APAH Unit 3 Greco Roman Vocab
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
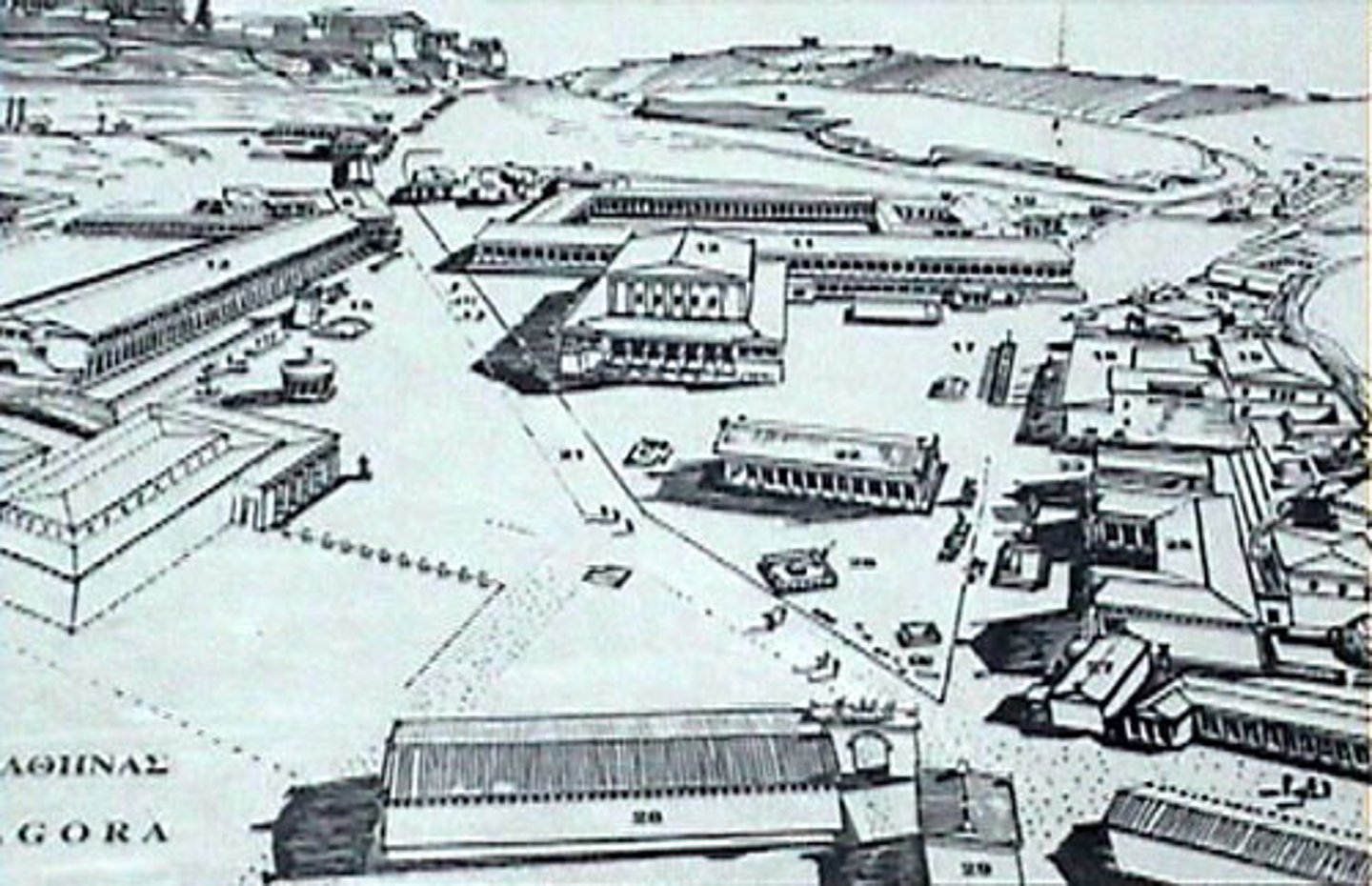
Acropolis
literally, a "high city," a Greek temple complex built on a hill over a city

Agora
a public plaza in a Greek city where commercial, religious, and societal activities are conducted
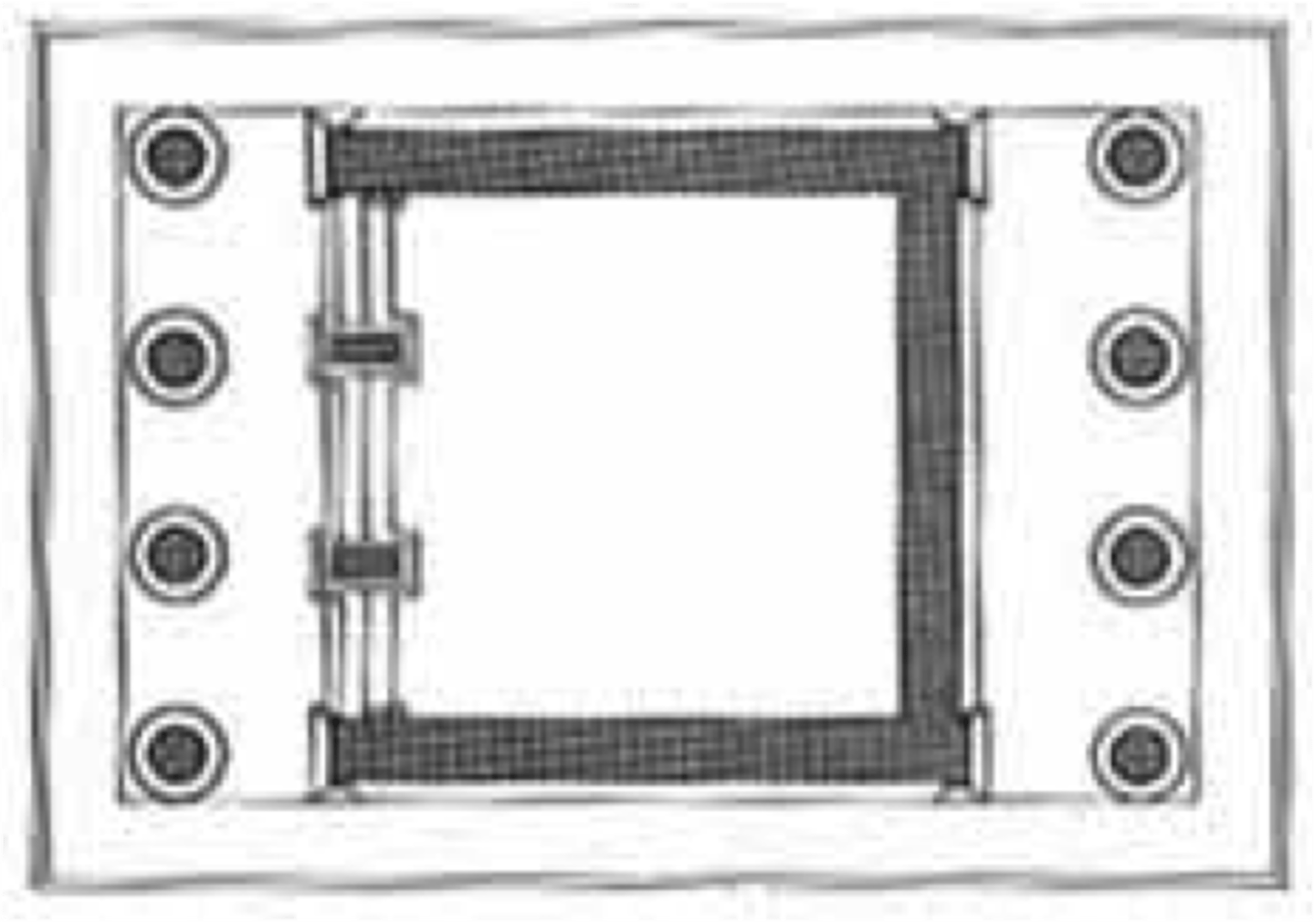
Amphiprostyle
having four columns in the front and rear of a temple
Amphora
a two-handled Greek storage jar

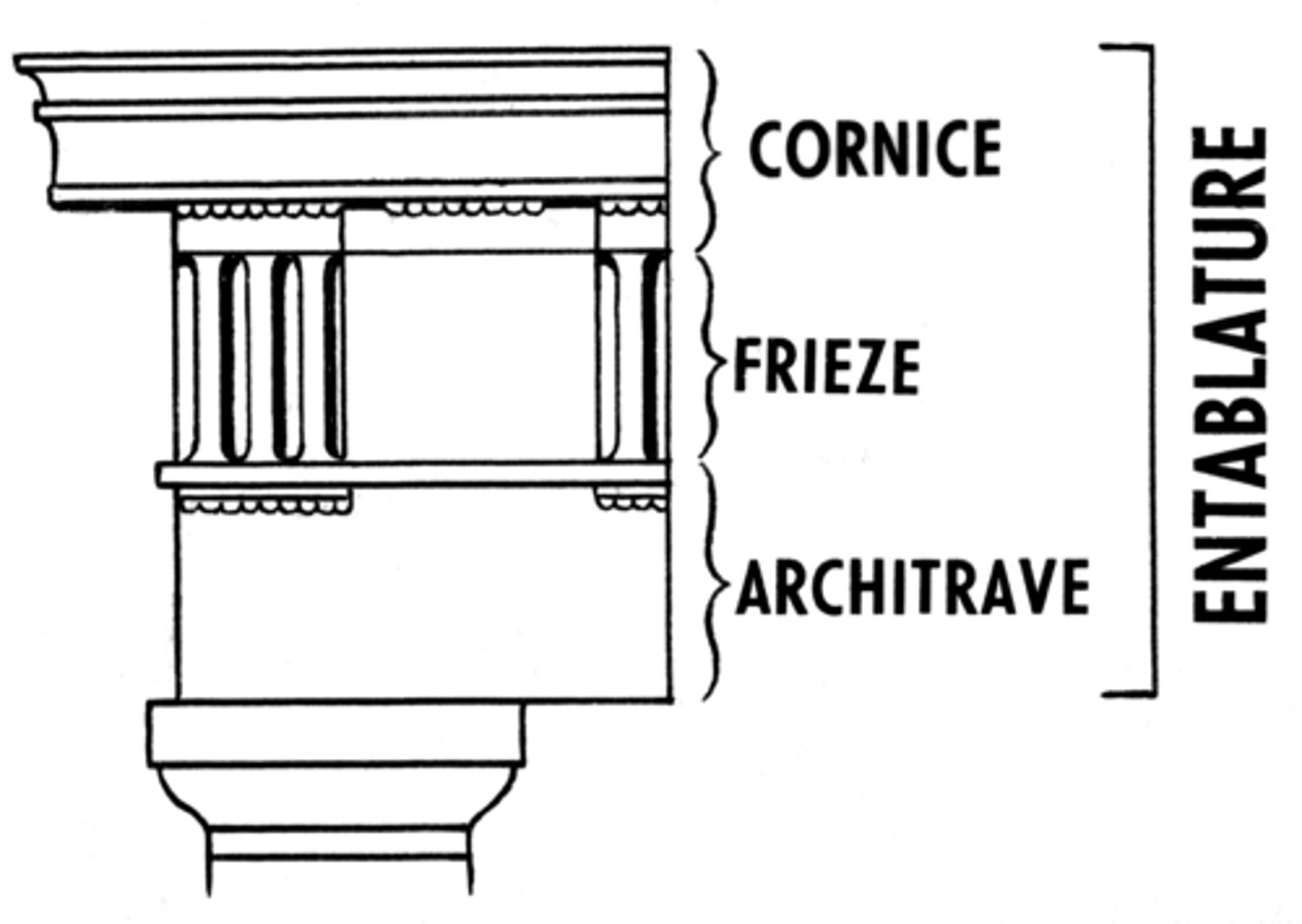
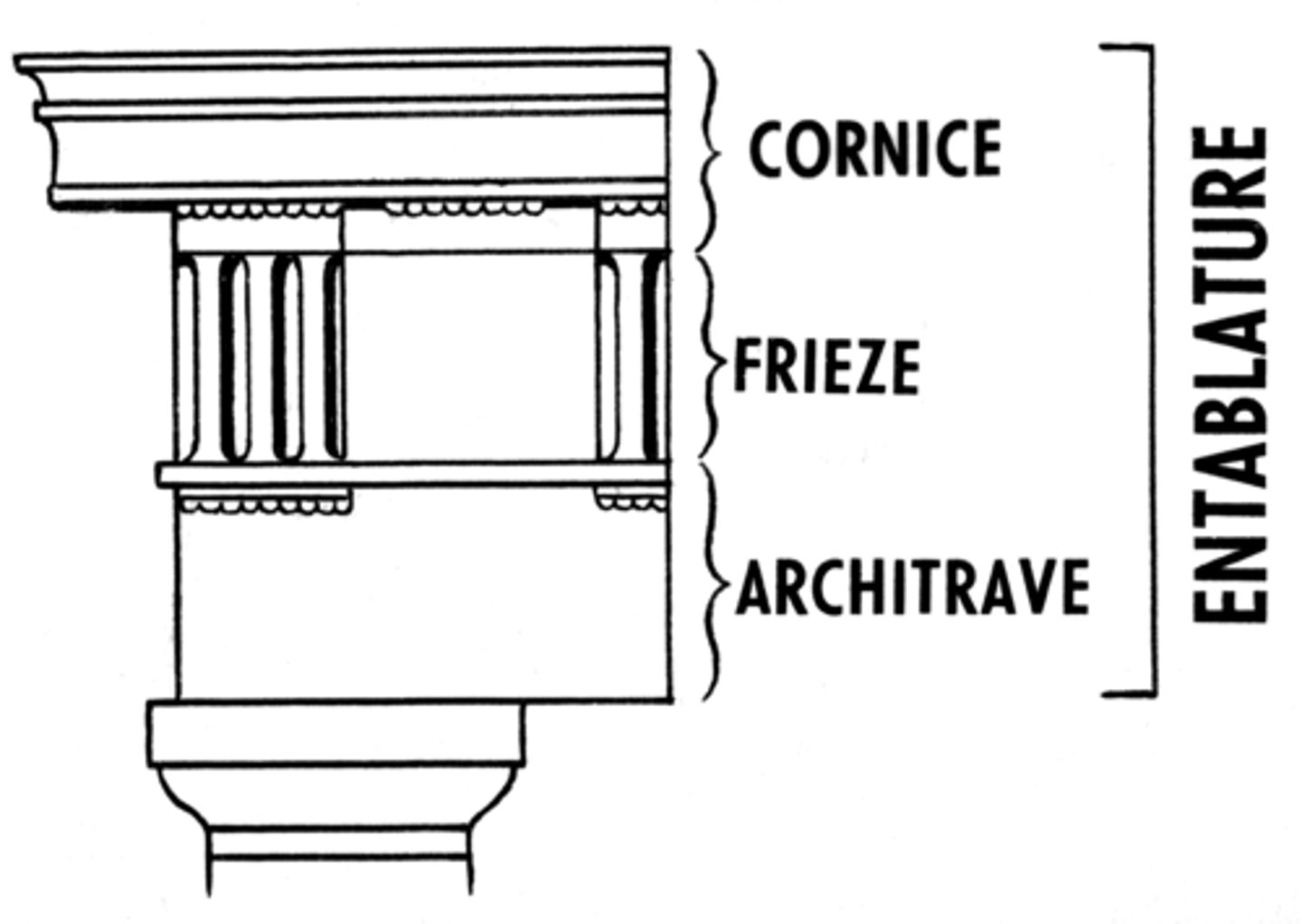
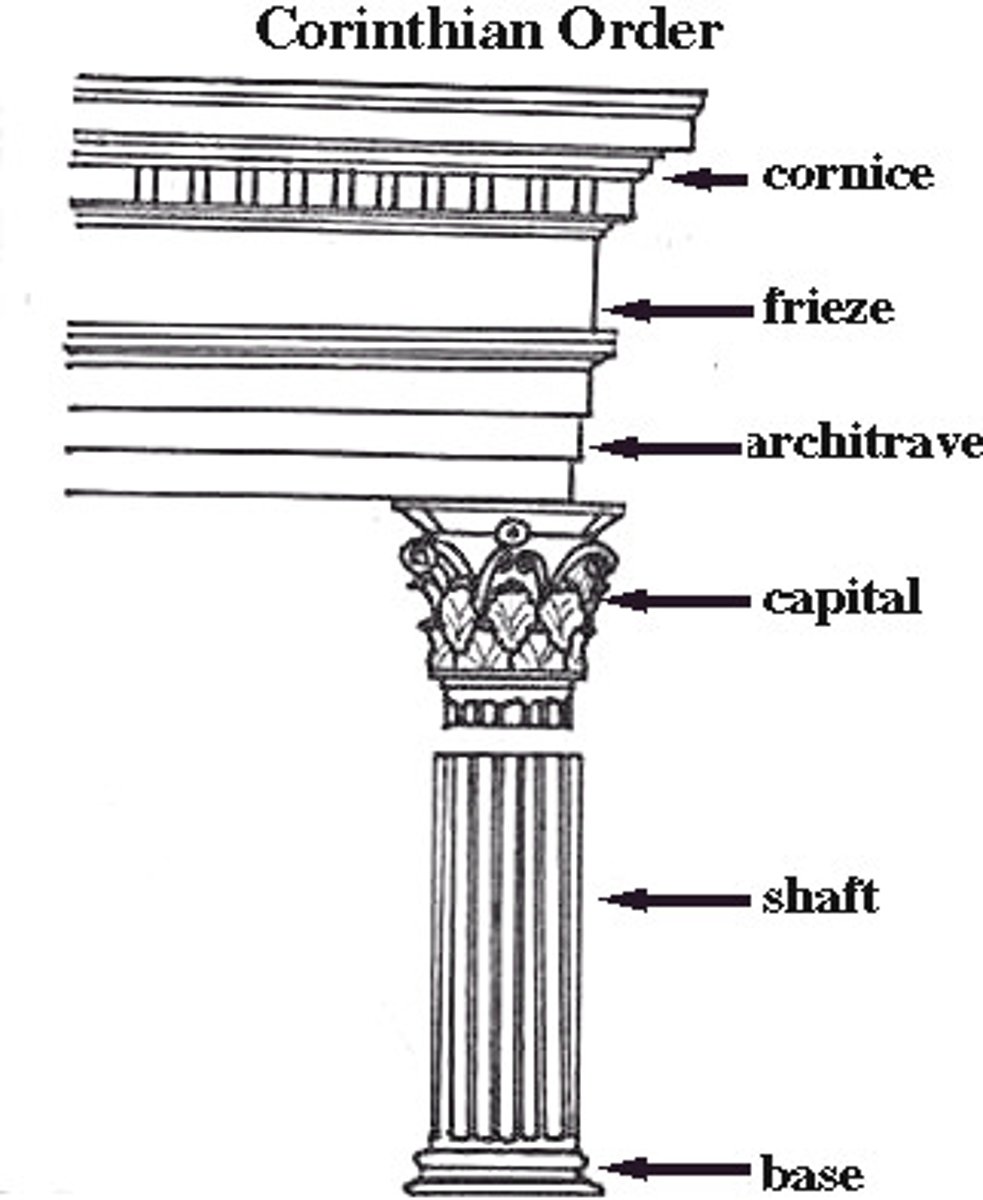
Architrave
a plain, unornamented lintel on the entablature
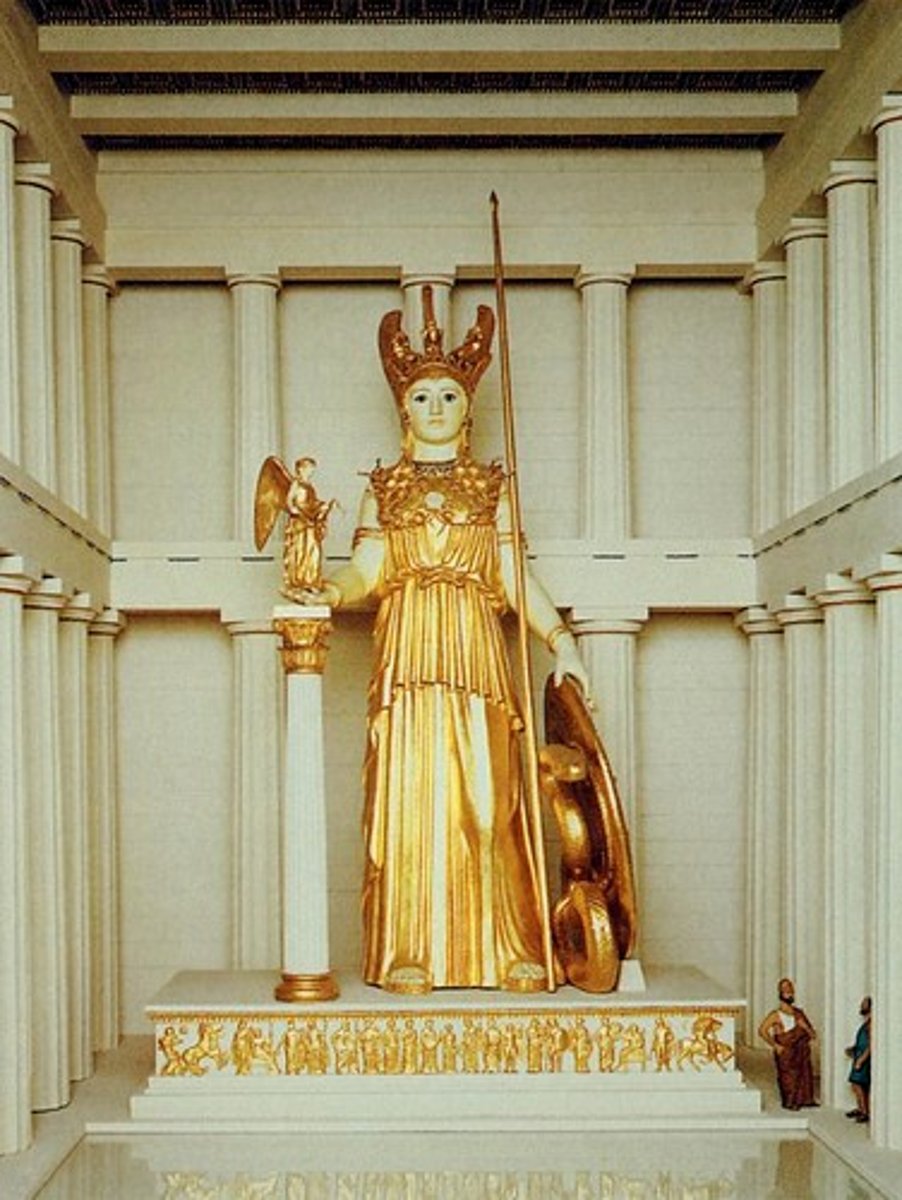
Athena
Greek goddess of war and wisdom; patron of Athens

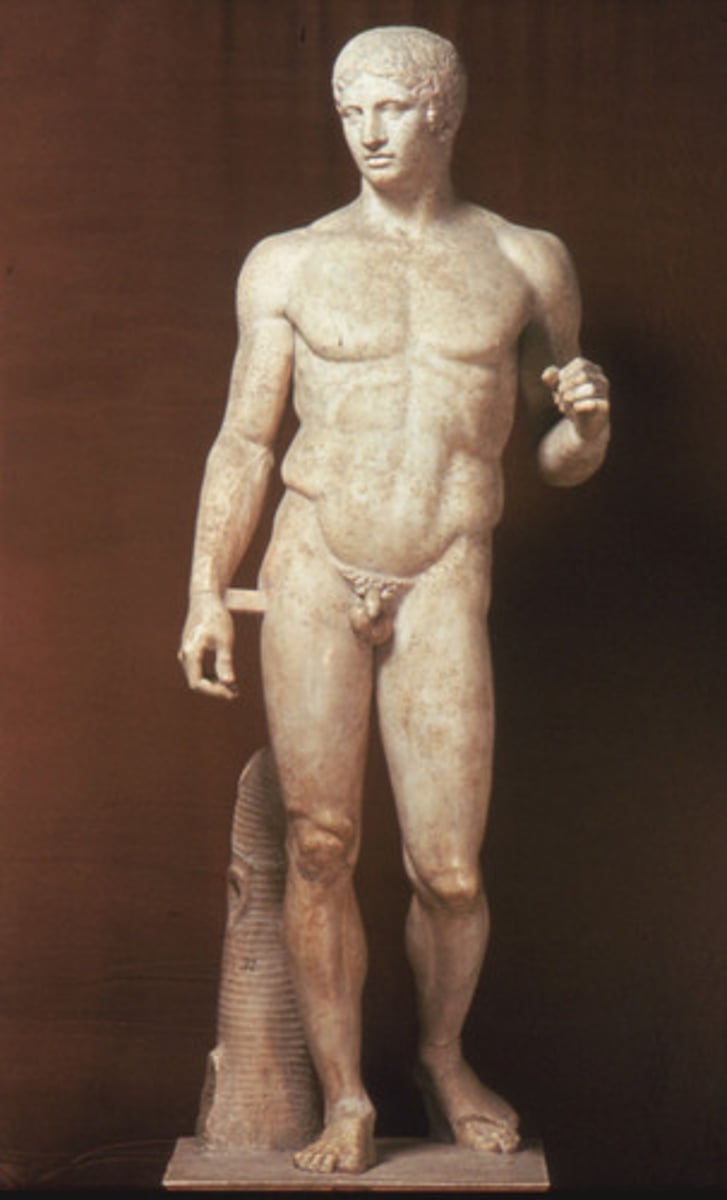
Canon
a body of rules or laws; in Greek art, the ideal mathematical proportion of a figure

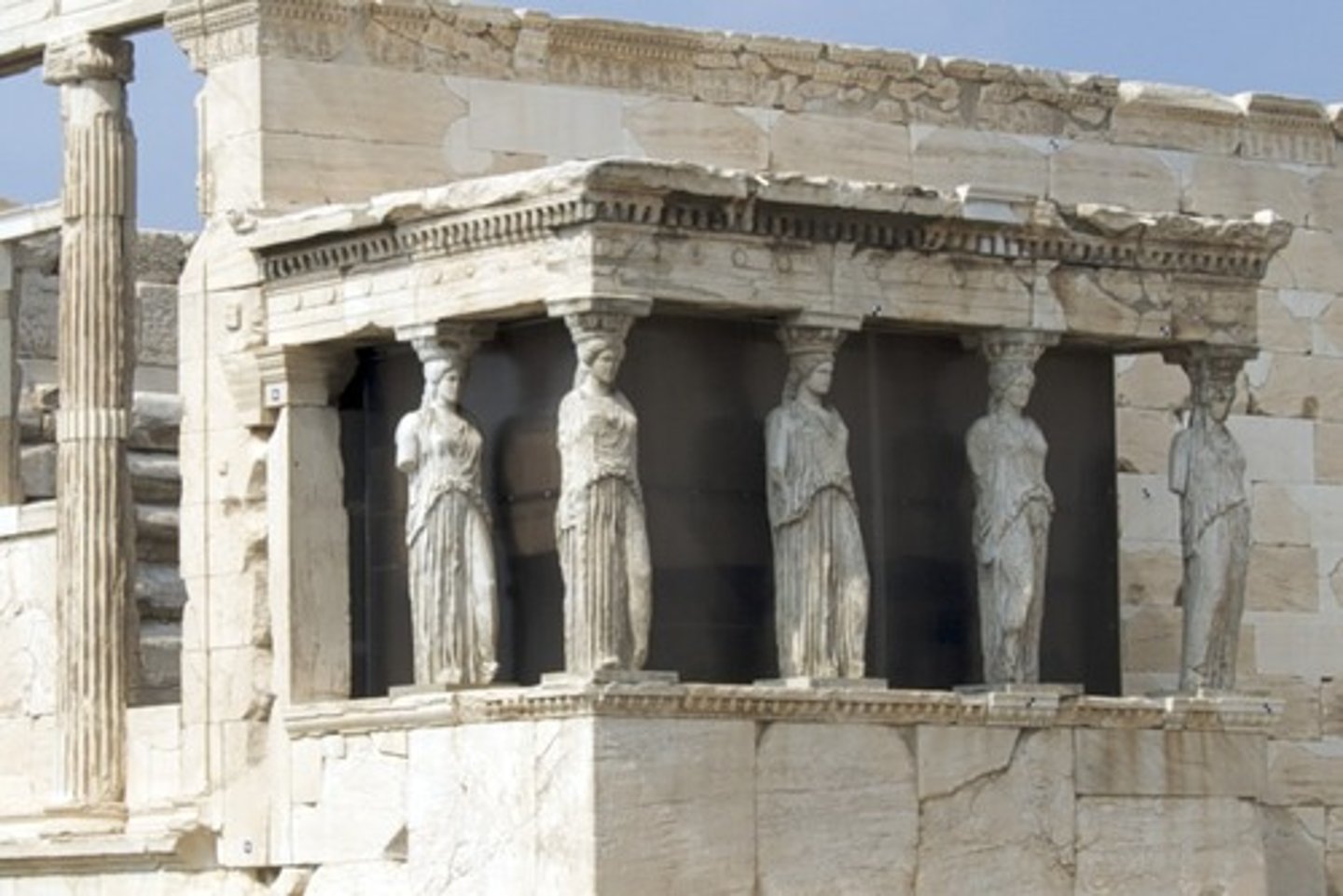
Caryatid (male: atlantid)
a building column that is shaped like a female figure

Cella
the main room of a temple where the god is housed

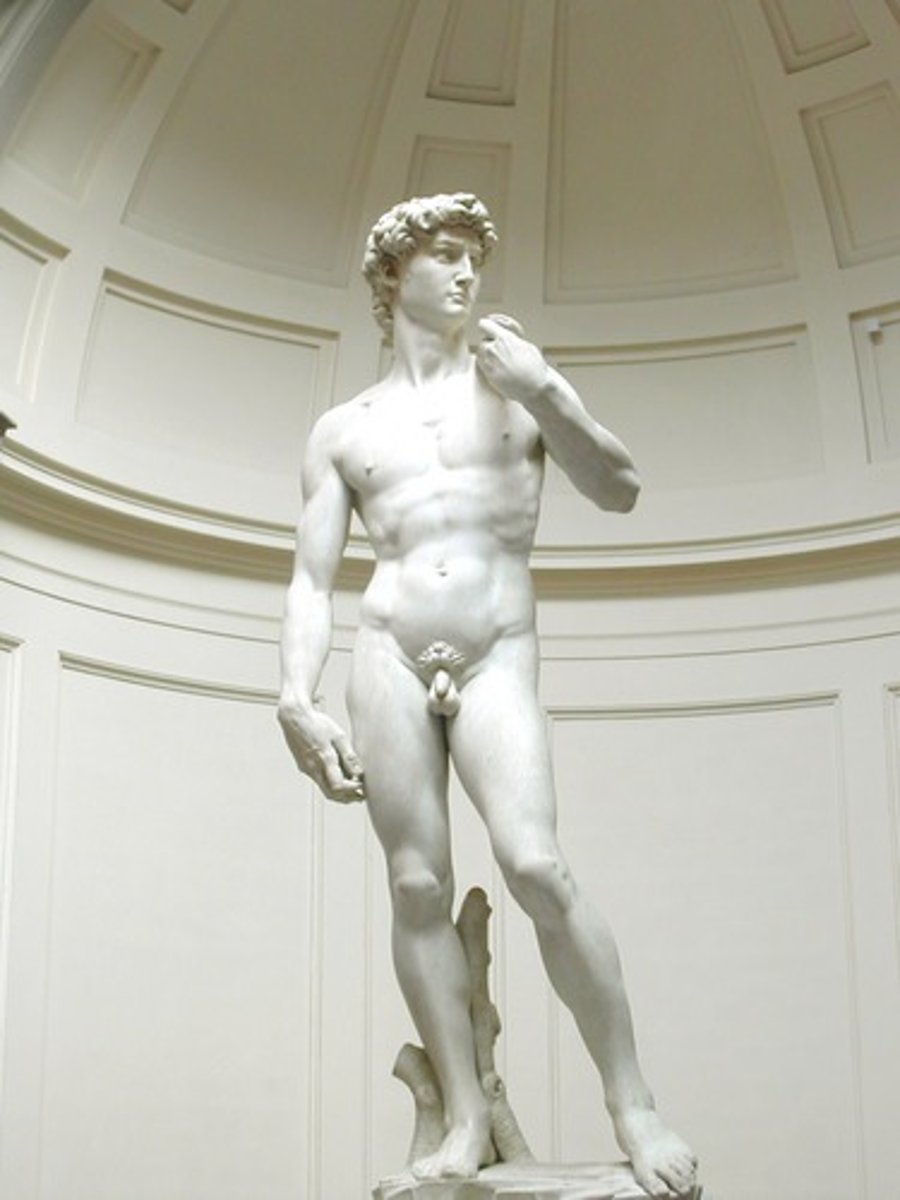
Contrapposto
a graceful arrangement of the body based on tilted shoulders and hips and bent knees

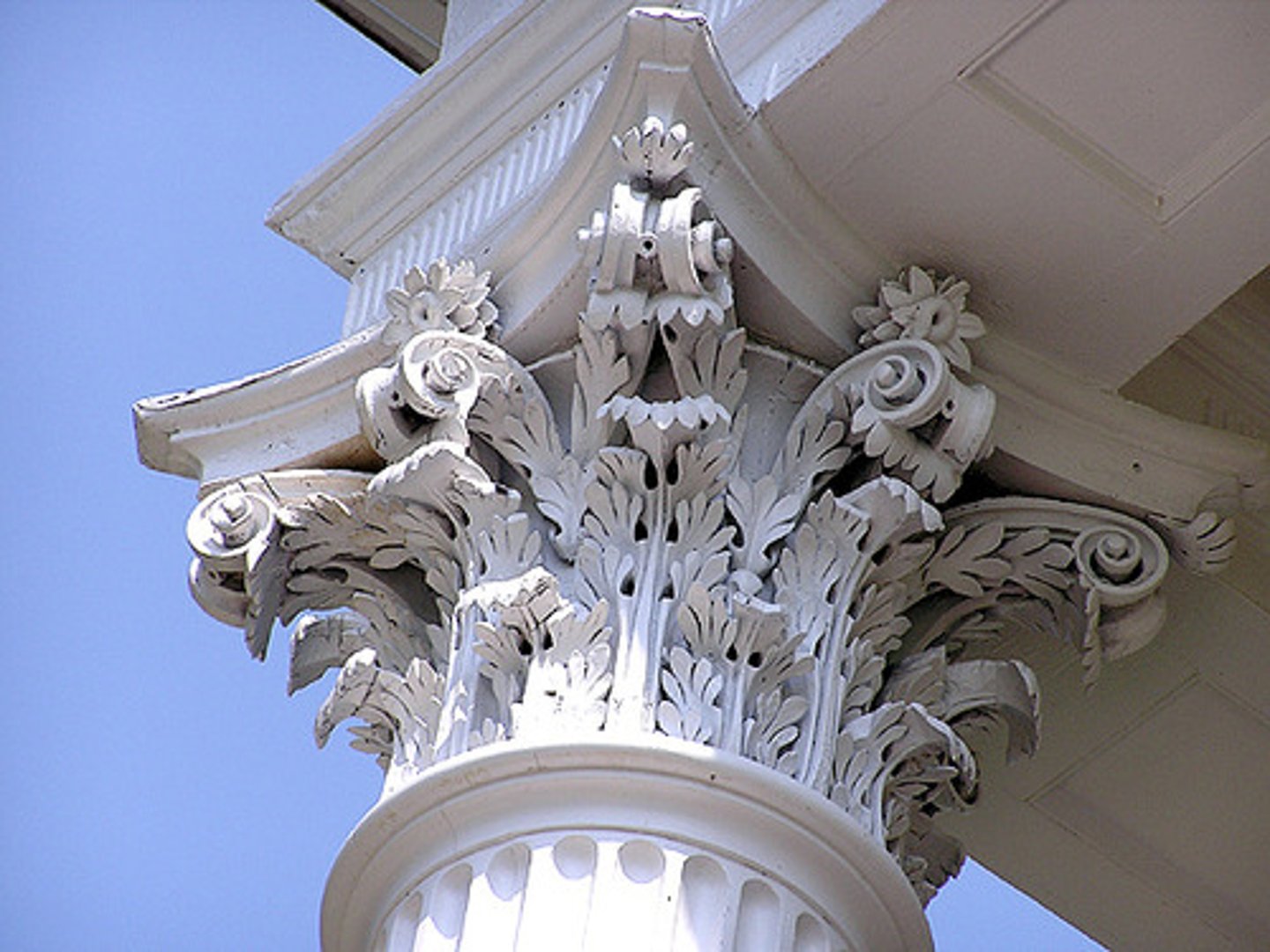
Corinthian
an order of ancient Greek architecture similar to the Ionic, except that the capitals are carved in tiers of leaves; this type of temple pillar was developed last

Cornice
a projecting ledge over a wall
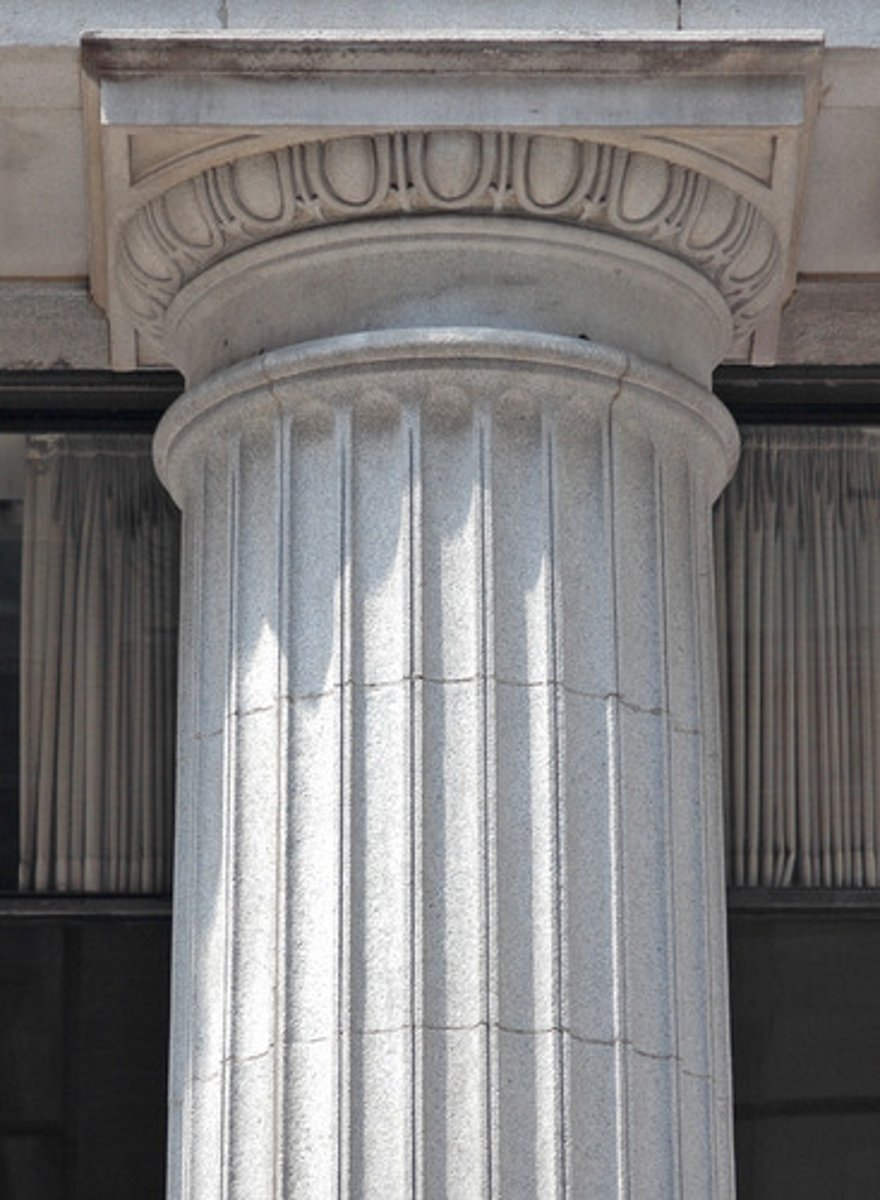
Doric
an order of ancient Greek architecture that features grooved columns with no grooved bases and an upper story with square sculpture called metopes; resonates with mainland Greece and its settlements

Encaustic
a type of painting in which colors are added to hot wax to affix to a surface

Entablature
the upper story of a Greek temple
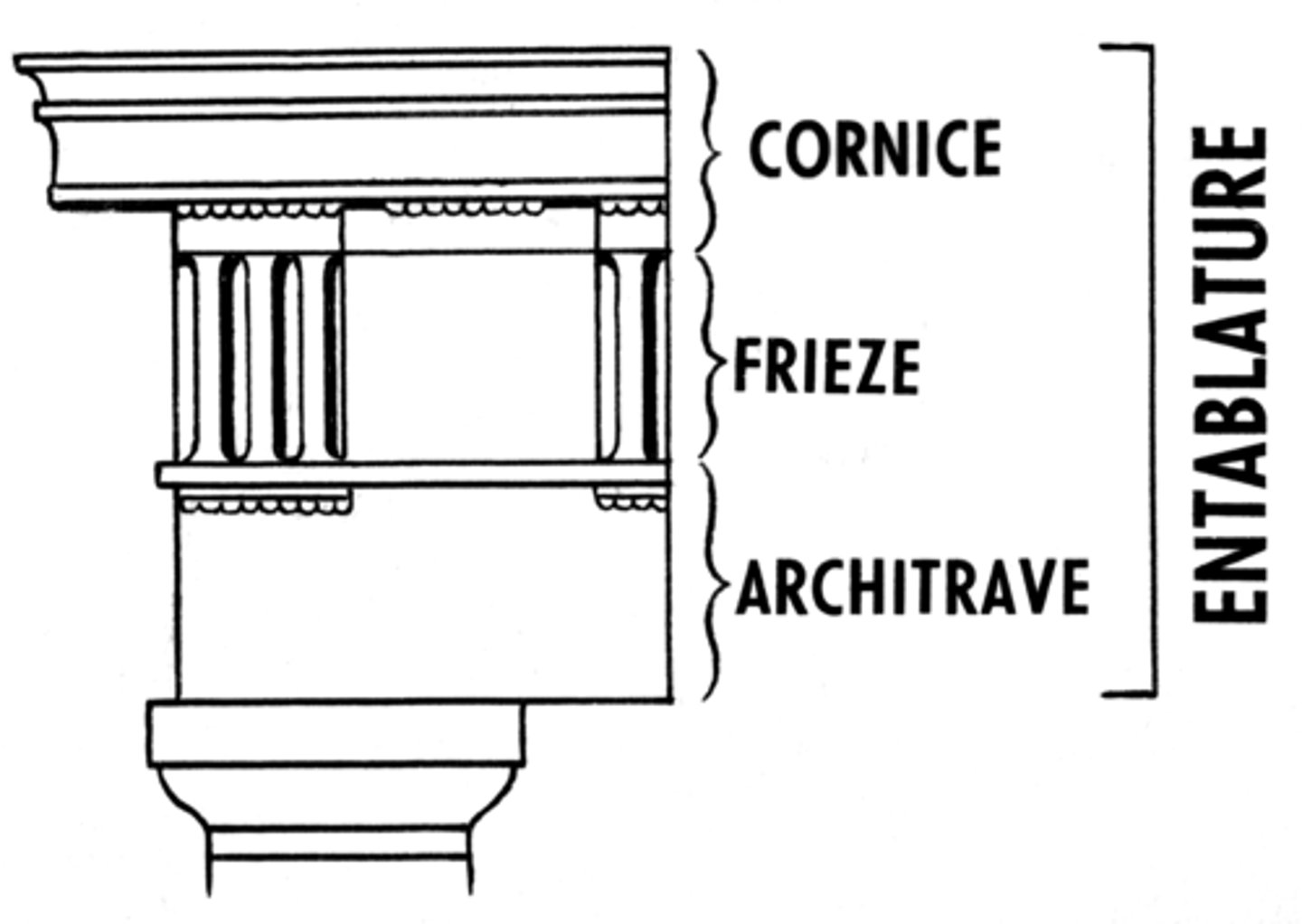
Frieze
a horizontal band of sculpture
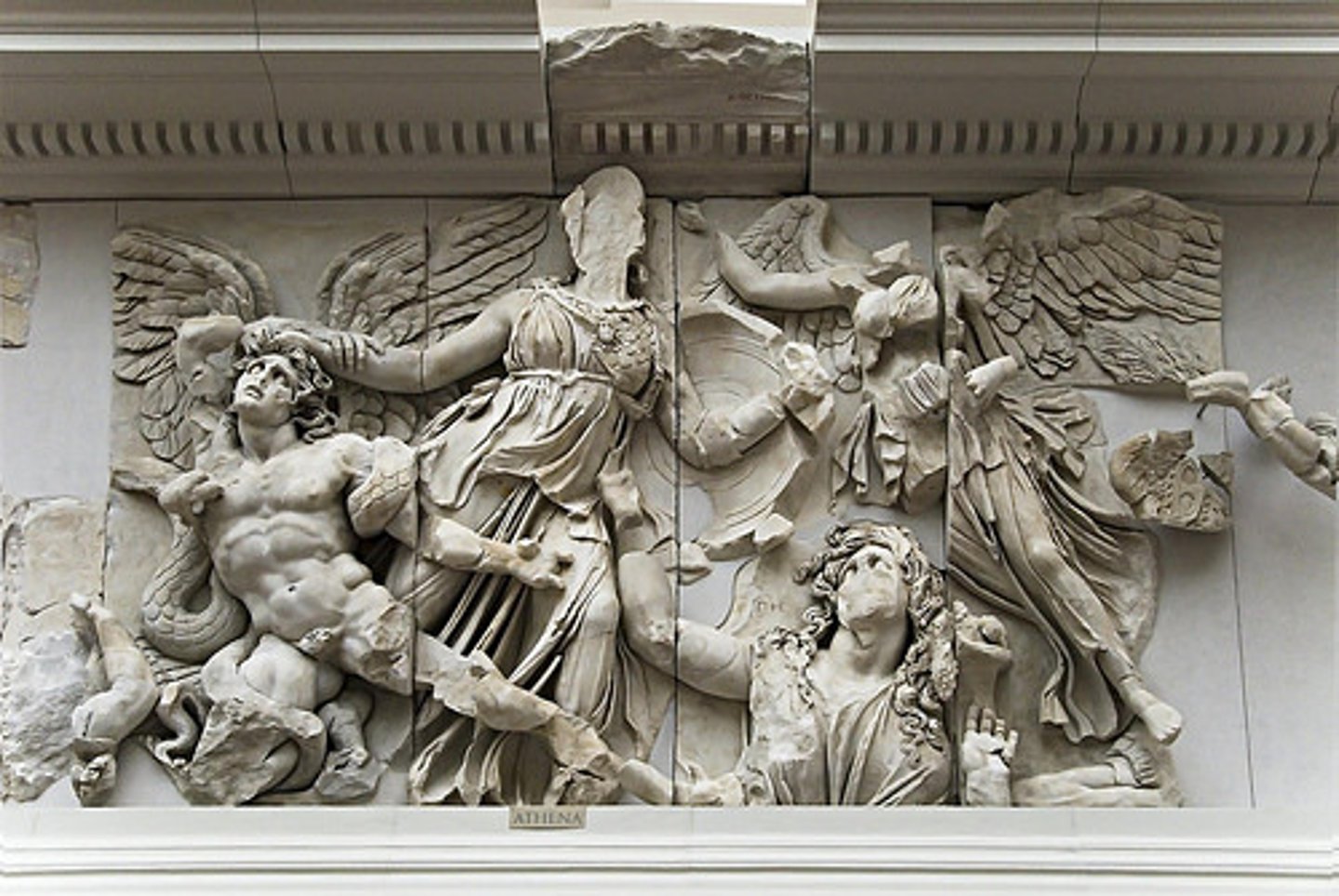
Gigantomachy
a mythical ancient Greek war between the giants and the Olympian gods

In situ
a Latin expression that means that something is in its original location
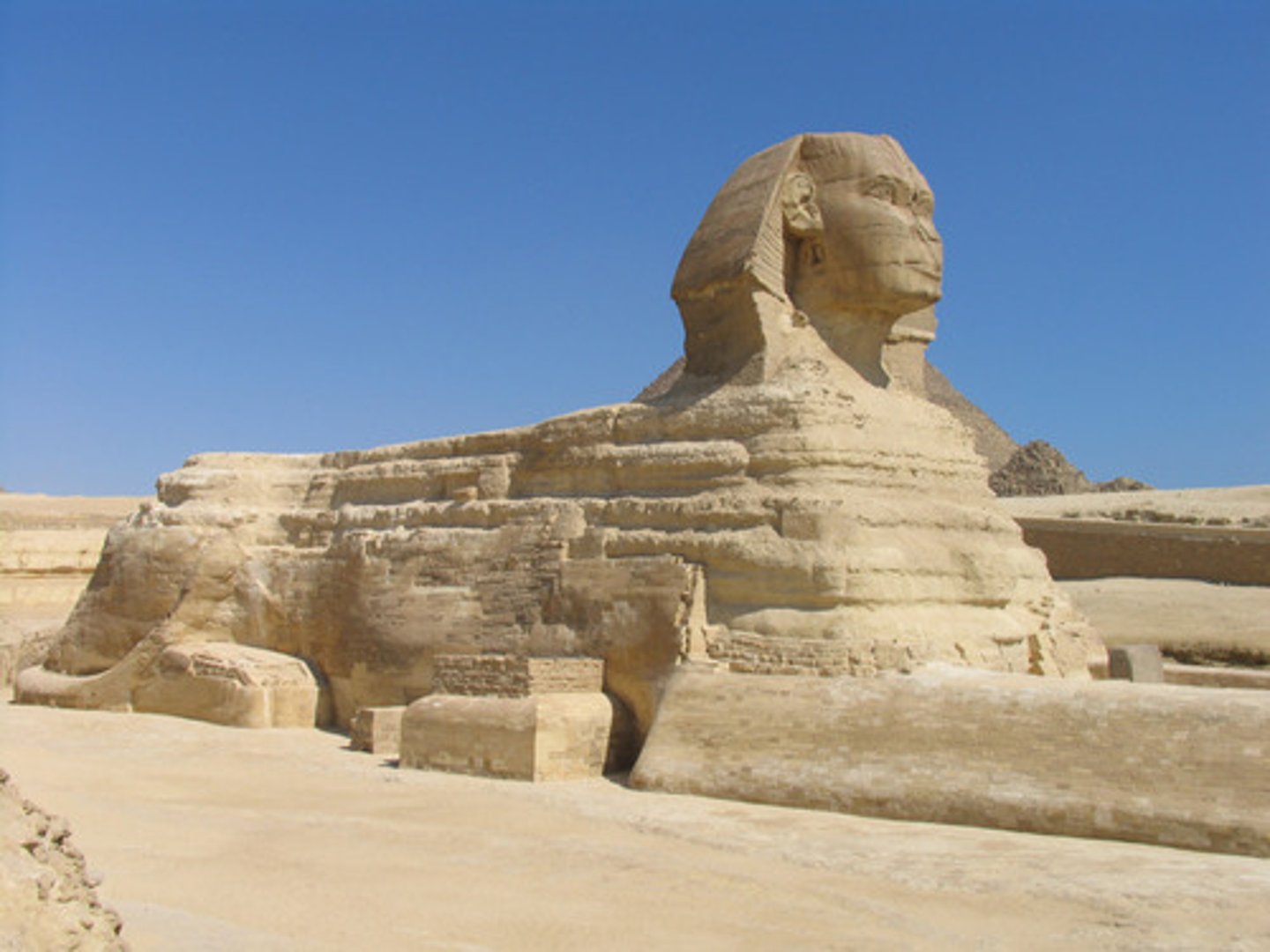

Ionic
an order of Greek architecture that features columns with scrolled capitals and an upper story with sculptures that are in friezes; preferred by Greek island architects
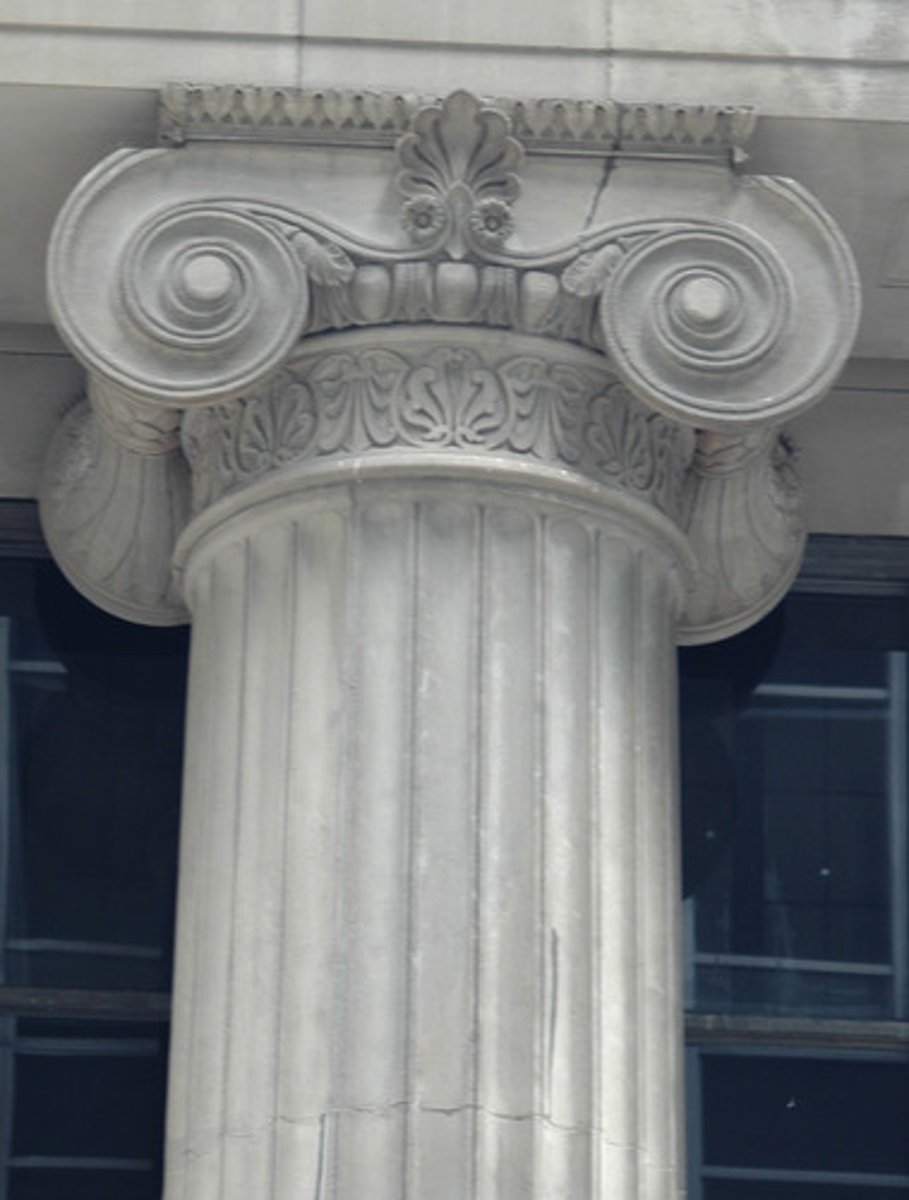

Isocephalism
the tradition of depicting heads of figures on the same level
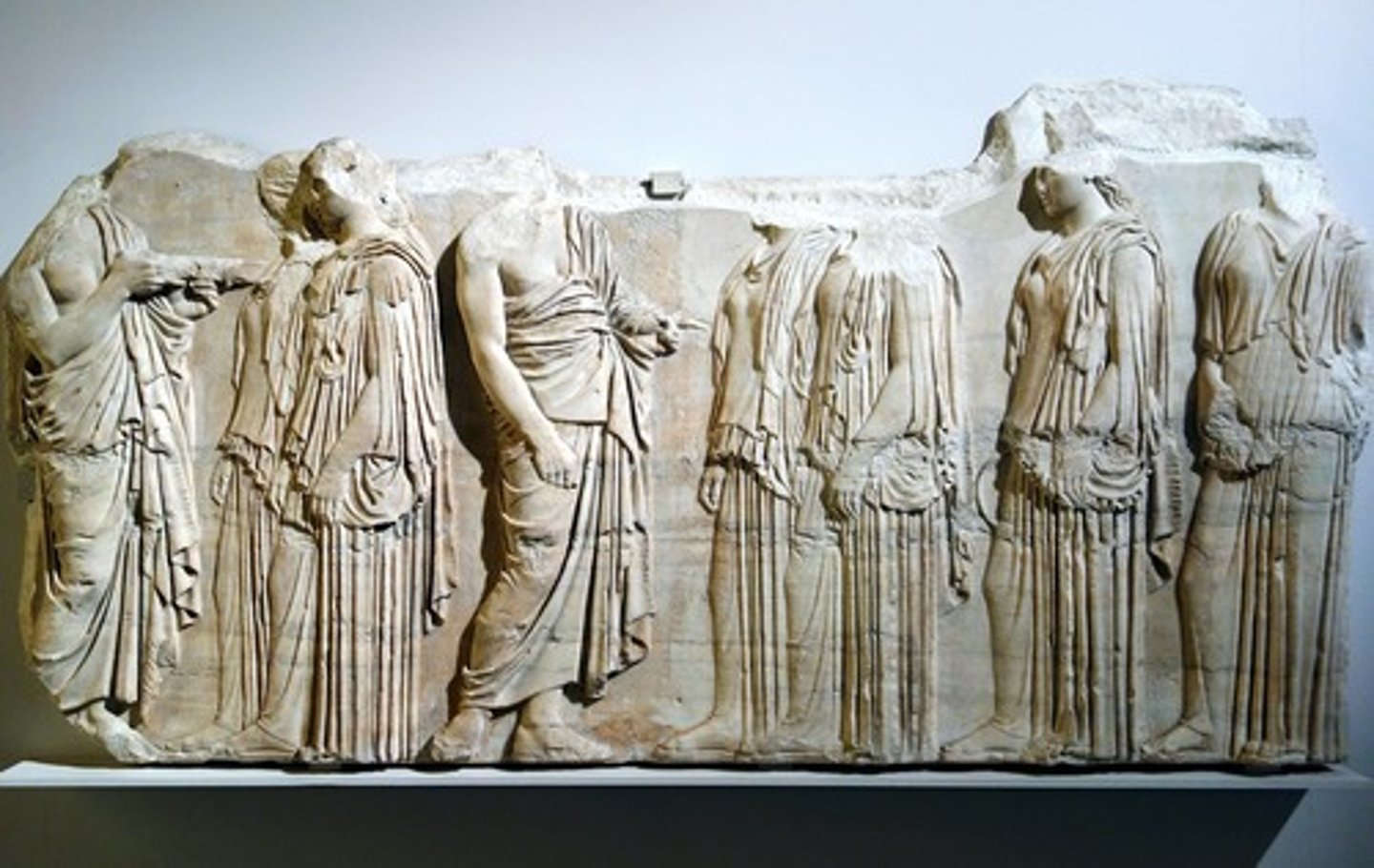

Kiln
an oven used for making pottery
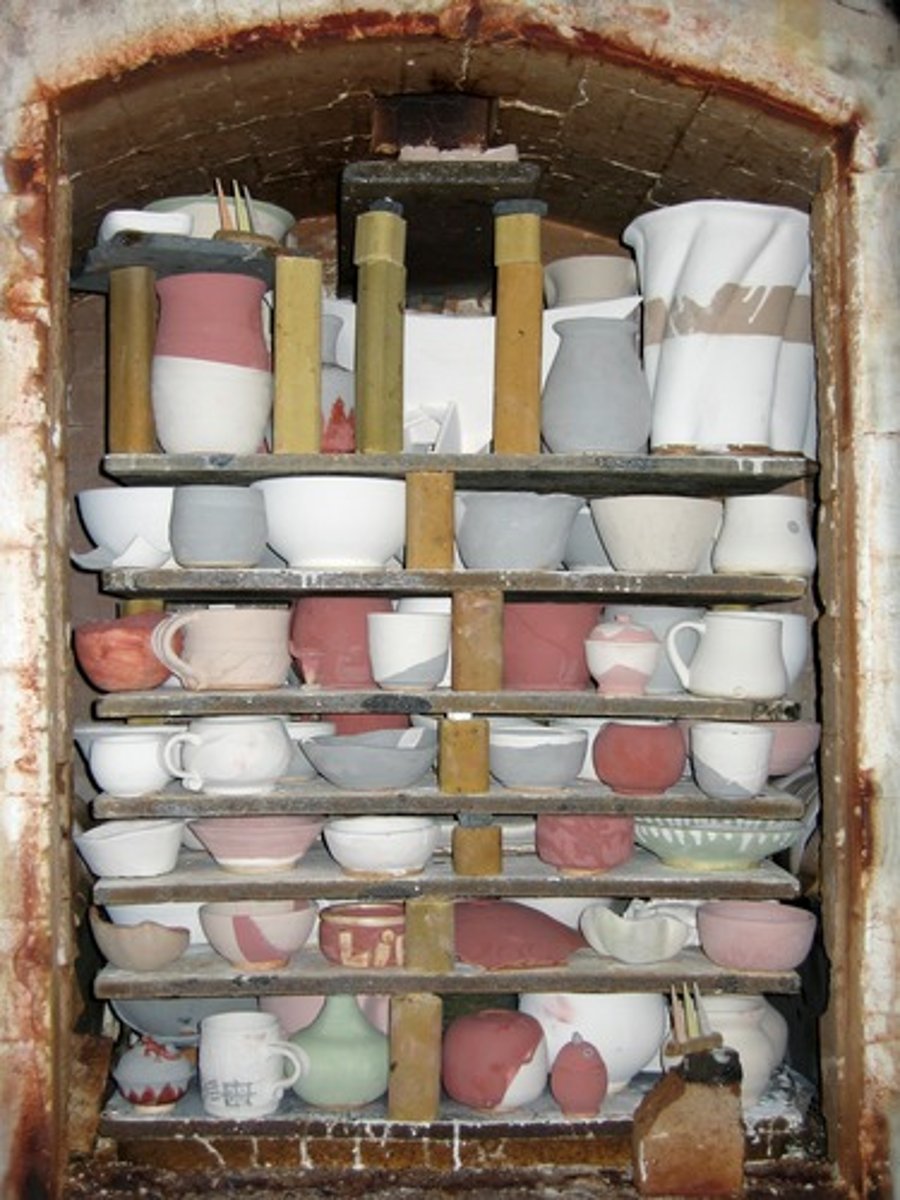

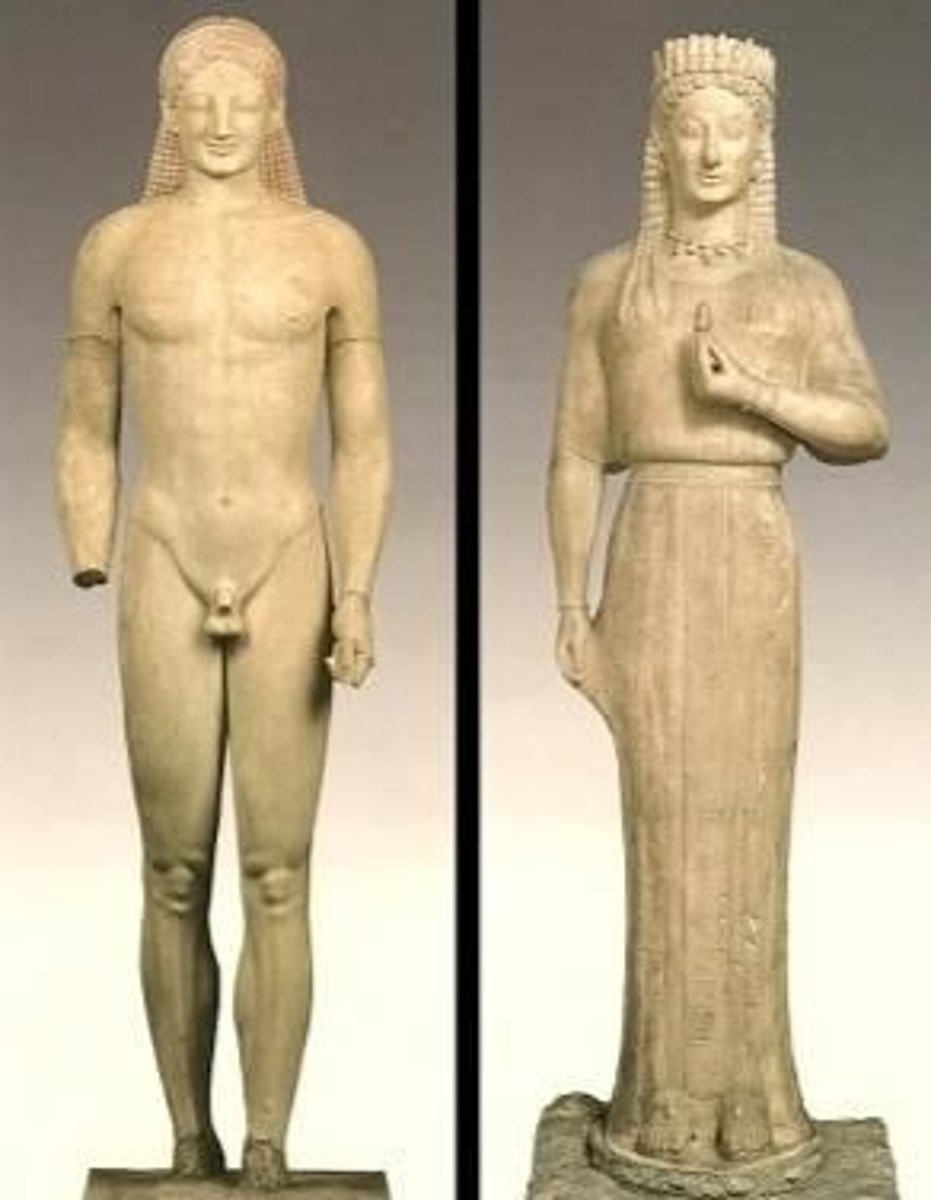
Kouros (female: kore)
an archaic Greek sculpture of a (frontal) standing youth

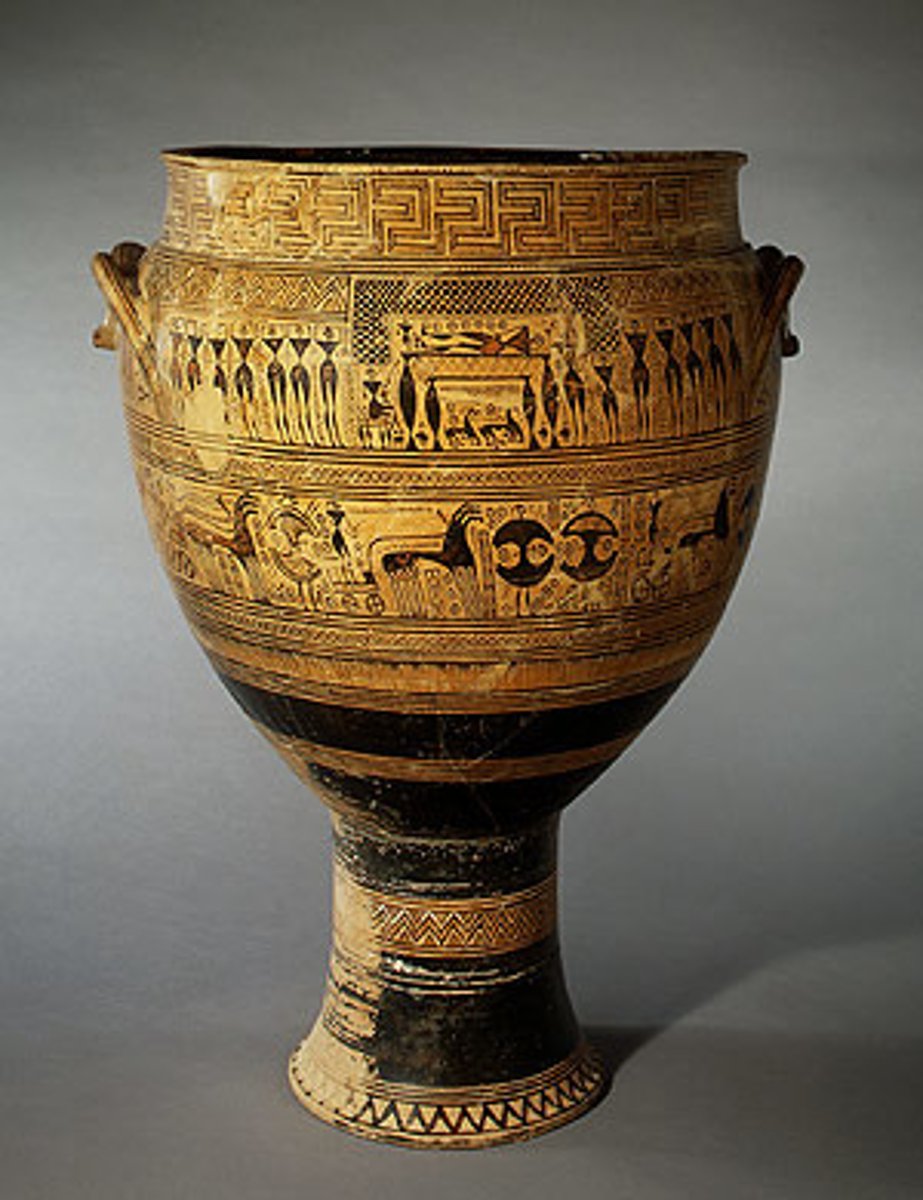
Krater
a large ancient Greek bowl used for mixing water and wine

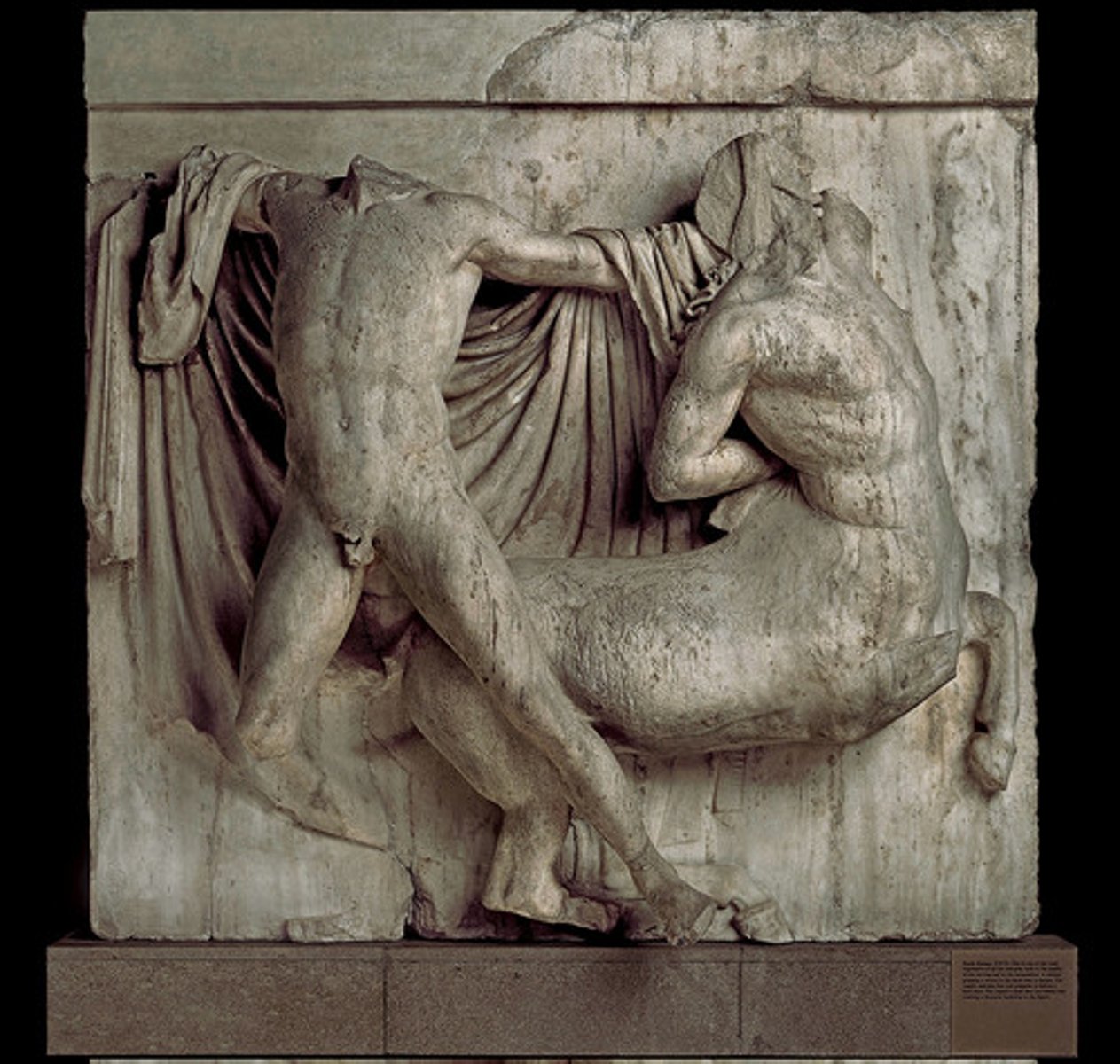
Metope
a small relief sculpture on the facade of a Greek temple

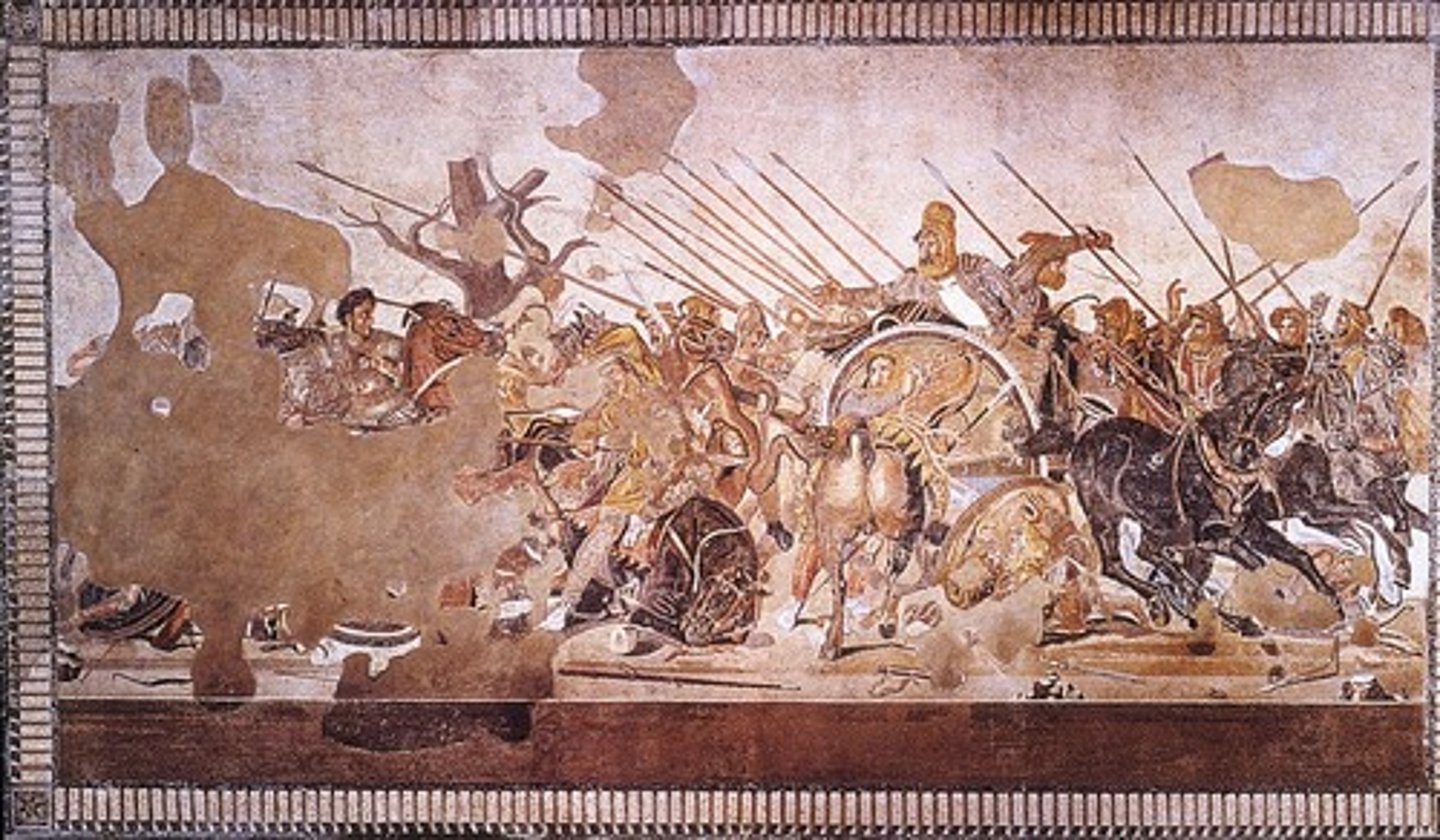
Mosaic
a decoration using pieces of stone, marble, or colored glass, called tesserae, that are cemented to a wall or a floor

Nike
ancient Greek goddess of victory

Niobe
the model of a grieving mother; after boasting of her fourteen children, jealous gods killed them

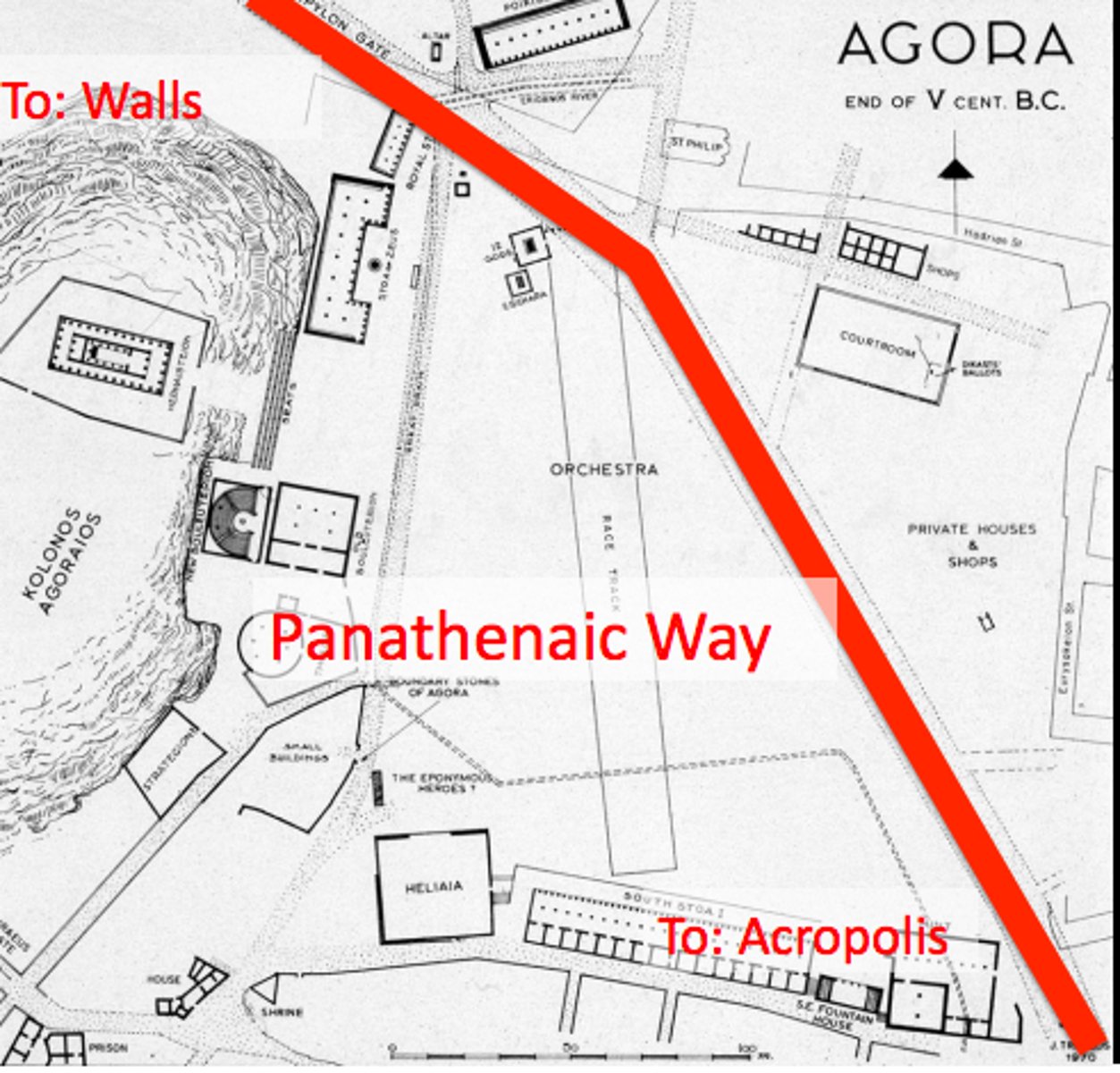
Panathenaic Way
a ceremonial road for a procession built to honor Athena during a festival
Pediment
the triangular top of a temple that contains sculpture

Peplos
a garment worn by women in ancient Greece, usually full length and tied at the waist

Peristyle
a colonnade surrounding a building or enclosing a courtyard
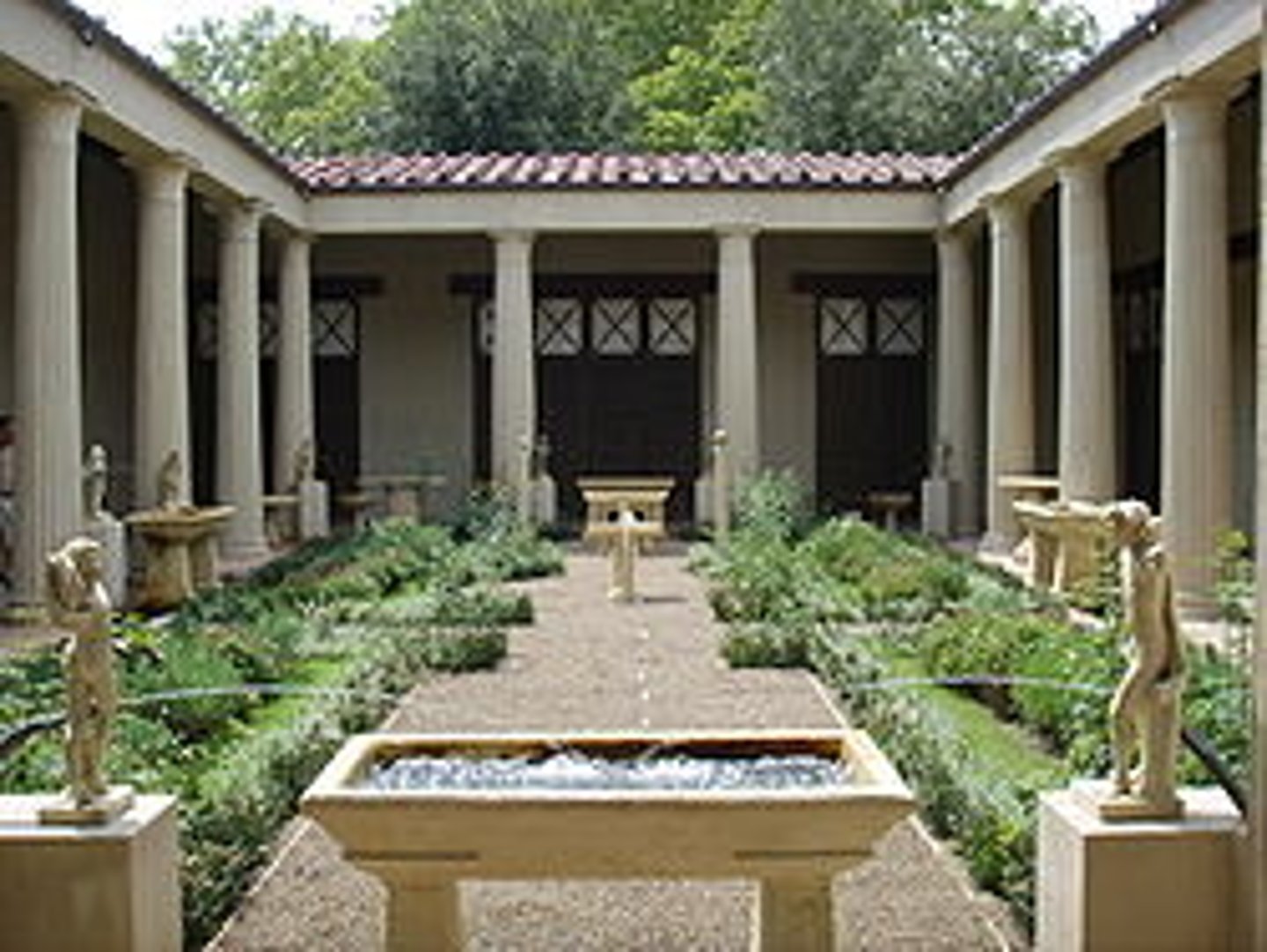

Propylaeum (plural: propylaea)
a gateway leading to a Greek temple
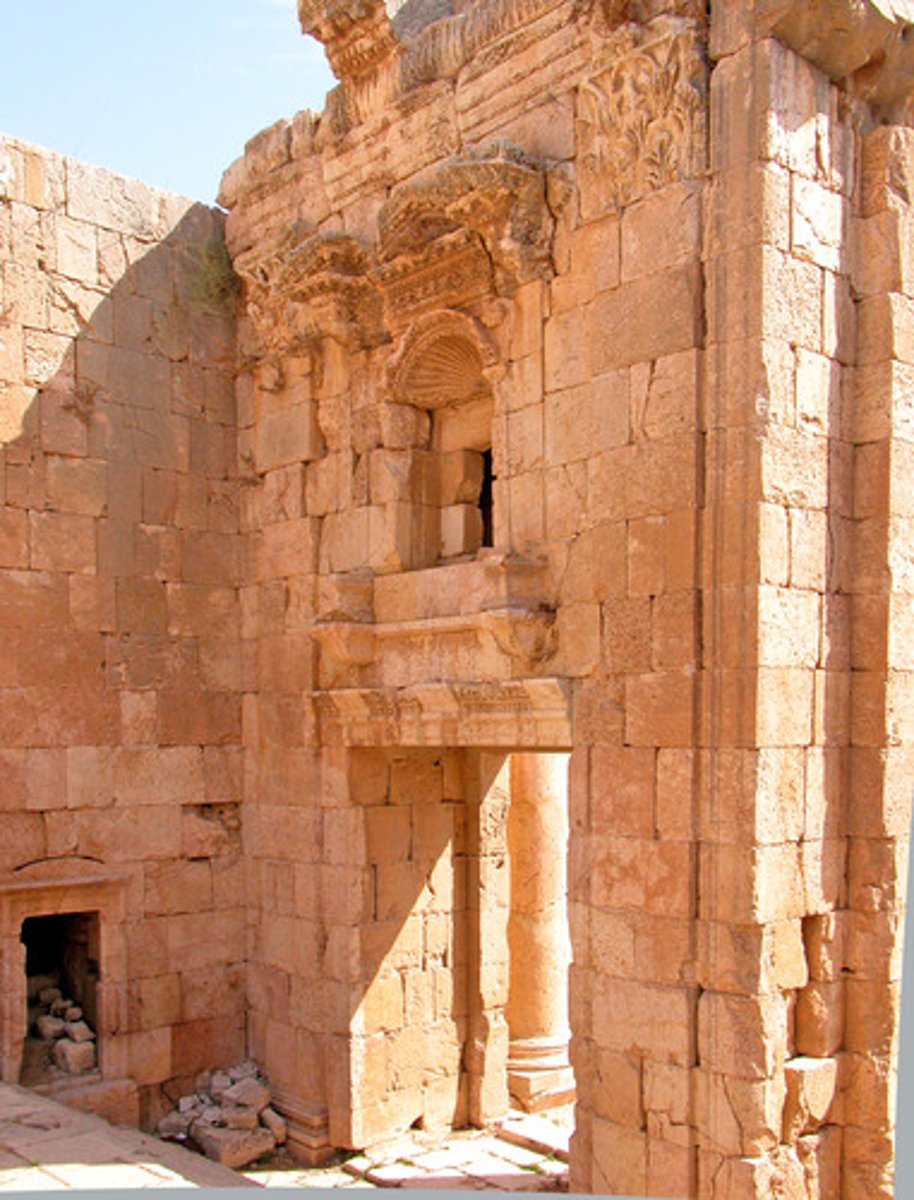

Relief sculpture
sculpture that projects from a flat background. A very shallow relief sculpture is called a bas-relief

Shaft
the body of a column
Stele (plural: stelae)
an upright stone slab used to mark a grave or a site

Stoa
an ancient Greek covered walkway having columns on one side and a wall on the other
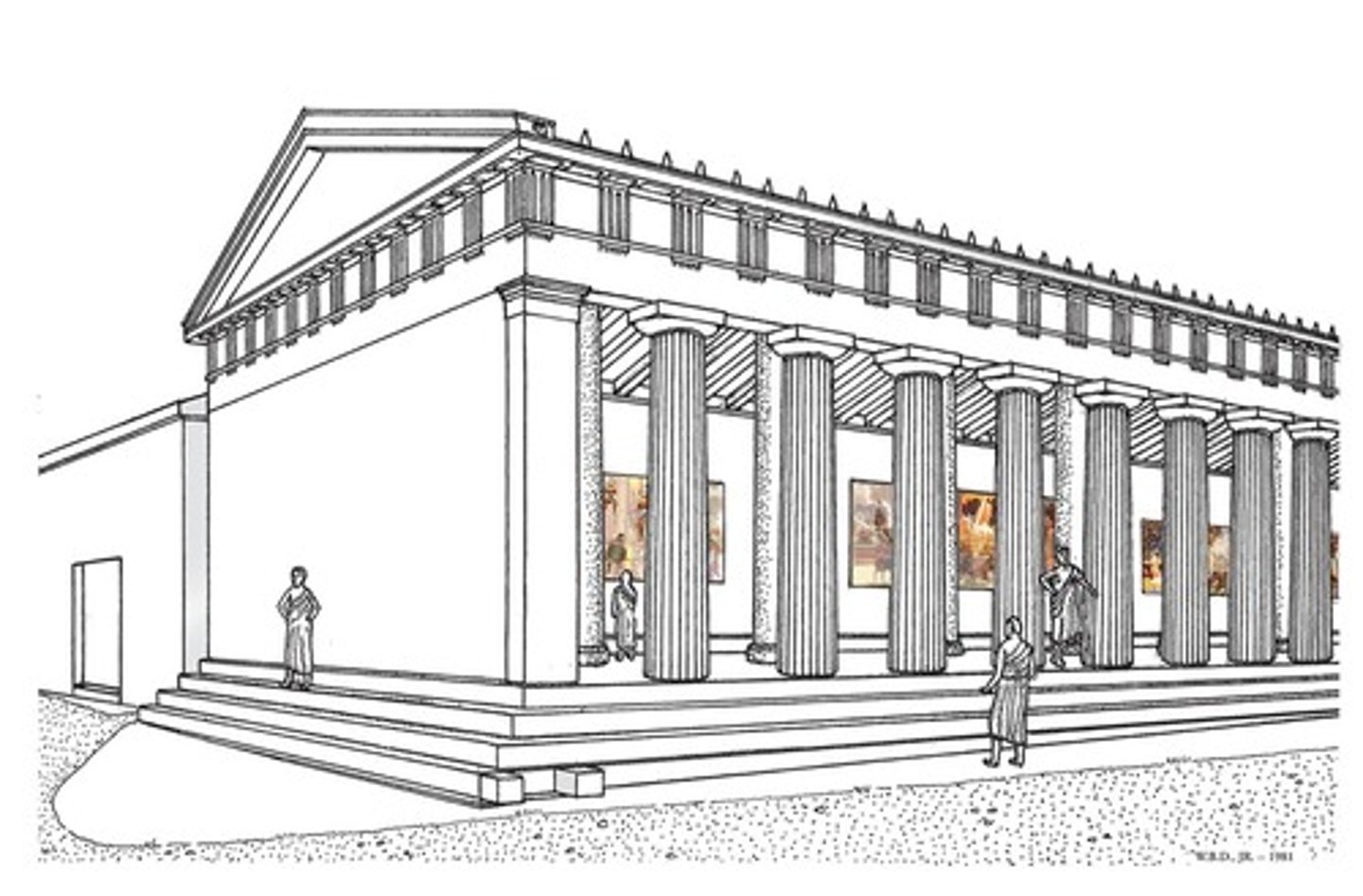
Tholos
an ancient Greek circular building

Triglyph
a projecting grooved element alternating with a metope on a Greek temple

Zeus
king of the ancient Gods; known as Jupiter to the Romans; god of the sky and weather

cire perdue
the lost wax process. A bronze casting method in which a figure is modeled in clay and covered with wax and then recovered with clay. When fired in a kiln, the wax melts away, leaving a hollow channel between the two layers of clay which can be used as a mold for liquid metal

Archaic Sculpture
Characterized by grave monuments such as kouros and kore figures made of primarily marble decorated with metallic accessories; one foot in front of the other and typically incorporates negative space; naturalistic expressions
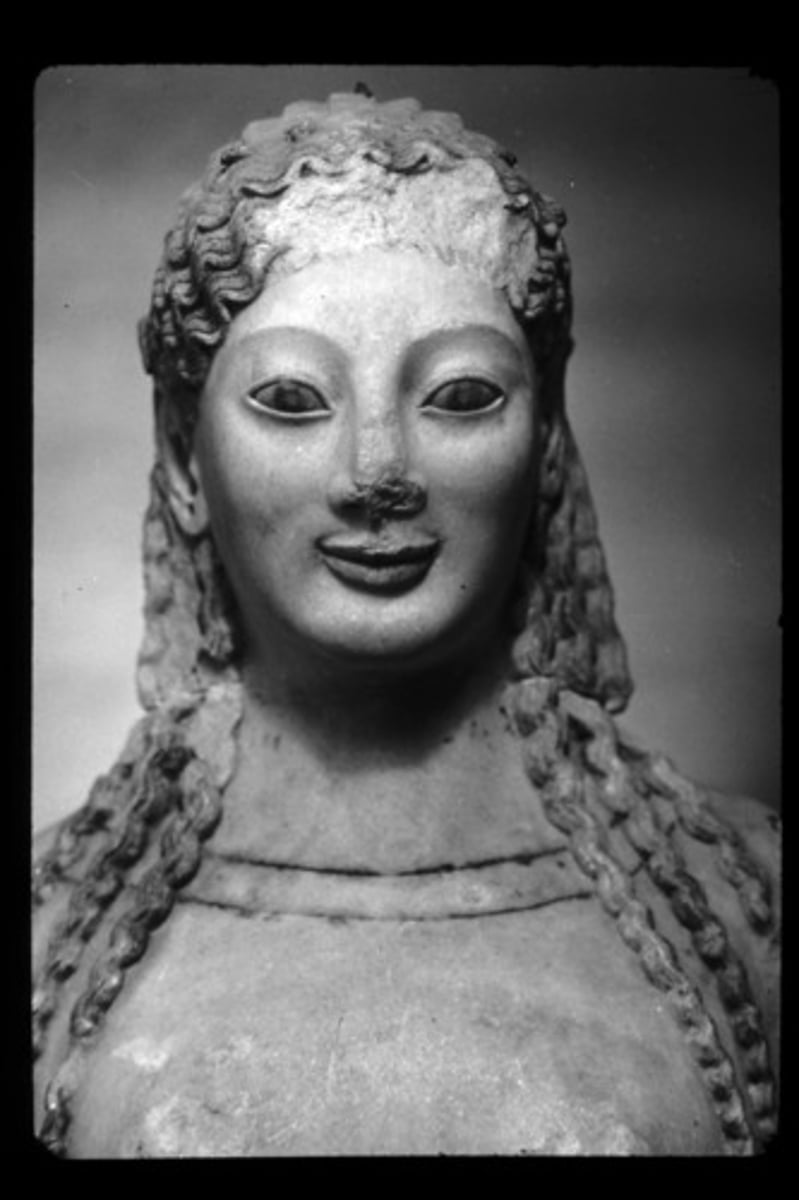

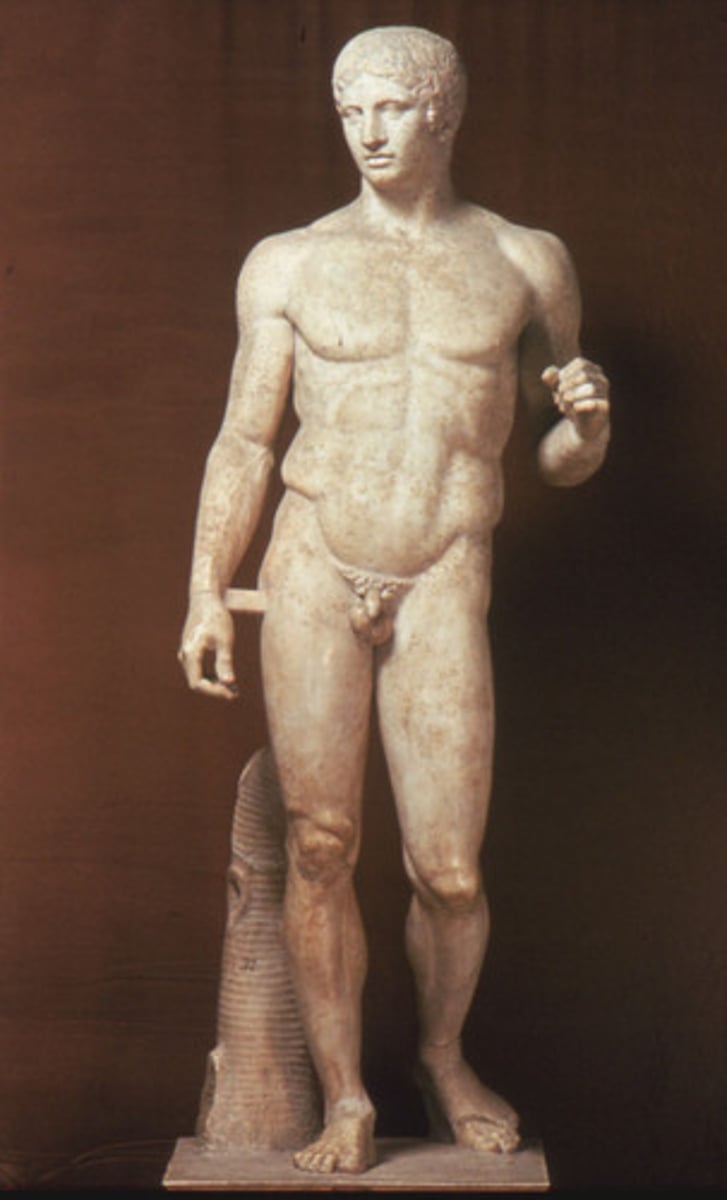
Classical Sculpture
Characterized by more fluid, relaxed stances and idealized forms ("heroic" bodies); canon of proportions dictated the head to be 1/7 the body

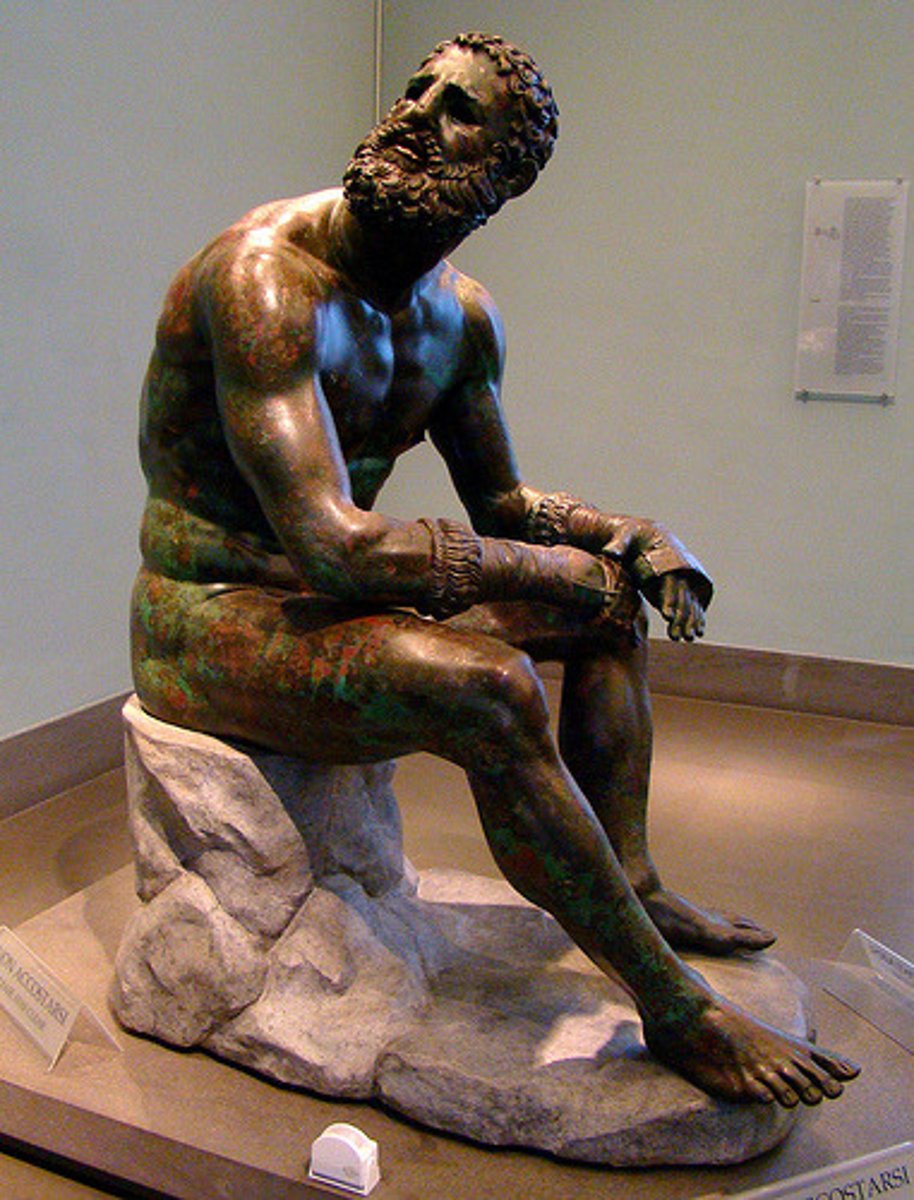
Hellenistic Sculpture
Explores themes untouched in prior eras, offering a wider range of realistic modeling and movement; not meant to be placed near a wall (all angles visible), and emotional themes such as childhood, old age, despair, anger, and drunkenness are common

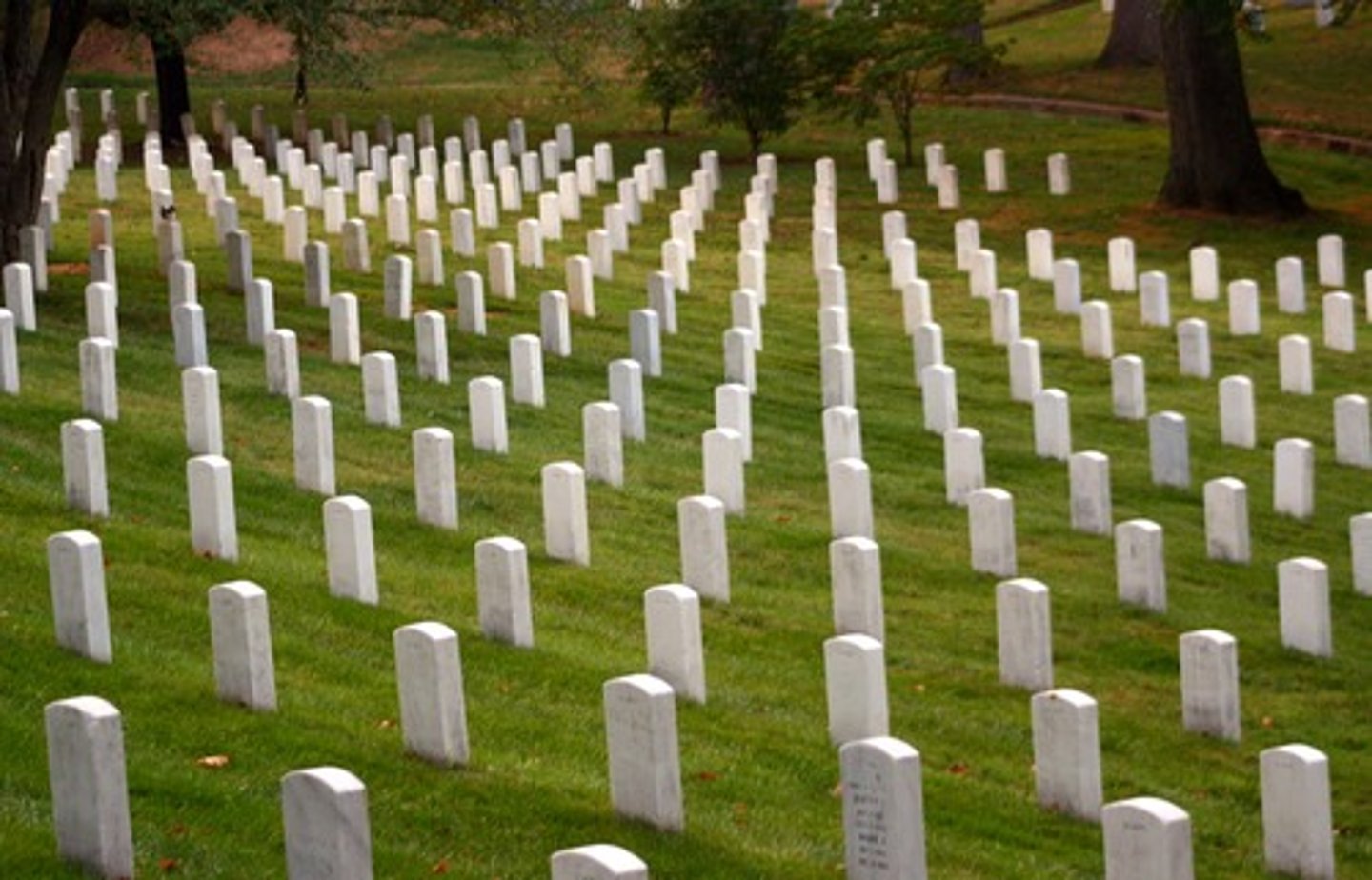
Necropolis (plural: necropoli)
a large burial area; literally, a "city of the dead"

Stucco
a fine plaster used for wall decorations or moldings

Terra cotta
a hard ceramic clay used for building or for making pottery

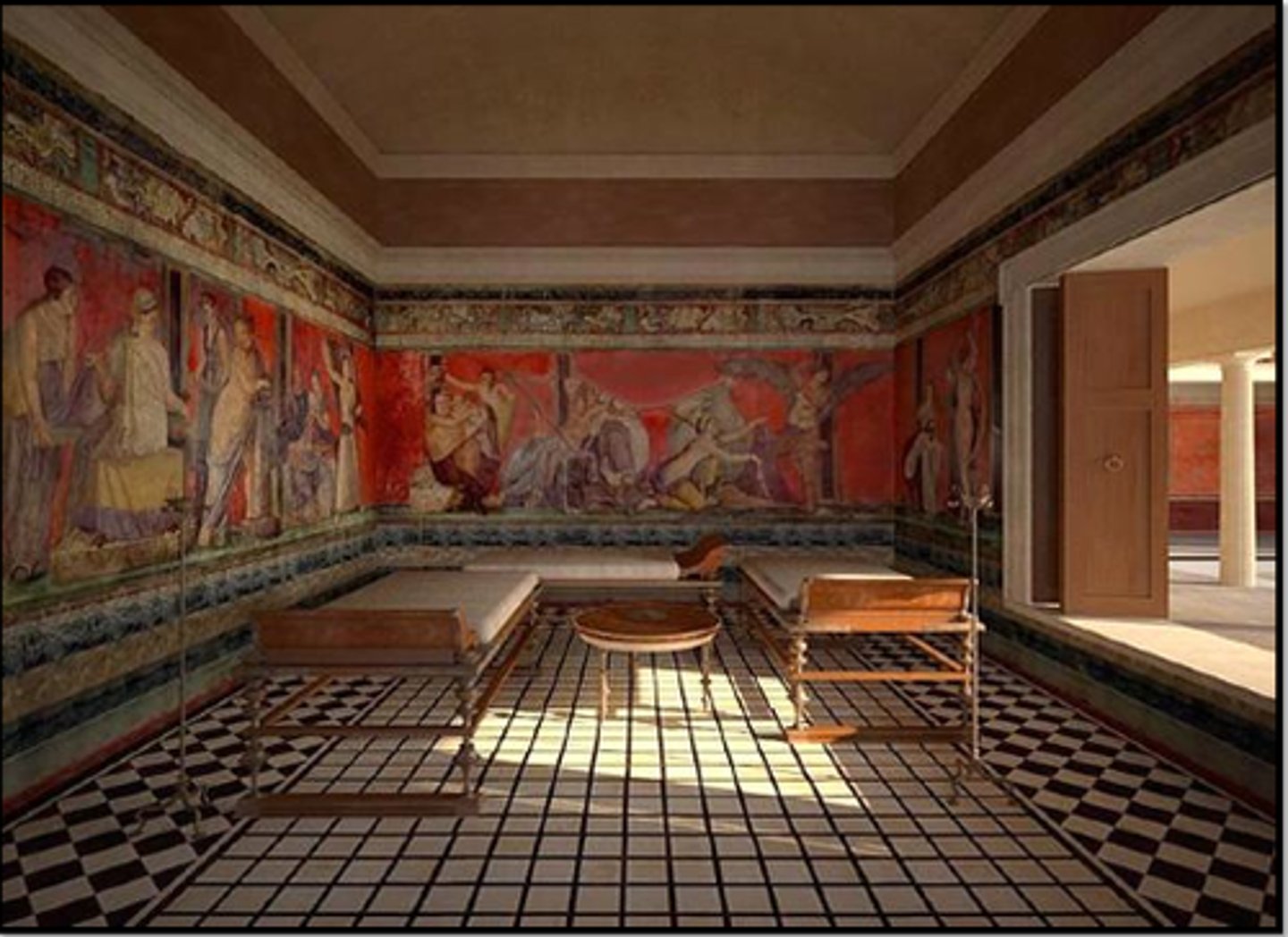
Triclinium
a dining table in ancient Rome that has a couch on three sides for reclining at meals

Tufa
a porous rock similar to limestone

Tuscan order
an order of ancient architecture featuring slender, smooth columns that sit on simple bases; no carvings on the frieze or in the capitals
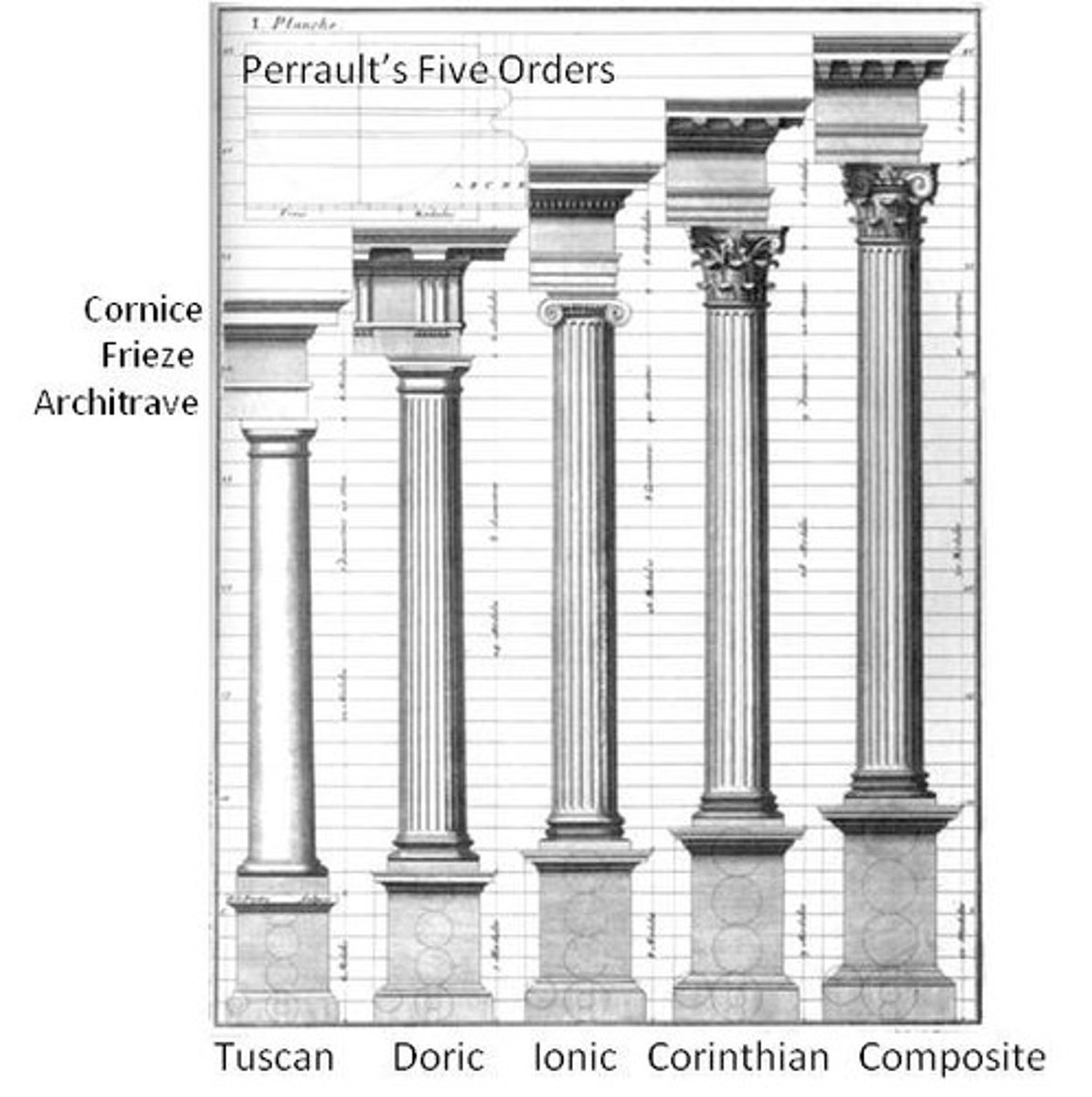
Ashlar masonry
carefully cut and grooved stones that support a building without the use of concrete or other kinds of masonry (this technique describes buildings without mortar)

Atrium (plural: atria)
a courtyard in a Roman house or before a Christian church

Basilica
in Roman architecture, a large axially planned building with a nave, side aisles, and apses

Bust
a sculpture depicting a head, neck, and upper chest of a figure

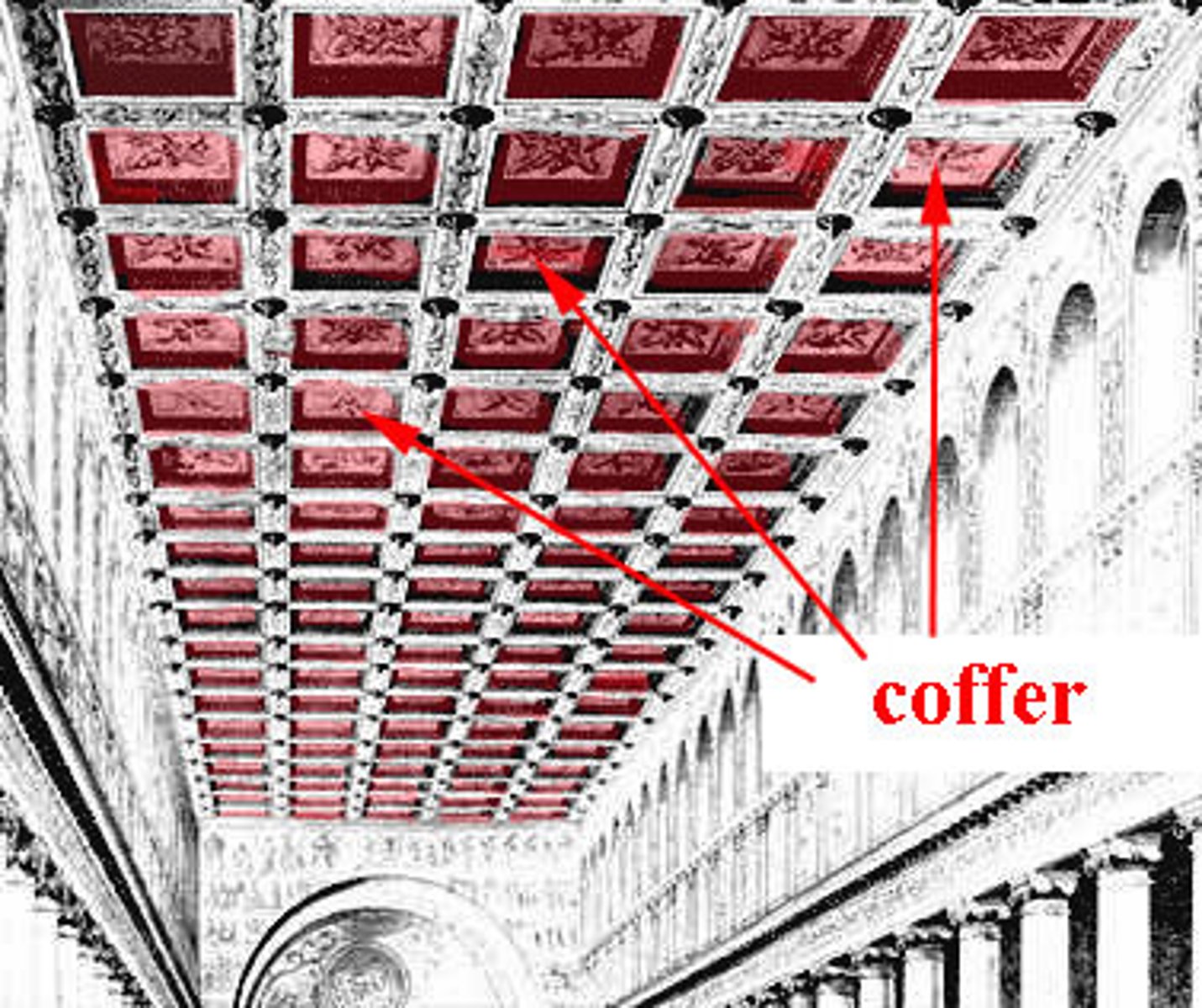
Coffer
in architecture, a sunken panel in a ceiling
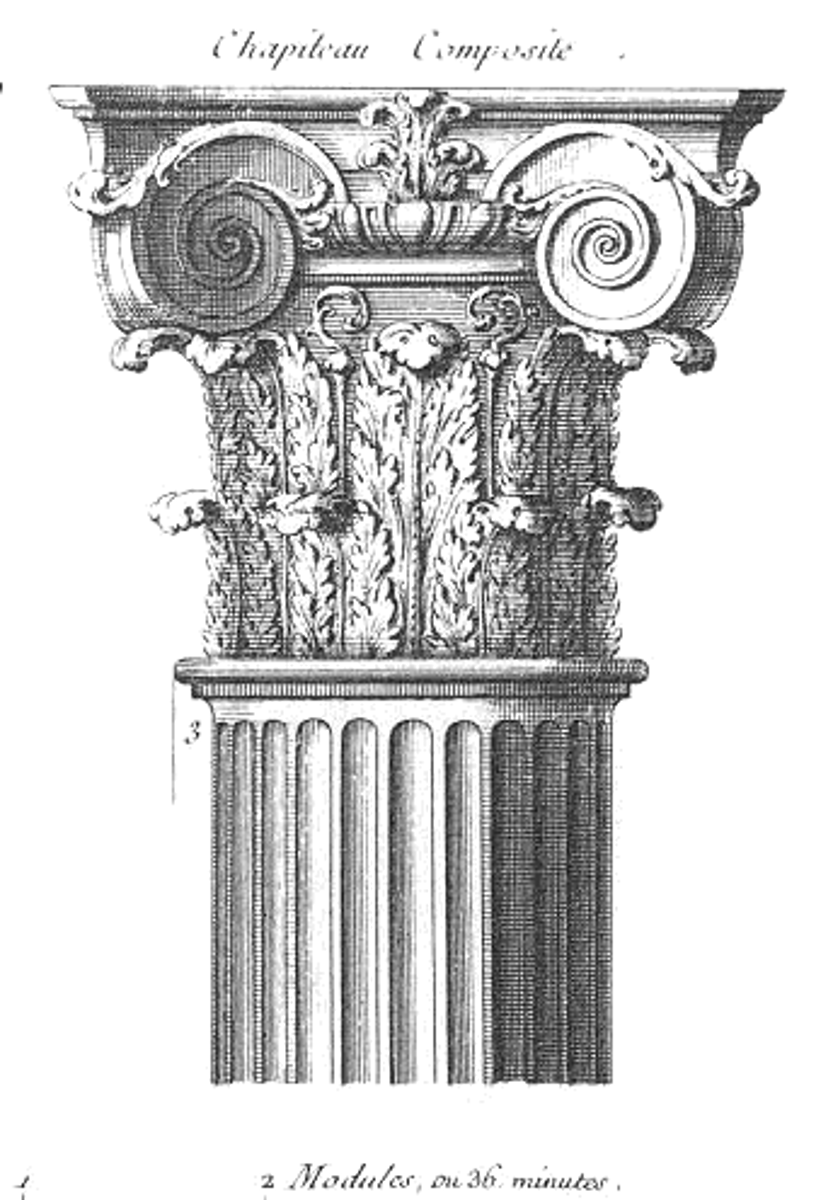
Composite column
one that contains a combination of volutes from the Ionic order and acanthus leaves from the Corinthian order
Continuous narrative
a work of art that contains several scenes of the same story painted or sculpted in continuous succession

Contrapposto
a graceful arrangement of the body based on tilted shoulders and hips and bent knees

Cubiculum (plural: cubicula)
a Roman bedroom flanking an atrium; in Early Christian art, a mortuary chapel in a catacomb

Cupola
a small dome rising over the roof of a building; in architecture, a cupola is achieved by rotating an arch on its axis

Encaustic
an ancient method of painting that uses colored waxes burned into a wooden surface
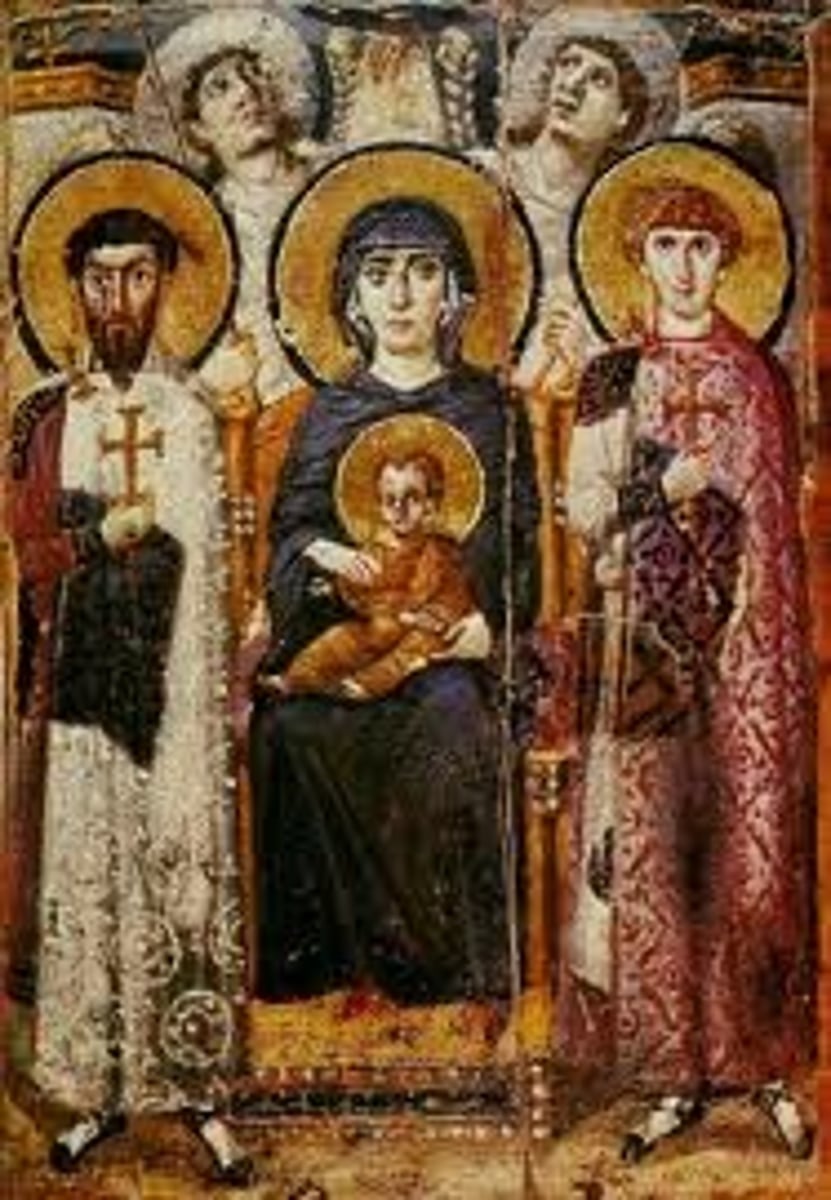

Foreshortening
a visual effect in which an object is shortened and turned deeper into the picture plane to give the effect of receding in space
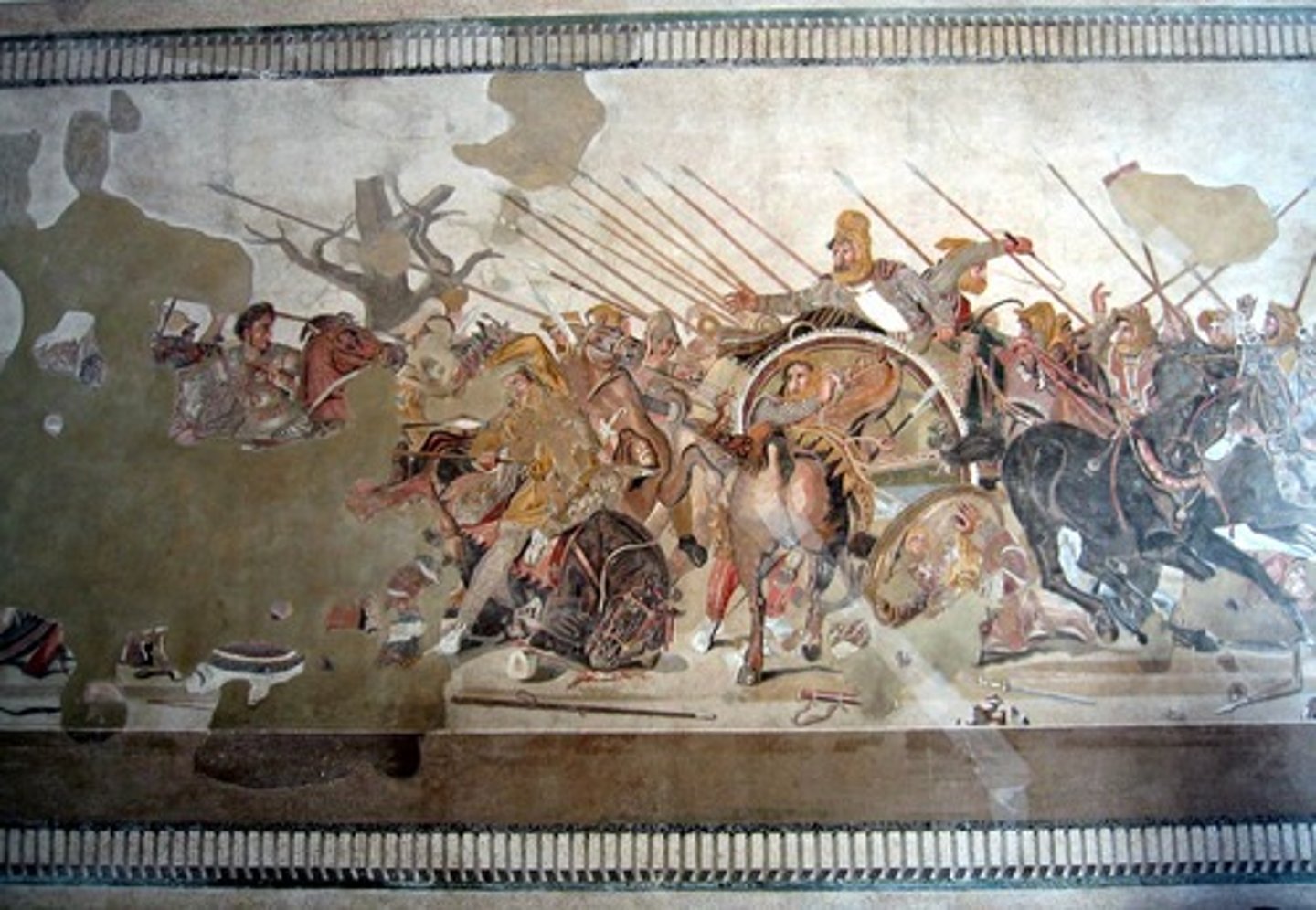

Forum (plural: fora)
a public square in a Roman city
Fresco
a painting technique that involves applying water-based paint onto a freshly plastered wall. The paint forms a bond with the plaster that is durable and long-lasting
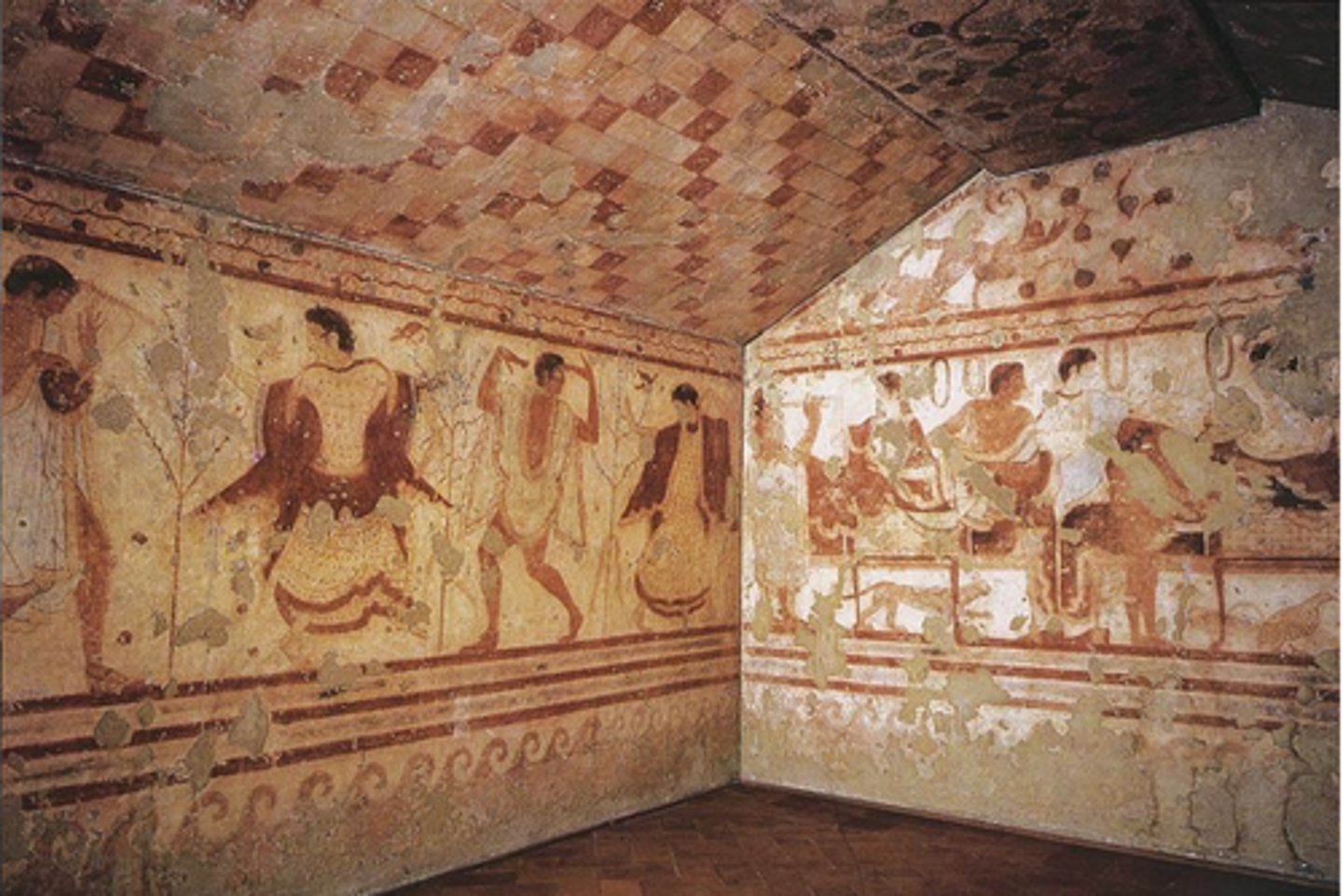

Horror vacui
(Latin for a "fear of empty spaces") a type of artwork in which the entire surface is filled with objects, people, designs, and ornaments in a crowded, sometimes congested way
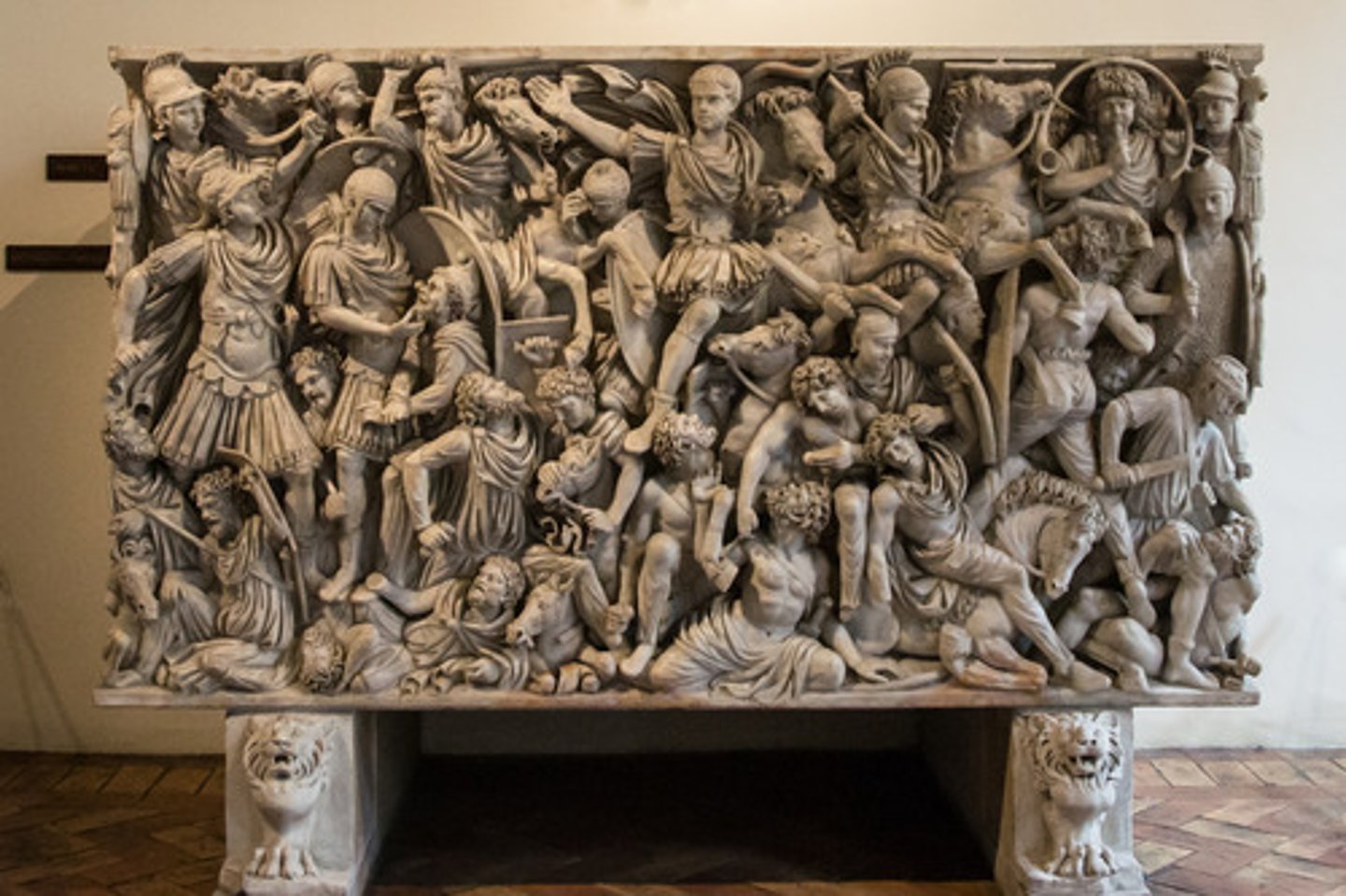

Impluvium
a rectangular basin in a Roman house that is placed in the open-air atrium in order to collect rainwater
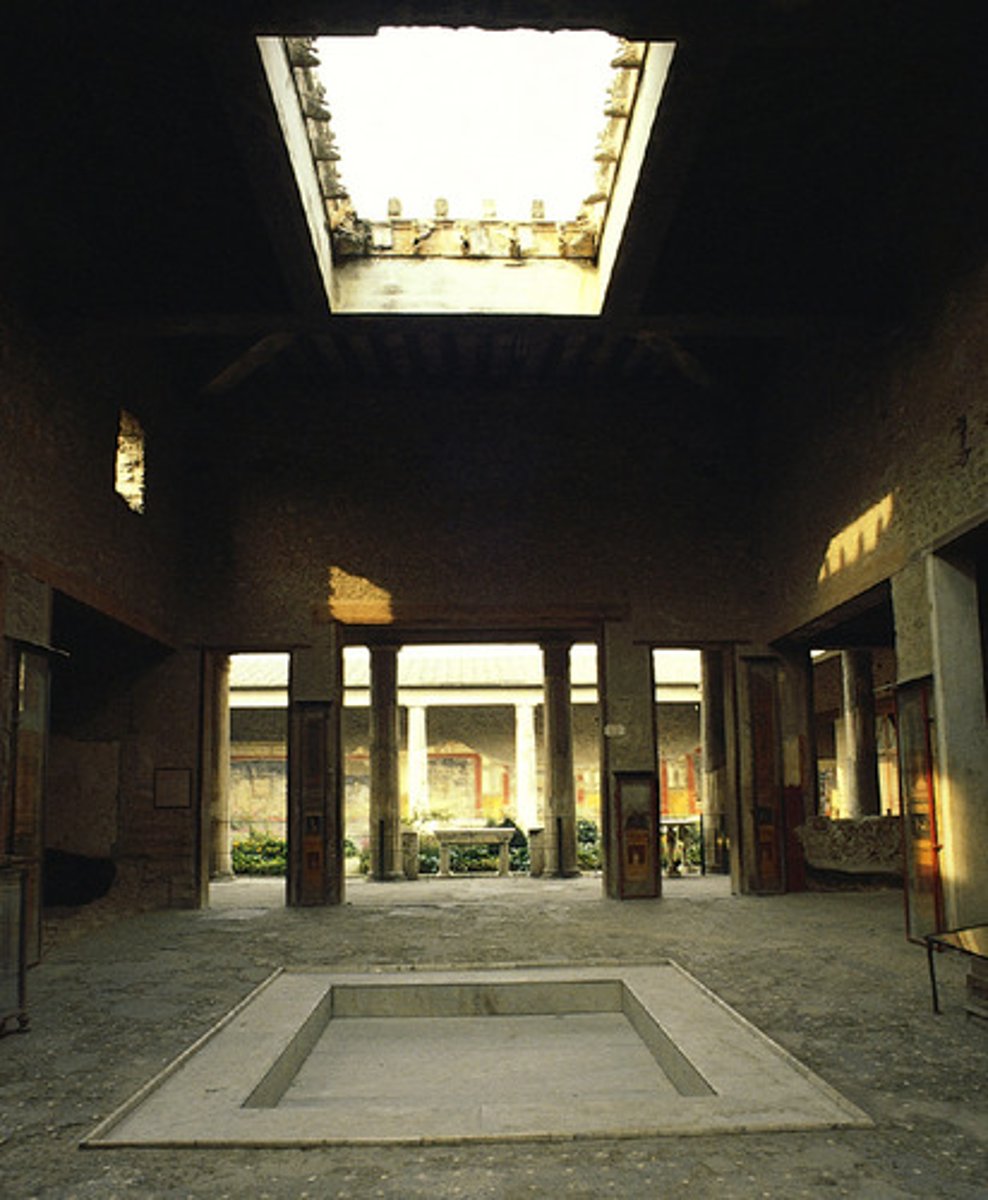

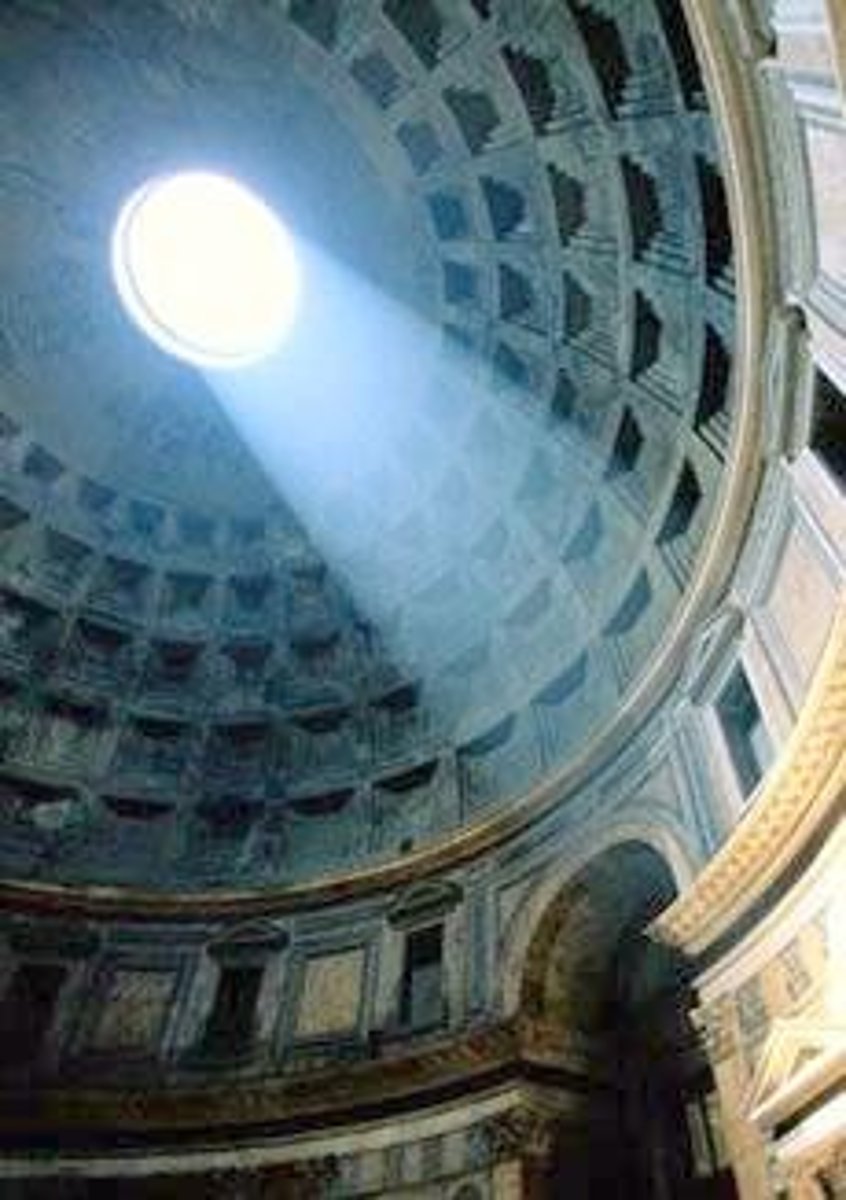
Oculus
a circular window in a church, or a round opening at the top of a dome

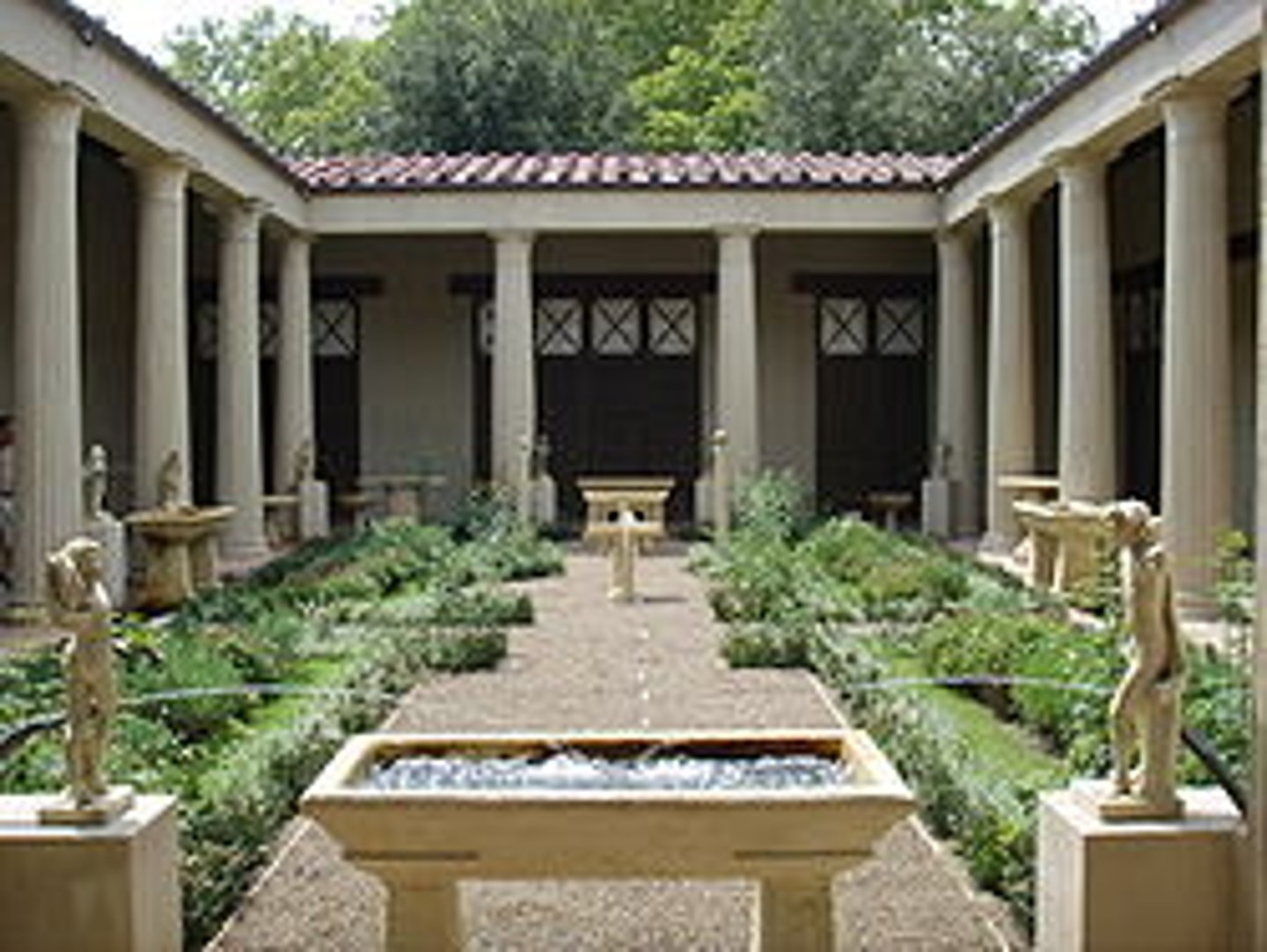
Peristyle
an atrium surrounded by columns in a Roman house

linear perspective
achieve a three-dimensionality in the two-dimensional world of the picture plane
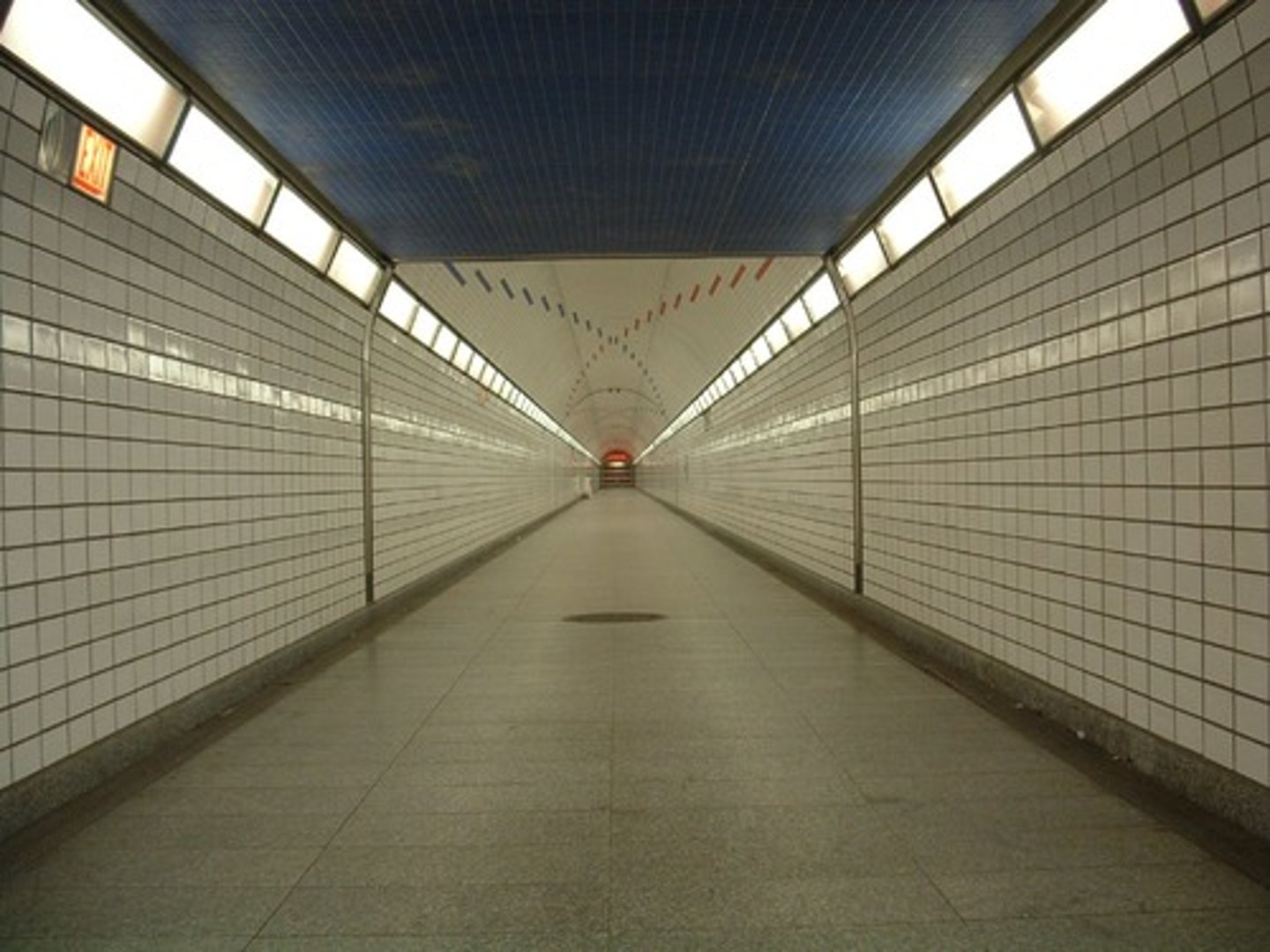

perspective
depth and recession in a painting or a relief sculpture. Objects shown in linear perspective achieve a three-dimensionality in the two-dimensional world of the picture plane. Lines, called orthogonals, draw the viewer back in space to a common point, called the vanishing point. Paintings, however, may have more than one vanishing point, with orthogonals leading the eye to several parts of the work. Landscapes that give the illusion of distance are in atmospheric or aerial perspective
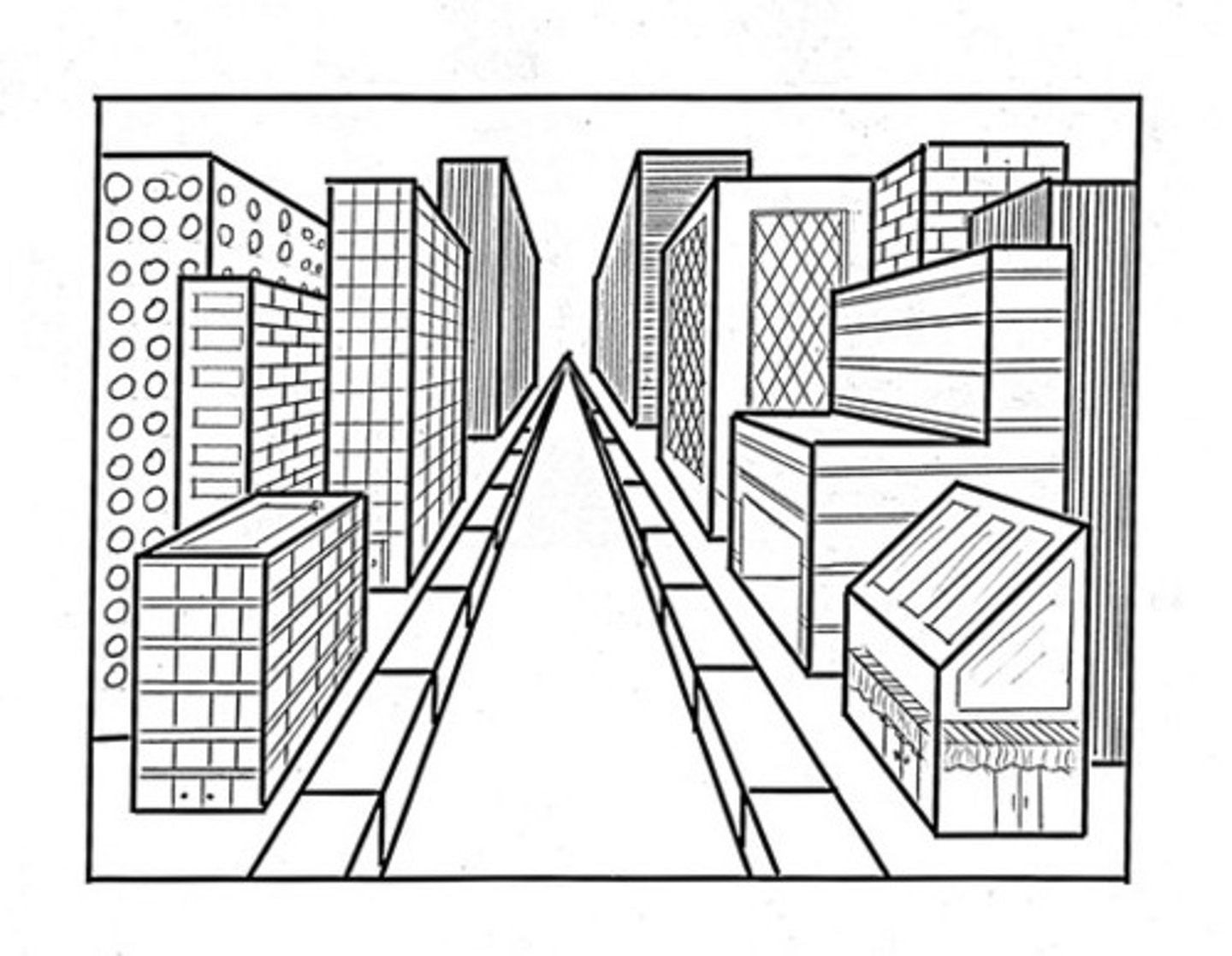
orthogonals
Lines that draw the viewer back in space to a common point, called the vanishing point. Paintings, however, may have more than one vanishing point, with "these lines" leading the eye to several parts of the work.
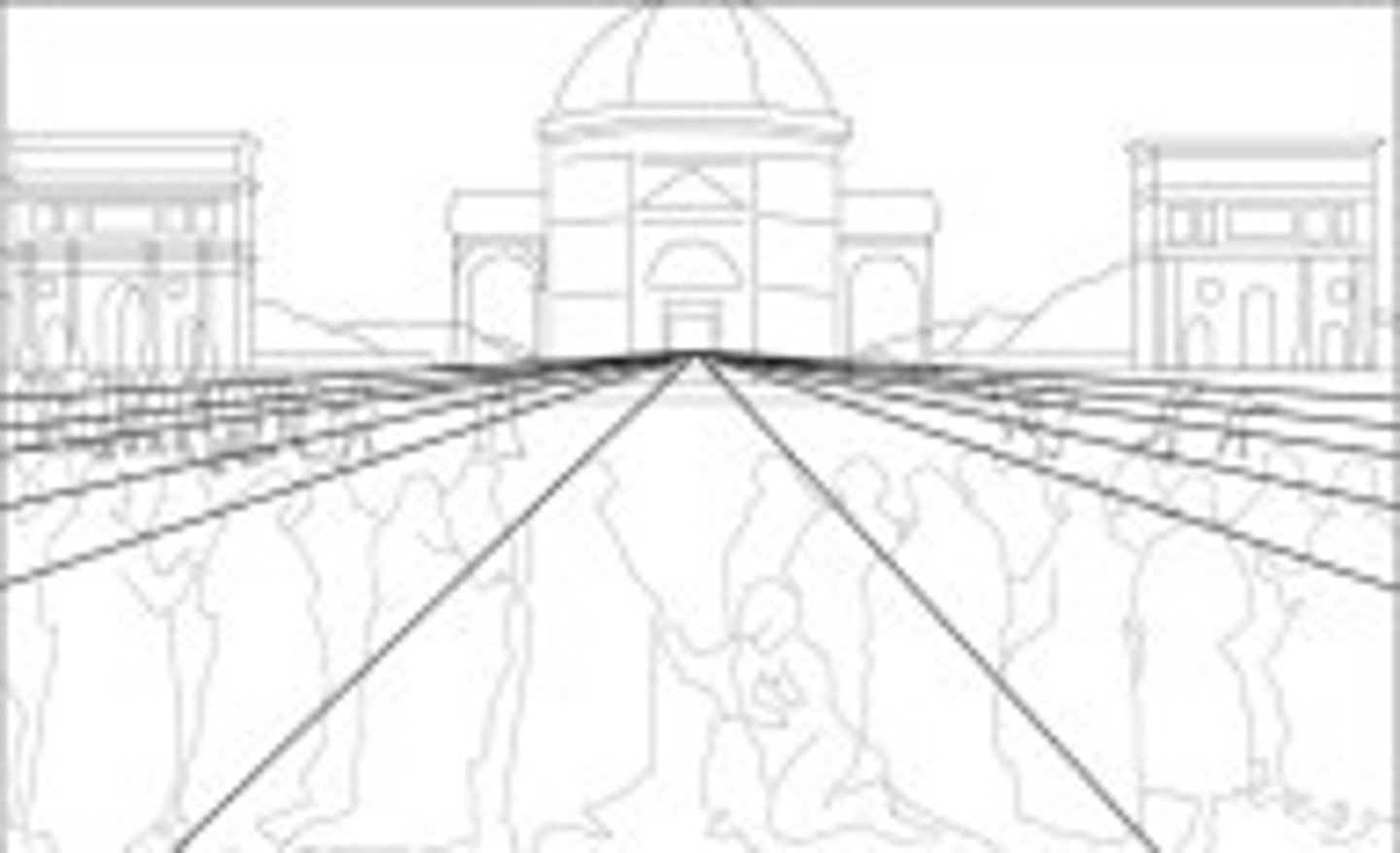
atmospheric/aerial perspective
Landscapes that give the illusion of distance are in...

Pier
a vertical support that holds up an arch or a vault

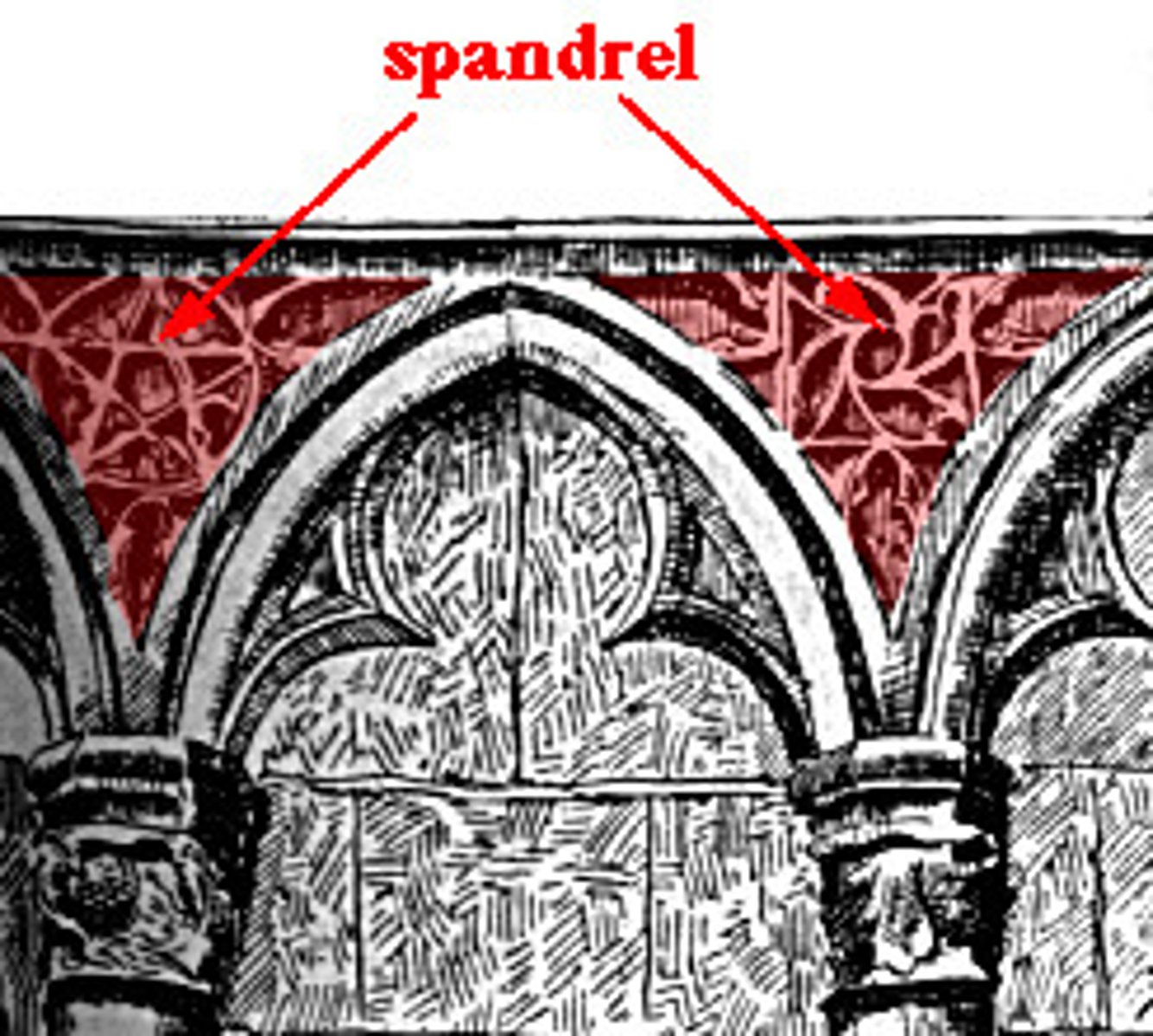
Spandrel
a triangular space enclosed by the curves of arches
Triclinium
a dining table in ancient Rome that has a couch on three sides for reclining at meals; or a room containing a triclinium

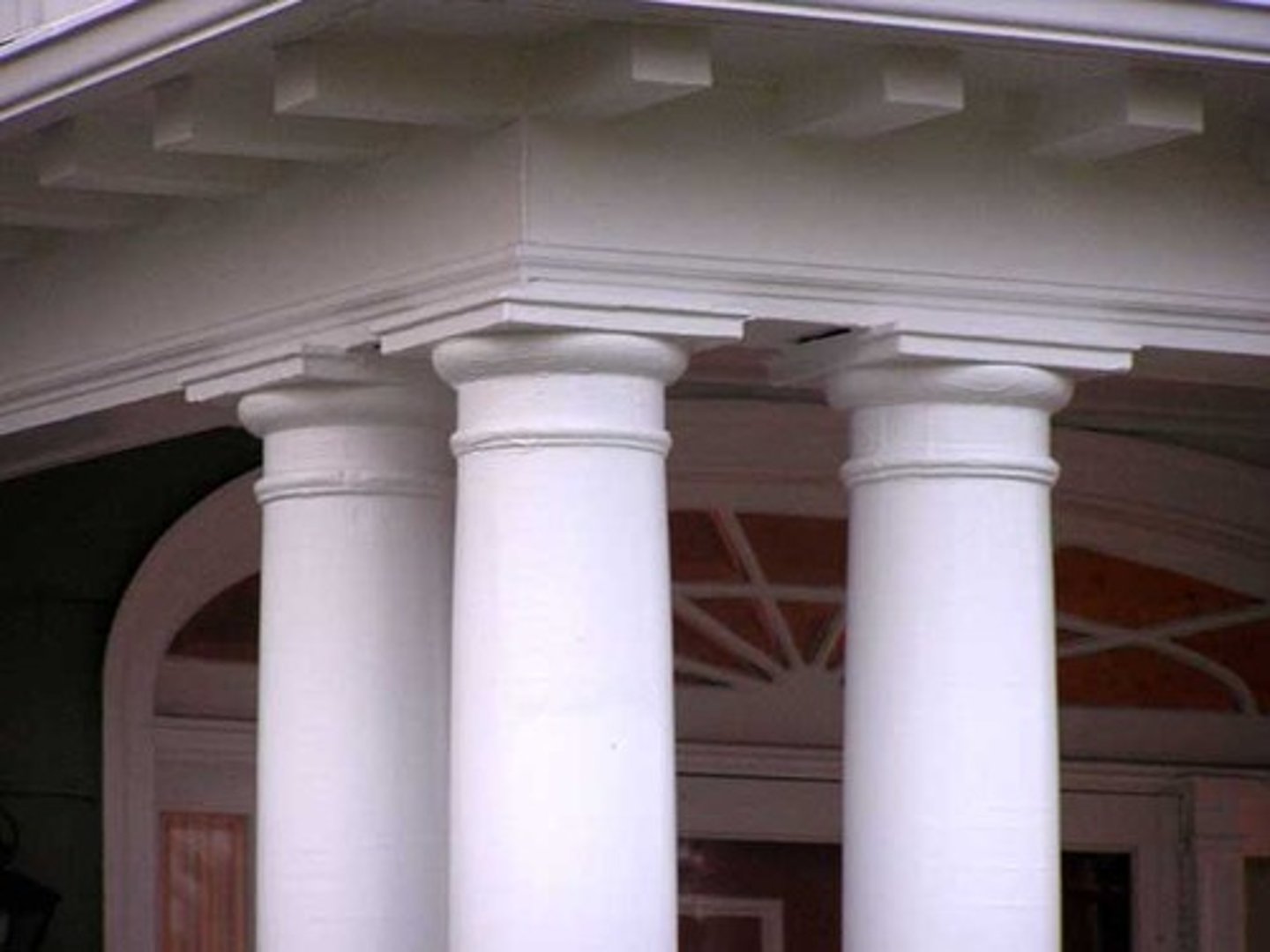
Tuscan order
an order of ancient architecture featuring slender, smooth columns that sit on simple bases; no carvings on the frieze or in the capitals; a Doric column but with an added base

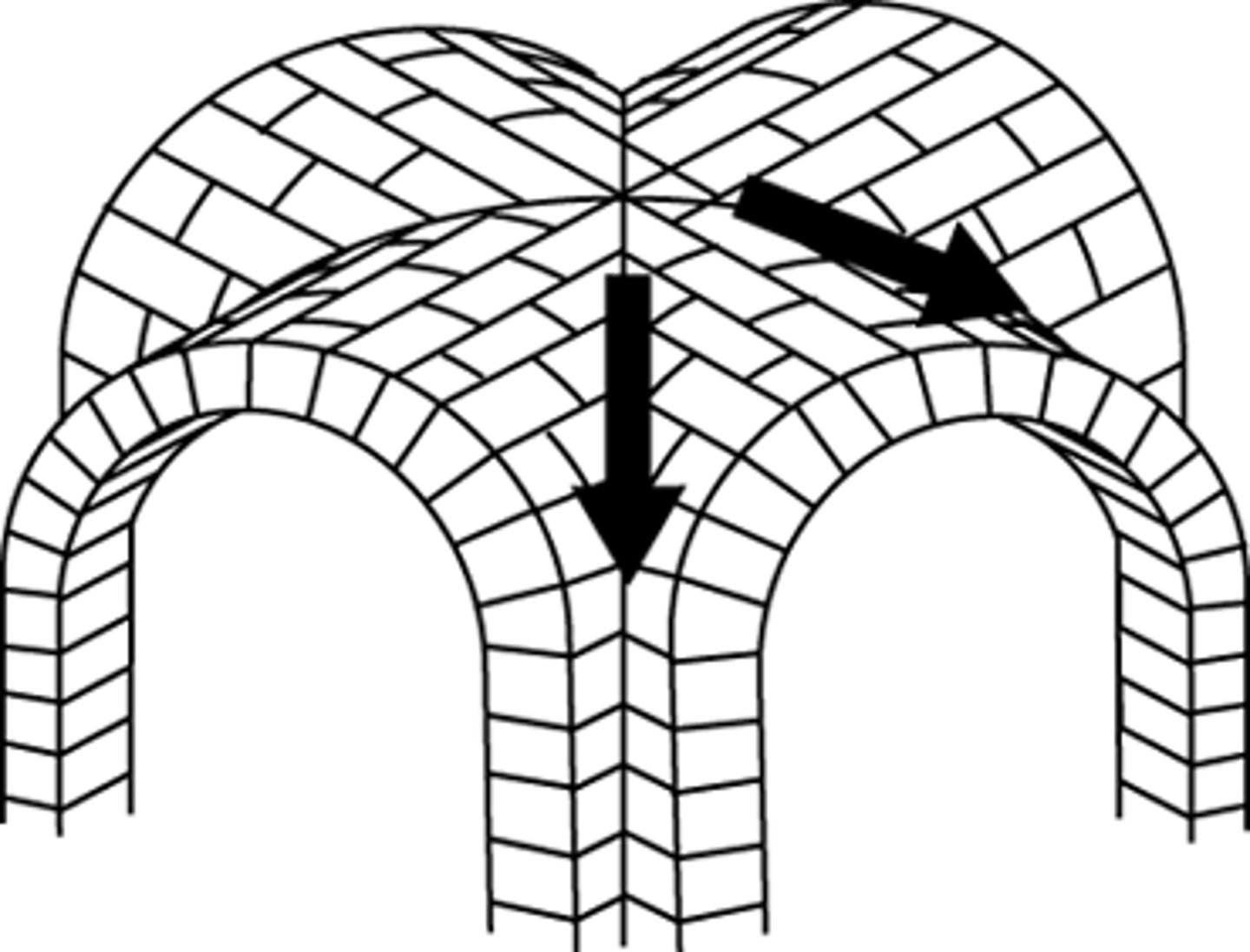
Vault
A roof constructed with arches. When an arch is extended in space, forming a tunnel, it is called a barrel vault. When two barrel vaults intersect at right angles it is called a groin vault.
Veristic
sculptures from the Roman Republic characterized by extreme realism of facial features
