AP Hug Unit 1 Vocab
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Cultural Landscape
Fashioning of a natural landscape by a cultural group
Cartography
The science of map making
Distortion
The shapes of areas; the distances between places; the relative size of different areas; the direction from one place to another
Distance Decay
the concept that the interaction between two points decreases as the distance between them increases.
Distortion
alteration of shape, area, distance, or direction that occurs when transferring the three-dimensional Earth onto a two-dimensional map. All map projections contain some form of distortion.
Distribution
arrangement of features or phenomena across Earth's surface. Geographers study the distribution of various elements like population, resources, or cultural practices.
Environmental Determinism
The theory that physical environment, particularly climate, determines human behavior and societal development.
Environmental Possibilism
The theory that while the environment may limit certain actions, people have the ability to adapt and choose from a range of possible actions.
GIS
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
GPS
A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
remote sensing
collects data about objects or areas from a distance, typically using satellites or aircraft equipped with sensors.
Scale
Size of the unit studied
Scale of analysis
The size or level of detail at which a geographical phenomenon is examined—local, regional, national, or global. Different patterns and processes may be visible at different scales.
Projection
The system used to transfer locations from Earth's surface to a flat map
map scale
mathematical relationship between the size of an area on a map and its actual size on earth
Site
The physical character of a place
Situation
The location of a place relative to other places
Spatial
the arrangement, appearance, or organization of people and objects across Earth's surface.
Time-Space Compression
The reduction in the time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place, as a result of improved communications and transportation systems
Formal Region
An area defined by one or more uniform characteristics throughout its extent. Examples include nations, states, or regions defined by climate or language.
Functional Region
An area organized around a central node or focal point, with the surrounding areas connected to that node through systems like transportation, communication, or economic activities. (ex: city)
Vernacular region
A region defined by people's perception and identification with it, often based on cultural identity or popular discourse. (ex: the South, the Middle East)
Choropleth map
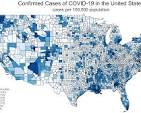
A map that uses different colors or shading patterns to represent statistical data aggregated over predefined regions (like countries or states).
Isoline Map
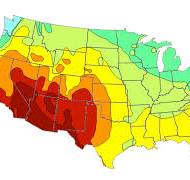
A map that uses lines to connect points of equal value (like temperature, rainfall, or elevation). Examples include contour maps and weather maps.
Dot Distribution map
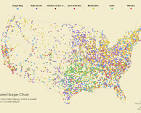
A map that uses dots to represent the presence of a feature or phenomenon. Each dot represents a certain number of occurrences.
Graduated Symbol Map
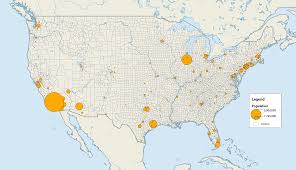
A map that uses symbols of different sizes to represent quantitative differences in a phenomenon. The size of the symbol is proportional to the value it represents.