Chapter 31: Sponges, Cnidarians, Ctenophores, and Protosomes
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
You have a sample of cat emesis (vomit) and find worms in the sample. The cylindrical worms are long and slender, pointed at each ends, with no other distinguishing characteristics. You conclude they are member of which phylum?
A.) Platyhelminthes
B.) Nematoda
C.) Cnidaria
D.) Annelida
E.) Nemertea
B.) Nematoda
What specialized structure do crustaceans use to sense gravity?
A.) antenna
B.) statocyst
C.) radula
D.) parapodium
E.) scolex
B.) statocyst
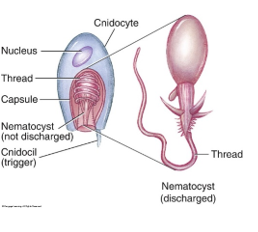
Cnidocyte Structure (3)
-Nematocyst: fluid filled organelles, thread extends when discharged
-Operculum: cover(lid)
-Cnidocil: trigger
Cnidarians are….
diploblastic, radial symmetry, two body forms (poly and medusa)
Cnidarian Featrues (4)
-gastrovascular Cavity: digestive cavity (one opening)
-mesoglea: jelly-like layer between endoderm and ectoderm
-nerve net: movement
-hydrostatic skeleton: movement (fluid filled)
Cnidarian classes
-hydrozoa: polyps
-scyphozoa: jellyfish
-anthozoa: flower animals (corals, anemones)
-cubozoa: box jellyfish
Ancestral Features of Lophotrochozoans
-multicellula, triploblastic, bilateral symmetry, protostomic
Phyla: platyhelminthes, mollusca, and annelida
Characteristic of Phylum Platyhelminthes
Class turbellaria
-acoleomate, unsegmented flatworms
-organ level (none for circulation or gas exchange, some for sense)
-simple nervous system (brain and nerve chords)
-gastrovascular cavity (digestion)
Four classes of Phylum Platyhelminthes
-turbellari: flatworms
Parasitic:
-trematoda: flukes
-monogenea: flukes
-cestoda: tapeworms
Class Cestoda Features
-parasitic faltworms, segmented flatworms (internal parasites of vertebrates)
-anterior end modified into hold-fast, lost digestive cavity, lost sense organs,
Molluscan features
-soft body, head, foot, coelom, circulation (open and closed), radula (tongue with chitinous teeth), complete digestive system
Phylum Mollusca Classes (3)
Gastropoda, Bivalvia, Cephalopoda
Class Gastropoda Features
(snails, slugs, conchs, sea slugs)
- cephalic: defined head
-chitin acts as file, depend on orientation (back and forth or drill)
-pulminate lungs'
-right and left handed coil shells→adaptation→ snake only eats one

Class Bivalvia features
(clams, oysters, mussels, scallops)
-two halves connected by hinge
-no head (asiphalic)
-heart, kidney, etc
-foot
Class Cephalopoda features
(octopus, squid, nautilus, cuttlefish)
-cephalic
-well developed head
-water in cyphon, into mantle cavity, coools cyphon
-loose skin: pigment can be concentrated or dispursed in cells=range of colors

Phylum Annelida features
(polychaeta, oligochaeta, hirudinea)
-segmented
-septa (internal membranous partitions)
-annuli (surface rings)
-nervous system, circulatory, digestive
-respiration across body surface
ceolomate
Class Polychaeta Features
blue crawl leg
-marine
-cephalic
-setae (multiple)
-jaws with pedipalps
-eyes, antennae, sensor tentacle, parapodia
Class Oligochaeta
earthworm
-all 3 habitat
-proteins, lipids, mucus (moisture)
-acephalic
-no jaws
-filter feeder
-no eyes, antennae, tentacles, or parapodia
-clitellum: undergoes reproduction, mucus, allows for exchange of sperm cells
Class Hirudinea features
leeches
-parasites
-annuli (surface rings)
-setae or appendages: none
-suckers: muscular structure at both ends
Clade Ecdysozoa features
-polyphyletic
-molting
-multicellular, triploblastic, protostomic development
Phylas of Ecdysozoa
nematoda and arthropoda
Phylum nematoda features
(Ascaris, hookworms, pinworms, trichin worm)
-elongated and round
-pseudocoelomate
-no annuli or setae
-hydrostatic skeleton
-eutely: fixed number of cells
-dioecious: separate sexes
-sexually dimorphic
phylum Arthropoda features
most succesful group
-coelomate
-segmented
-paired, jointed-may functions
-protein outer layer (waxes protect again moisure)
-Chitin and protein inner layer
-senses: antennae and compound eyes
-gills or trachael tubes
-book lungs
Subphylum Chelicerata features
-adapted fangs or pinchers
-pedipalps second pair of appendages
-cephalothorax abdomen
Chelicerata Suphylum classes
-Merostoma: horsehoes crabs
-Arachnida: spiders, scorpions, ticks, daddy long legs
4 pairs of legs
Subphylum Crustacea
(crayfish, lobsters, crabs, shrimp, barnacles)
-mandibles and maxillae
-nonbranched antennae
-branched
2 pairs antennae (taste and touch)
-cephalothorax and abdomen
-dioecious and sexually dimorphic
-compound eyes
-antennal glands
Hexapoda Class Insecta features
-head, thorax, abdomen
-uniramous appendages (3 pairs of legs)
-wings (one or two pairs)
-1 pair antennae
-eye spots
-mandibles and maxillae( chewing, piercing, lapping labial parts)