Inflammatory Response - Neutrophils and Macrophages
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
innate immunity
molecules and cells that distinguish host from infectious agents by recognizing conserved motifs
adaptive immunity
cells with exquisitely specific receptors for a potentially unlimited number of targets
sentinel cells
if antigens make it into the body, what recognizes the invaders and generates signals to attract and activate defensive cells
dendritic cells, mast cells, macrophages, eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes
give some examples of sentinel cells (the first three listed are the MAIN THREE)
true; the body sees damages cells as foreign
true/false: the inflammatory/immune response can be set off both by foreign substances and by cellular damage
damage associated molecular patterns
what does DAMP stand for?
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns
What does PAMP stand for?
Toll-like receptors
What allows the host cell to recognize DAMPs or PAMPs?
intracellularly (the TLRs are transmembrane proteins)
When the toll like receptors bind to PAMPs, they initiate a signal WHERE?
Nuclear factor - Kappa B (NF-kB)
the binding of TLRs to PAMPs initiates a signal pathway that culminates in _______________.
inflammatory gene transcription
NF-kB is a major regulator of what?
sentinel cells
TLRs are found on the surface of what type of cells?
vasodilation
______________ is the hallmark of the acute inflammatory response
cytokines
sentinel cells release ______ in order to cause vascular changes and attract and activate phagocytic cells
neutrophils
What are the first cells to arrive after cytokines have been released? These cells also deal with the majority of invading organisms.
macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells
what are the three most important sentinel cells
true
true/false: macrophages are scattered through most of the body but may have different names based on location
Pro-inflammatory cytokines;
TNF-alpha, IL-1, IL-6
What specific substance is produced to call other macrophages to the area and give some examples.
NF-kB, pro-inflammatory genes, Cytokines
BIG PICTURE:
Sentinel cells circulate and recognize pathogens via PAMP/TLR interactions. They then send intracellular signals to activate __________ which leads to the regulation of ______- ________________ and production of ______________________.
tumor necrosis factor alpha
What does TNF-a stand for?
endothelial cells, vasodilation
both TNF-a and IL-1 activate ________________ in order to cause __________________
IL-1, IL-6, chemokines
What 3 cytokines (that we were given) do macrophages and endothelial cells both produce?
causes bone marrow to release more macrophages
AND
causes the liver to produce acute phase protein
What does interleukin-6 (IL-6) actually DO?
regulate cell movement
what do CHEMOkines actually do?
lamellipodia
Cytokines trigger the formation of _________ on leukocytes.
Beta integrins
cytokines increase the expression of adhesion molecules (specifically _________) on leukocytes
IL-1B, IL-6, TNF-a
what inflammatory mediators come from macrophages and activate leukocytes and endothelial cells + systemic reactions
redness, heat, swelling, pain, loss of function
what are the five cardinal signs of inflammation?
redness and heat
what signs of inflammation are caused by increased blood flow to the site
swelling
what sign of inflammation is caused by accumulation of fluid and cells?
pain
what sign of inflammation is caused by stimulation of sensory neurons by inflammatory mediators
loss of function
what sign of inflammation is caused by tissue damage
loss of appetite, fever, anorexia, sleepiness, depression
when cytokines act on the hypothalamus, what reactions occur?
increased synthesis of acute-phase proteins, iron sequestration
when cytokines act on the liver, what reactions occur?
increased white cell production, neutrophilia
when cytokines act on the hypothalamus, what reactions occur?
liver
what organ produces increased amounts of acute phase proteins in response to the proinflammatory cytokines
acute phase proteins
the liver produces increased amounts of ________ in response to proinflammatory cytokines
proinflammatory cytokines
the liver produces increased amounts of acute phase proteins in response to what?
a1, a2, B
what are the three specific protein fractions that are features of inflammation?
y fraction
which fraction of the serum protein electrophoresis are the antibodies found in?
serum protein electrophoresis
what is this?
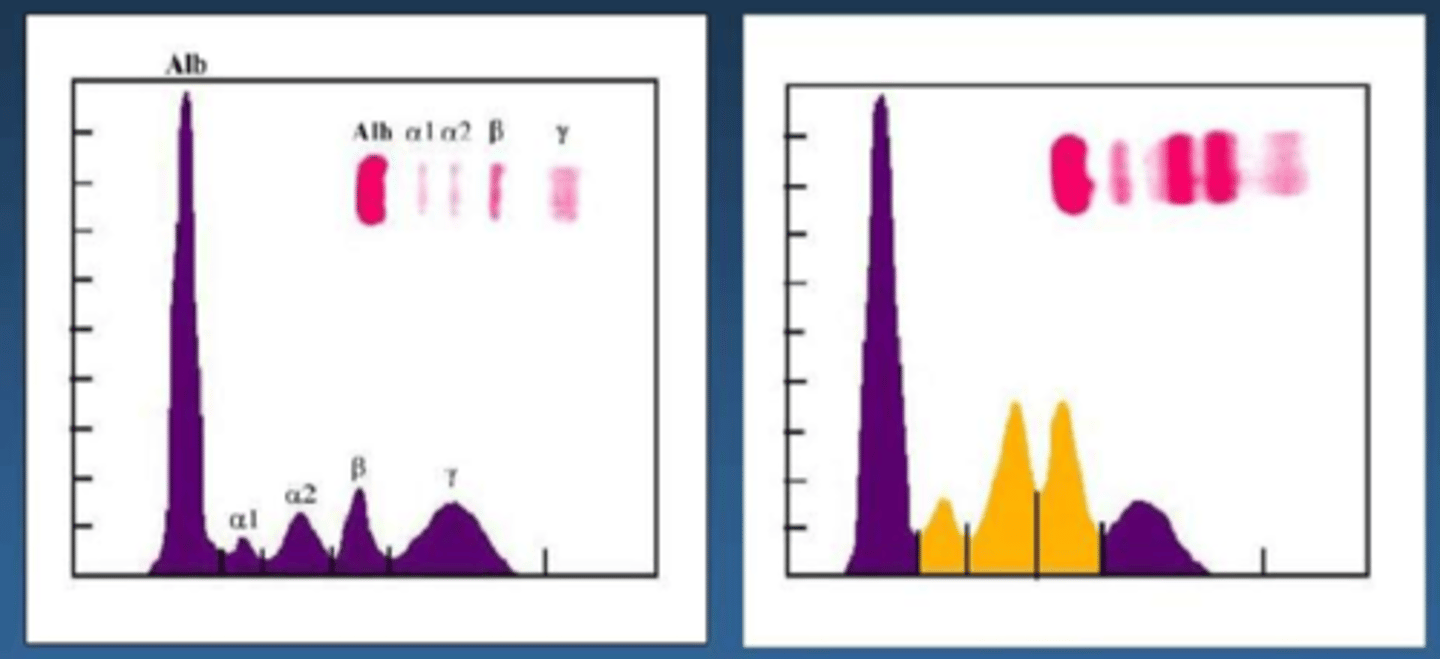
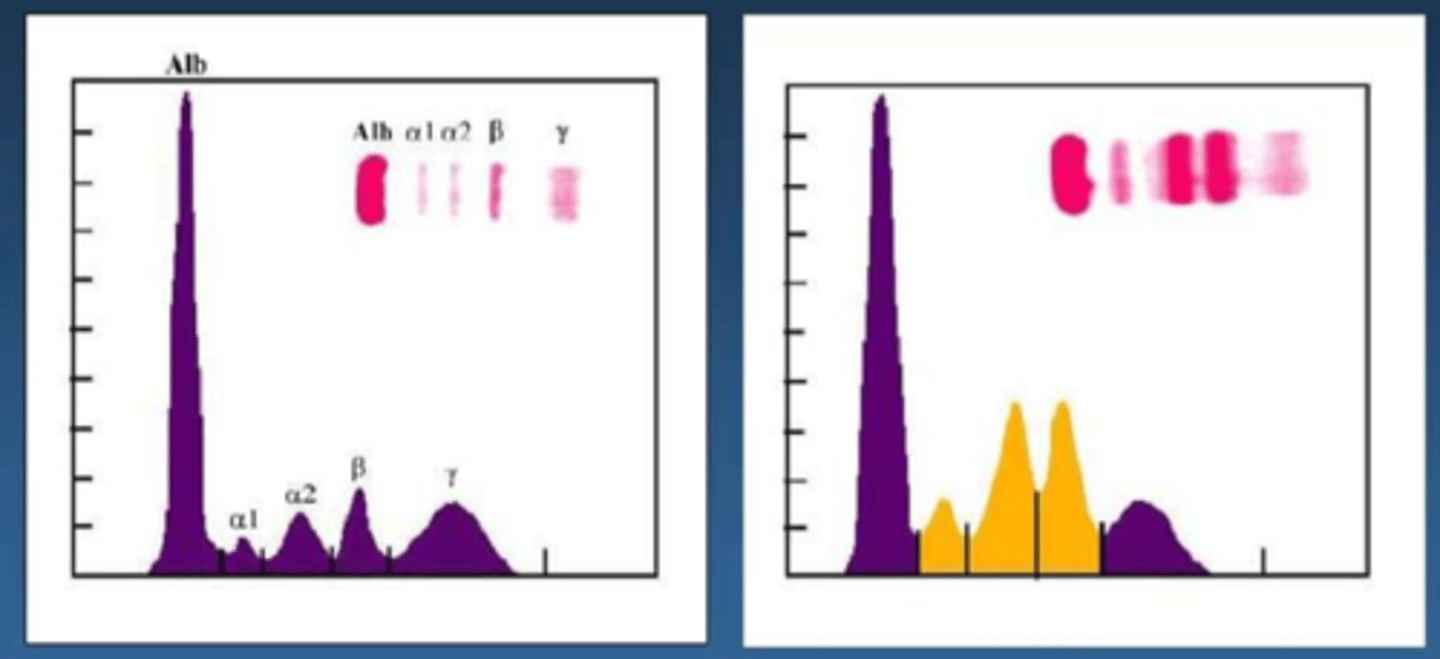
right side
which of these charts is showing a sample with inflammation?
arterioles dilate,
capillaries become more permeable,
leukocytes leave vessels
inflammation consists of what three changes in the vessels around the area of infection?
false; vasoconstriction happens first BRIEFLY to stop potential hemorrhage
True/false: Vasodilation is the hallmark of acute inflammation because it is the first step that happens
cytokines
What directs which type of WBCs get to squeeze through the interstitial space and where the WBC go.
high affinity state integrins
during the initial stages of the leukocyte adhesion cascade, the WBC rolls along the edges of a vessel and binds to the surface epithelium in a fast-on/fast-off sequence. What actually brings the WBC to a stop?
toll-like receptors, cytokines (TNF, IL-1), vasodilation
________ are activated on macrophages and cause them to release ________ which act on the blood vessel's epithelium to cause ____________
vasodilation causes turbulence which pushes them to the outside
normally, WBCs hang out in the center of the blood vessel. What pushes them to the outside during inflammatory response?
suppurative bronchopneumonia
what example of leukocyte adhesion cascades were we given where cytokines increase blood flow to the lungs, resulting in leukocytes entering alveolar spaces?
leukocyte adhesion cascade
generally speaking, what mechanism enables the leukocytes to move from circulation to the site of inflammation?
neutrophil
what is the major blood leukocyte in most animals?
neutrophil
which WBCs are the first cells to arrive at the site of inflammation?
Macrophages
which cells follow the neutrophils to inflammatory sites
true
true/false: in order for a neutrophil to perform a specific action, the correct receptor must first be triggered
neutrophil net
Activated neutrophils only get one shot, so they release ________ to direct neutrophil granules towards the inflammatory stimulus
MPO, elastase, cathespin G
what are some things that are released from a neutrophil in the neutrophil net?
nuclear envelope ruptures
what is the first step when releasing the neutrophil net?
proteolytic breakup of chromatin
What is the second step of the release of a neutrophil net
plasma membrane ruptures, releasing the net
what is the third and final step of the release of a neutrophil neT?
respiratory burst
in addition to casting the neutrophil net, neutrophils ungergo ________ by which numerous antimicrobial compounds and radicals are produced that can neutralize or eliminate pathogens
oxygen
respiratory burst MUST occur in the presence of what?
NADPH oxidation and superoxide production
what is the first step of respiratory burst
hydrogen peroxide
superoxide radicals are very intense radicals that can become what? (this is the second step of respiratory burst)`
further conversion of hydrogen peroxide into other ROS
what is the third step of respiratory burst
simultaneous neutralization of ROS
what is the fourth step of respiratory burst
defensins, myeloperoxidase, neutral and acid hydrolase, lysozyme
what are in the primary granules in neutrophils
lactoferrin, collagenase, lysozyme
what are in secondary granules in neutrophils?
bactericidal
what do defensins do?
spurs respiratory burst
what does myeloperoxidase do?
degrades bacteria
what do neutral and acid hydrolases do?
destroys bacterial cell walls
what does lysozyme do?
binds iron
what does lactoferrin do?
degrades connective tissue
what does collagenase do?
TNF-a
what potent macrophage stimulator does Elastase Cathepsin G trigger when it's released from the neutrophil
myeloid stem cells
what do macrophages arise from?
monocytes
what do macrophages mature into in the blood stream?
true
true/false: just like literally everything else in this class, macrophages have specific receptors that must be triggered to enable that they perform the correct functions
Interleukins 1, 6, 12, 18, 23, and Tumor necrosis factor a
what are the important cytokines produced by macrophages? (6 of them)
stimulates T cell growth and acute phase responses, triggers inflammation, cytotoxic
what does tumor necrotic factor a do?
costimulator of Th2 cells, stimulates acute-phase responses
what does IL-1 do?
promotes B cell differentiation, stimulates acute-phase responses
What does IL-6 do?
costimulator of Th1 cells
what does IL-12 do?
promotes IFN-y production by Th1 cells
what does IL-18 do?
stabilizes Th17 cells
what does IL-23 do?
macrophages
when neutrophils degrade, they also damage tissue and someones gotta clean that up. Who?
macrophages
what is the most efficient phagocytic cell?
neutrophils, monocytes, dendritic cells
what are some phagocytic cells besides macrophages?
chemotaxis, adherence, ingestion, digestion
what are the four steps of phagocytosis?
chemotaxis
__________: migration to the offending agent via chemotactic agent
adherence
_______: mediated by cell surface receptors, step 2 of phagocytosis
ingestion
________: when the macrophage engulfs the particle
digestion
_________: breakdown of particle effectively neutralizing or killing the agent
binding of a pathogen to phagocyte surface
what triggers phagocytosis?
true
true/false: because it is a powerful reaction, more than one receptor is needed to trigger phagocytosis
opsonization
______________ is a process by which molecules bind to the surface of a pathogen making it more susceptible to phagocytosis
opsonins
the molecules that bind to pathogens in order to complete opsonization are called _________
crosstalk
interactions between different signal transduction pathways or between different types of cells (neutrophils and macrophages) to coordinate movement and battle strategies
dog, rabbit, guinea pig, rat, mouse
what species clear particles in the blood primarily in the liver and spleen
calf sheep and cat
what species clear particles from the blood primarily in the lungs?
when toll like receptors bind to damage or pathogens (DAMP/PAMP)
what is the point of no return that will set in motion the inflammatory response?