Pulmonary Circulation
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Pulmonary Capillary Pressure normal value
10 mm Hg
Colloidal Osmotic Pressure normal value
25 mm Hg
What keeps alveoli dry
Suction force of 15 mmHg (colloidal osmotic pressure - pulmonary capillary pressure) draws fluid from the pulmonary interstitial fluid into pulmonary capillaries
What happens if pulmonary capillary pressure rises above 25 mm Hg
Fluid escapes into interstitial spaces
Leads to pulmonary oedema
What conditions would raise pulmonary capillary pressure
Exercise at high altitude
Left heart failure
Mitral stenosis
Pulmonary fibrosis
Four factors influencing blood flow in the lung
Arterial to Venous Pressure Gradient
Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR)
Gravity
Alveolar pressure
Mean Pulmonary Artery Pressure
15mmHg (25/8mmHg)
Left Atrial Pressure
5mmHg
Arterial to Venous Pressure Difference Driving Blood into Pulmonary Circulation
15-5 = 10mmHg
Pulmonary pressure is what compared to systemic circulation
about 1/10 of the pressure in the systemic circulation
Greatest pressure drop in pulmonary sys is where
across capillary bed

What are these signs of
Pulmonary Vascular Disease (PVD)
What can Pulmonary Vascular Disease (PVD) lead to
Right ventricular failure
Loss of left atrial compliance
Mitral regurgitation
Left ventricular dysfunction
Passive backwards transmission of left-sided filling pressures (from left side to pulmonary circulation)
Vascular resistance
The degree to which the blood vessels impede the flow of blood
Vascular resistance formula

Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) formula
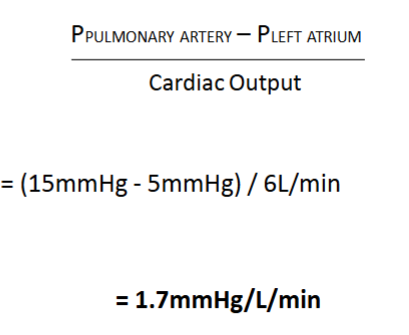
Pulmonary vascular resistance is high/low
Very low
Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) value
17mmHg/L/min
Hypoxia in the systemic circulation causes vasodilation/vasoconstriction
vasodilation
Hypoxia in the pulmonary circulation causes vasodilation/vasoconstriction
vasoconstriction
(Pulmonary hypoxia causes vasoconstriction to redirect blood flow away from poorly ventilated areas, improving V/Q matching and gas exchange)
Factors that affect PVR
Blood pressure
Hypoxia
Lung volume
Increased blood pressure increases/decreases PVR
decreases
By what mechanisms does increased blood pressure decrease PVR
Recruitment - open previously closed vessels (& vessels that were open but not conducting now conduct blood)
Distension - increase in caliber of vessels (vessels widen with pressure)
How does pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) change during exercise
During exercise, sympathetic stimulation increases cardiac output, leading to higher pulmonary artery pressure (PAP)
During exercise how does the pulmonary capillary transit time remain sufficient for oxygenation
increased blood flow distribution
Effect of recruitment & distention during exercise
Decreases PVR - Prevents pulmonary hypertension during exercise and ensures efficient oxygen delivery to tissues
Pregnancy leads to a ______% increase in blood volume and cardiac output,
30-50%
Effect of pregnancy on PAP
Raises it slightly
What is the physiological effect of a slightly increased PAP in pregnancy & significance of this
The increased PAP opens additional pulmonary capillaries (recruitment) and widens existing vessels (distension), decreasing PVR and improving pulmonary circulation.
Significance:
Prevents pulmonary hypertension
Increases pulmonary blood flow to meet the increased oxygen demand of both the mother and foetus.
What is Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension characterised by
narrowing, remodelling, and fibrosis of the pulmonary arteries, leading to increased resistance to blood flow
Effect of pulmonary arterial hypertension on pressure & resistance in the circulatory system
The increased resistance to blood flow forces the right ventricle (RV) to generate higher pressures to push blood into the pulmonary circulation
PVR is increased
To overcome the increased PVR, the right ventricle pumps with greater force, raising pulmonary artery systolic and mean pressures
(In summary PAH leads to elevated RVP, PVR & PAP)
At what mPAP is PAH diagnosed
Pulmonary artery pressure is diagnosed when mean pulmonary artery pressure is >20 mmHg at rest
Results of decreased pulmonary blood flow in PAH
Capillary recruitment and distension are impaired
Hypoxia
Exercise intolerance
The increased afterload on the right ventricle leads to right ventricular hypertrophy and eventually right heart failure due to the inability to sustain high pressures.
Difference between normoxia, acute hypoxia & chronic hypoxia
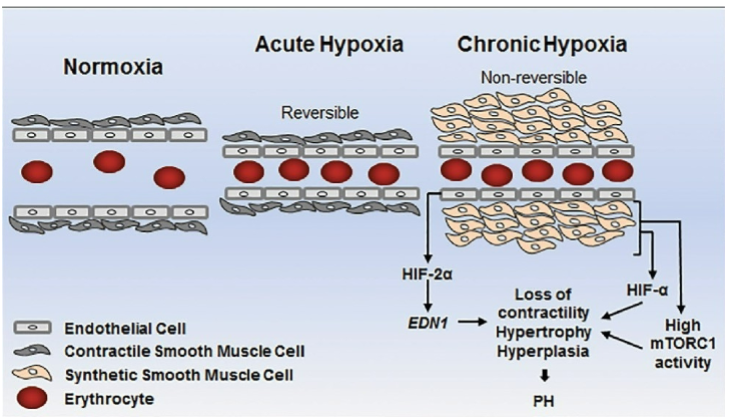
How does the pulmonary system respond to hypoxia
hypoxia-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction
How does hypoxia-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction work
There are oxygen sensitive K+ channels in the smooth muscle that surrounds blood vessels within alveolar walls
When PO2 within alveoli falls, K+ channels close.
This triggers increased intracellular calcium → increased smooth muscle cell depolarisation → contraction → vasoconstriction of pulmonary vessels
Blood flow to poorly ventilated lung regions is reduced - blood is diverted to alveoli that are better ventilated
How does hypoxia-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction help in high altitude
High altitude hypoxia Increases pressure in pulmonary artery - better perfusion of lung apex
How does hypoxia-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction help in utero
It limits blood flow through the (not-yet-functioning) lungs of the foetus
Possible risk of chronic hypoxia
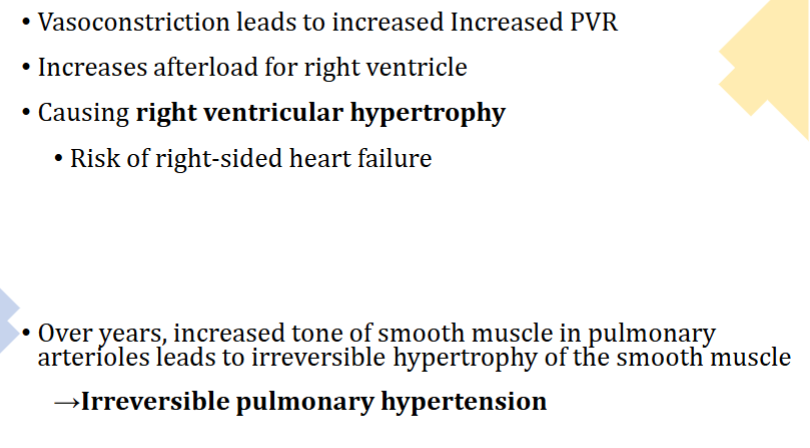
How does hypoxia-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction affect people with COPD
In COPD persistent vasoconstriction leads to vascular remodeling and fibrosis, raising mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) and causing pulmonary hypertension. The right ventricle (RV) faces increased afterload, resulting in right ventricular hypertrophy and eventually cor pulmonale (right heart failure).
Symptoms of right heart failure
dyspnea, peripheral edema, jugular venous distension (JVD), and hepatomegaly
Effect of oxygen therapy on COPD patients
Oxygen therapy helps reduce HPV (🫁 Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction), lowering PVR and alleviating right ventricular strain
COPD patients have a large liver why?
Increased heart size irritates liver, creating an inflammatory response
When is pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) at its lowest
FRC
PVR Increases at Both High and Low Lung Volumes
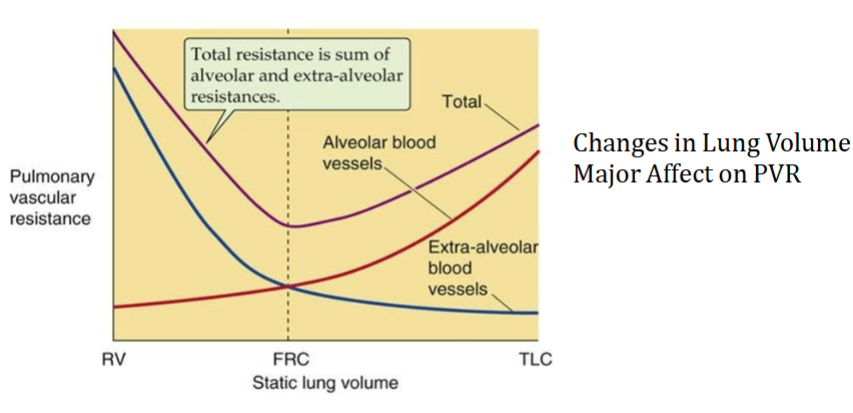
FRC
Amount of air left in lungs after a normal expiration
Pulmonary circulatory vessels have thick/thin walls
Thin
(pulmonary arteries have less smooth muscle in their walls than systemic arteries)
(they are distensible & compressible)
Pressures surrounding pulmonary vessels can distend/compress them. How does this work

What keeps large pulmonary vessels open
Large blood vessels near the hilum are exposed to negative intrapleural pressure which keeps them open
What is the effect of high lung volume on PVR

What is the effect of low lung volume on PVR

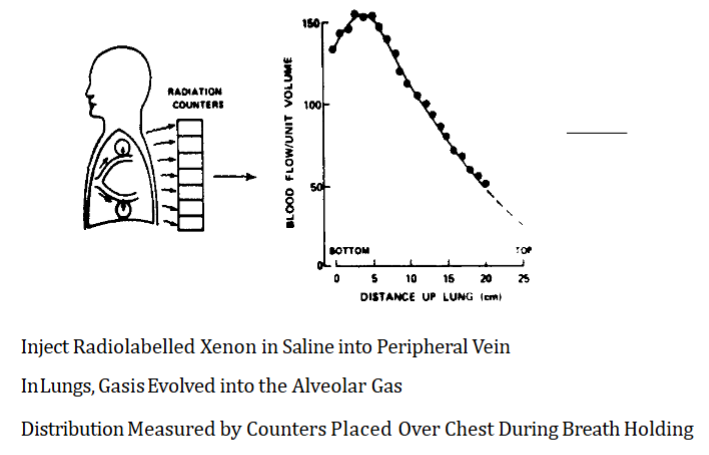
Best perfused area of lungs
Base (bottom) of the lung
Why is the top of the lung not as well perfused as the bottom
Due to gravity, pulmonary arterial pressure is greatest at the base of the lungs
There is just about enough pressure to bring blood to the top of the lung due to gravity
Pressure Differs from Top to Bottom of 30cm high Lung
about 23mmHg
Mean pressure in lung
15 mmHg
Pressure at base of lung
25 mmHg
Pressure at apex of lung
2 mmHg
How is perfusion throughout the lung measured
A 64-year-old male with severe emphysema presents with progressive dyspnea and reduced exercise tolerance. Pulmonary function tests show increased total lung capacity (TLC) and residual volume (RV), consistent with lung hyperinflation. On examination, the patient has barrel chest, distant heart sounds, and an accentuated P2 heart sound.
What is the problem?
What treatment can be given?
What could happen without treatment?
The excessive lung volume compresses pulmonary capillaries, increasing pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) and impairing pulmonary blood flow. Over time, the right ventricle (RV) must work harder to overcome the elevated PVR, leading to right ventricular hypertrophy and pulmonary hypertension.
Long-term oxygen therapy and bronchodilators help reduce hyperinflation, lower PVR, and improve pulmonary circulation.
Without treatment, persistent high lung volumes may lead to cor pulmonale (right heart failure) and worsening dyspnea.
This case shows the effects of high lung volume on PVR
A 45-year-old patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is placed on mechanical ventilation with high tidal volumes due to severe hypoxemia. This leads to acute right ventricular strain and then failure. Why?
The patient develops systemic hypotension and poor oxygenation. Why?
What should be done instead?
What could happen if left untreated?
The high lung volumes lead to alveolar overdistension, compressing pulmonary capillaries and increasing pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR). As a result, pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) rises, forcing the right ventricle (RV) to work harder, which can lead to acute right ventricular strain or failure.
This suggests ventilator-induced pulmonary hypertension
To reduce PVR, the ventilator settings are adjusted to lower tidal volumes (lung-protective ventilation) and optimize positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP).
If untreated, persistent high lung volumes can lead to cor pulmonale and worsening oxygenation.
This case shows the effects of high lung volume on PVR
A 58-year-old female with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) presents with progressive shortness of breath and dry cough over the past year. Pulmonary function tests reveal a low total lung capacity (TLC) and reduced forced vital capacity (FVC), consistent with restrictive lung disease.
Would you expect her PVR to be high/low?
How would you confirm this?
Over time, what would the persistent vascular remodelling and fibrosis lead to?
As the disease progresses, the right ventricle struggles to overcome the elevated afterload, leading to what?
The low lung volume leads to compression of pulmonary capillaries, increasing pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) and reducing pulmonary blood flow.
Right heart catheterization confirms increased PVR
Elevated mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP), leading to pulmonary hypertension.
Peripheral edema, jugular venous distension (JVD), and exertional dyspnea.
This case shows the effects of low lung volume on PVR
what 2 things does pressure in pulmonary arterioles depend on
both mean pulmonary artery pressure and the vertical position of the vessel in the chest, relative to the heart.
In a healthy in individual, capillary/alveolar pressure is always greater than the pressure in capillaries/alveoli
capillary
alveoli
(otherwise the capillaries would be squashed!)
What west zones are generally found in the lungs
Zone 2 and 3 are found in healthy individuals
Zone 1 is only found in unhealthy individuals (e.g. during a haemorrhage)
How does flow in each of the west zones differ

What pressure is responsible for opening alveoli
Transpulmonary pressure
How is transpulmonary pressure calculated
Alveolar pressure - (inter)pleural pressure
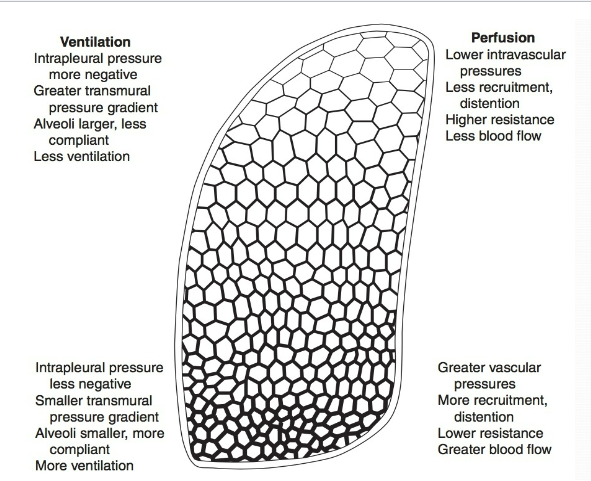
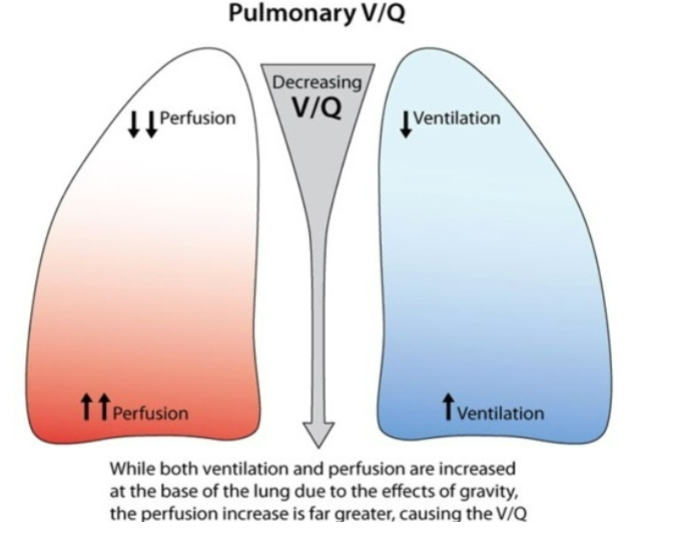
How does ventilation & perfusion compare at the top & bottom of the lung
Why are neonatal heart beats so high (140bpm)
Their stroke volume is very low
What is the ventilation-perfusion ratio formula

Normal ventilation-perfusion value
around 0.8 - 1
Why does the V and the Q have to be measured in the same alveolar unit

How many alveoli do we have
300 million
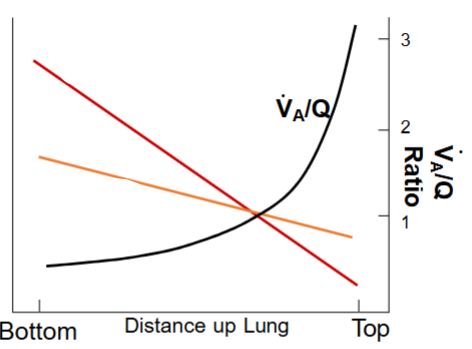
What does each line represent in this graph representing flow of blood & air
1 line is perfusion
1 line is ventilation
KNOW THIS DIAGRAM
Know where there’s a high/low ventilation perfusion match
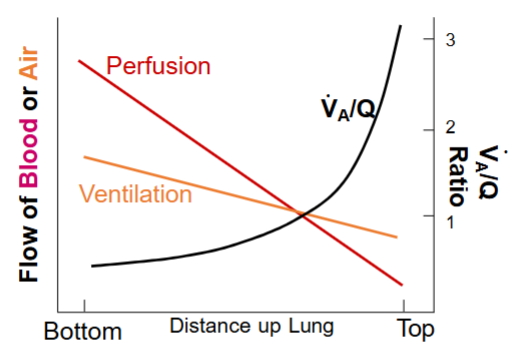
The ventilation perfusion ratio is highest at the top/bottom of the lung
Top
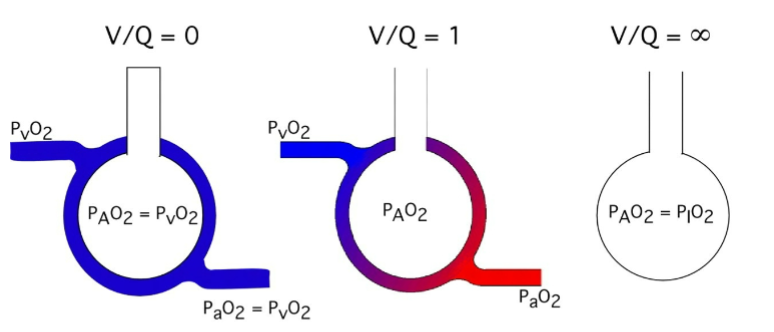
What is happening in alveolus 1
Shunting
There’s a blockage
Perfusion of blood without ventilation
Unoxygenated blood enters systemic circulation
What is happening in alveolus 3
Dead space
Ventilation of lungs without perfusion
Gas enters and leaves lungs without contacting blood - wasted ventilation
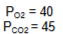
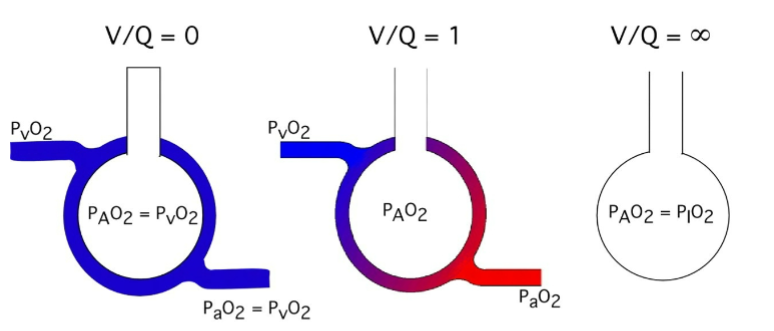
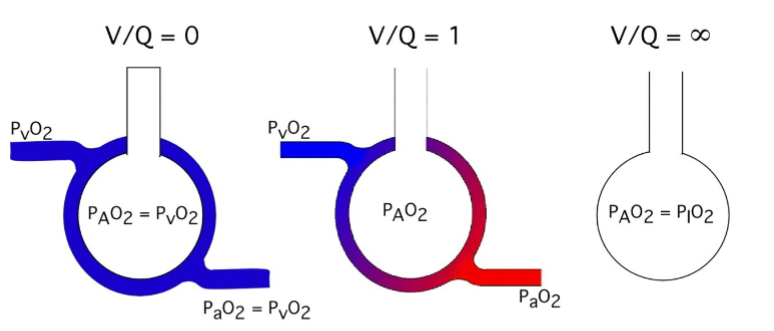
Is this low, normal or high VA/Q
low ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) ratio
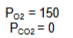
Is this low, normal or high VA/Q
This represents a case of very high V/Q ratio — in fact, it's essentially infinite V/Q, like in dead space ventilation.
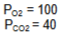
Is this low, normal or high VA/Q
Normal
Normal alveolar ventilation Approx ___L/min
4
Normal pulmonary capillary perfusion Approx ___L/min
5
Why is normal ventilation perfusion ratio around 0.8

V/Q ratio changes throughout alveoli in lung
Alveoli at apex are underperfused (overventilated)
Alveoli at the base are underventilated (overperfused)

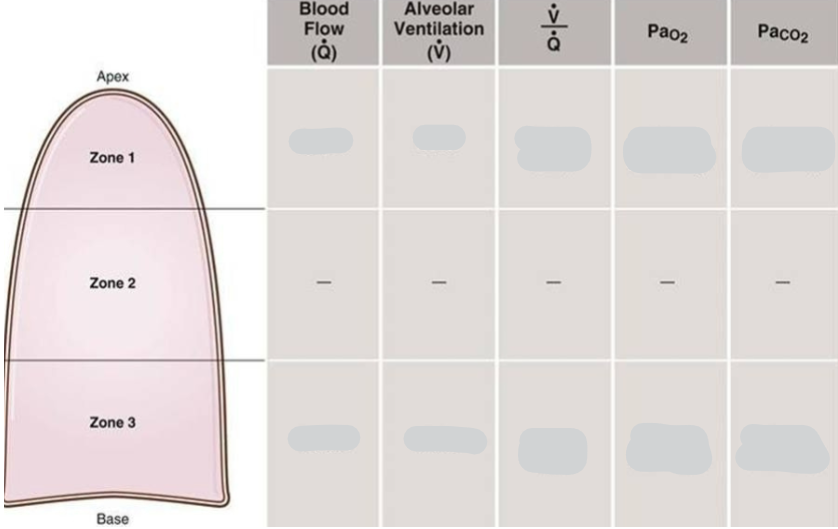
Put in higher & lower (& last 3 columns values)
Which is more dangerous - a high or low V/Q ratio
Low
High V/Q ratio adds relatively little more O2 to the blood
Low V/Q ratio can be fatal - causes hypoxemia - low blood oxygen levels
Patient Profile: Age/Sex: 45-year-old male
Presentation: Sudden onset of shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain (sharp and worsened by deep breaths), and a rapid heart rate.
Risk Factors: Recent prolonged travel and a history of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Clinical Findings:
•Vital Signs:
• Tachypnea (rapid breathing rate)
• Tachycardia (rapid heart rate)
• Slight hypotension
Examination:
• Normal lung auscultation (no wheezes or crackles)
• Signs of right heart strain on an ECG may be present
What is diagnosed: Pulmonary embolism
What is the resulting V/Q ratio
V/Q > 1
Areas that are ventilated but not perfused cannot effectively exchange oxygen into the blood, leading to an overall decrease in arterial oxygen levels (PaO₂). The body responds by hyperventilating, which often leads to a low arterial carbon dioxide level (PaCO₂).
In the alveolar oxygen tension (PAO2) formula what does each letter stand for
We use Patm instead of PB

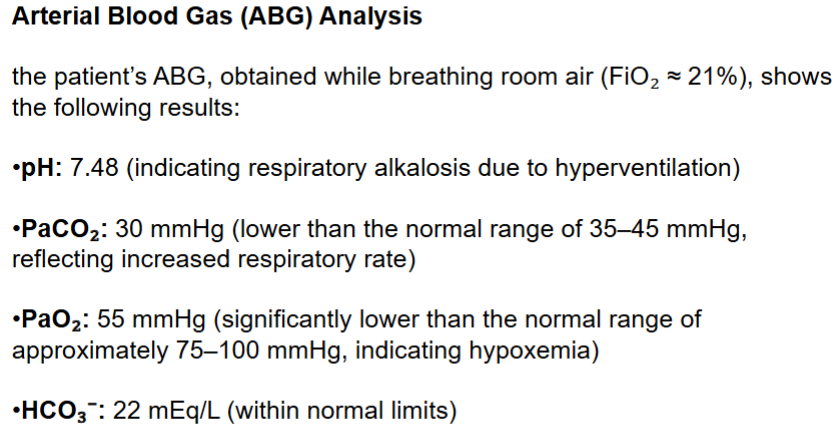
Calculate if the A-a gradient is normal
Alkalosis can indicate that the person is breathing quickly/slowly
Quickly - Hyperventilating
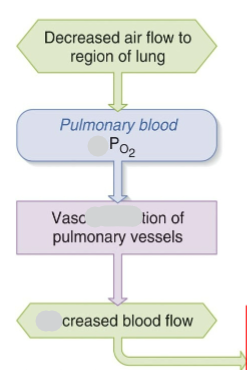
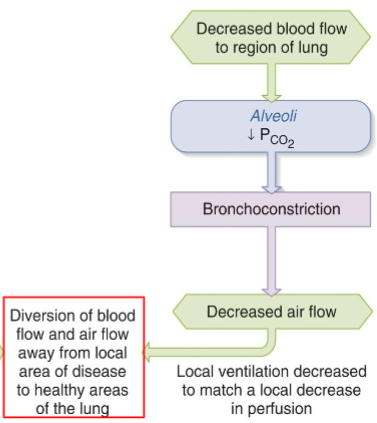
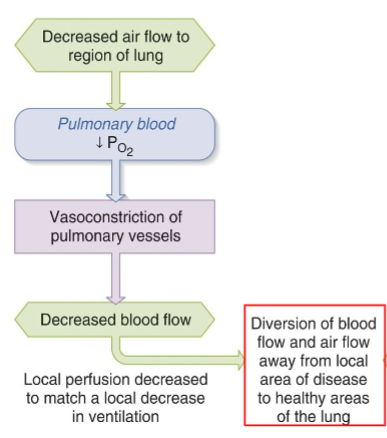
How does the body deal with decreased air flow to a region of a lung.
Do pulmonary blood oxygen levels go up or down
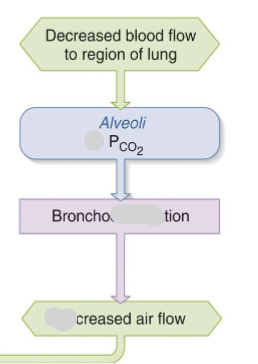
How does the body deal with decreased blood flow to a region of a lung.
Do alveolar carbon dioxide levels go up or down