MACROECONOMICS
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
competition
In every economy people vie for the economy's rationing device, a process called
macroeconomics
The study of an economy's price level is explicitly a part of
what should be
In all cases, normative economics deals with
Opportunity cost
cost is the value of the most highly valued forfeited alternative when a choice is made.
Entrepreneurship
the talent for organizing the use of land, labor and capital, among other things.
the less likely an individual will go to college.
The higher the opportunity cost of attending college
The entire economy
In all cases, macroeconomics deals with
direct
In general, there is a ______________ relationship between the number of hours spent studying for a test and the grade earned on the test.
Ceteris paribus
"all other things constant" or "nothing else changes."
inversely related
If variable X rises as result of variable Y falling, then X and Y are
positive economics.
The absence of value judgments is the essence of
A person with a high opportunity cost of time
It usually takes less time to buy a six-pack of Pepsi, a loaf of bread, and a bag of potato chips at a small convenience store (such as 7-Eleven) than at a large, full-service grocery store. Which of the following persons is most likely to buy these items at a convenience store?
Labor
The physical and mental talents people bring to production processes comprise the resource called
Positive
Attempts to determine "what is" are part of __________ economics.
"science of scarcity”
In the textbook, economics is defined as
what of available goods and resources
A rationing device is a method used to resolve who gets
inverse relationship
If variable X rises as a result of variable Y falling, then X and Y have an
Limitations of GDP as a measure of economic welfare
Some economists argue that GDP overstates overall economic welfare because it does not include the impact of bads such as pollution.
personal consumption
Largest component of GDP (expenditure approach)
indirect business tax
Sales tax is what type of tax?
Net Exports
It measures the net demand for a country’s goods and services from the rest of the world. A positive value indicates a trade surplus; a negative value indicates a trade deficit.
Net Exports = Exports – Imports
Net Exports Formula
Easterlin paradox
The research of economists Stevenson and Wolfers tends to support the
Easterlin paradox
As income rises, happiness increases only up to a point—beyond basic needs, more money doesn't guarantee more happiness over time.
Contraction
In which phase of the business cycle does a recession occur?
lower GDP
Increases in import spending _____________________, ceteris paribus.
base-year dollars
Real GDP is always measured in
the capital consumption allowance
To derive net domestic product (NDP) from gross domestic product (GDP), we must subtract ________________ from GDP.
NDP = GDP – Capital Consumption Allowance (Depreciation)
NDP Formula
Net Domestic Product (NDP)
is the total value of all goods and services produced within a country after accounting for depreciation (the wear and tear on capital goods like machines and buildings).
Intermediate Good
A good used in the production of a final good or service.
Not counted in GDP separately to avoid double counting.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
is the total market value of allfinal goods and services produced annually within a country's borders.
compensation of employees.
The largest component of national income in the United States is
federal, state, and local governments
Government purchases consist of the total dollar amount(s) spent on goods and services by the
consumption
The sum of durable goods, nondurable goods, and services equals
Consumption, Investment, Government Spending, Net Exports
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is made up of four main components
GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
GDP Formula
exports minus imports
Net exports equals
It overstates GDP due to double counting.
What happens if intermediate and final goods are both counted in GDP?
recurrent swings (up and down) in Real GDP.
A business cycle refers to the
70
Consumption expenditures in the U.S. usually account for approximately __________ percent of GDP.
Yes
Can a country consume beyond its PPF?
Productive efficiency
implies that it is impossible to obtain gains in one area without losses in another.
constant opportunity costs
A PPF is a straight line as a result of
outward and inward
Production Possibilities Frontiers (PPFs) can shift both _________
outward
An ________ shift of the PPF represents economic growth or an increase in resources or technological improvements.
inward
An ________ shift can occur due to events like natural disasters, wars, a decline in the labor force, or destruction of capital, which reduce an economy's productive capacity.
the right of
In a Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) graph, points that lie beyond to _______ the curve represent combinations of goods that are currently unattainable given the existing resources and technology.
inward
A decrease in the quantity of resources available causes the production possibilities frontier (PPF) to shift ________.
reallocation, shift
A movement from one point to another along a given PPF represents a __________ in resource allocation, while a change in resource quantity causes the PPF to __________.
Productive efficiency
An economy is producing the maximum possible output from its available resources and technology, meaning it cannot produce more of one good without reducing the production of another.
reducing
Productive efficiency implies that all resources are fully and efficiently utilized, so producing more of one good requires __________ the production of another.
Productive efficiency implies that
it is impossible to obtain gains in one area without losses in another.
shifts the PPF outward.
An increase in the quantity of resources available
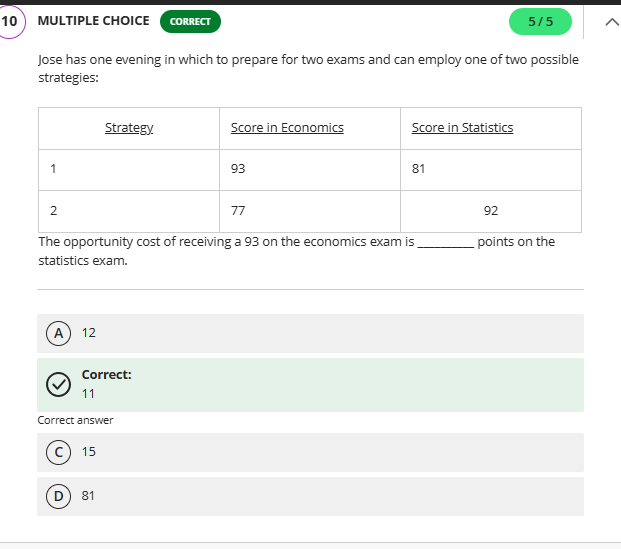
92
what is the opportunity cost here?
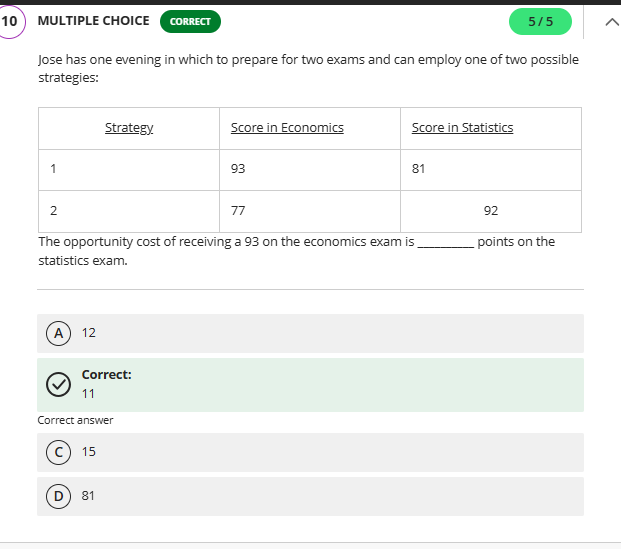
difference between 92 and 81 opportunity cost and what she choose
why 11?
maximum output with given resources and technology
An economy is productive-efficient if it produces
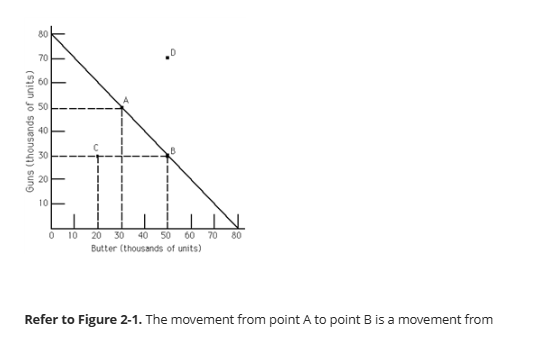
a productive efficient point to another productive efficient point
The movement from point A to point B is a movement from
the implementation of a new law that interferes with productive efficiency
Suppose the economy goes from a point on its production possibilities frontier (PPF) to a point directly to the left of it. Assuming that the PPF has not shifted, this could be due to
attainable and productive inefficient
Points that lie inside (or below) the PPF are
shifting outward (away from the origin)
In the production possibilities framework, economic growth is depicted by the PPF
productive-efficient
If the economy is producing at a point on its production possibilities frontier (PPF), the economy is
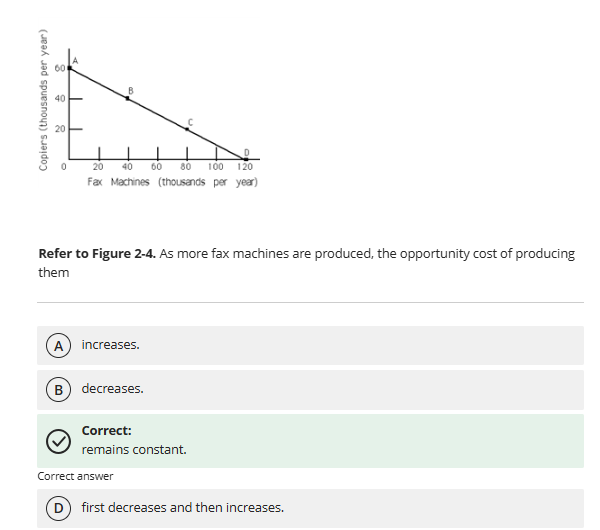
remains constant
As more fax machines are produced, the opportunity cost of producing them
Adam Smith
The concept that economic growth can do more than just give us more goods and services goes back to ________
Adam Smith
In macroeconomics, _________ is regarded as the father of modern economics and one of the earliest and most influential thinkers in economic theory, although he is primarily associated with classical economics, which predates the formal division into macro and microeconomics.
Absolute real growth
ow much the whole economy is growing.
Per-capita real growth
how much the economy is growing per person (more relevant to average income and standard of living).
Doubling time (in years) = 70 ÷ annual growth rate (%)
Rule of 70
17.5
If the annual growth rate in Real GDP is 4 percent, then it will take ____ years for the economy to double in size.
11.6
If the annual growth rate in Real GDP is 6 percent, then it will take ____ years for the economy to double in size.
human capital
refers to education, training and experience.
3.5
An economy doubles in size every 20 years if it maintains a steady annual growth rate of about __________ percent
Per-capita Real GDP= Real GDP/ Population
Per-capita Real GDP formula
Per-capita GDP = (Total Real GDP in dollars) ÷ (Total population)
Per-capita GDP = (Total Real GDP in dollars) ÷ (Total population)
per-capita Real GDP
Per-capita real economic growth refers to an increase from one period to the next in
Real GDP
Absolute real economic growth is an increase in __________ from one period to the next.
Real GDP
"Absolute real economic growth" is defined as an increase in __________ from one period to the next.
$40,000
Real GDP in a small country is worth $8 billion. The population of the country is 200,000. What is per capita Real GDP?
$24,000
Real GDP in a small country is worth $40 billion. The population of the country is 1.666,000. What is the country's approximate per capita Real GDP?
religion
Two Harvard economists, Robert Barro and Rachel McCleary, have researched the role that ________________ plays in economic growth.
the resources labor and capital
Neoclassical growth theory emphasized how __________ contribute to growth.
ideas
According to new growth theory, discovering and implementing new __________ is what causes economic growth.
property
__________ rights refer to the range of laws, rules, and regulations that define rights for the use and transfer of resources.
39
An economy growing at a steady rate of 1.8 percent per year doubles in size approximately every __________ years.
quantity demanded
To an economist, an increase in demand means the same thing as an increase in
law of demand
A demand curve is the graphical representation of the
equilibrium price
A surplus will occur in a market when the price of the product is greater than the
Neutral good
emand does not change with income.
Normal good
demand changes with income.
price and quantity supplied.
A vertical supply curve represents an independent relationship between _____ and __________
vertical supply curve
Supply is fixed — price changes do not affect the quantity supplied because it's perfectly inelastic.
price; inversely
The law of demand states that ____________and quantity demanded are _____________ related, ceteris paribus
inversely related, ceteris paribus
The law of demand states that price and quantity demanded are
A minimum wage law (that sets the minimum wage above the equilibrium wage) can be expected to reduce the number of unskilled workers employed and/or reduce the number of hours worked by unskilled workers.
a tie-in sale
Yves is an excellent barber. However, all customers who come to him for a haircut must buy a bottle of shampoo. This type of arrangement is known as
result in a shortage of the good
A price ceiling set below the equilibrium price will
minimum wage
If the _________ is set above the equilibrium wage, then there will be fewer labor hours purchased by employers than at the equilibrium wage. This leads to reduced employment opportunities for unskilled workers, as businesses may hire fewer employees or cut hours to manage costs.
downward
Because discouraged workers are not considered unemployed, the unemployment rate may be biased ______
unemployed
If Carlos is waiting to be called back to his job from which he has been temporarily laid off, the Bureau of Labor Statistics will classify him as _______
unemployed
A seamstress who quits her job in Houston and moves to New York where additional seamstresses are needed is said to be frictionally _______