SAT math formulas
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
sum of the roots
-b/a
product of the roots
c/a
discriminant
number of roots
b²-4(a)(c)
discriminant*

Finding roots*

Finding the vertex
-b/2a or (root 1 + root 2)/2
Finding the vertex*

vertex form
y = a(x-h)² + k
vertex form*

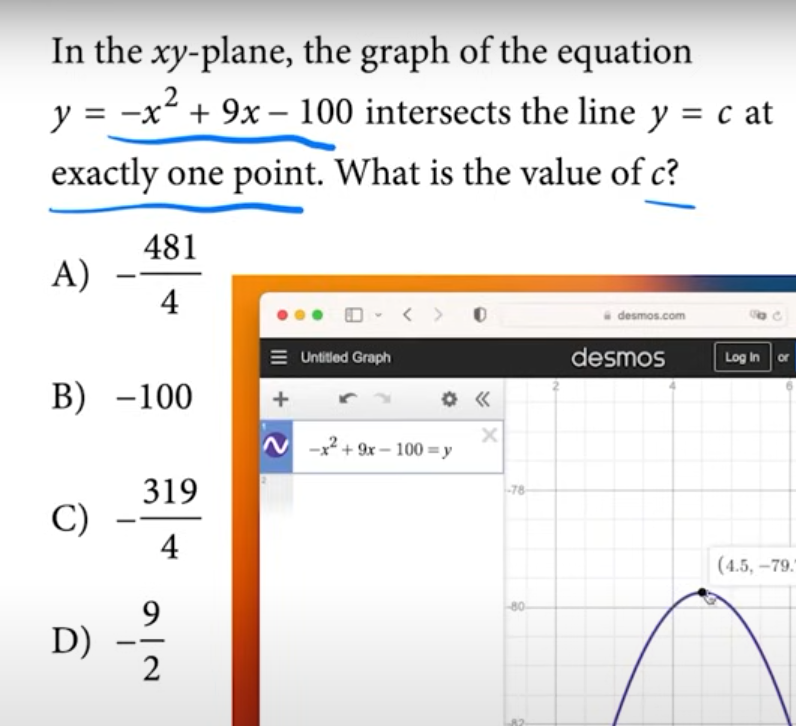
standard form of a parabola
y = ax² + bx + c
factored form*

if the discriminant [b²-4(a)(c)] is LESS than 0…
no solutions. Set value <0

if the discriminant [b²-4(a)(c)] is EQUAL than 0…
1 solution. Set value = 0
if the discriminant [b²-4(a)(c)] is GREATER than 0…
2 solutions. Set value > 0
the y-intercept of a parabola*

the line of symmetry*

Absolute value: copy and paste*

Absolute value:
copy and paste inequality

Absolute value:
copy and paste inequality

polynomial long division*

Polynomial long division:
finding the denominator
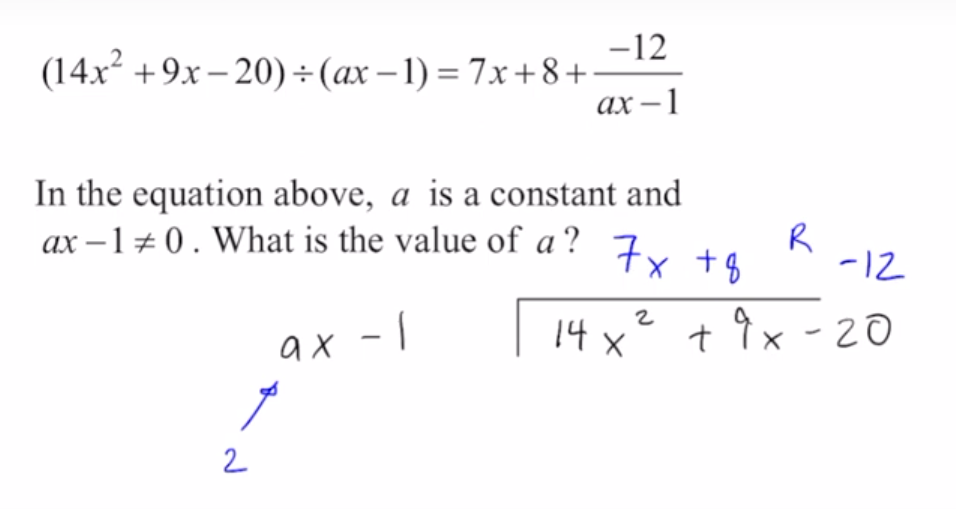
synthetic division:
finding the remainder
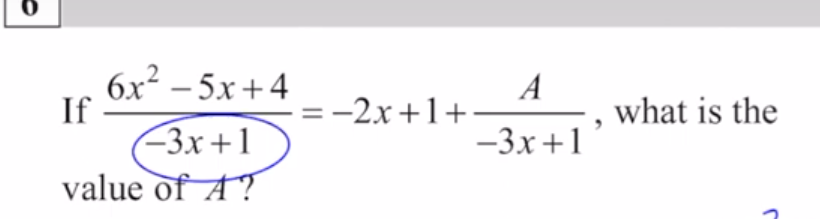
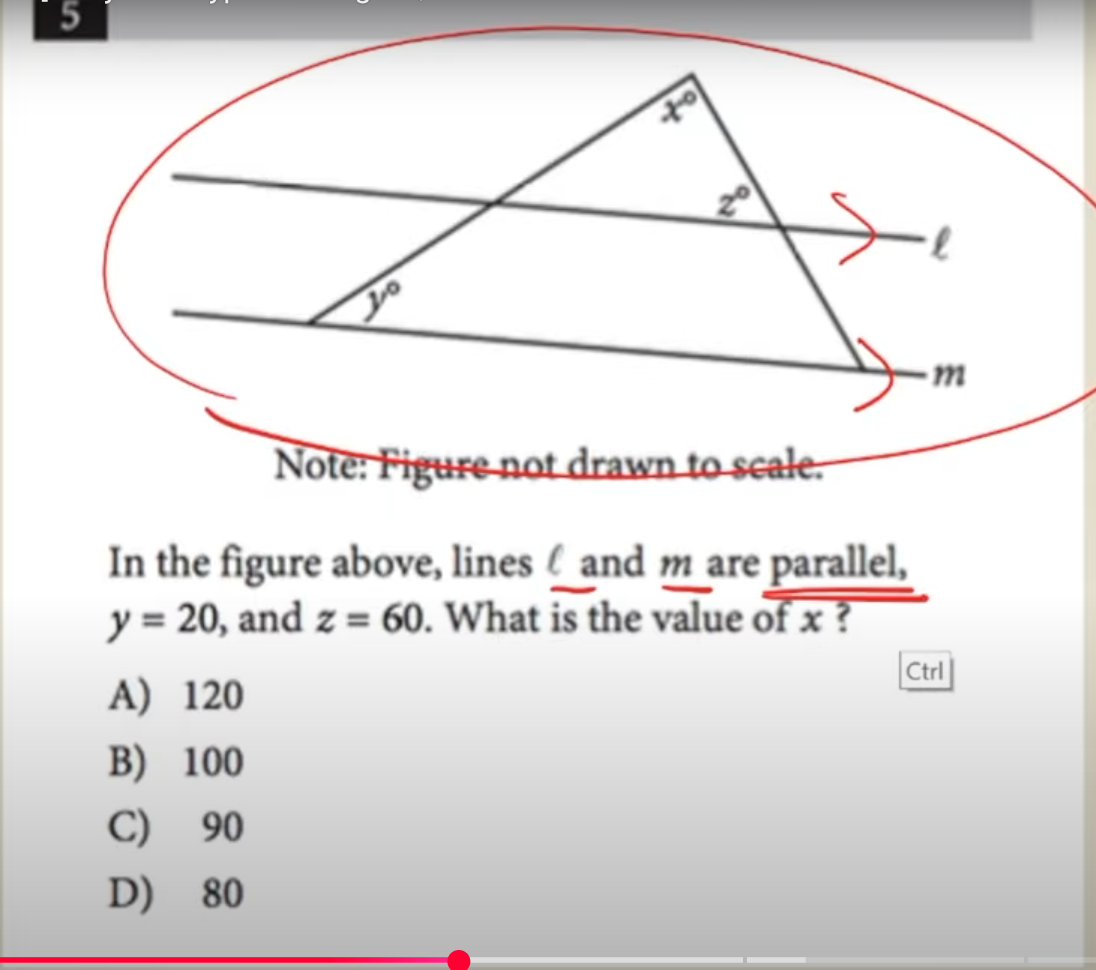
parallel lines*
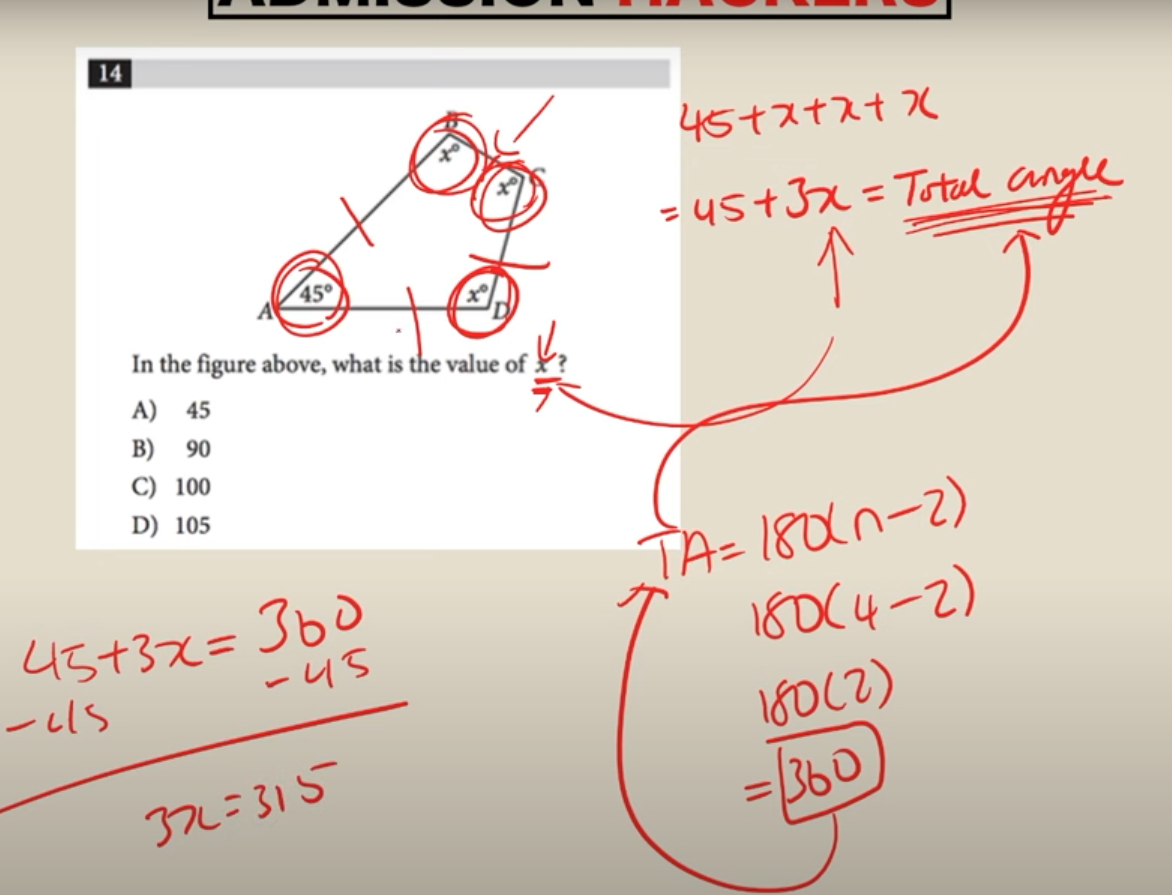
total angle formula
180(# of sides - 2)
total angle formula*
tangent
a right angle
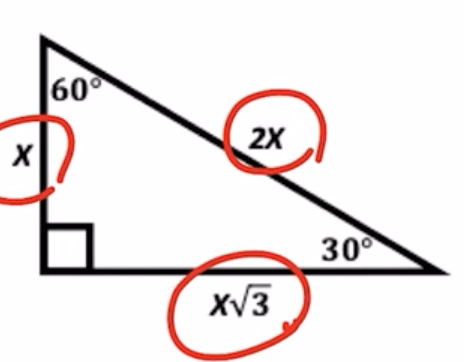
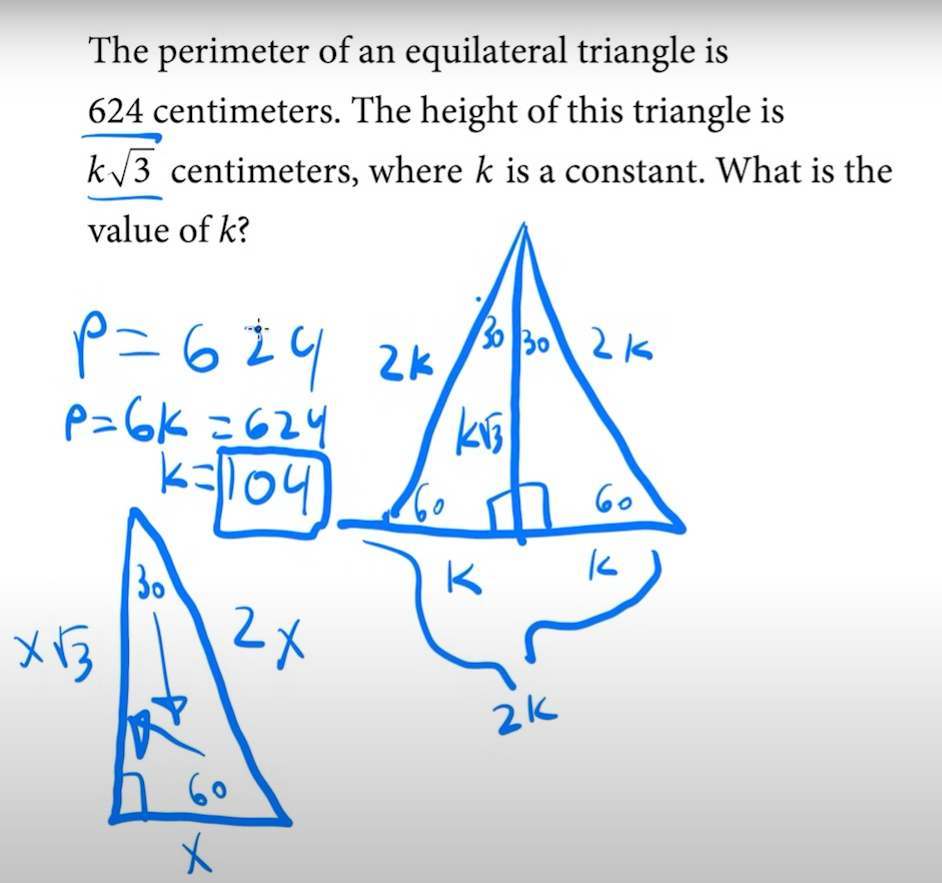
30, 60, 90 right triangle
x, x√3, 2x
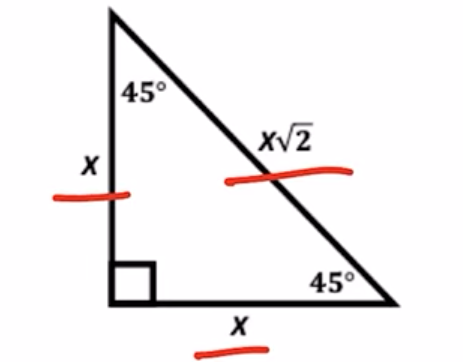
45, 45, 90 right triangle
x, x, x√2
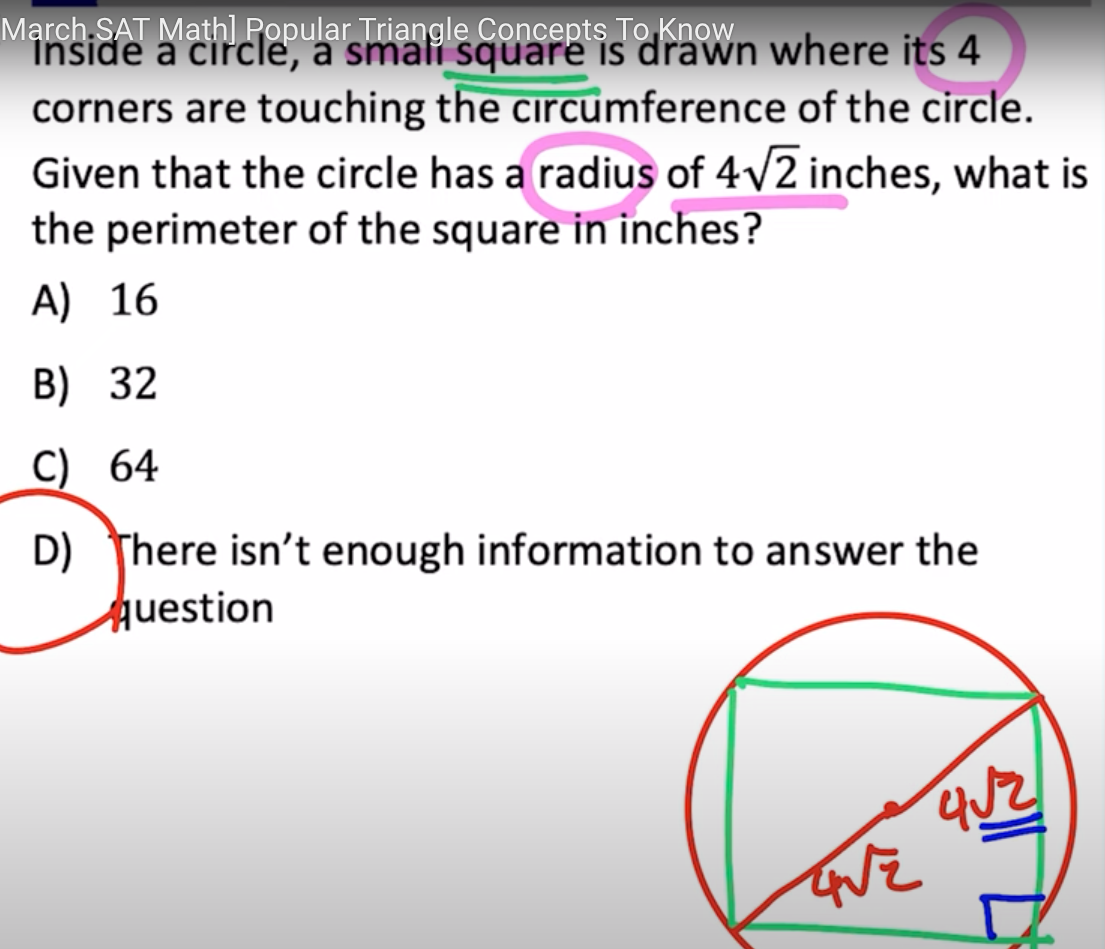
special right triangles:
45, 45, 90
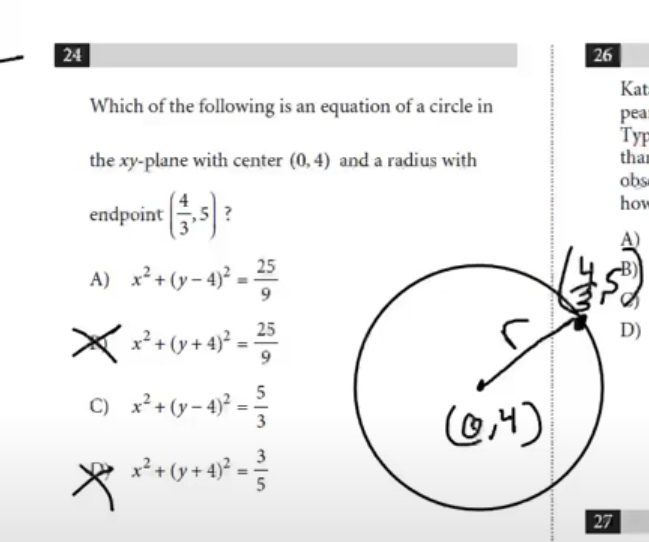
equation of a circle
(x-h)² + (y-k)² = r²
distance formula
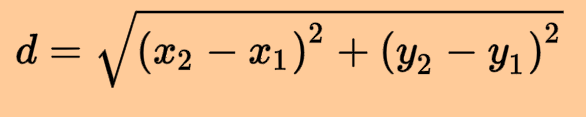
1) equation of a circle*
2) distance formula
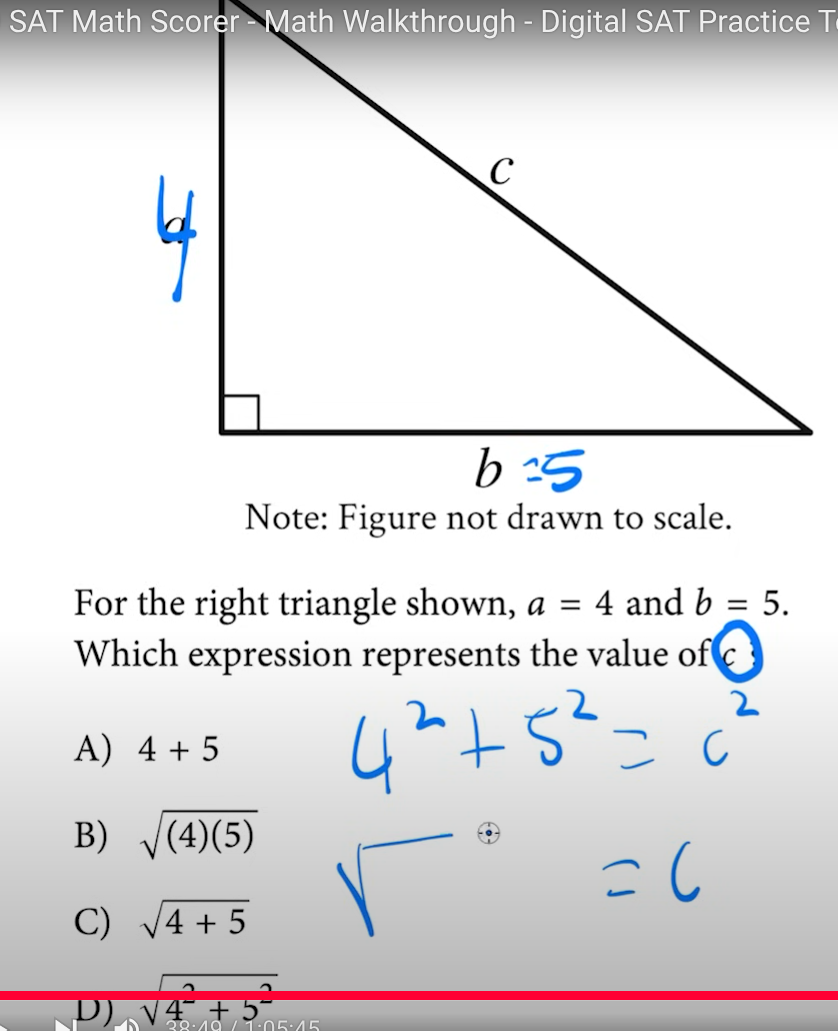
Pythagorean theorem:
a² + b² = c²
special right triangles: 30, 60, 90:
perimeter formula
SOH CAH TOA*
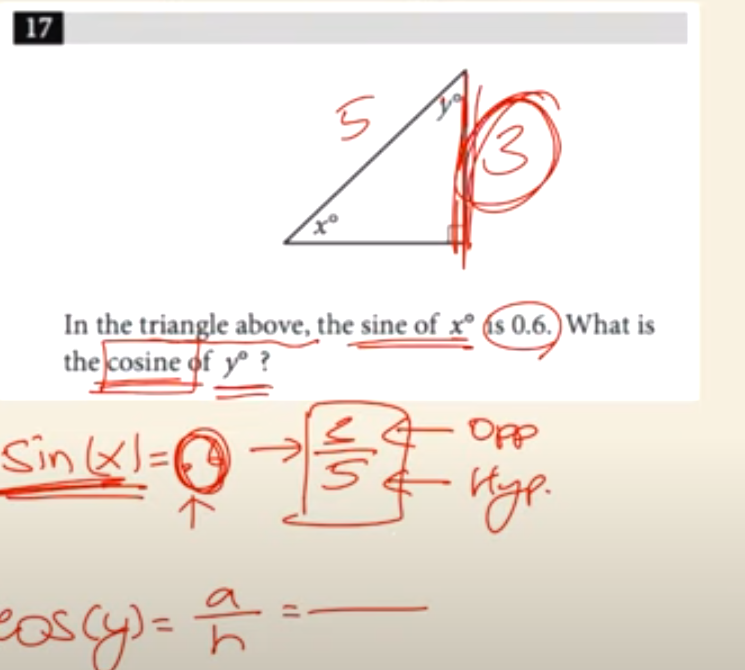
Finding the x-intercept:
finding b

Complementary Rule
sin(x) = cos(90-x)
cos(x) = sin(90-x)

Pythagorean Theorem triplets:
3,4,5; 5, 12, 13; 7, 24, 25
what 16 represents in the equation of a circle
radius
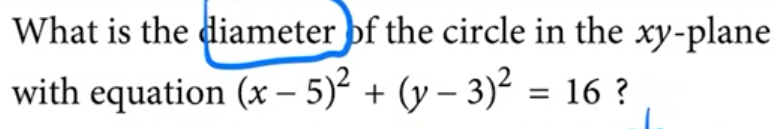
what 5 and 3 represent in the equation of a circle
the center of the circle
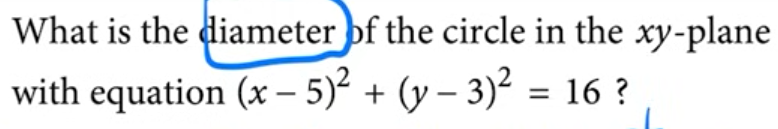
slope: -a/b*

polynomial remainder theorm

x-coord of the vertex
-b/2a
Ax + Bx = C
standard form of a linear equation
y- y1 = m(x - x1)
point-slope form of a linear equation (b is the y-int)
c/b
shortcut to y-int when in standard form (Ax + Bx = C)
pi x D or 2 x pi x r
the circumference of a circlce
center of a circle
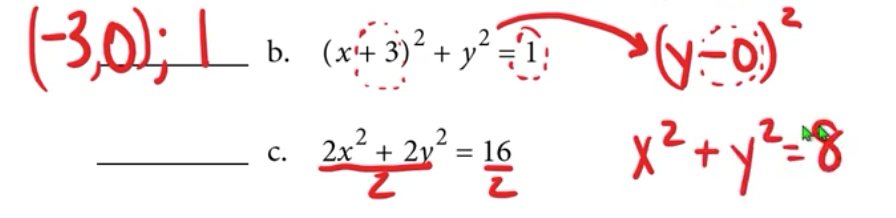
converting radians and degrees
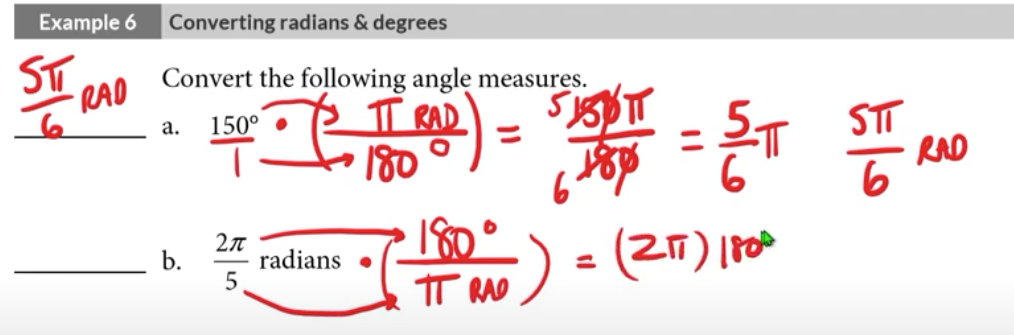
distance formula