Reflexes & Respiration Slides
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what senses and responds to stimuli
Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS) contains
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) contains
nerves extending to/from the CNS
a rapid response to a sudden, intense, and unexpected
stimulation
Reflexes
Reflexes Function
protection, preparation for fight-or-flight response
Reflexes are a combination of
PNS, CNS, and muscle
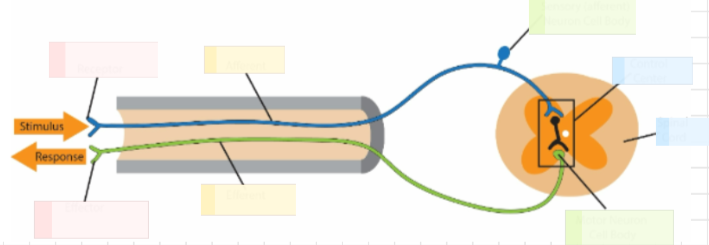
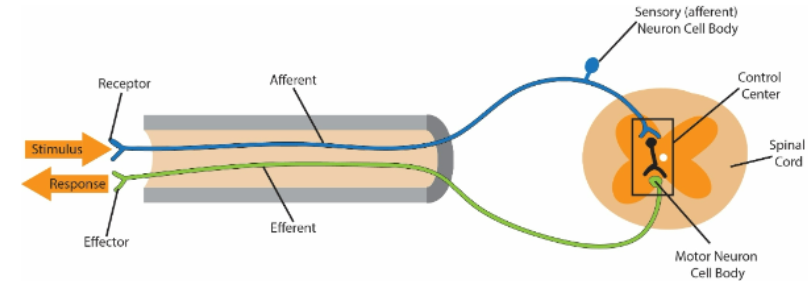
In all reflexes:
1. A _________ that detects change.
2. An _________________ that relays information.
3. A ____________ (interneuron or spinal cord) that evaluates incoming information and determines an
appropriate response.
4. An ______________ that carries information away from the control center.
5. An__________, which stimulates the action at the target site
1.receptor
2.afferent or sensory neuron
3.control center
4.efferent or motor neuron
5. effector (muscle)
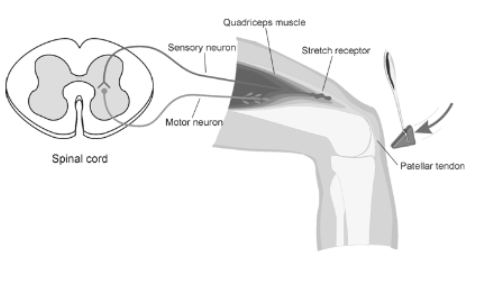
Simple (short-latency) reflex pathway
sensory neuron → motor neuron
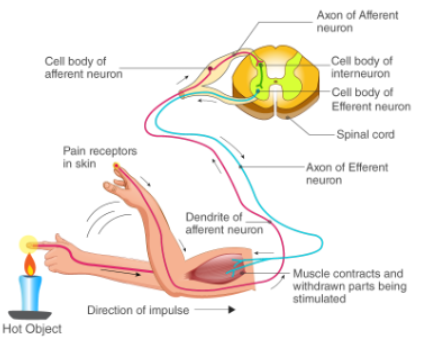
Complex (long-latency) reflex pathway
sensory → interneuron → motor neuron
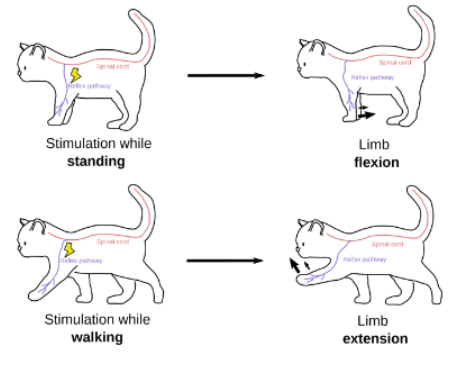
Reflex Modulation
Reflex Modulation: Reflexes can be….
adaptable and flexible: can vary in speed, intensity, and direction
Reflex Modulation Example
Priming
-A prime stimulus is presented just before the reflex stimulus
-This prime stimulus is learned, then the reflex response occurs quicker
Process by which the body obtains and utilizes oxygen and produces and eliminates carbon dioxide
Respiration
Respiratory control center in the brain:
Medulla
Respiration divided into 5 parts
-Pulmonary Ventilation
-Pulmonary Gas Exchange
-Gas Transport
-Tissue/blood gas exchange
-Cellular Respiration
movement of gases between the lungs and the environment
pulmonary ventilation
movement of gases between the lungs and bloodstream
Pulmonary Gas Exchange
movement of gases within the bloodstream
Gas transport
movement of gases between the bloodstream and tissues
Tissue/blood gas exchange
consumption of oxygen and production of carbon dioxide by cells/organelles
Cellular Respiration
Diffusion occurs in the
Alveolar sacs
3 factors influencing diffusion
-surface area
-diffusion distance
-concentration gradient
Pathway of defusion
Ventilation is produced by
skeletal muscle contraction
-muscles contract creating a _____
-Air moves in to fill voided space = ________
-Muscles that contract during inspiration: _______ and ______
-When muscles relax, air is pushed out = _______
-Expiration is _____ in a resting individual
-voided space
-INSPIRATION
-diaphragm and intercostal muscles
-EXPIRATION
-passive
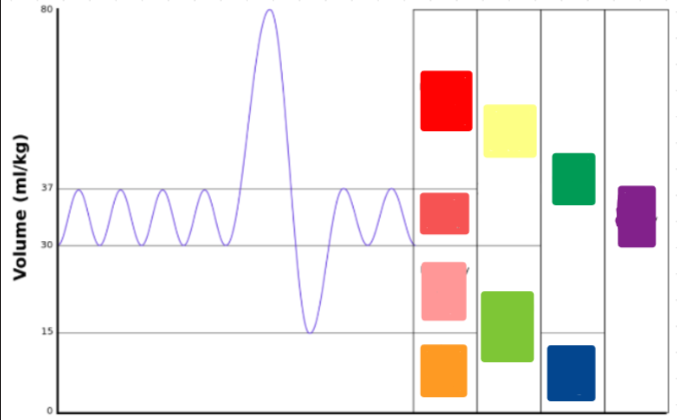
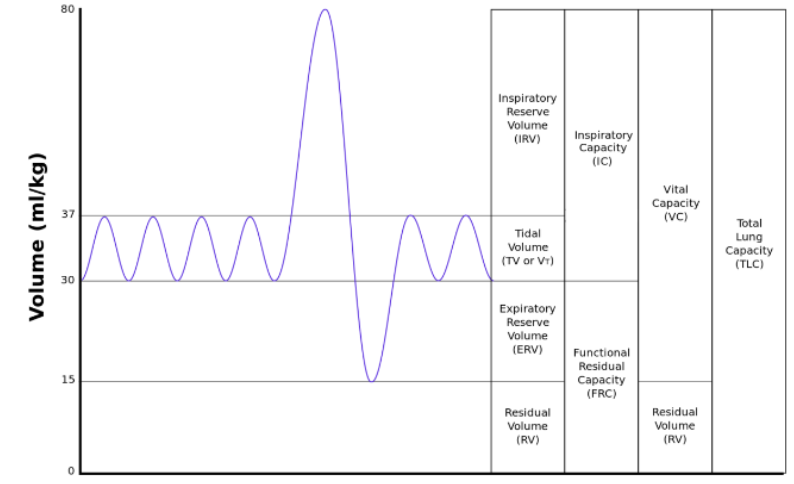
amount of air moving into or out of the lungs during any single breathing cycle
Tidal Volume (TV)
possible air breathed in after a normal breath
Inspiration Reserve Volume (IRV)
air that is still possible to breathe out after a normal breath
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
air ALWAYS left in lungs
Residual Volume (RV)
The sum of two or more lung volumes
Lung Capacity
TV + IRV
Inspiratory Capacity (IC)
Maximum amount of air that can be moved through the lungs ( TV+IRV+ERV)
Vital Capacity (VC)
Starting volume of a breathing cycle (ERV+RV)
Functional residual capacity (FRC)
TV + IRV + ERV + RV
Total lung capacity (TLC)