Worksheet 2 + Quiz 2
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
As a cow is advancing its thoracic limb forward the brachiocephalicus m. attached at the humerus is known as the point of _____________.
insertion
Inflammation of the supraspinous bursa in horses is commonly known as?
fistulous withers
This muscle is a very strong adductor of the shoulder ___________.
pectoral m.
This muscle is an extensor of the hip ___________.
semitendinosus m.
Within the spinal cord sensory neurons project through the _____________.
dorsal root
A postganlionic fiber (neuron) of the sympathetic system will release what neurotransmitter?
norepinephrine
Where all of the ganglion come together in the thoracolumbar division of the nervous system?
sympathetic trunk
Autonomic NS controls:
smooth & cardiac muscles
Somatic NS controls:
skeletal muscles
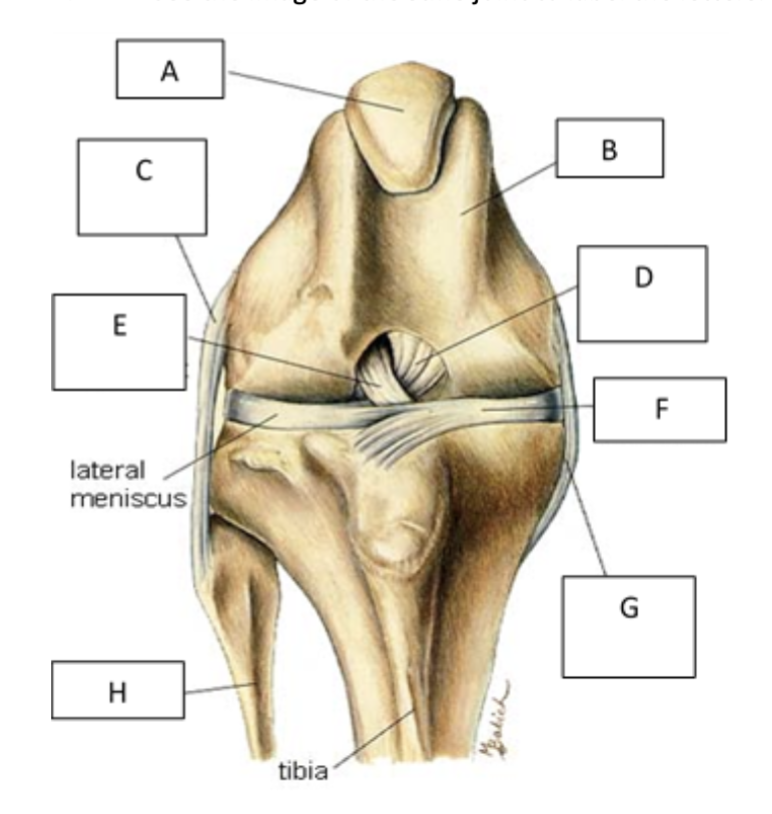
A
patella
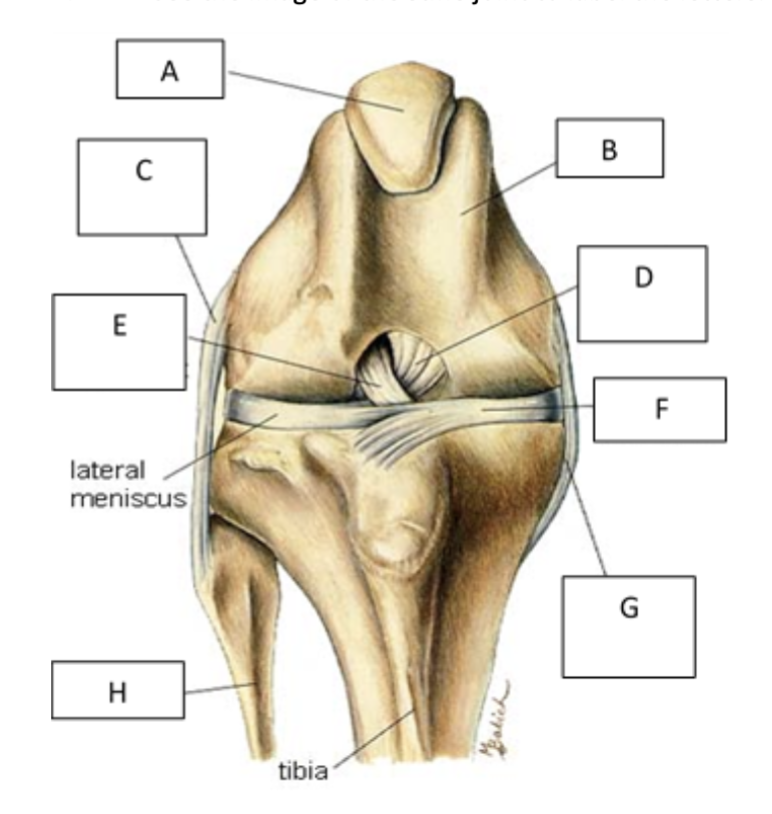
B
femur
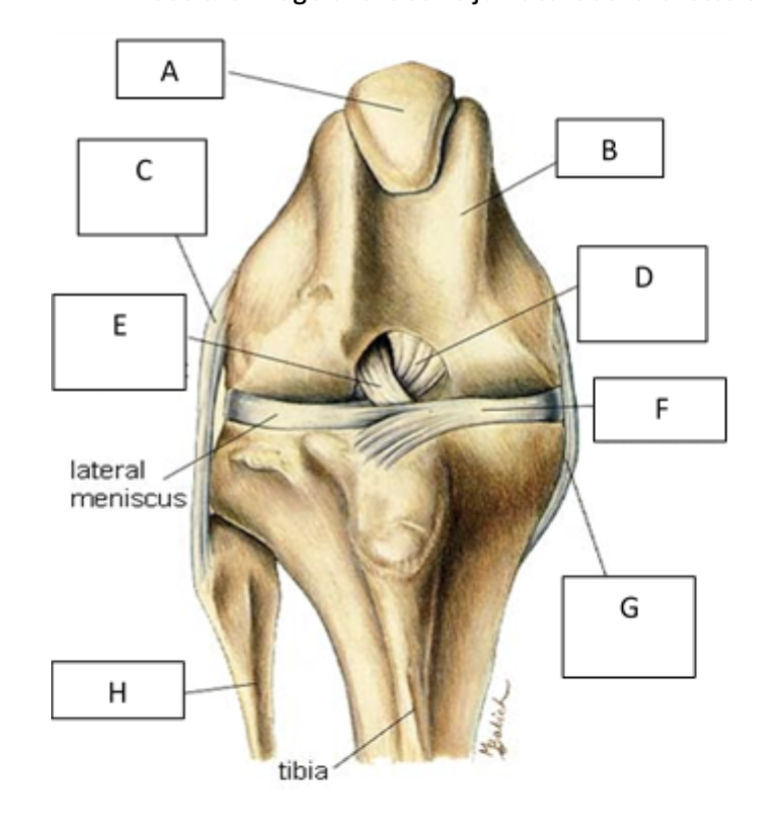
C
lateral collateral ligament
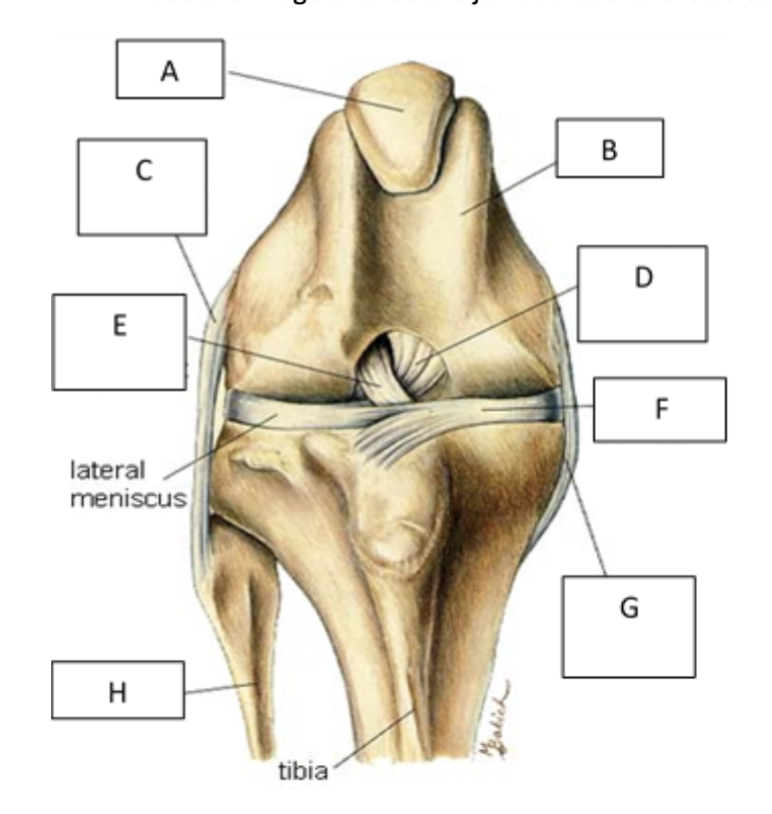
D
caudal cruiate ligament
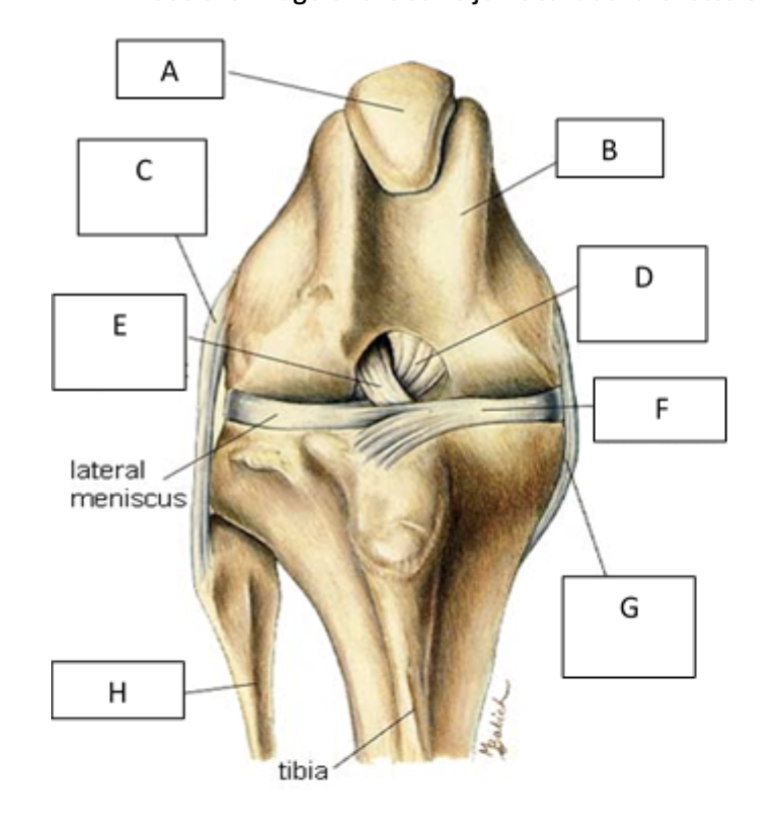
E
cranial cruciate ligament
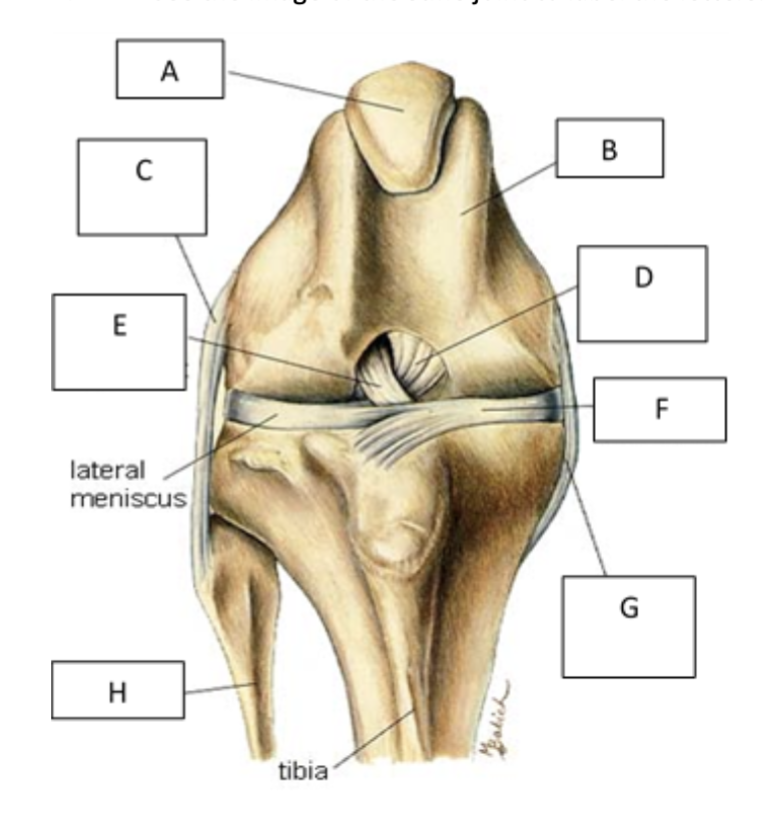
F
medial meniscus
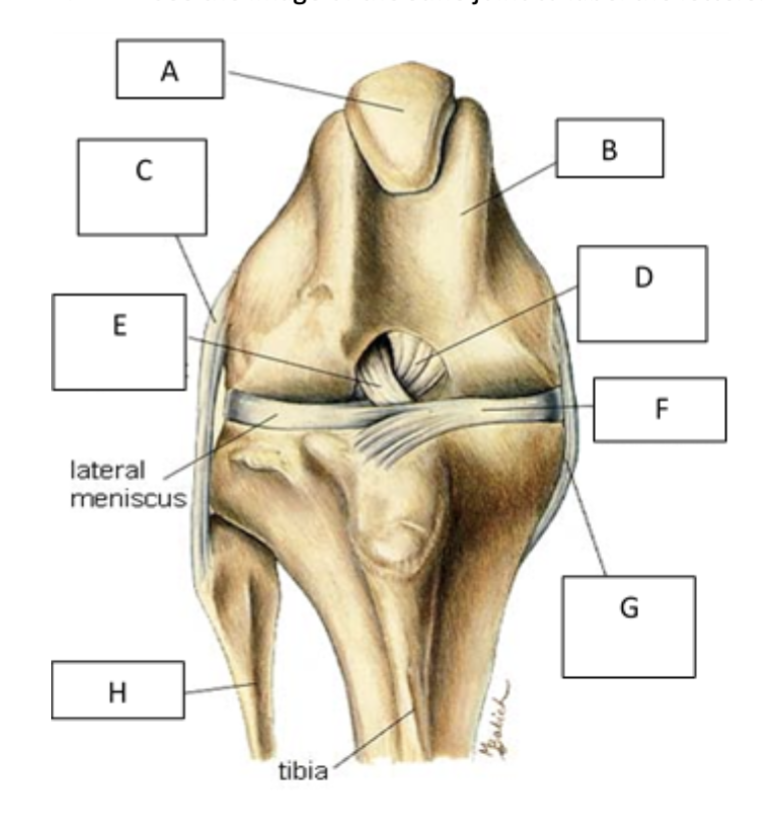
G
Medial collateral ligament
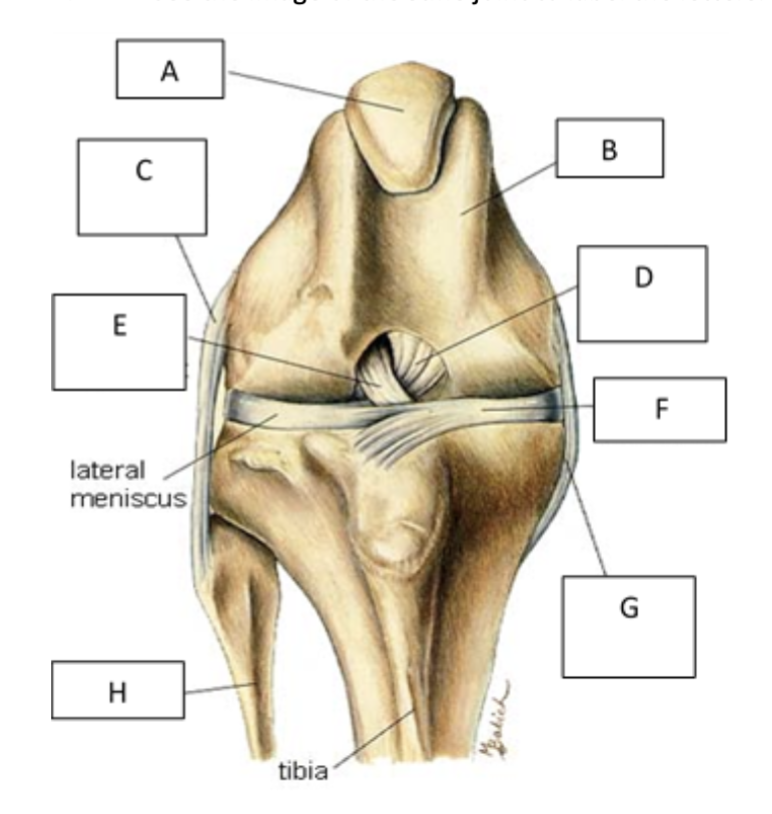
H
fibula
Atlanta bursa =
evil pon
vagus =
cranial nerve
Glutamine =
excitatory neurotransmitter
y-amino buturic acid =
most prevalent inhibitor
Synergists =
assist another muscle in performing a movement
Brachiocephalicus
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Triceps brachii
Semitendinosus
Biceps femoris
Grastrocnemius
Supraspinatus
Agonists =
the muscles that are primarily responsible for producing a specific movement at a joint
biceps brachii
brachialis
Antagonists =
muscles that oppose or reverse a movement
biceps brachii
triceps brachii
Brachiocephalicus =
attached to cervical vertibrae + skull cranially & humerus caudally
extensor of shoulder
Biceps brachii =
cranial side of the limb
extends from scapula to radius
flexor of elbow
Brachialis =
distal to the bicep muscle of the forearm
flexor of elbow
Triceps brachii =
caudal side of the limb
extensors of the elbow
Semitendinosus
superficial
in hindquarters
extensor of hip
flexor of stifle
Biceps femoris =
makes up the hamstrings
extensor of hip
Grastrocnemius =
caudal surface of femur
extensor of hock
flexor of stifle
Supraspinatus =
in the shoulder
extensor of shoulder
Infraspinatus =
lateral collateral ligament of the shoulder joint
flexor of shoulder
Deltoideus
superficial shoulder muscle
flexor of shoulder
Middle Gluteal =
glutes
extensor of hip
Quadraceps =
on the front of the femur
extensor of stifle
Iliacus =
pelvic region
flexor of hip
Strong adductor of shoulder =
pectoral
Abductor of hip =
superficial gluteal
Abductor of shoulder =
infraspinatus
Parallel Fibers =
entire length of muscle
fast/extension movement
speed
greatest potential for shortening, but weak
Both Parallel and Pennate Fibers =
fundamental muscle contraction
Pennate Fibers =
muscles axis of force transmission
large forces/heavy moving
force
increased power but less potential for shortening
What is aponeuroses?
a flattened, connective tissue, that helps connect muscle to bones
pearly white fibrous tissue similar to tendon
Origin =
more stable attachment site
Insertion =
more mobile end
Brachiocephalicus — Advance thoracic limb when foot is off ground:
Origin = C1
insertion = humerus
Brachiocephalicus — flex neck to the side if foot is bearing weight:
origin = humerus
insertion = C1
1) Action potential arrival
a nerve impulse arrives at the axon terminal of the motor neuron at the neuromuscular junction
2) Acetylcholine release
the action potential triggers the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels, allowing calcium ions to enter the axon terminal, thus releasing Ach
3) Ach Binding
ach binds to nicotinic receptors on the muscle fibers sarcolemma, causing ion channels to open, allowing sodium ions to enter and potassium to leave
How many Na in and K out?
3 Na+ in
2 K+ out
4) Action Potential Muscle Fiber
the depolarization spreads along the sarcolemma, leading to the generation of an action potential in the muscle fiber
5) T-tubule
the action potential travels along the sarcolemma and down into the t-tubules, which penetrate the muscle cell
6) Calcium Release
the action potential in the t-tubules triggers voltage sensitive receptors on the sarcoplasmic reticulum, causing calcium ions to be released from the SR into cystol
7) Muscle Contraction
the released calcium binds to troponin, causing conformational change in tropomyosin, exposing the active sites on actin filaments, allowing cross bridge formation with myosin heads - resulting in contraction
Myosin =
1500 thick myofilaments
Actin =
3000 thin myofilaments
1) Calcium binds to
C troponin
2) Conformational
change of troponin
3) Tropomyosin shifts
uncovering myosin binding sites
4) Cross bridge formation
as myosin heads attach to actin
5) power stroke occurs
as myosin heads pivot and pull actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction
6) ATP binding
to myosin head (allowing it to reattach to a new position) causing myosin to detach from actin
7) ATP is
hydrolyzed into ADP and P, which re-energize myosin head
8) Repeat
cycle for muscle contractions
Smooth 1
stimulus causes calcium ions to enter smooth muscle cell
Smooth 2
calcium then binds to protein calmodulin, forming a calcium calmodulin complex
Smooth 3
the calcium-calmodulin complex activates enzyme myosin light chain kinase
Smooth 4
activated MLCK phosphorolates the MLC in the myosin head, which enables myosin to interact with actin
Smooth 5
phosphorolated myosin forms cross bridges with actin filaments, allowing the sliding of actin and myosin to pass each other
Smooth 6
sliding of actin and myosin shortens the smooth musclecell, causing contraction
Smooth 7
relaxation
Describe the roles of the autonomic nervous system in causing contraction
ANS regulates smooth muscle contractions based on the body’s needs with the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic NS
ANS can trigger different contractions in blood vessels or digestive tract
Describe the roles of the autonomic nervous system in causing relaxation
ANS ensures smooth muscle relaxation is balanced with contraction
ANS can relax various tissues for blood flow regulation and gastrointestinal motility
Draw and label the preglanglionic and postglanglionic fibers of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system. Label the neurotransmitter released and the receptor which binds said neurotransmitter.
do on paper
Ion channels associated with generating an action potential at the plasma membrane of the axon:
Na+/K+ pump
Voltage gated Na+ channels
Action Potential
Hyperpolarization
Return to resting potential
Na+/K+ pump
maintain the resting membrane potential of -70mv
Voltage gated Na+ channels
these open, allowing Na+ influx and rapidly increasing membrane potential
Action Potential
voltage gated Na+ channels inactivate and K+ channels open — allowing K+ efflux, returning the membrane potential to negative
Hyperpolarization
K+ channels remain open longer than needed, causing overshoot of negative charge
Return of Resting Potential
K+ channels close, and the Na+/K+ pump restores the original ion concentration
Once this action potentials reaches the nerve terminus (end plate) describe the series of events leading to release of a neurotransmitter.
The release of neurotransmitters involves the arrival of an action potential, opening of voltage gated Ca2+ channels, influx of Ca+ ions, fusion of synaptic vesicles with the membrane + endocytosis of neurontransmitters into the synaptic cleft, leading to communication with the postsynaptic neuron.
How to remove neurotransmitter:
enzyme degrades it
cell membrane absorbs it
neurotransmitter diffuses away
Draw the diagrams drawn in class
on paper
Draw the nervous system flowchart
on paper