Bio 11 - Anatomy - cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory systems
1/102
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
cells are striated, 1-2 nuclei
T-tubules wide, less numerous. SR simpler than skeletal muscle
large mitochondria = 25-35% cell volume
Intercalated Discs
junctions between cells; anchor
Desmosomes
prevent cell from separating during contraction
Gap Junctions
allow ions to pass from cell to cell, electrically couple adjacent cells
Pacemaker Cells
noncontractile cells that spontaneously depolarize
Fibrillation
rapid irregular contractions - heart becomes useless for pumping blood → circulation stops, may result in brain death
Defibrillation
“clean slate,” interrupts chaotic twitching to start regular depolarizations
Medulla Oblongata
Controls rythym and speed of contractions via cardiovascular center of autonomic nervous system
Cardioacceleratory Center
sends signals through sympathetic trunk to increase rate and force;
stimulates sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes via vagus nerve
Sympathetic
increases rate and force of contraction
Parasympathetic
decreases rate of contraction
P Wave
depolarization of SA node → Atria
QRS Complex
ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
T Wave
ventricular repolarization
Junctional Rythm
Sinoatrial node nonfunctional, atrioventricular node is backup pacemaker
P-waves absent; 40-60 BPM
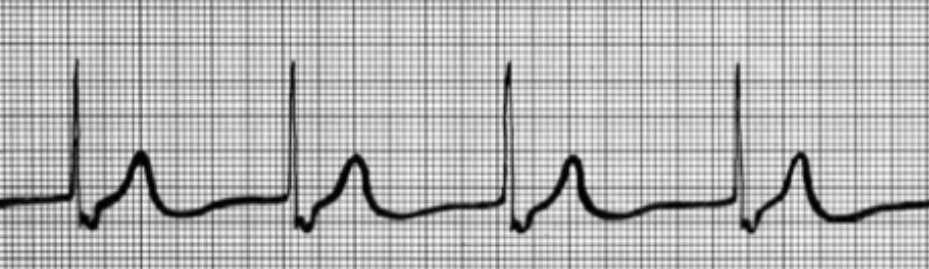
Second Degree Heart Block
AV node fails to conduct some SA node impulses
~2 P waves per 1 QRS complex
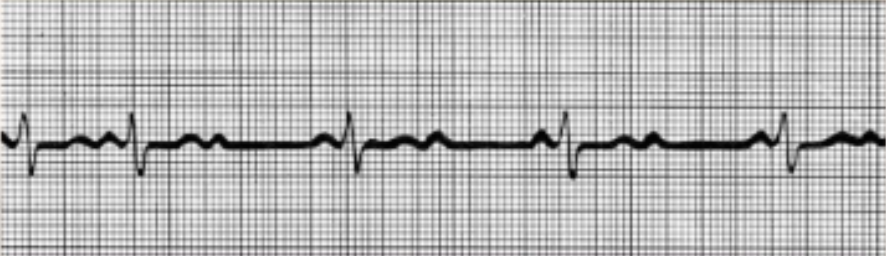
Ventricular Fibrillation
Electrical activity disorganized, random action potentials.
Systole
contraction of a chamber
Diastole
relaxation of chamber
Atrioventricular Valves
(2) closure causes first “lubb”
Semilunar Valves
(2) at base of great arteries; closure causes second “dupp”
Ventricular Systole
ventricles contract, semilunar valves open, AV valves close “lubb”
Ventricular Diastole
ventricles relax and fill with blood, atrioventricular valves open, semilunar valves close “dupp”
Systolic Pressure
pressure exerted in aorta during ventricular contraction
Diastolic Pressure
lowest level of aortic pressure when heart is at rest
Right Atrium
receives blood returning from systemic circuit
Left Atrium
receives blood returning from pulmonary circuit
Right Ventricle
pumps blood through pulmonary circuit
Left Ventricle
pumps blood through systemic circuit
Serous Pericardium
parietal layer, visceral layer, and cavity of heart
Anastomosis
convergence of two or more vessels; veins do more than arteries, and end arteries do not.
Tunica Intima
endothelium (simple squamous lining) and subendothelial layer of areola connective tissue
Tunica Media
circularly arranged smooth muscle; sympathetic activity causes smooth muscle vasoconstriction
forms valves in veins
Tunica Externa
anchors blood vessels to surroundings; requires vaso vasorum (small blood vessels that supply bigger ones)
Elastic Arteries
largest. walls, especially tunica media, contain many elastic fibers. most are near heart (aorta, pulmonary)
Muscular Arteries
medium. elastic fibers in two concentric rings: internal and external elastic lamina. proportionally thicker tunica media
Arterioles
smallest. <6 layers of cell layers of smooth muscle in tunica media. sympathetic innervation causes vasoconstriction - elevates upstream BP, decreases downstream blood flow.
Capillaries
in all tissues except cartilage, epithelia, cornea and lens and eye
Metarteriole
feeds capillary beds
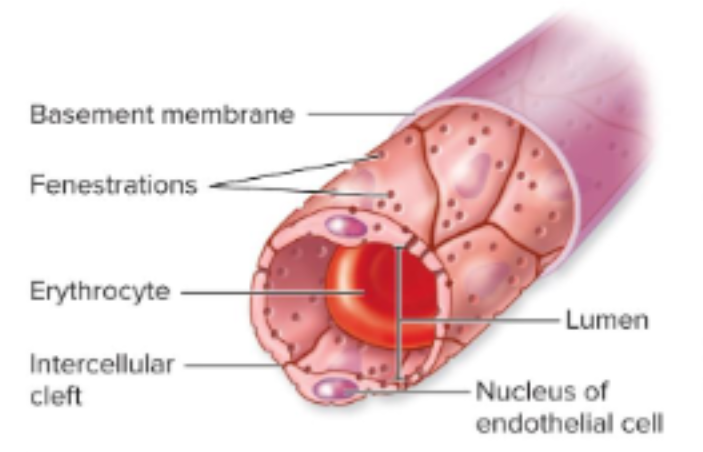
Continuous Arteriole
endothelial cells form a complete lining aided by tight junctions.
most common, esp muscle and brain
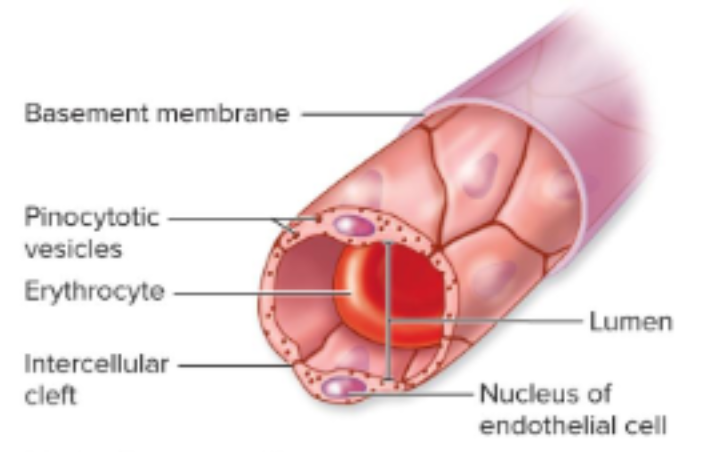
Fenestrated
endothelial cells contain pores that allow fluid exchange; exchanges nutrients for high metabolic needs
most common in small intestine and kidneys
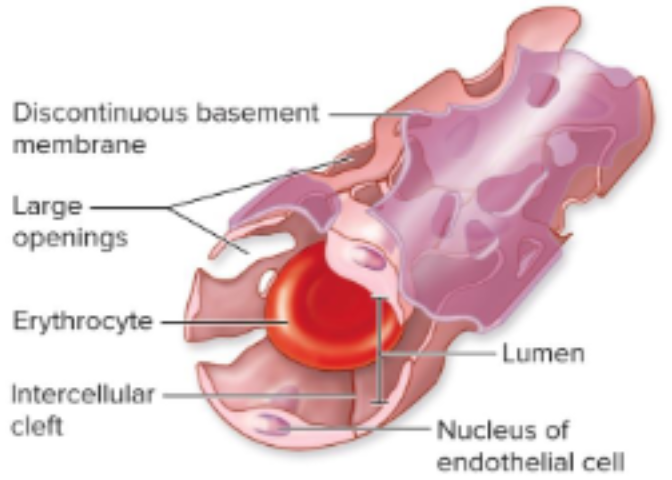
Sinusoids
large gaps between endothelial cells and discontinuous basement membrane - allows transport of large molecules + cells to/from blood; bone marrow and liver
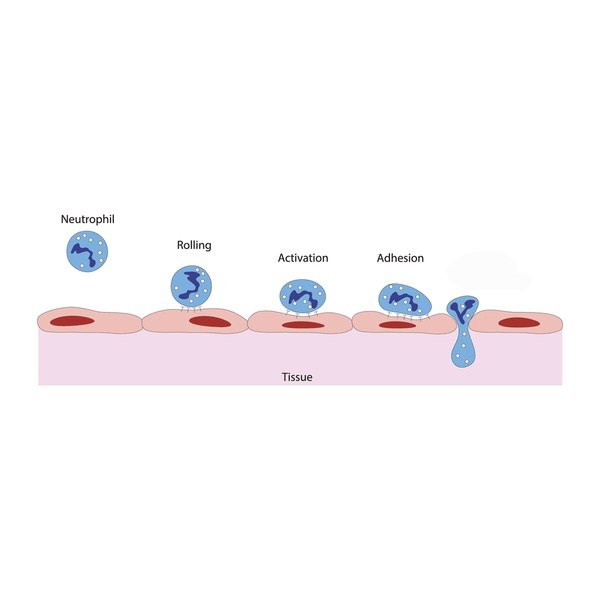
Diapedesis
leukocytes migrating from bloodstream to interstitial fluid, occurs thru walls of post capillary venules (smallest vein)
Large veins travel with
elastic arteries
Small + Medium veins travel with
muscular arteries
Aortic Arch
3 arterial branches emerge: brachiocephalic, left common carotid artery, left subclavian artery
Brachiocephalic Trunk
bifurcates into right common carotid and right subclavian
4th lumbar vertebrae
aorta bifurcates into left + right common iliac arteries
Hepatic Portal Vein
fusion of 3 abdominal veins: superior + inferior mesenteric vein, splenic vein
Inferior Mesenteric Vein
drains distal part of colon
Splenic Vein
drains spleen, pancreas and stomach
Superior Mesenteric Vein
drains blood from proximal part of colon, small intestine, pancreas, and stomach
Hepatic Veins
collect blood from liver, return to inferior vena cava
Superior Vena Cava
fusion of right + left brachiocephalic veins, drains into right atrium
Inferior Vena Cava
returns blood to right atrium from lower limbs, pelvis, perineum, abdominal structures
Ductus Venosus
Ligamentum Venosum
Foramen Ovale
Fossa Ovalis
Ductus Arteriosus
Ligamentum Arteriosus
Umbilical Vein
Median Umbilical Ligaments
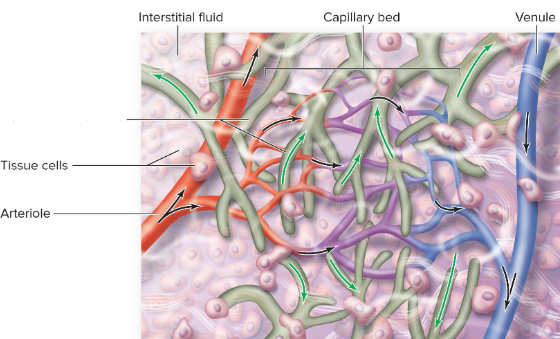
Lymphatic Capillaries
closed ended tubes interspersed among blood capillary beds; overlapping endometrial cells = one way flaps
Afferent Lymphatic Vessels
bring lymph to a lymph node
Efferent Lymphatic Vessels
transport filtered lymph away from lymph node
Lymphatic Trunks
form from merging lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic Ducts
form from converging lymphatic trunks
Thoracic Duct
largest lymphatic vessel
Macrophage
monocyte that has left blood
Special Epithelial Cell
Nurse cell; secretory cells in thymus
Dendritic Cells
internalize antigens, present them to lymphocytes
Lymphocytes
most abundant lymphoid cells
T-cells
70-85% of lymphocytes; cytotoxic + helper
B-cells
15-30% of lymphocytes; produce antibodies / immunoglobins
NK Cells
kill infected cells and cancer cells
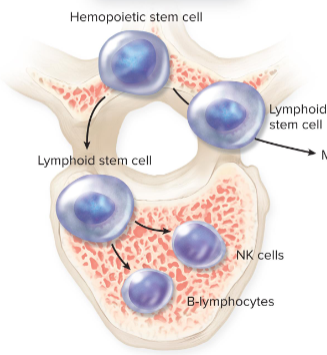
Red Bone Marrow
lymphopoeisis; hemapoetic stem cell → lymphoid stem cell → B and NK cells
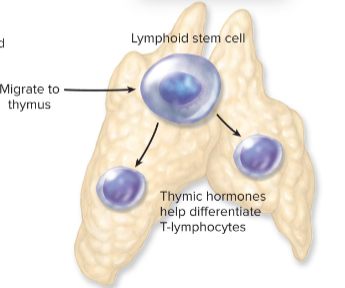
Thymus
lymphopoesis of T cell, differentiated by thymic hormones
Lymphatic Nodule
clusters of lymphatic cells, some extracellular matrix without connective tissue capsule.
Germinal Center
center of lymphatic nodule; contains proliferating B + NK
MALT
mucous associated lymphatic tissue; lymphatic nodules in GI, respiratory, genital, urinary tracts
monitor + respond to antigens
Peyer Patches
MALT nodules in ileum
Tonsils
large clusters of lymphatic cells and matrix (mostly) in the pharynx
form “crypts” for trapping antigens, facilitate antigen identification by lymphocytes
Palatine Tonsils
posterolateral wall of oral cavity
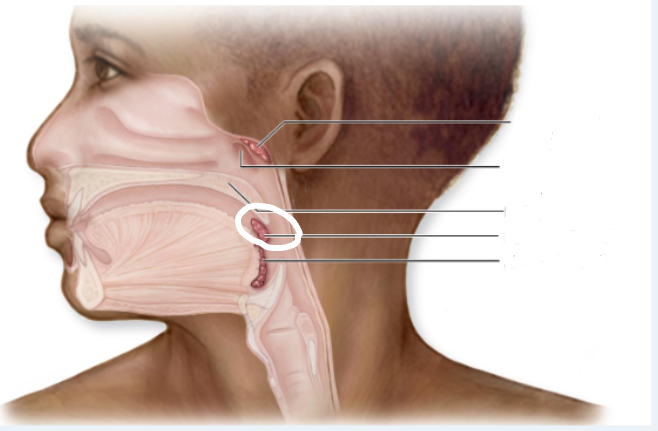
Lingual Tonsils
posterior 1/3 of tongue
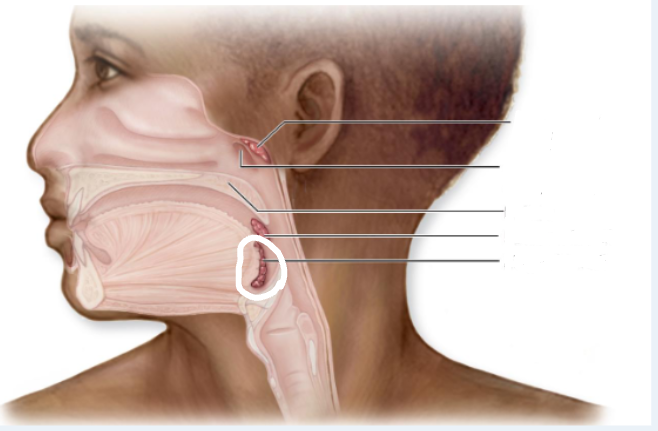
Pharyngeal Tonsils
Adenoids; posterosuperior wall of nasopharynx
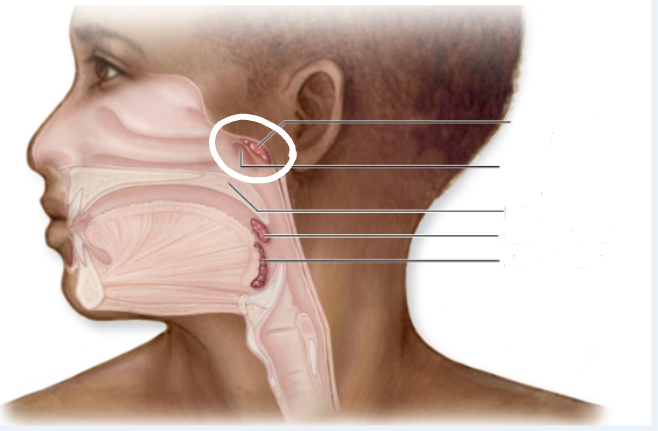
Thymus
biloped; superficial to heart
grows in size until puberty, then shrinks in size / function
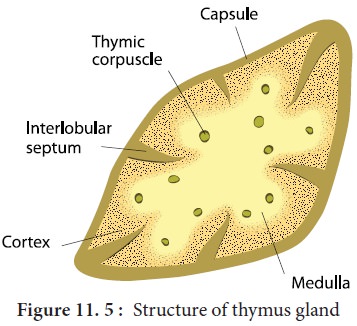
Thymus Medulla
(inner) contains mature T-lymphocytes and epithelial cells
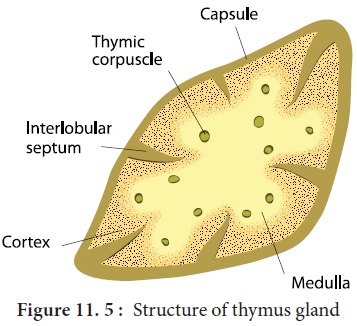
Thymus Cortex
(outer) contains immature T-lymphocytes, nurse, and macrophage cells
Lymph Nodes
small oval structures on pathways of lymph vessels; filter antigens from lymph + initiate immune response
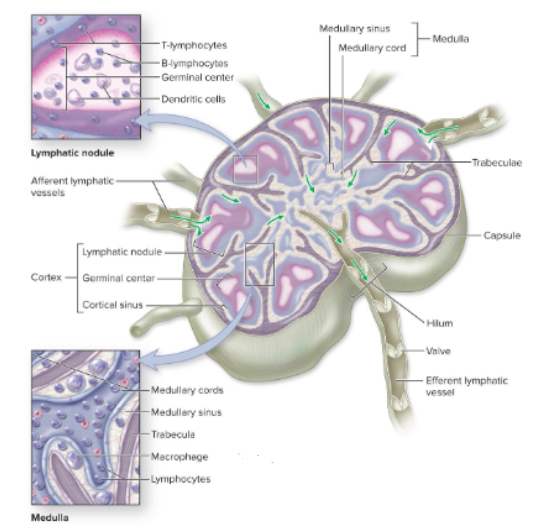
Trabeculae
internal extensions of the lymph node capsule, project inwards
Lymph Cortex
(outer)
Lymph Medulla
(inner)
Spleen
Largest lymphatic organ. Lateral to left kidney
Dense irregular connective tissue capsule sends red / white trabeculae into organ
White Pulp
Arterial supply; clusters of T, B, and macrophages
Red Pulp
Venous Supply; splenic cords + splenic sinusoids containing RBCs, platelets, macrophages, and some plasma
Infectious Mononucleosis
Caused by epstein-barr virus; affects ¼ teenagers, symptoms ~2 weeks- 6 months
Photophobia, white patches on tonsils, throat soreness, fever, spleen enlargement, lymph node swelling, etc
Conducting Portion
air transport
Respiratory Portion
gas exchange
External Respiration
Exchanges gases between atmosphete and blood / lungs
Internal Respiration
Exchanges gases between blood and body's cells / tissues
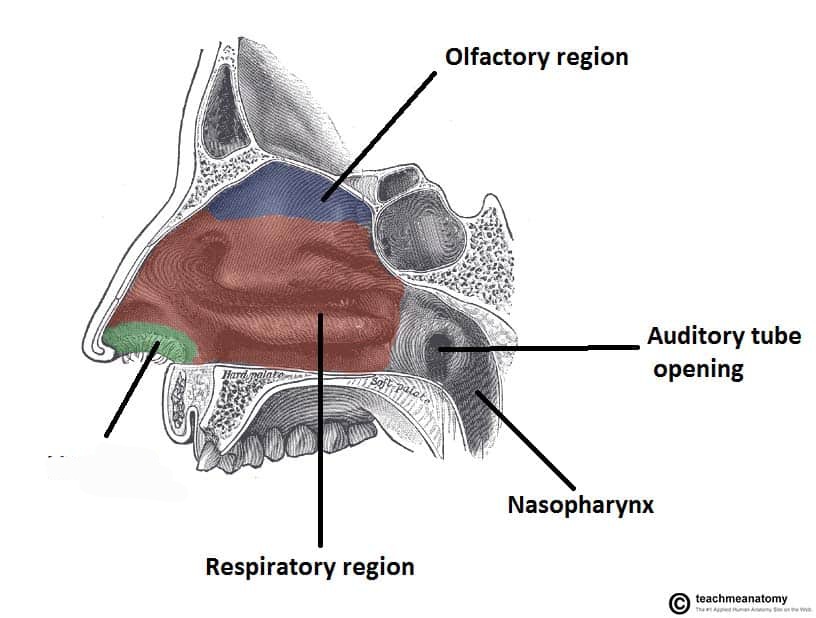
Choanae
Openings to nasopharynx, end of nasal cavity
Nasal Conchae
Form lateral wall for each cavity, has nasal meats (air passage) underneath.
Vestibule
anterior region of nasal cavity, nearby vibrissae hairs