Chronic Illness Trajectory
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the chronic illness trajectory (CIT)?
Persistent changes in mental, physical, and spiritual health status, requiring long-term management
What is the definition of chronic disease?
has a long duration (>3 months) with a long latency period, clinical course, is of multi-factorial etiology, has no definitive cure, changes over time…
What is the definition of chronic illness?
An alteration in health or function that lasts for an extended period of time, usually 6 months or longer, and often for the duration of the individual’s life.
What are the attributes of Chronic Illness Trajectory?
Care Transitions
Self-Care Management
Health-Related Quality of Life
Uncertainty
What is self-management?
A dynamic process in which individuals actively manage chronic illness
What is health-related quality of life?
Pertaining to life satisfaction and life concerns; may change over time; impacted by health and illness; affecting individual/family
What is uncertainty?
The inability to determine the meaning of illness-related events; unable to predict outcomes accurately
What are care transitions?
A proactive plan of care with goals - patient-family centered, dynamic, shared with care team.
Care Transitions Attribute:
"Care across transitions (a proactive plan of care with goals)
Created, documented, executed, and updated with every patient
Comprehensive- includes community and nonclinical services with health care services that incorporate the patient's needs, preferences, and resources to achieve the patient's goals
Developed and shared across providers and patient's support system
Revised as needed
Patients most likely to benefit identified
Patient-centered and family-focused”
Involves movement between levels of care and/or environmental locations: for example developmental transitions (e.g. childhood to teen to adulthood, etc), or transitions between types of care (e.g. from home to hospital to rehab to long-term-care, etc).
Self-Care Management attribute:
"Is a process in which individuals actively manage chronic illness”
Health provider interventions support behavioral skills to manage conditions independently including medications, equipment, health monitoring, and engagement in self-care decision making.
Health-Related Quality of Life attribute:
A broad and dynamic concept pertaining to life satisfaction and life concerns that may change overtime and are impacted by health and illness, affecting both the individual and their family
Uncertainty attribute:
The unpredictable nature of a chronic illness can create _______ – a subjective experience influenced by the ambiguity of an illness; complexity of treatment; communication with healthcare providers (or inadequate information) about the severity of a condition; or the erratic nature of the illness trajectory
the inability to determine the meaning of illness-related events, occurring when the decision maker is unable to assign definite value to objects or events, or is unable to predict outcomes accurately (Mishel, 1988)
Prevents or delays coping, increases emotional & psychological distress.
What is the Corbin Strauss Model of Chronic Illness?
Shows the phases of CIT
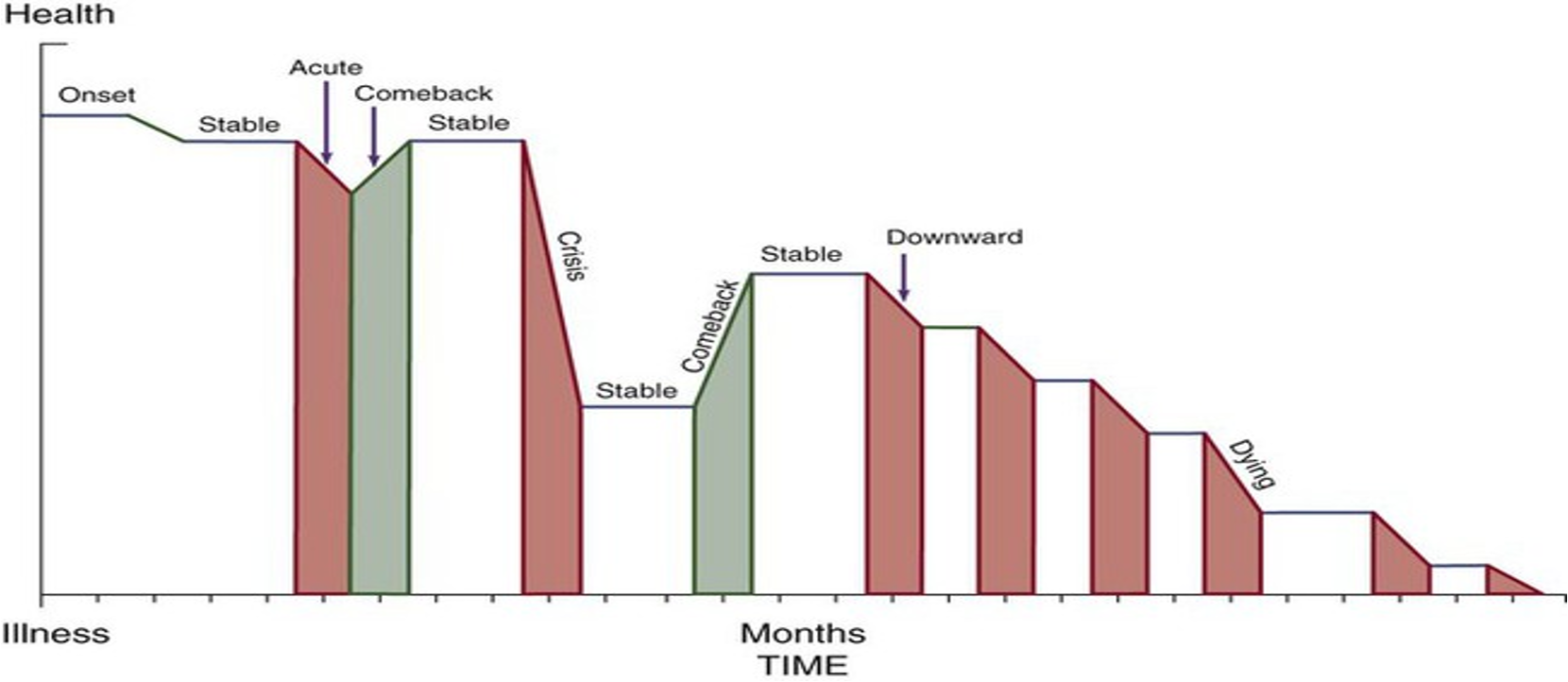
What are the phases of CIT?
Onset
Stable
Acute
Comeback
Crisis
Unstable
Downward
Dying
Description of the Onset phase:
Signs and symptoms present
Diagnostic period
Description of the Stable phase:
Illness course and symptoms controlled by treatment regimen
Person maintains everyday activities
Description of the Acute phase:
Active illness with severe and unrelieved symptoms or complications
Hospitalization may be required for management
Description of the Comeback phase:
Gradual return to an acceptable way of life
Description of the Crisis phase:
Life-threatening situation occurs
Emergency services are necessary
Description of the Unstable phase:
Unable to keep symptoms or disease course under control
Life becomes disrupted while patient works to regain stability
Hospitalization not required
Description of the Downward phase:
Gradual and progressive deterioration in physical or mental status
Accompanied by increasing disability and symptoms
Continuous alterations in everyday life activities
Description of the Dying phase:
Patient has to relinquish everyday life interests and activities, let go, and die peacefully
Immediate weeks, days, hours preceding death
What are the seven tasks of people experiencing chronic illness?
Prevent and manage crisis
Carry out prescribed treatment regimen
Control symptoms
Reorder time (e.g. challenging to make appts, need to eliminate some activities)
Adjust to changes in course of disease (most have unpredictable courses)
Prevent social isolation (adjust, embarrassment, e.g. aphasia, ostomy bags, etc.)
Attempt to normalize interactions with others (e.g. COPD, stop catch breath/window shop)