Unit 1, Module 2, Lesson 3-combined
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Nutrients
Parts of food used by the body to grow and survive.
Calories
Units of energy provided by food.
Digestive system
The system in the body responsible for breaking down food and providing energy from nutrients to different parts of the body.

Mechanical digestion
Breaking down food into smaller pieces through physical means, such as biting and chewing.

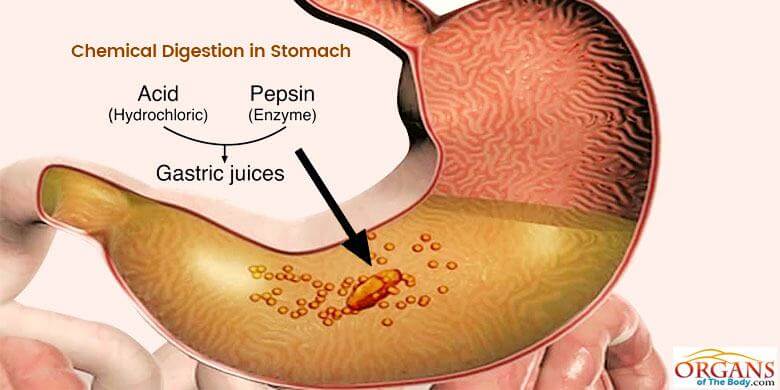
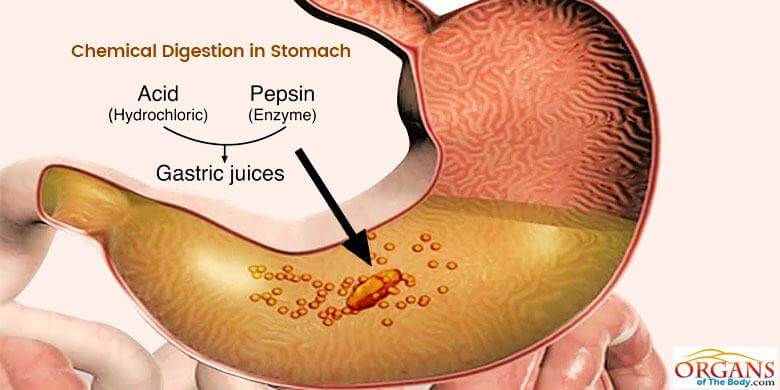
Chemical digestion
Breaking down food into small molecules through chemical reactions, aided by enzymes and stomach acid.
Esophagus
The food pipe that pushes down food to the stomach through peristalsis.
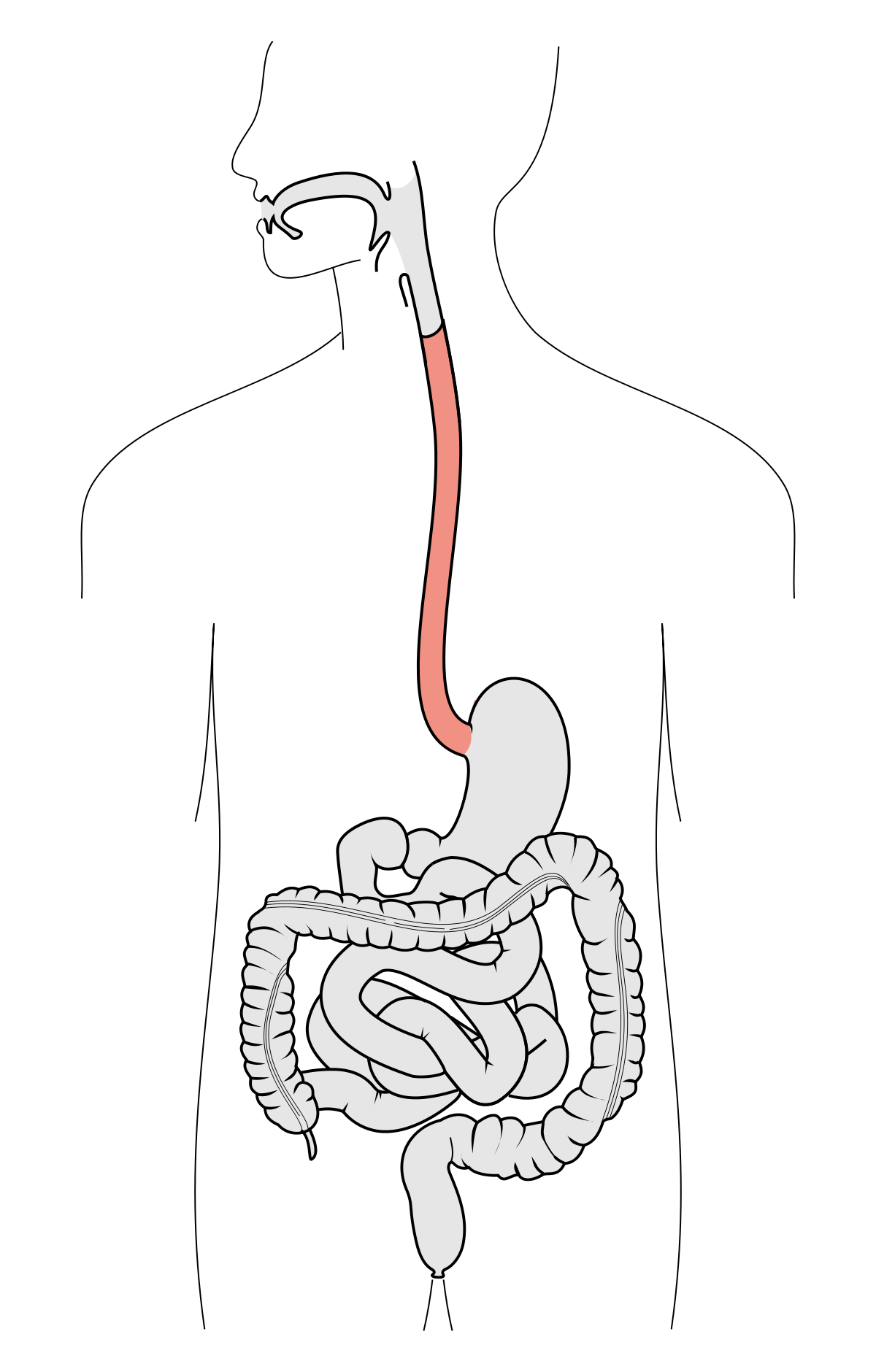
Stomach
A large hollow organ that aids in chemical and mechanical digestion.
Small intestine
A tube where most of the chemical digestion and nutrient absorption of food occurs.
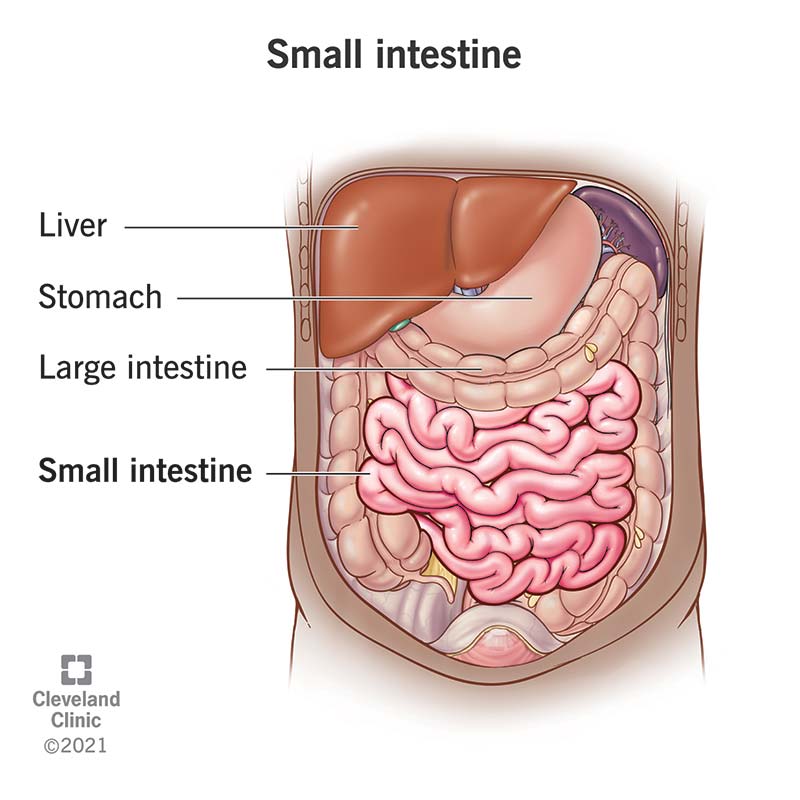
Large intestine
A tube that collects waste from the digestive system and absorbs more water, solidifying the waste.
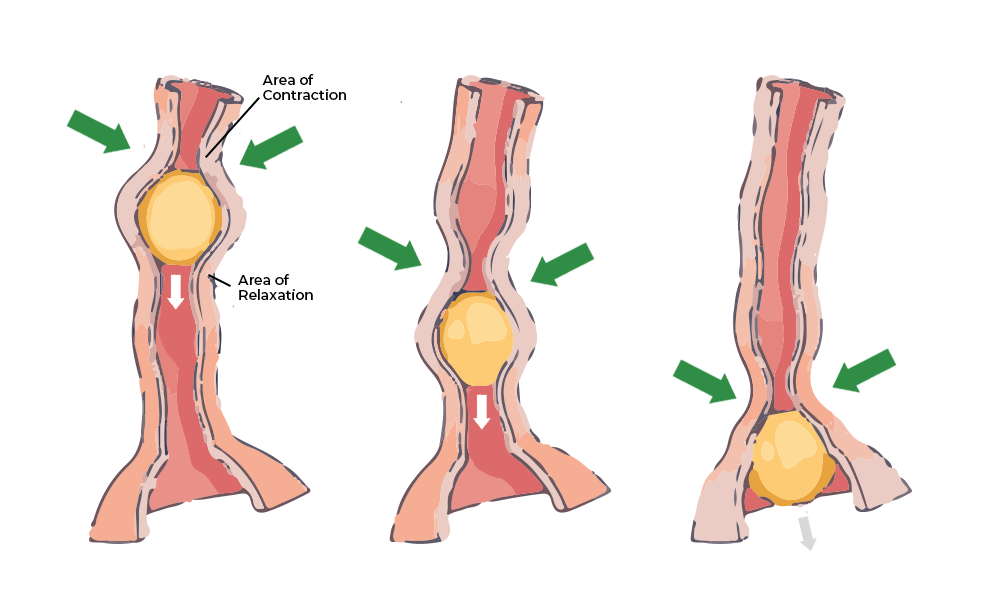
Peristalsis
Waves of muscle contraction that push food through the digestive system.
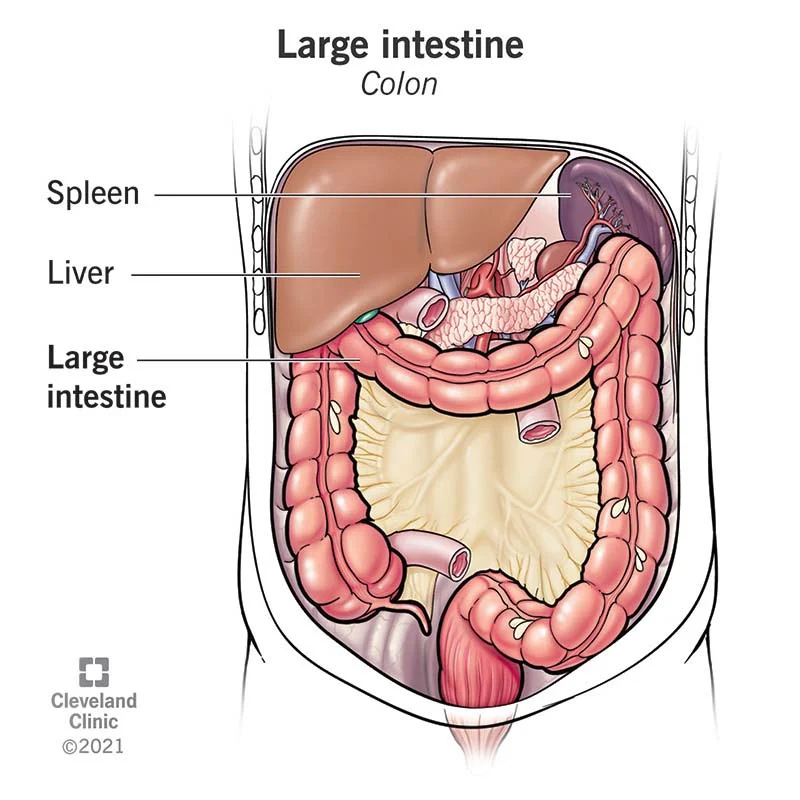
Excretory system
The system in the body responsible for collecting and eliminating wastes and regulating fluid levels.
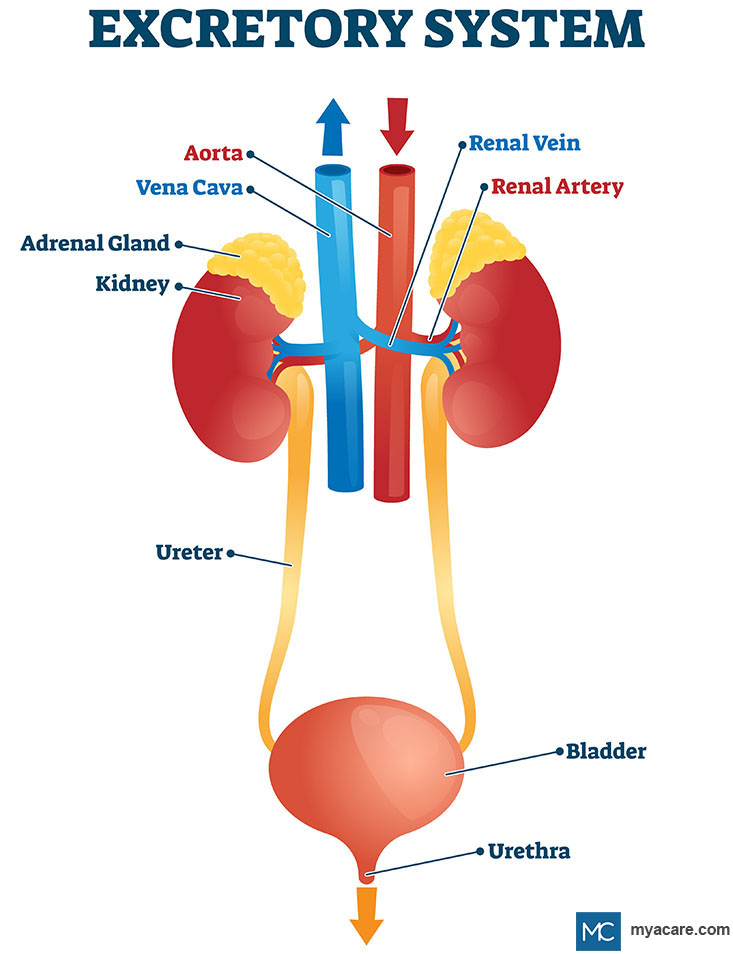
Urinary system
Part of the excretory system that removes liquid waste (urine) from the body.
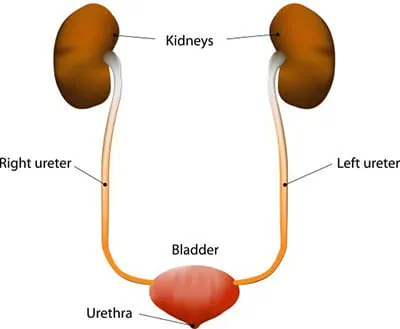
Kidneys
Bean-shaped organs that filter waste from the blood and are part of the urinary system.
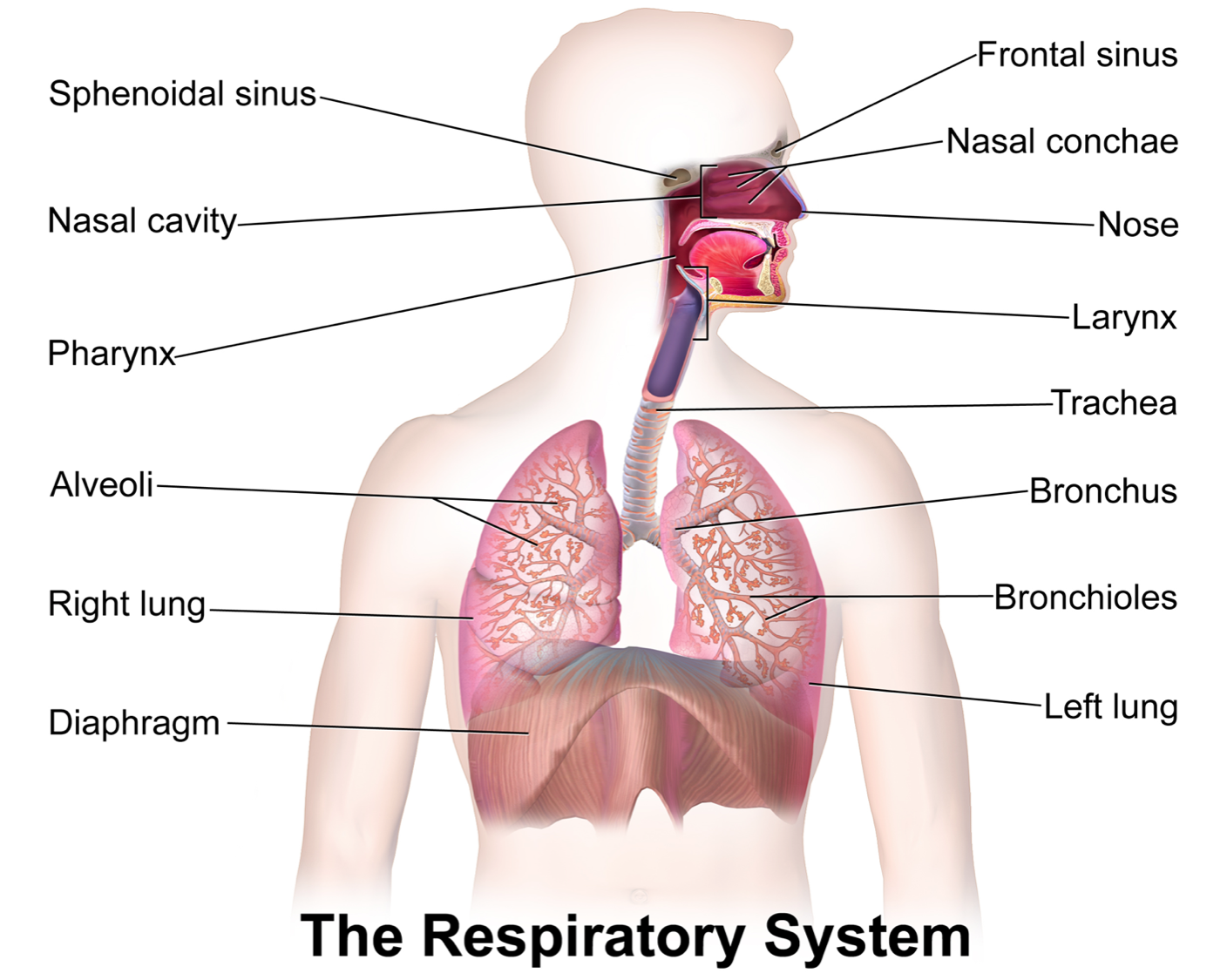
Respiratory system
The system in the body responsible for taking in oxygen and removing carbon dioxide and water vapor.
Integumentary system
The system in the body that includes the skin and helps release excess salt and water through sweat glands.

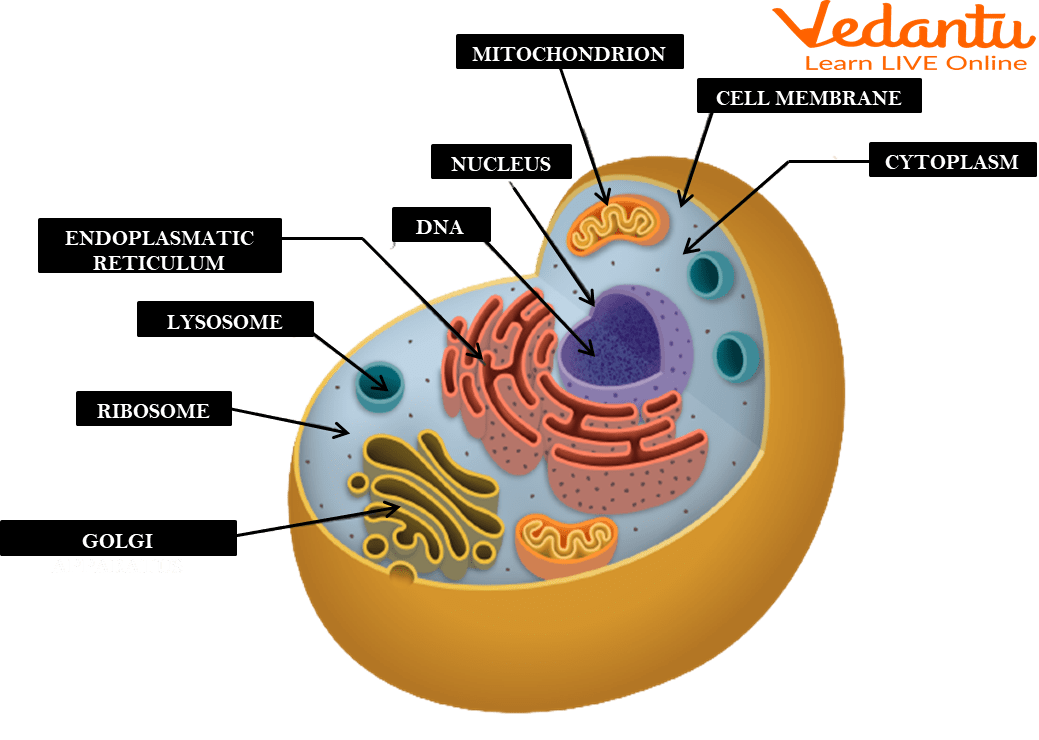
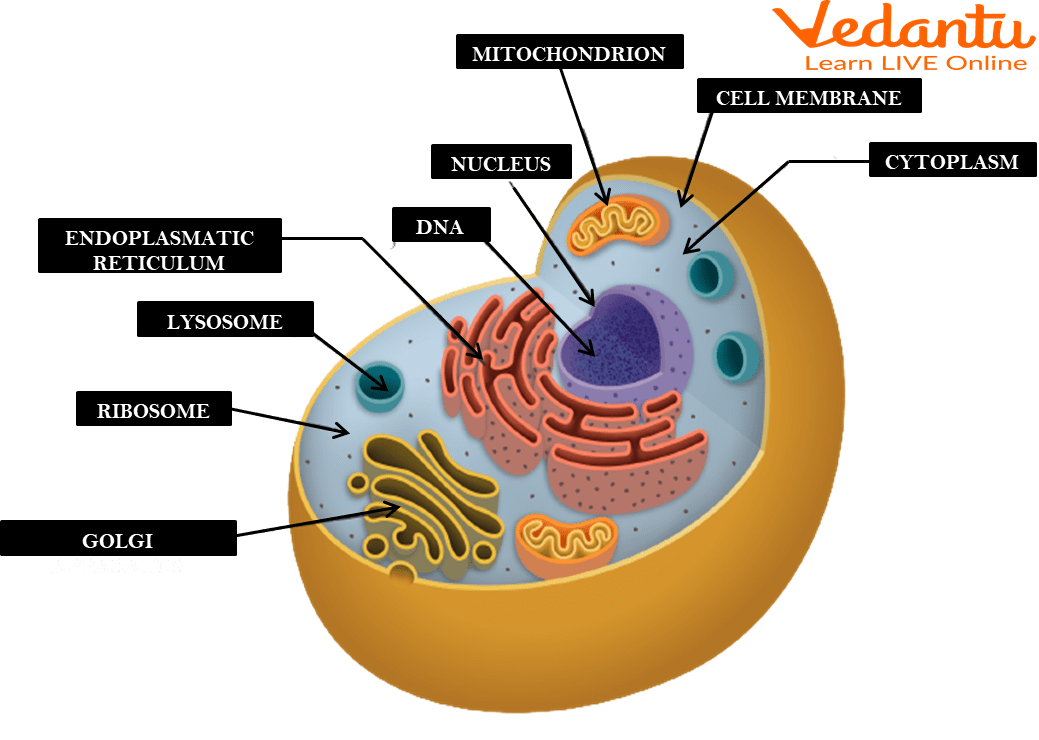
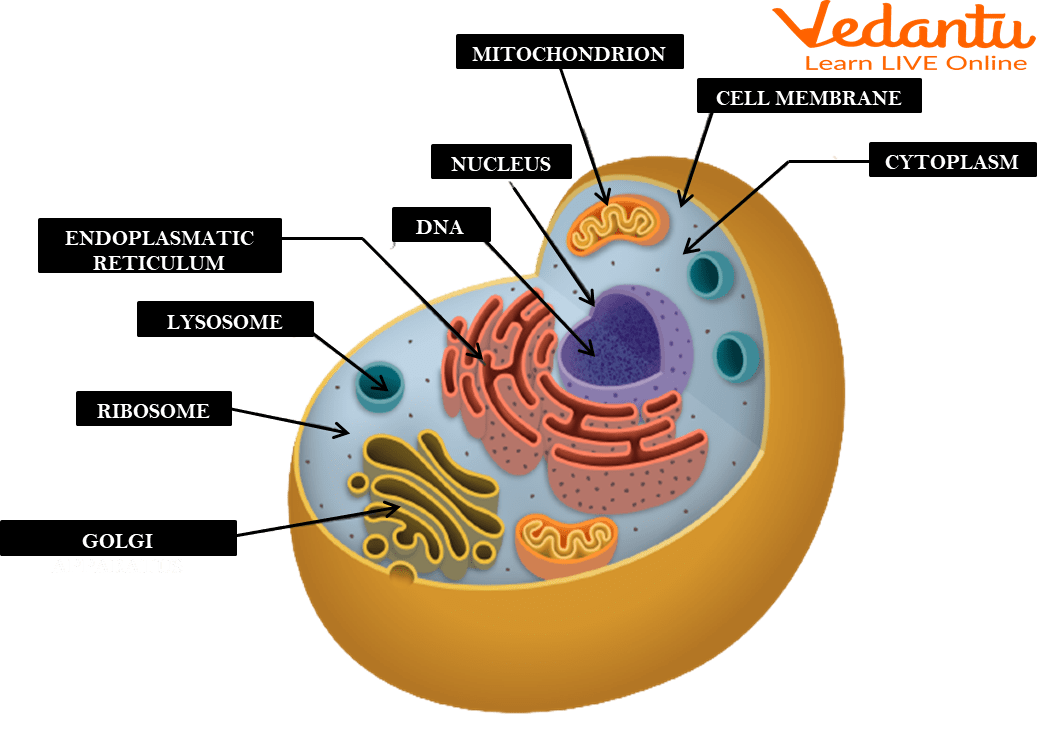
Cell membrane
A flexible, semi-permeable covering that protects the cell and controls the movement of substances into and out of cells.
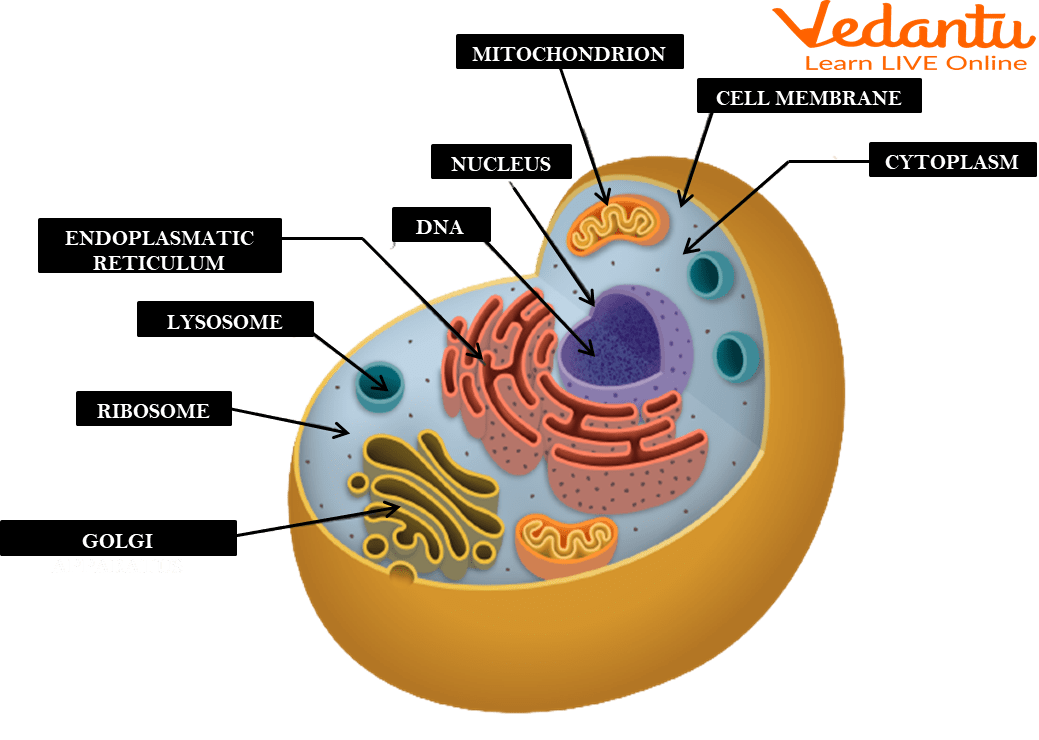
Cytoplasm
A jelly-like fluid that fills the cell and holds the organelles together.
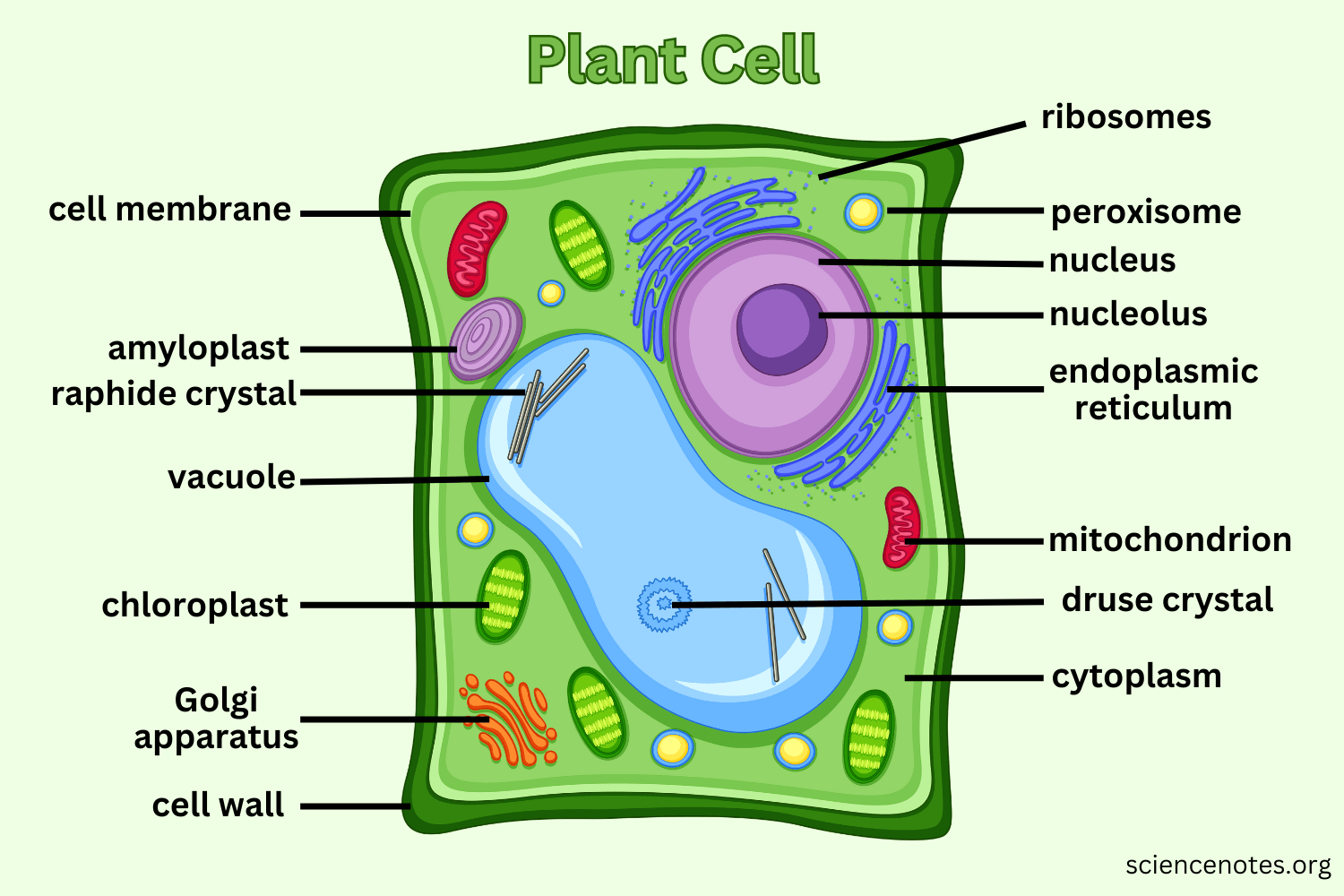
Cell wall
A stiff structure outside the cell membrane that provides protection and structural support to plant cells, fungal cells, bacteria, and some protists.
Ribosomes
Organelles involved in the production of proteins.
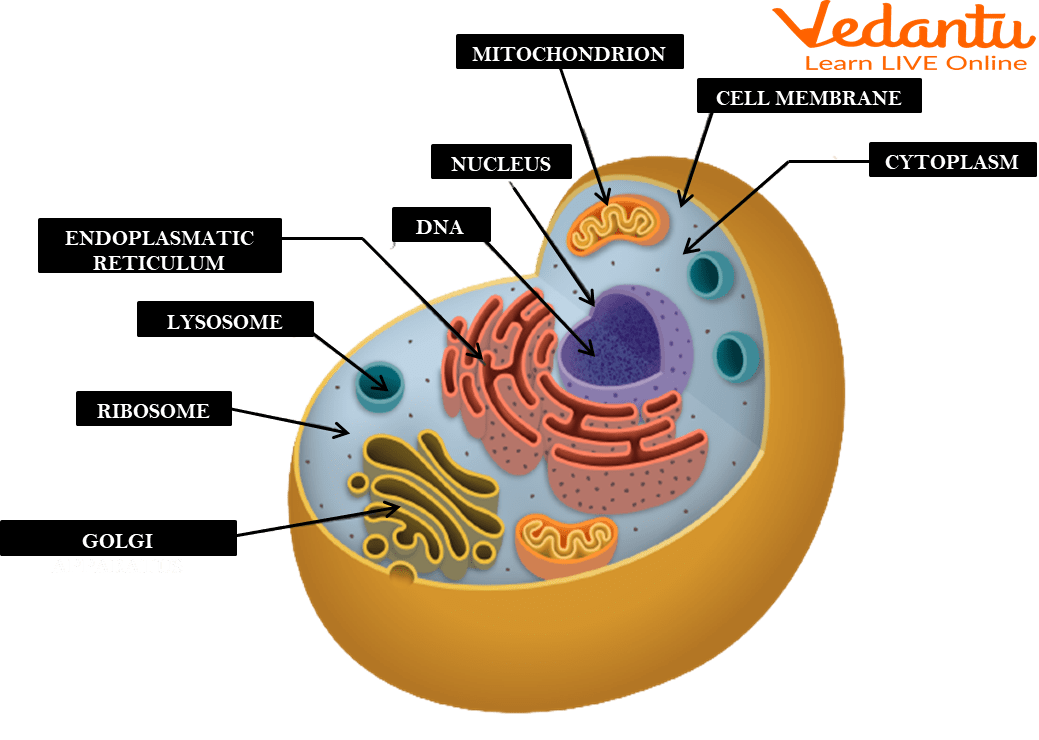
Endoplasmic reticulum
An organelle involved in the production, storage, and transport of materials within the cell.
Vacuoles
Organelles involved in the storage of materials within the cell.
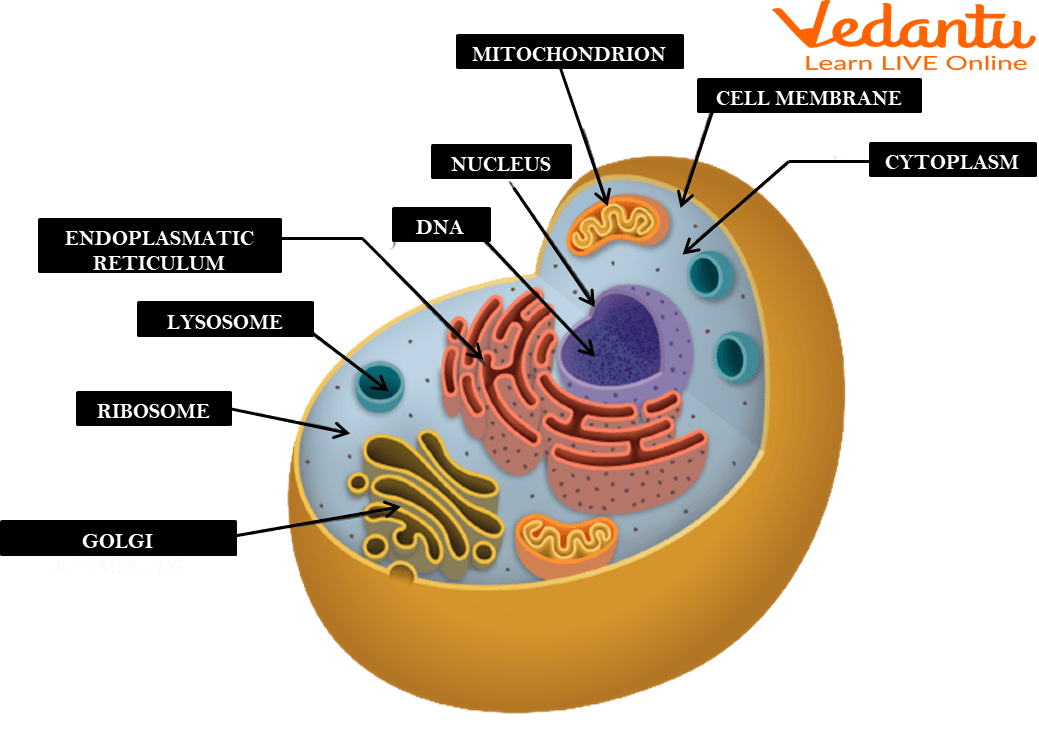
Golgi apparatus
An organelle involved in the processing, packaging, and distribution of materials within the cell.
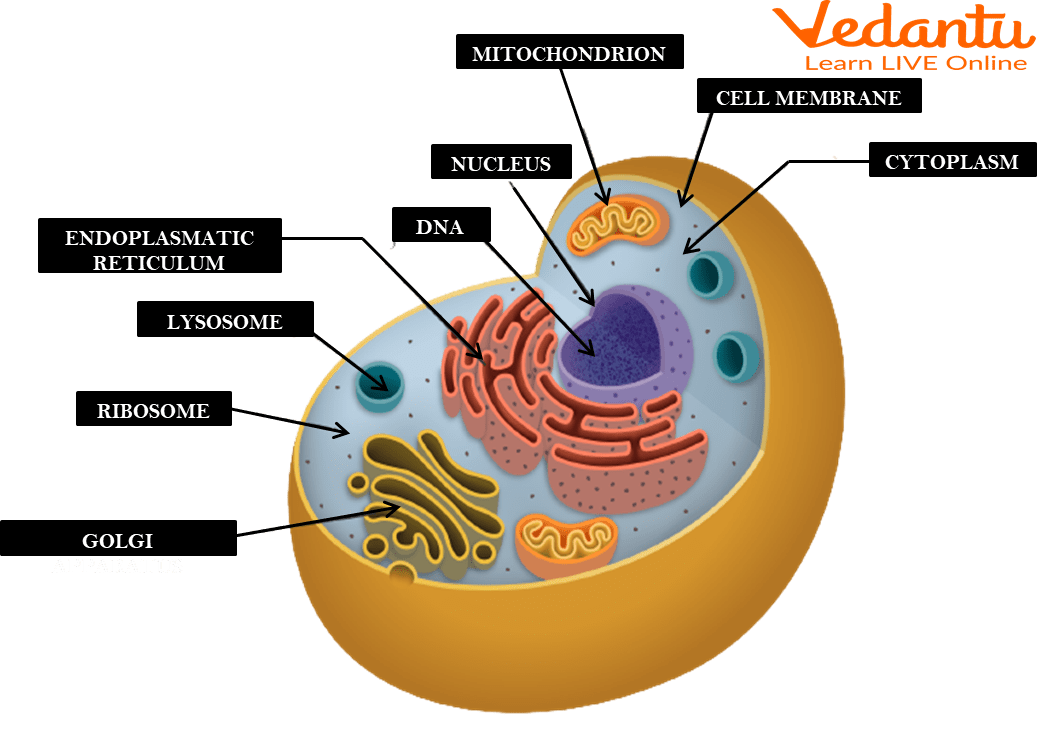
Ribosomes
Small structures where amino acid molecules join together to form long chains called proteins. They help cells communicate with each other and transport substances inside cells. They are not surrounded by a membrane.
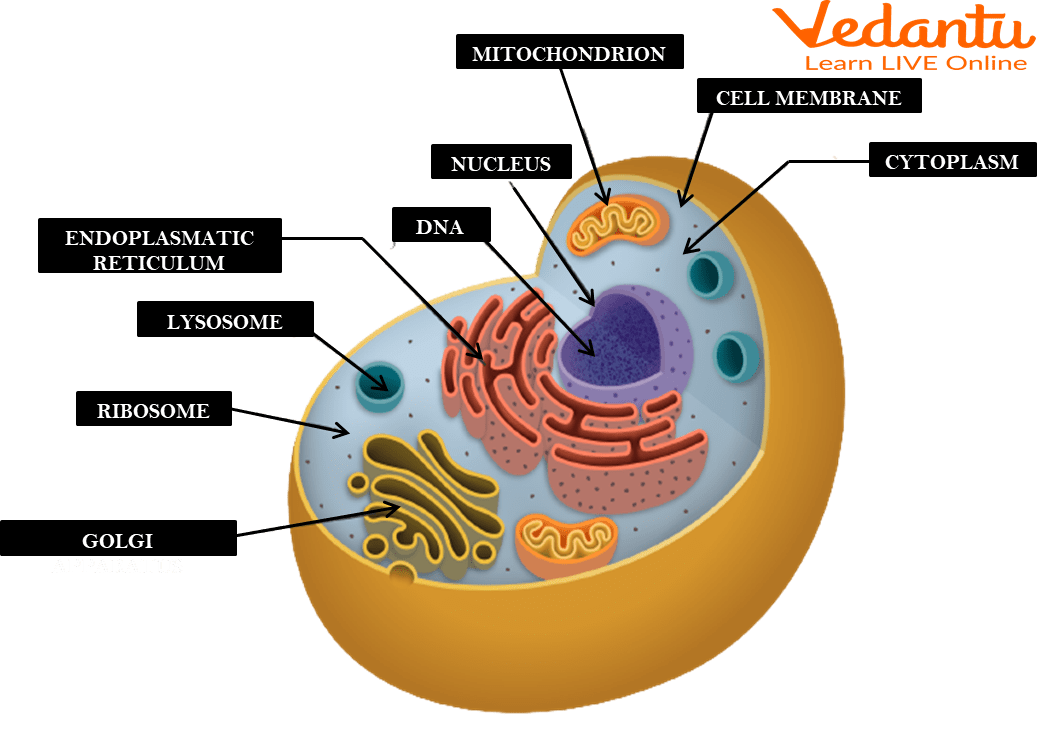
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
A web-like organelle that spreads from the nucleus throughout most of the cytoplasm. There are two types:smooth ER, which removes harmful substances from the cell, and rough ER, which is attached to ribosomes and is the site of protein production.
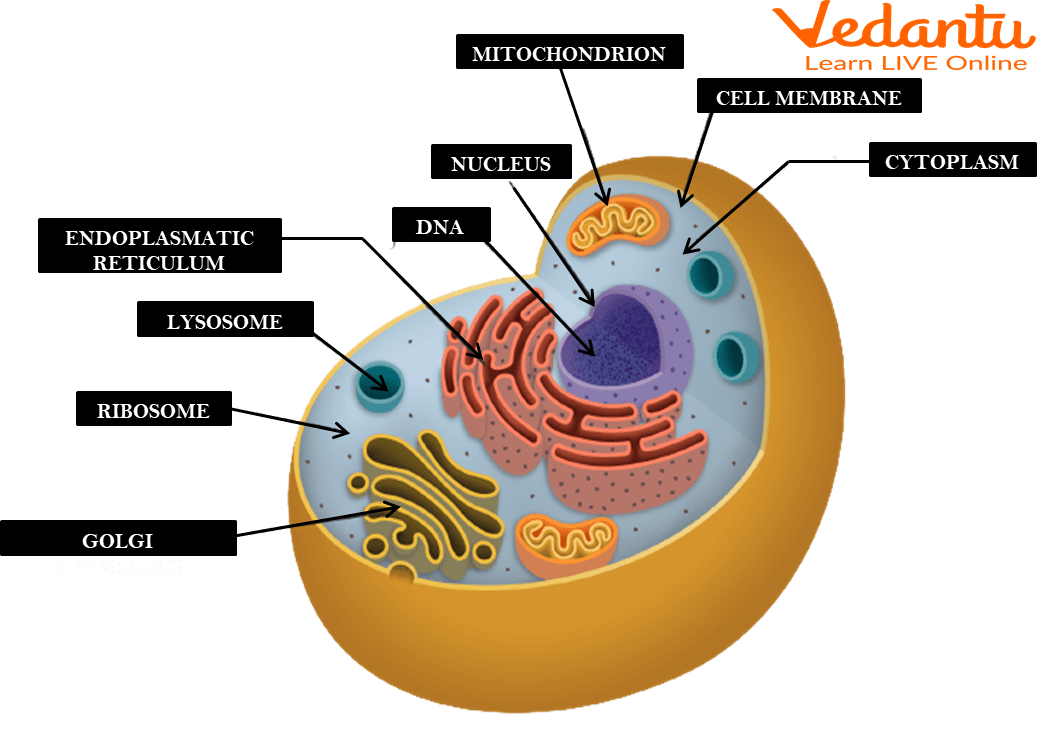
Vacuoles
Sac-like structures that store food, water, and waste material. In plant cells, there is one large vacuole that helps the cell stay rigid and supported when filled with water. In animal cells, there are many small vacuoles.
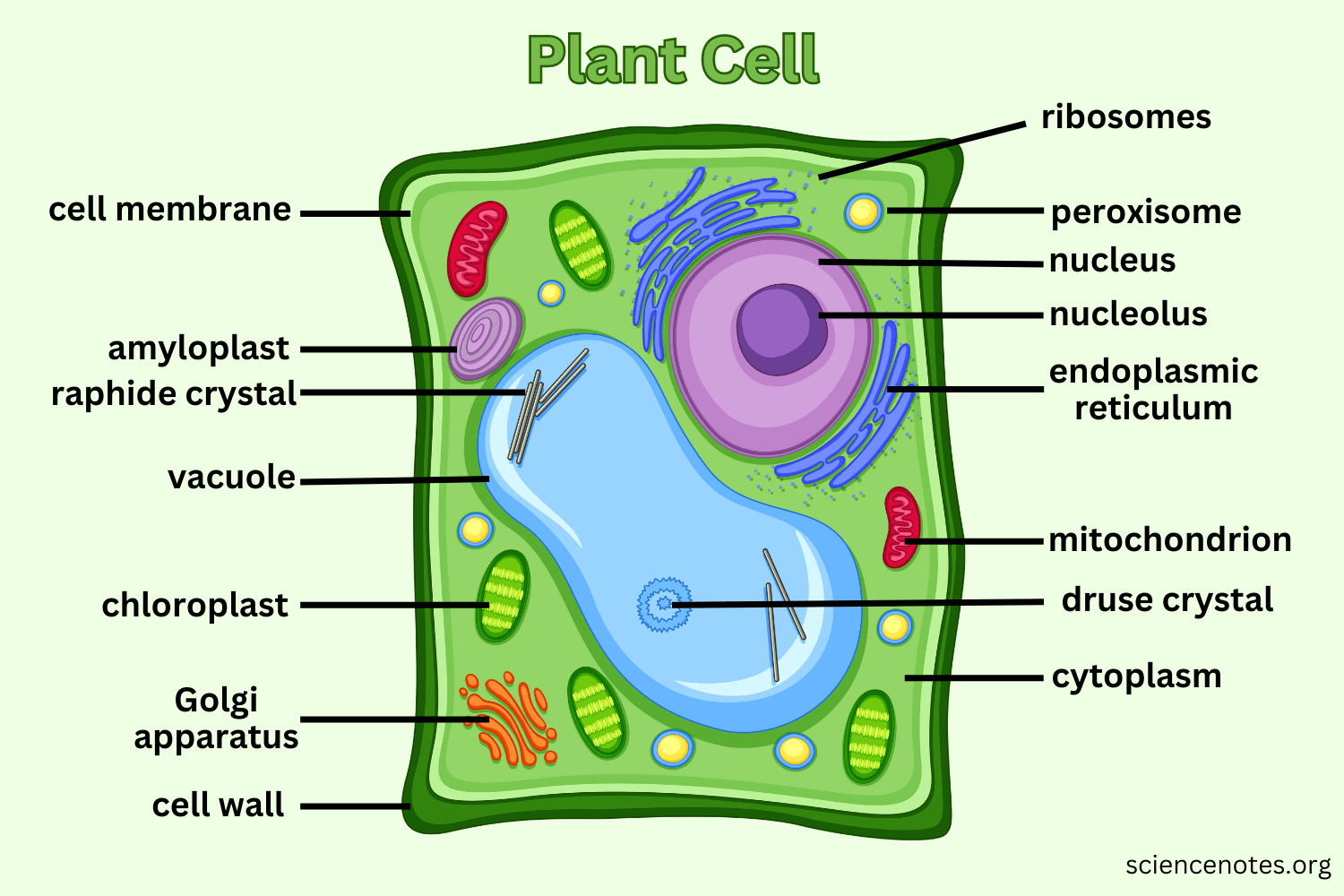
Golgi apparatus
An organelle that helps process and package proteins and lipid molecules into tiny, membrane-bound, ball-like structures called vesicles. Vesicles transport substances from one area of a cell to another. In animal cells, some vesicles are called lysosomes, which break down cellular wastes.
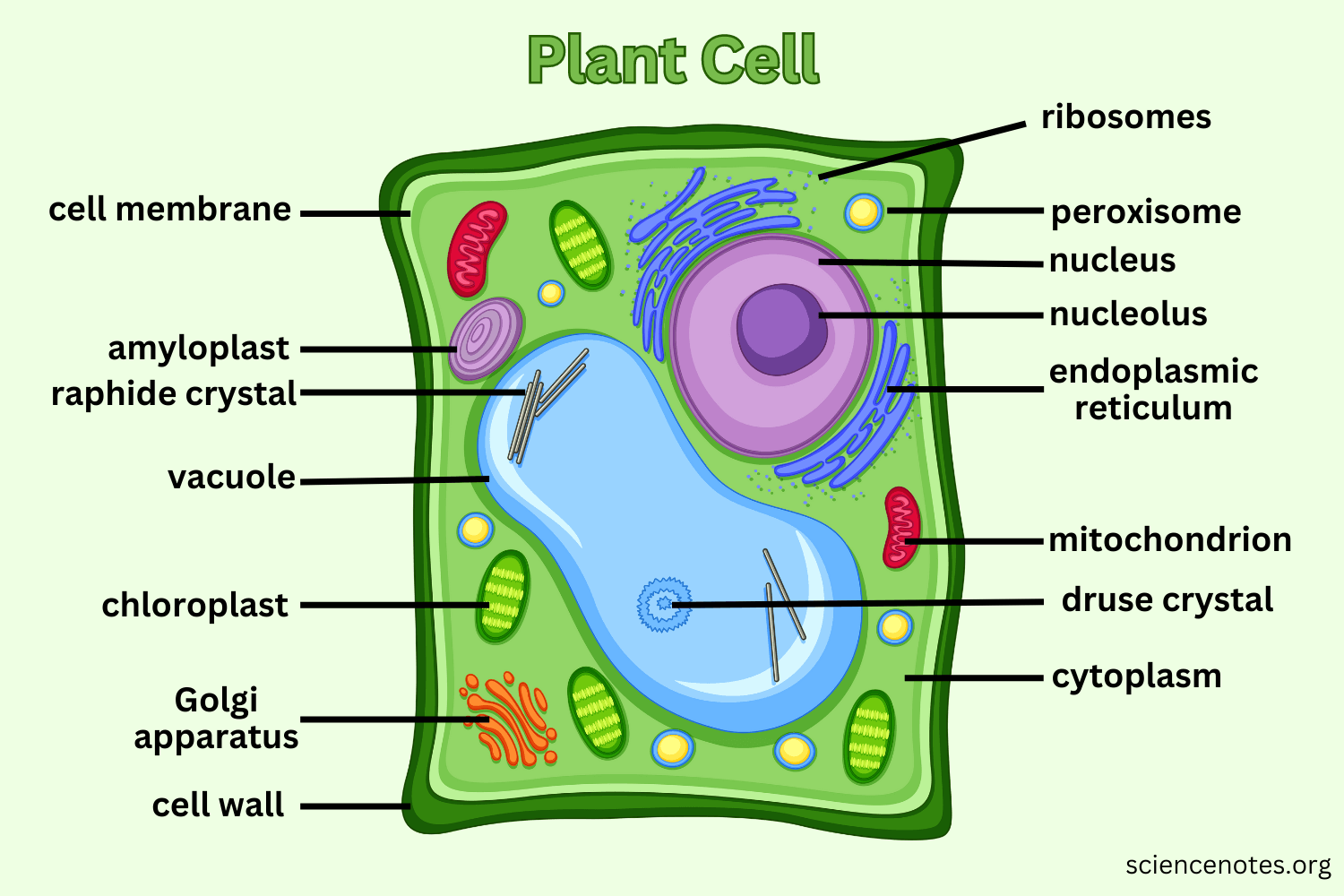
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell found in both animal and plant cells. It produces energy through a process called cellular respiration, which generates ATP (energy molecule).
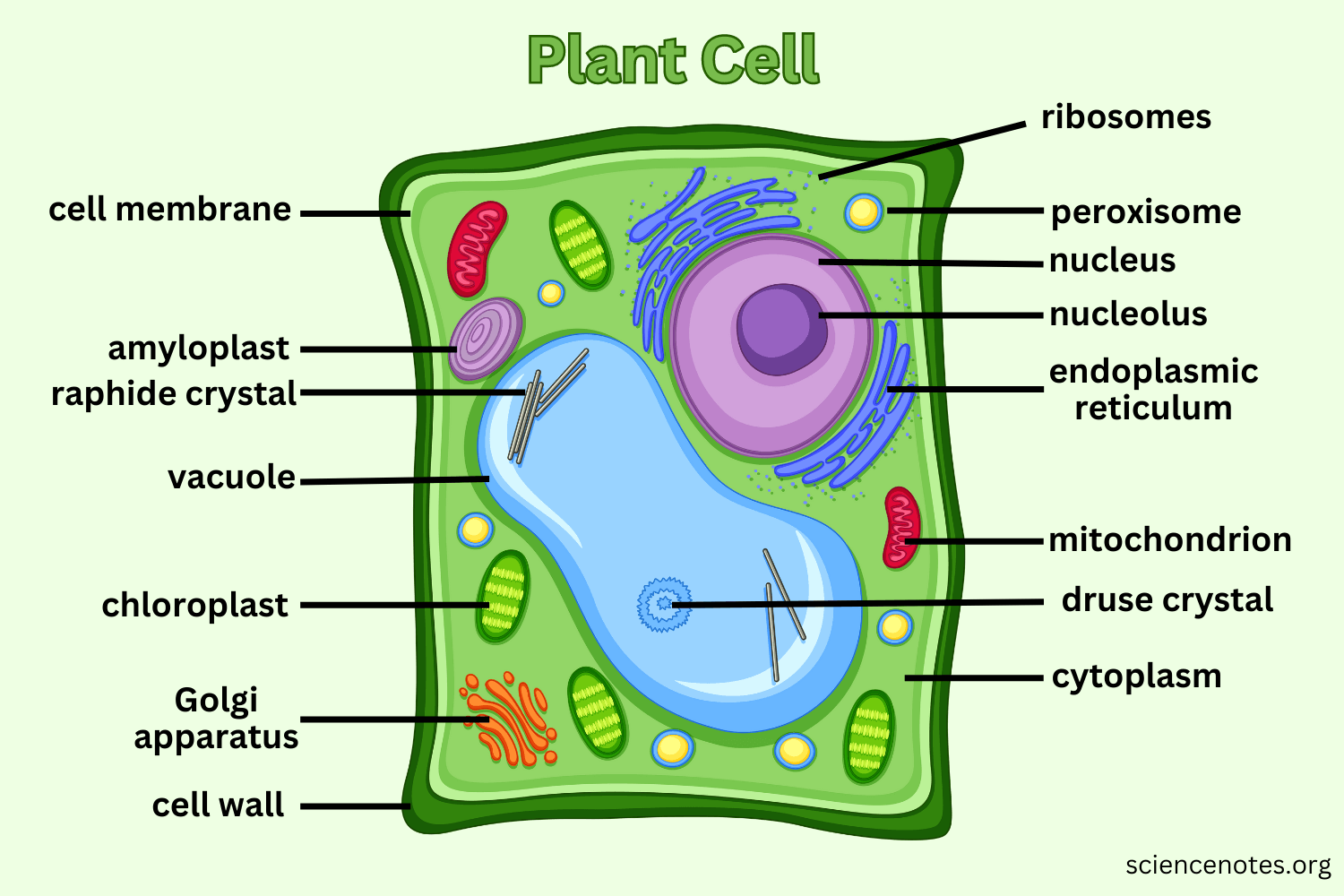
Chloroplast
Found in plant cells, it absorbs sunlight to make sugar (glucose) through photosynthesis. It also gives the plant cell its green color and contains chlorophyll.
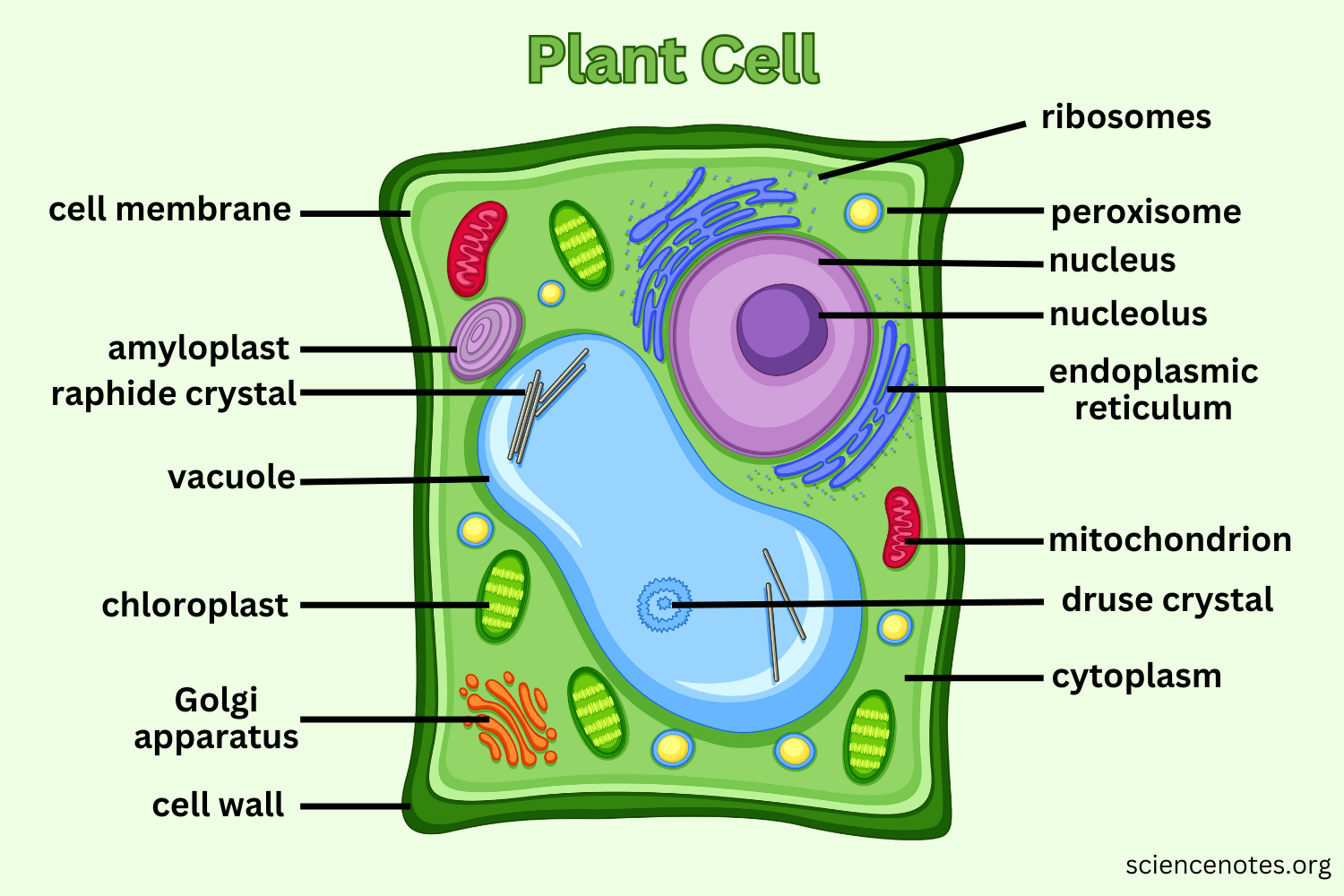
Nucleus
The brain of the cell and the largest organelle in animal cells. It controls all the cell's activities, contains the genetic material (DNA) of the cell, and has a nucleolus that plays a role in producing ribosomes.
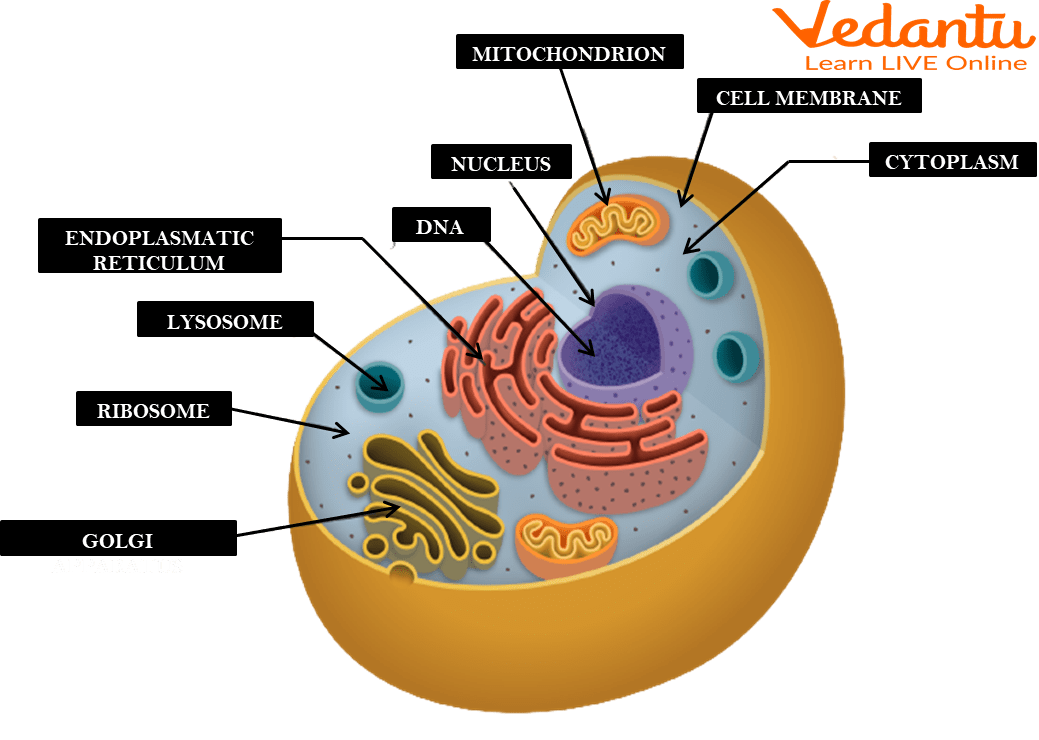
Cell membrane
Surrounds the cell and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
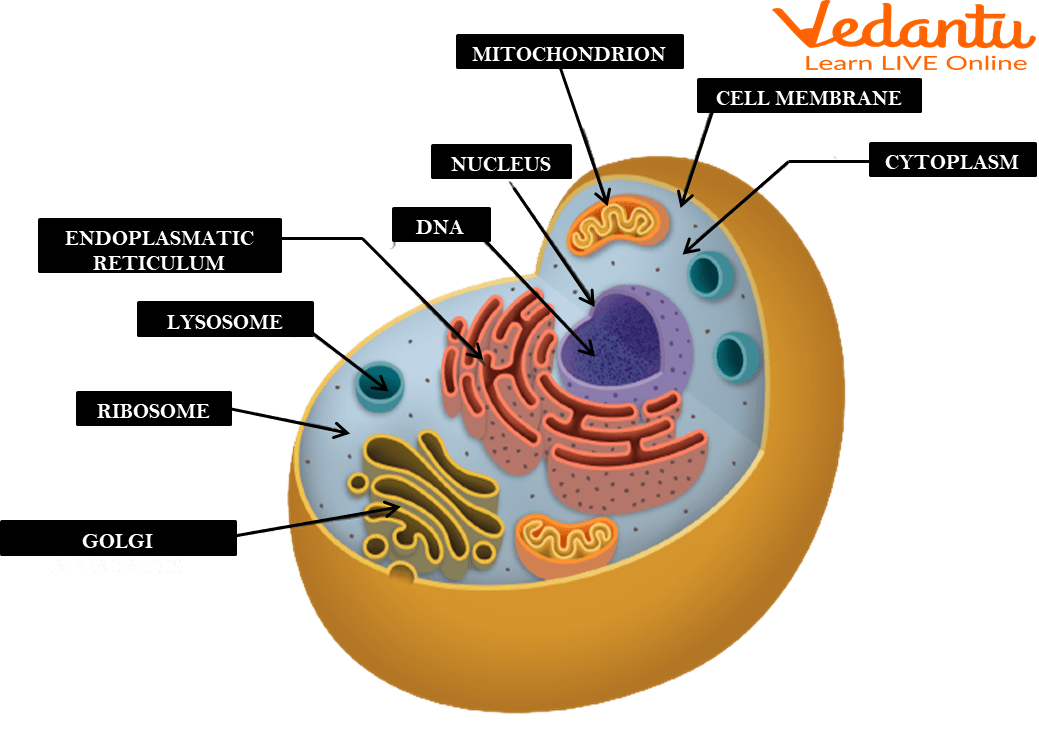
Cell wall
Present in plant cells, it provides structure and support to the cell.
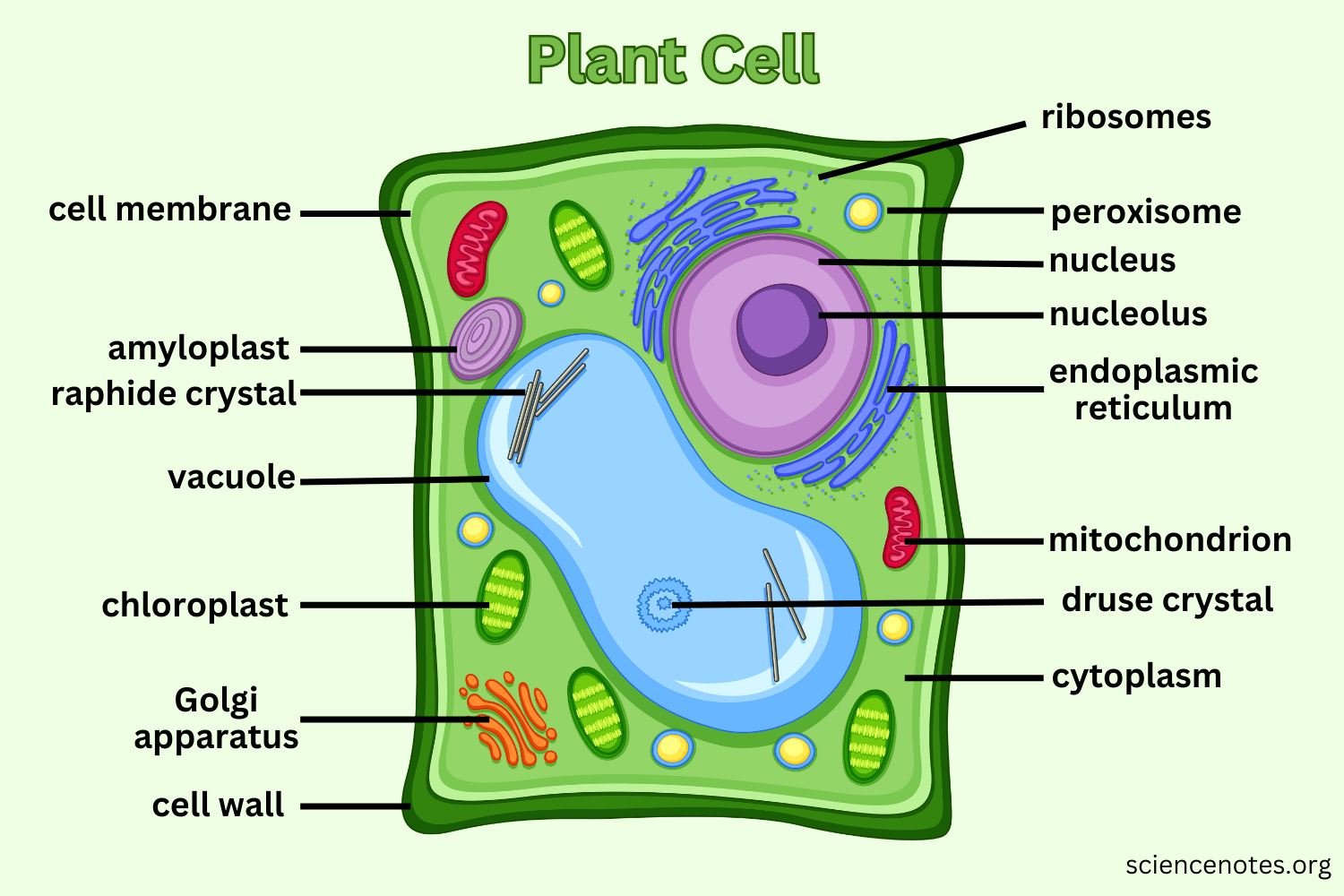
Cytoplasm
The gel-like substance inside the cell where organelles are suspended.
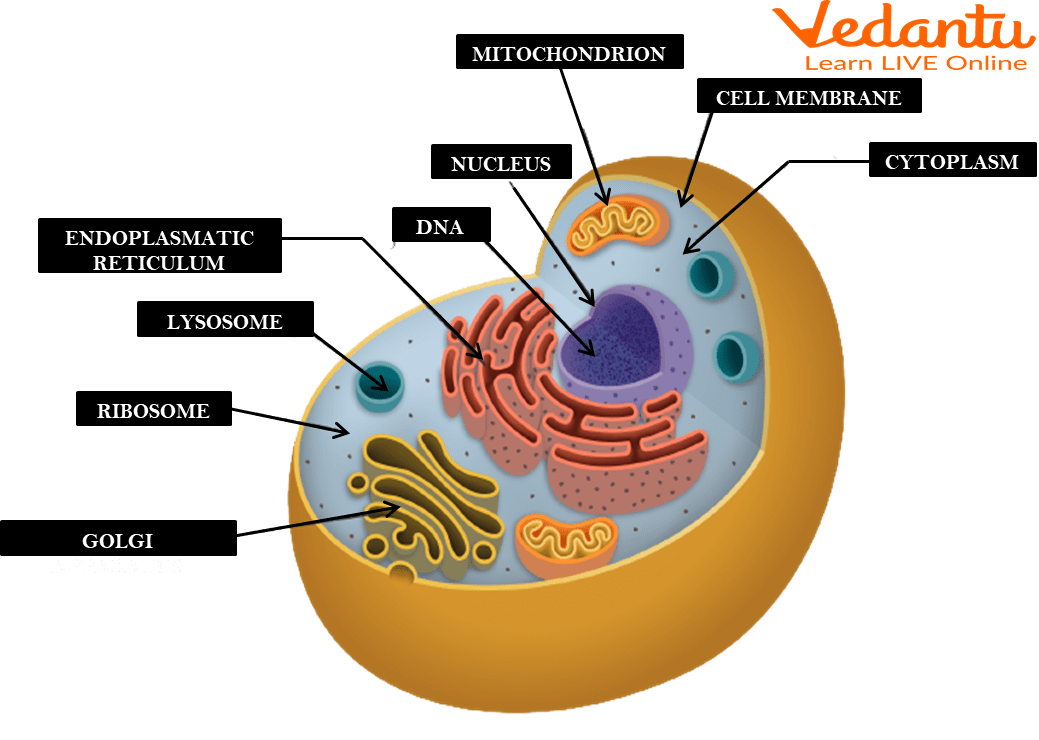
Lysosomes
Some vesicles in animal cells that contain substances to break down and recycle cellular components.
Nucleolus
Found within the nucleus, it plays a role in producing ribosomes.

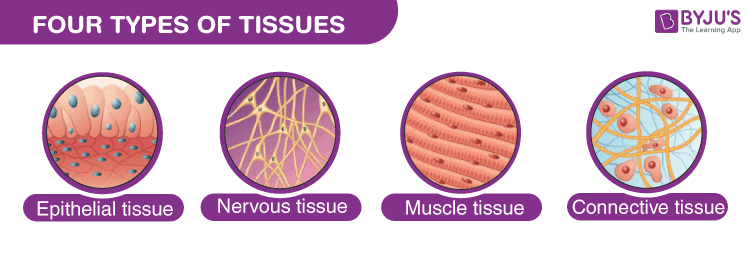
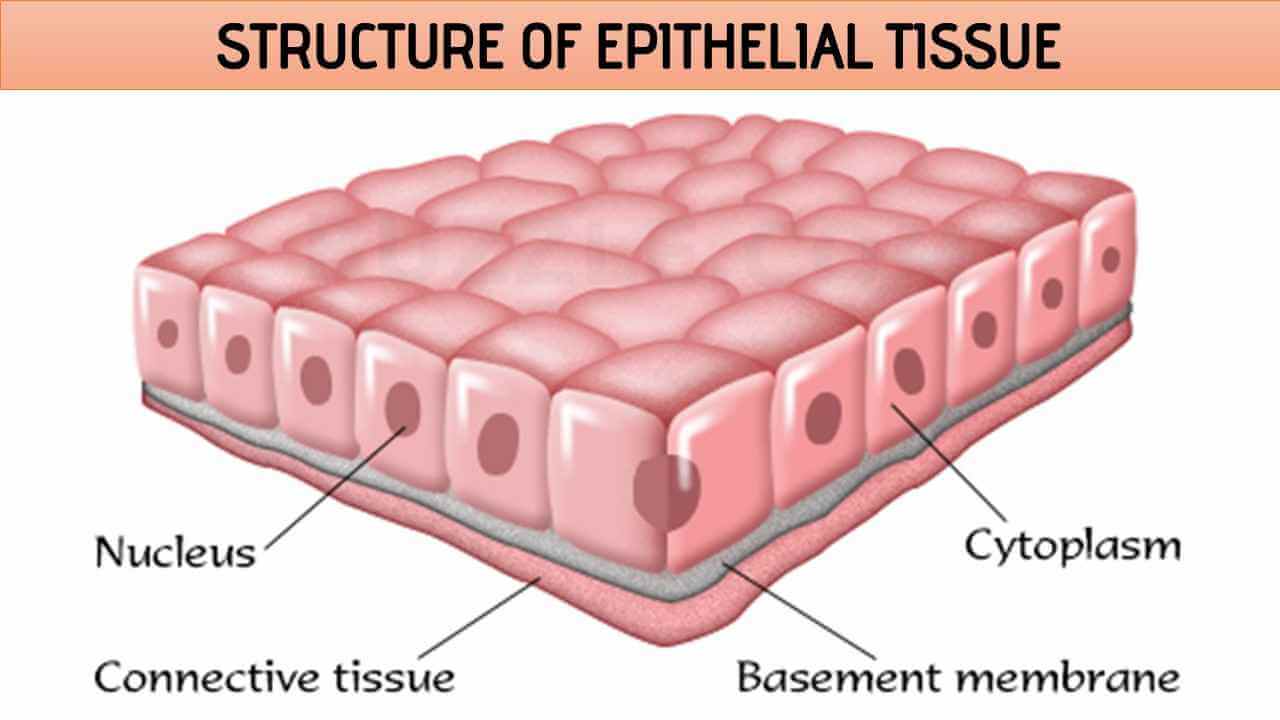
Epithelial Tissue
Protects the skin and provides lining for internal organs in animals.
Muscle Tissue
Helps in movement in animals.