Measuring and Calculating Growth Performances in cultured Fish/Shellfish
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Definition of growth?
The irreversible increase in size, mass, or cell number of an organism over time
The net result of energy intake and expenditure (usually influenced by environmental conditions)
Parameters that exhibit growth?
Length (long term changes)
Weight (biomass or weight changes)
Importance of Measuring Growth?
Assessing the health and welfare of aquatic organisms
Evaluating the effects of environmental factors and feed quality
Applications in aquaculture management, stock assessment, and conservation
Absolute growth
The simplest and frequently used methods in describing growth is the absolute increase in units measured
Simple increase in units measured (weight or length)
Very shallow and insufficient information (as there is no relation to time)
Unit = cm or g
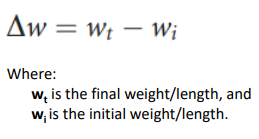
Absolute growth rate (AGR)
unit = cm/day or g/day
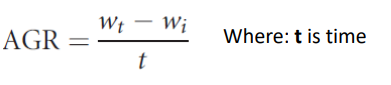
Relative growth rate (RGR)
The rate of growth of an organism relative to its initial size over a given period, and reported as percentage increase over time
unit = % in x days
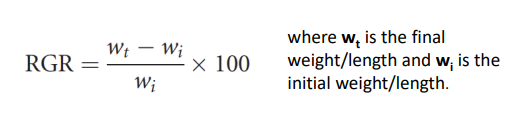
Instantaneous growth rate (IGR)
A measure of how quickly an organism grows over a short period, expressed as a percentage of its initial size per unit time
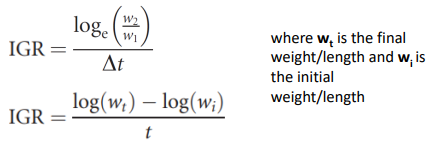
IGR new formula
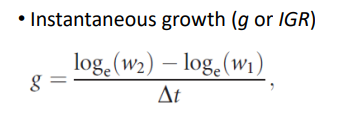
Specific growth rate (SGR)
Rate of growth of an organism as a percentage of its body weight per day
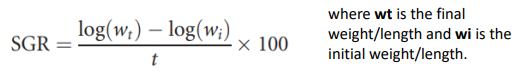
SGR new formula
Factors influencing growth?
Intrinsic factors
Extrinsic factors
Intrinsic factors?
Genetic factors: species, strains, and family differences
Age and life stage (larvae, juveniles, adults)
Extrinsic factors?
Water temperature, salinity, oxygen levels
Feed quality and quantity (nutrition)
Stocking density and habitat quality
Effects of size?
The growth rate of fish increases at a declining rate with size or weight
Anabolic and catabolic processes may be paced at different rates in relation to fish weight, with subsequent effect on fish growth
Example of effect of species and genetics
Grouper and tilapia
Grouper (carnivorous) has slower growth
Tilapia (omnivore) has faster growth
Due to: digestive system, enzyme production (affecting feed digestibility) and metabolism
Effects of food availability
Scope for growth (SFG) is estimated from the difference between the energy gain (energy absorbed) and energy expenditure (loss via respiration and excretion)
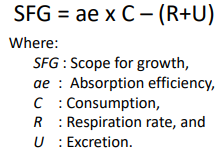
Methods of measuring growth?
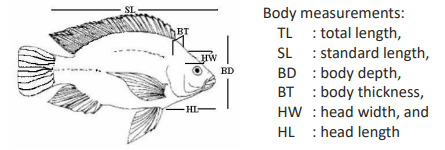
Morphometric measurements
Length: total length, fork length, standard length, and body depth
Weight: whole-body weight, condition factor, and gonadosomatic index
Body proportions: using equations like the length-weight relationship (LWR) to estimate growth
Tools and techniques for Measuring Growth
Field and Laboratory Measurement Techniques
Calipers
Scales
Rulers and Measuring boards
Calipers
Used to measure body dimensions
Digital calipers provide more precise readings compared to manual versions
Commonly applied in studies assessing growth variations in cultured or wild fish, crustaceans, and shellfish
Scales
Used to measure the weight or organisms at different growth stages
Electronic balances provide high accuracy
Spring scales are more common in field conditions
Important for determining condition factor, growth rates, biomass estimation
Rulers and Measuring Boards
Used for standard length, total length, and fork length measurements in fish
Measuring boards help standardize fish length measurements and minimize handling stress
Particularly useful for rapid assessments in fisheries fieldwork
Challenges in Measuring Growth
Sampling bias
Precision and accuracy
Environmental variability
Sampling bias
Handling variation in individual growth rates
Seasonal effects
Selective sampling
Precision and accuracy
Human and instrumental errors
Repeated measurements on the same fish
Marking and identification issues
Environmental variability
Unpredictable events: disease outbreaks, parasite infestations, or harmful algal blooms can stunt fish growth or cause mortalities, altering expected growth patterns
Fluctuation in water quality: changes in DO levels, salinity, pH, or ammonia concentrations can impact metabolic rates and growth performances
Nutritional variability: in both aquaculture and wild populations, food availability plays a critical role in growth