Ozone
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
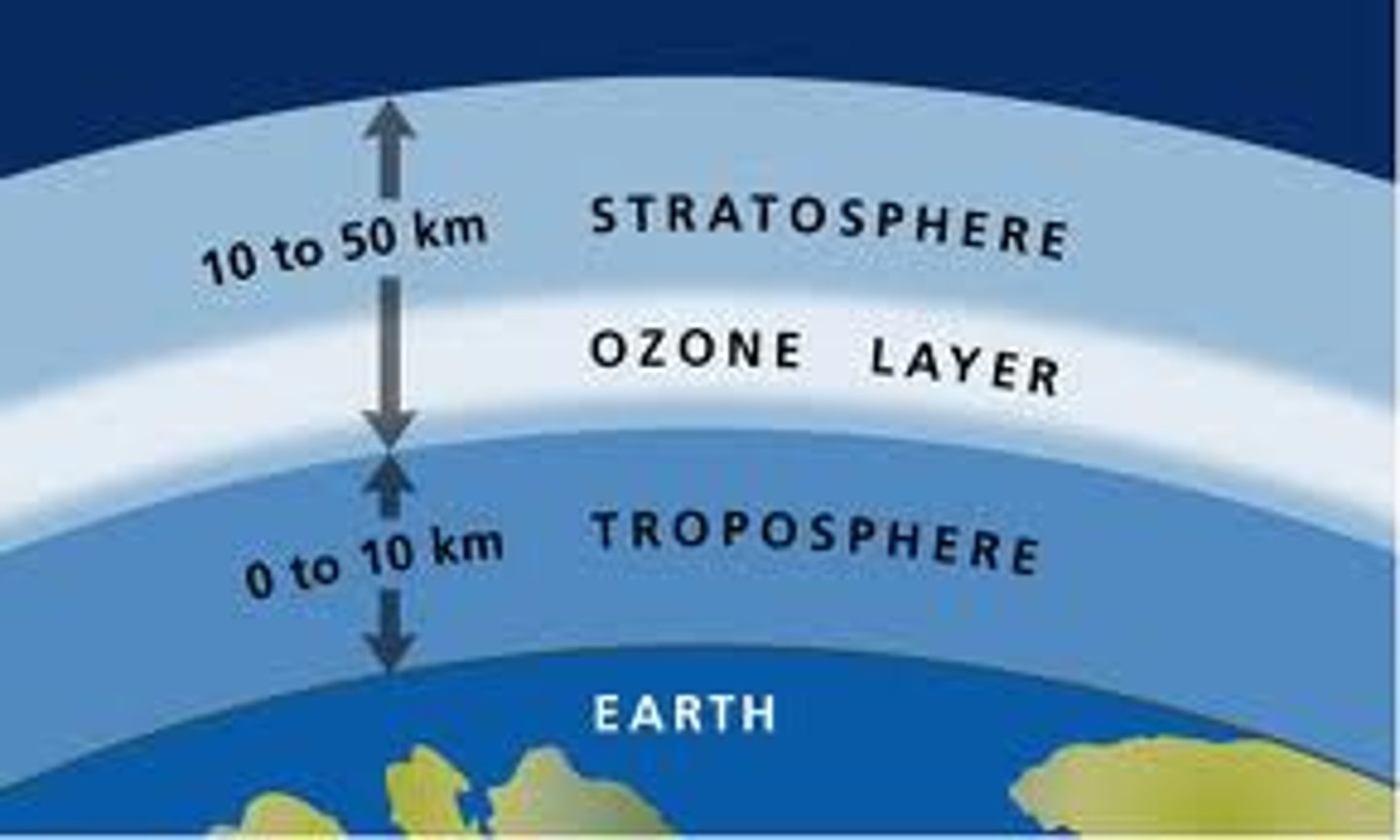
Troposphere
Extends from Earth's surface up to about 6 miles (10km). This layer of the atmosphere contains almost all weather and virtually all human activities. The temps decrease with altitude. As warm air rises, it cools, falling back to Earth through convection (don't need to know every detail). Important: Ozone in this level is harmful to breathe and damage crops, trees, and other vegetation. It is the main ingredient to urban smog.
Stratosphere
Extends from about 6 miles to 31 miles. Commercial airlines fly in lower altitudes of this layer. Gets warmer at higher altitudes. Important: Ozone in this layer is produced and destroyed naturally. It protects life on Earth from suns UV rays.
Ozone
Gas that occurs in both the Earths upper atmosphere and at ground level. Can be good or bad depending on if in troposphere or stratosphere.
The Ozone Layer
Atmospheric ozone is concentrated in a layer in stratosphere, about 9 to 18 miles above Earth's surface.
Ozone Hole
It is an annual occurrence of extremely low amounts of ozone over Antarctica that has occurred during the Antarctic spring since the early 1980s.
How is Ozone Destroyed?
When it comes in contact with Chlorine and Bromine atoms
1970s
74- began to understand how CFCs deplete ozone
78- US banned aerosol sprays containing CFCs
81- United Nations (UN) calls for international agreement to protect ozone layer
Vienna Convention
There was no hard and fast, concrete action from this meeting. Thus, adopted by 20 countries (effective in '88). It has become universally ratified . Parties involved continued to meet every three years to make decisions designed to administer the Convention.
1985 International Controls
2 months after the Vienna Convention, it was announced findings of the ozone hole over the Antarctic. Caught the attention of the general public.
DuPont
(1986) announced it could produce substitutes for CFCs within 5 years with proper incentives (regulatory phase-out of CFCs)
Montreal Protocol
A protocol on substances that deplete the ozone layer. 60 countries participated, 24 adopted. This froze production and consumption levels of CFCs and halons, producing a phase-out over the longer term. This did not mandate production decreases, but allowed reduced production and did not require equal reduction across all CFCs. This regularly tightened reduction schedules and extend provisions to new ODS.
Phase-Out Prohibition
1. Imports of ODS, like air conditioners, refrigerators, and fire extinguishers
2. Exports of ODS to countries that are not a party to the Protocol
3. Exception: Prohibitions do not apply to a non-party country that can demonstrate full compliance with phase-out
Where CFCs were Produced
Developed countries consumed 88% of CFCs with less than 25% of the world's population, and there consumption was increasing. CFC manufacturing is low-tech, low cost, and mobile. There was a grace period for these countries to allow for initial increase, then a decrease over 10 years to reduce by at least 50%
Effect of Montreal Protocol
There was a drastic decrease in emissions however, the bigger concerns are of the concentrations of CFCs that are in the atmosphere. Good, stratospheric ozone layers were on the decline, but started increasing in 2005.
Climate models without reductions
predicted that there would have been an ozone hole over the arctic eventually because of the rapid increase of CFCs in the atmosphere that would have occurred.
Lessons Learned
1. Necessity of international cooperation to address environmental challenges
2. Importance of participation of non-governmental actors
3. Importance of flexible approach both in terms of initial design and modification over time.
Who caused an increase in recent history after CFCs were declining?
Companies in China that were illegally producing a foam insulation containing CFCs. They were caught, and China effectively put an end to it.