Pre Q Graphics - 1.3d Plastic forming processes
1/13
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms

Image_
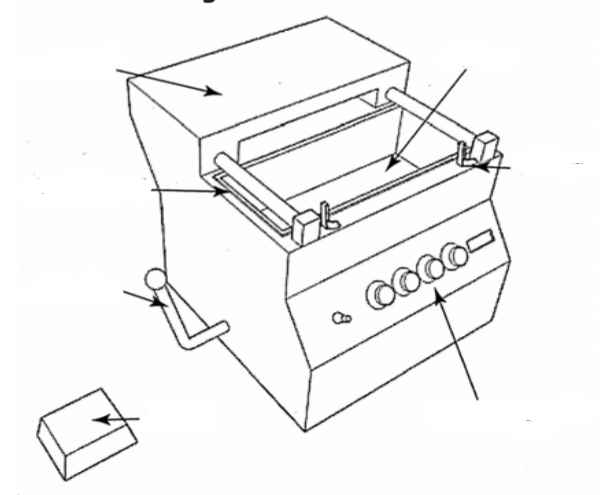
Line bender
Image_
Vacuum former
Image_
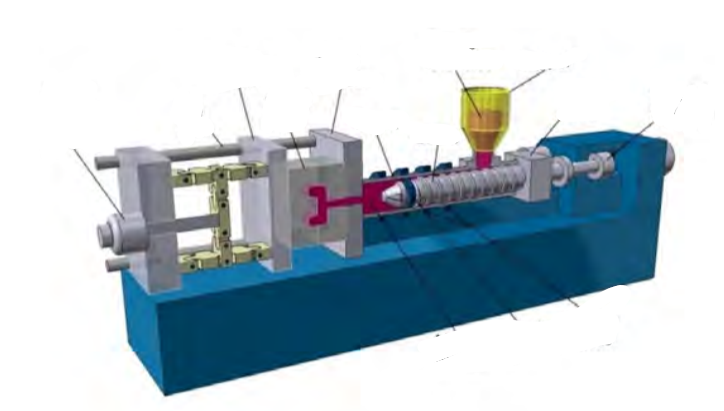
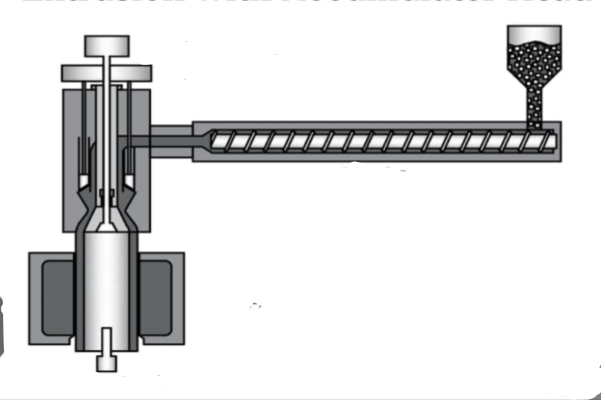
Injection moulder
Image_
Extrusion mould
Image_
Blow moulder
Line bender process
1. Use a marker pen or chinagraph pencil to mark out where the bend lines will be
2. Turn on the ____ so that it comes up to a working temperature
3. Put on heat-proof gloves and have a tray of water ready to cool the workpiece
4. Place the marked line of the workpiece across the heating strip
5. Allow the plastic to heat through (the time needed will depend on the thickness of the material, thicker materials may need to be turned over to heat from both sides)
6. Test for flexibility as the workpiece approaches the right temperature (too cool can lead to it cracking, too hot can lead to scorching and blistering)
7. Bend the workpiece to the required angle (a jig or former may be used to ensure accuracy)
8. Once the workpiece has set it can be cooled in the water tray.
Vacuum Forming Process
1. The mould is placed on the platen.
2. A thermoplastic sheet is placed over the airtight seal and clamped above the platen.
3. The heater is pulled accross.
4. The platen is raised so the mould is sitting underneath the plastic.
5. The ___ is turned on and the plastic is sucked over the mould
Injection Moulding Process
1. Granules of the chosen plastic are fed into the hopper 2. The hopper feeds the Archimedes screw that drags the granules past a heater, where they are softened and become plasticised as they travel forward 3. The plastic is in a soft, pliable form as it reaches the end of the screw, where it collects until there is enough to fill the mould 4. At this point a hydraulic piston forces the softened plastic into the mould under pressure, filling it up 5. The plastic sets quickly, the mould is separated and ejector pins release the moulding 6. The process is repeated.
Blow moulding process
Heated plastic is poured into the mould
The mould is closed and gripped in place
Compressed air is blown into the mould which inflates the plastic
The plastic fills the mould
Product gets trimmed and is removed from the mould
Glass Reinforced plastics process
Apply a layer of release agent on mould
add layer of coloured gellcoat resin
add sheet of glassfibre
add layer of polyester resin
set and release from mould
Rotational moulding process
Powered plastic is inserted in the mould
The mould is closed and heated
The mould slowly rotates to evenly coat walls of the mould
The rotating mould is cooled with a water spray to make the plastic set. The mould is then opened.

Image_
Rotational moulding
Image_
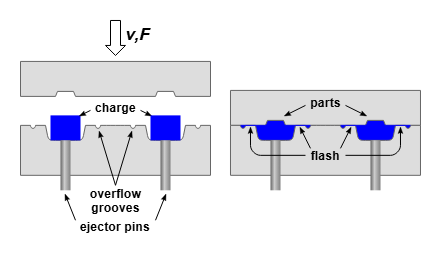
Compression moulding
Compression moulding process
Granular plastic is being poured into the mould
The two halves of the heated mould closes and squeezes the plastic
Plastic melts and fills the shape of the mould
Mould opens and ejector pin removes the product