[E.1] ILLUMINATION AND LIGHTING
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Natural Light
Daylight. This is achieved by using windows, skylights, or light shelves, and is sometimes used as the main source of light during daytime in buildings
Artificial Light
Light from electrical sources, and is man-made, which can be turned on and off at a flick of a switch
General Lighting
Background or ambient lighting; gives overall glow to a room
Local Lighting
Lighting designed to provide a relatively high level of illumination over a small area producing pools of light with a surrounding area of lower intensity from spill light
Task Lighting
Provides localized light in certain areas where tasks are done
Accent Lighting
Directional lighting to emphasize a particular object or to draw attention to a part of the field of view
Highlight
Used to emphasize an object by illuminating with a strong light
Backlight
Illuminates from behind in order to enhance depth or to separate the subject from its background
Sidelight
Light coming or produced from the side
Soft Light
Diffused light that produces little contrast and poorly defined shadows on the subject
Hard Light
Direct light that produces high contrast and distinct shadows on the subject
Information Lighting
Also known as orientation or utility lighting, this provides visual information for our safety and comfort. It is often used in areas with total blackness
Indirect
A method of light distribution wherein 90-100% of light output is directed towards the ceiling of the upper walls
Semi-indirect
A method of light distribution wherein 60% to 90% of the light is directed upwards; 40% to 10% downwards
Direct-indirect
A method of light distribution wherein there is equal distribution of light upwards and downwards
Semi-direct
A method of light distribution that is 60-90% downwards, 40-10% upwards
Direct
A method of light distribution wherein 90-100% is directed downwards
General
A method of light distribution wherein light is distributed equally on all sides
Cornice Lighting
System where light sources are shielded by a panel parallel to the wall and attached to the ceiling to distribute light downwards over the wall
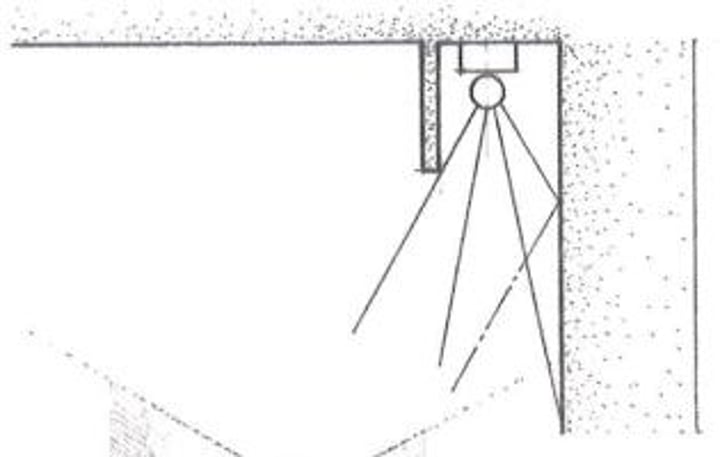
Soffit Lighting
Cornice lighting is also known as
Under Cabinetry Soffit Lighting
Similar to cove lighting but is used for cabinetries
Cove Lighting
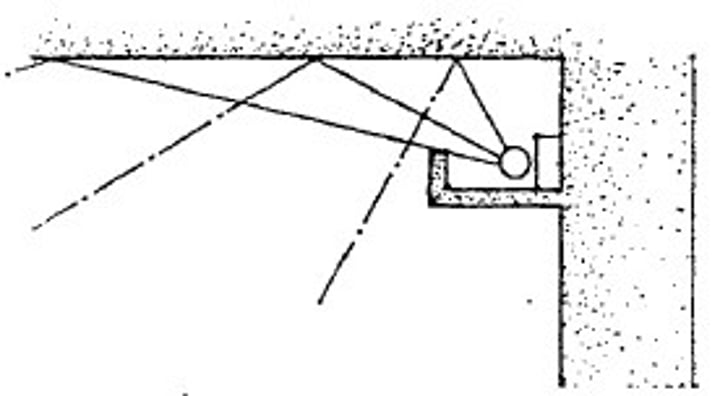
A system where light sources are shielded by a ledge to distribute light upwards over the ceiling and upper wall. It is a form of indirect lighting
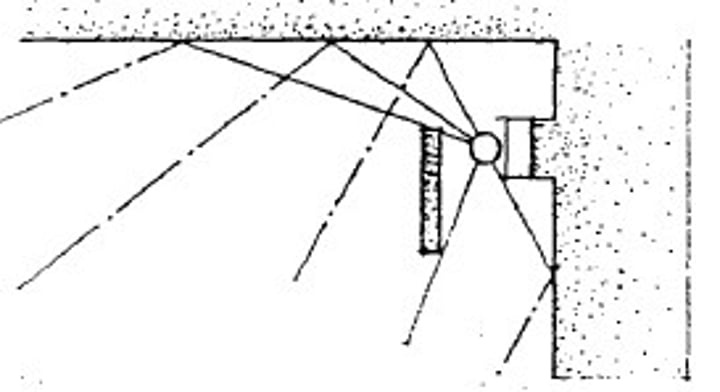
Valance Lighting
A system where light sources are shielded by a panel parallel to the wall usually across the top of a window. This provides light both upwards and downwards over the wall
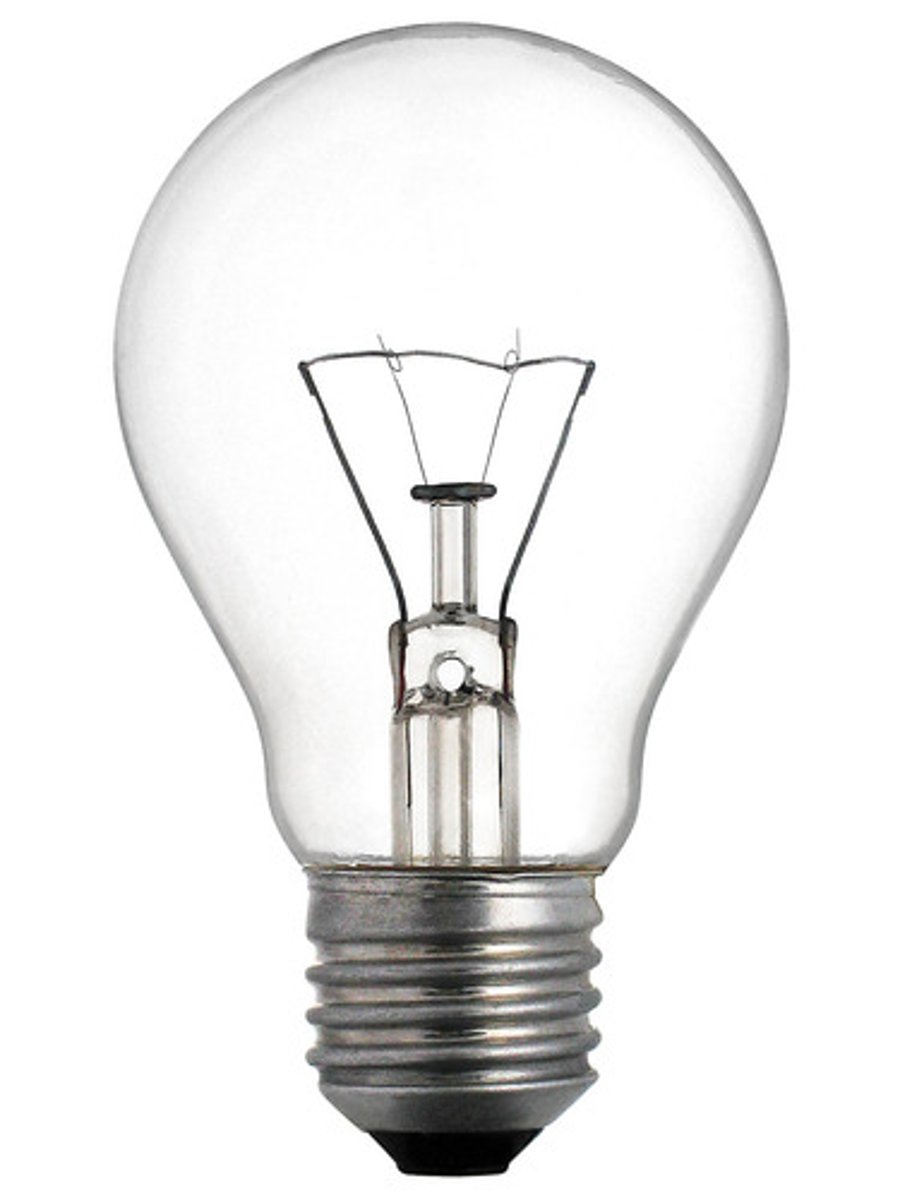
Lamp
Any of various devices furnishing artificial light, as by electricity or gas
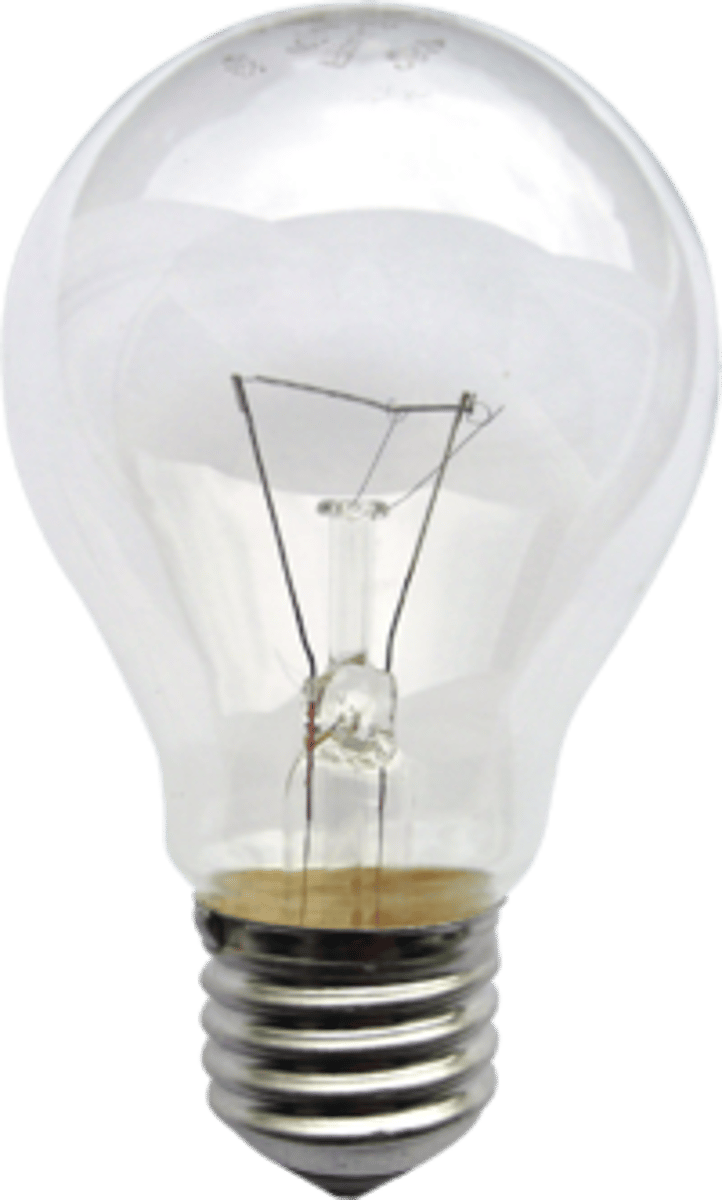
Incandescent Lamp
A filament lamp. The first type of modern electric light. Source of artificial light that works by incandescence
Filament
Threadlike conductor of an electric lamp
Bulb
Glass housing of a lamp
Lamp Base
A part of a bulb that connects to the lamp holder
A Bulb
Incandescent lamp with standard rounded shape for general-service incandescent lamp

B Bulb
Incandescent lamp with flame-shaped bulb for low-wattage, decorative incandescent lamps
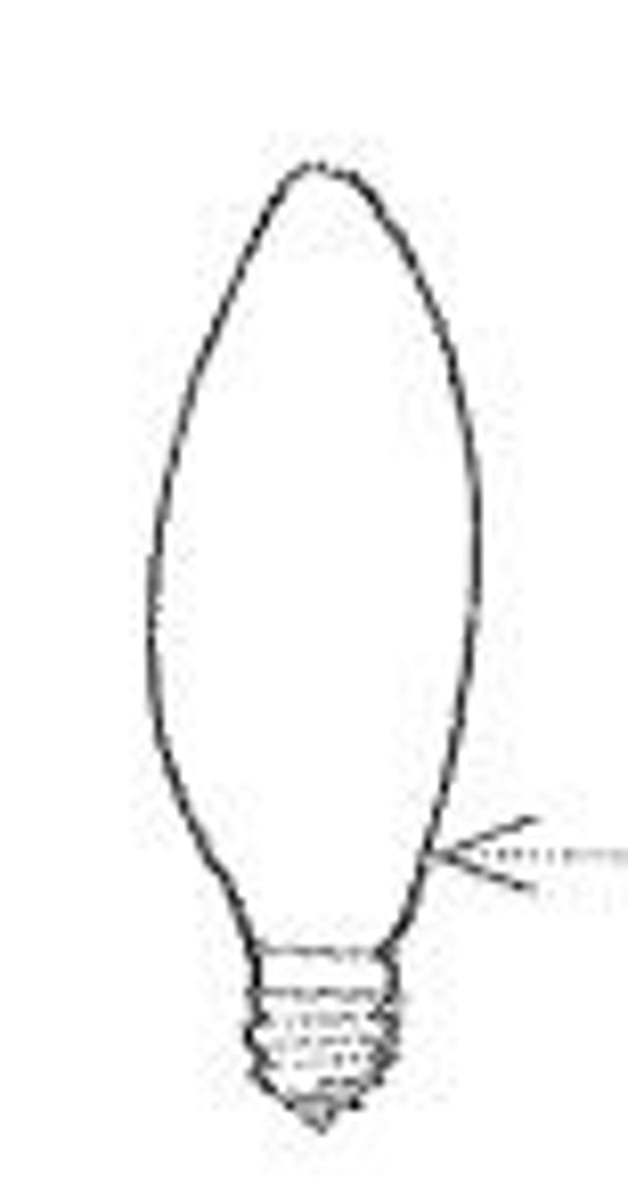
C Bulb
Incandescent lamp with cone-shaped bulb for low-wattage, decorative incandescent lamps

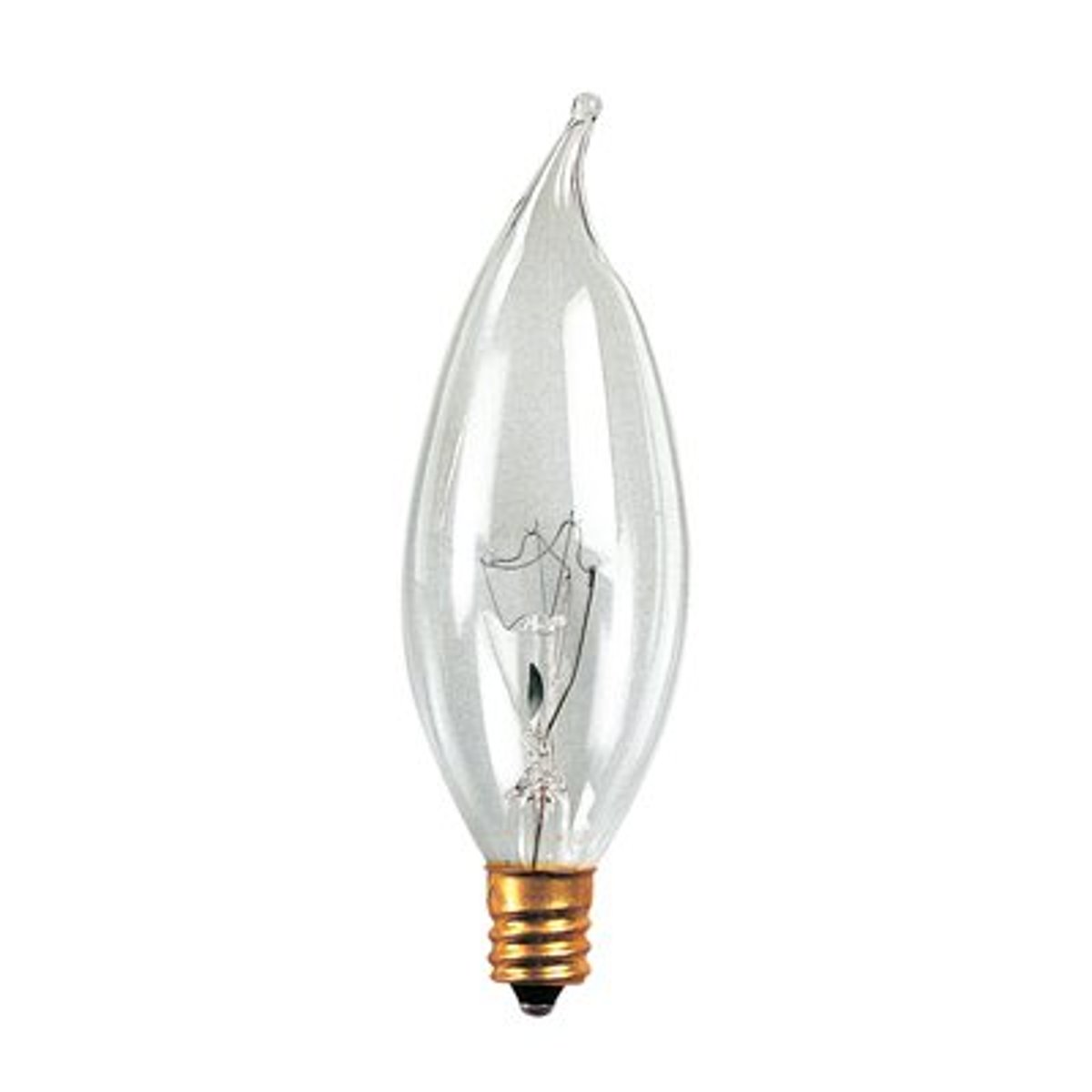
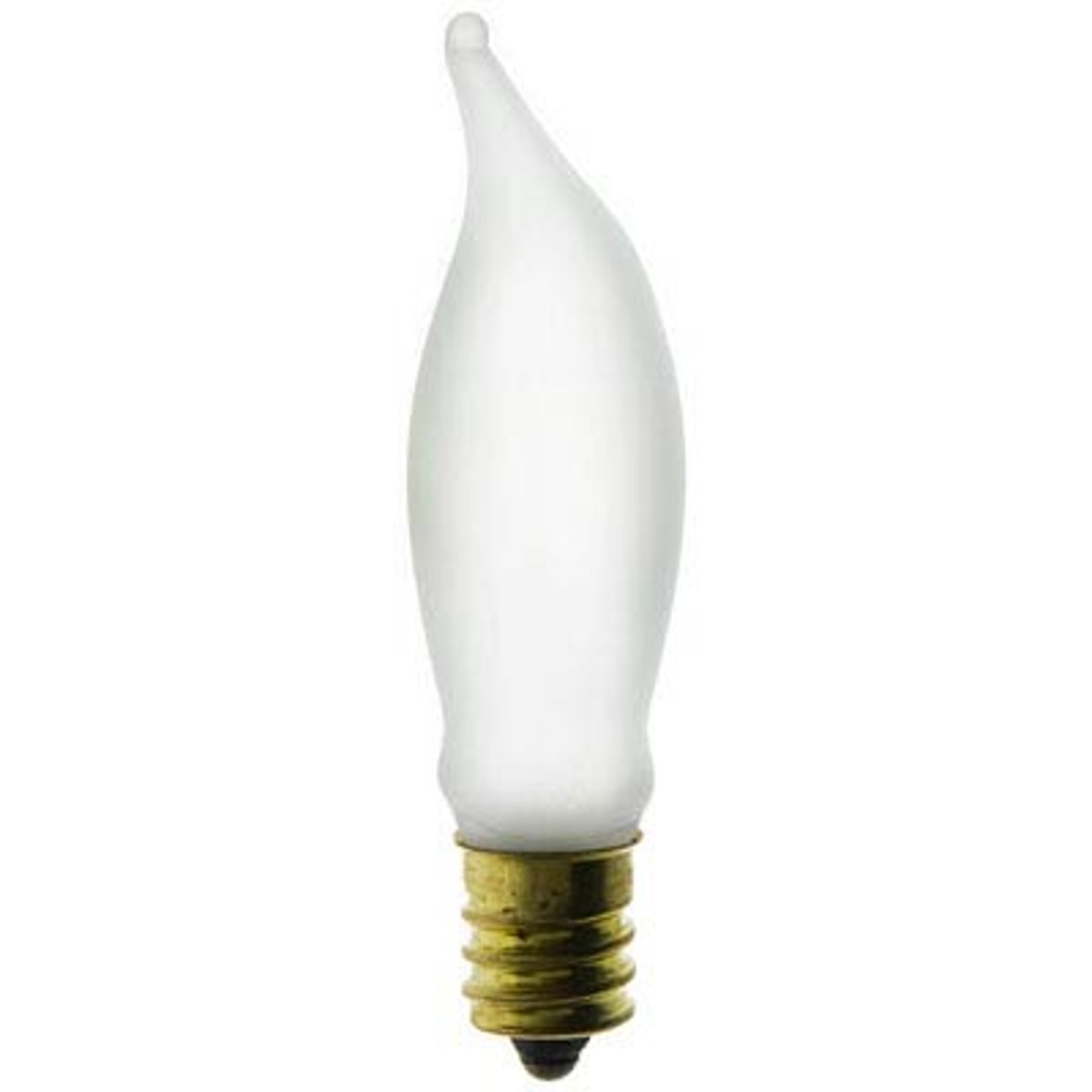
CA Bulb
Incandescent lamp with candle-shaped bulb for low-wattage, decorative incandescent lamps

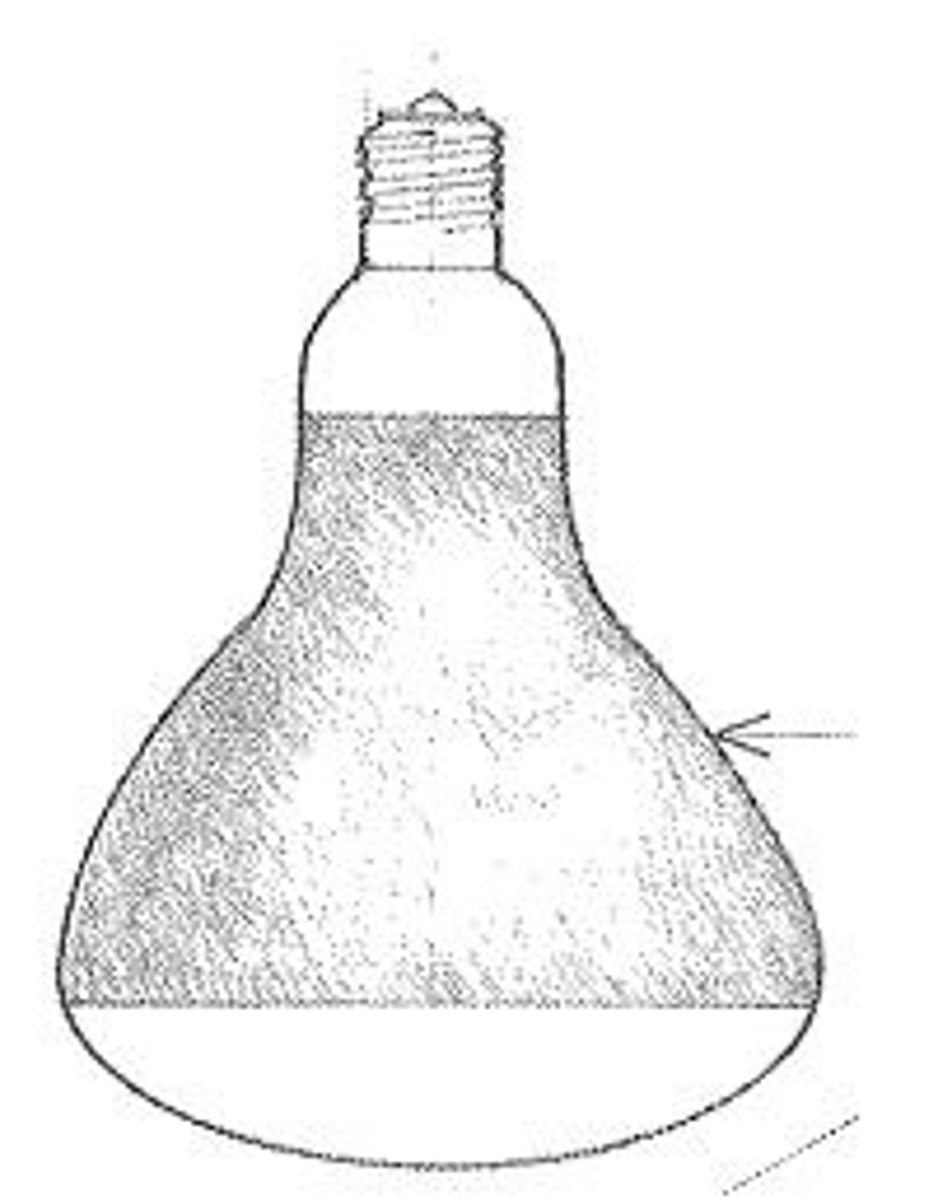
R Bulb
Incandescent lamp with reflector bulb of blown glass for incandescent and high-intensity-discharge lamps, having an internal reflective coating and either a clear or frosted glass front to provide the desired beam spread
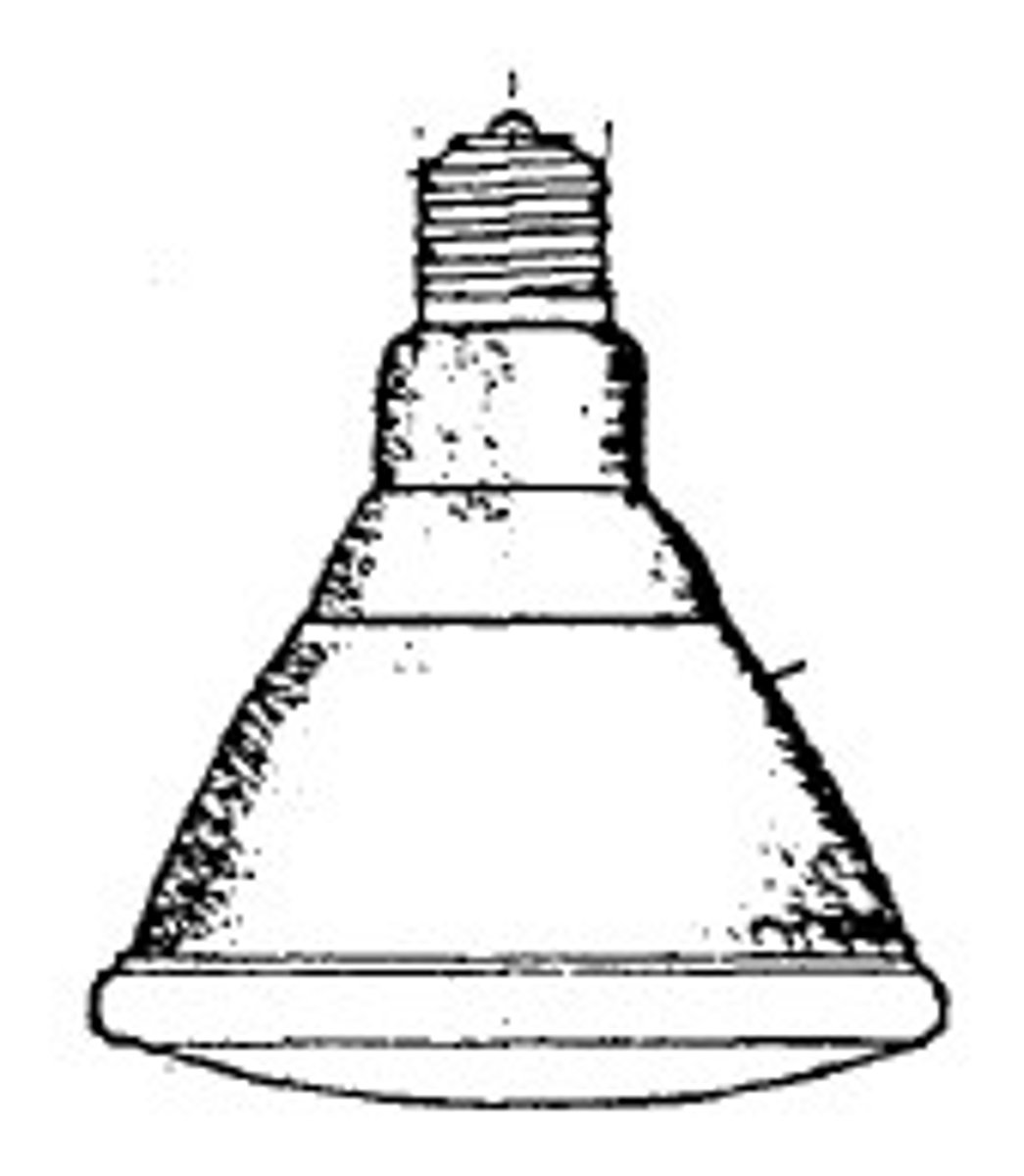
PAR Bulb
Incandescent lamp with parabolic aluminized reflector bulb cast glass for incandescent and high intensity discharge lamps, having a precisely formed internal reflector and a lensed front to provide the desired beam spread
ER Bulb
Incandescent lamp with ellipsoidal reflector bulb for incandescent lamps, having a precisely formed internal reflector that collects light and redirects it into a dispersed pattern at some distance in front of the light source
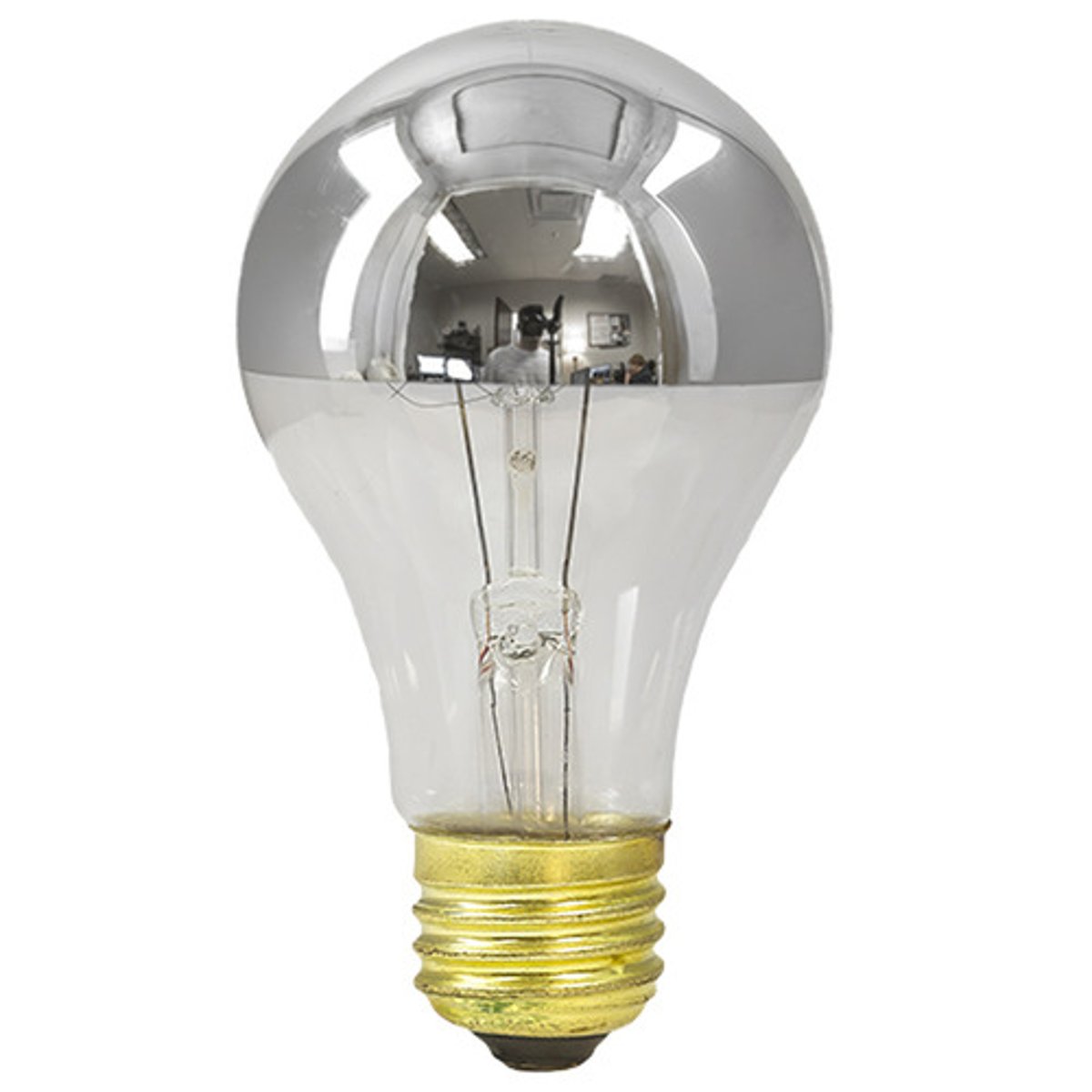
A/SB bulb
Incandescent lamp with a bulb having a hemispherical reflective silver bowl opposite the lamp base to decrease glare

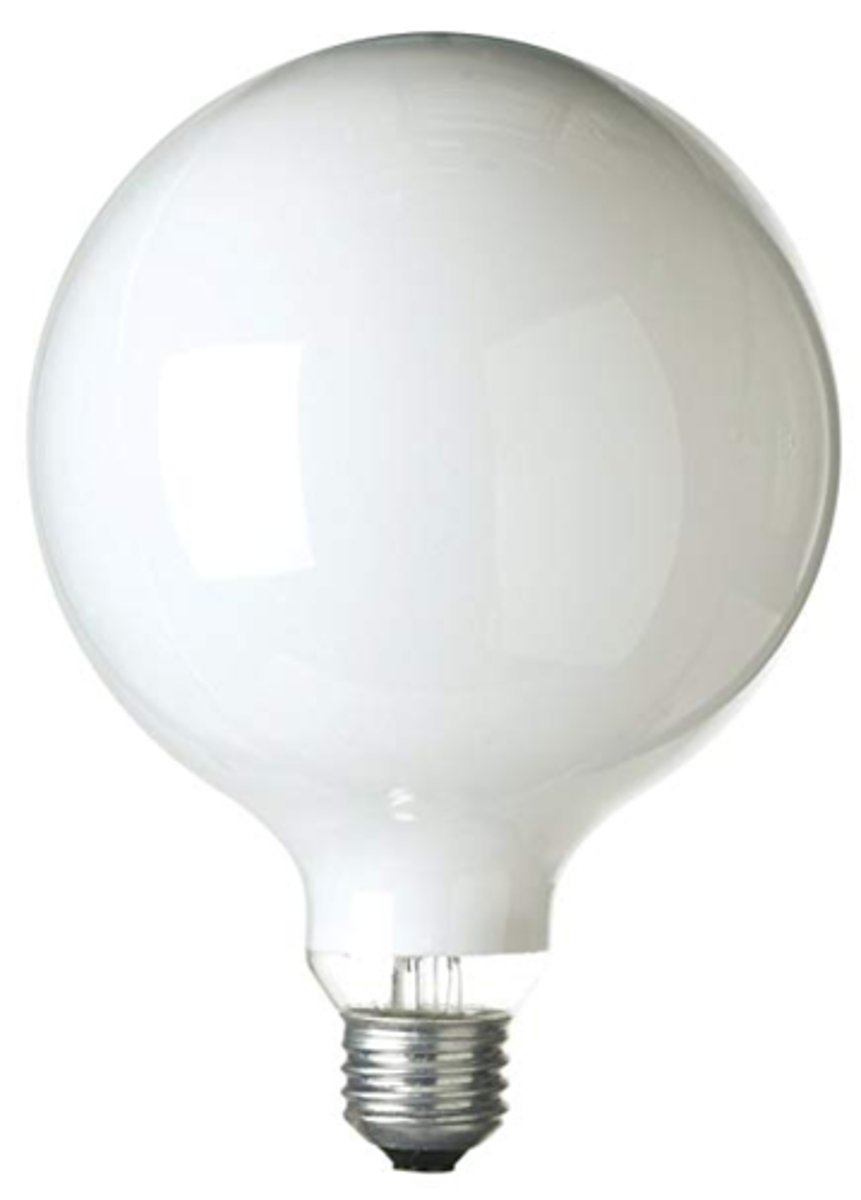
G bulb
Incandescent lamp with a globe-shaped bulb for incandescent lamps, having a low brightness for exposed use

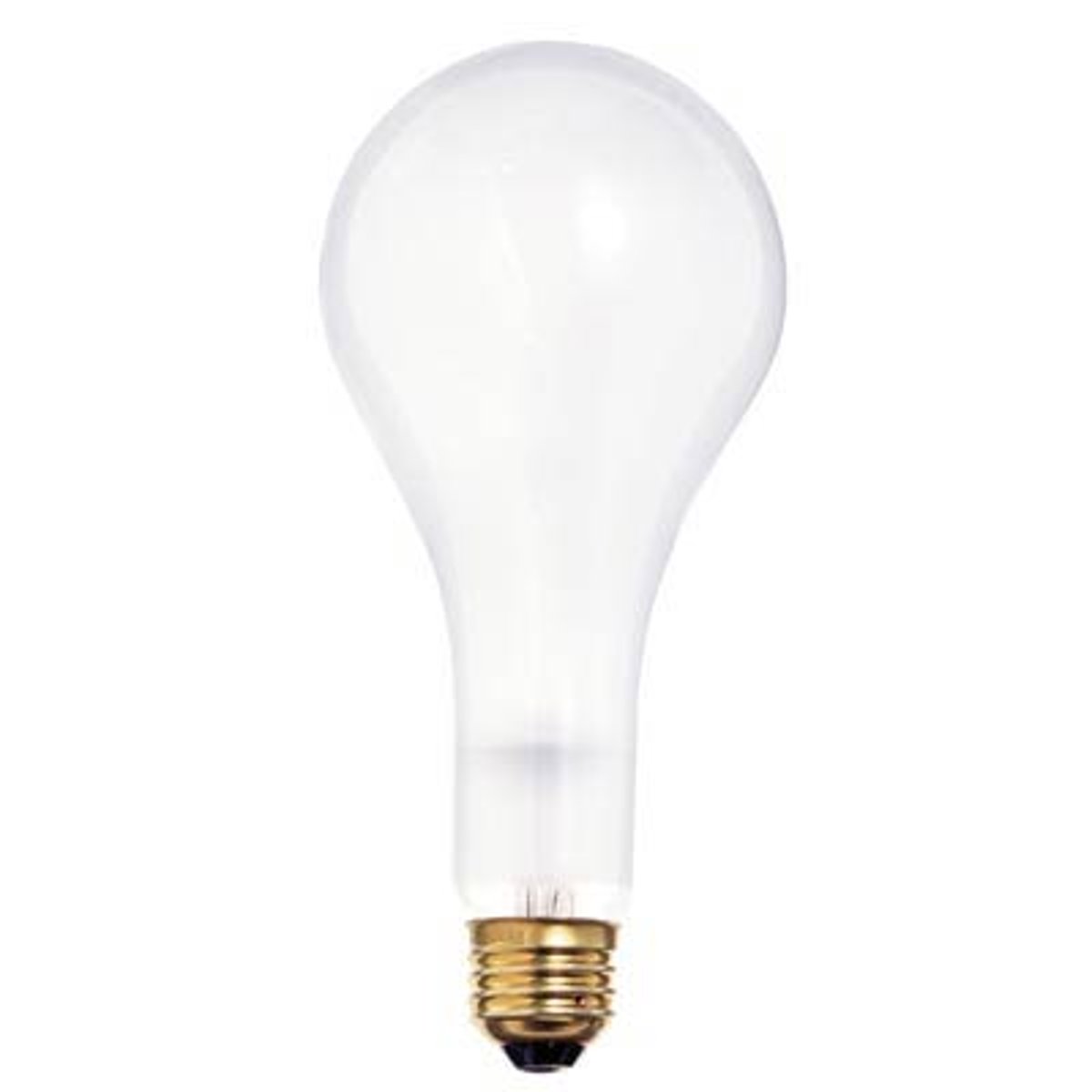
PS bulb
Incandescent lamp with a pear-shaped bulb for large incandescent lamps

S bulb
Incandescent lamp with straight-sided bulb for low-wattage decorative incandescent lamps
Advantages of Incandescent Lamps
1) Cheaper
2) Instant start and restart
3) Simple inexpensive dimming
4) Simple and compact installation requiring no accessories
5) High power factor
6) Can be focused
7) Its life is independent of the number of starts
8) Has good color
Disadvantages of Incandescent Lamp
1) Has low efficacy
2) Shorter life
3) Sensitive and critical to voltage changes or fluctuations
4) High maintenance cost
5) Produces more heat than light
6) Poor energy characteristics
Tungsten-Halogen
Also called "quartz" or "quartz-iodine lamps.” Uses a halogen gas cycle to prevent rapid depreciation of the lamp filament and darkening of the transparent envelop. Can pose fire and burn hazards and sunburn

Floodlights
A halogen lamp that is broad-beamed, high-intensity bulb. They are often used to illuminate outdoor playing fields

R/BR Light
A type of floodlight wherein "R" stands for reflector meaning they contain built-in reflector surface. Soft glass
J Type Bulb
A halogen lamp that is double-ended and commonly used as security lighting. 78-254 MM
JC Type
A halogen lamp that has a low voltage bulb, commonly found under counters in desk lamps, or as accent lighting. They come in capsule shape, with 2 pins at the base
JCD Type
A halogen lamp that has a higher voltage found in under counters, desk lamps, accent lighting. G6.35, G8, G9
Peanut Bulbs
JC and JCD type bulbs are also known as
JDD Type
A halogen lamp that is generally used in the foodservice industry and come in the standard base size. They have a halogen filament enclosed in glass, and then surrounded again by an overall glass jacket
MR Bulb
A halogen lamp that has a multifaceted reflector bulb for tungsten-halogen lamps; polished reflector arranged in discrete segments to provide desired beam spread

JDR Type
Halogen lamp with small reflector floodlights that are commonly used in range hoods or as track lighting. Come in clear or frosted glass finishes. Either screw in, G10 or G3.5

Fluorescent Lamp
A gaseous discharge lamp that comprises a cylindrical glass tube, sealed at both ends and containing a mixture of an inert gas, usually argon and mercury vapors

Fluorescence
A process in which phosphorescent material converts radiation into visible light
Phosphor
Number of substances that emit light when energized by radiation
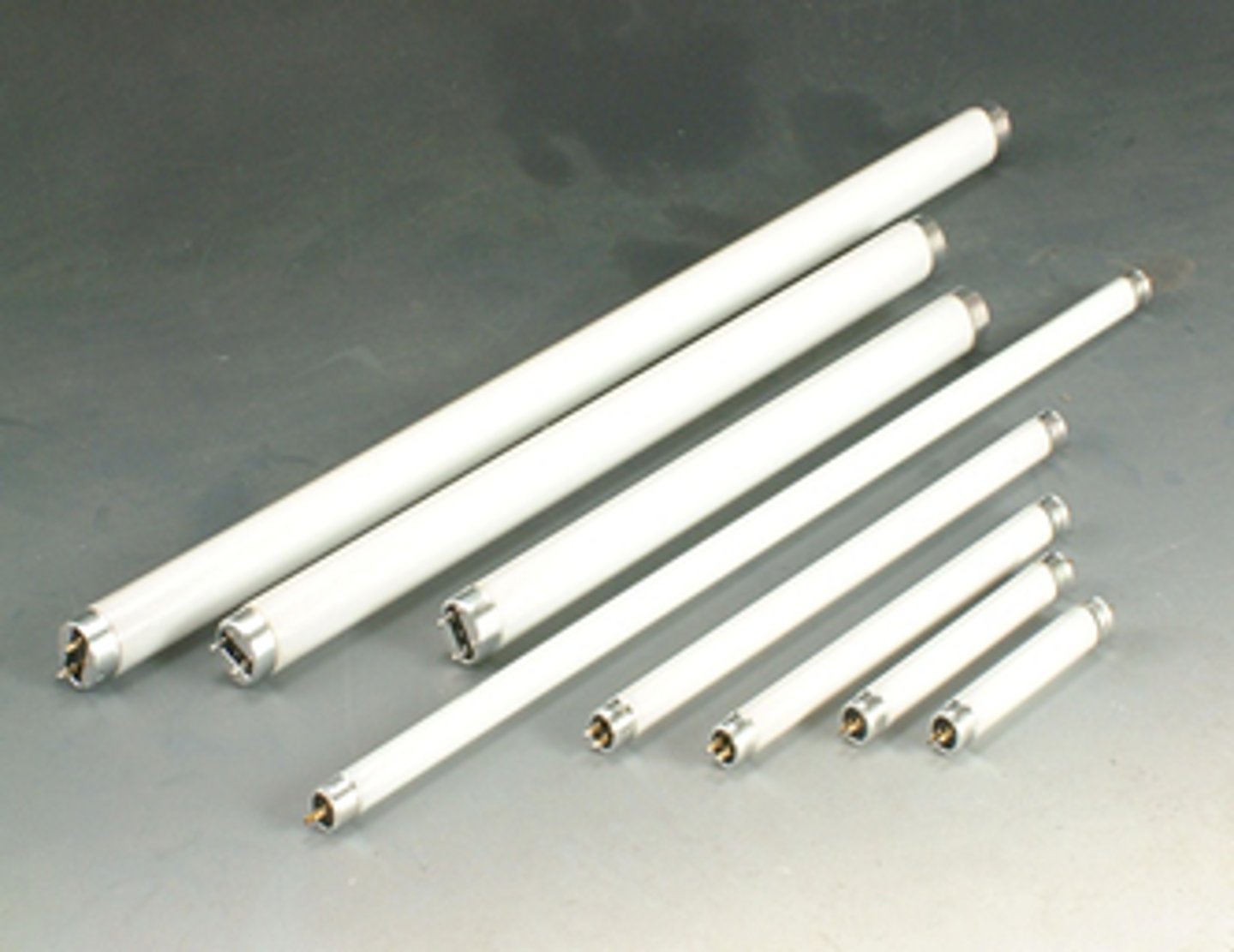
Standard of T-Bulb
Standard shape of Fluorescent bulb; tubular form
4 types: T12, T8, T5, and T4
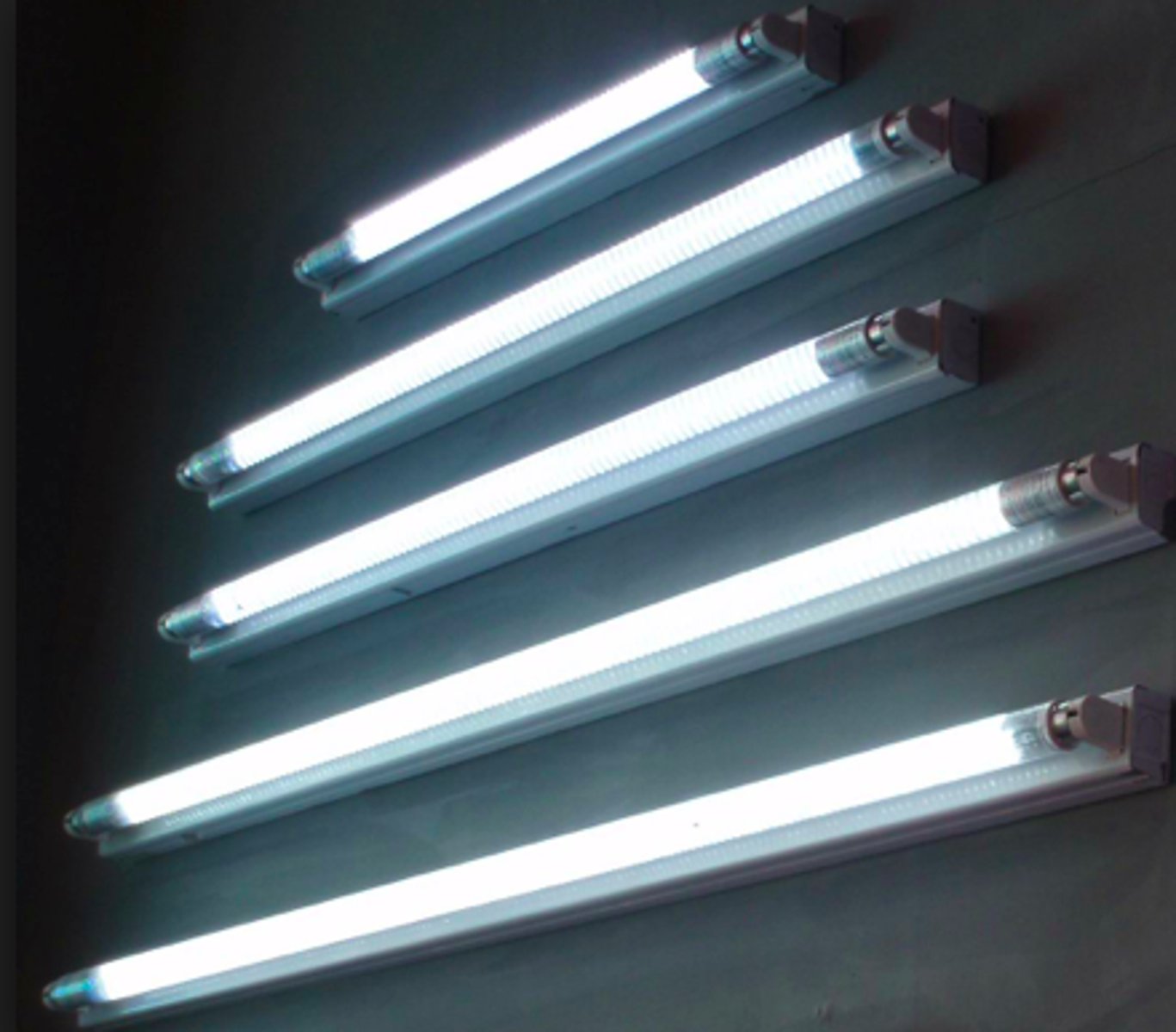

Slim-line
Fluorescent lamp that does not require a starter, have a single-pin base
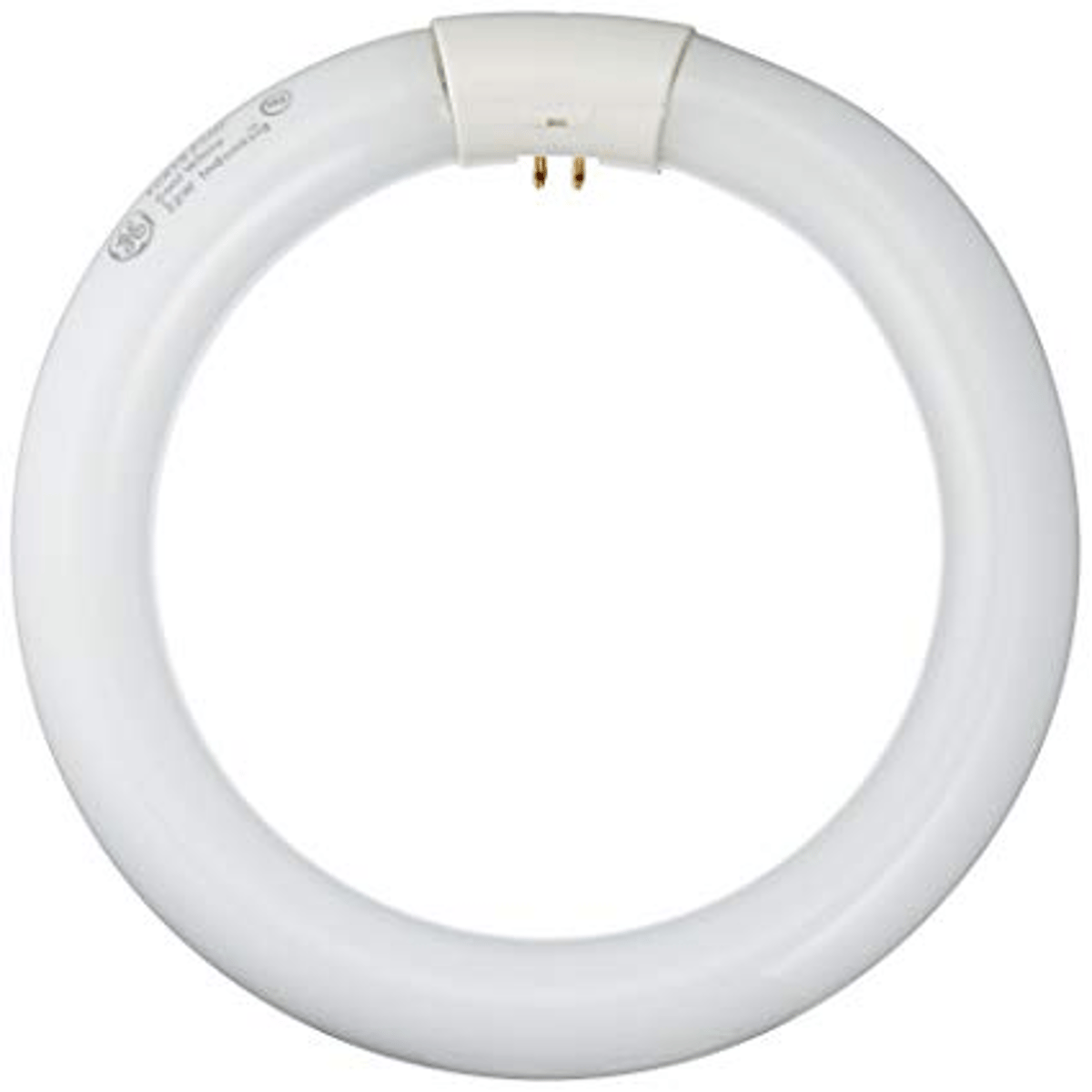
Circline
Type of fluorescent bulb that is donut shaped for circular luminaires

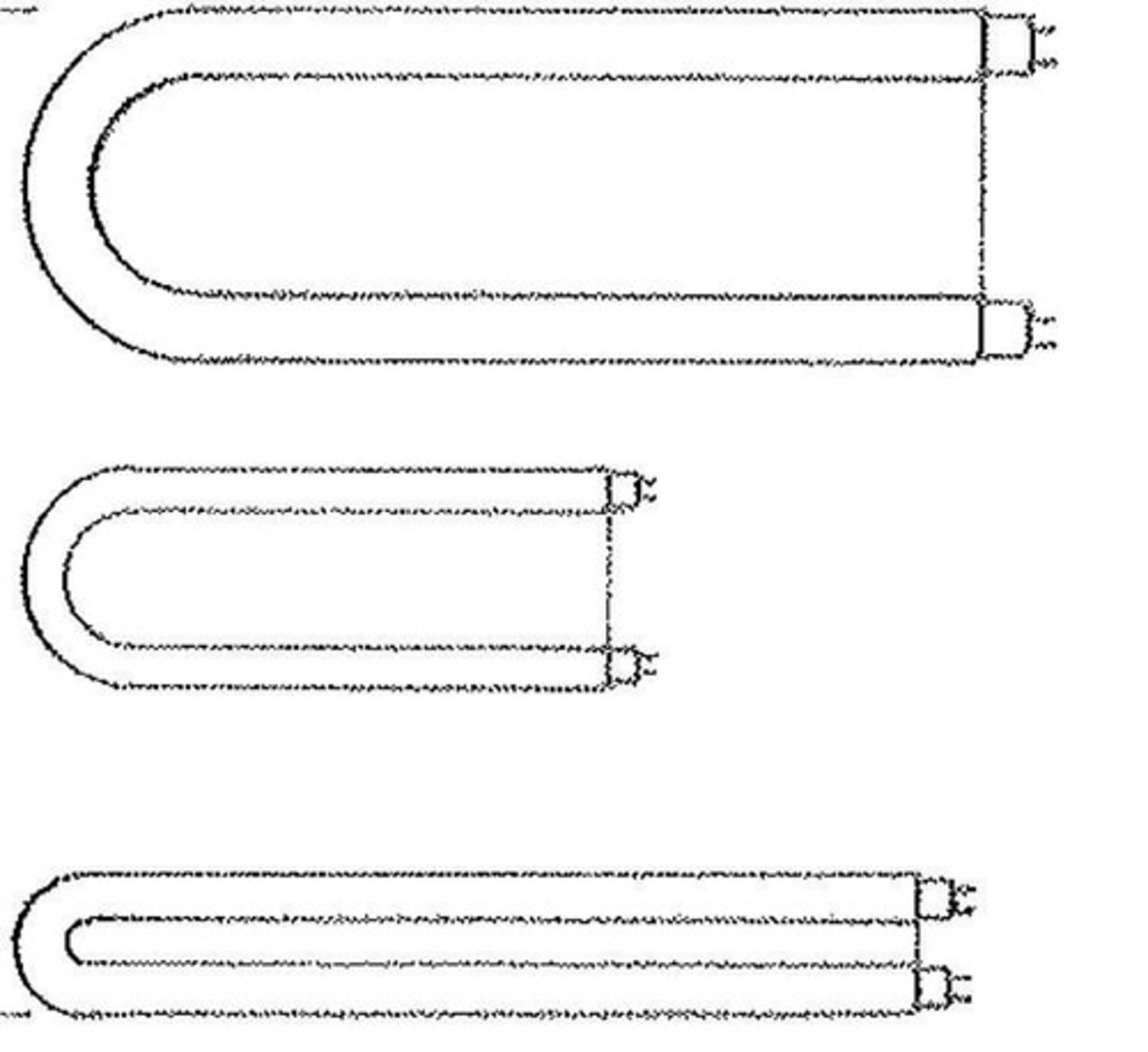
U-bent
U shaped fluorescent lamp used for square or rectangular luminaires
Pre-heat
requires a starter which preheats the cathodes so that less voltage is required to strike an arc. There is 2.5 seconds delay after switch is on. Also called "switch start" or "starter-start" lamp
Instant Start
When a lamp is first switched on, a sufficient voltage is applied between the electrodes to strike the arc without preheating them. These lamps start as soon as the current is turned on and eliminates the need for external starters
Rapid Start
Most recent development and widely used. These lamps use low-resistance electrodes which can be heated continuously with low current loses. These are the only fluorescent lamps that can be electrically dimmed or flashed. They start as quickly as instant start lamps and require no external starters
Choke Coil or Ballast
Supply the high voltage necessary to start the arc and limiting the current in the arc
Automatic Switch or Starter
Self contained in a small tubular jacket which is inserted in the fixture body and is a replaceable part
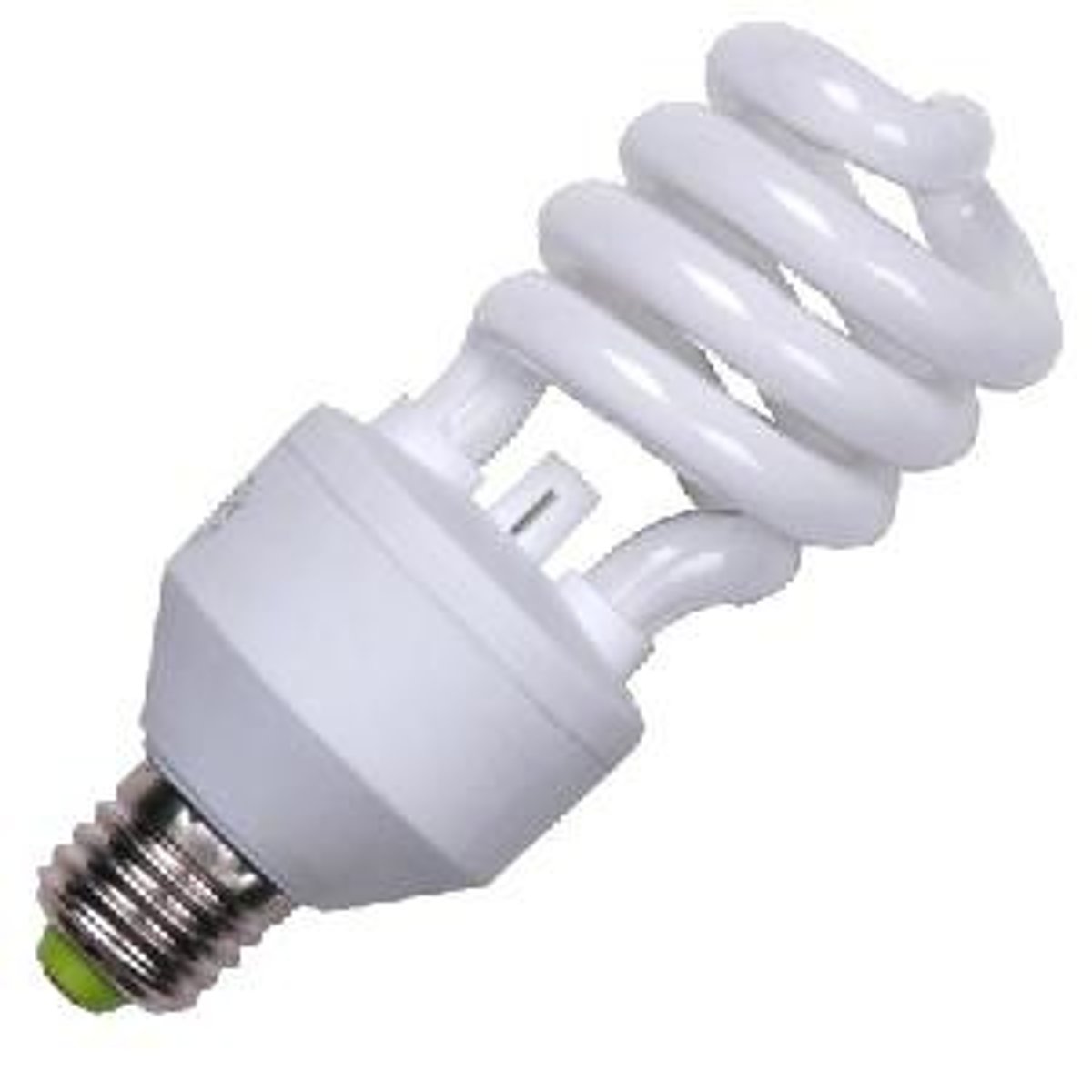
Compact Fluorescent Lamp (CFL)
A small fluorescent lamp, used as a more efficient alternative to incandescent lighting; also called a PL, twin-tube, or biax lamp. (EPA)
Have longer rated light and uses less energy
Spiral
CFL that is most popular and can be used anywhere

Incandescent Lamp
CFL that has an A-shaped bulb; dome of clear glass that mimics an incandescent bulb

Globe
CFL that is meant to be in display in pendant light

Tube
First CFL available to consumers

Candle-shaped
CFL that is shaped like an incandescent candle light bulb. These are smaller, sleeker, and more appropriate for decorative lighting tasks

Post
Spiral CFLs on the inside with a durable cover for outdoor
Reflector
CFL used in place of incandescent floodlights, track lights, directional lights; indoor and outdoor
Neon Vapor Lamps
CFL that is a cold cathode lamp emitting a glow when a high voltage is applied across two electrodes in a neon filled glass-tube. It discharges a lamp even not heated
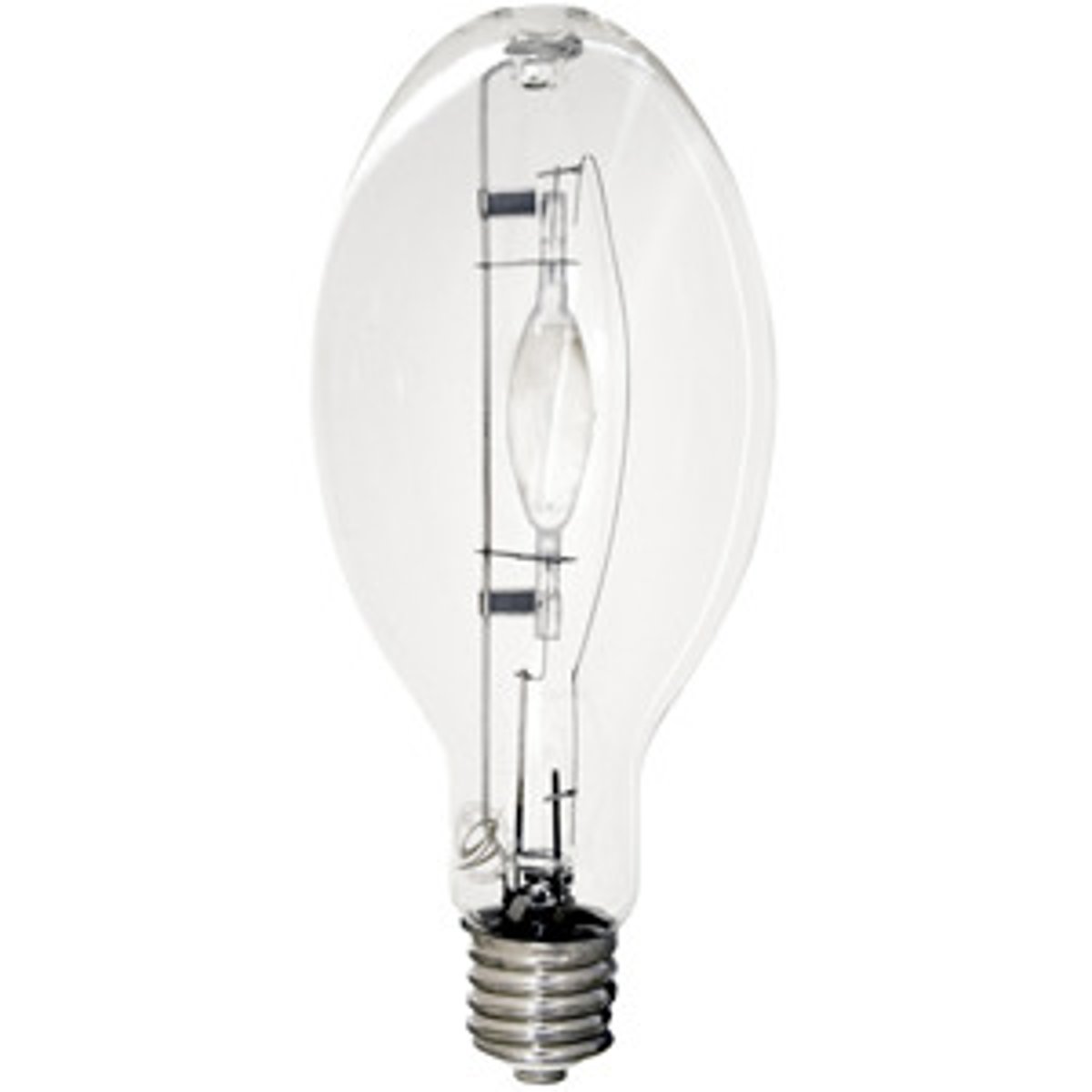
High-intensity Discharge Lamps
Type of lamp which are members of the electric discharge family of light sources (as are fluorescent lamps). Light is produced when a HIGH-PRESSURE electric arc is passed through a gas vapor, rather than by a low-pressure arc as in fluorescent lamps
Mercury Vapor Lamp
A high intensity gas discharge lamp. Mercury vapor in clear quartz arc tube; blue-green. Can be used for street lights
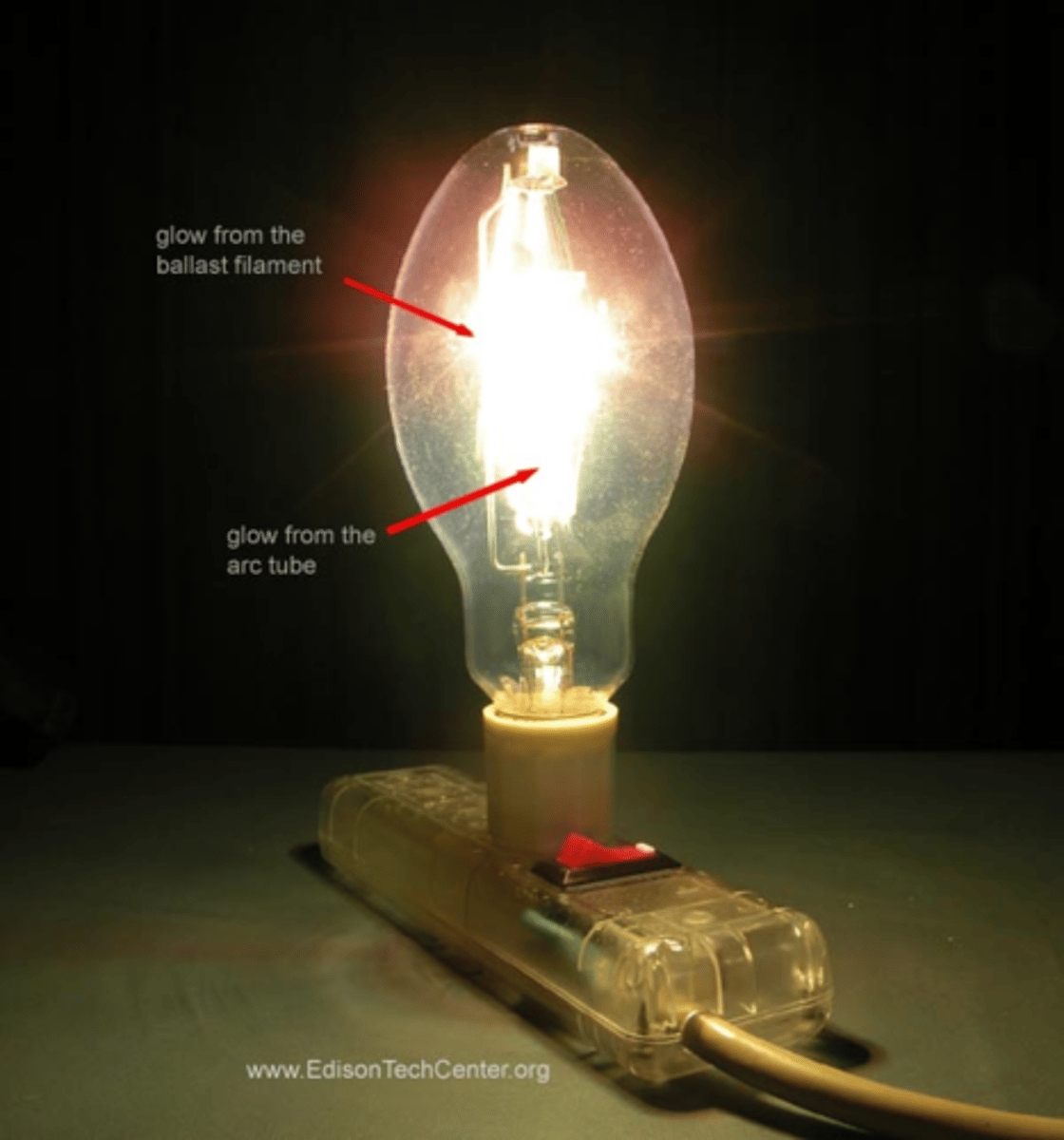
Metal Halide Lamp
A high intensity gas discharge lamp. Light is produced by the radiation from a mixture of a metallic vapor. For stadiums and play fields

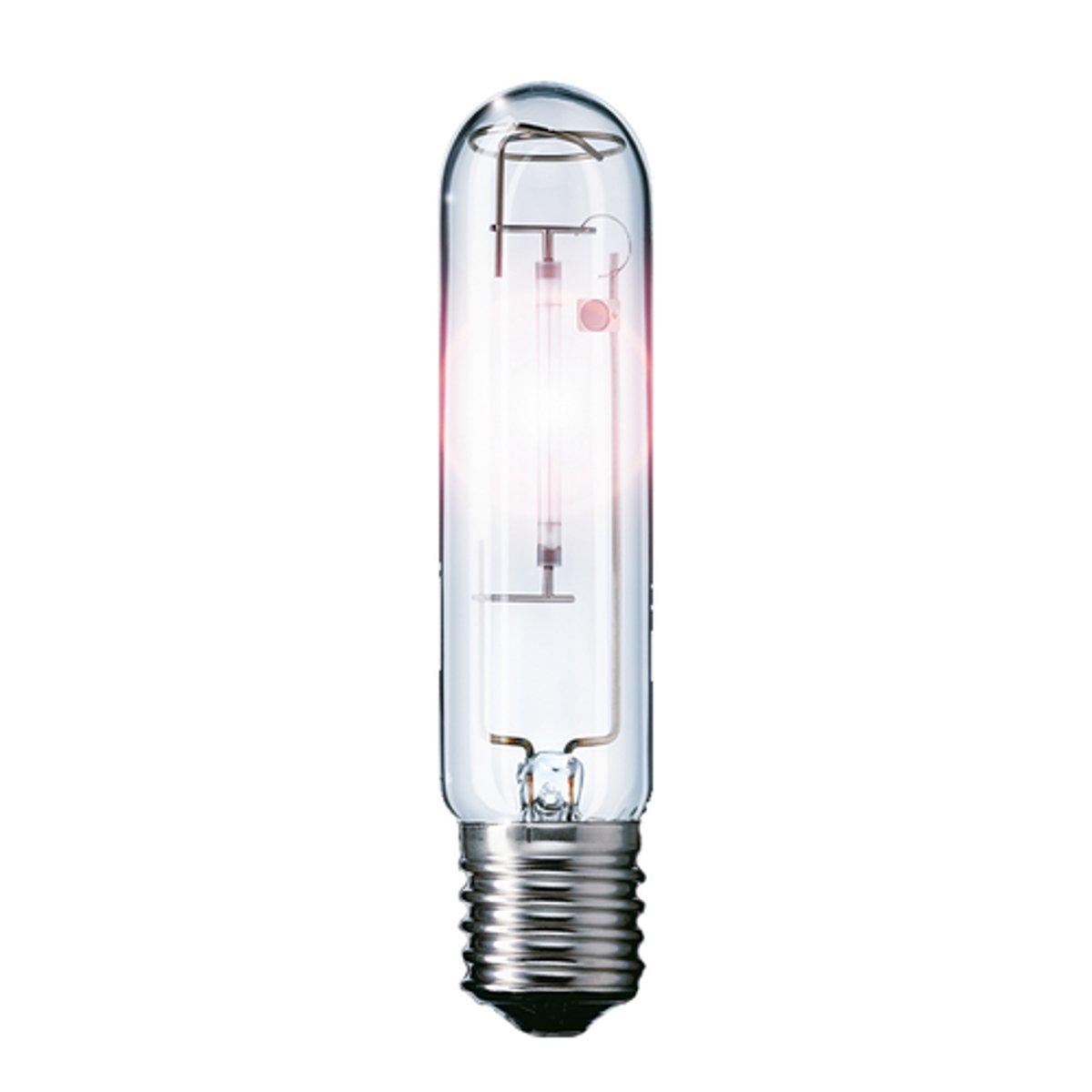
High Pressure Sodium Lamp
A high intensity gas discharge lamp. Made of high density polycrystalline alumina. Airport lights

Solid-state Lighting
A type of lighting that utilizes light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Light in this type of lamp is emitted from a solid object, which is a block of semiconductor. Creates visible light with reduced heat generation.
Longer life span and not hazardous; doesn't shatter
Luminaires
Also called a lighting fixture. A complete lighting unit consisting of a lamp or lamps together with the housing
Reflector
Is a surface for reflecting light heat, or especially the device on a luminaire having such a surface for controlling the distribution of light emitted by a lamp
Lens
Piece of transparent material either glass or plastic that controls the light emitted
Diffuser
Translucent materials for filtering glare of a light source
Louver
Grid type of optical assembly used to control light distribution from fixture
Suspended Ceiling Lights
The most common type of light fixture offering the greatest variety of designs. The light distributed can be any method depending on the shade you choose and the length of cord to which the bulb hangs
Chandelier
A decorative hanging light with branches for several light bulbs or candles
Droplight
A lighting fixture suspended from a ceiling or wall by a flexible cord, by which it can be raised or lowered
Pendant Light
Like a droplight, but is fixed and is suspended by a cord, wire, or chains
Wall Lights
A wall mounted light fixture that diffuses light into the room, usually through a translucent housing
Sconce
A decorative wall bracket for holding candles or lights
Wall Washers
Used to bathe a wall in an even stream of light usually ceiling mounted, recessed into the ceiling or mounted on a lighting track. These lights are wholly directional, using a reflector or a baffle to distribute the light at a certain angle
Ceiling Lights
Ceiling-mounted lighting that is not recessed. It provides general lighting
Downlights
A luminaire consisting of a lamp set in a metal cylinder, recessed into or mounted on a ceiling to direct a beam of light downward
Troffer Lights
Rectangular light fixtures that fits into a modular dropped ceiling grid
Prismatic
This type of troffer light uses a prismatic lens that distributes light over a spectrum and distribute a concentrated light source over a large surface area
Parabolic Louvered
This type of troffer light is the solution for people complaining about the output and uneven distribution of light in a prismatic fixture. They are popular for their ability to reduce the brightness and glare of bare bulbs
Uplights
Sends light upward; freestanding; can be fitted with a dimmer and some types are switched on with a foot pedal
Spotlights
Directs light in a controlled beam; ceiling, wall or floor mounted or attached to a track
Floor Lamps
Light fixtures that are freestanding. Lighting distribution depends on the shade used
Table Lamps
A variety of decorative lights which give a soft glow. Can be used as bedside reading lights or in the living room
Desk Lamps
Provides task lighting and gives a concentrated directional light to a specific area
Strip Lighting
Rigid flexible tape with exposed low-voltage light sources; 1 node/ 1 watt