Aldehydes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
what is an aldehyde
molecule with carbonyl group bonded to 1 carbon and 1 hydrogen or 2 hydrogens
what is a keetone
carbonyl group bonded to 2 carbons
suffix for aldehydes
-anal
suffix for ketones
-anone
position number
what is reduction in organic chemistry
when a carbon forma a bond with less electronegative element
what does aldehydes reduce to
1’ alcohols
what do ketones reduce to
2’ alcohols
aldehyde/ ketone + NaBH4 →
Alcohols
why NaBH4
acts as a source of H- ions
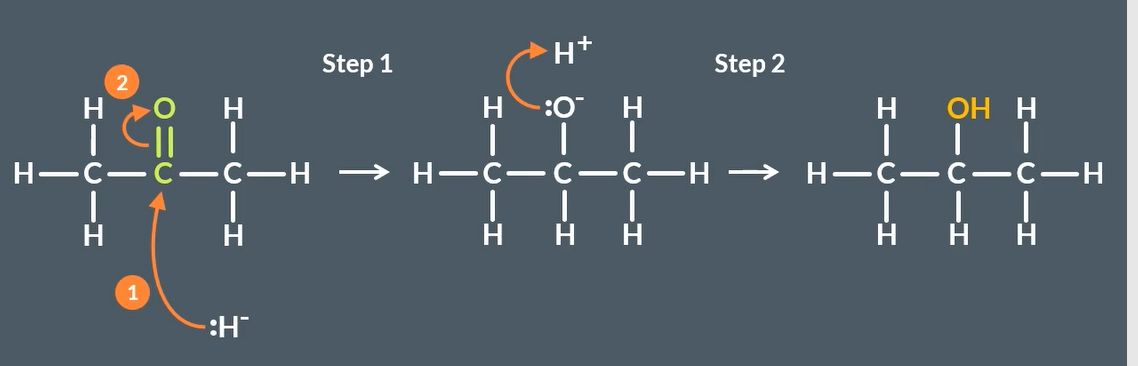
reduction mechanism for aldehydes
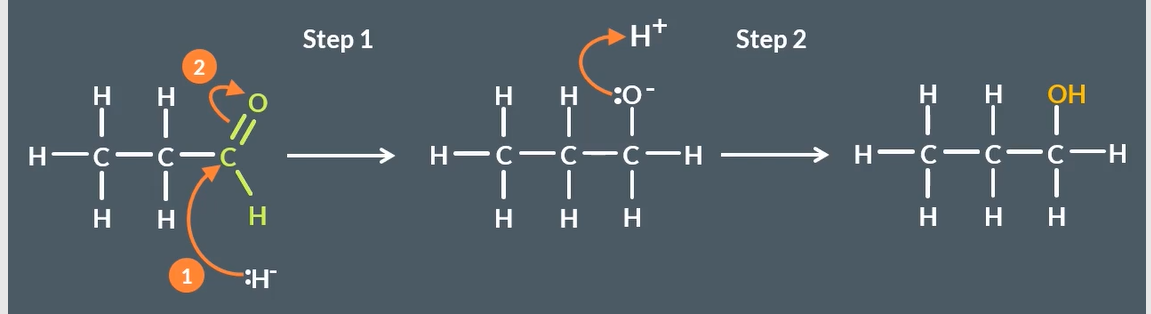
reduction mechanism for ketones
products of reducing unsymmetrical ketones and why
equal mixture of enantiomer- racemic mixture
equal probability that hydrogen will bond to either side of molecule
which CN compound is not a salt
HCN - covalently bonded gas in room temp
why CN not used in school
deadly
functional group and bond angle when CN bond to molecules
nitrile groups and 180’
how to name molecules with nitrile groups
alkane chain ( include carbon in CN) and suffix ‘nitrile’
what do ketones/ aldehydes + nitrile group make
hydroxy nitriles
what are hydroxy nitriles
Molecules that contain both alcohols and nitrile groups
how to name hydroxynitriles
C in nitryl group is position 1
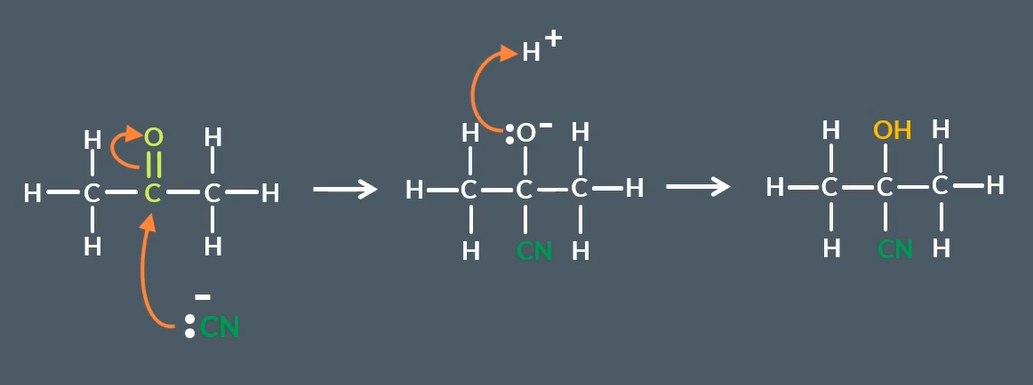
nucleophilic addition mechanism for aldehydes to hydroxy nitriles
reagents used for nucleophilic addition of ketones/aldehydes to hydroxy nitriles and dangers
KCN + H2SO4
KCN - deadly if ingested
H2SO4 - deadly if inhaled
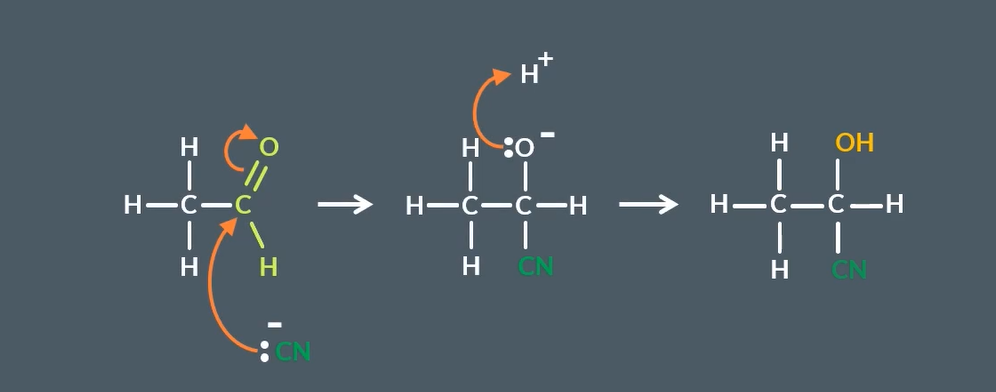
nucleophilic addition mechanism for ketones to hydroxy nitriles