C5 - Energy Changes
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
In chemical reactions, energy is __________.
conserved
What happens in a chemical reaction (in terms of energy)?
Energy is transferred either to or from the surroundings.
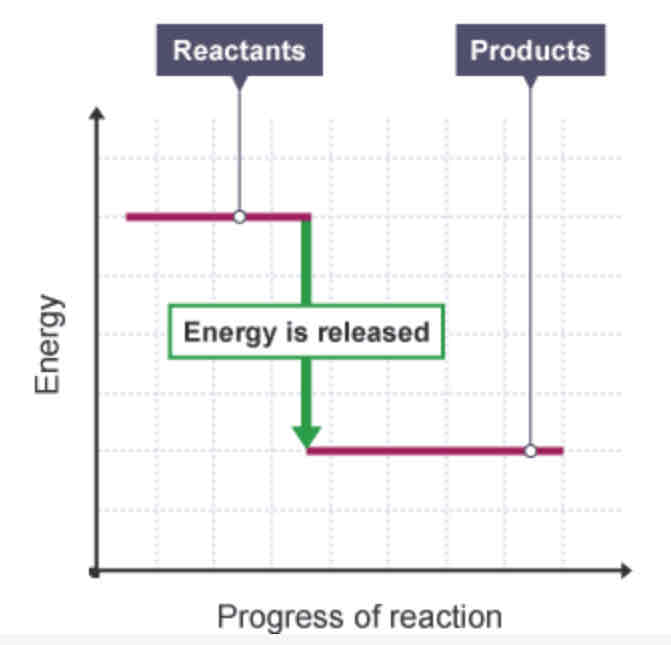
What happens in an exothermic reaction?
Energy is transferred to the surroundings.
What happens to the temperature of the reaction in an exothermic reaction?
It increases
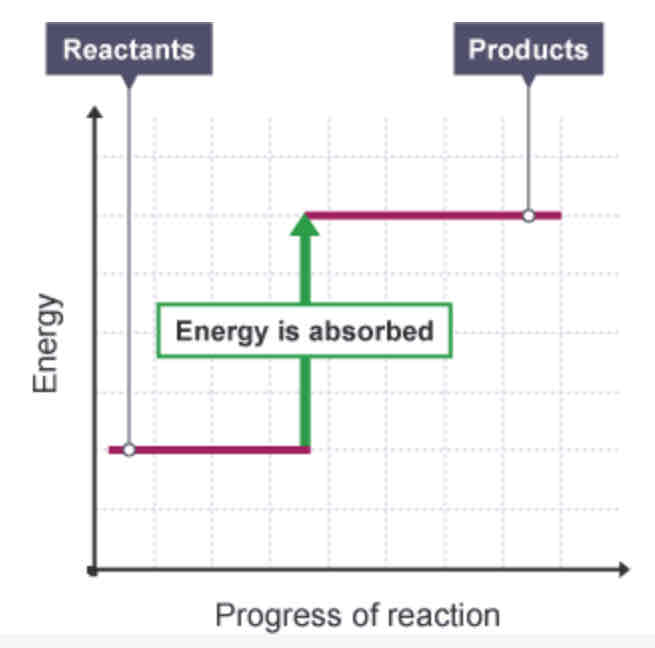
What happens in an endothermic reacton?
Energy is transferred to the reaction.
What happens to the temperature of the reaction in an endothermic reaction?
It decreases
What are examples of exothermic reactions? (3)
combustion reactions
many oxidation reactions
most neutralisation reactions
What are everyday uses of exothermic reactions? (2)
Self-heating cans
Hand warmers
What are examples of endothermic reactions? (2)
thermal decomposition reactions
the reaction of citric acid and sodium hydrogencarbonate
What are everyday uses of endothermic reactions? (1)
instant ice packs
What is the equation of an endothermic neutralisation reaction?
ethanoic acid + sodium carbonate → sodium ethanoate + water + CO2
What is the required practical for this topic?
Temperature changes in reacting solutions
What can be used to display energy changes in a reaction?
A reaction profile
An energy level diagram
Exothermic reaction - energy level diagram
Endothermic reaction - energy level diagram
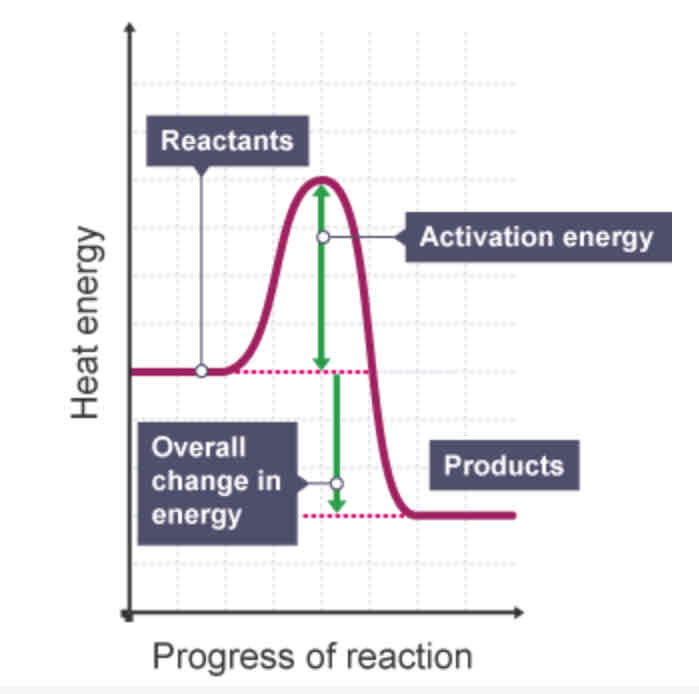
Exothermic - reaction profile
Endothermic - reaction profile
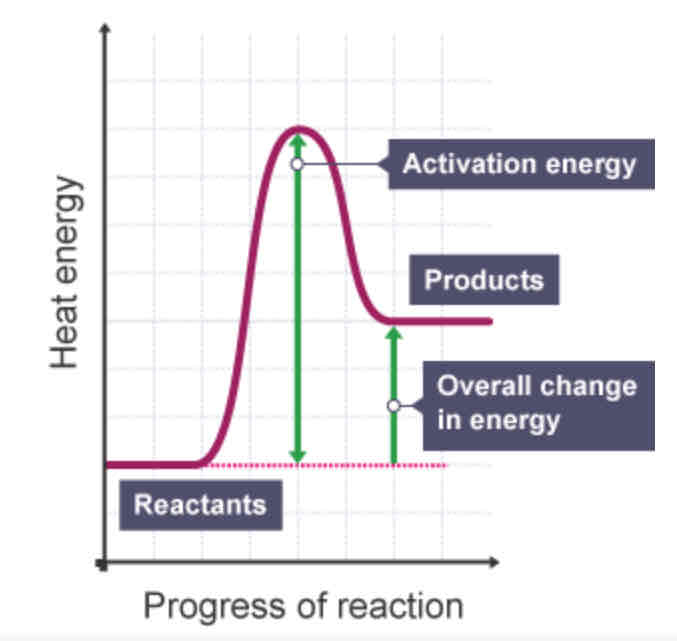
Which is typically more useful in displaying energy changes, an energy level diagram or a reaction profile? Why?
A reaction profile, because it includes the activation energy
activation energy
The minimum amount of energy that colliding particles must have for them to react.
How can you tell from a reaction profile that a reaction is exothermic?
The overall change is negative, as the products have less energy than the reactants.
How can you tell from a reaction profile that a reaction is endothermic?
The overall change is positive, as the products have more energy than the reactants.
When is chemical energy transferred?
When bonds are broken or formed.
Breaking bonds is exothermic/endothermic.
endothermic
Breaking bonds takes/gives heat energy in/out.
Breaking bonds takes heat energy in.
Forming bonds is exothermic/endothermic.
exothermic
Forming bonds takes/gives heat energy in/out.
Forming bonds gives heat energy out.
What happens during a chemical reaction?
Bonds in the reactants are broken
New bonds are made in the products
What determines the type of reaction?
The difference between…
Energy needed to break bonds - energy released when new bonds are formed
broken - formed = final
In an exothermic reaction, what happens? (in terms of bond energies)
More heat energy is released in making the bonds in the products than is taken in when reading bonds in the reactants.
In an endothermic reaction, what happens? (in terms of bond energies)
Less heat energy is released in making the bonds in the products than is taken in when breaking the bonds in the reactants.
What is a bond energy>
The amount of energy needed o break one mole of a particular covalent bond.
How can you calculate an energy change for a reaction? (step-by-step method)
Add together all reactant bonds’ bond energies.
This is energy in.
Add together all product bonds’ energies.
This is energy out.
energy change = energy in - energy out
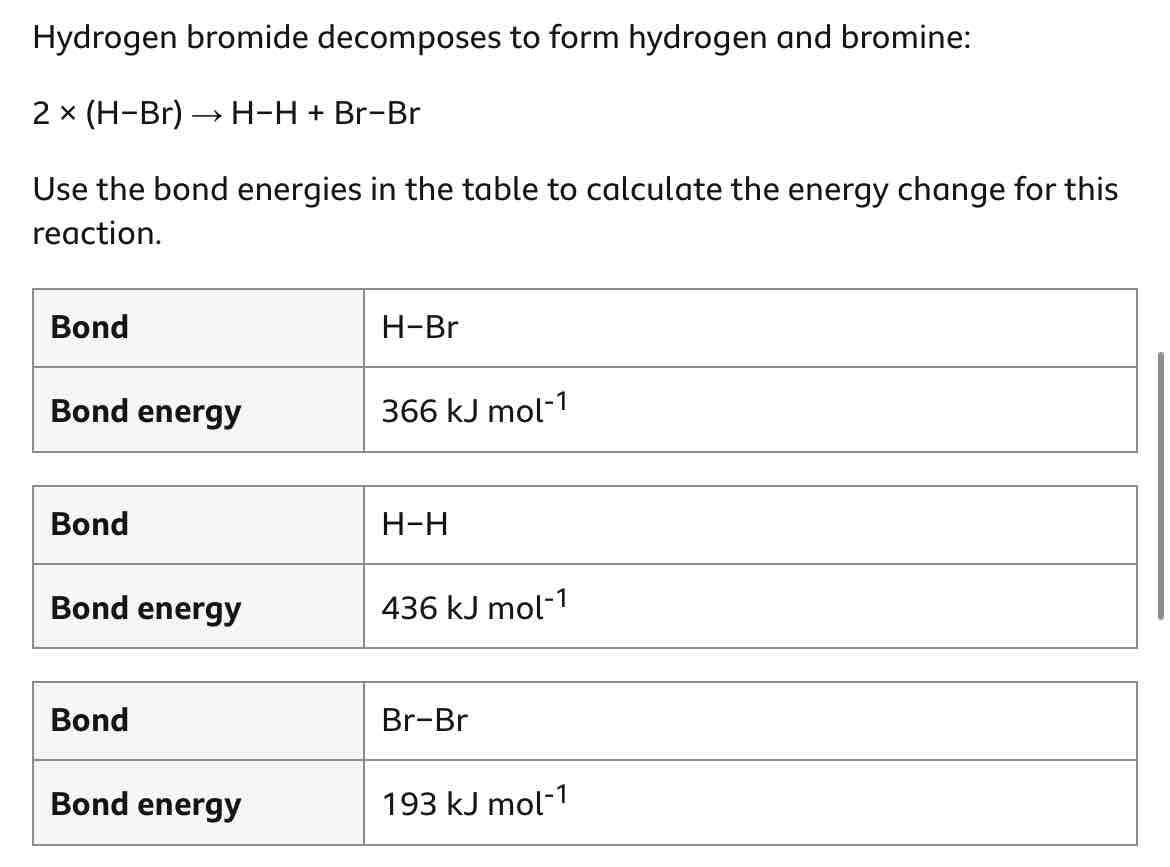
Work out this question.

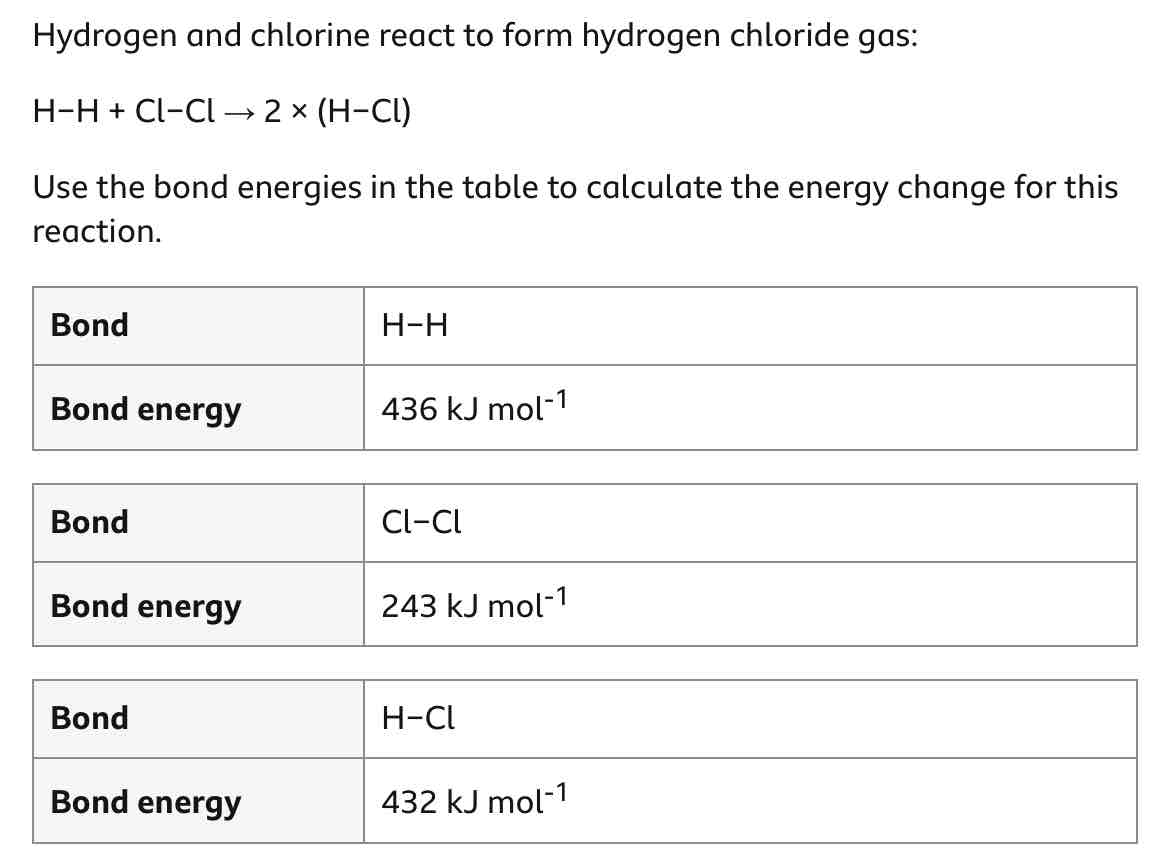
Work out this question.

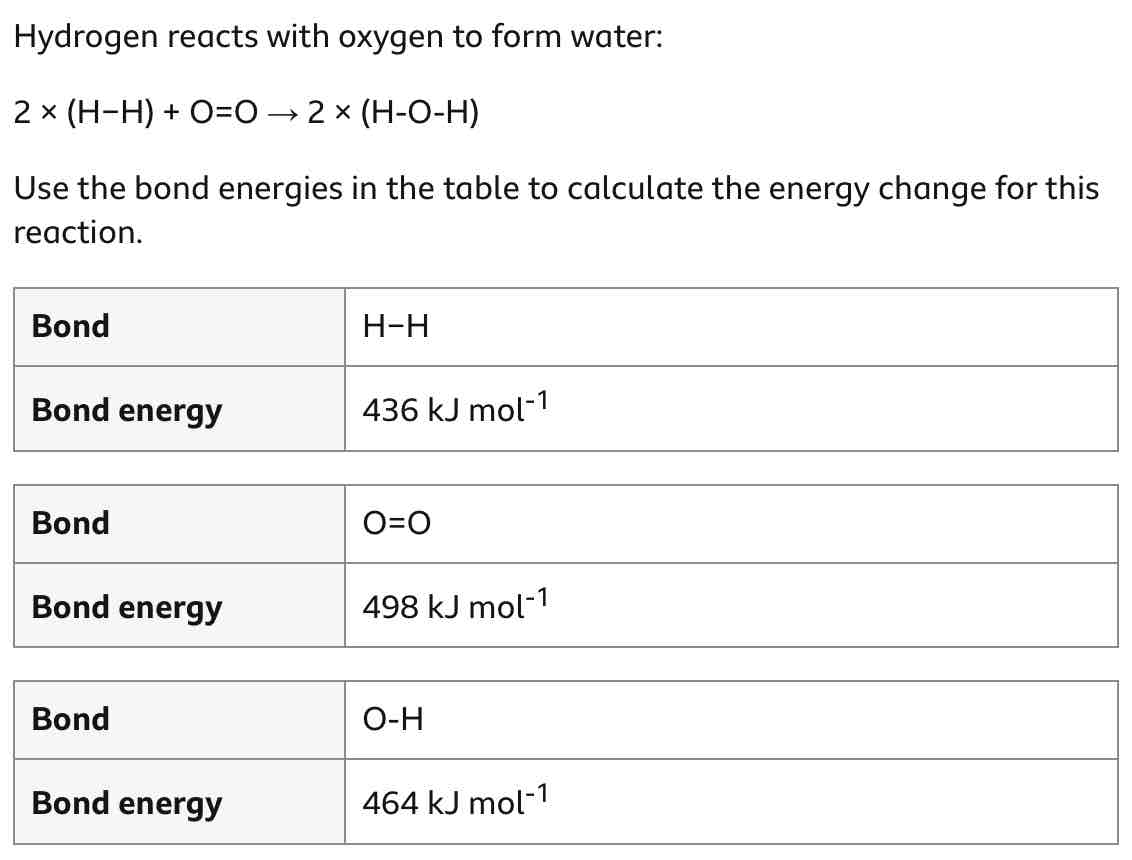
Work out this question.

What is a chemical cell?
A store of internal energy that can be transferred as an electric current in a circuit.
Chemical cells use ____________________ to transfer energy by ___________.
Chemical cells use chemical reactions to transfer energy by electricity.
What does the voltage of a cell depend upon?
A number of factors, including…
What the electrolytes are made from
The substance used as the electrolyte
In a cell, which is the positive electrode?
Cathode
In a cell, which is the negative electrode?
Anode
How can a simple cell be made?
By connecting 2 different metals in contact with an electrolyte.
How can a battery be made?
By connecting a number of cells in series.
A battery has a ______ voltage than a single cell.
A battery has a higher voltage than a single cell.
What are the 2 types of batteries?
non-rechargeable (alkaline) batteries
rechargeable batteries
How do non-rechargeable batteries work?
A voltage is produced until one of the reactants becomes limiting (is used up), and the battery ‘goes flat’.
How do rechargeable batteries work?
The chemical reactions can be reversed when an external circuit is supplied.
How can you achieve a cell with the highest voltage?
By using electrodes of the largest difference in reactivity.
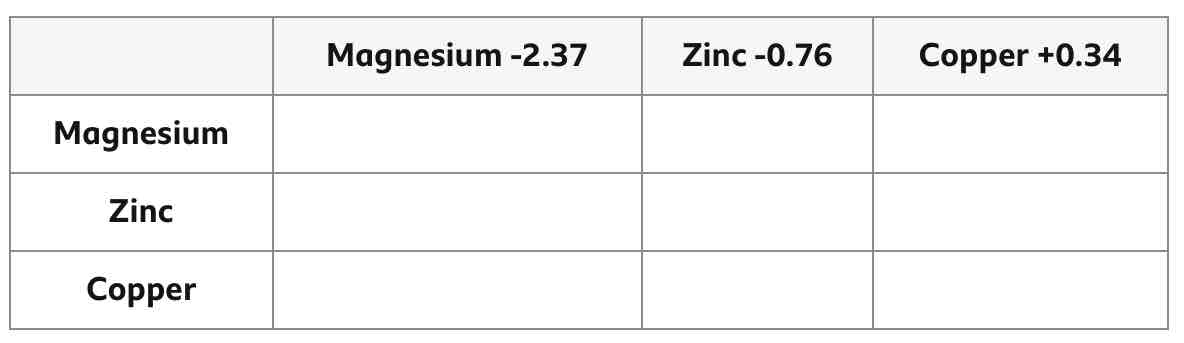
Finish this table.
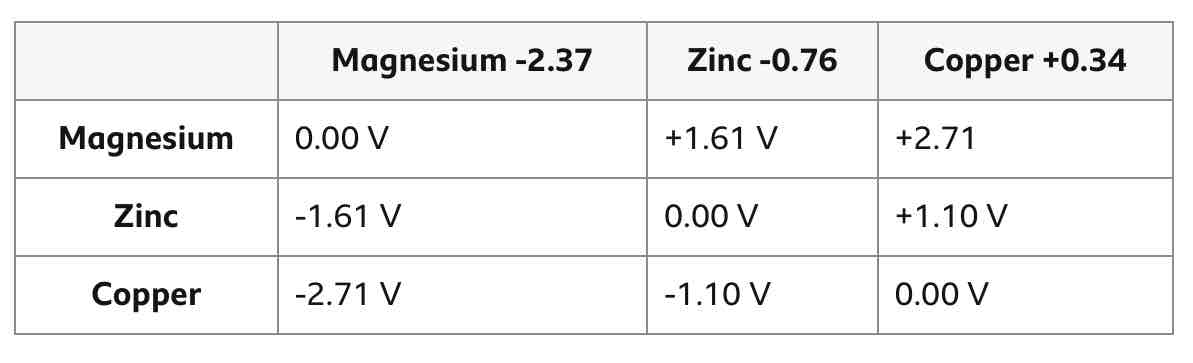
Swapping the 2 electrodes means that the recorded voltage becomes __________.
negative
To achieve a positive voltage, which electrode should go on which side?
Left: more reactive
Right: less reactive
What is a fuel cell?
Device that produces a voltage continuously when supplied with a fuel and oxygen.
Is the fuel cell reaction economically efficient?
Yes
Why is the fuel cell reaction economically efficient?
The fuel is oxidised electrochemically, rather than being burned, so the reaction takes place at a lower temperature than if it was to be burned.
Which is a very common fuel cell example?
The hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell
What is the word equation of hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells?
hydrogen + oxygen → water
Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell
Electrode half equation - anode
Anode is negative.
2H2 + 4OH- → 4H2O + 4e-
Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell
Electrode half equation - cathode
Cathode is positive.
O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-
Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell
Overall equation
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Non-rechargeable cells are also known as…
…alkaline cells.
Alkaline cells - Advantages (1)
Cheaper to manufacture
Alkaline cells - Disadvantages (2)
May end up in landfill sites once fully discharged
Recyclable, but it is expensive
Rechargeable cells - Advantages (2)
Can be recharged many times before being recycled
Reduces use of resources
Rechargeable cells - Disadvantages (1)
Costs more to manufacture
Hydrogen fuel cell - Advantages (3)
Easy to maintain as there are no moving parts
Small size
Water is the only chemical product
Hydrogen fuel cell - Disadvantages (3)
Very expensive to manufacture
Needs a constant supply of hydrogen fuel
Hydrogen is a flammable gas
Where are fuel cells often used?
in…
spacecraft
vehicles
What may be a problem with using hydrogen fuel cells in space?
Much be supplied with hydrogen fuel and oxygen, which aren’t present in space.
How is the problem of no oxygen in space overcome?
Spacecraft in orbit, eg. ISS, have solar cells to convert light into electricity, so the hydrogen and oxygen are replaced by the electrolysis of water.
Why are fuel cells still used, instead of just the electrolysis of water alone?
Solar cells only work when they are in light, so the fuel cells allow electricity to be produced even when the spacecraft is in the dark.
What is the ISS?
International Space Station