Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is mitosis?
The process of nuclear division that results in 2 nuclei, each with the same number and type of chromosomes.
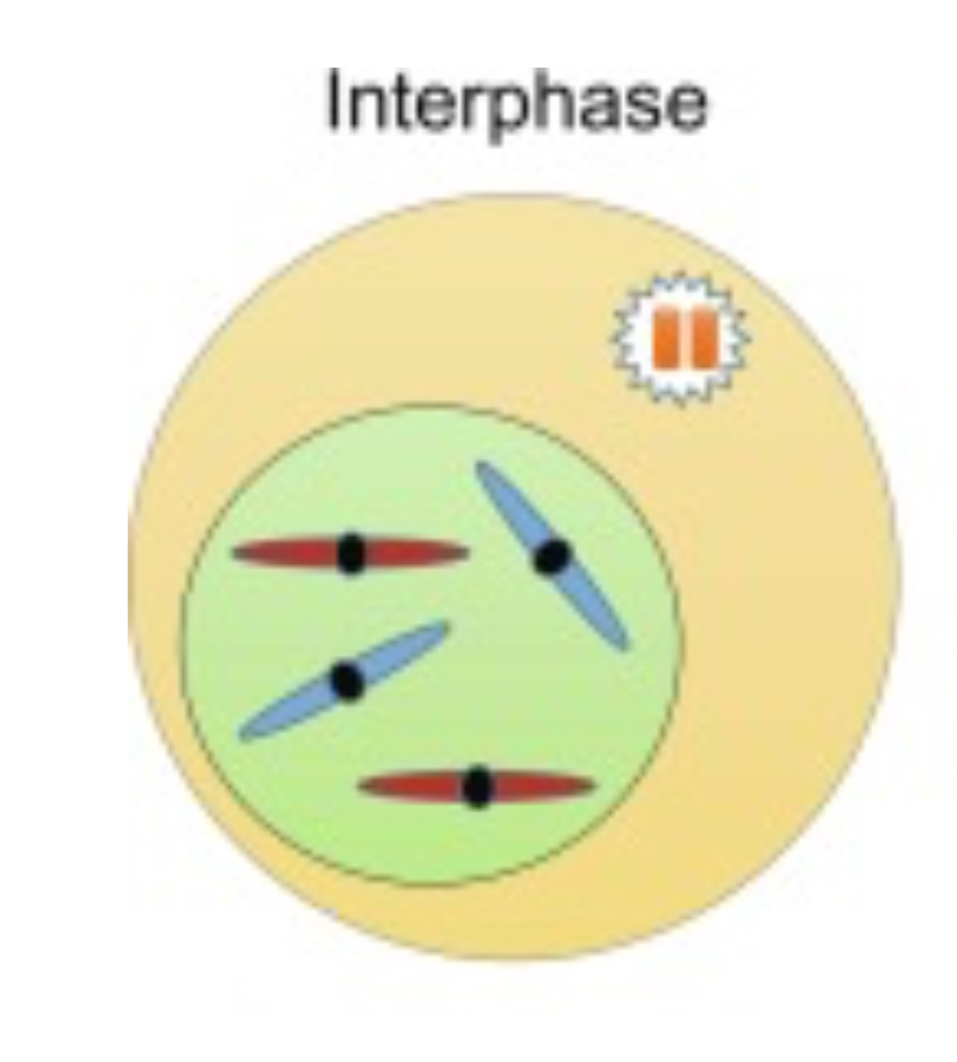
What occurs during interphase?
the size of cell increases
Organelles are made
Chromosomes are not visible (the chromatids have not condensed and are unwound)
Protein and ATP is synthesised
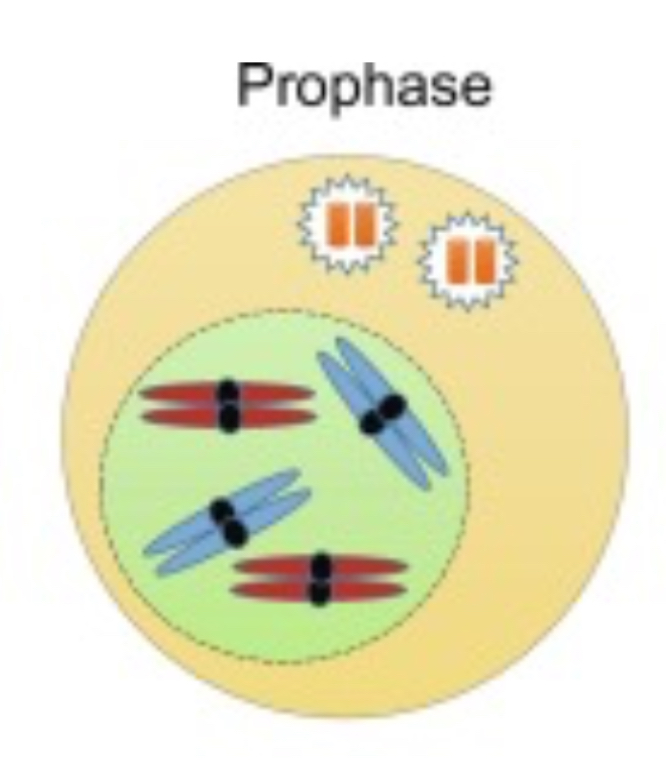
What occurs during prophase?
The chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down and the mitotic spindle begins to form.
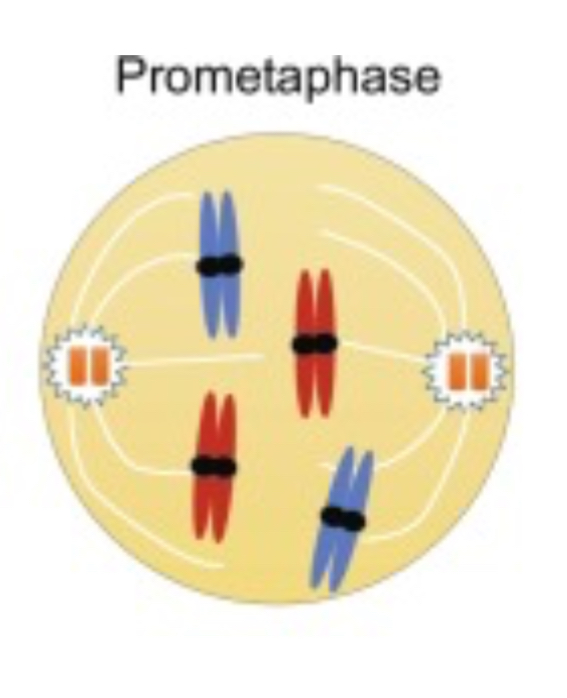
What occurs during PROmetaphase?
the nuclear envelope breaks down
the chromosomes condense further
the mitotic spindle microtubules attach to the kinetochores on the chromosomes, preparing them for separation in the next phase.
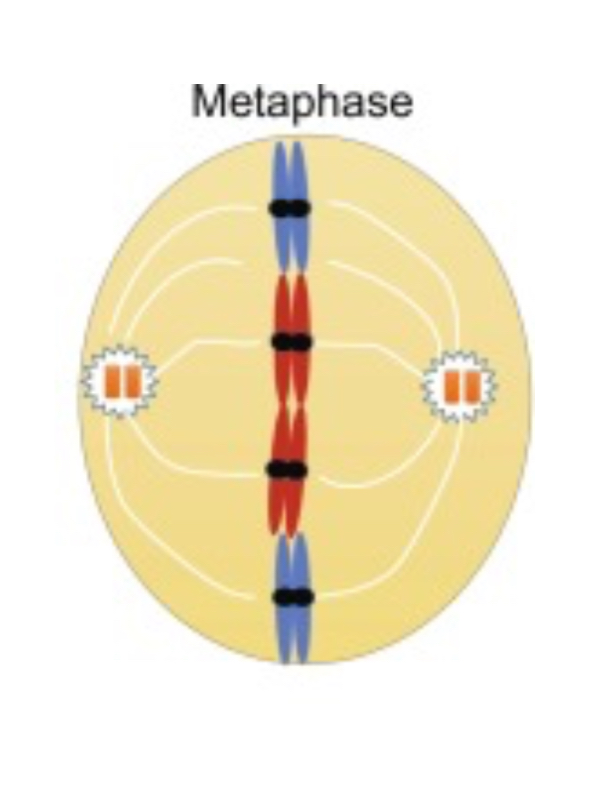
What happens during Metaphase?
The chromosomes align at the metaphase plate (an imaginary line) - this is the cells equatorial plate.
Spindles attach to the centromere of the chromosomes.
The cell's nucleus dissolves
Chromosomes condense and move together
Microtubules from centrosomes on opposite poles of the cell attach to kinetochores on chromosomes
What occurs during Anaphase?
Sister chromatids are pulled to the opposite poles of the cell.Sister chromatids are pulled to the opposite poles of the cell.
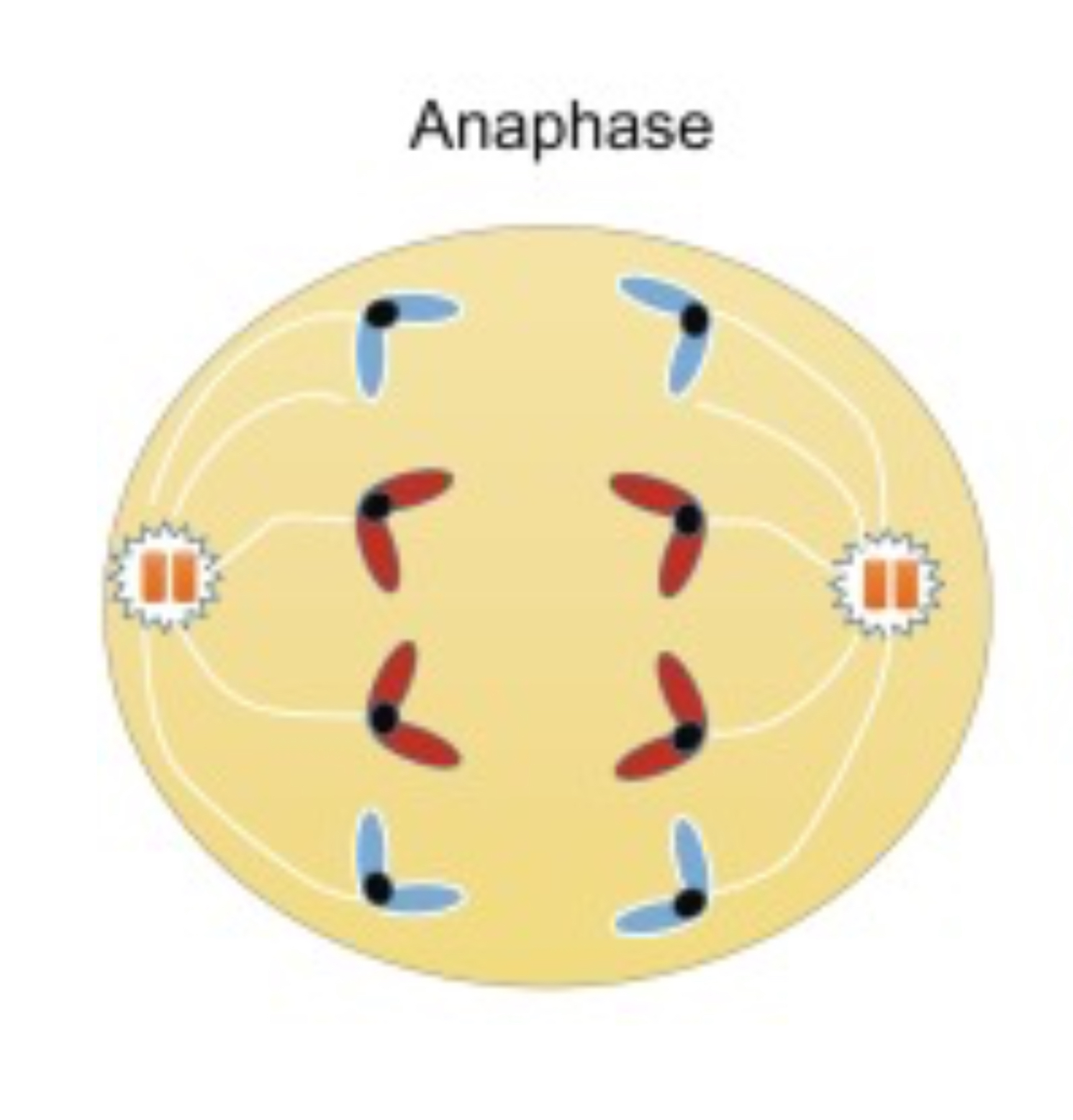
What occurs during Telophase?
The separated chromatids reach the poles , the nuclear envelope re forms around each set of chromosomes.
The chromosomes being to de-condense back into chromatin
Fibres break down
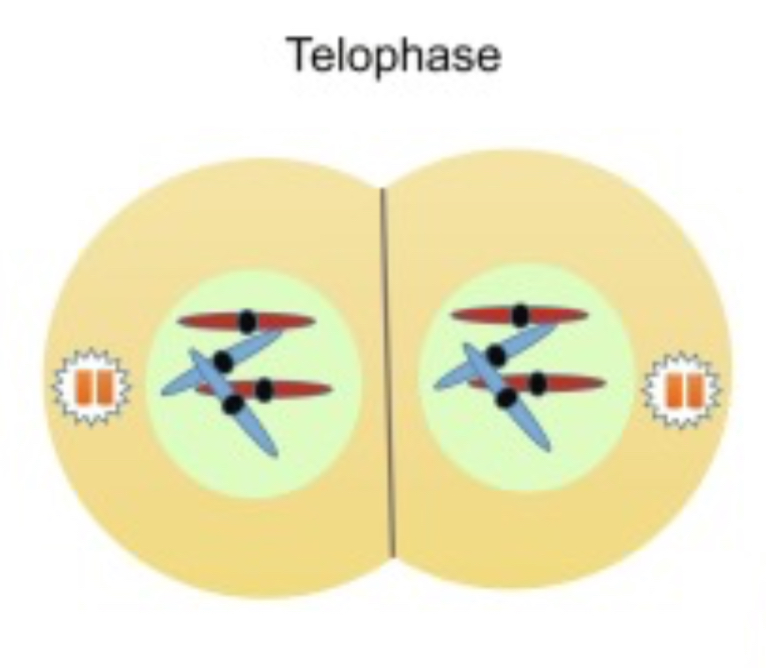
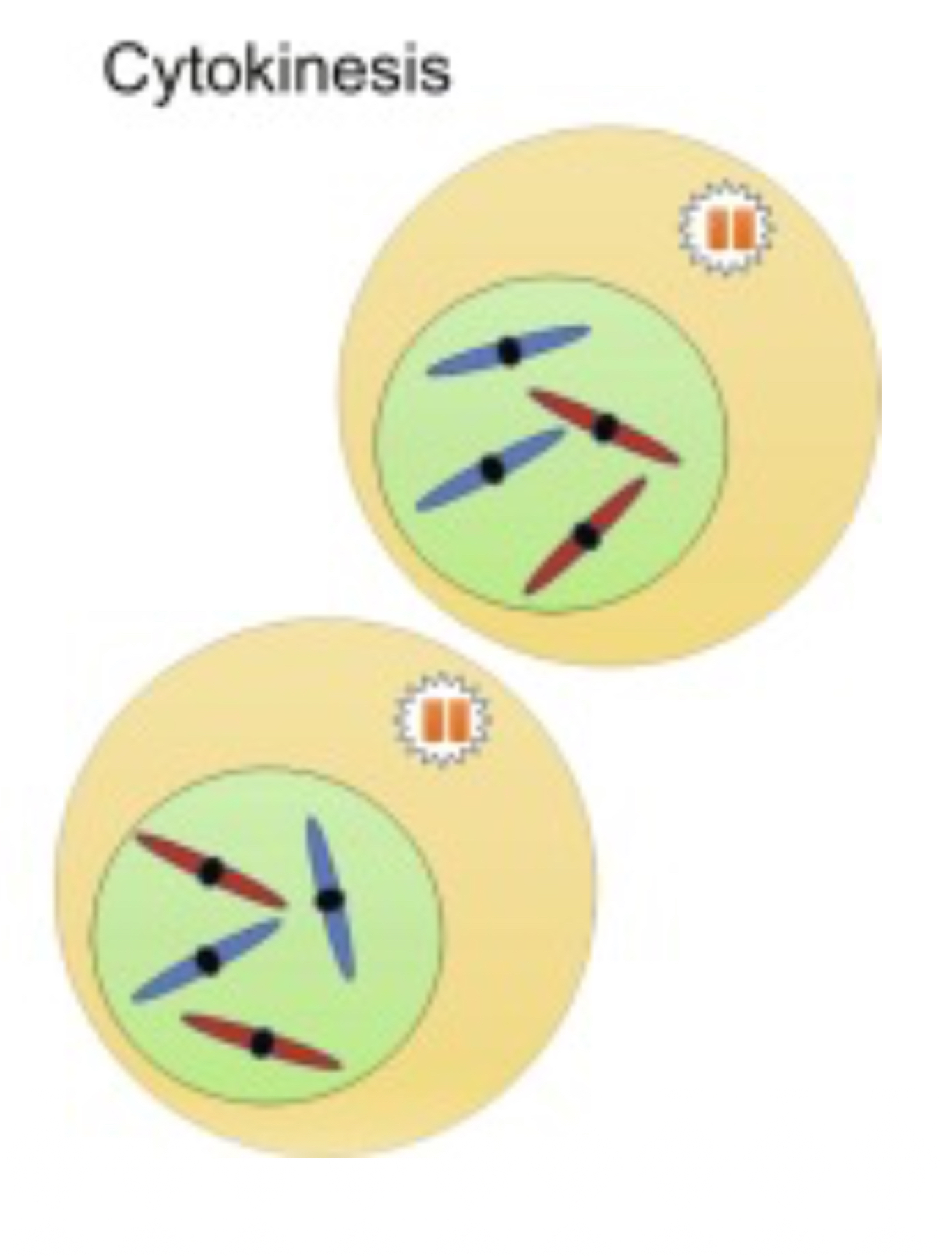
What occurs during Cytokinesis?
Cyto —> Cytoplasm, this is the process of cytoplasmic division.
This process follows mitosis and ensures that each daughter cell has its own nucleus and cellular organelles.
These are diploid.
Each cell form has a new nucleus.
How does mitosis differ from meiosis?
Mitosis results in two genetically different daughter cells while meiosis produces four genetically diverse gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Why is mitosis important to multi cellular organisms?
Mitosis is crucial for…
Growth
Development
Repair of tissues
Allows for the replacement of dead or damaged cells.
What processes are part of the cell cycle but NOT mitosis?
Interphase and Cytokinesis.
What is a chromosome?
A thread like structure made of protein and DNA
What are Homologous chromosomes?
A pair of chromosomes, one maternal and one paternal.
The same size and shape.
What is a chromatid?
One of the two copies of a chromosome that are joined together by a single centromere prior to cell division.
What is the Centrometre?
The region where the 2 sister chromatids are attached; the point where the miotic spindle attaches during metaphase.
What is a haploid cell?
Cells that contain a single set of Chromosomes.
What is a diploid cell?
A cell which contains 2 sets of Chromosomes
Give 5 reasons for mitosis?
Maintain chromosomes number
Growth
Tissue repairs
Replace cells that have died
Asexual reproduction
In plants, mitosis occurs in the…
Meristem.
Give 5 places where mitosis happens…
Skin
Gut lining
Bone marrow
Hair follicles
Meristem cells in plant root/ shoot tips.
Where does mitosis not occur?
The central nervous system
This is due to the neurones not having a centromere/ centrioles which is necessary for mitosis.
Also, the cells are highly specialised and the addition of new nerve cells could disrupt those pathways, affecting the normal function of the body.
If a cell plate occurs during telophase…
The mitosis is in a plant cell.
What is meiosis?
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically different gametes.
List the stages of meiosis in order?
The stages are PMAT x 2
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase
What occurs during Prophase I?
Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over, forming tetras.
The nuclear envelope breaks and the spindle apparatus forms.
Chromosomes become shorter and thicker.
What occurs during Metaphase II?
Bivalent alligator at the metaphase plate and spindle fibres attach to the centromeres of the Homologous chromosomes.
What occurs during Anaphase I?
Spindle fibres pull apart the genetic material by moving to opposite sides of the cell.
What occurs during Telophase I?
The chromosomes reach the poles and he nuclear envelope may reform the cell undergoes cytokinesis resulting in 2 haploid daughter cells.
What occurs during Prophase II?
The nuclear envelope breaks down again and the spindle appratus
What occurs Metaphase II?
The second division of meiosis.
Chromosomes align along the metaphase plate.
Spindle fibres extend from the centromeres and attach to the
What occurs during Anaphase I?
What occurs during Telophase II?
Why is meiosis important?
Provides genetic variation.
Produces genetic diversity.
It form sex cells during sexual reproduction.
It maintains the correct number of chromosomes.
How does meiosis keep the chromosome number constant between different generations?
Synapsis
the moving together of homologous chromosomes in prophase I
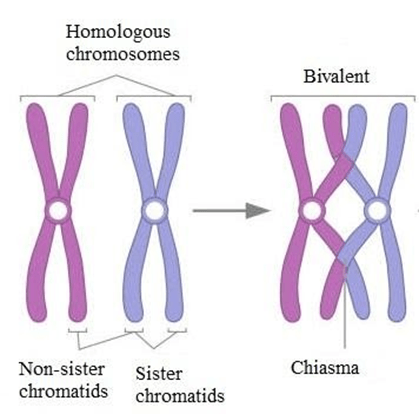
What does Bivalent mean?
Homologous (NON-SISTER) chromosomes which cross over
What is the Chiasma?
The point of contact, the physical link, between two (non-sister) chromatids belonging to homologous chromosomes.
What is Synapsis?
The pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis.
How are mitosis and meiosis involved in the production of spermatazoa?
What is the proto-oncogene?
Normal healthy gene that codes for proteins to make the cell cycle happen.
What is the oncogene?
A mutated version of the proto-oncogene that is over expressed and leads to uncontrolled mitosis.
What does malignant mean?
What does benign mean?
What is a tumour suppressor gene?
A gene that normally slows the cell cycle to prevent uncontrolled cell divisom
What is binary fission?