Unit 2: Cellular Processes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

14 Terms
Semipermeable
membranes that allow some substances through but not others
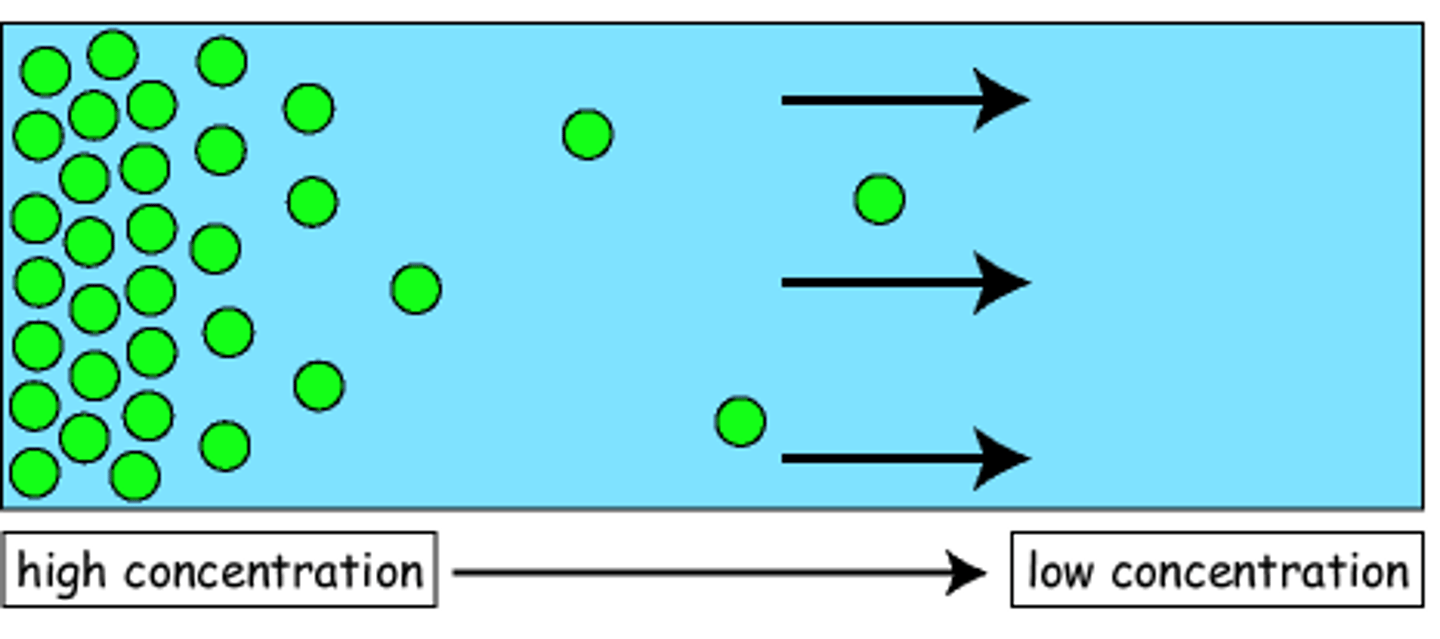
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
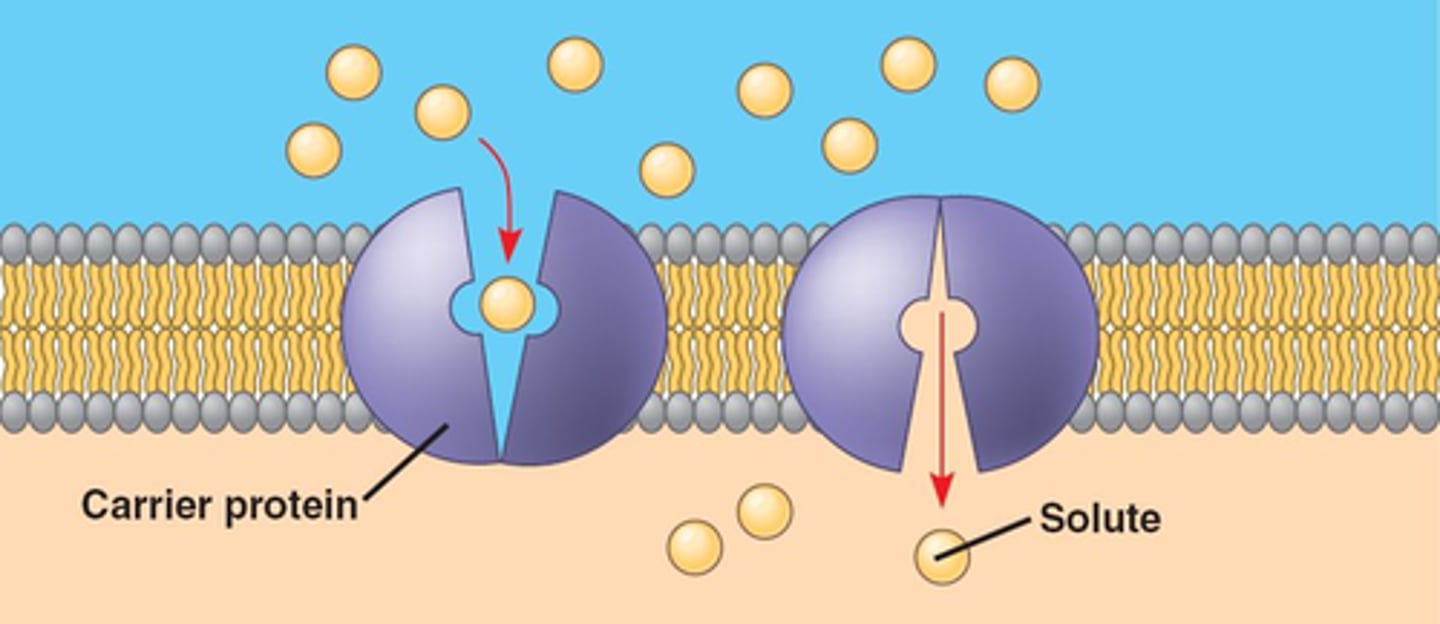
Facilitated Diffusion
the transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of carrier proteins
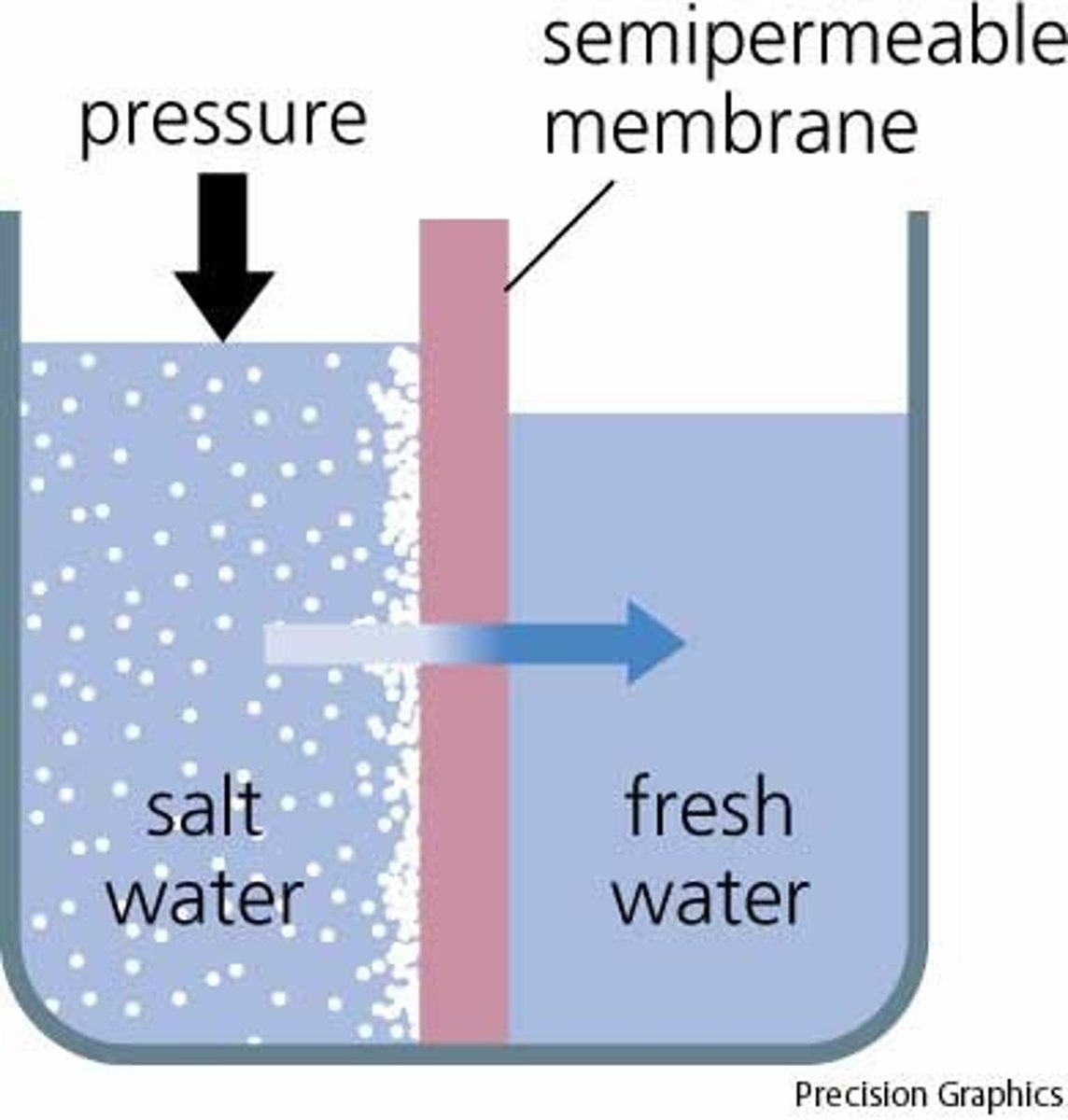
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
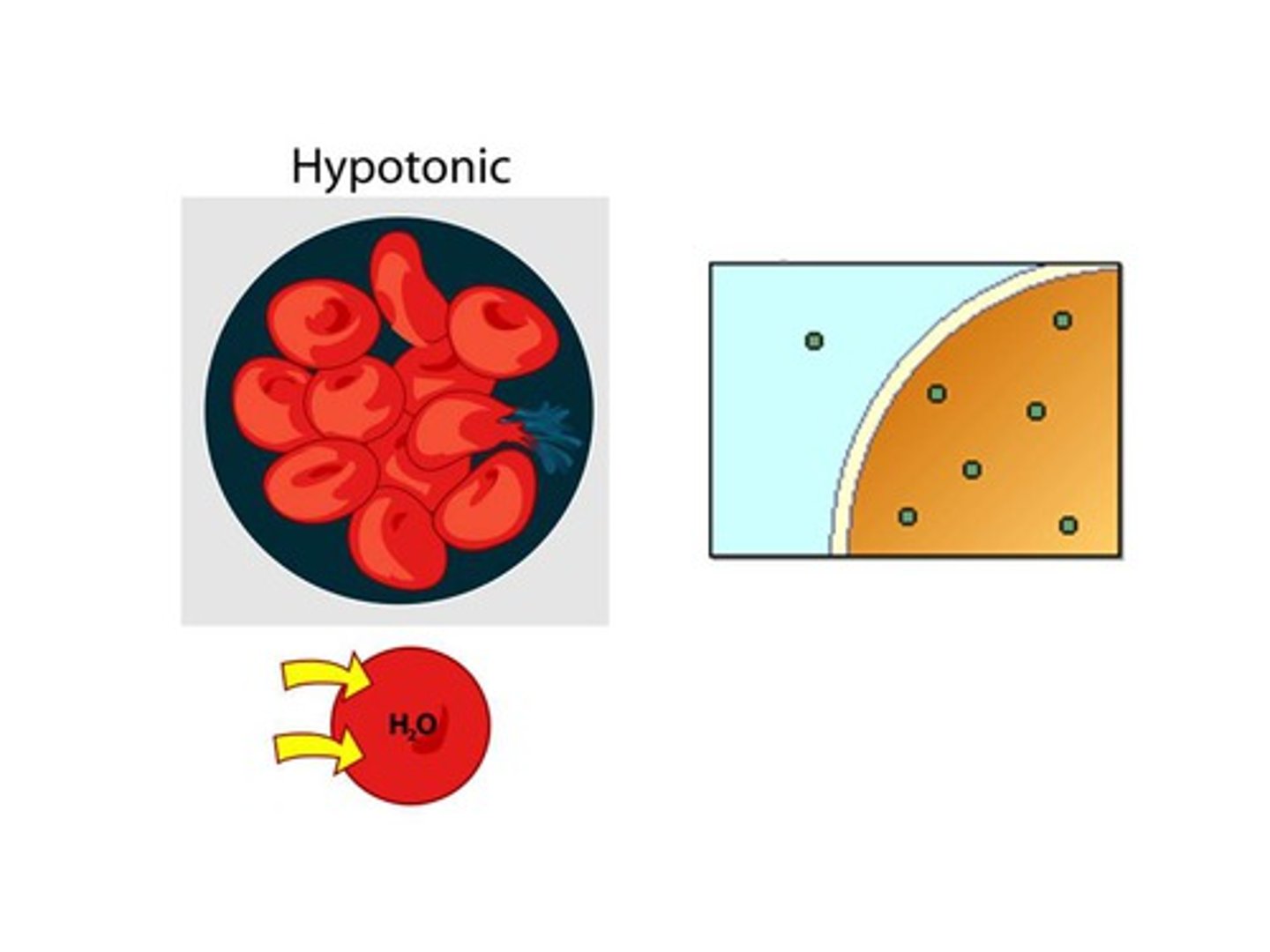
Hypotonic
a solution that has a lower concentration of solute outside than inside the cell, causing water to flow into the cell
Isotonic
a solution with the same concentration of water and solutes as inside a cell, resulting in the cell retaining its normal shape because there is no net movement of water
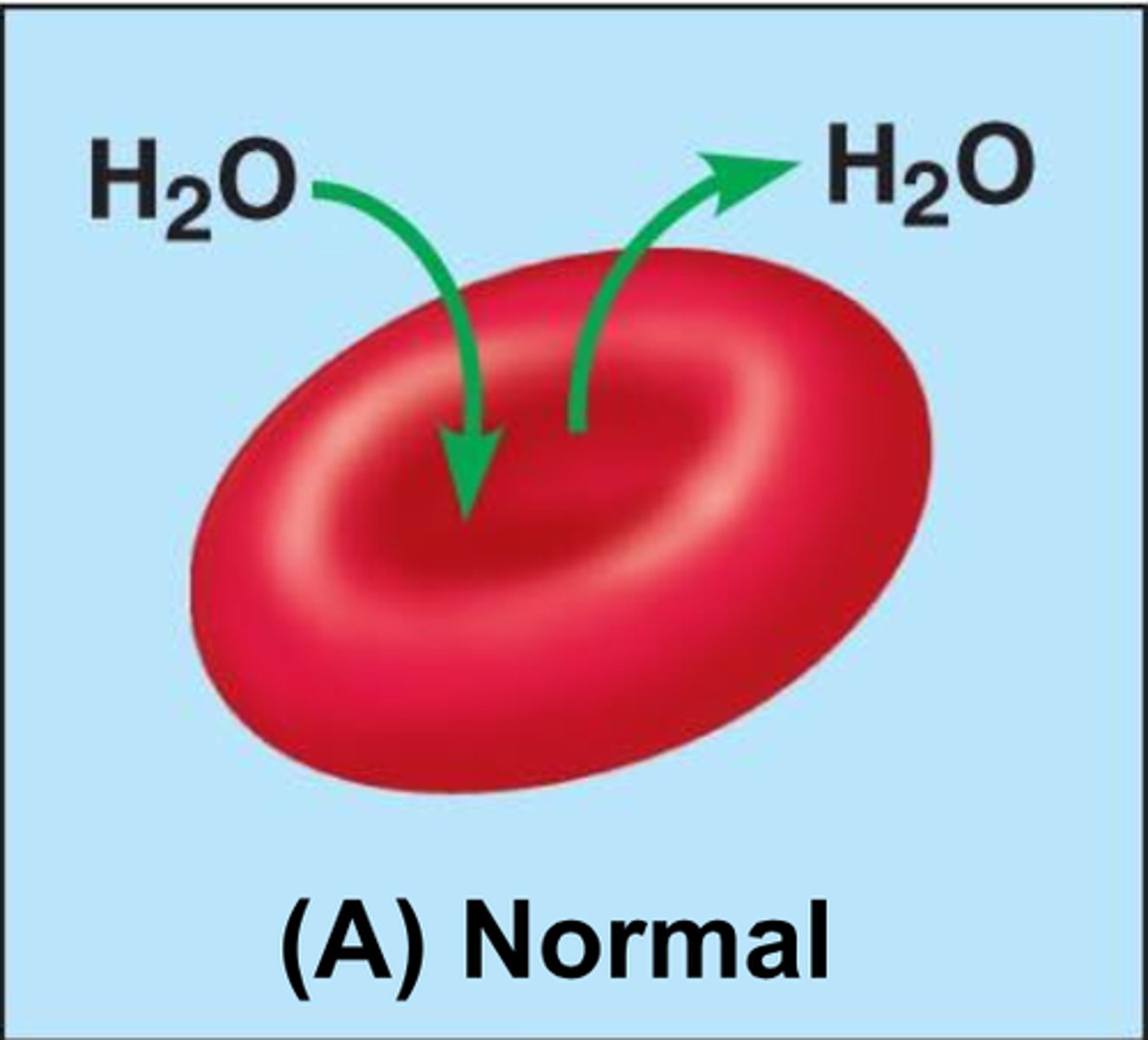
Active Transport
the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy.
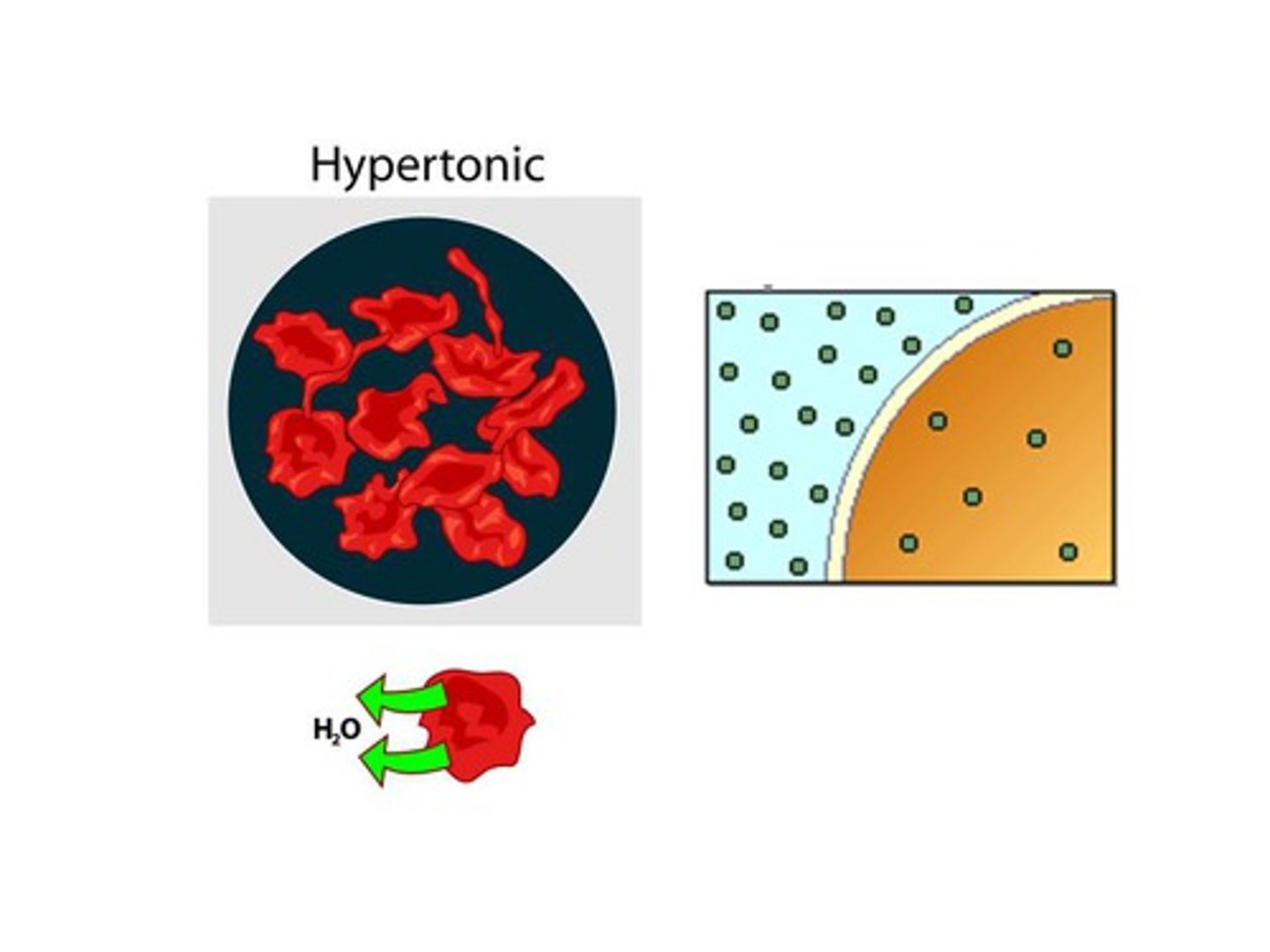
Hypertonic
a solution that has a higher solute concentration outside than inside the cell, causing water to leave the cell
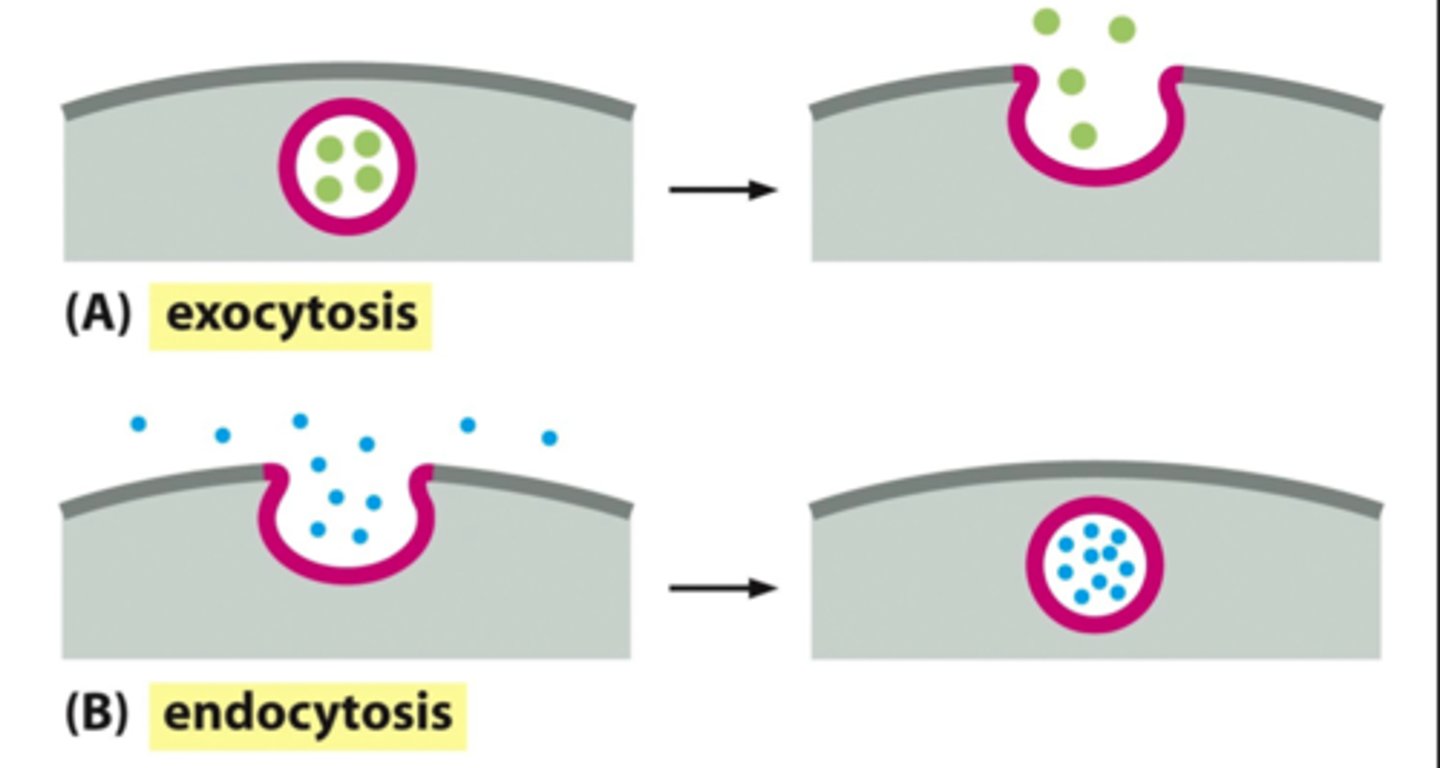
Endocytosis
energy-requiring process by which large substances from the outside environment can enter a cell
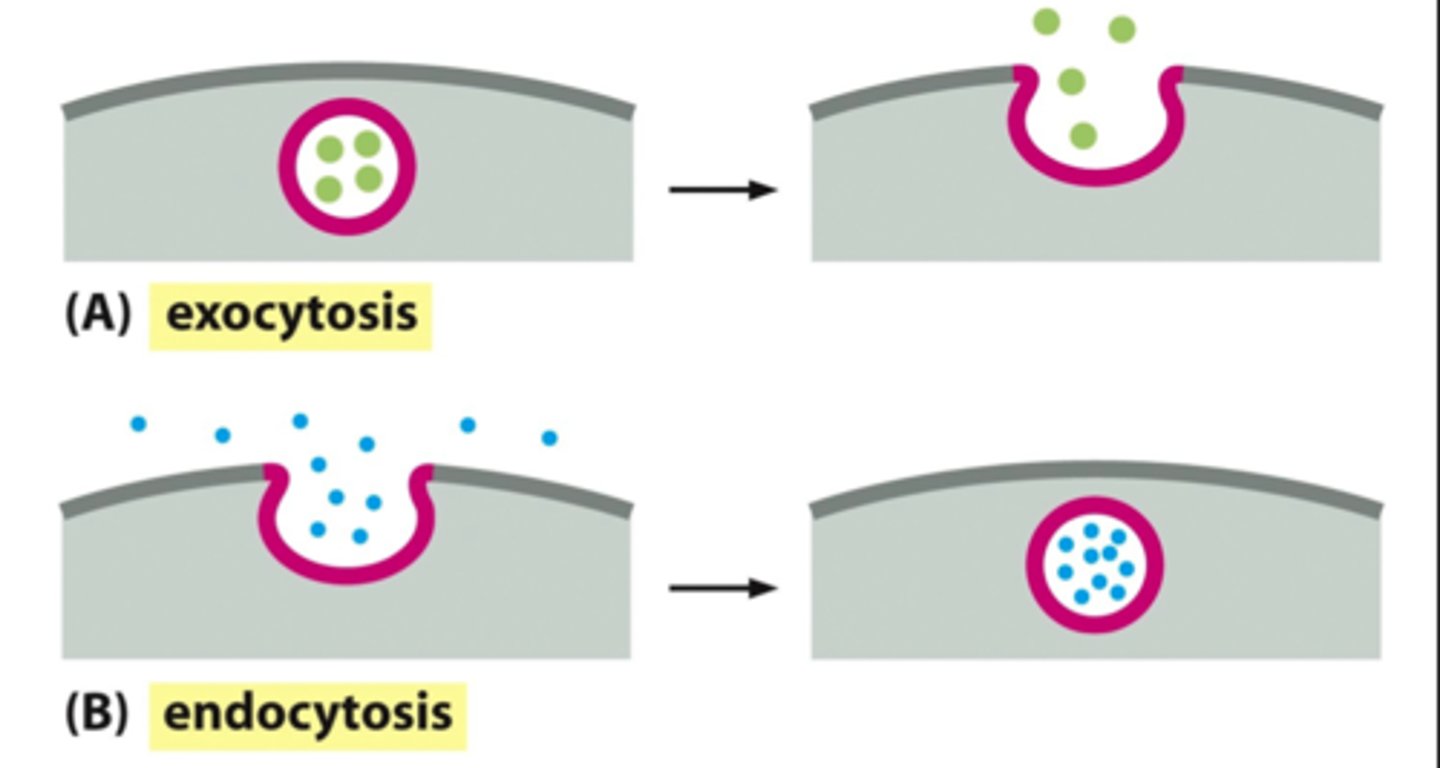
Exocytosis
energy-requiring process by which a cell expels wastes and secretes substances at the plasma membrane
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
lysogenic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which the viral DNA is added to the host cell's DNA and is copied along with the host cell's DNA
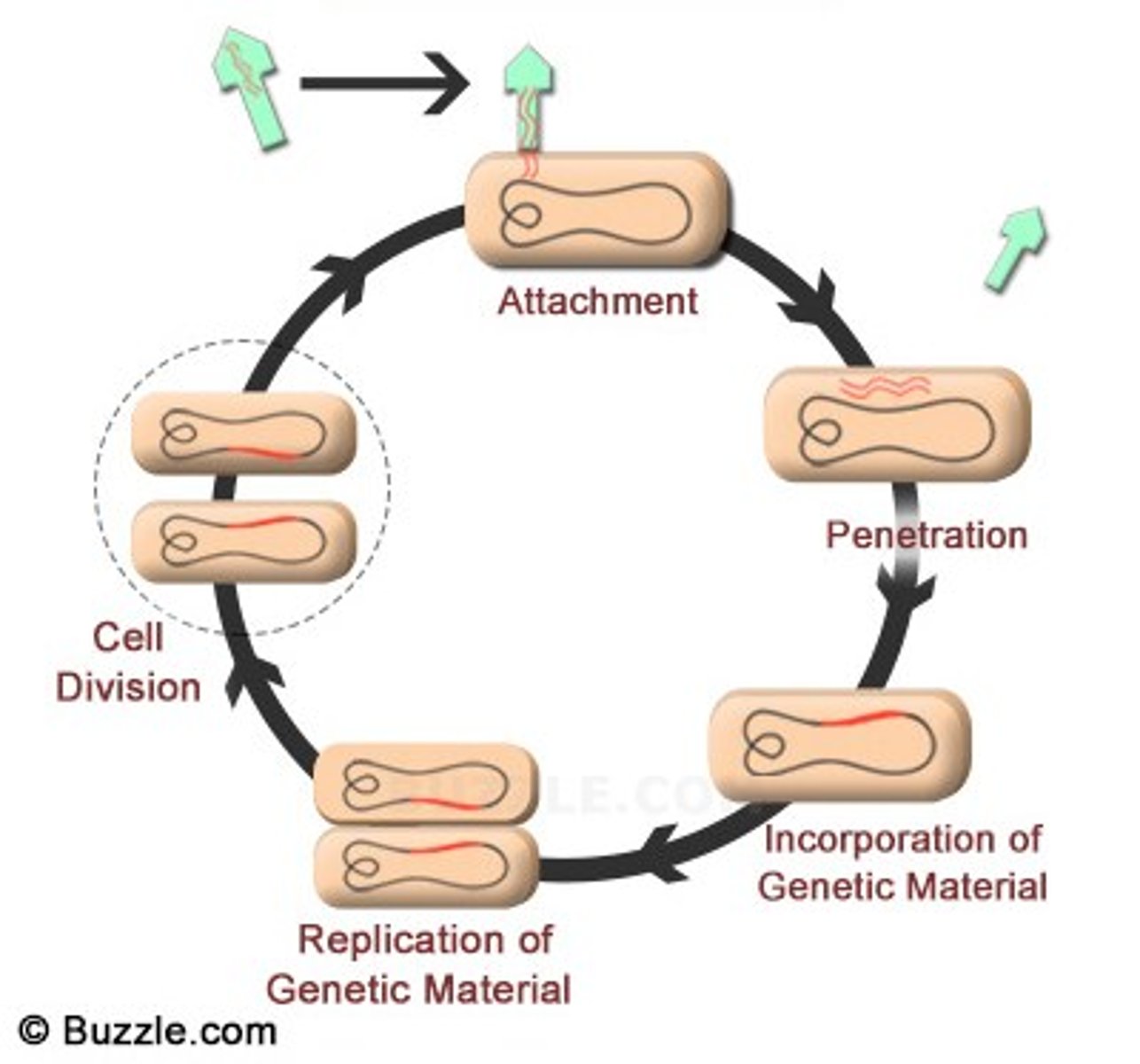
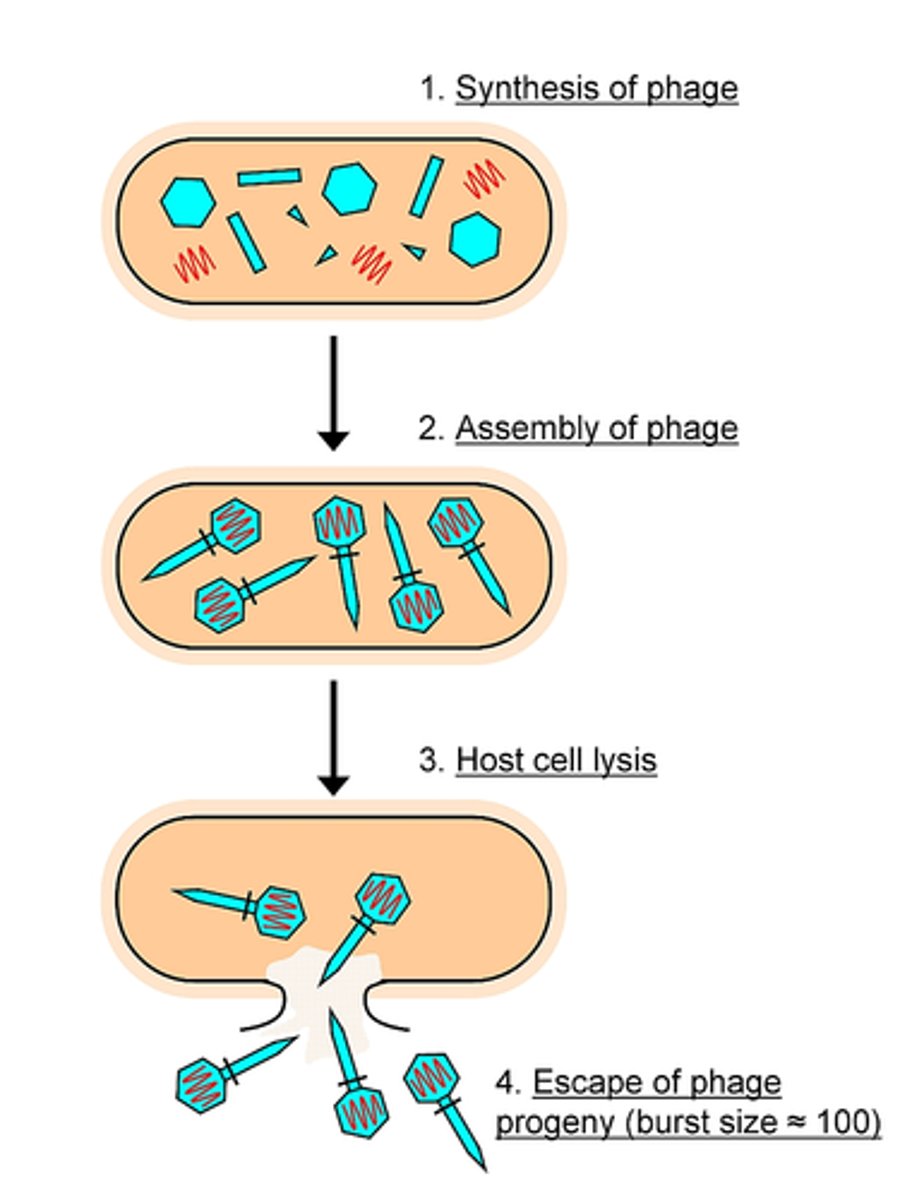
lytic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which copies of a virus are made within a host cell, which then bursts open, releasing new viruses
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell