9-Pancreatic Function and Carbohydrate Metabolism
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Pancreatic Islets (Islets of Langerhans)
Endocrine cells of the pancreas
Types of Pancreatic Islets (what do they each secrete?)
Beta cells secrete insulin
Alpha cells secrete glucagon
Delta cells secrete somatostatin
F cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide
Digestive enzymes of the pancreas (exocrine functions)
Lipase
Peptidases
Amylases
Exocrine pancreas things:
Digestive enzymes
Bicarb
70-130 mg/dL
Typical blood glucose value!
Insulin
increases after each meal and decreases as time passes
THIS and glucose are positively related to each other
Glucagon
decreases after each meal and increases as time passes
THIS and glucose are negatively related to each other
Peptide Hormones
Insulin and Glucagon are both THIS.
They both go through the typical processing for THIS:
preprohormone → prohormone → hormone
Blood glucose is above 80 mg/dL
When insulin is secreted from pancreatic beta cells:
Glucose
Insulin causes liver and skeletal muscle to absorb and metabolize THIS
Blood glucose is below 70 mg/dL
Glucagon is secreted from pancreatic alpha cells when:
Release Glucose
Glucagon causes the liver to do THIS:
Hypoglycemia (fasting)
In prolonged states of THIS, ketone synthesis from acetyl groups (2 C) becomes increasingly more significant
GLUT 1 and GLUT 3
Location:
Erythrocytes
Neurons
Cornea
Placenta
Transport:
Passive & Bidirectional
NOT Regulated by Insulin
Function:
Allow locations to access plasma glucose at all times
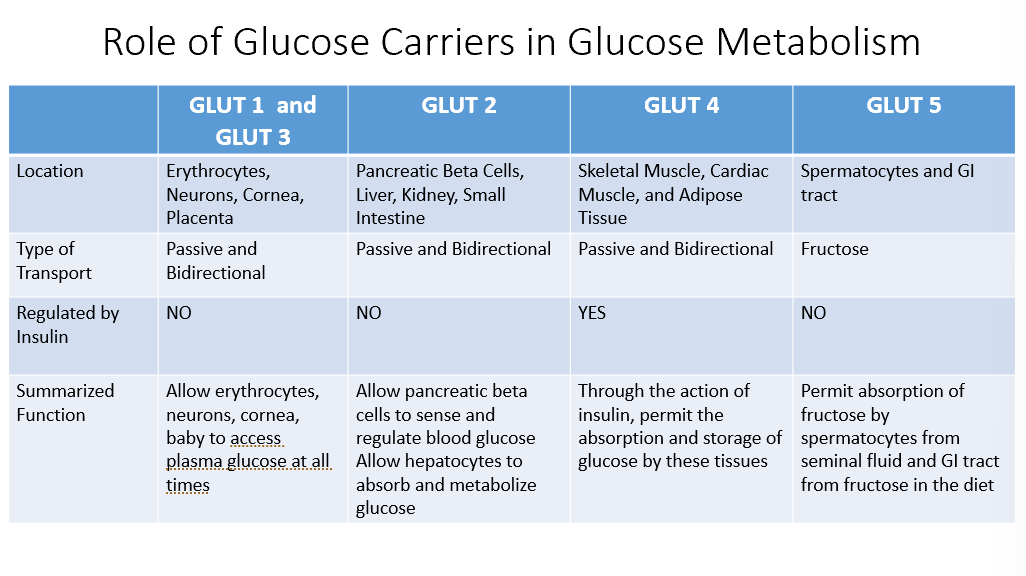
GLUT 2
Location:
Pancreatic Beta Cells
Liver
Kidney
SI
Transport:
Passive & Bidirectional
NOT regulated by Insulin
Function:
Allows beta cells to detect/regulate blood glucose
Allows hepatocytes to absorb/metabolize glucose
GLUT 4
Location:
Skeletal Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Adipose
Transport:
Passive & Bidirectional
REGULATED BY INSULIN!
Function:
Via insulin, allows absorption/storage of glucose in locations
GLUT 5
Location:
Spermatocytes
GI Tract
Transport:
Fructose!
NOT regulated by Insulin
Function:
Allows absorption of fructose by locations
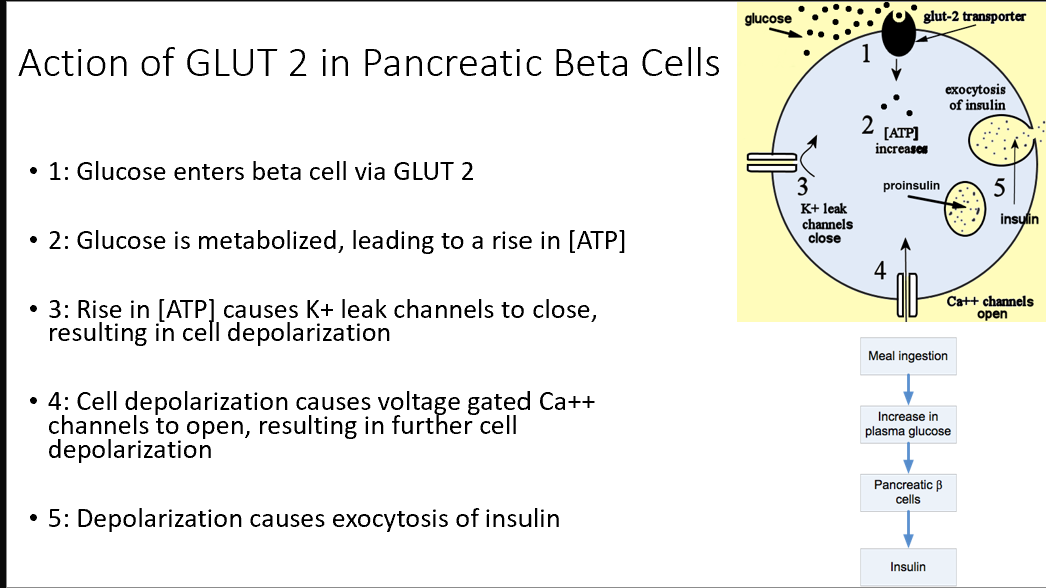
Action of GLUT 2 on Pancreatic Beta Cells
Glucose enters beta cell via GLUT 2
Glucose metabolized → Increases ATP
Increased ATP → K leak channels close → Cell depolarizes
Depol. → Voltage-Gated Ca channels open → More depol.
Depol. → Exocytosis of Insulin!
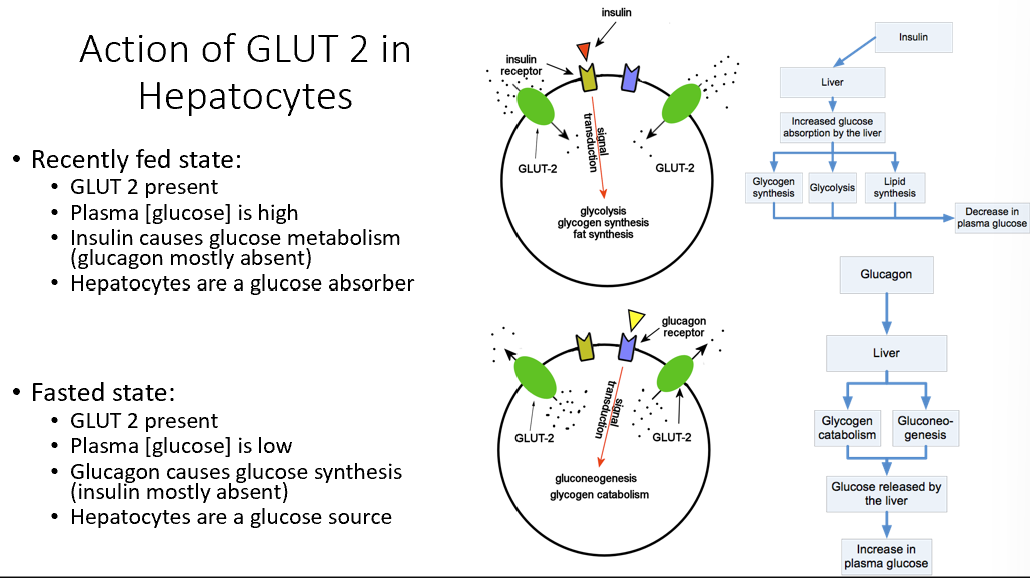
Recently Fed State GLUT 2
GLUT 2 present
Plasma glucose high
Insulin metabolizes glucose
Hepatocytes absorb glucose
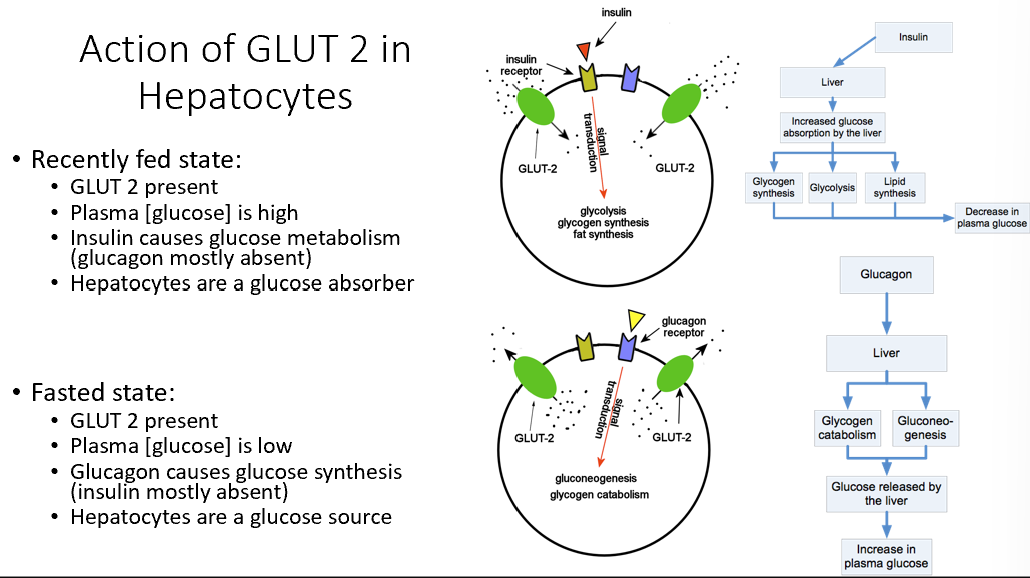
Fasted State GLUT 2
GLUT 2 present
Plasma glucose low
Glucagon causes glucose synthesis (no insulin present)
Hepatocytes are glucose source
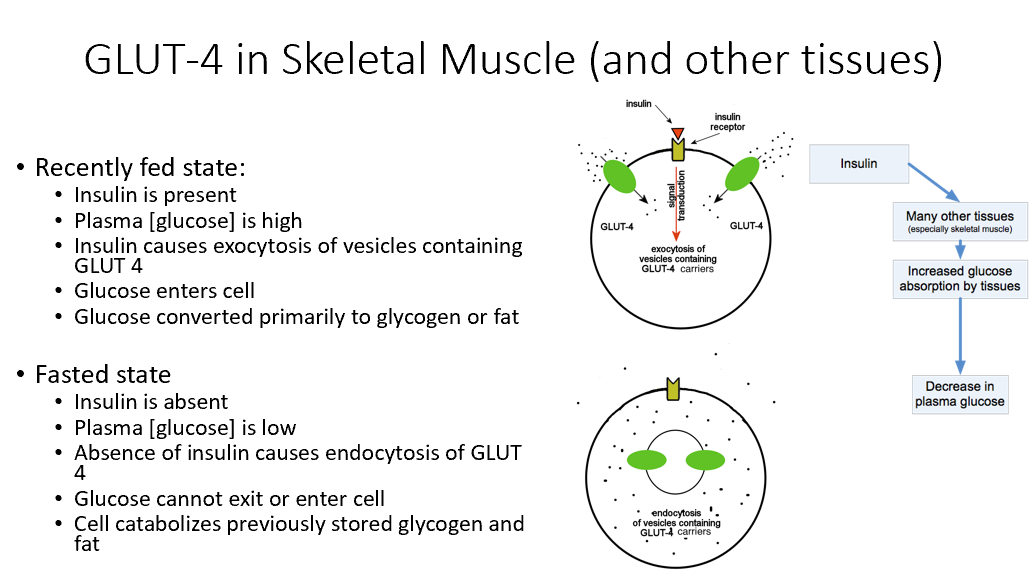
Recently Fed State GLUT 4
Insulin present
Plasma glucose high
Insulin causes exocytosis of GLUT 4
Glucose enters cell, converts to glycogen/fat
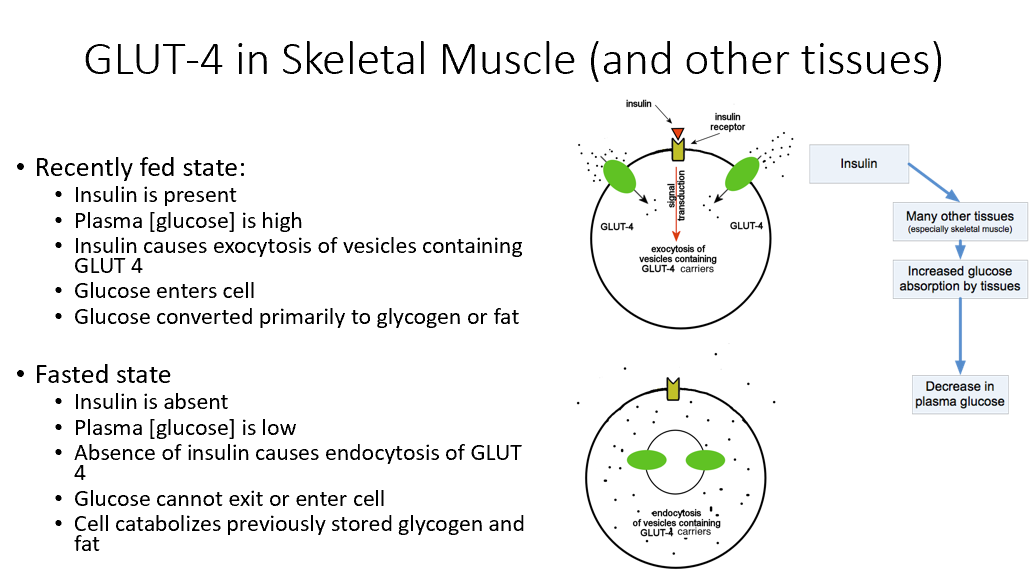
Fasting State GLUT 4
Insulin absent
Plasma glucose low
No insulin → endocytosis of GLUT 4
Glucose cannot exit or enter cell
Cell breaks down stored glycogen/fat
Insulin Deficiency
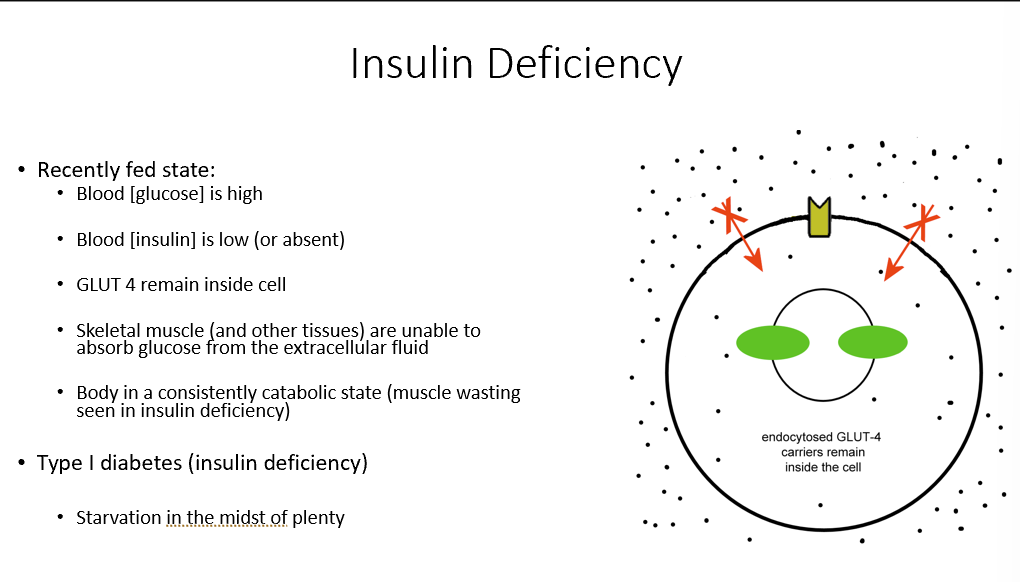
Recently Fed State
Blood glucose high
Blood insulin low
GLUT 4 stays inside the cell
Muscles can’t absorb glucose from ECF
Body stuck in catabolic state (muscle wasting!)
T1D
Starvation in the midst of plenty
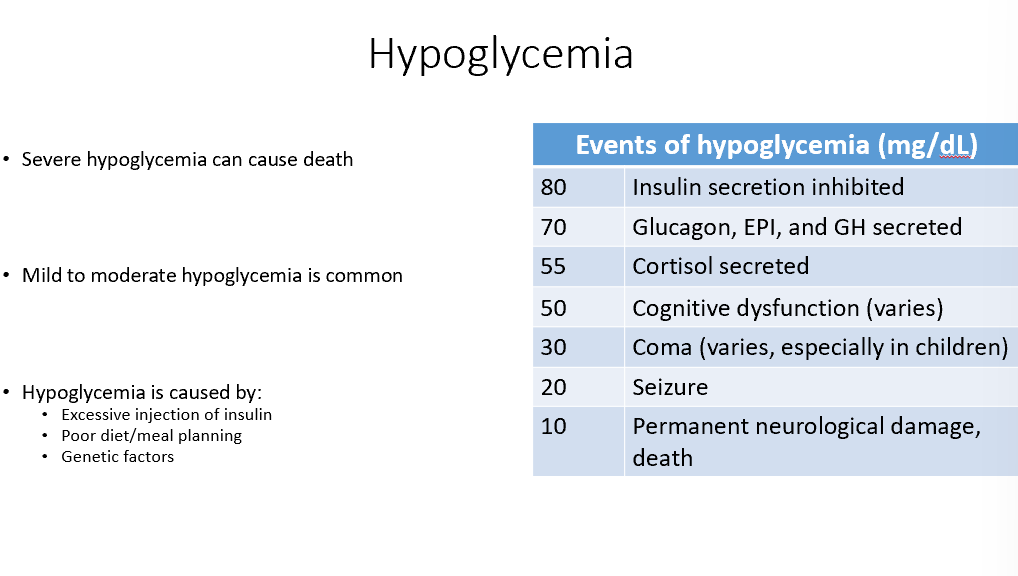
Hypoglycemia
Too little glucose!
Severe → Death
Mild/Moderate → Common
Caused by:
Excessive insulin
Poor diet
Genetics
C Peptide
Byproduct of insulin secretion
Indicates how much insulin is in blood
Hypoglycemia
Too little glucose!
Reactive THIS is triggered by glucagon secretion by the pancreas
Attempts to increase blood glucose (tremors, tachycardia, etc.)