Final Exam - Fundamentals of Speech & Hearing Science + Cranial Nerves
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
4
How many ventricles are there?
gustation
term meaning taste
ventricle
fluid filled cavities in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid to protect, cushion, and nourish the CNS
corpus callosum
the major commisural pathway that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain
oligodendrocytes
glial cells in the CNS that produce myelin sheaths around axons
Schwann cells
glial cells in the PNS that produce myelin sheaths around axons
glial cells
neuronal cells in the nervous system that provide support and protection to neurons, maintain homeostasis, and produce myelin; act as the “dough” to the neurons
neurons
the basic functional units of the nervous system that transmit information throughout the body using electrical and chemical signals; responsible for receiving sensory input, sending motor commands, and relaying signals
brain and spinal cord
What are the parts of the CNS?
cranial nerves and spinal nerves
What are the parts of the PNS?
arcuate fasciculus
a white matter bundle in the brain that acts as a crucial pathway for language processing; connects Broca’s and Wernicke’s area
afferent
carry sensory signals from body to brain (from PNS to CNS)
efferent
carry motor signals from brain to body (from CNS to PNS)
brainstem
What is the origin of the cranial nerves?
thalamus
What is the pink structure labeled #1?
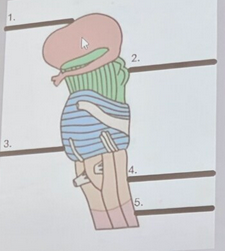
midbrain
What is the green structure labeled #2?
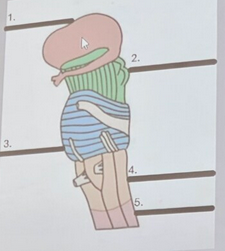
pons
What is the blue structure labeled #3?

medulla oblongata
What is the orange structure labeled #4?
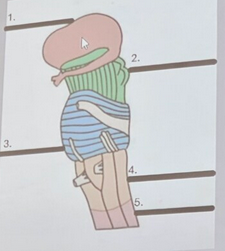
spinal cord
What is the red structure labeled #5?
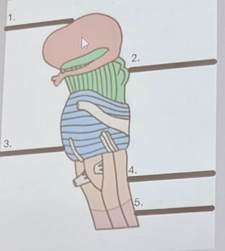
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
What are the 3 layers of the meninges from outermost to innermost?
False
(T/F) The lobes of the brain in either hemisphere are mirror images in structure and function.
medulla oblongata
Where do the nerves decussate to the opposite side of the body to maintain contralateral control?
frontal lobe
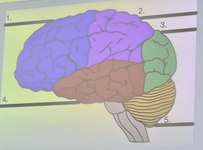
What is the blue structure labeled #1?
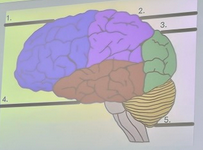
parietal lobe
What is the pink structure labeled #2?
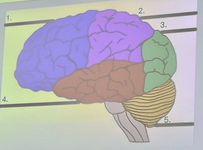
occipital lobe
What is the green structure labeled #3?

temporal lobe
What is the red structure labeled #4?
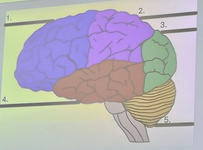
cerebellum
What is the yellow structure labeled #5?
astrocyte
What is the most common type of glial cell?
False
(T/F) There is a 1:1 correspondance between vowels and their formant frequencies.
Hertz
the measurement used for the frequency of sound
modal register
vocal register most commonly used in normal conversational speech
True
(T/F) The cochlea houses the organ of Corti.
tonotopic organization
the term for the differenital frequency response of the basilar membrane
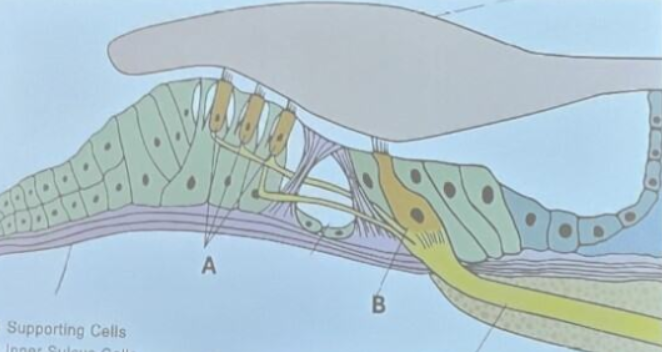
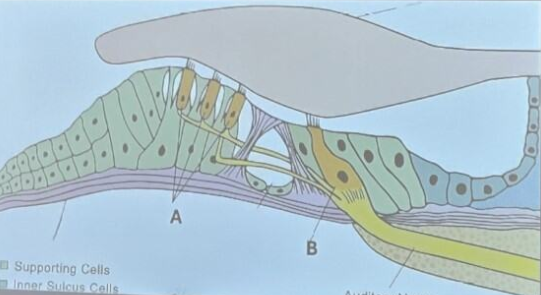
A: 3 rows of outer hair cells
B: 1 row of inner hair cells
Name the structures labeled A & B.
stop oral plosive
On a spectrogram, the acoustic features of a silent gap (silence), release burst (burst noise), voice onset time (VOT), and formant transitions (post-plostive vowel formant transition) occur in what?
False
(T/F) During speech breathing, older adults can produce more syllables per breath.
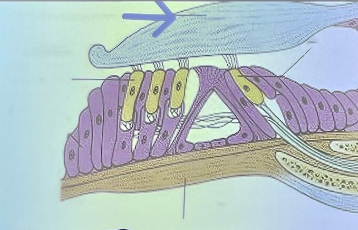
tectorial membrane
What is the name of the structure the blue arrow is pointing to?
decibels (dB)
the measurement used for the intensity of sound
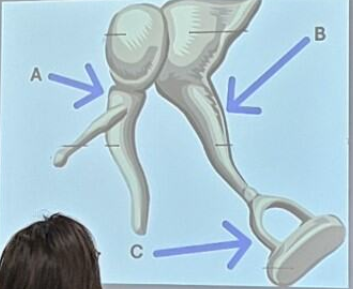
A: malleus
B: incus
C: stapes
Identify the bones of the ossicular chain labeled with A, B, and C.
Equalize pressure and keep the middle ear space ventilated
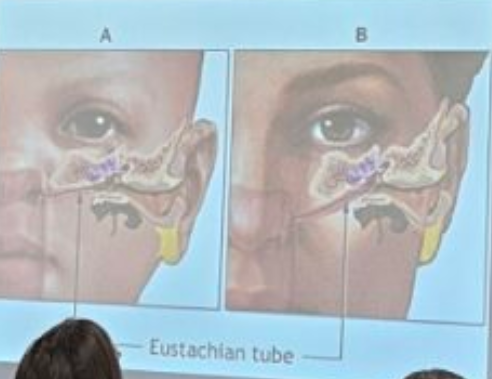
What is the purpose of the Eustachian tube?
frequency
The number of cycles of vibration completed in a second refers to the ____ of the sound.
F1: low
F2: high
What is the vowel acoustic pattern/relationship between F1 and F2 for a high front vowel?
snake’s hiss, static on the radio/TV
What is an example of a continuous, aperiodic sound?
Boyle’s Law
P1/V1 = P2/V2; in a container with a constant temperature, pressure and volume are inversely related
respiration
What is an example of Boyle’s Law?
deflate
What do the lungs do when the diaphragm relaxes?
expand
What do the lungs do when the diaphragm contracts?
A: Infant/child ET runs more horizontally
B: Adult ET is more angular (which helps fluid in the middle-ear space drain down into the nasopharynx)
What is the difference between the eustachian tubes in A & B?
1) size difference between tympanic membrane and oval window increases sound pressure
2) lever action of the ossicles/osicular chain adds energy
What are the two mechanisms of the auditory system that are responsible for impedance matching?
apex/apical portion
What portion of the basilar membrane is the most responsive to low-frequency sounds?
base
What portion of the basilar membrane is the most responsive to high-frequency sounds?
greater intensity, lower frequency
Vowels, compared to consonants, have ______ intensensity & _____ frequency.
vocal folds (fundamental frequency)
What is the source of your voice based on the source-filter theory?
vocal tract (formants)
What is the filter of your voice based on the source-filter theory?
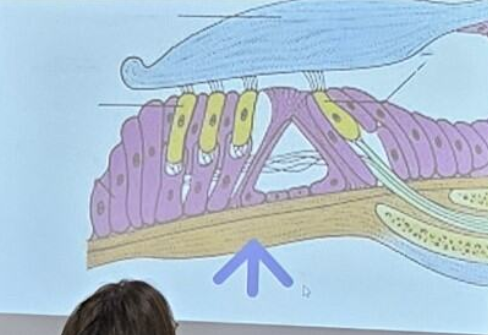
basilar membrane
What is the name of the structure the blue arrow is pointing to?
The myoelastic theory of phonation is a theory that explains how voice is produced through the interaction of muscle force and airflow. According to this theory, the vocal folds must adduct to close the glottis. As the glottis closes due to medial compression, air pressure builds up beneath the vocal folds. When the pressure becomes strong enough, it overcomes the resistance of the glottis, forcing the vocal folds apart. A puff of air escapes into the vocal tract, setting the air in the tract into vibration, which creates a sound wave. This sound wave travels through the vocal tract, where it is articulated and resonated into speech. Meanwhile, the vocal folds begin to adduct again, preparing for the next cycle of vibration.
What is the myoelastic theory of phonation?
Olfactory
Cranial Nerve I
Optic
Cranial Nerve II
Oculomotor
Cranial Nerve III
Trochlear
Cranial Nerve IV
Trigeminal
Cranial Nerve V
Abducens
Cranial Nerve VI
Facial
Cranial Nerve VII
Vestibulocochlear
Cranial Nerve VIII
Glossopharyngeal
Cranial Nerve IX
Vagus
Cranial Nerve X
Accessory
Cranial Nerve XI
Hypoglossal
Cranial Nerve XII
On On On They Traveled And Fought Against the Great Voldemort At Hogwarts
What’s a mnemonic to remember the twelve cranial nerves?
Cerebral hemispheres
What is the anatomic origin of the olfactory nerve?
Diencephalon
What is the anatomic origin of the optic nerve?
Midbrain
What is the anatomic origin of the oculomotor nerve?
Midbrain
What is the anatomic origin of the trochlear nerve?
Pons
What is the anatomic origin of the trigeminal nerve?
Pons
What is the anatomic origin of the abducens nerve?
Pons
What is the anatomic origin of the facial nerve?
Pons & medulla
What is the anatomic origin of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
Medulla
What is the anatomic origin of the glossopharyngeal nerve?
medulla
What is the anatomic origin of the vagus nerve?
medulla & spinal cord
What is the anatomic origin of the accessory nerve?
medulla
What is the anatomic origin of the hypoglossal nerve?
control of smell
the function of the olfactory nerve
control of vision
the function of the optic nerve
control most eye movements & pupil constriction
the function of the oculomotor nerve
control of downward and inward (towards nose) eye movement
the function of the trochlear nerve
jaw movement & face, mouth, and jaw sensation
the function of the trigeminal nerve
control of outward (towards ear) eye movement
the function of the abducens nerve
control of facial movement, hyoid elevation, stapedius reflex, salivation, lacrimation, and taste for the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
the function of the facial nerve
control of hearing & balance
the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve
control of pharyngeal movement, pharynx and tongue sensation, & taste on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve
pharyngeal, palatal, and laryngeal movement and sensation
the function of the vagus nerve
control of shoulder and neck movement
the function of the accessory nerve
control of tongue movement
the function of the hypoglossal nerve
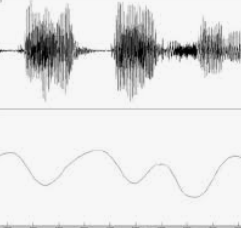
a waveform
What is this a picture of?
time
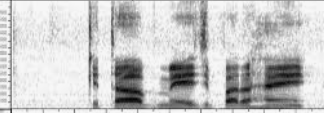
When examining a spectrogram, which measurement is displayed horizontally?
frequency
When examining a spectrogram, which measurement is displayed vertically?
more intensity
What do dark/colored areas mean on a spectrogram?
a spectrogram
What is this a picture of?
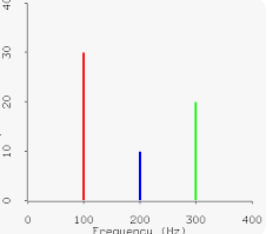
line spectrum
What is this a picture of?
inverse
Frequency and wavelength have a (direct/inverse) relationship