AP Psych Study Guide Terms
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Psychology
Scientific study of behavior and mental processes in both humans and animals
Behavior
Anything you can observe
Mental Processes
Individual thoughts and feelings, cannot be directly observed
Psychology is a science because...?
1. Uses the scientific method to answer research questions
2. Uses Empirical Evidence
Perspectives
Psychologists use a variety of ways to explain why someone may act a certain way
Evolutionary Perspective
Basic principles of evolution & natural selection and applying them to a psychological phenomenon
Behavioral Perspective
Focused on observable behavior and learned behaviors. (People/Animals are controlled by their environment)
Humanistic Perspective
Human capacity for choice & growth to fulfill their potential. Positive.
Biological Perspective
Genetics and brain chemistry effects thinking/behavior. (Physical & Biological processes)
Psychodynamic Perspective
Behavior is determined by past experiences that are left in the unconscious (childhood)
Cognitive Perspective
Focuses on memory, intelligence, problem solving, language & learning (Processes of the mind) influences behavior. [ex. worried what others think]
Sociocultural Perspective
Society & Culture shapes behavior, cognitive and eclectic approach.
Biopsychosocial Approach
Eclectic combining links between genetic & environment.
[ex. 1-Biological 2-Psychological 3-Sociocultural]
Basic Research
Increase scientific knowledge base
Applied Research
Research to find a solution to specific problems
Quantitative Data
Numerical, qualities
Qualitative Data
Description, non-numerical
Case Study
An observation technique in limited individuals is studied (Rare & Complex)
Limitations of a Case Study
Unrepresented. Not much potential to apply to greater population
Strengths of a Case Study
1. Lots of information
2. Sheds light on problems that are unethical to study in other ways
Survey Method
Self-reports of symptoms, behavior, and belief etc.
Limitation of Survey Method
Responses aren't always accurate
Strengths of Survey Method
Large sample size and information
Naturalistic Observation
Careful observation of animals or people in their natural environment.
Limitations of Naturalistic Observation
1. No control
2. Bias
3. Doesn't allow for firm conclusions about cause and effect.
Strengths of Naturalistic Observation
1. Observe in natural setting
2. First stages of research
Hawthorne Effect "Observer Effect"
When people know they're being watched they are less likely to behave naturally.
Observer Bias "Research Bias"
Unconsciously skewing observation to fit to their research goals.
Correlational Studies
Research used to see if 2 variables are related & make prediction based on relationship (no manipulation)
Limitations of Correlational Studies
Correlation is not cannot be taken to imply causation
Strengths of Correlational Studies
Allows researcher to clearly see if there is a relationship between variables
Correlation Coefficient (r)
The direction of the relationship between variables and its strength, helps us see how close two things vary together. Thus, one predicts the other.
Is -0.49 stronger than 0.4?
YES, -0.49 is closer to -1
0 is...
-1 and 1 are...
Weak correlation
Strong correlation
Scatterplot
A graph to display data to show a relation between 2 variables
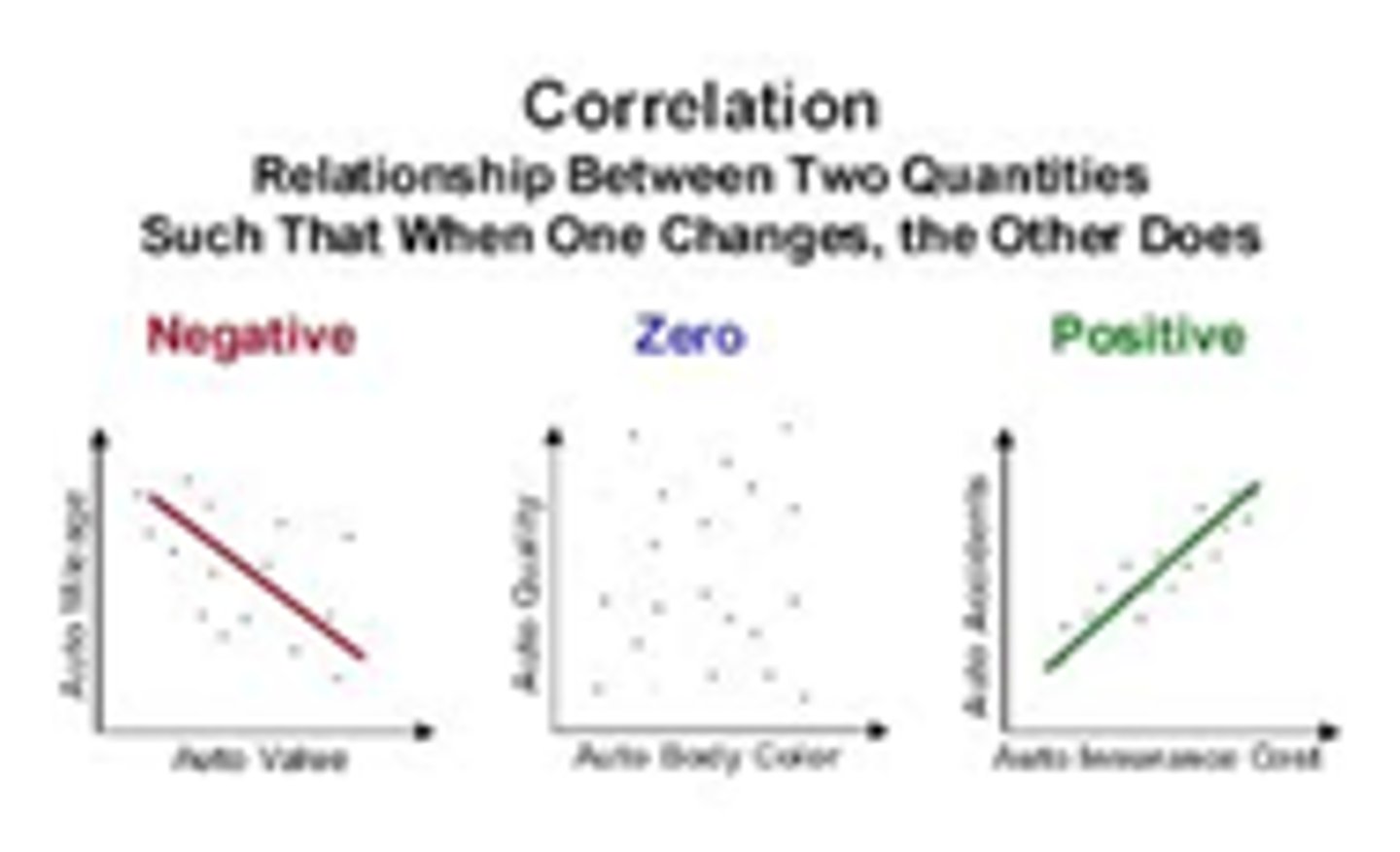
Positive correlation
Increasing or decreasing together
Negative correlation
As one is increasing the other is decreasing
Illusory (no) correlation
No correlation between variables
Third Variable Problems
Researcher cannot rule out the possibility that a 3rd variable causes both other variables to increase or decrease
Experimental Method
Only way to establish causes & effect relation between 2 variables. (Change in one changes another)
Strengths of Experimental Method
1. Researchers control situations
2. Identify cause and effect
Limitations of Experimental Method
Can create unrealistic situation
Variable
Anything that can change
Independent Variable (IV) "Treatment"
Factor that the experiment controls and manipulates (If __ then)
Dependent Variable (DV) "Outcome"
Being measured/tested in an experiment
Cofounding Variable "Lurking"
Anything that can affect relationship IV and DV
Operational Definitions
Definition of the variable in terms of precisely how it is to be measured (allows others to replicate experiment)
Population
All individuals in a group which the study applies to.
Confederate
Individuals who seem to be participants but are actually apart of the research team
Representative Sample
Sample that closely matches the characteristics of its whole population
Random Sample
Select people in research in a way that everyone in the population has an equal chance of being included
Control group
No treatment, Normal group.
Experimental Group
Group exposed to the independent variable and receives manipulation.
Random Assignment
Process that ensures all members have an equal chance of being placed (assigned) in control or experiment group.
Quasi Experiment
Experiment but participants are not randomly assigned to the experiment group. (IV can't be random)
Weakness of Quasi Experiment
Lack of random assignment can weaken conclusions
Placebo Condition
Allows to separate effects of variables from expectations from participants
Single-Blind Studies
Participants don't know what treatment group they're in experiment or control.
Double-Blind Studies
Both participants and researchers eliminate researcher bias.
Frequency Distribution Table
Arragnement of scores indicating the frequency each score on group of scores.
Histogram
Plot shows underlying frequency distribution (Shape of a set of continuous data) *allows to look for outliers/skew
Measure of Central Tendency
Describes the average or most typical scores for a set research data distribution
Mean "Average"
1. Add all numbers
2.Divide numbers by # of numbers
Median "Middle"
A single score that represents a whole set of numbers
Mode "Most"
Most frequently occurring score in a data set.
Range
Spread distribution (High-Low)
Standard Deviation
Scores in a group differ from the mean. (Large SD- More spread out, Small SD- Bunched)
Z Score
The number of standard deviations from the mean data point. (-3 SD, 3 SD)
Normal Distributions
"Bell Curve" Mean, median, mode is all the same #.
SD -1,+1 =
SD -2,+2=
SD -3,+3=
1. 68.26%
2. 95.44%
3. 99.72%
Negative Skew (Skewed Left)
Mean shifts to the left, is less than the rest of the data.
Positive Skew (Skewed Right)
Mean is greater to the right
Inferential Statistics
Are used to interpret data to draw conclusions (small sample to large sample)
Statistical significance
A measure of likelihood that the difference between groups are a result from a real difference rather than chance.
P-Value
Common cut off is 0.05 (5%) is statistically significant
Null Hypothesis
Predicts there will not be a significant relation.
(What researchers are trying to disprove)
Meta-Analysis (Technique)
Combining data from other studies to reach a conclusion
Ethics/General Principle
Correct rules of conduct and moral principles necessary when carrying out research. (Psychologists do not harm) *All experiments cause stress
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
Review proposals for research that includes human participants *Required
Informed Consent
Written description of what participants can expect, including potential risks. *Must sign
Discounting Participation
Participants are capable of discounting participation
Confidentiality
Any data collected in an experiment must remain confidential.
Deception
Misleading participants to maintain the integrity of an experiment but not to the point of harm.
Debriefing
Process of giving participants a completed research project a fuller explanation than what was possible before.
Animal Testing
Animals are acceptable substitution for research that would be unethical for humans
Why are animals used in research?
1. Shorter lives
2. easy to control
3. similar behavior
Charles Darwin
Evolutionary Perspective - Natural Selection/Evolution
Dorothea Dix
Advocated for the mentally ill. Created the first mental hospitals.
Sigmund Freud
Psychoanalytic Perspective
B.F. Skinner
Behaviorism/Behavioral Perspective, Operant Conditioning, Schedules of Reinforcement
John B. Watson
Behaviorism/Behavioral Perspective, Aversive Conditioning
Carl Rogers
Humanistic Perspective, Client centered therapy
Counseling Psychologist
help people adapt to change or make changes
Developmental Psychologist
study psychological development throughout lifespan
Educational Psychologist
Focuses on how effective teaching and learning take place
Experiment Psychologist
Does research and adds new knowledge to the field.
Industrial Psychologist
Aims to improve productivity and quality of work by applying psychological principles.
Personality Psychologist
focus on traits, attitudes and goals of the individual
Social Psychologist
How a person's mental life and behavior are shaped by interactions with others
Positive Psychologist
focuses on what makes life most living, well-being