DENT Fun. I - Cell Structure & Organelles
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Non-Membrane Bound Organelles
- Ribosomes
- Proteasomes
- Cytoskeleton
- Centrioles/Basal Bodies
- Cilia/Flagella
Membrane-Bound Organelles
- Plasma Membrane
- Nucleus
- ER
- Golgi
- Lysosomes
- Endosomes
- Peroxisomes
- Mitochondria
Functions of Cell Membranes
- Structural Integrity
- Selective Permeability
- Regulates Cell-Cell Interactions
- Carries Receptors
- Transduces Extracellular signals into Intracellular Events
Composition of Cell Membranes
Lipids
- Phospholipids
- Glycolipids
- Cholesterol
Proteins
- Integral Proteins: Transmembrane
- Peripheral Proteins: Located on one side of the membrane
Lipids are ____.
amphipathic; have hydrophilic and hydrophobic components
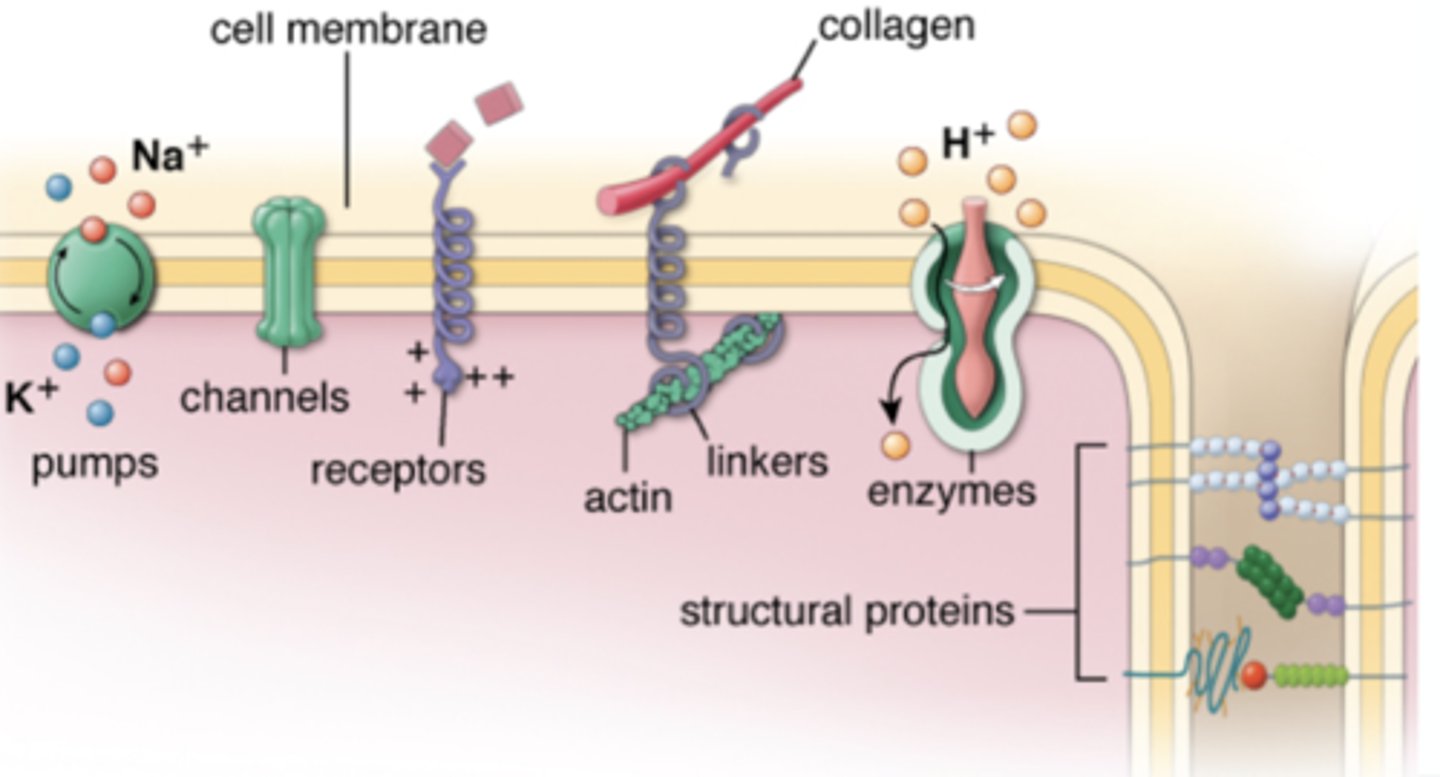
What are the 4 Membrane Proteins?
- Channel
- Pumps/Carriers
- Surface Receptors
- Linkers/Structural
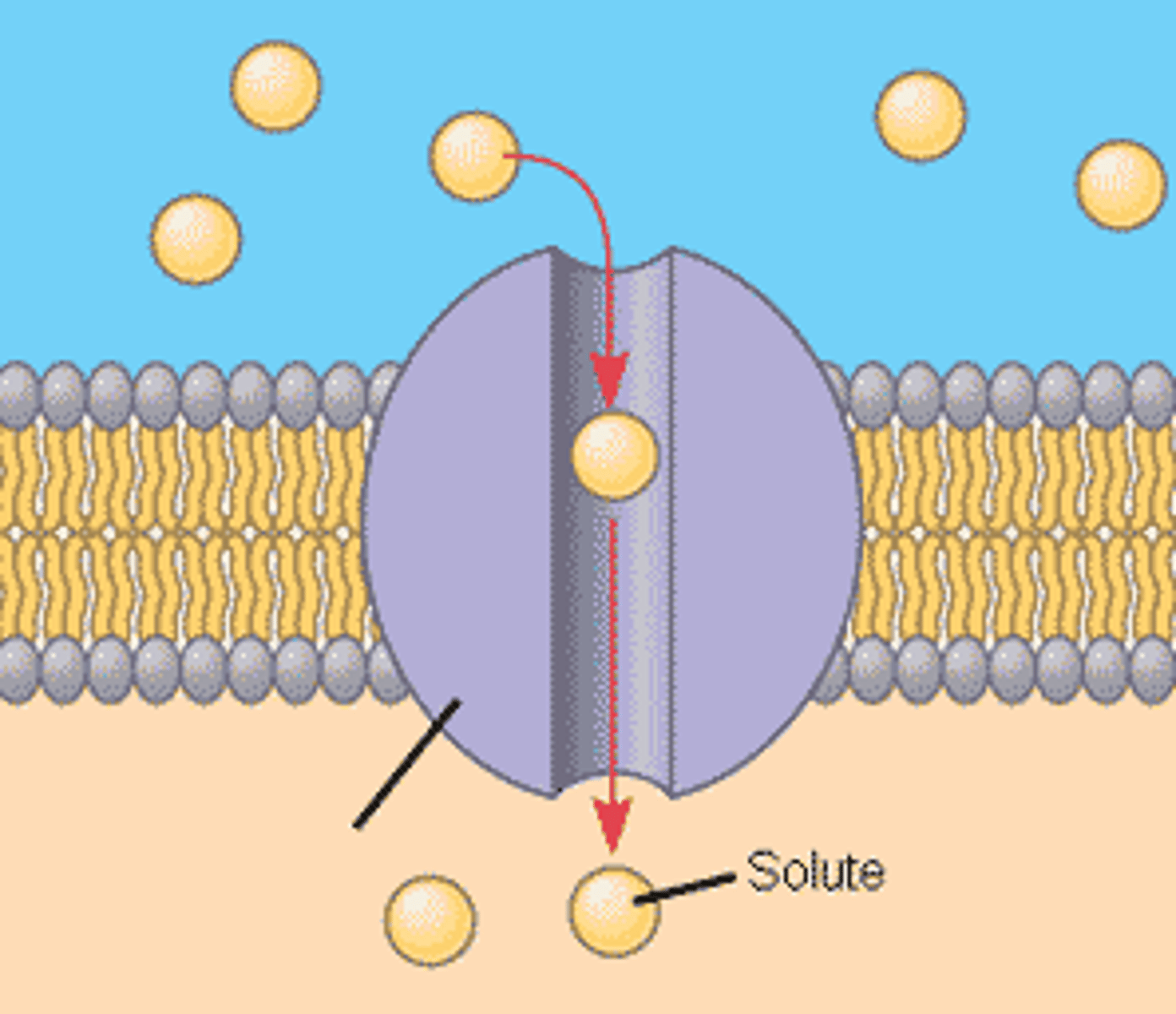
Channel Proteins
Allow passage of a specific ion
- Voltage-Gated
- Ligand-Gated
- Mechanical
Pump/Carrier Proteins
Bind and transport molecules/ions
- Na/K Pump
- Glc Transporter
Surface Receptors
Bind extracellular ligands to elicit a cellular response
- Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
- G-Proteins
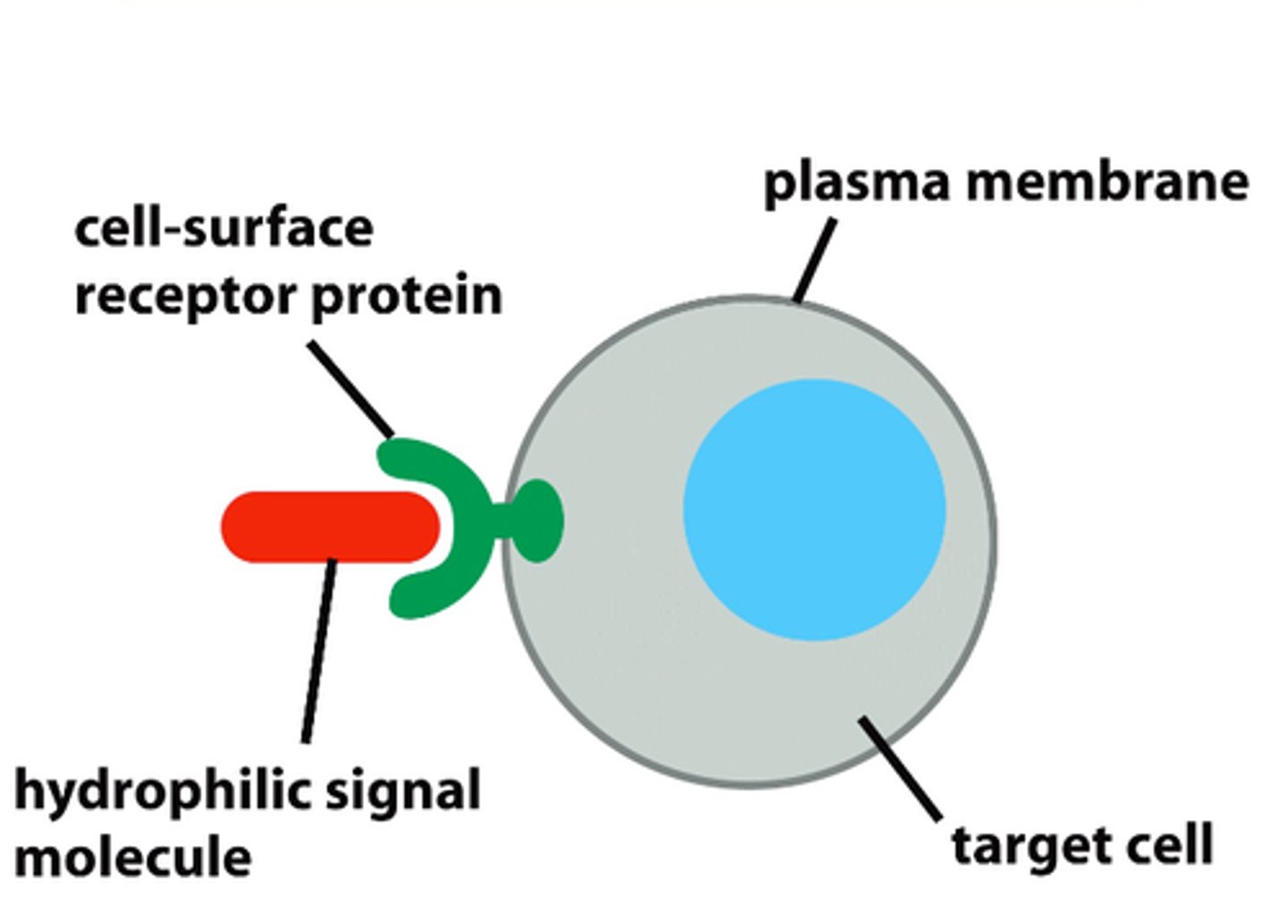
Linkers/Structural Proteins
- Involved in cell-cell and cell-matrix attachment
- Serve as scaffolds for cytoskeleton
Major Proteins in the Nucleus
- Histones
- Ribosomal Proteins
- Replication/Transcription Factors
The nucleus during interphase contains both ____ and ____.
heterochromatin/euchromatin
The nucleus has a ____ nuclear envelope.
double-membrane
it is still continuous with the cell membrane
Nuclear Envelope
Double-membrane system that separates the genetic material from the cytoplasm
- Inner Membrane is associated with the Nuclear Lamina
- Outer Membrane is contiguous with the ER
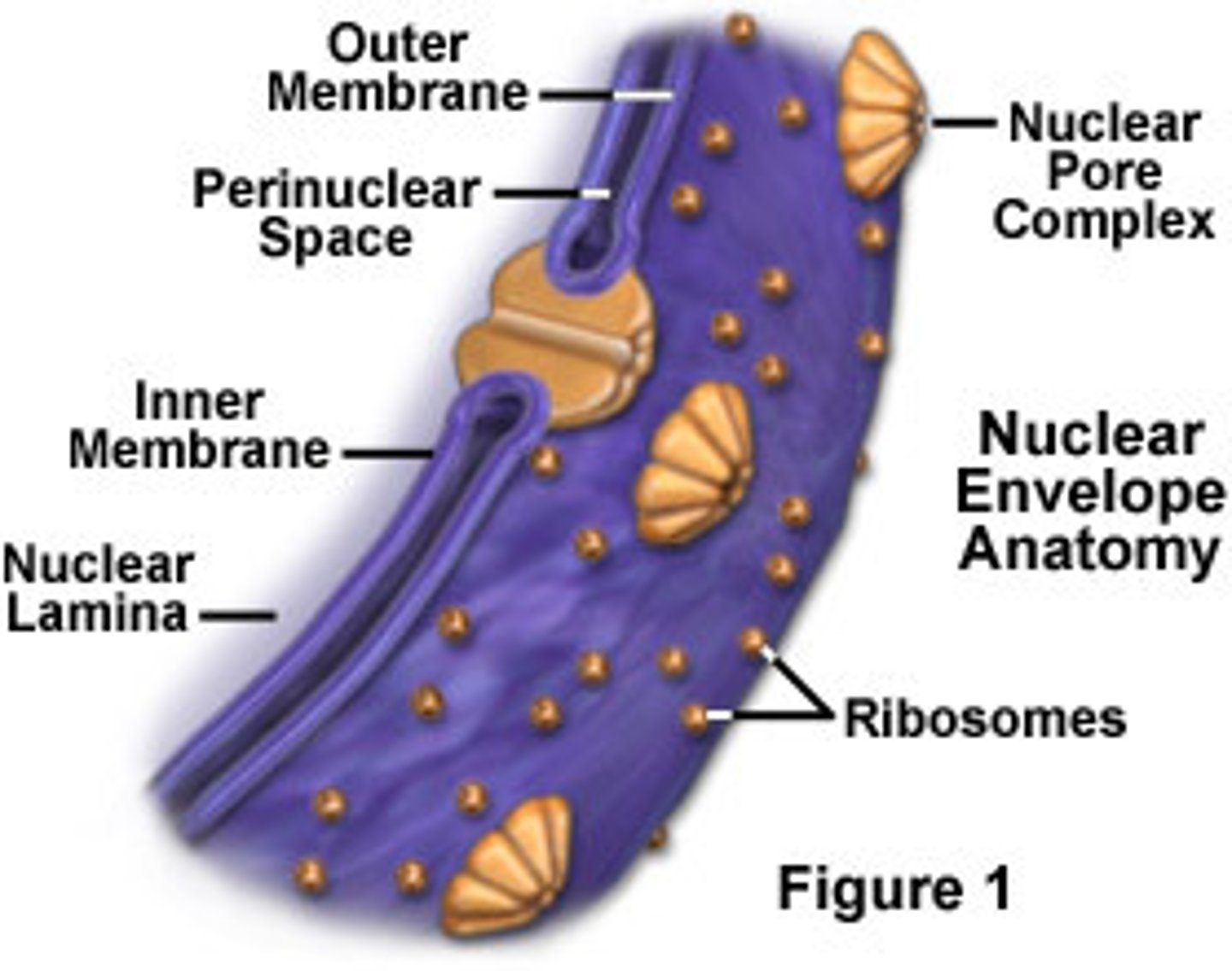
Nuclear Pores
Structures in the nuclear envelope that allow passage of smaller molecules between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm
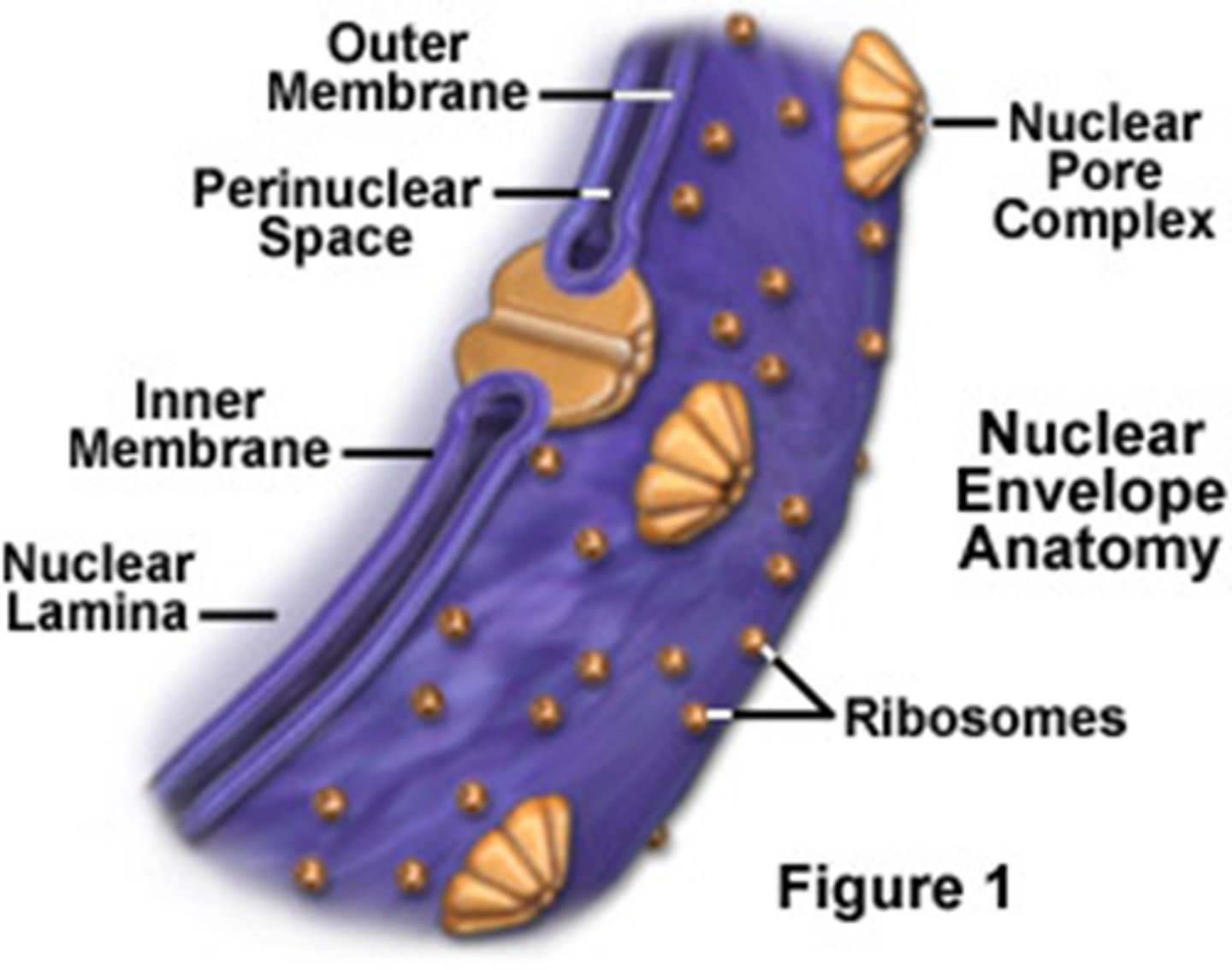
Larger molecules require a ____ to enter the nucleus.
nuclear localization signal
Amino acid sequence
RNA is transported through Nuclear Pore Complexes as ____.
ribonucleoproteins
Nucleolus
Site of rRNA synthesis and ribosome assembly
Nucleosome
- Functional unit of Euchromatin
- Consists of a core of Histone Proteins
Cell Cycle
(1) G1: Interphase
(2) S: Synthesis
(3) G2
(4) M: Mitosis
Mitosis
(1) Prophase
(2) Metaphase
(3) Anaphase
(4) Telophase
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death via caspases that are activated within the cell
What's the difference between Apoptosis and Necrosis?
Apoptosis is an active process while necrosis results from acute injury
Ribosomes
- Creates proteins from mRNA and tRNA
- Consists of a small and large subunit
As many as 11-15 ribosomes can be on one mRNA, creating a ____.
polyribosome
ER Signal Sequence
A short amino acid sequence that marks a polypeptide for transport to the ER, where synthesis of the polypeptide chain is completed
Where can proteins made in the cytosol go to?
- Cytosol
- Mitochondria
- Peroxisomes
- Nucleus
Where can proteins made in the ER go to?
- Cell Membrane
- Secreted from Cell
- Lysosomes
Any protein made in the ER will be involved in the ____ pathway.
secretory
Anterograde Trafficking
Movement of substances away from the center of the cell
Retrograde Trafficking
Movement of substances to the center of the cell
Rough ER
Site of synthesis for membrane and secretory proteins
Smooth ER
Site of lipid synthesis
The Rough and Smooth ER are separate structures (T/F)
False; they are contiguous
____ concentration is kept high in the ER.
Ca2+
5' Cap
A modified form of guanine nucleotide added onto the 5' end of a pre-mRNA molecule
Poly-A Tail
Modified end of the 3' end of an mRNA molecule consisting of the addition of 50-250 adenine nucleotides
Golgi Apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
Proteins are terminally ____ in the Golgi Apparatus.
glycosylated
Produces glycoproteins that are placed in the cell membrane
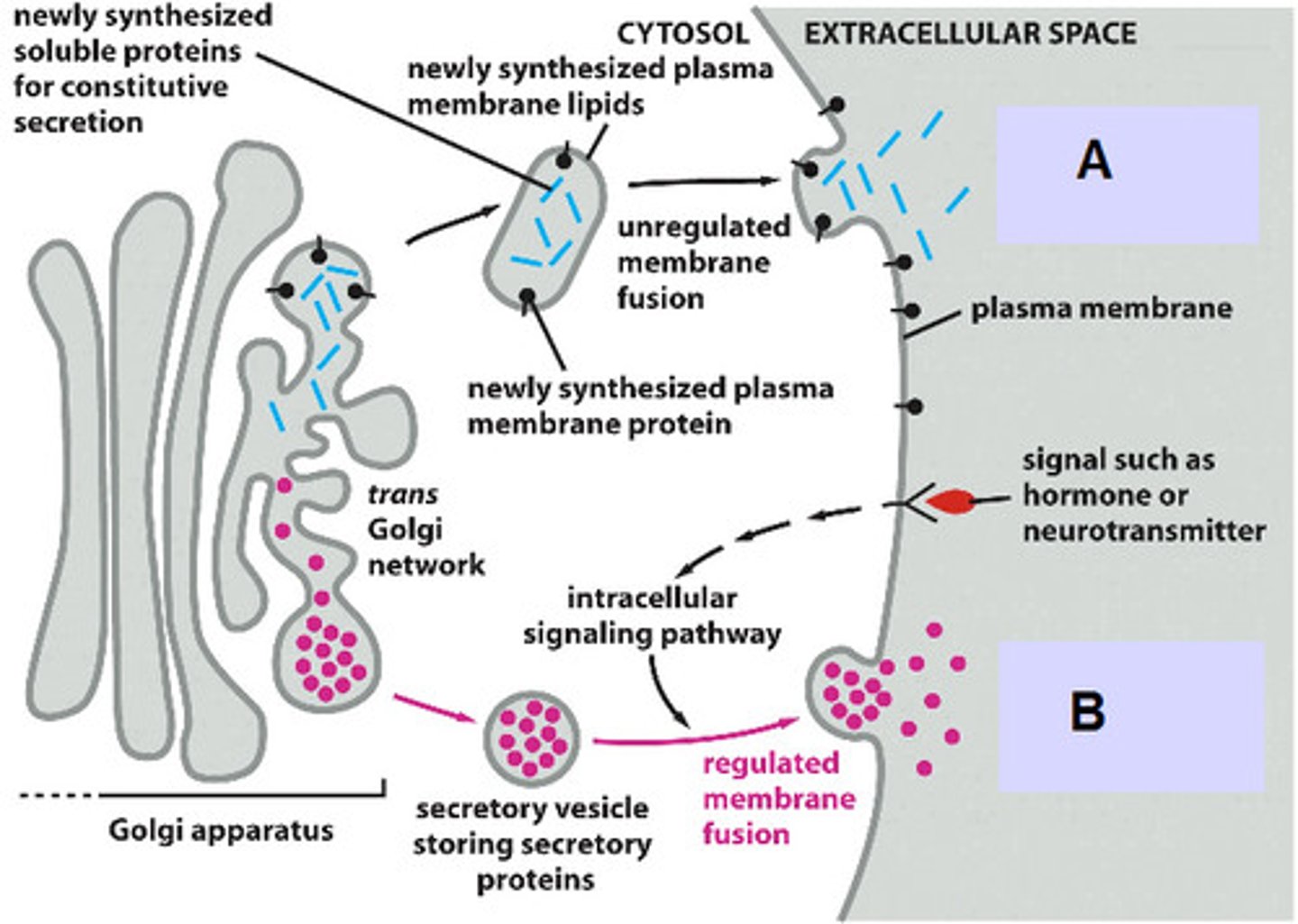
Constitutive Secretory Pathway
Proteins sent in vesicles from Golgi immediately to cell surface with no regulation
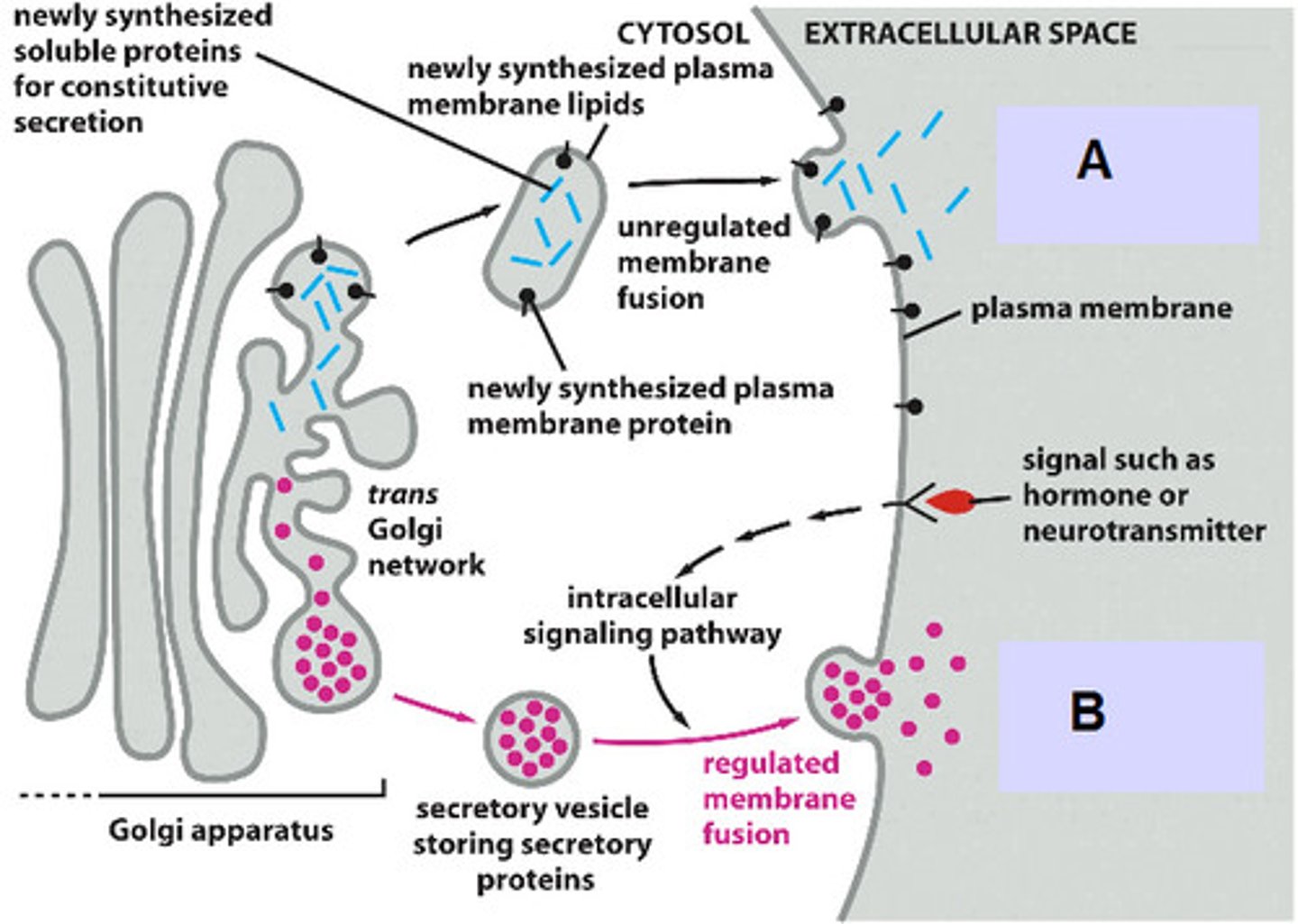
Regulated Secretory Pathway
Secretory pathway in which large amounts of proteins, stored in secretory vesicles, are released from the cell in response to the appropriate signals
ie. Neurotransmitters
Lysosome
An organelle containing digestive enzymes
- pH = 4-5 maintained by proton pumps
Proteins destined for the lysosome contain a recognition site consisting of a ____.
phosphorylated mannose (M6P)
These proteins are transferred to the lysosome via vesicular transport
What are the 3 types of Endocytosis?
- Phagocytosis
- Pinocytosis
- Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Phagocytosis
Involves extension of pseudopodia to intake larger molecules
Pinocytosis
Cell invaginates to take in small molecules
General Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
(1) Binding via Plasma Membrane Receptor
(2) Endocytosis
(3) Uncoating
(4) Endosome Fusion
(5) Return of Receptors to Plasma Membrane
What are the 4 Fates of Endocytic Cargo?
- Receptor Recycled/Ligand Degraded
- Receptor Recycled/Ligand Recycled
- Receptor Degraded/Ligand Degraded
- Receptor Transported/Ligand Transported
Slide 39
Peroxisomes
Membrane-Bound Organelles containing enzymes that participate in oxidative reactions
Peroxisomal proteins are synthesized in the ____.
cytoplasm
Peroxisomal proteins are transported to the peroxisome via a specialized targeting ____.
amino acid sequence
Catalase
Breaks down hydrogen peroxide, a product of lysosomes
Mitochondria
Double-Membraned Organelle that synthesizes ATP from nutrients
Mitochondria contain ____ and can make ____.
their own DNA/their own proteins
Mitochondria divide synchronously with cell division (T/F)
False
Proteasome
Second major compartment for proteolysis
- Abnormal and misfolded proteins are tagged by ubiquitin, which directs the proteasome to break them down
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
What are the 3 components of the Cytoskeleton?
- Actin Filaments (Microfilaments)
- Intermediate Filaments
- Microtubules
All of these structures are held together by noncovalent bonds
Functions of Cytoskeletal System
- Pulls chromosomes during division
- Intracellular traffic
- Supports plasma membrane/Cell Shape
- Flagella movement
Actin Filaments
Smallest filament composed of polymerized cross-linked G-Actin
- Acts as the "muscle" of cells
- Creates plasma membrane projections
- Aids in movement of proteins along microtubules
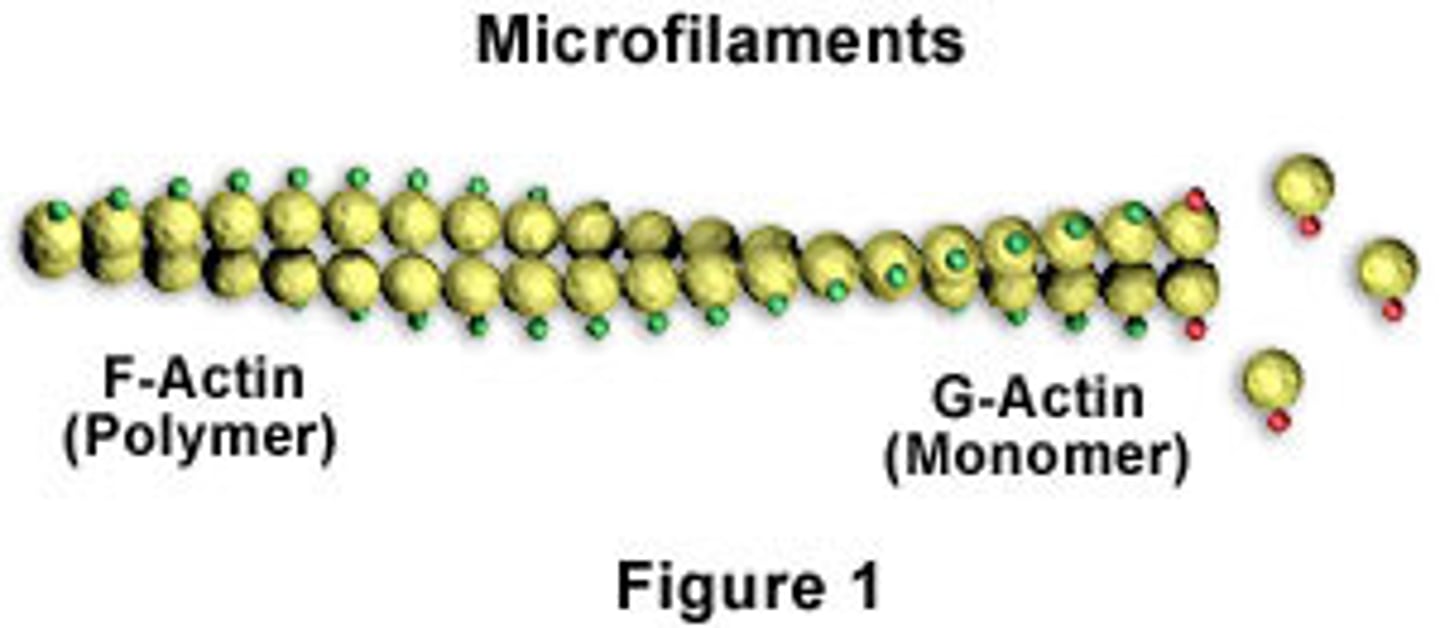
Polymerized G-Actin creates ____.
F-Actin
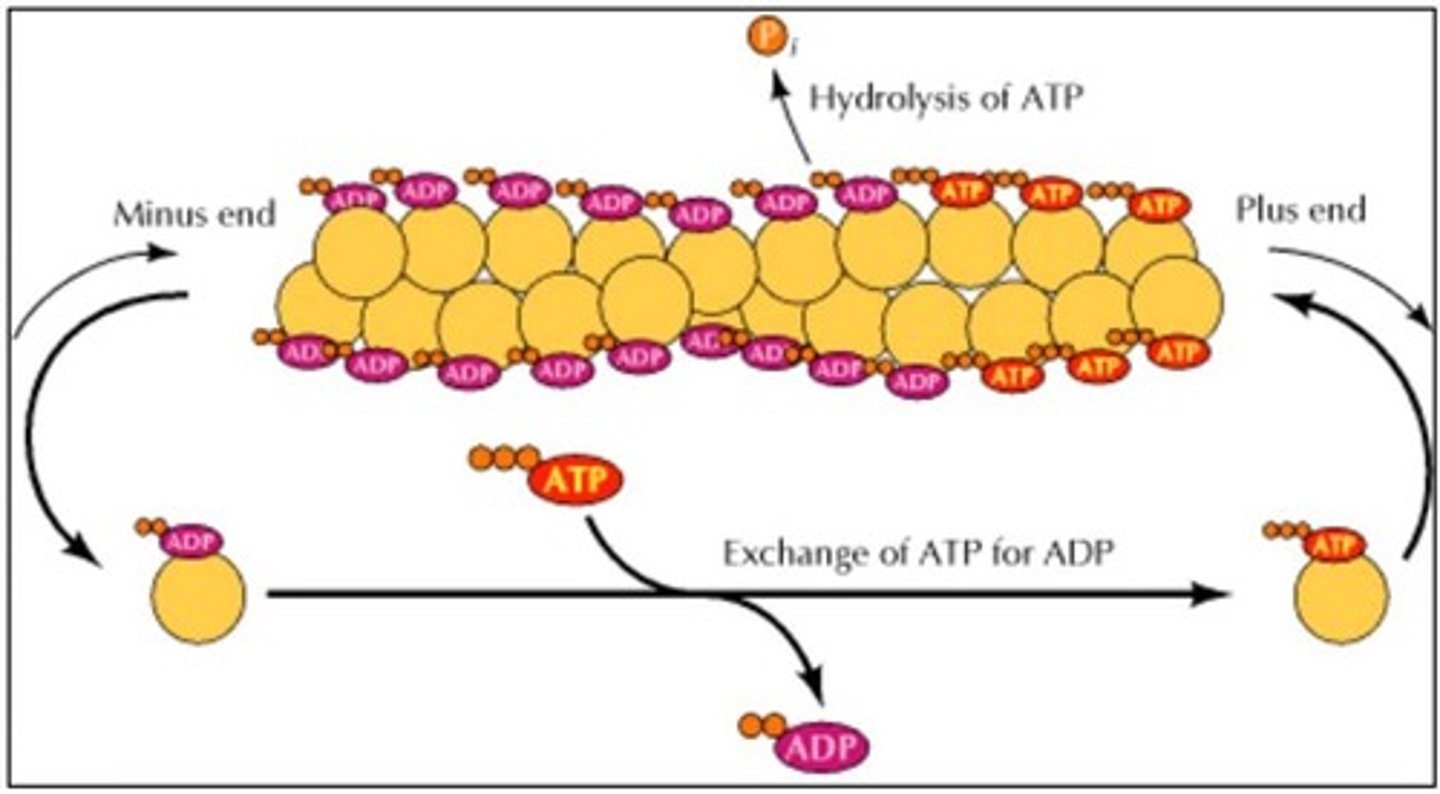
Plus End
The rapidly growing end of an actin filament/microtubule
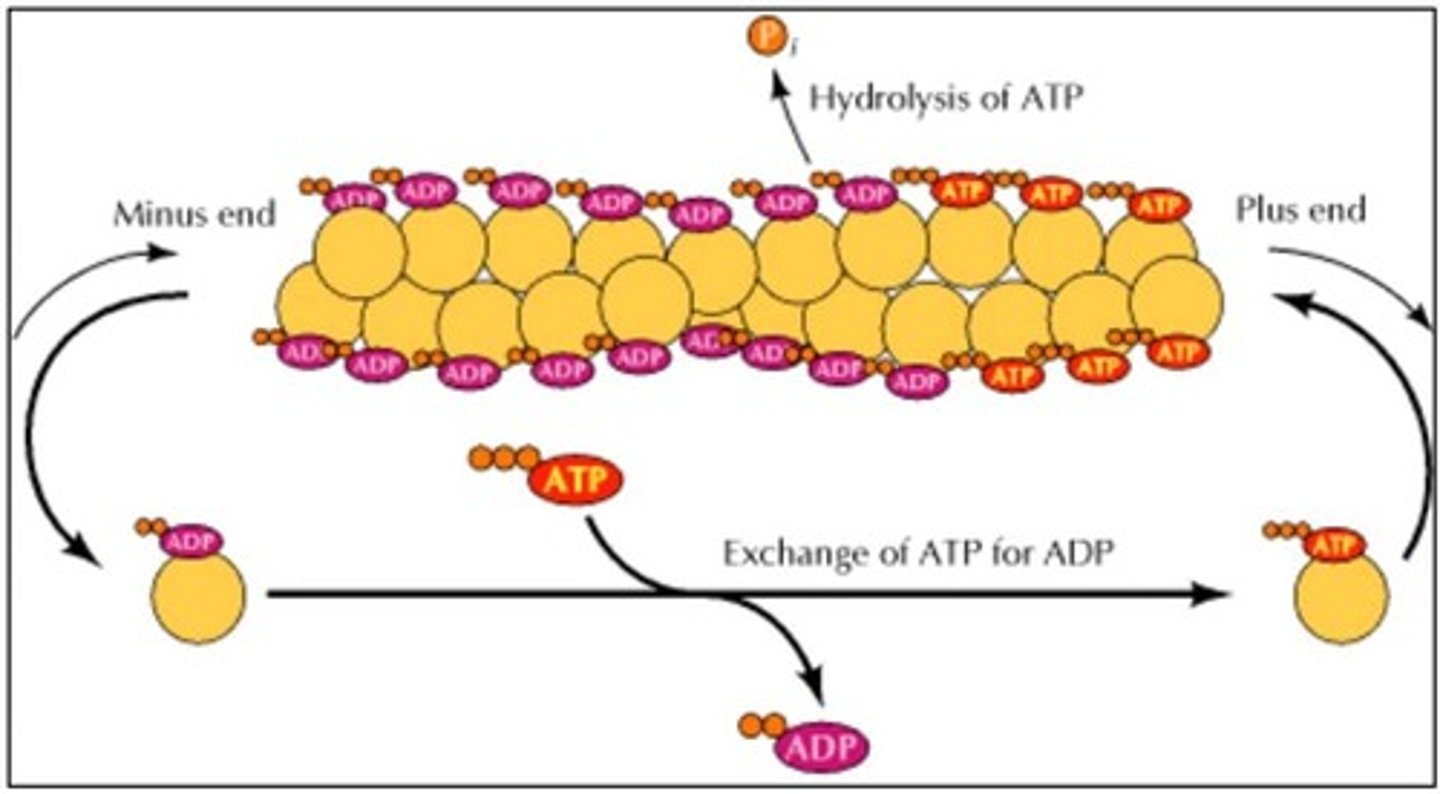
Minus End
The less active end of an actin filament/microtubule
Intermediate Filaments
Made up of fibrous keratin-like subunits
- Reinforce the nuclear envelope
Microtubules
Largest cytoskeletal element composed of polymerized dimeric tubulin
- Direct motor proteins in "traffic"
- Form spindle fibers
- Major component of cilia/flagella
Tubulin Dimer Composition
- alpha-Tubulin
- Beta-Tubulin
MTOCs
Microtubule Organizing Centers
- Organized around centrioles/basal bodies
Actin Filaments and Microtubules are more ____.
stiff/rigid
Intermediate Filaments are ____ and ____.
strong/flexible
What are the 4 major tissue types?
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Muscle
- Nerve
Immunohistochemistry detecting components of the electron transport chain would stain very definitively the ____.
inner mitochondrial membrane
Proteins destined for the lysosome via the secretory pathway will contain which modification for proper transport?
Phosphomannose
A patient taking cancer medicine that specifically acts by disrupting tubulin formation will consequently arrest the cell in which stage of the cell cycle?
Mitosis