Biology IGCSE - Coordination and Response
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Electrical impulses travel along neurones
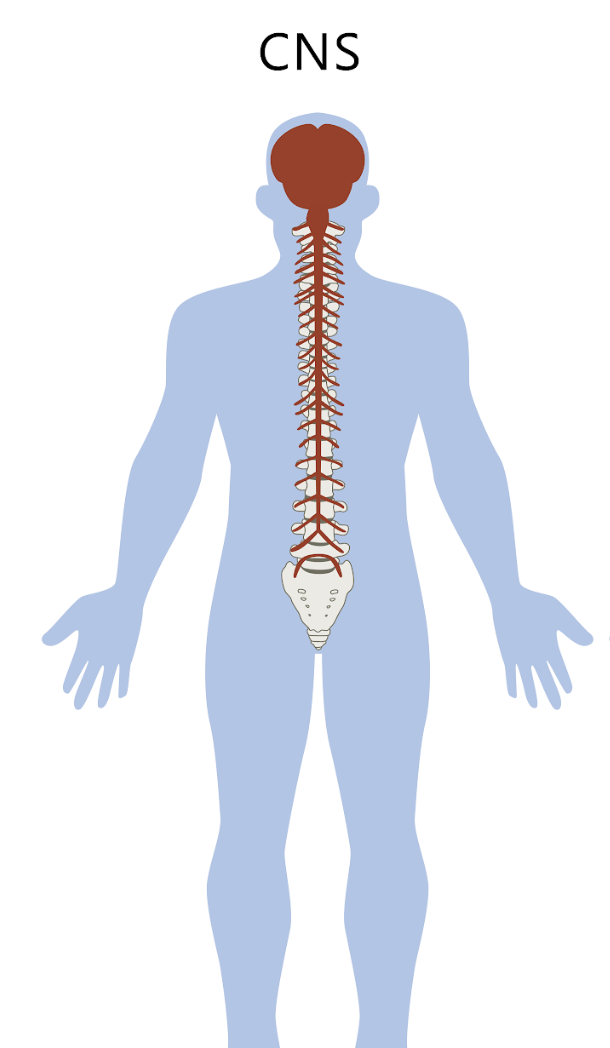
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
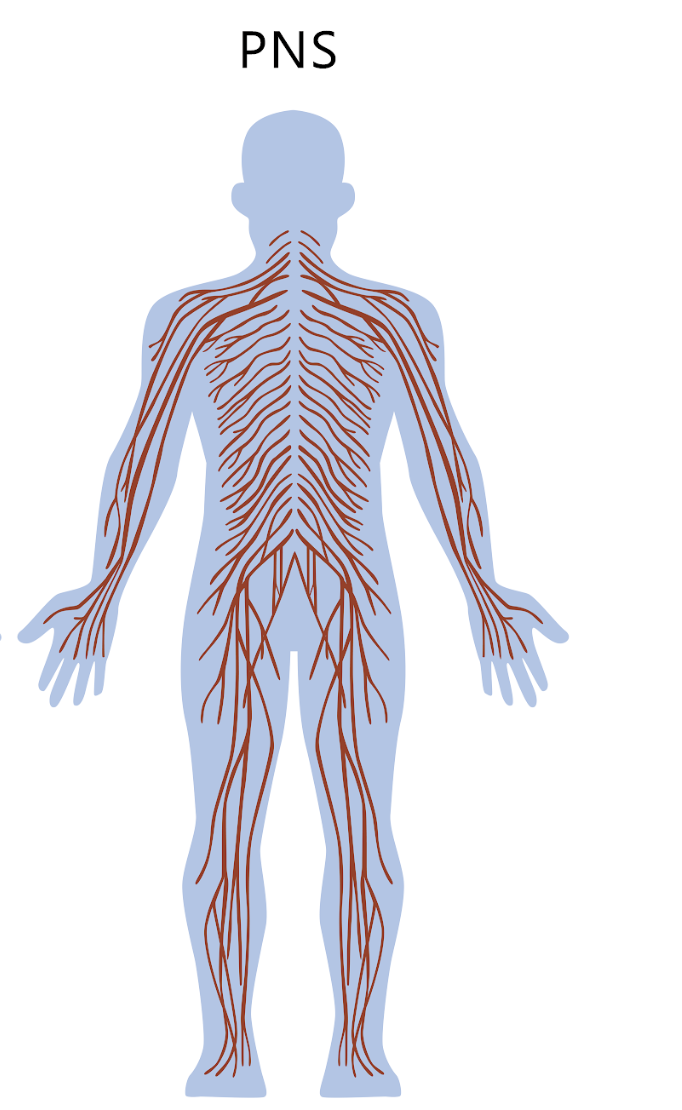
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
nerves outside of the brain + spinal cord
Role of nervous system
coordinates + regulates body functions by detecting stimuli + sending electrical impulses to bring a response
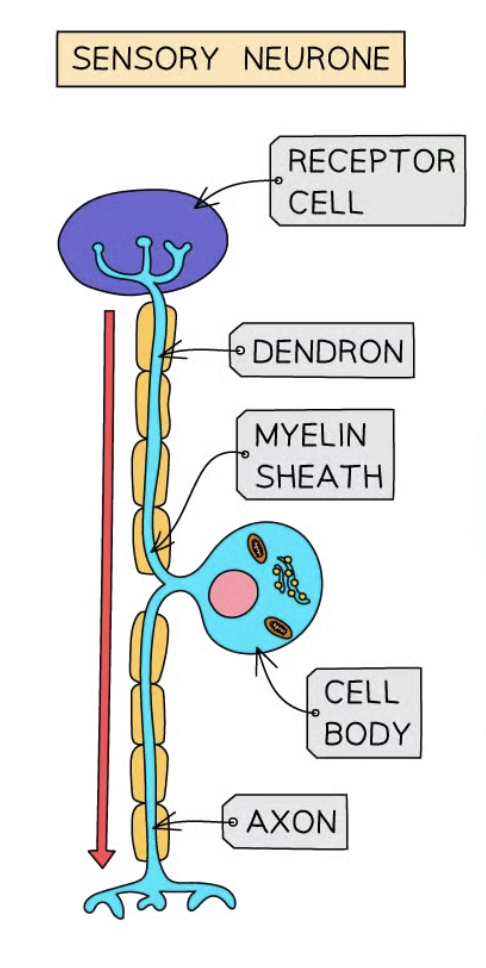
Sensory neurones
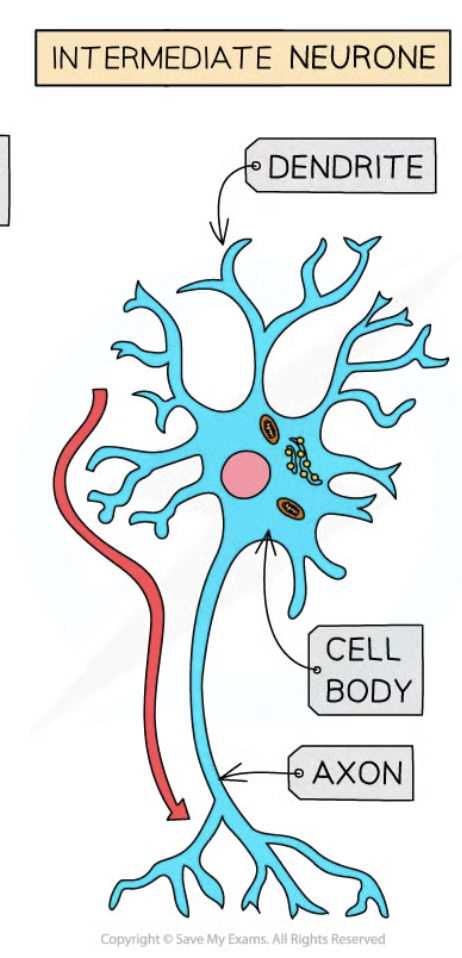
Relay neurones
Motor neurones
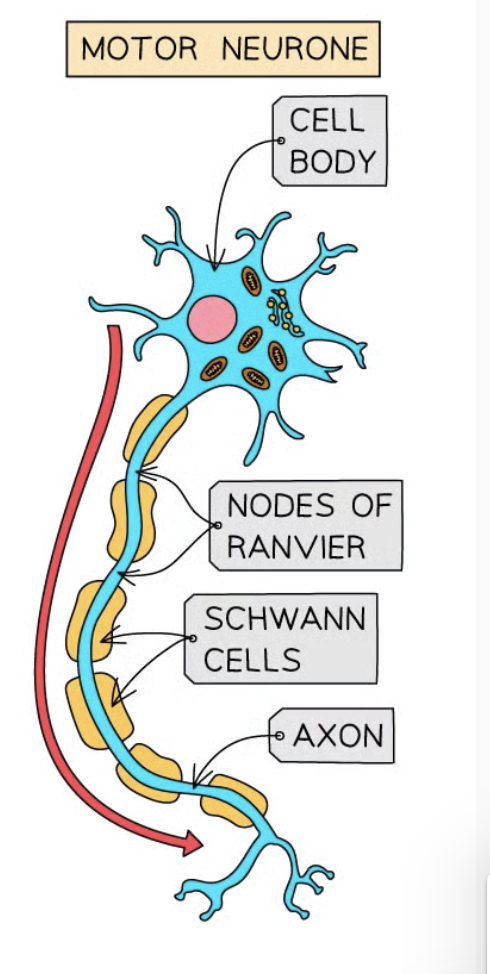
Simple reflex arc
Our bodies detect changes in environment → change in environment is called a stimulus → e.g. light or temperature → sense organs → e.g. eyes help to detect stimuli using specialised cells → called receptor cells → receptor cells create electrical signal called a nerve impulse → travels down a neurone → pass the nerve impulse to each other until reaches effector → e.g. muscle or gland carries out response
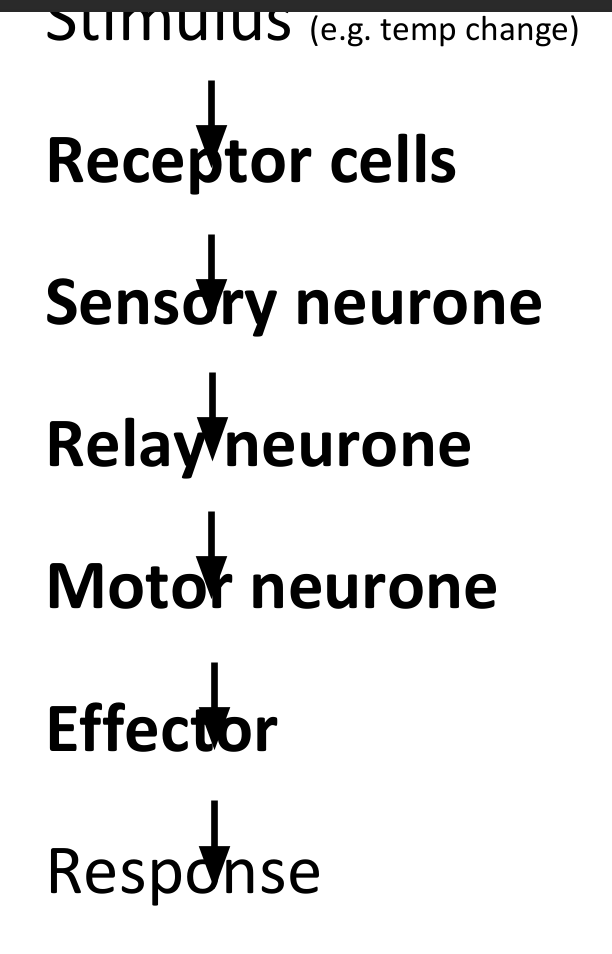
Common reflex arc diagram
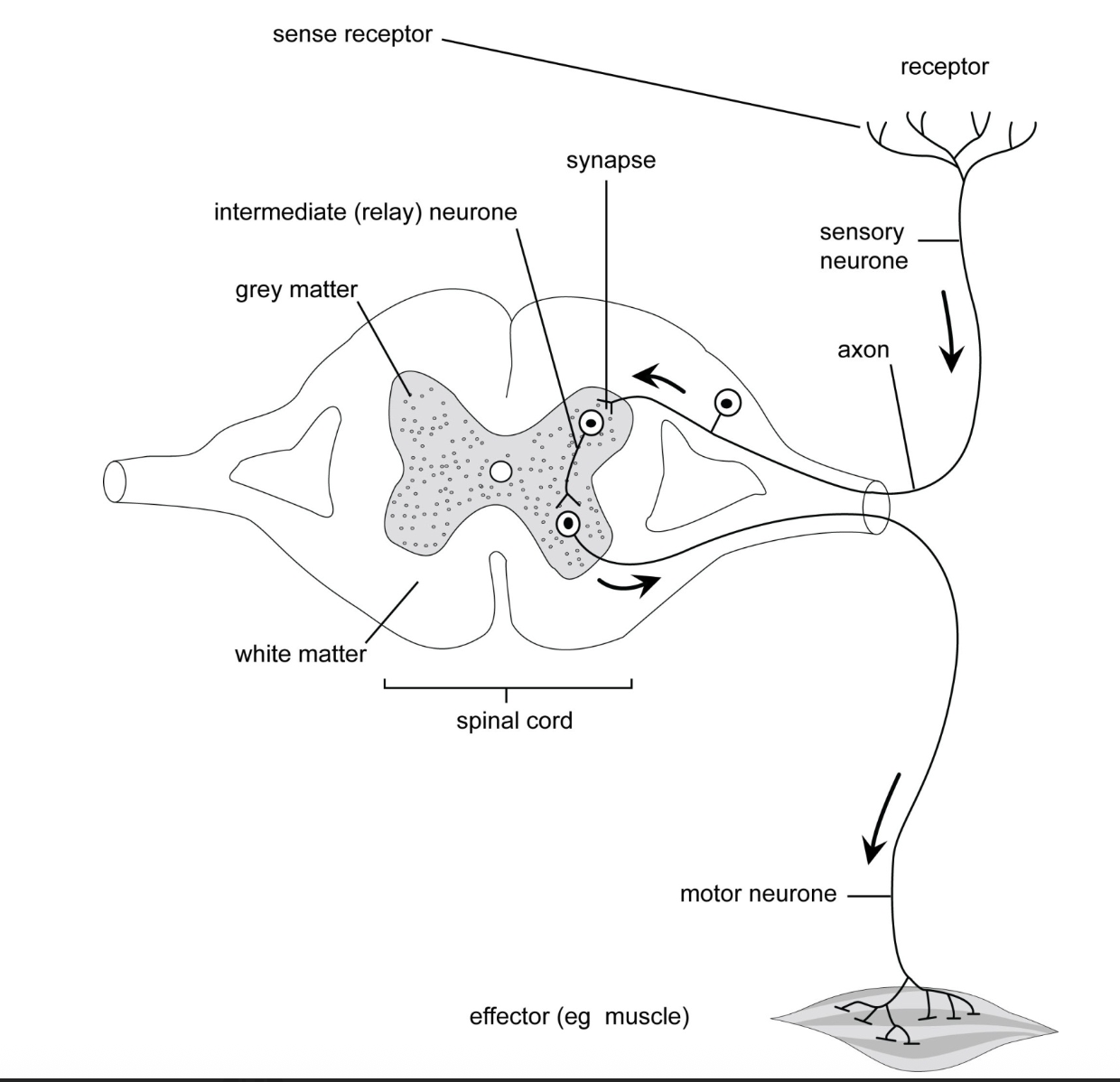
Reflex action
means of automatically (unconsciously) + rapidly integrating + coordinating stimuli wit responses of effectors → e.g. muscles + glands
Response of effectors
Muscles contract
Gands secrete chemicals
Sense organs
groups of receptor cells responding to specific stimuli → e.g. light, sound, touch, temperature + chemicals
Hormone
chemical substance → produced by a gland → carried by the blood → alters the activity of one or more specific target organs
Hormones VS nervous system
Hormones can act very rapidly, but compared to nervous system → effects are slower, but longer lasting
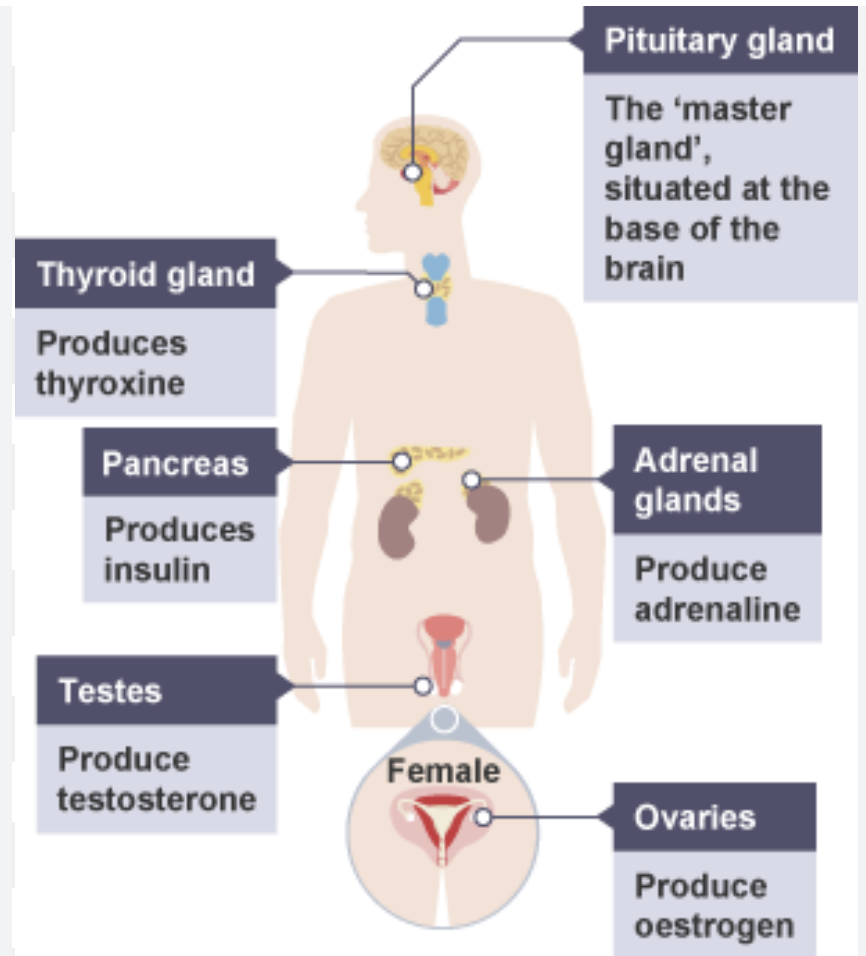
adrenal glands → adrenaline
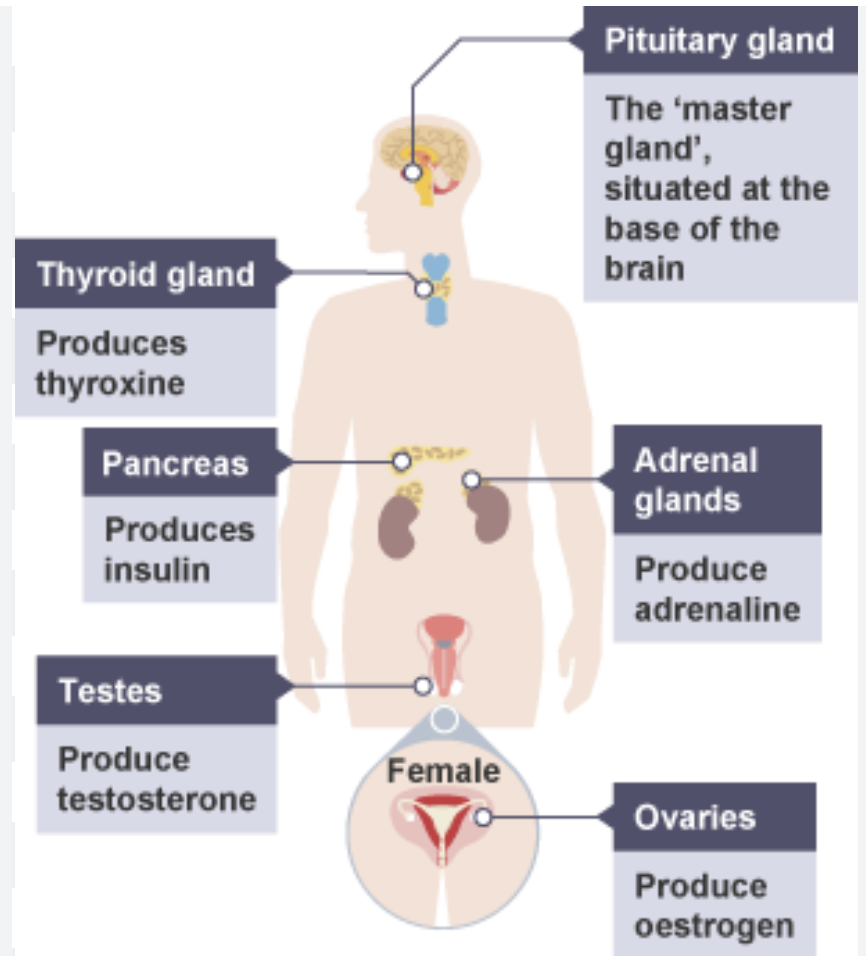
pancreas → insulin
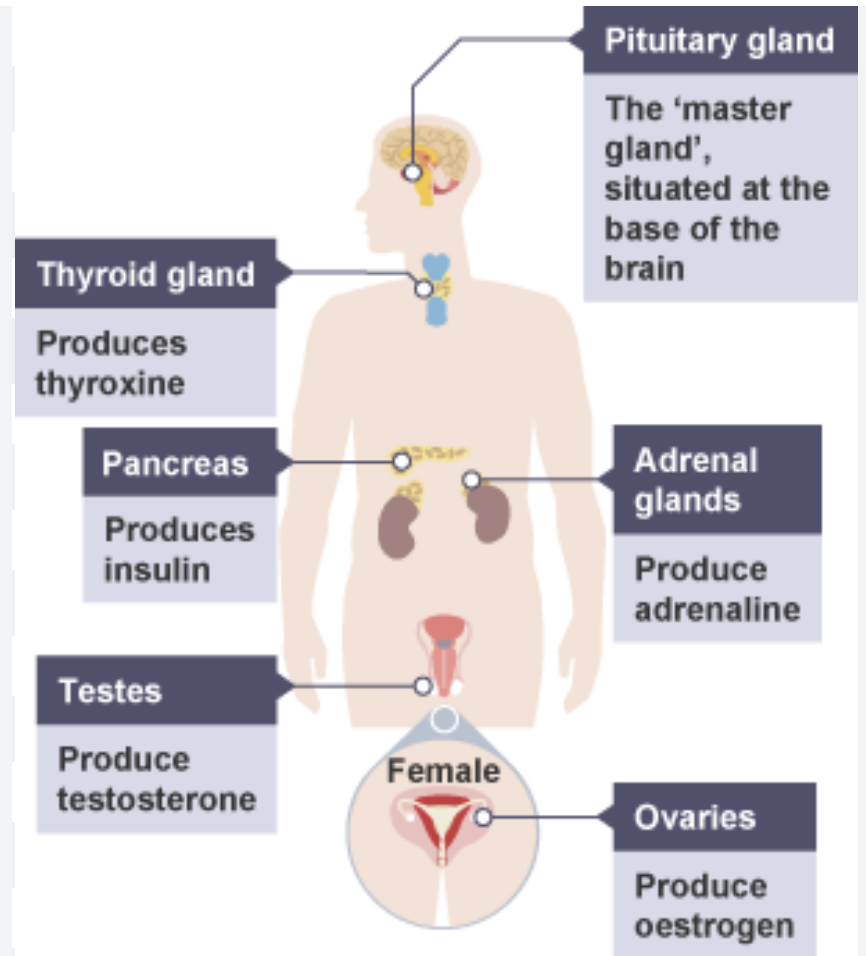
testes → testosterone
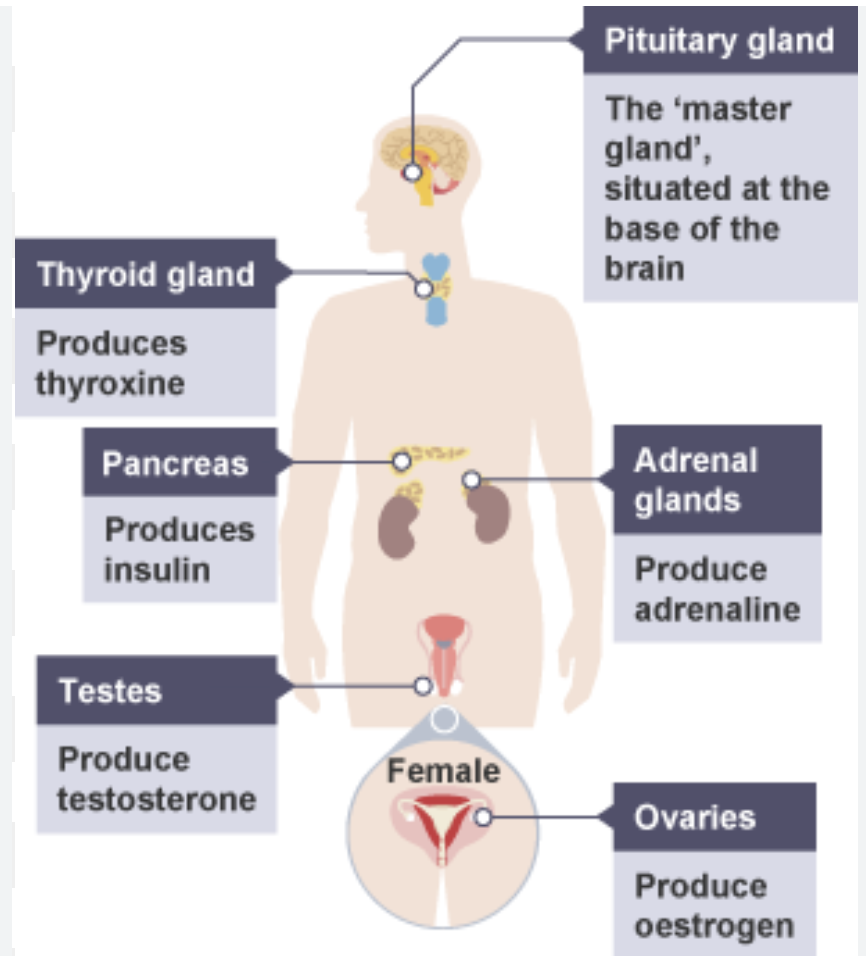
ovaries → oestrogen
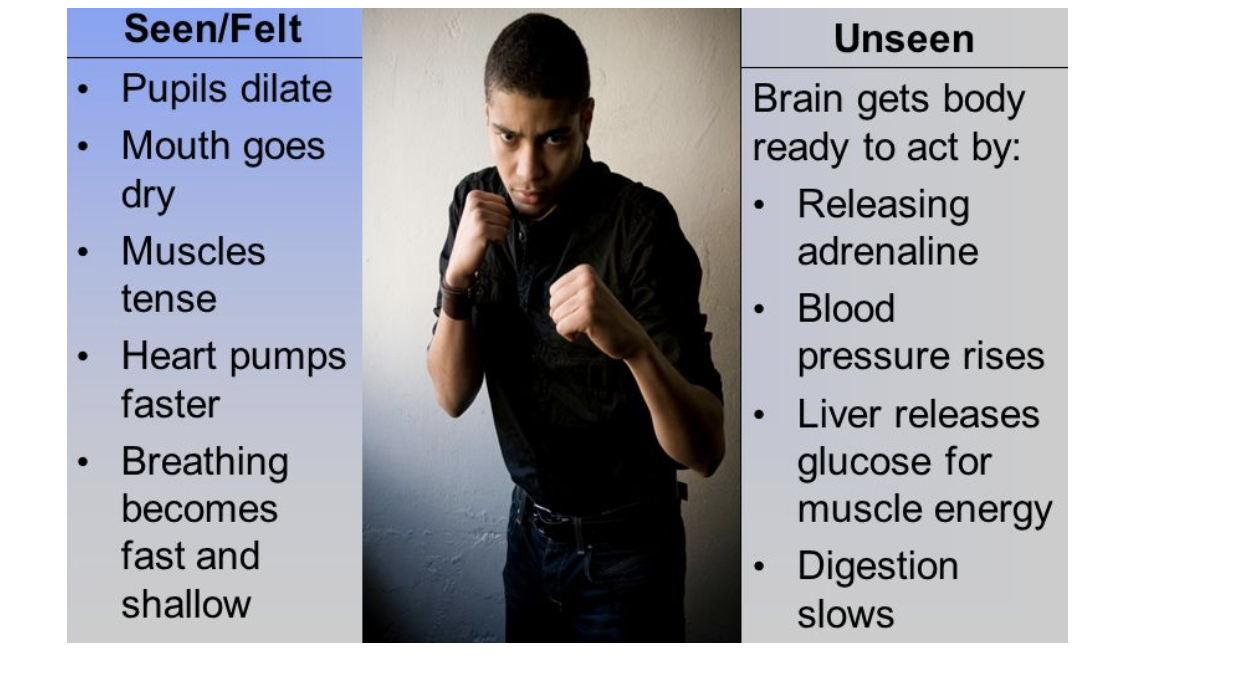
Adrenaline
Hormones secreted in ‘fight or flight’ situations
Adrenaline effects
Increased heart rate
Increased breathing rate
Pupils dilate
Causes liver to convert glycogen → glucose → increases blood glucose concentration → ready for more respiration for fighting or running away
Glucagon is secreted by the pancreas
Homeostasis
maintenance of a constant internal environment
Homeostatic control by negative feedback
Negative feedback → process that returns a system to its set point if it moves too far from it
How negative feedback works
Change is detected → e.g. too hot/too much glucose
Body responds to counteract the change
Internal environment returns to normal
Control of blood glucose concentrations by the liver
Regulated by the pancreas + liver
Control of blood glucose concentrations → insulin
Insulin → secreted when blood glucose high) → produced by pancreas → tells the liver to convert glucose into glycogen for storage → lowers blood glucose
Insulin
Insulin helps cells absorb glucose → lowers blood glucose

Control of blood glucose concentrations → glucagon
Glucagon → secreted when blood glucose is low → produced by pancreas → tells the liver to convert glycogen into glucose → Raises blood glucose
Glucagon
When glucose is gone, you release glucaGON → tells liver to release glucose into blood → raises blood sugar

Diagram of skin
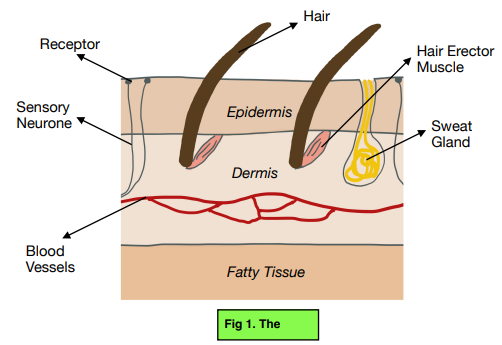
Maintenance of a constant internal body temperature → insulation
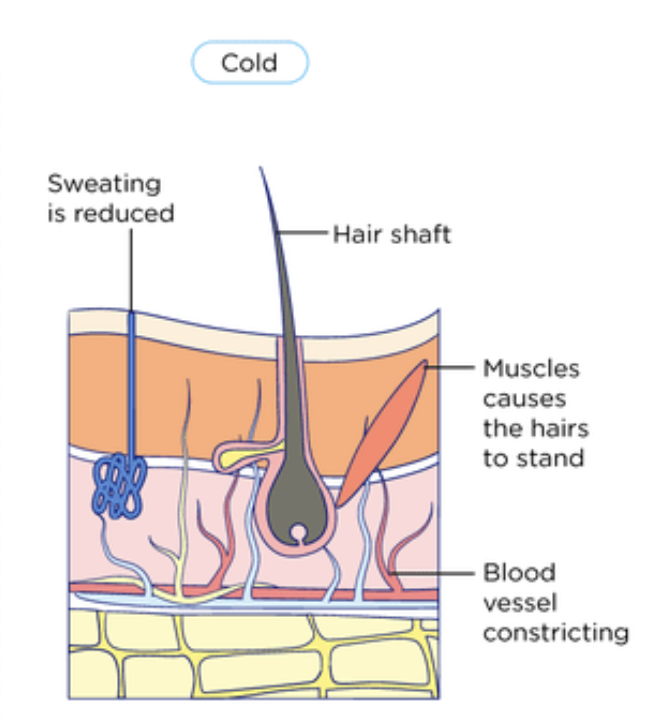
When body temperature low → hair erector muscles contract → makes hairs stand upright → traps layer of air close to skin → acts as insulation
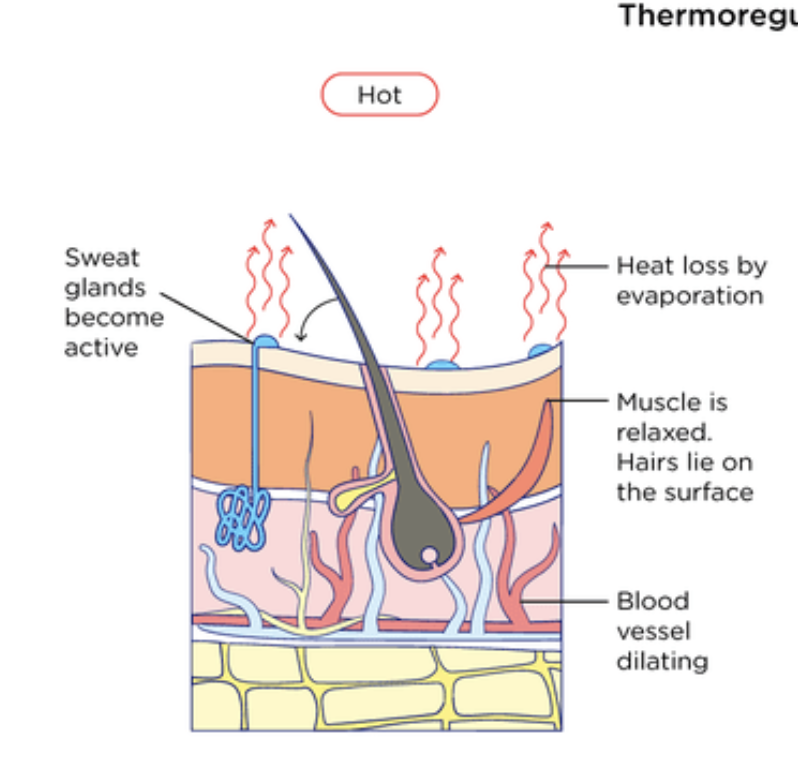
Maintenance of a constant internal body temperature → sweating
Body temperature high → sweat glands release more sweat → as sweat evaporates from skin → thermal energy is lost → cools the body
Maintenance of a constant internal body temperature → shivering
Shivering → rapid contraction + relaxation of muscles → increases respiration in muscle cells → releases heat to warm body
Maintenance of a constant internal body temperature → role of the brain
Hypothalamus in brain → detects changes in blood temperature → triggers responses → e.g. sweating or shivering to maintain a stable internal temperature
Maintenance of a constant internal body temperature → vasodilation
Vasodilation → widening of arterioles near skin surface → increases blood flow to skin → allows more heat to escape
Maintenance of a constant internal body temperature → vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction → narrowing of arterioles near skin surface → reduces blood flow → less heat is lost from body
Vasodilation
Vasodilation = ventilation → opening windows to let heat out
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction = wearing a tight jacket → keeps warmth in