Dental Occlusion Quiz 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
gypsum products types 1
impression and mounting palster
gypsum products type 2
model and laboratory plaster
gypsum product type 3
model and laboratory stone
gypsum product type 4
dental stone, high strength
gypsum product type 5
dental stone, high strength and high expansion
are type 1 and type 2 gypsum products stones or plasters
plasters
type 3-5 gypsum products are stones or plasters
stone
type 1 and type 2 are produced by
calcination- heating the raw materials to drive off part of crystal water and impurities
calcination rxn of type 1 and 2 dental plasters
gypsum dihydrate → open kettle, dry heat → calcined gypsum beta-hemihydrate form
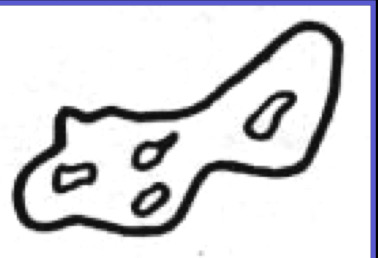
characteristics of beta-calcium sulfate hemihydrate
irregular shaped particle, loose and porous white-powder, mounter plaster, model plaster
type 3 dental stones is produced by
calcination
calcination rxn of type 3 dental stones
gypsum dihydrate → autoclave, steam + pressure → calcined gypsum alpha-hemihydrate form

alpha-calcium sulfate hemihydrate characteristics
prismatic- shaped particle, dense white-powder, hard and strong products
type 4 and type 5 high strength stones rxn
dihydrate form → boiling in 30% CaCl2 and MgCl2 solution, wash w boiling water/dry/grind → modified alpha-calcium sulfate hemihydrate form
modified alpha-calcium sulfate hemihydrate characteristics
uniform-shaped particle (high in strength), denser powder, harder an stronger products
gypsum products vary in
water/powder ratio, working/setting time, dimensional accuracy, surface resistance and strength, reproduction detail
from type 1 going to type 5, how does the water:plaster change
as you go up in types of gypsum products- the ratio decreases so you need less water
as water:plaster increases, how does porosity % change
increases- more will form inside the final cast
setting time
the elapsed time from the beginning of mixing until the material hardens
after working time
the consistency of the mix is no longer acceptable for the product’s intended purpose, or the mixture fails to flow under manipulation or vibration
type 1 impression plaster edentulous ridge
polyether, alginate
type 1 mounting plaster characteristics
quick-setting, low-strength, low-expansion
type 3 mounting stone characteristics
fast-setting, high-strength, low-expansion
type 5 has increased expansion to compensate for…
shrinkage of vinyl polysiloxane and elastomeric impression materials
rank the gypsum products in order from highest to lowest working time
type 5 = type 4 > type 3-model/laboratory stone = type 2 > type 3- mounting stone > type 1
rank the gypsum products in order from highest to lowest setting time
type 5 > type 2 > type 3-model and laboratory stone > type 4 > type 3 mounting stone > type 1
rank the gypsum products in order from highest to lowest setting expansion
type 5 > type 2 > type 3- model/laboratory stone > type 4 = type 1 > type 3 mounting stone
which type of gypsum product would you use to make trimming full models, ditching dies, and scanning easier and more reliable… why?
UltiRock- ISO type 4 bc of it’s smooth non-reflective surface and is highly durable
which gypsum product is scannable where models can be used w CAD/CAM systems, eliminating the need for a specific scan stone or spray
LeanRock XL5- ISO Type 5
what should you do prior to pouring you water/powder ration in the bowl
rinse mixing bowl and shake out excess water
what gypsum products must you hand mix and is not recommended to use the vacuum mix
Type 1- mounting plaster and Type 3- mounting stone
what class does the semi adjustable articulator fall under
class 3
what are some characteristics of a semi adjustable articulator (5)
inc ability to reproduce mand movement, more accurate dimensions/accept face bow transfer or Kois sys, commonly used for occlusal analysis, fabrication for bridge fixed PD or CD, multiple units for prosthetics
what is reproducible in a semi adjustable articulators (5)
delayed side shift, horizontal condylar inclination, incisal guidance, protrusive movement, R/L lateral movements
what is non-reproducible in semi adjustable articulators (2)
inter condylar distance and immediate side shift
delayed side shift
during lateral translatory movement of the mandible, the condyle will move .5 mm laterally
what motion analogues are available in delayed side shift in a semi adjustable articulator
.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 mm
digital dentistry
use of dental technologies/devices that incorporates digital/computer-controlled components to carry out dental procedures rather than using mechanical or electrical tools
what do the input→ process→ output stages look like in digital dentistry
data acquisition→ design → manufacturing
analog workflow
process of performing a task using physical means and materials, usually carried out by hand as opposed to using digital technology
digital workflow
converting physical or “analog” structure into a digital format to be manipulated using CAD software
additive manufacturing
a process of joining materials to make objects from 3D model data, usually layer upon layer (3D printing)
digital light processing (DLP)
using a projector to cure liquid resin into solid objects layer by layer
lithography-based ceramic manufacturing (LCM)
polymerizes a ceramic powder suspended in a photosensitive resin, an LED light source projects into the resin, and through mask expose it selectively cures the resin and builds up the part layer-by-layer
CAD/CAM
Computer Aided Design & Computer Aided Manufacturing
CEREC
CEramic REConstruction
a semi-adjustable articulator w the condyle in the lower membrane is arcon or non-arcon
arcon
what kind of articulator do we use
semi-adjustable
the purpose of occlusal registrations strips is to
evaluate the amount of a contact