MCAT Psych/Soc Chapt 1
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
franz gall
phrenology. brain shape determined function
pierre flourens
function of specific brain parts through ablation
william james
functionalims
john dewey
a latter functionalist thinker
paul broca
used brain lesions to determine functional impairement (Broca’s Area)
Hermann van Helmholtz
speed of nerve impulse
Sir Charles Sherrington
a pioneering neurophysiologist known for his work on synapses and reflexes.
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
the part of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord, responsible for connecting them to limbs and organs.
somatic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movements and transmits sensory information to the central nervous system.
afferent nerves
“affect” brain. sensory neurons that transmit information into brain
efferent neurons
“effect” of brain. motor neurons
autonomic nervous system
automatic functions such as heart beat, breath, pupil dilation
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest. opposes sympathetic response and conserves energy. acetylcholine
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight. responds to stress by increasing HR, dilating pupils, decreasing digestion, increasing glucose in blood, releases epinephrine
brain stem
most primitive region of the brain (hindbrain and midbrain)
hindbrain
cerebellum, medulla oblongata, pons
cerebellum
part of hindbrain responsible for coordination, movement, and balance
medulla oblagata
keeps heart beating
pons
controls breathing, arousal
midbrain
sensorimotor and relay center
forebrain
higher processing. contains cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system, thalamus, and hypothalamus
prosencephalon
forms into forebrain
mescencephalon
forms into midbrain
rhombencephalon
forms into hindbrain
EEG
uses electrical stimulation to map brain activity
rCBF
maps brain activity to blood flow
fMRI
maps brain activity via hydrogen in blood flow and magnets (assumed that hydrogen activity associated with neural firing)
meninges
tissue between brain and skull
cerebospinal fluid
liquid that cushions brain
thalamus
sensory relay system (everything but smell)
hypothalamus
responsible for hunger and pleasure
lateral hypothalamus
controls ability to feel hungry
ventromedial hypothalamus
controls satiety
anterior hypothalamus
controls reproductive behavior
posterior pituitary
site of release for ADH and oxytocin. connects to HT
pineal gland
releases melatonin (regulates sleep)
basal ganglia
controlled movements and coordination (signals extrapyramidal system not MOTOR neurons)
executive movements
limbic system
controls emotion and memory
amygdala
“angry” amy
controls anger and aggressive response
hippocampus
responsible for long term memory
septal nuclei
primary pleasure center
anterior cingulate cortex
higher order thinking
retrograde amnesia
cannot remember old memories
antegrade amnesia
cannot form new memories
cerebral cortex
“neocortex”
bumpy area. divided into frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
frontal crotex
higher order thinking, executive function
parietal lobe
touch, temperature, pain. sensory center and spatial awareness. contains wernicke’s area (interpret speech)
occipital lobe
vision
temporal
hearing
association areas
part of brain that integrates information from diverse regions of brain
projection areas
part of brain that performs rudimentary tasks
dominant hemisphere
(usually left) responsible for analytical activity
nondominant hemisphere
associated with intuition, creativity, spatial processing
neurotransmitter
chemical responsible for paracrine neural signaling
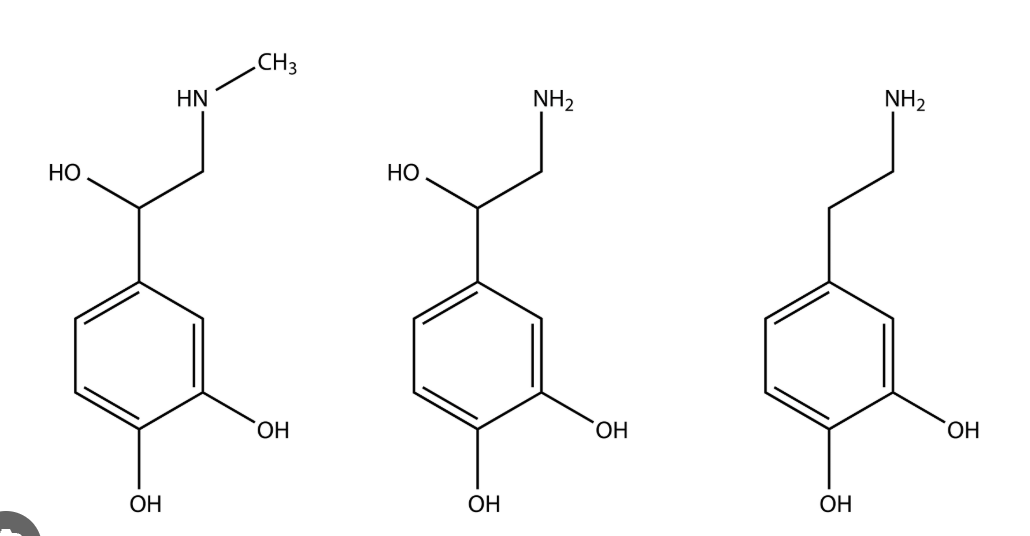
catecholamines
NTs involved in emotion. (dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine). they have similar structure
acetylcholine
responsible for voluntary movement, para
sympathetic nervous system. lack is associated with Alzheimer’s
dopamine
responsible for movement and posture. active in basal ganglia
low levels of dopamine are associate with…
parkinson’s
high levels of dopamine are associate with…
schizophrenia
seratonin
associated with mood stabilization, sleeping,eating dreaming. low levels associated with depression
epinephrine
acts as response to fight or flight. can act as hormone or NT
norepinephrine
acts as fight or flight response locally. low levels are associated with depression. high levels are associated with a manic disorder
GABA/glycine
major inhibitory NT. causes hyperpolarization
glutamate.
major excitatory NT
neuromodulator
peptides that are slow acting in the neurotransmission process
endorphins
bodies natural pain killers (neuromodulators)
pituitary gland
master gland. controls hormone release
anterior pituitary
connects to hypothalamus and receives signals for hormones. releases its own hormones
adrenal glands
sit on top of kidneys. medulla releases epinephrine for sympathetic nervous. cortex releases corticosteroids such as cortisol, testosterone, estrogen
gonads
sex glands that produce sex hormones in higher concentratuins
neurulation
notochord stimulates ectoderm to differentiate
neural tube
from furrowing of ectoderm forms CNS.
neural crest
spreads through body to form various tissues. alar plate develops into affective or sensory neurons
basal plates into effective or motor
rooting reflex
infants turn towards things that touch cheek
Babinski reflex
toes spread when touching heel
grasping reflex
infant curl fingers
moro reflex
infants put hands over head when head moves
gross motor skills progress..
head→ toe
core→ periphery