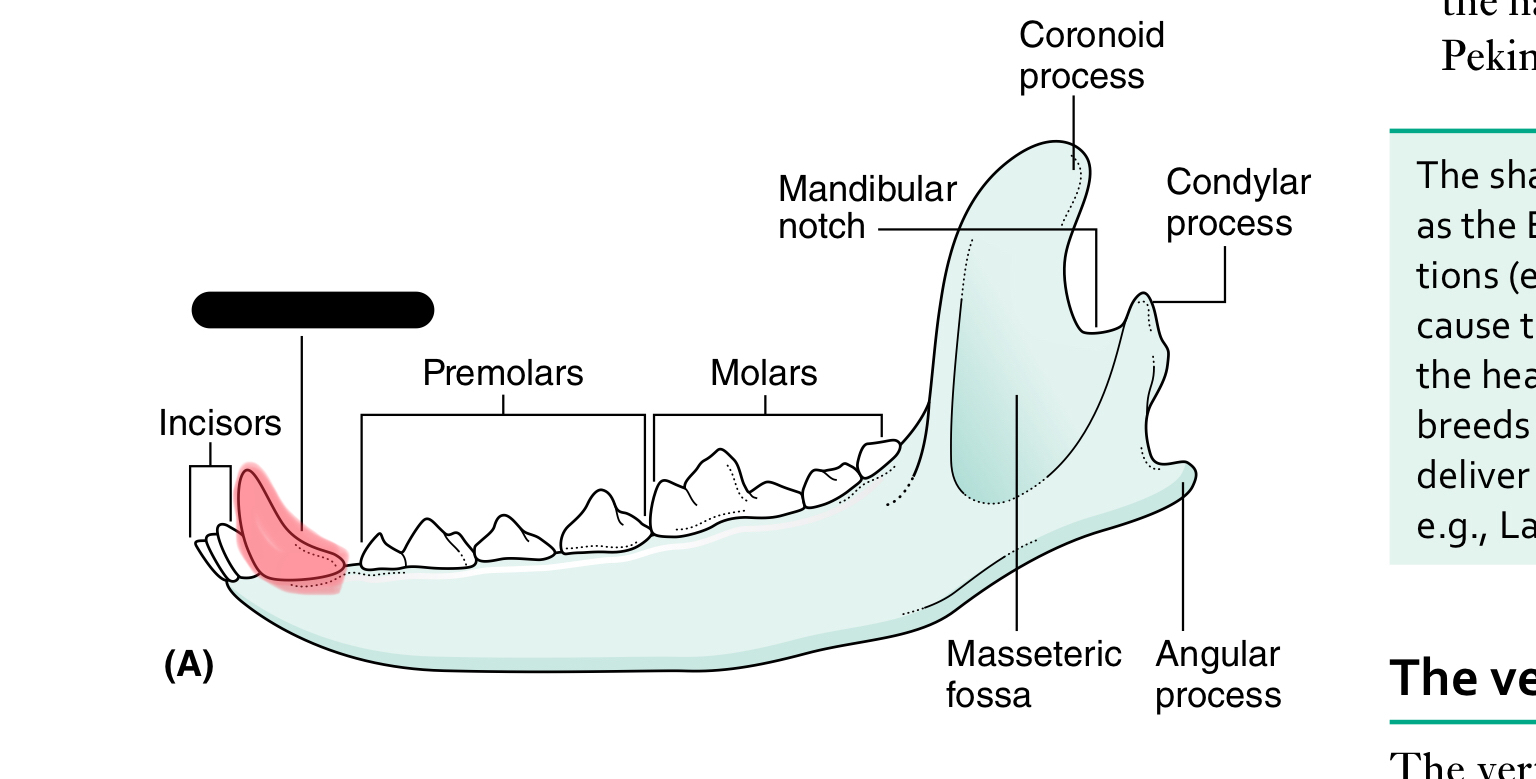
incisors
canine tooth
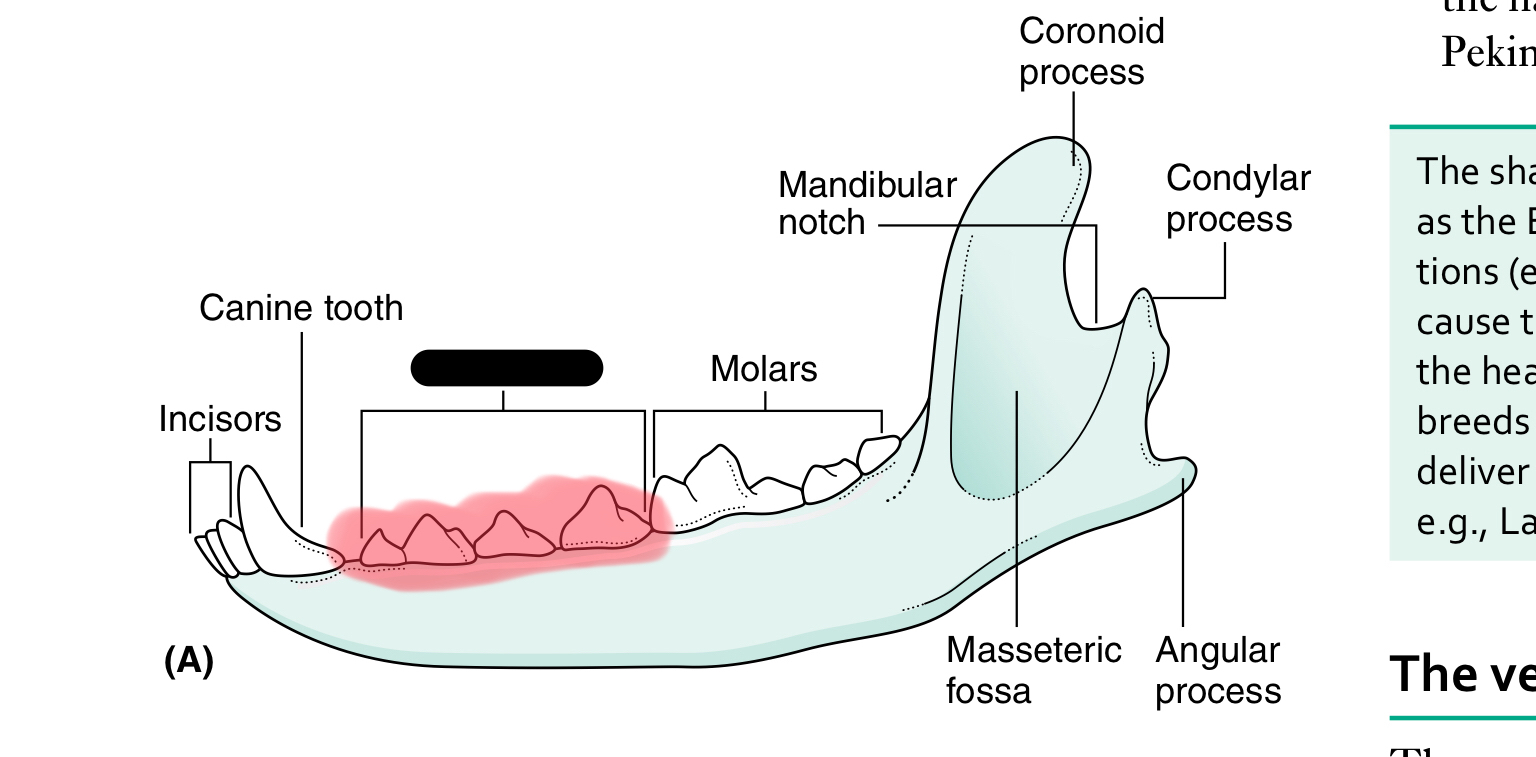
premolars
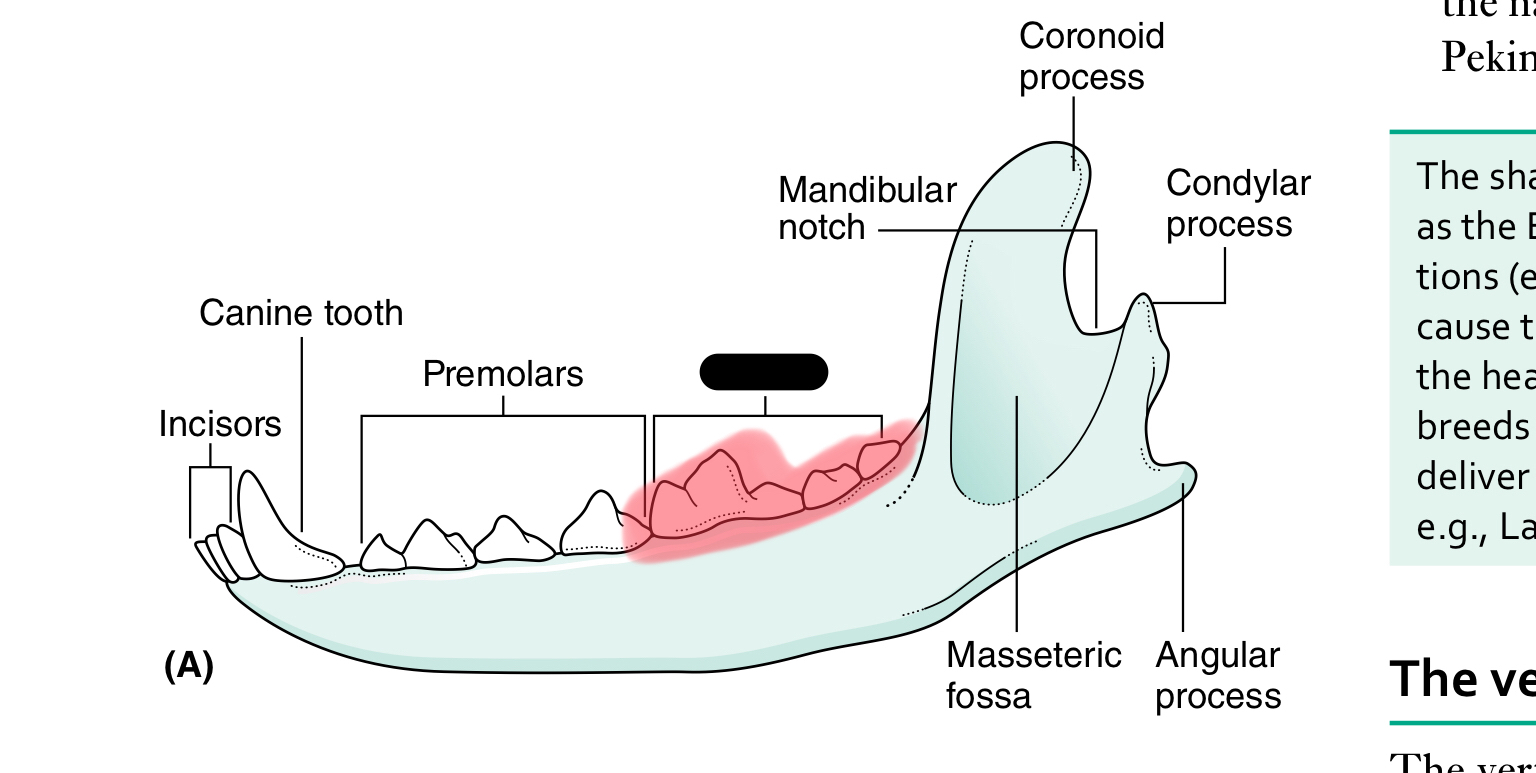
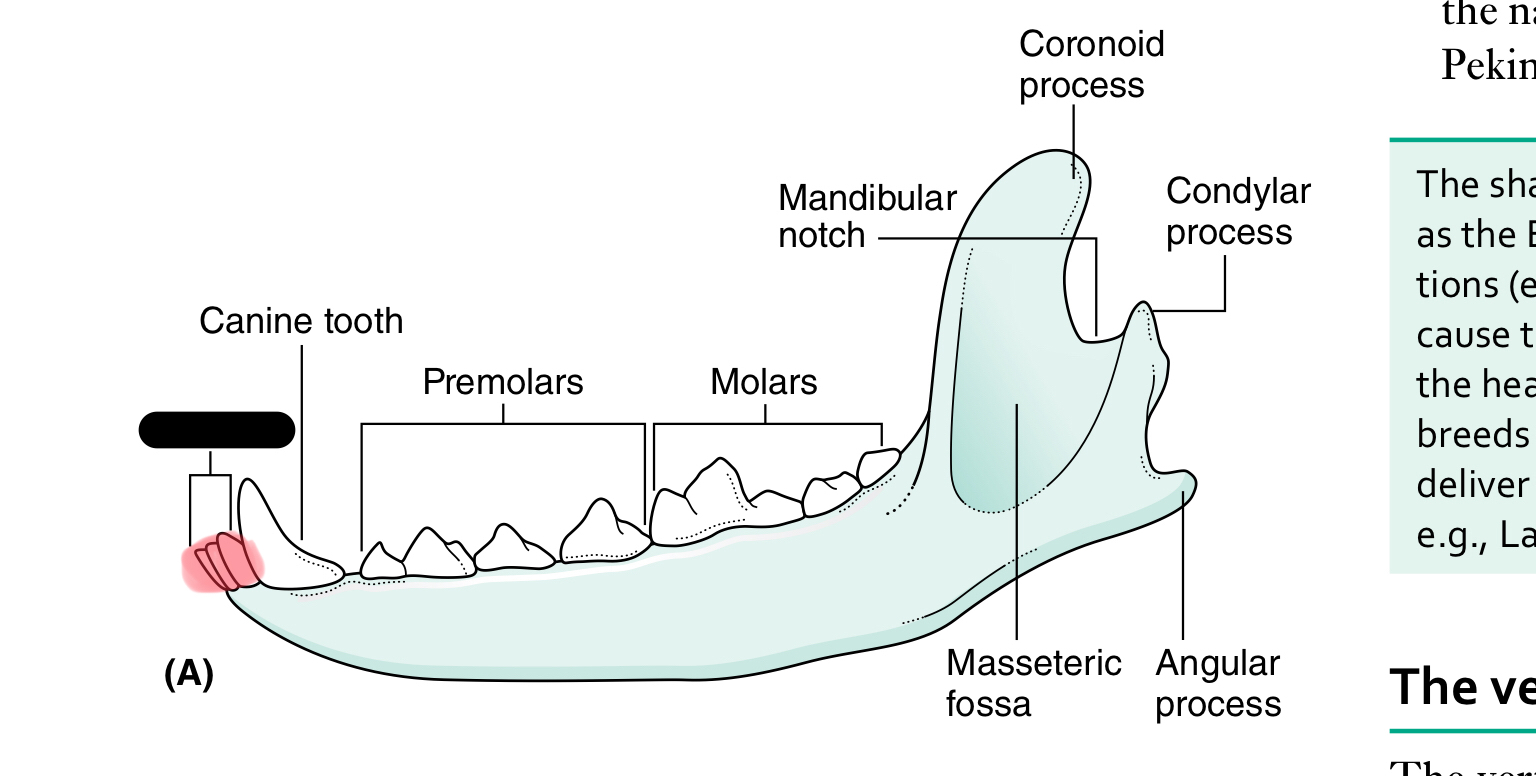
molars
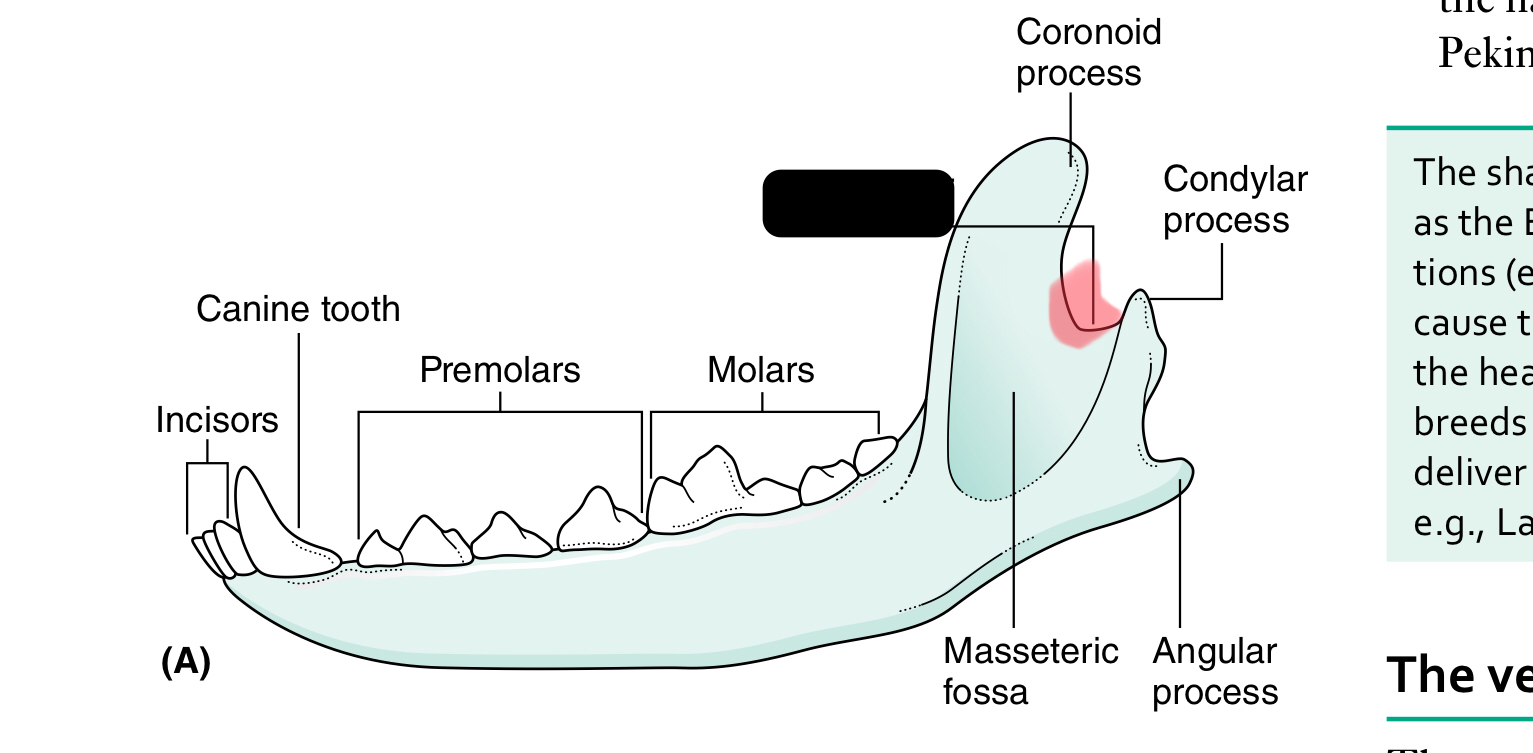
mandibular notch
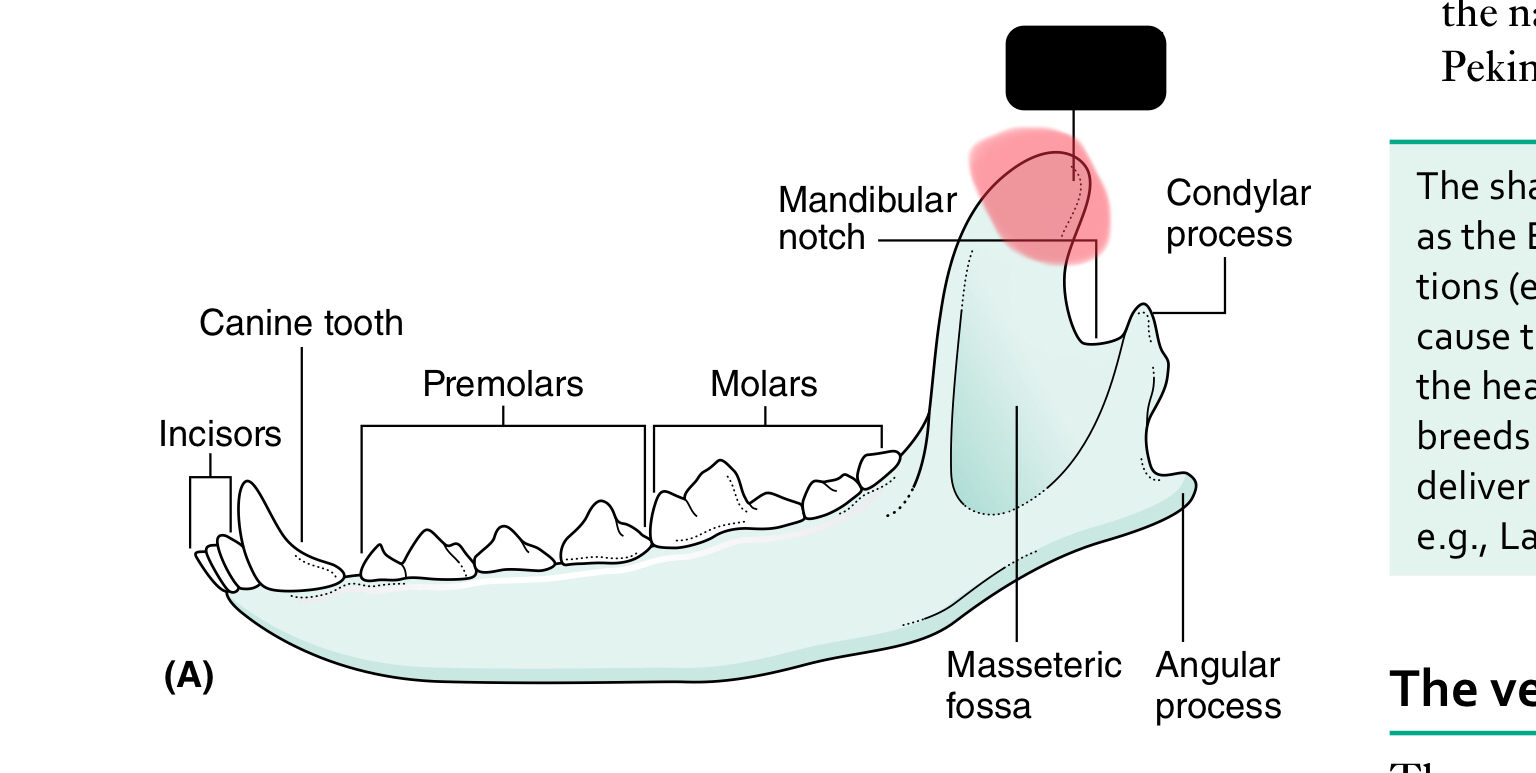
coronoid process
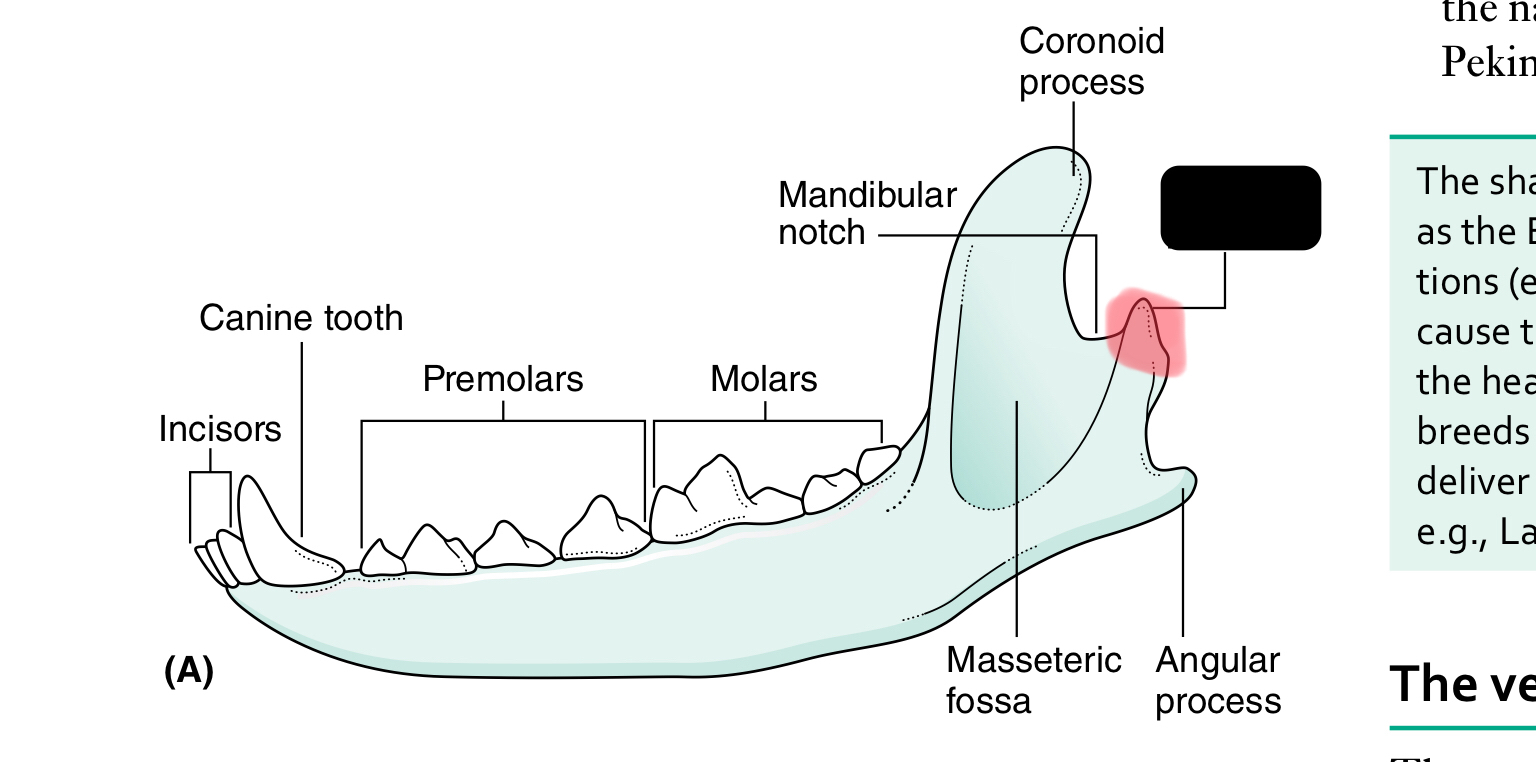
condylar process of mandible
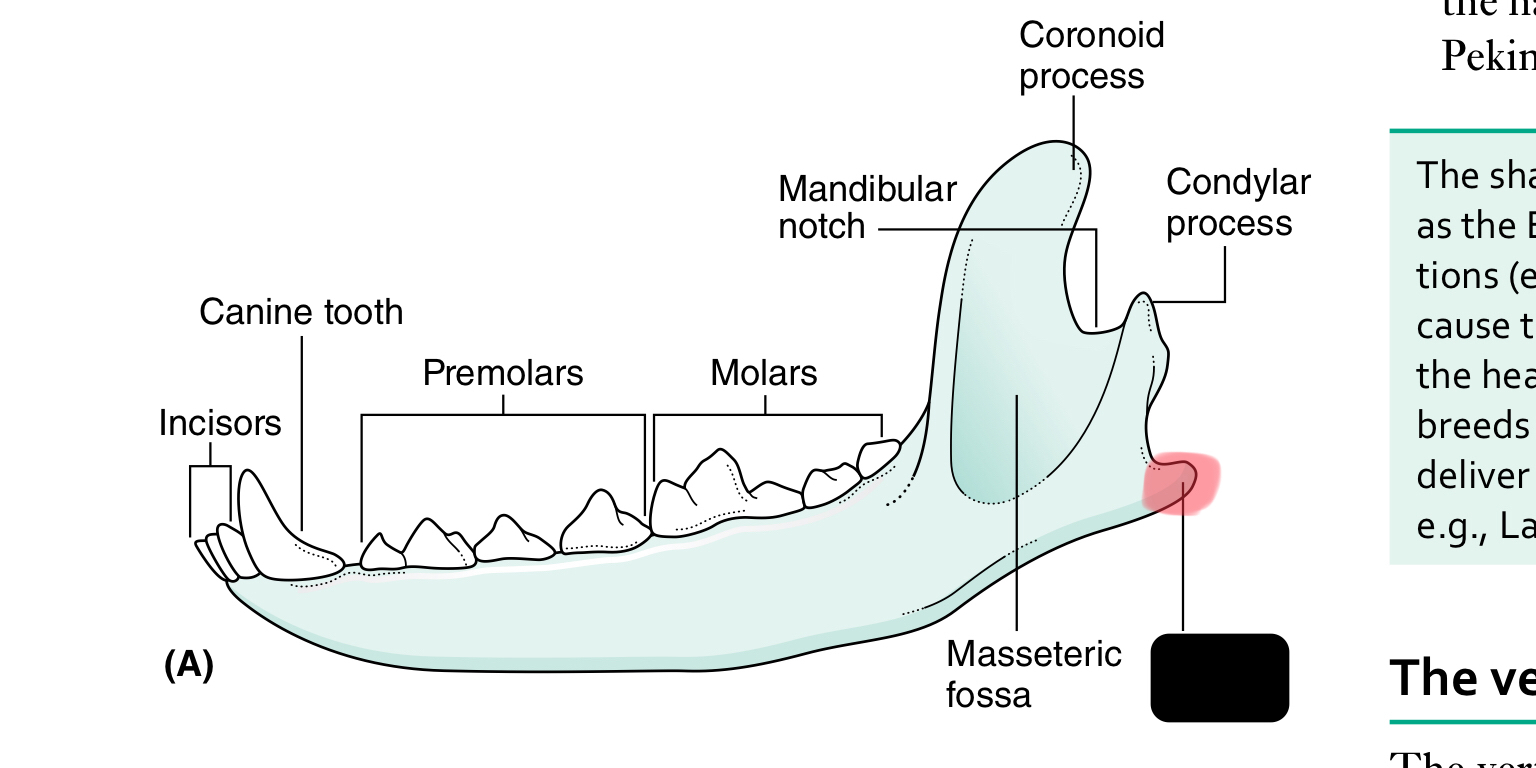
angular process of mandible
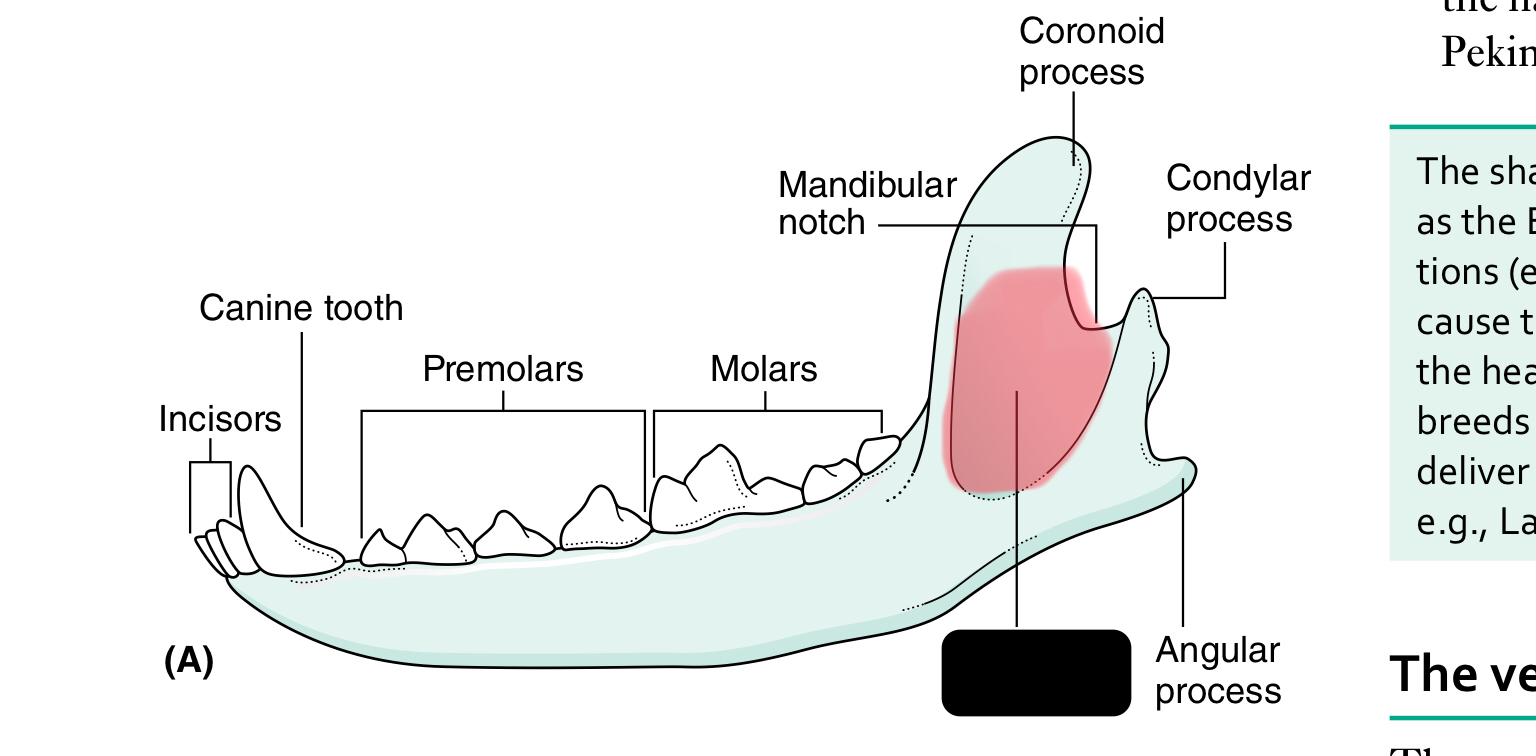
masseteric fossa
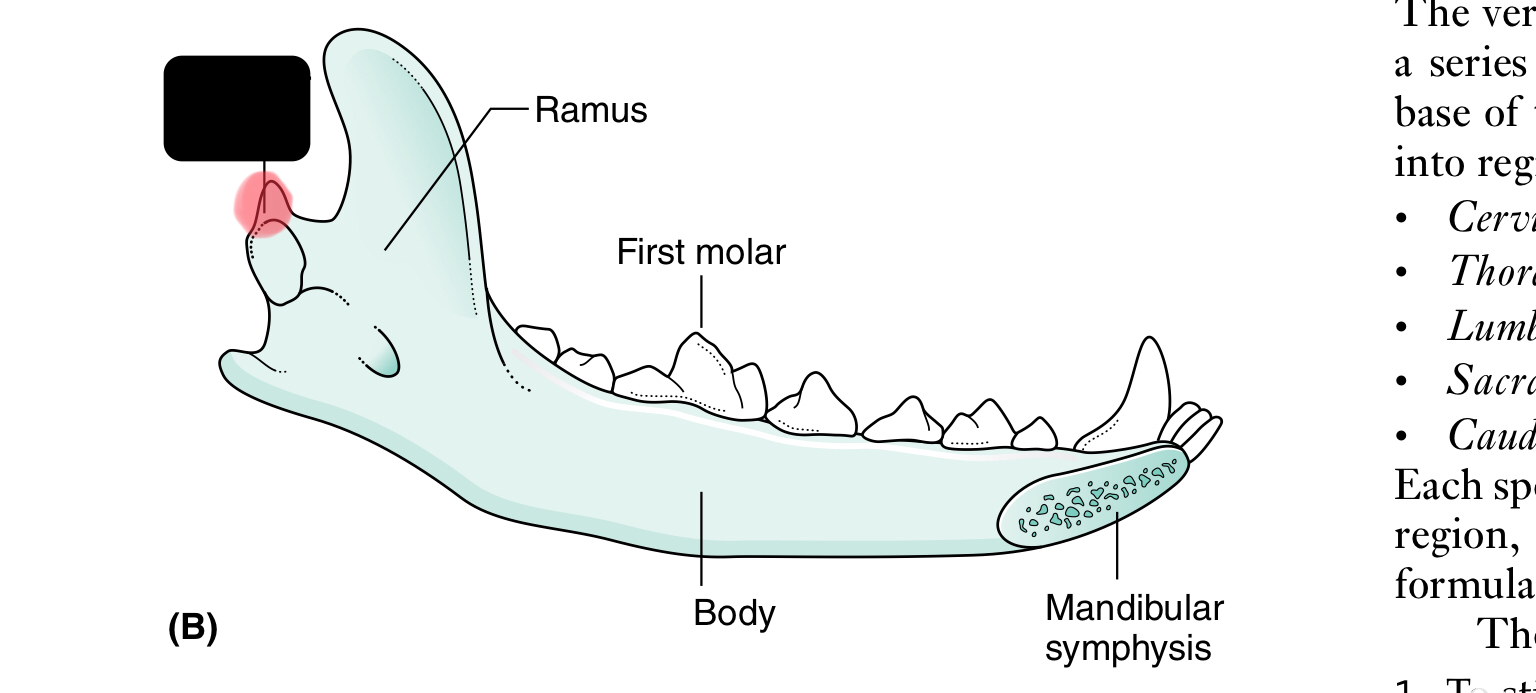
condylar process of mandible
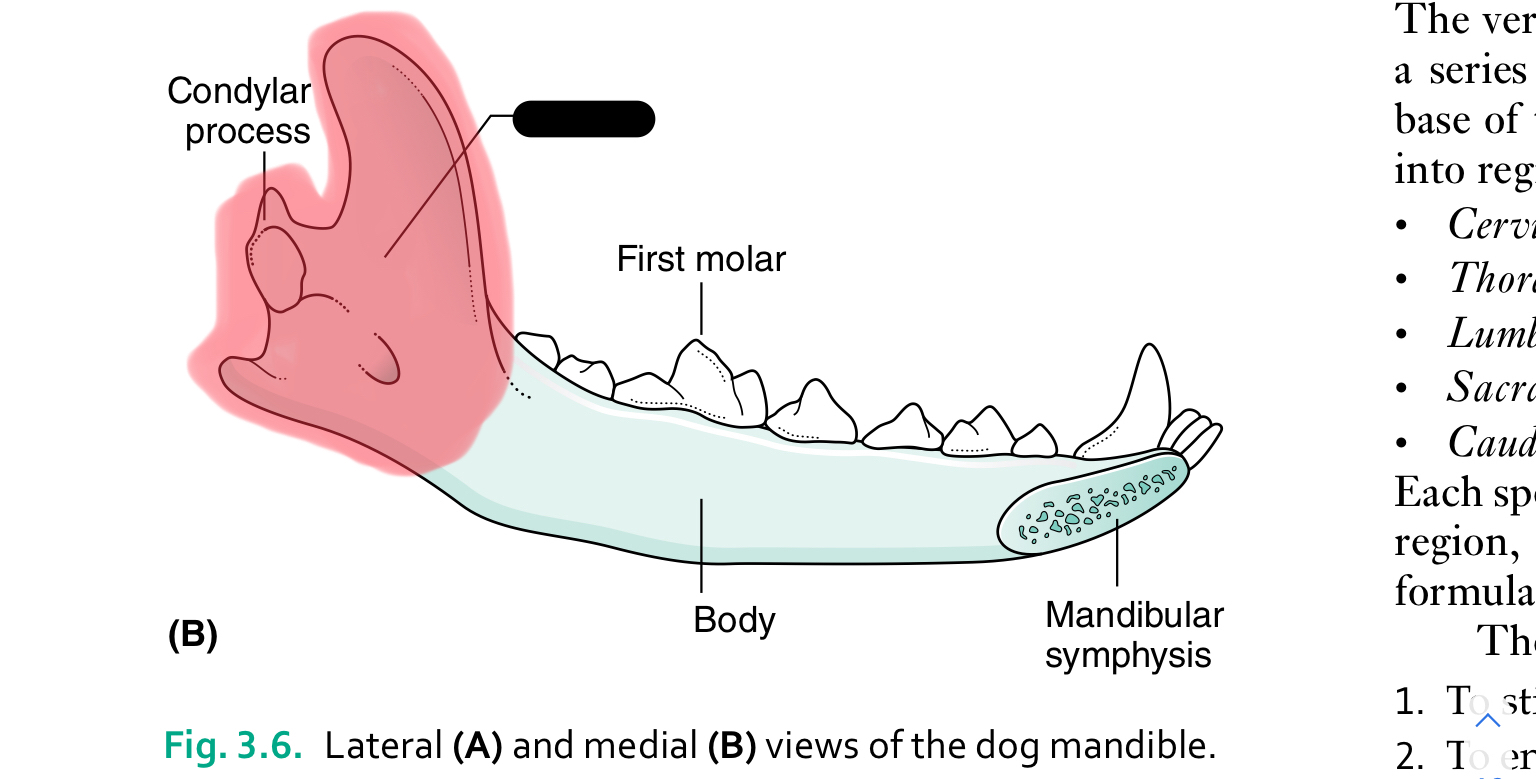
ramus of mandible
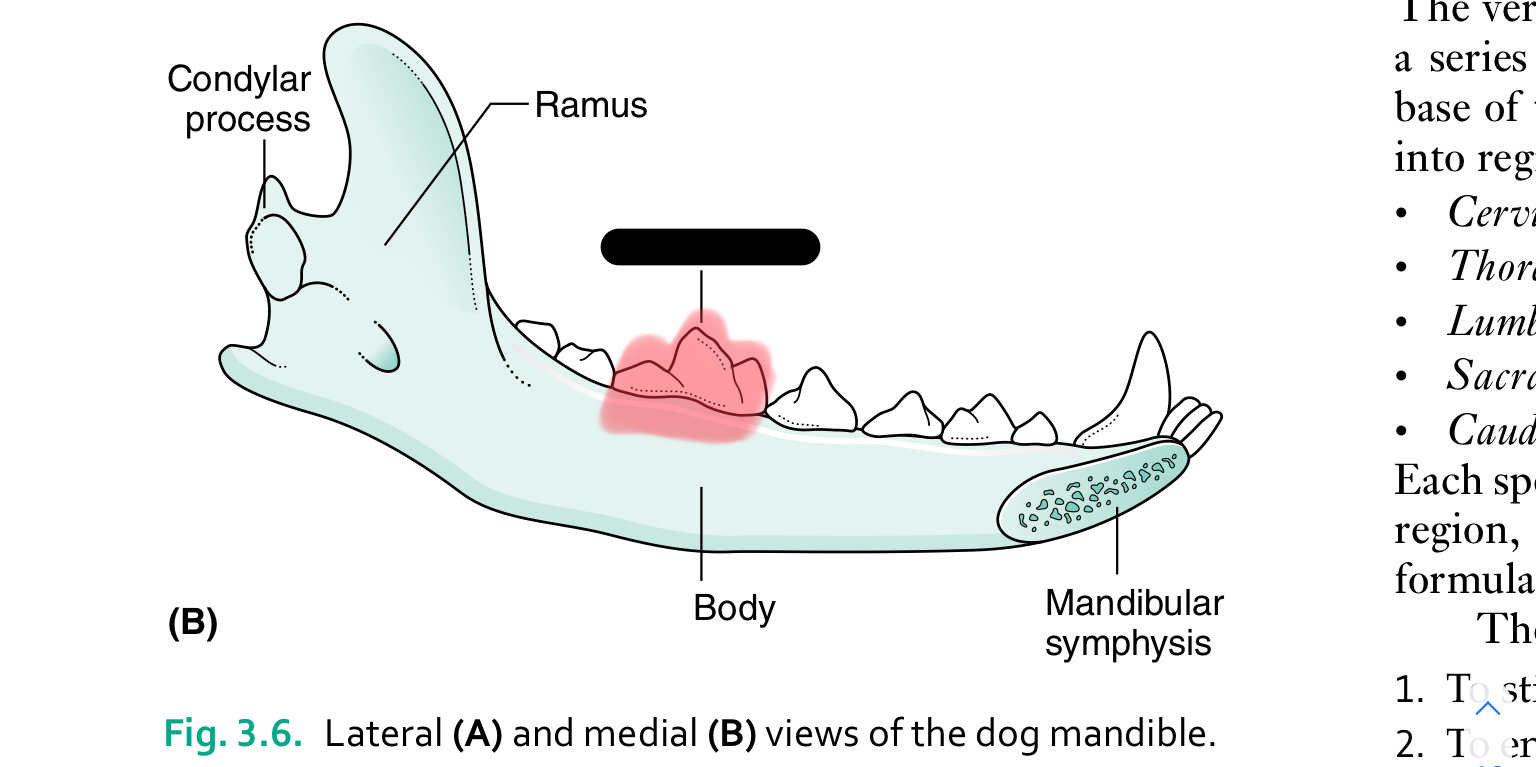
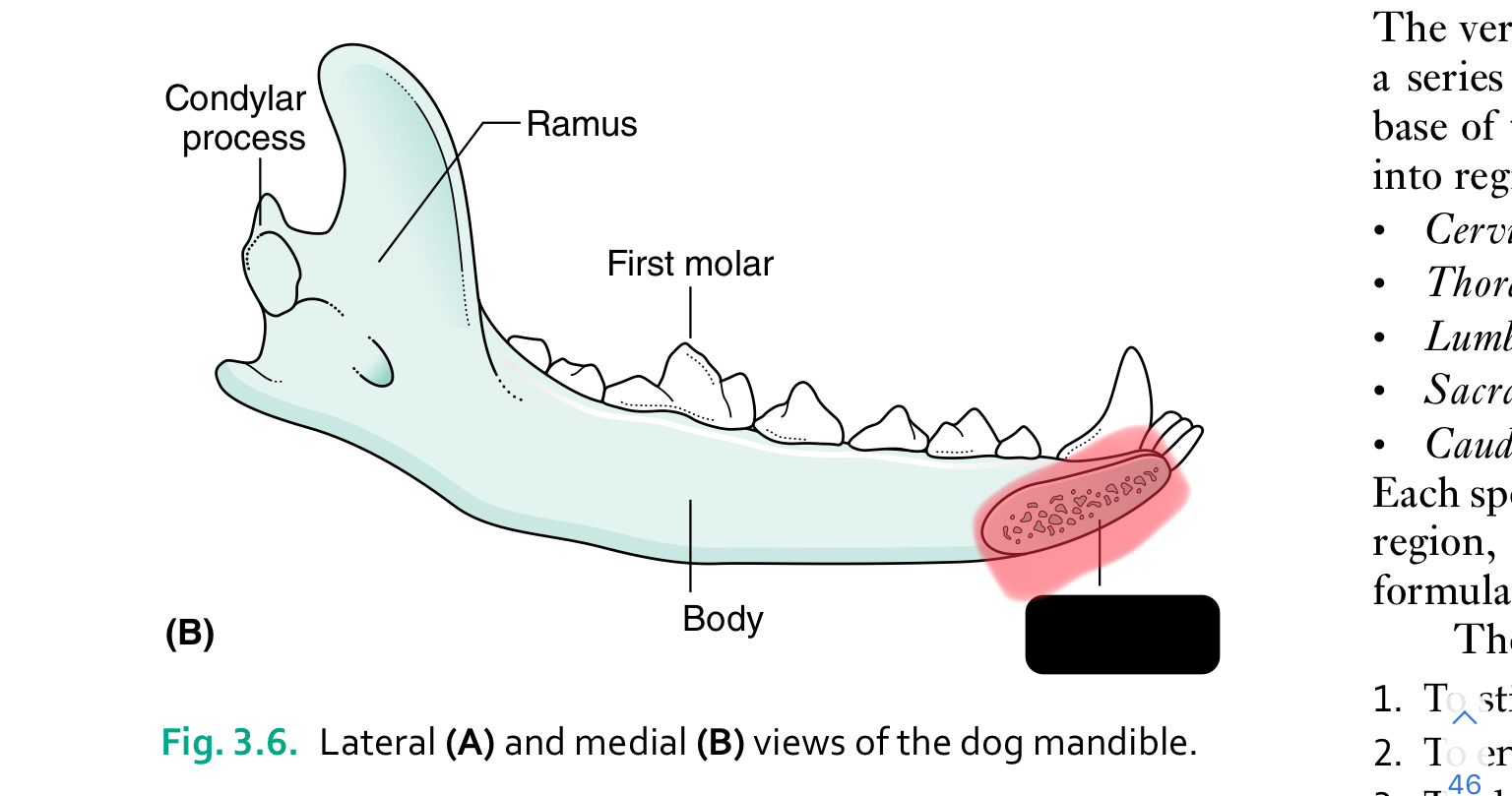
first molar
mandibular symphysis
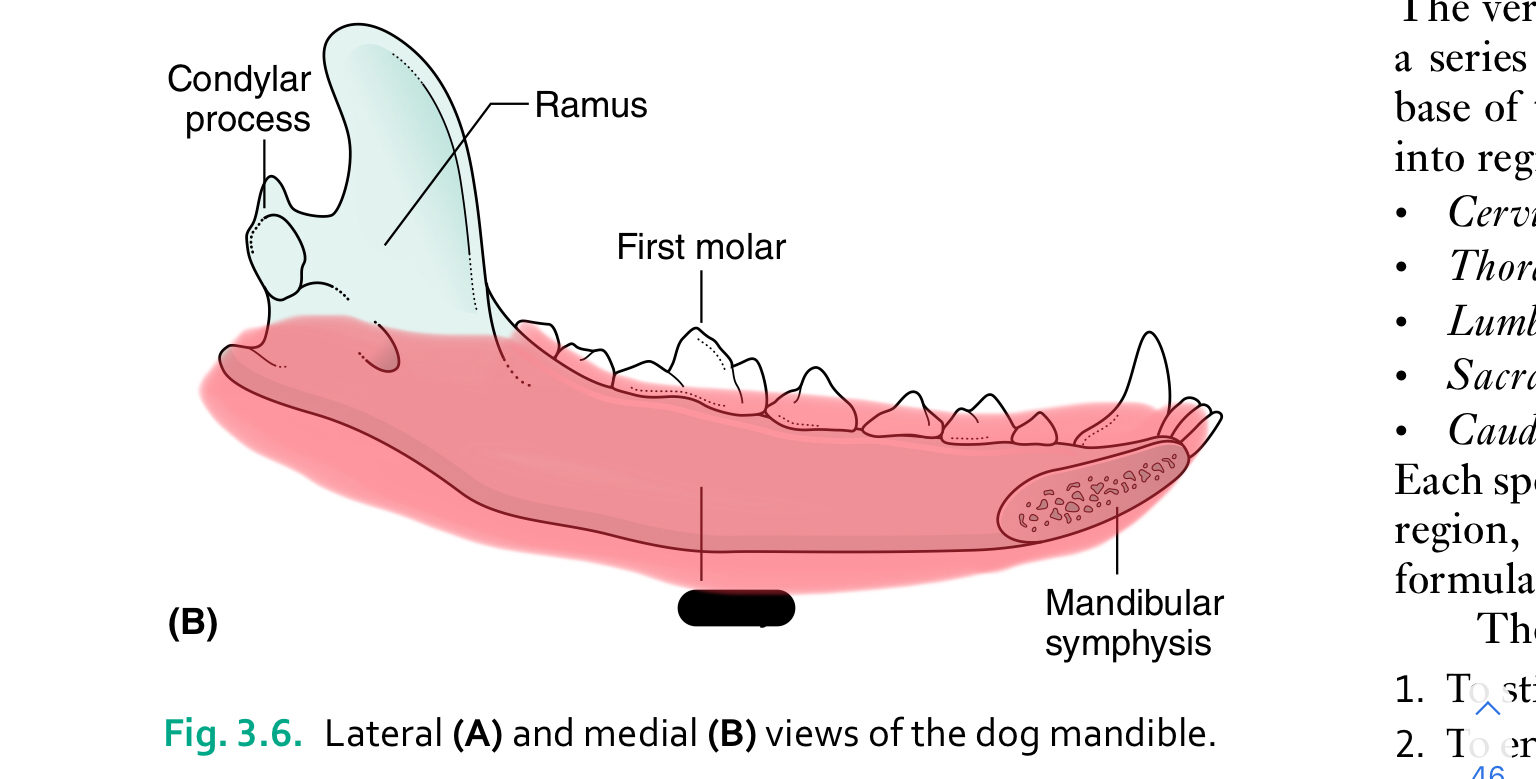
body of mandible
The mandible (lower jaw) comprises two halves called _____ joined together at the _____
dentaries, mandibular symphysis
Each half of the mandible is divided into ___ (horizontal part) and ____ (vertical part)
body, ramus
the body of the mandible carries the ____ for the teeth
sockets (alveoli)