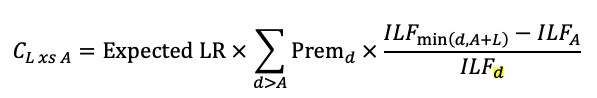EXAM 5 SECTION C
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
risk classification
grouping risks w/ similar risk characteristics (expected costs) for purpose of setting prices
adverse selection
Insurer not using risk characteristic used by competitors
Competitors will attract lower risk insureds
While insurer left w/ higher than proportional share of higher risks
High risks undercharged → unprofitable
favorable selection
when you recognize risk char not recognized by competitor
Strategy: raise rates for low risks to be just below competition’s
so they’ll still move over to your company AND maximize profit!
proxy underwrite accept market
What if a rating variable is prohibited?
Find correlated _____ variables and rate based on those
Can still _____ based on the risk char to only _____ lower risk insureds
_____ to lower risk insureds & avoid marketing to higher risk
skimming the cream uw marketing
_____: insurer uses a risk characteristic in _____ or _____ to attract lower cost risks WITHOUT lowering prem!
Protects insight from competitors
Rates have to be made publicly available
UW guidelines don’t
significance homogeneity credibility objective expense verifiable affordability causality controllability privacy
Criteria for Rating Variables:
Statistical Criteria
Statistical _____
_____
_____
Operational Criteria
_____
_____
_____
Social Criteria
_____
_____
_____
_____
Legal Criteria
statistical significance expected costs homogeneity individ class subclasses loss potential credibility large
Statistical Criteria for Rating Var
_____ _____: _____ _____ should vary by class w/ acceptable lvl of stat confidence
_____: expected costs for _____ risks within _____ should be similar
No clearly identifiable _____ w/ significantly diff _____ _____
_____: classes _____ enough to allow cred statistical predictions
But a class doesn’t need to be fully credible on its own
operational objective measurable defined expense obtaining verifiable manipulate
_____ Criteria for Rating Var
_____: classes are _____ & clearly _____; exhaustive & mutually exclusive
_____: cost of _____/maintaining data not too high
_____: easily verifiable, hard to _____
social affordability negative causality intuitive acceptance controllability chance privacy
_____ Criteria for Rating Var
_____: esp a problem when there’s _____ correlation between income & rates
_____: _____ relationship between rating var & cost
Increases public _____
_____: encourages insureds to reduce _____ of loss for lower rate
Increases public acceptance
_____: not too intrusive
legal
_____ Criteria for Rating Var
in compliance w/ local laws & regulations
exposure
Overall Rate Indications → overall avg rate for book
Class Relativities → relative costs between classes
Univariate Analysis
Multivariate Analysis
Preferred bc correctly adjusts for _____ correlation
simple correlation OL levels rels
Univariate Pricing Approaches:
PP Approach
Pro: _____
Con: least accurate when there’s exposure _____
LR Approach
Pro: partially corrects for exp corr
Con: requires _____ prem by _____ of var
Adjusted PP Approach
Pro: partially corrects for exp corr
Con: cumbersome to calculate wtd-avg _____ for many variables
***Identical results as LR Approach!
exposure correlation
exposures of levels of X1 are correlated w/ exposures of levels of X2
“double counts” experience of correlated variables
exposures at base adj exposures rebase
Univariate Pricing Approaches w/ Credibility
Need ind rel & complement to be on same basis!
Ind Rel to Total
Normalized Complement
Make them relative to a WEIGHTED total
PP → weigh by earned _____
LR → weigh by prem _____
Adj PP → weigh by _____
Don’t forget to _____!
pp
Univariate Pricing approach → _____
Ind Rel = PPclass / PPbase
lr prem at base olep curr rel
Univariate Pricing approach → _____
Ind Rel Chg Factor = LR / Total LR
Ind Rel = Curr Rel x Chg Factor
SHORTCUT: Cred Complement is Current Rates
Weigh Chg Factor with 1!
Other complements → weigh rels by _____
calculate relativities first then weigh
Prem at Base = _____ / _____
adj pp
Univariate Pricing approach → _____
For each level of a variable:
Adj Exp = EE wtd by Curr Rel of Other Var
sequential analysis
sequence of using Adj PP Approach
Pro: partially corrects for exp correlation
Con: order matters
Steps
Perform univariate analysis to get ind rel for Var1
Use Var1 ind rels to adjust exp for Var2
Apply Adj PP approach
Use Var2 ind rels to adjust exp for Var3
Apply Adj PP Approach
…
class rel
Ind Class 1 Rel = Ind RateClass 1 / Ind RateBase
Assuming same VE & profit:
Ind Class 1 Rel = (PPClass 1 + FE per ExpClass 1) / (PPBase + FE per ExpBase)
If no FE:
Ind Class 1 Rel = PPClass 1 / PPBase
cats lr
Adjustments in Class Ratemaking
Cat & Large Loss → replaced w/ loads
Consider whether some classes are more prone to _____
One-Time Changes → need to on-level
esp for _____ Approach
Credibility → important bc individual classes have less data
Ignored:
Trends → assume all class trending at same rate
Development → assume all class developing at same rate
Expense & Profit → assume same variable loads for all classes
univariate
_____ Class Ratemaking
Pros: simpler to explain, intuitive
Cons: don’t properly account for exposure correlation
systematic noise diagnostics interactions response
Multivariate Classification (ex: GLMs)
Accounts for exposure corr
Attempts to focus on _____ effects in data & ignore _____
Provides statistical _____ (ex: CIs)
Considers _____ between rating vars → _____ correlation
minimum bias procedure
a Multivariate classification
Pro: corrects for exposure corr
Cons:
Computationally inefficient (iterative)
Doesn’t test vars for statistical significance
link random software lr prem granular theoretical rates
Generalized Linear Models (GLMs)
Corrects for exposure corr
Select a dependent variable to run on → PP, Freq, Sev
Select _____ function & underlying _____ process
Use _____ to solve GLM and estimate relativities
NOT typically run on _____ bc:
_____ needs to be on-levelled at _____ level
no common _____ distr for modeling LR
LR models become obsolete when _____ change
exponential normal constant
GLM vs Classical Linear Model
Response Variable
GLM → member of _____ family of distributions
Classical Lin Model → _____
Variance
GLM → doesn’t have to be constant
Classical Lin Model → _____
data anomalies ratemaking
Actuary’s Role in GLMs
Obtaining reliable _____
Exploring _____ w/ additional analysis
Consider model results from statistical & business perspective
Develop appropriate methods to communicate model results based on company’s _____ objectives
geo demographic weather property insured
External Data to use in GLMs
_____-_____ info → pop density
_____ → avg rainfall
_____ characteristics → sq footage, quality of local fire dept
Info ab _____ → credit scores
ded
GLM Outputs
**Check output makes sense
Higher rates for higher _____ → doesn’t make sense
May be due to limited data at higher ded
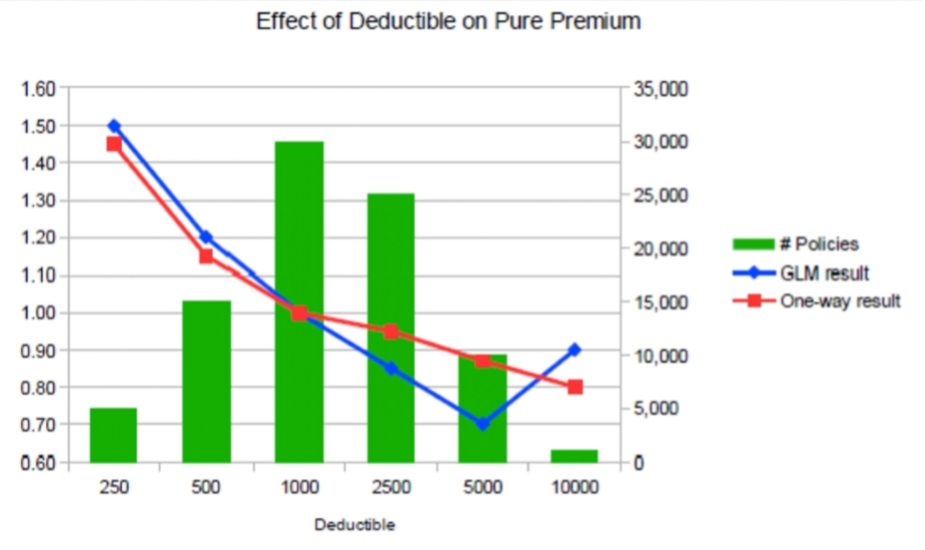
wide 1 same rel
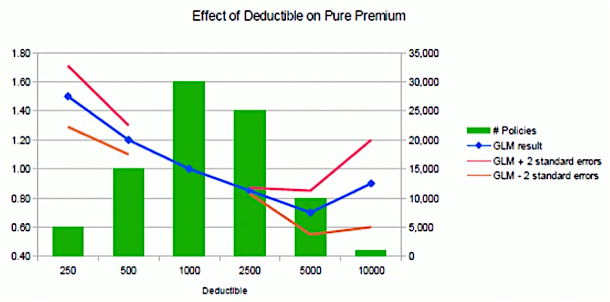
GLM Confidence Intervals
Low volume of data → _____ CI
Shows if each level & var as a whole is statistically significant
If CI includes _____ → no stat sig diff between that class & base
Overlapping CIs → reasonable from statistical significance perspective to charge _____ _____
deviance tests
compares GLM models
Chi-Squared Test, F-statistic, AIC/BIC
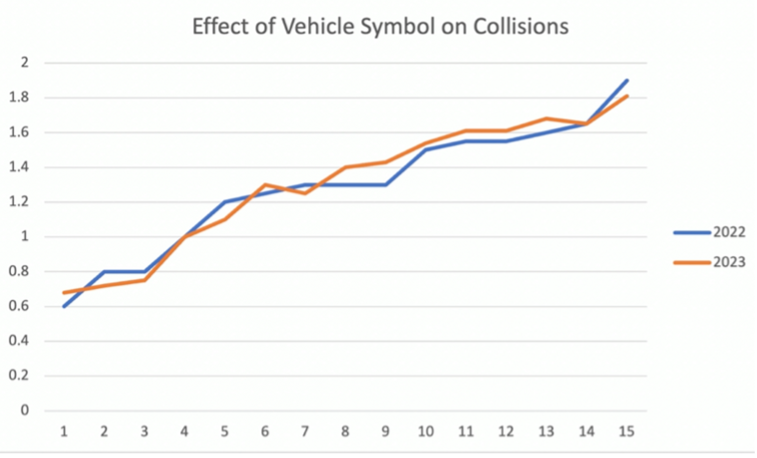
time consistency
tests whether GLM estimated parameters are consistent over time
if diff years have similar patterns → model performing consistently
model validation overfitting underfitting
_____: measures model performance on unseen data
compares prediction vs actual results
Reasons for not performing well:
_____
_____
factor cluster groups cart
Data Mining Techniques
_____ Analysis: reduce # of vars needed in GLMs
Ex: using a single symbol var to capture multiple risk chars
_____ Analysis: combine similar risks into _____, resulting in fewer vars
Ex: combining ZIPs into Territory variable
_____: build set of if-then rules to identify most important vars
Detect interactions
Classification & Regression Trees
territorial ratemaking
Challenges: highly correlated w/ other var → can use GLMs
small geographic areas have low cred
Steps:
Establish territorial boundaries
Determine ind rates for each territory (using GLM)
spatial smoothing distance weather urban rural physical boundaries adjacency socio demographic
_____ _____: cred-weighting ind rates of neighbouring territories so no large discrepancies
_____-based → better for _____
Assumes distance has same impact for _____ & _____ risks
Doesn’t consider _____ _____
_____-based → better for _____ _____ perils (ex: theft)
Better reflects urban & rural differences
Considers physical boundaries
Over-smoothing: using geo units too far away, not relevant
Under-smoothing: giving local results too much cred → results too volatile
unit systematic residual spatial smoothing territories non contiguous
Establishing Territorial Boundaries:
Define geographic _____ (ex: ZIP code, counties)
Est geographic _____ risk for each unit → using GLMs
Unexplained geographic var incorporated into a _____ variable
Apply _____ _____ on residual var
Smooth results across neighboring areas
Cluster units into _____
Add constraints to avoid _____ _____ territories
ILFs less data impractical
Increased Limits Ratemaking
Rated using _____ (Increased Limit Factors)
ILF = 1 → Basic Limit
Can’t use standard ratemaking to price
______ _____ for higher amts → volatile
_____ results → ex: higher price for higher limit
Importance:
Ppl need more covg as wealth grows
Trends have more impact on increased lim than basic lim
More lawsuits, higher jury awards
ILF trend develop layer variable same freq indep
Standard _____ Approach
_____ & _____ data first!
bc they may vary by _____
Assumptions:
All UW expenses & profit are _____ and _____ for all lims
_____ same for all lims
Freq & sev _____
expense profits freq
ILF(H) = RateH / RateB
= (PP incl LAEH / 1-VH-QH) / (PP incl LAEB / 1-VB-QB)
= PP incl LAEH / PP incl LAEB → same UW _____ & _____
= (FreqH x SevH) / (FreqB x SevB)
= SevH / SevB → same _____
=LAS(H) / LAS(B)
full losses claims
Limited Avg Severity (LAS):
For loss < H → _____ loss amt
For loss > H → # of claims x H
LAS(H) = _____ capped at H / # of _____
x-h k
LAS for layer K xs H:
Below H → don’t contribute
Between [H, H+K] → contribute only what’s above H, i.e. _____
Above H+K → contribute full _____
Denominator → Only include losses that contributed to num
i.e. exclude claims below H
LAS(K xs H) = Losses in layer / # Claims contributing to layer
lower
LAS for Censored Data
Lowest limit → same as uncensored
Higher limit → calculate incrementally
LAS(H2) = LAS(H1) + LAS(layer between H1, H2) x Pr(X > H1)
Can’t use data from _____ limits bc don’t know uncapped loss!
Pr(X > H1) → Only based on policies that could have claim above H1
exclude claims capped at lower lims
deductible pricing
2 Types of Deductibles:
Flat dollar
Percentage
**Trend & develop data first!
expenses profits variable xs ratio ler
Ded Pricing: Loss Elimination Ratio (LER) Approach
Assumes all UW _____ & _____ are _____
Base = no ded → Ind Rel = 1
Ind Rel(D) = _____ _____(D)
= Loss&LAE above D / Ground-up Loss&LAE
= 1 - Loss&LAE below D / Ground-up Loss&LAE
= 1 - ____(D)
**Denom is ALL ground-up loss (not basic loss!)
ler behaviour incentive
_____ Approach to ded pricing assumes claimant ______ will NOT vary by ded
GLM & Univariate Analysis → can vary!
Ex: financial _____ in filing a $501 claim w/ $100 ded vs $500 ded
1 - ler(d w/ base b)
LER for censored data
Don’t know claims below ded
Can only use claims where amt at BOTH ded are known!
LER(D w/ base B) = Diff in Loss assuming diff deds / Loss assuming B ded
Ind Rel(D) = ______
dollar caps coverage percentage
Deductible impact on Premium
Higher ded = lower prem
Problem if increasing ded lowers prem more than ded difference
Limit prem impact by:
_____ _____ on prem credit for ded
Vary ded factors by _____ amount
_____ ded
lower censored
Problems w/ Deductible or Limit data to price ded:
Policies w/ ded may only have data for loss xs of ded
Sol’n:
GLM
LER approach using only data from ded _____ than ded you’re pricing
Policies w/ lim may only have data for loss _____ by historical lim
Sol’n: GLM
dec undercharged overcharged expense constant fe size writing prem discount larger
Work Comp Size of Risk
FE as % of prem should _____ as prem inc
So small risks are not _____, large risks not _____
_____: accounts for ____ that don’t vary by _____ of risk
so small risks not undercharged
prem might not be enough to cover FE of _____ the policy
_____: % discount for _____ policies
so large risks not overcharged
to recognize that expenses are a lower % of prem than small risks
lowest expense reduction portion
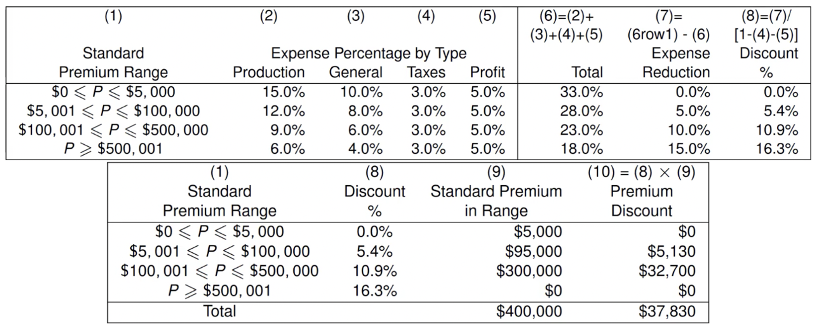
Premium Discount
Sum expenses for each range of loss
Expense Reduction = diff w/ expense of _____ range
Discount % = _____ _____ / (1 - VE)
VE % are same for all claim sizes → Taxes, Profit
Std Prem in Range = _____ of std prem in each range
Start w/ smallest range until it adds up to full amt of std prem
Prem Discount = Std Prem in Range x Discount %
safety return injured experience rating prevent loss constants
Small Work Comp insureds have worse loss experience bc
Have less sophisticated _____ programs
Don’t have _____ to work programs for _____ workers
Not as impacted / don’t qualify for _____ _____
Less incentive to _____ injuries
Price for this diff using GLMs or _____ _____
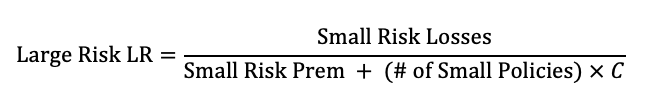
expected loss experience equalizes
Loss Constants: accounts for fact that small risks have worse _____ _____ _____ than large risks
_____ LR between small & large risks
Added to prem of either 1) small risks only; or 2) both risks
Steps:
Equate LR of small & large risk
Add C x # of policies to prem in Denom
Solve for C
covg amt replacement cost
Insurance to Value (ITV)
For Homeowners or Commercial Property insurance
Coverage Amt = Face Amt
ITV = _____ / _____
underinsured inc dec
_____: when ITV < 100% → i.e. covg < replacement
Ind Rate per $1k covg _____ as ITV _____ (if partial loss possible)
fully covered rates inadequate vary coinsurance
Issues when Underinsured:
Insured not _____ _____ in event of total or near-total loss
If insurer assumes 100% ITV in _____, prem will be _____
Sol’ns:
_____ rates by ITV
_____
covg amt
ITV:
Ind Rate = PP = Freq x Sev
Ind Rate per $100k covg = PP / (_____ _____/100)
higher undercharged
Underinsured will pay _____ rate per $1k covg
So if charging all at same rate, underinsured will be _____
adequate equitable
_____: prem ≥ expected policy costs (loss + expenses)
_____: prem relatively fair across insureds
Equal LR for all risks
should not be subsidizing
*Compare prem to expected costs
sev dec constant inc
ITV → _____ Distribution
As ITV dec, ind rate per $1k covg inc
As ITV inc, ind rate per $1k covg dec!
Rate depends on sev distr!
As covg inc, ind rate per $1k covg will DECREASE at…
Right-skewed (small loss likely) → _____ rate
Uniform → _____
Left-skewed (large loss likely) → _____ rate
tools home characteristics inspections
Guaranteed Replacement Cost (GRC)
If home insured at 100% ITV, total loss guaranteed will be covered regardless of actual cost
Past: hard to est Replacement Cost
NOW:
Better _____ to estimate RC based on _____ _____
Property _____ → get more accurate info for est
coinsurance underinsurance penalty
_____: insured also responsible for a portion of loss
Another sol’n to _____
Instead of inc rates, insurer reduce loss!
Implemented by coinsurance clause
Coinsurance requirement = X% ITV
If ITV < X% → coinsurance _____ apply
proportional underinsurance penalty PP underinsured
Coinsurance & EQUITABLE rates:
Adjust amt insurers pay on claims _____ to amt of _____
After coinsurance _____ applied, all risks will have equal _____ per $1k covg
Makes single rate per $1k covg for all ITV levels is equitable
Coinsurance & ADEQUACY:
Reduce paid loss on _____ risks s.t. the same rate as risks insured to coinsurance requirement will be adequate
replacement covg loss
COINSURANCE
Coinsurance Apportionment Ratio:
a = min(1, Covg / (Coins Req% x _____ Cost))
Indemnity before ded: I = min( a x Loss , _____)
Indemnity after ded: I - ded
Coinsurance Penalty = min(_____, Covg) - I
less loss
Coinsurance Penalty will be positive if 2 conditions:
Insured for _____ than coinsurance req
_____ occurs that’s less than coinsurance req
covg coinsurance requirement
Coinsurance Penalty Graph
Max penalty @ loss = _____
Dec to 0 @ loss = _____ _____
credibility
when historical data is volatile or small in volume → may not be fully reliable
give some weight to other related experience to improve ests
decreasing
3 Criteria for Credibility:
0 ≤ Z ≤ 1
As n inc, Z inc → dZ/dn ≥ 0
As n inc, Z inc at _____ rate → d/dn (Z/n) < 0
evpv/vhm
Buhlmannn (Least Squares) Credibility
k = _____
Z = n / (n+k)
accurate unbiased indep available compute logical
5 Desirable Qualities for a Cred Complement
_____
Stable, low var, large volume
_____
Adjust for diff between states / another company’s book of business
Statistically _____ from base stat
Subject isn’t large portion of complement
_____
Easy to _____
Ex: use same methods used to produce small insurer ind on large insurer data
______ relationship to base stat
Ex: both insurers write personal auto in same state
larger group related rate change present harwayne trended competitor
Complements in First Dollar Ratemaking
LC of _____ _____ that includes group being rated
LC of larger _____ group
_____ _____ from larger group applied to _____ rates
_____’s Method
_____ Present Rates
_____’s Rates
accurate available compute logical biased
Complement: LC of Larger Group that includes group being rated
Pro: _____, _____, easy to _____, _____
Indep if subject experience excluded
Con: _____ bc there’s reason why subject is separated from larger group
indep available compute biased
Complement: LC of Larger Related Group
Pro: _____, _____, easy to _____
Possibly accurate, logical relationship
Con: _____
biased
Complement: Rate Chg from Larger Group applied to Present Rates
Adj ver of LC of Larger Grp → less _____
Pro: easy to compute
C = Current LCSubject x (Ind LCLarger / Current Avg LCLarger)
accurate unbiased available logical compute exposures adj factor
Complement: Harwayne’s Method
Adjusts for overall LC diff between states, exposure distr differences
Pro: _____, _____, mostly indep, _____, _____ relationship
Con: hard to _____
EX: Want complement for State A Class 1 LC
Calculated Wtd-Avg PP for State A
Calculate Wtd-Avg PP for other states using State A’s _____
_____ _____ = Wtd-Avg PPState A / Wtd-Avg PPother state
For each other state: Adj Class 1 LC = Class 1 LC x Adj Factor
C = wtd avg of all Adj Class 1 LC using Class 1 exposures
residual unbiased available compute logical inaccurate ind implemented
Complement: Trended Present Rates
Adjust current rates for trends & _____ indication
Pro: _____, _____, easy to _____, _____ relationship
Con: may be _____ if ind volatile, may or may not be indep
Trend Period:
From OG target effective date of last review (NOT actual implementation date)
To: target effective date of next rate chg
PP Method:
C = Trended Curr Rate x (Prior _____ LC / Prior _____ LC)
LR Method:
Note: LR Trend = Loss Trend / Prem Trend
C = LR Trend Factor x (Prior Ind Rate Chg Factor/Prior Imp Rate Chg Factor) - 1
k p
Classical Cred:
Observed is within _____ of its expected mean w/ prob = _____
# claims for full cred = (z(p+1)/2 / k)2
indep loss distr accurate biased expected lr compute
Complements in XS Ratemaking
Complement for layer L xs of A → (A, A+L)
Inc Limits Analysis
Use ground-up loss up to attachment pt A
Pro: _____
Con: biased if ILFs based on a diff _____ _____, inaccurate due to low volume of data
Lower Limits Analysis
Use data capped at lower lim d
Pro: more _____ than inc lim
Con: more _____
Limits Analysis
Use data capped at all limits greater than A
Pro: for reinsurers that don’t have ground-up data
Con: biased, inaccurate, assumes same _____ _____ for all limits
Fitted Curves
Pro: accurate, less biased, logical relationship
Con: less indep, hard to _____, data may not be available
inc lim analysis

lower lim analysis

limits analysis
For all limits d > A